Symbiotic Fungus Serendipita indica as a Natural Bioenhancer Against Cadmium Toxicity in Chinese Cabbage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
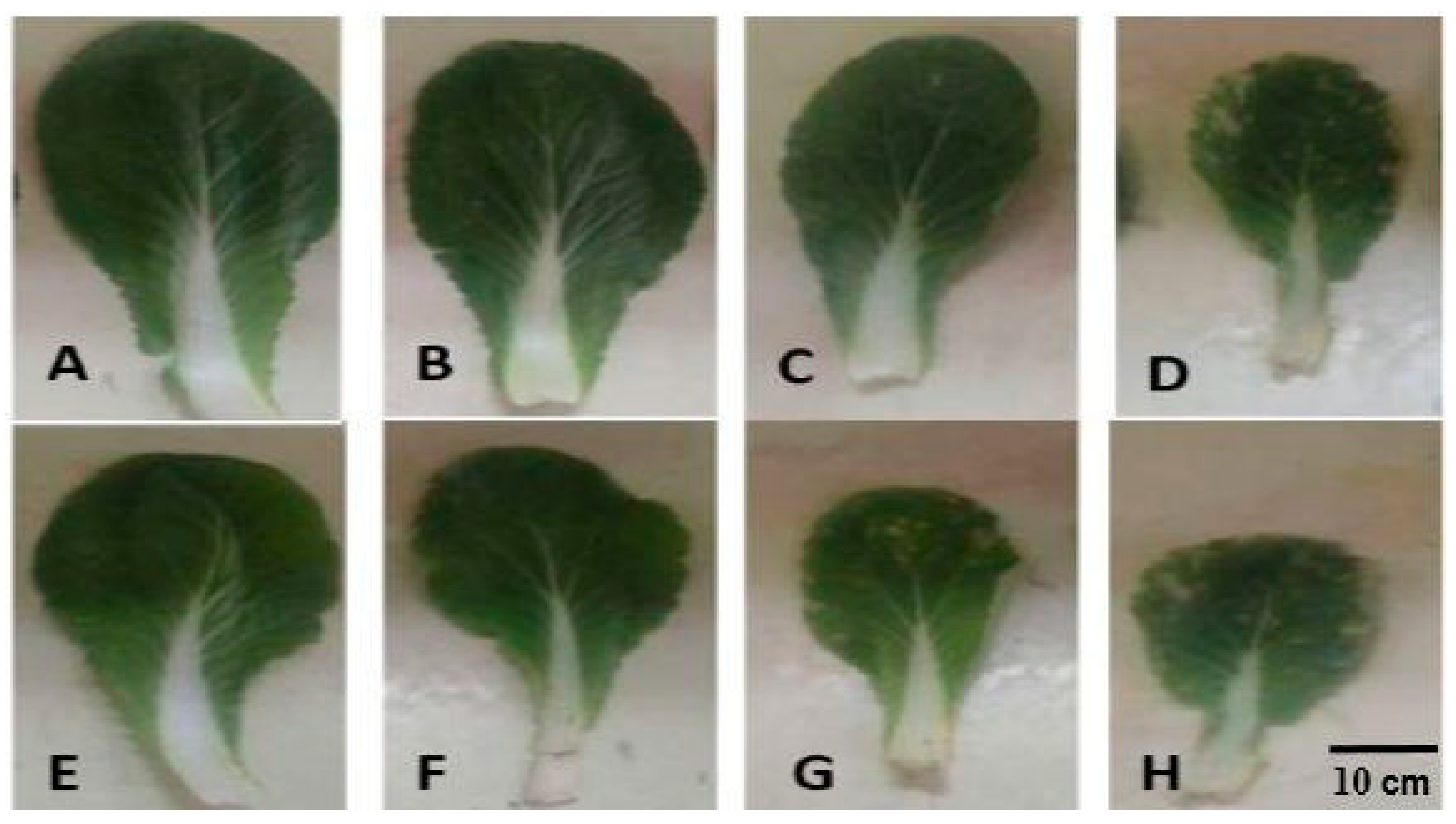
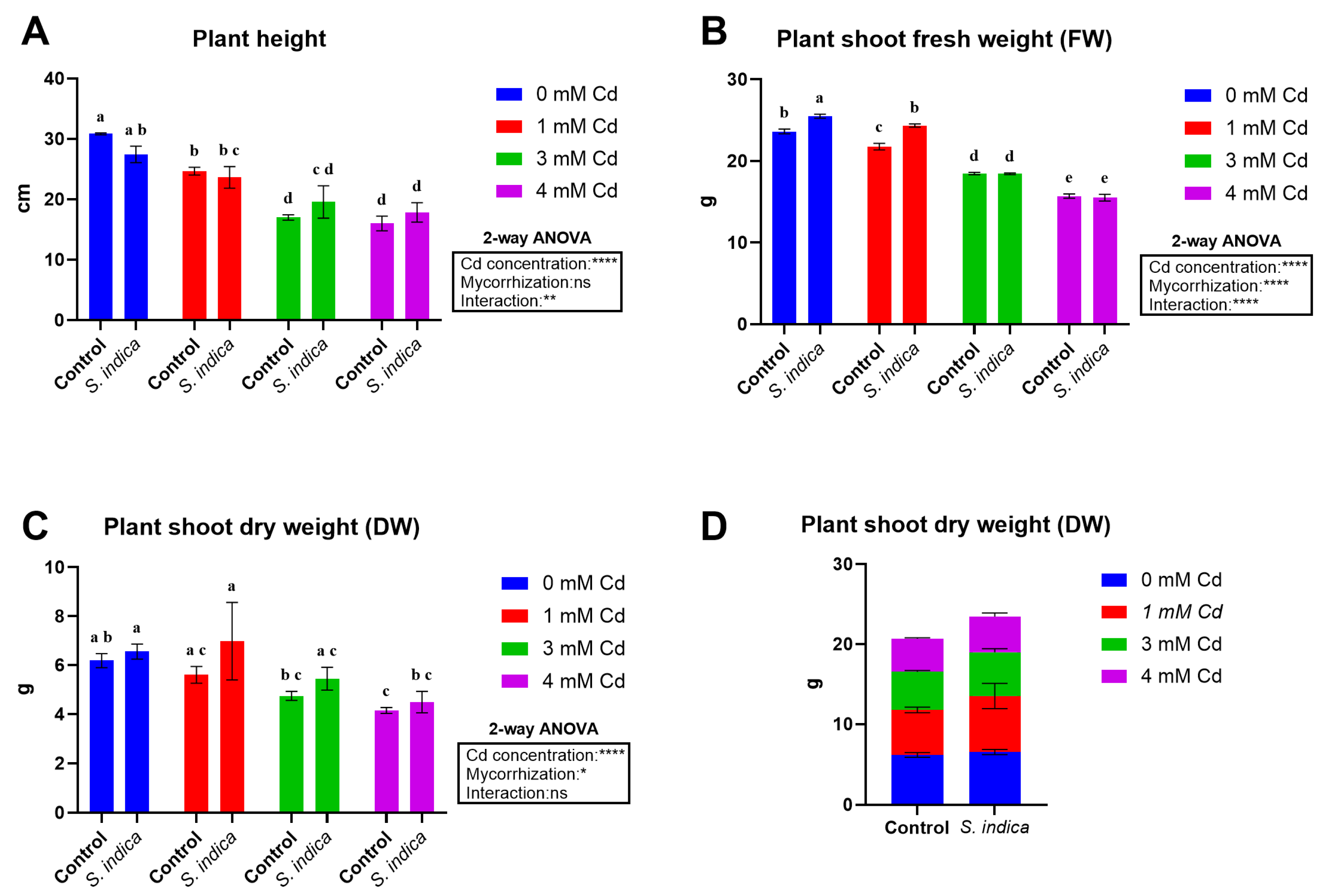
