Research Progress on High-Protein Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Varieties in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Main Text
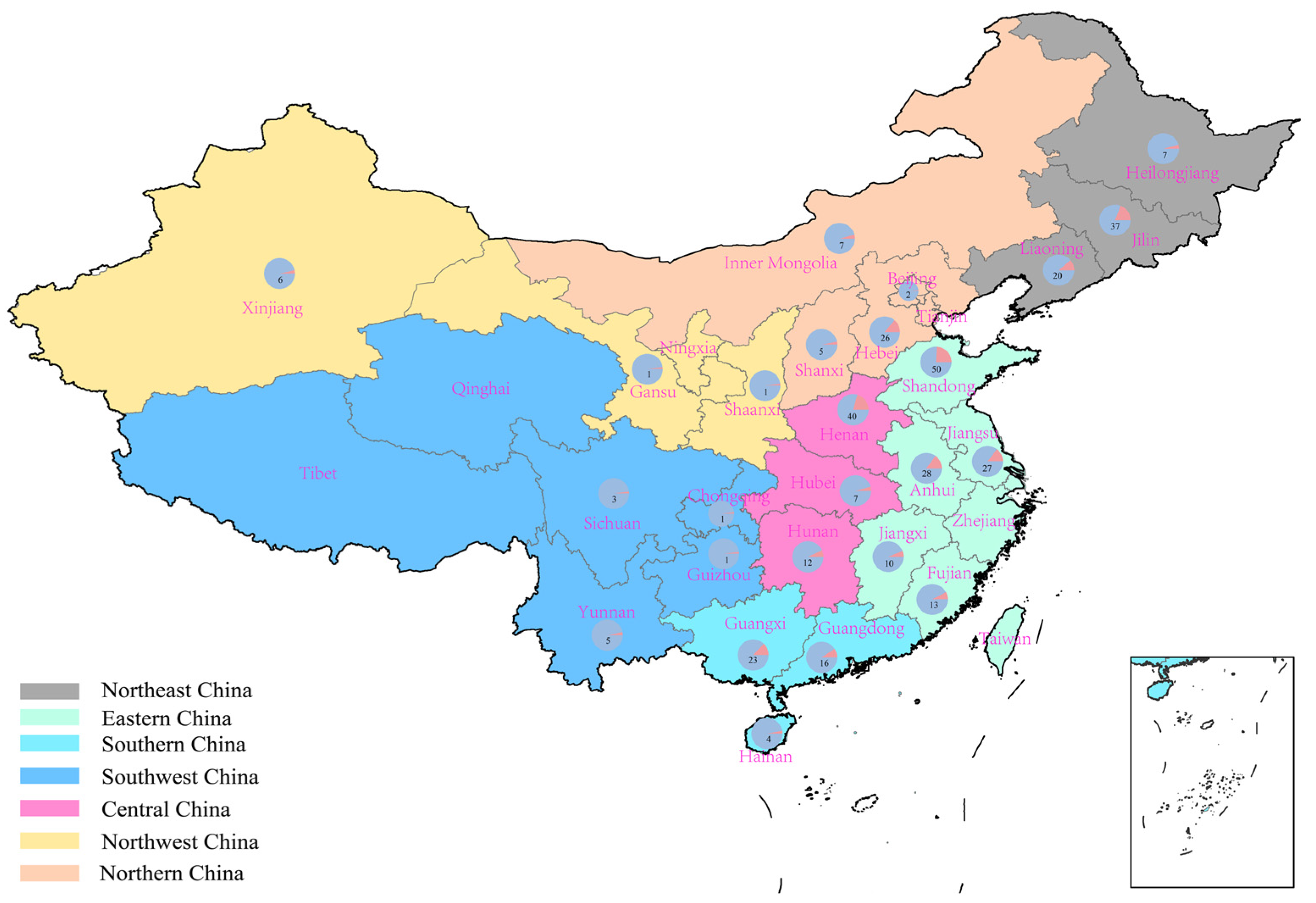
2.1. Suitable Regions for High-Protein Peanut Varieties in China
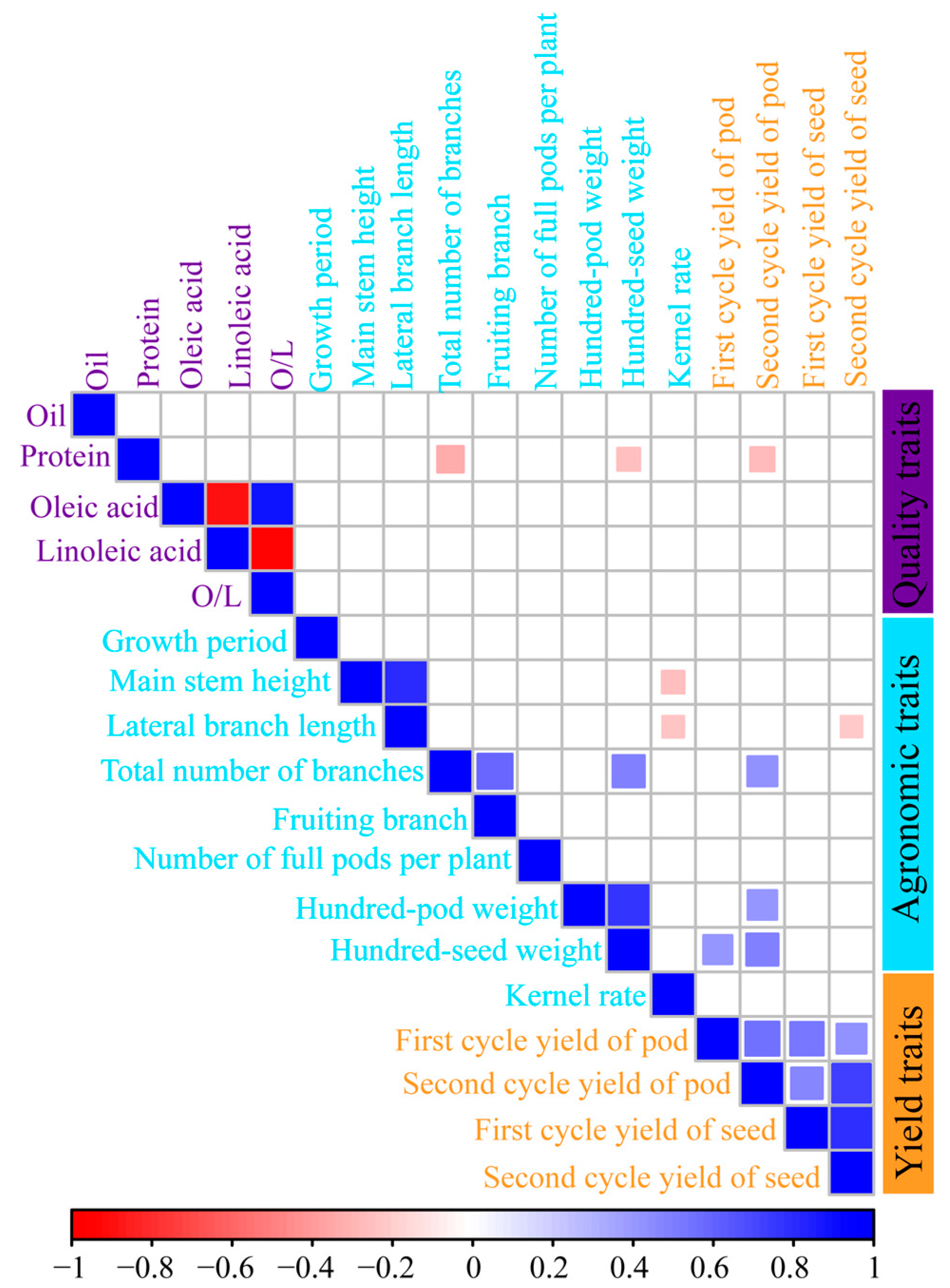
2.2. Agronomic, Quality, and Yield Traits of High-Protein Peanut Varieties
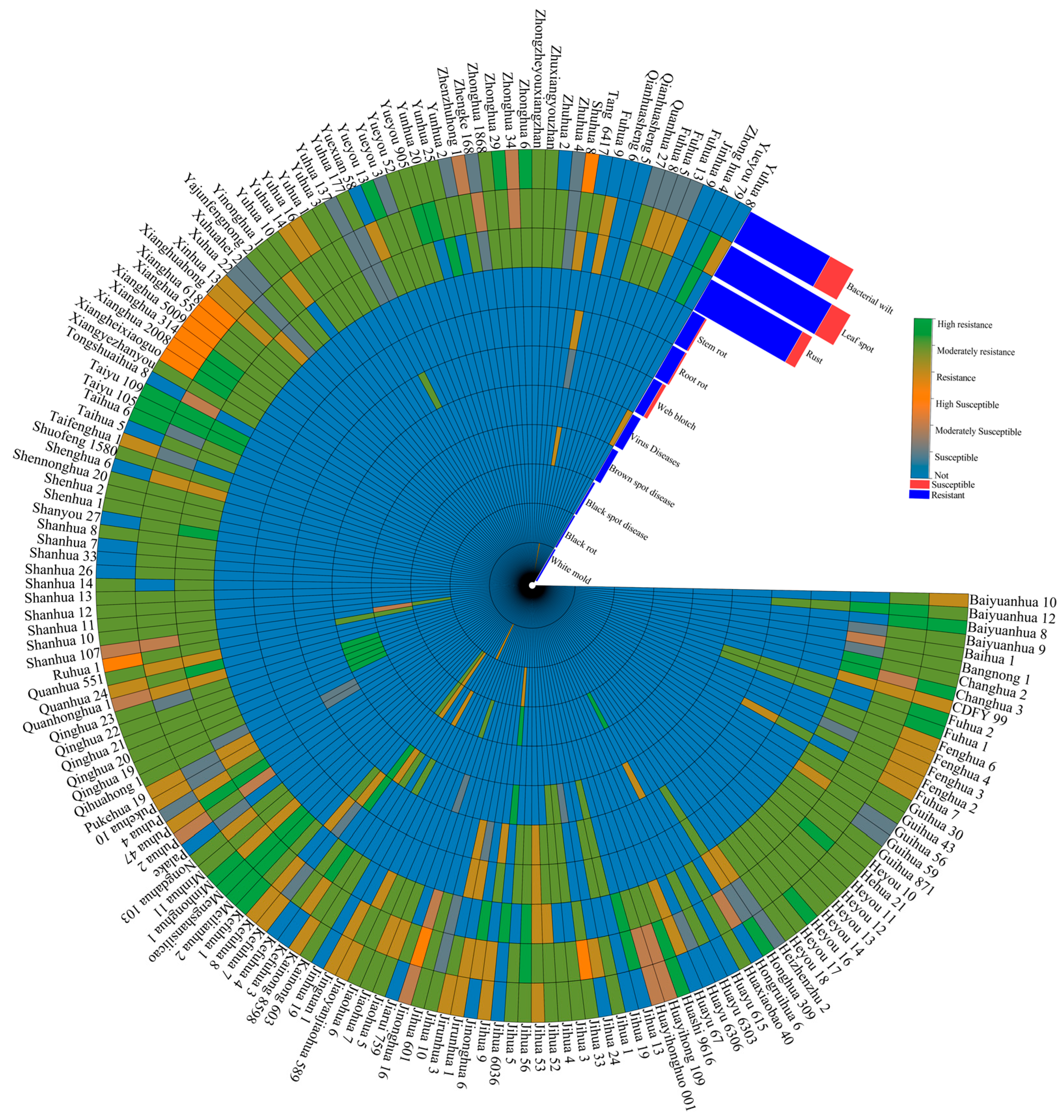
2.3. Disease Resistance and Environmental Adaptability
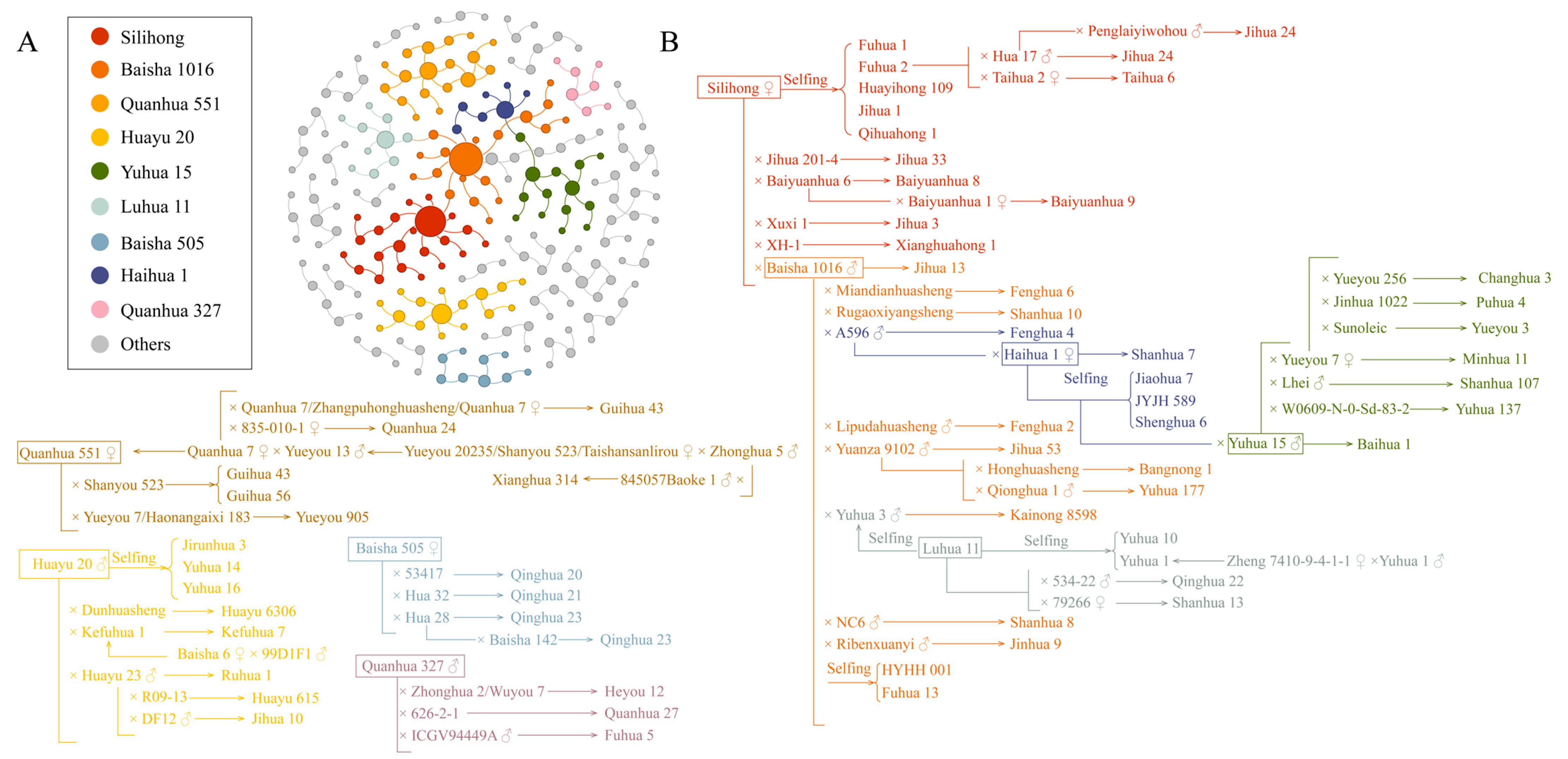
2.4. Pedigree Analysis of High-Protein Peanut Varieties
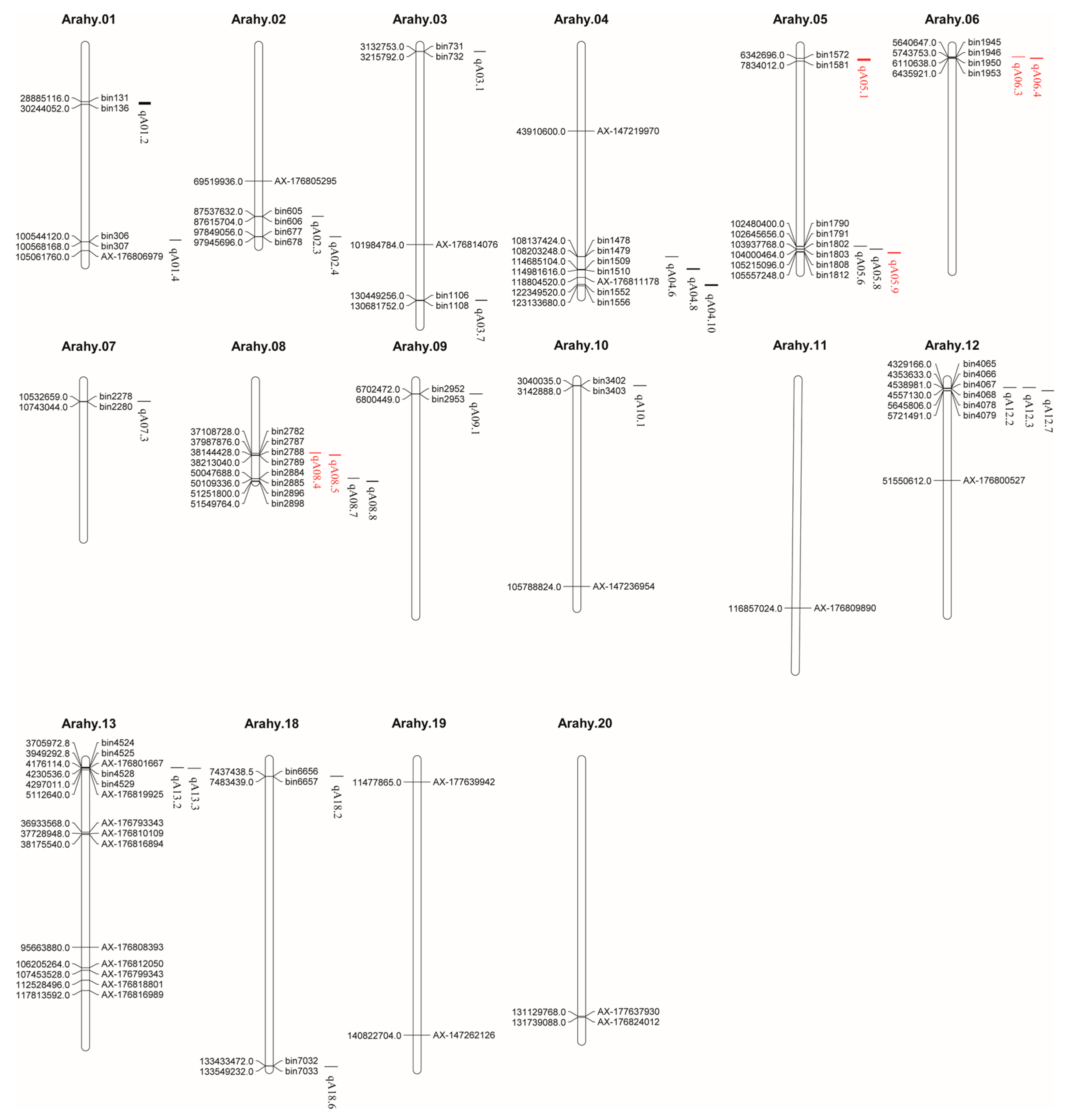
2.5. Identification of Protein-Related QTLs
2.6. Candidate Genes of Protein Content in Peanut Seeds
3. Challenges and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, J.P.; Dean, L.L. Peanut composition, flavor and nutrition. In Peanuts; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2016; pp. 289–345. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Tonnis, B.; Pinnow, D.; Davis, J.; An, Y.C.; Dang, P. Changes of seed weight, fatty acid composition, and oil and protein contents from different peanut FAD2 genotypes at different seed developmental and maturation stages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3658–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, E.; Singh, A.; O’Keefe, J.H. Nuts: Natural pleiotropic nutraceuticals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; McClements, D.J.; Xu, X.; Jiao, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, H.; Xiong, L.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Dai, L. Peanut proteins: Extraction, modifications, and applications: A comprehensive review. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2023, 6, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, R.L.; Conkerton, E.J. Supplementation of bakery items with high protein peanut flour. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1983, 60, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.S.; Salve, A.R.; Chauhan, S. Peanuts as functional food: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, N.; Huang, L.; Huai, D.; Xu, R.; Chen, X.; Guo, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H. Identification of a major QTL for seed protein content in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Using QTL-Seq. Plants 2024, 13, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Jin, H.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, F. NIR hyperspectral imaging with multivariate analysis for measurement of oil and protein contents in peanut varieties. Anal. Methods 2017, 99, 6148–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.L.; Jambunathan, R.; Nigam, S.N.; Raghunath, K.; Shankar, K.R.; Nagabhushanam, G.V.S. Relationship of seed mass to oil and protein contents in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Peanut Sci. 1990, 17, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Van, K.; Sung, M.; Nelson, R.; LaMantia, J.; McHale, L.K.; Mian, M.A.R. Genome-wide association study of seed protein, oil and amino acid contents in soybean from maturity groups I to IV. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 1639–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Guo, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, B.; Huang, L.; Luo, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Lei, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. High-resolution mapping of a major and consensus quantitative trait locus for oil content to a ~0.8-Mb region on chromosome A08 in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Deng, L.; Gu, J.; Miao, J.; Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y.; Huang, B.; Sun, Z.; Qi, F.; et al. Genome-wide association study and development of molecular markers for yield and quality traits in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, W.; Zhang, L.M.; Wu, X.Y.; Hao, H.Q.; Jing, H.C. Genome-wide