2.1. Morphological Traits
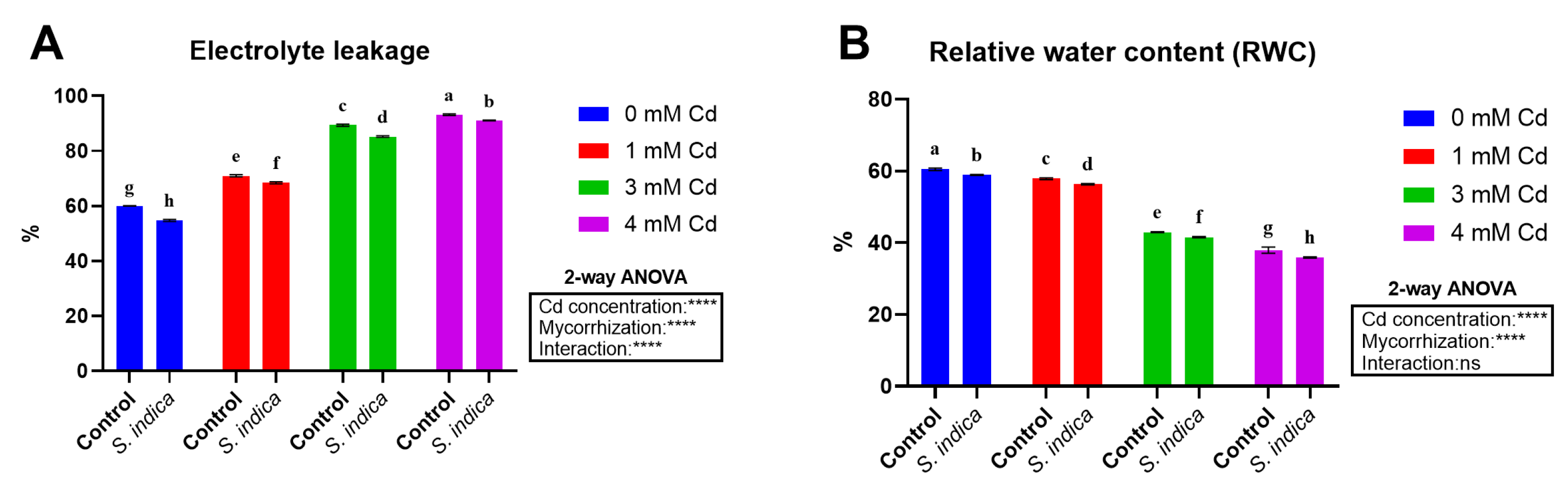
2.2. Electrolyte Leakage (EL) and Relative Water Content (RWC)
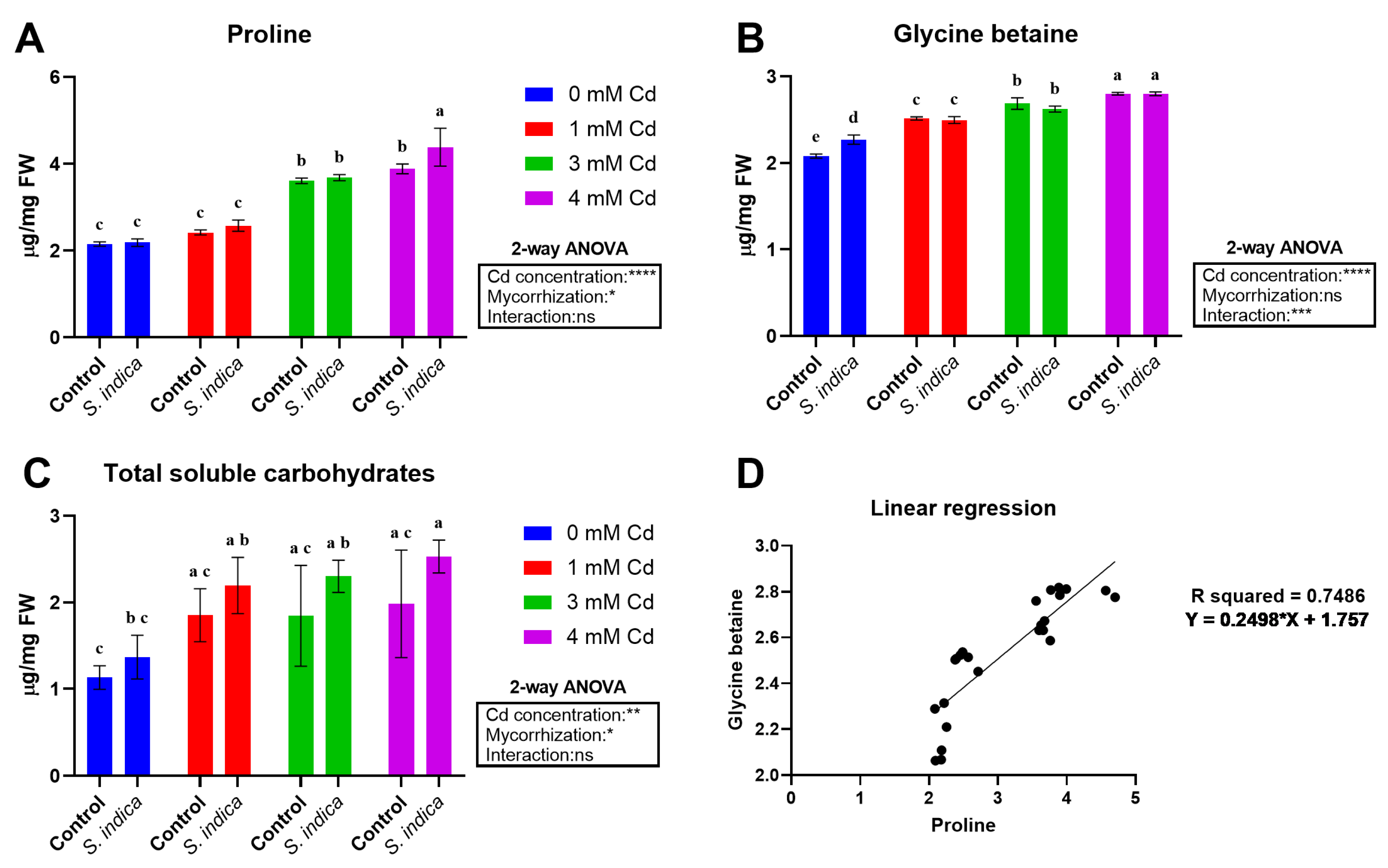
2.3. Proline and Carbohydrate Contents