association study reveals that different pathways contribute to grain quality variation in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Qi, F.; Liu, H.; Qin, L.; Xu, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, L.; Huang, B.; Dong, W.; et al. QTL mapping of quality traits in peanut using whole-genome resequencing. Crop J. 2022, 10, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.H. Research on the changes of peanut geographic concentration in china. J. Agric. Econ. 2018, 9, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Bai, B.; Cui, F.; Xu, F.; Du, F.; Zhang, J.; et al. Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome reveals molecular mechanisms regulating oil and protein content in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 26586–26598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xian, P.; Cheng, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lian, T.; Ma, Q.; Nian, H.; Ge, L. MOTHER-OF-FT-AND-TFL1 regulates the seed oil and protein content in soybean. New Phytol. 2023, 239, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.P.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Dang, Y.R.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.G.; Ma, X.L.; Li, Z.F.; et al. Comprehensive analysis and selection of high oleic peanut varieties in China: A study on agronomic, yield, and quality traits. Oil Crop Sci. 2024, 9, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.R.; Liu, Y.H.; Fan, Y.; Qiu, D.; Li, Z.F.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Gong, F.P.; Yin, D.M. Comprehensive analysis of high-oil peanut cultivars in China: Agronomic performance, disease resistance, and breeding insights. Reprod. Breed. 2025, 5, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Müller, C.; Pugh, T.A.M.; Chen, A.; Wang, T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.X.Z.; et al. Occurrence of crop pests and diseases has largely increased in China since 1970. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalker, H.T. Utilizing wild species for peanut improvement. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1102–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 2401-2013; Guidelines for the Safe Use of Pesticides in Agricultural Production. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Fávero, A.P.; Custodio, A.R.; Dinato, N.B.; Godoy, I.J.; Seijo, J.G.; Michelotto, M.D. Transference of multiple resistance to peanut through the development of cross-compatible complex hybrids of wild Arachis. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2020, 43, e20190099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, M.; Kemerait, R.; Bertioli, D., Jr.; Leal-Bertioli, S. Strong resistance to early and late leaf spot in peanut-compatible wild-derived induced allotetraploids. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Pandey, M.S.; Catto, M.; Leal-Bertioli, S.; Abney, M.R.; Bag, S.; Hopkins, M.; Culbreath, A.; Srinivasan, R. Evaluation of wild peanut species and their allotetraploids for resistance against thrips and thrips-transmitted tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (TSWV). Pathogens 2023, 12, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Pandey, M.K.; Khan, A.W.; Wu, B.; Guo, J.; Ren, X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, L. Next-generation sequencing identified genomic region and diagnostic markers for resistance to bacterial wilt on chromosome B02 in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 2356–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, A.K.; Ozias-Akins, P.; Holbrook, C.C. Recent technological advancements for identifying and exploiting novel sources of pest and disease resistance for peanut improvement. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhao, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Q.; Su, J. Genome-wide association study identifying candidate genes influencing important agronomic traits of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) Using SLAF-seq. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.L.; Park, C.A.; Reecy, J.M. Building a livestock genetic and genomic information knowledgebase through integrative developments of Animal QTLdb and CorrDB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D701–D710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvamangala, C.; Gowda, M.V.C.; Varshney, R.K. Identification of quantitative trait loci for protein content oil content and oil quality for groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Field Crops Res. 2011, 122, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; He, H.; Chen, W.; Ren, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Liao, B.; et al. Quantitative trait locus analysis of agronomic and quality-related traits in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, M.P.; Gangurde, S.S.; Hake, A.A.; Yadawad, A.; Mahadevaiah, S.S.; Pattanashetti, S.K.; Gowda, M.V.C.; Shirasawa, K.; Varshney, R.K.; Pandey, M.K.; et al. Genotyping-by-sequencing based genetic mapping identified major and consistent genomic regions for productivity and quality traits in peanut. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 668020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Wang, P.; Dang, C.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, S.; Lamb, M.; Chen, C. Identification of potential QTLs and genes associated with seed composition traits in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) using GWAS and RNA-Seq analysis. Gene 2021, 769, 145215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, R.; Pandey, M.K.; Han, Y.; Cui, F.; Zhang, J.; Guo, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Genomic insights into the genetic signatures of selection and seed trait loci in cultivated peanut. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 42, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.J.; Lu, Q.; Huang, L.; Batool, R.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Qianxia, Y.; Varshney, R.K.; Pandey, M.K.; et al. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic basis of amino acids contents variations in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Raina, S.N.; Rajpal, V.R.; Singh, A.K. Seed protein fraction electrophoresis in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) accessions and wild species. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2018, 24, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, E.T.H.C.; Mensink, R.P.; Joris, P.J. Effects of tree nut and groundnut consumption compared with those of l-arginine supplementation on fasting and postprandial flow-mediated vasodilation: Meta-analysis of human randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Traits | Mean | Range | SD | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil content (%) | 50.90 | 36.40–59.32 | 2.92 | 5.75 |
| Protein (%) | 29.52 | 27.99–36.40 | 1.44 | 4.86 |
| Oleic acid (%) | 47.02 | 33.00–90.60 | 10.64 | 22.63 |
| Linoleic acid (%) | 32.56 | 1.92–44.72 | 8.97 | 27.55 |
| Growth period (d) | 122.25 | 100.00–138.00 | 7 | 5.78 |
| Main stem height (cm) | 43.79 | 16.87–67.60 | 8.89 | 20.30 |
| Lateral branch length (cm) | 46.74 | 8.50–75.20 | 9.60 | 20.54 |
| Total number of branches | 7.95 | 3.66–20.00 | 2.09 | 26.29 |
| Fruiting branch | 6.74 | 3.51–14.48 | 1.48 | 22.00 |
| Number of full pods per plant | 16.96 | 6.70–50.00 | 5.16 | 30.40 |
| Hundred-pod weight (g) | 191.18 | 69.90–332.00 | 40.52 | 21.20 |
| Hundred-seed weight (g) | 76.25 | 32.23–169.70 | 17.70 | 23.22 |
| Kernel rate (%) | 70.86 | 61.66–85.00 | 3.38 | 4.78 |
| First cycle yield of pod (kg) | 300.55 | 110.10–520.60 | 69.33 | 23.07 |
| Second cycle yield of pod (kg) | 286.81 | 130.29–511.00 | 69.40 | 24.20 |