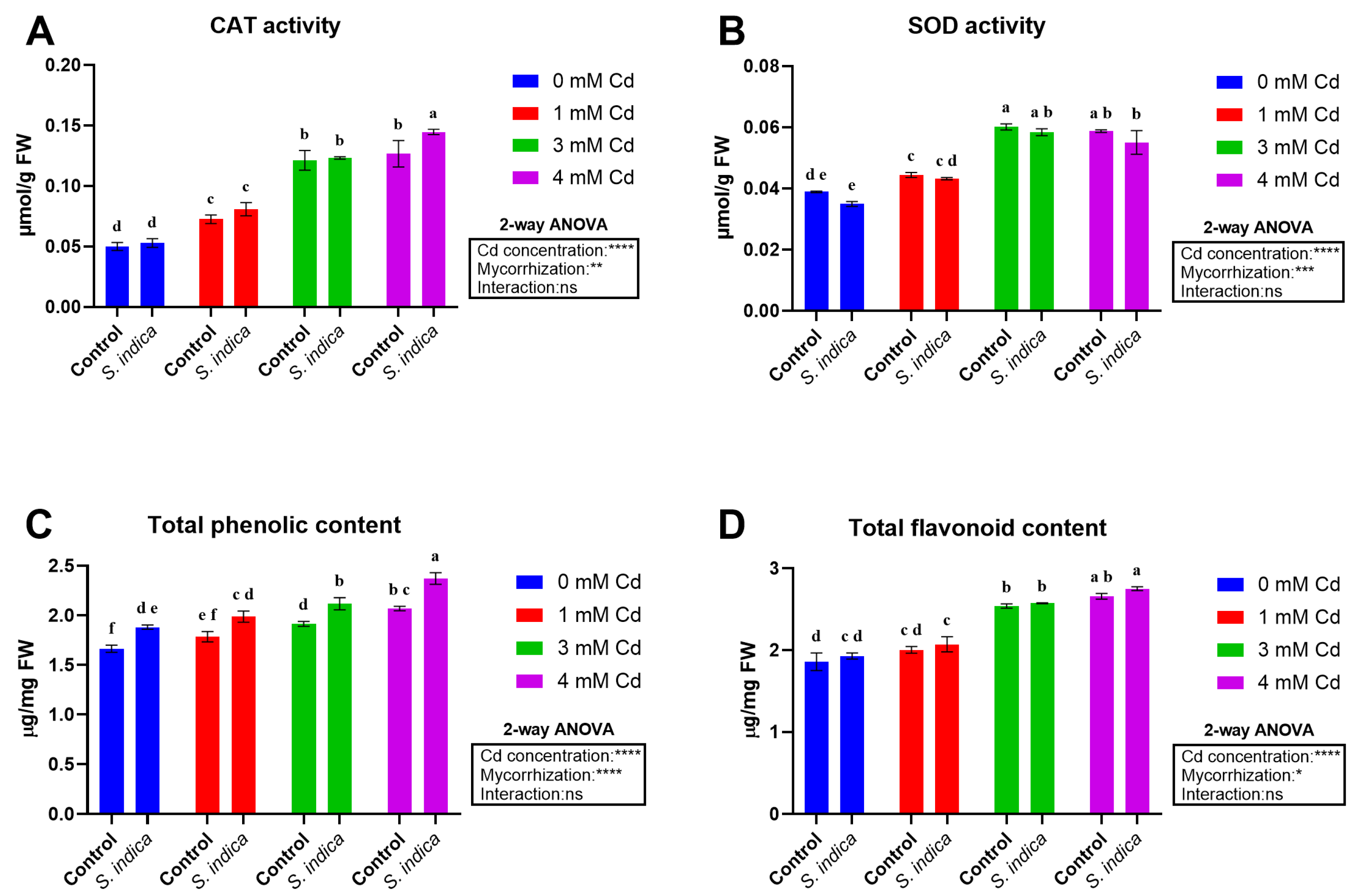
2.4. Enzyme Activities and Total Metabolites
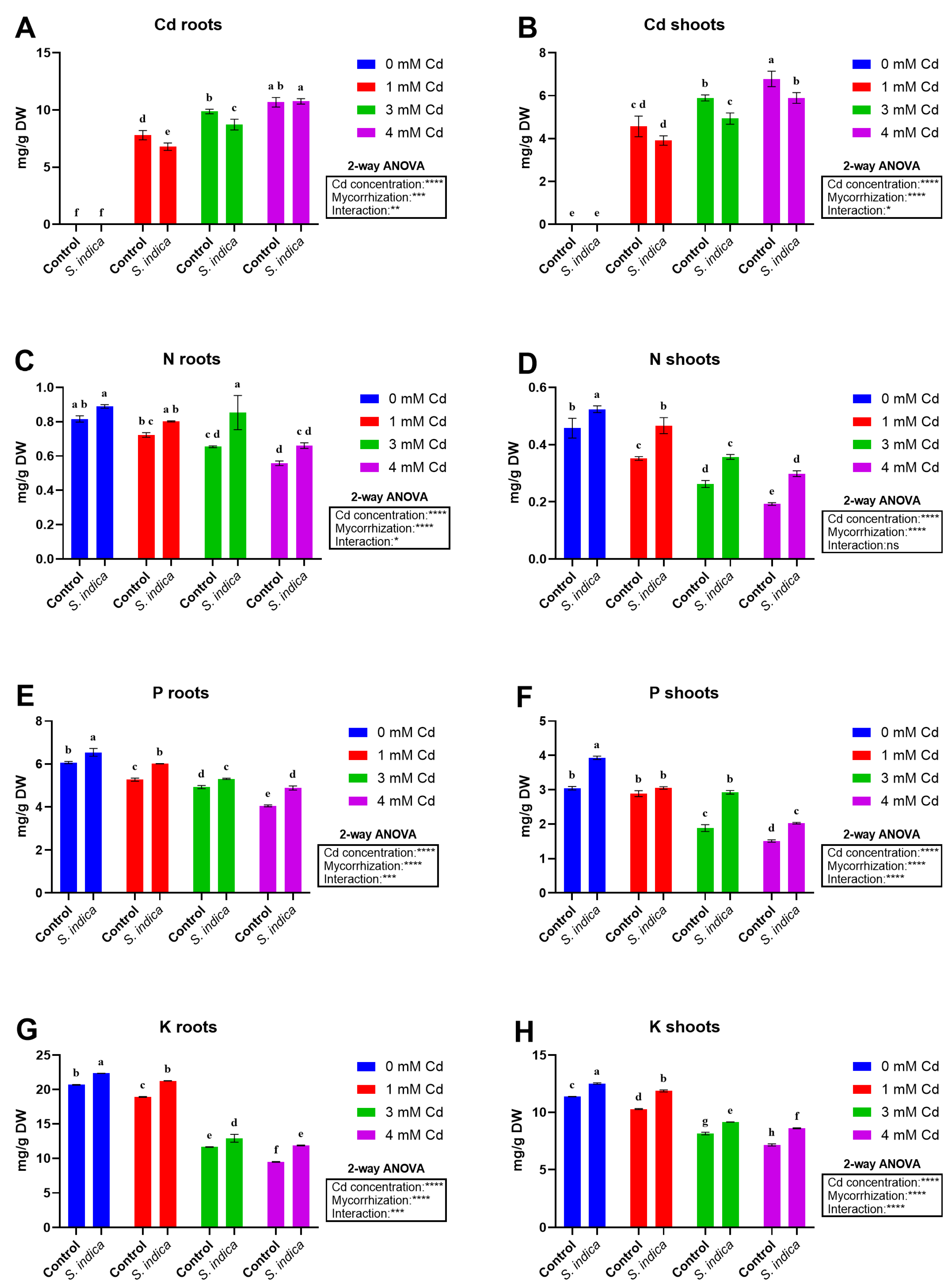