| First cycle yield of seed (kg) | 230.58 | 115.51–505.80 | 59.29 | 25.72 |
| Second cycle yield of seed (kg) | 217.44 | 128.71–388.40 | 52.26 | 24.03 |
| Variety Name | Protein (%) | Oil (%) | Oleic Acid (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heizhenzhu 2 | 28.90 | 55.91 | 79.24 |
| Pukehua 10 | 28.09 | 55.40 | 76.07 |
| Yuhua 14 | 28.11 | 59.32 | 41.5 |
| Yuhua 16 | 28.20 | 58.94 | 40.7 |
| Heyou 10 | 28.33 | 56.83 | 45.2 |
| Zhuxiangyouzhan | 28.65 | 56.13 | 46.2 |
| Ruhua 1 | 29.10 | 56.00 | 51.7 |
| Hehua 21 | 28.90 | 55.87 | 48.4 |
| Zhongzheyouxiangzhan | 28.35 | 55.62 | 45.3 |
| Yueyou 3 | 29.40 | 55.49 | 45.4 |
| CDFY 99 | 28.43 | 55.46 | 45.6 |
| Shanhua 11 | 28.22 | 55.46 | 51.5 |
| Xiangyezhanyou | 28.62 | 55.35 | 46.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Qiu, D.; Li, Z.; Gong, F.; Yin, D. Research Progress on High-Protein Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Varieties in China. Plants 2025, 14, 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182917
Li Z, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Fan Y, Qiu D, Li Z, Gong F, Yin D. Research Progress on High-Protein Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Varieties in China. Plants. 2025; 14(18):2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182917
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhuo, Yaru Zhang, Yinghui Liu, Yi Fan, Ding Qiu, Zhongfeng Li, Fangping Gong, and Dongmei Yin. 2025. "Research Progress on High-Protein Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Varieties in China" Plants 14, no. 18: 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182917
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Fan, Y., Qiu, D., Li, Z., Gong, F., & Yin, D. (2025). Research Progress on High-Protein Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Varieties in China. Plants, 14(18), 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182917