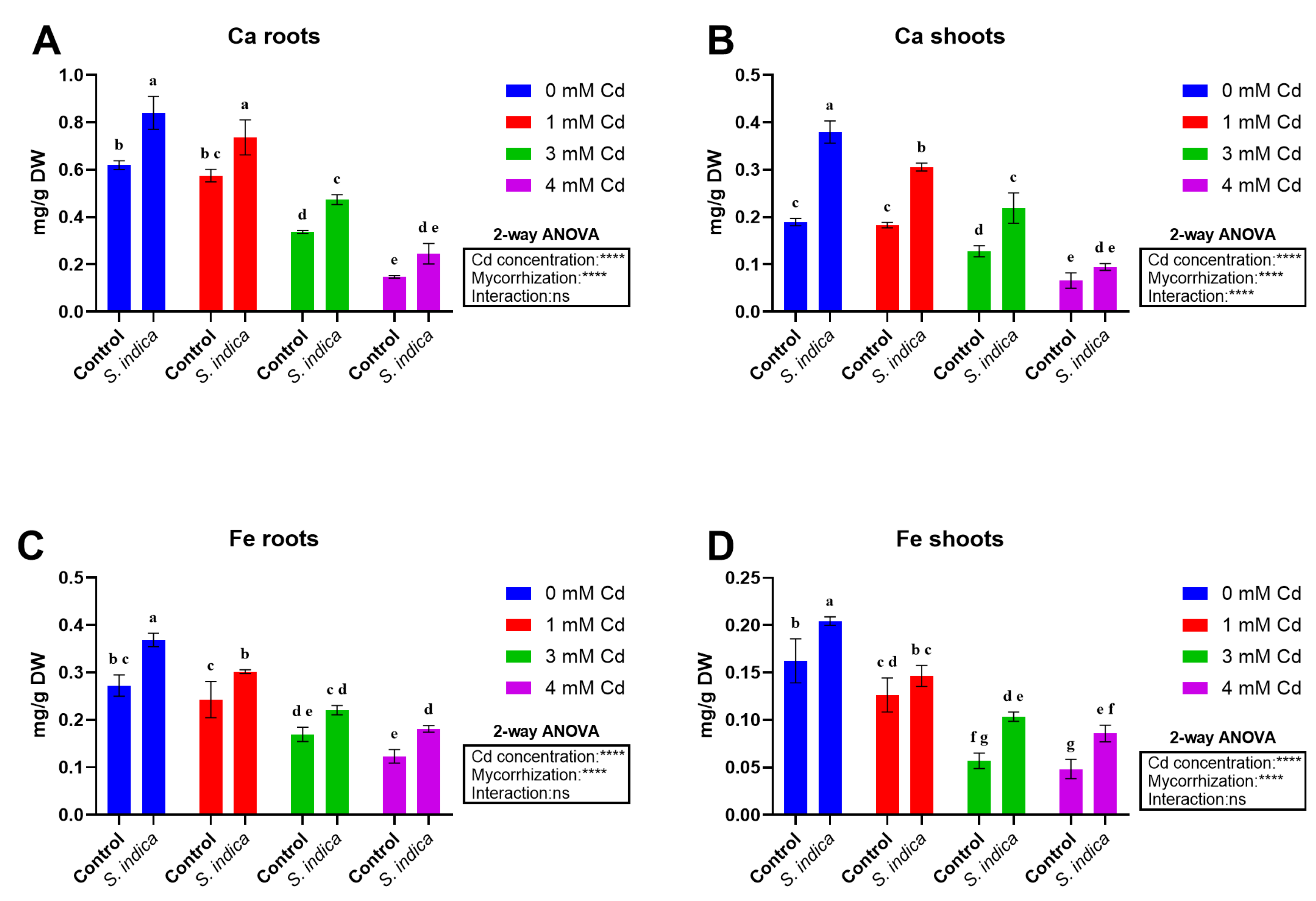
2.5. Elements
2.5.1. Cd
2.5.2. N
2.5.3. P
2.5.4. K
2.5.5. Ca
2.5.6. Fe
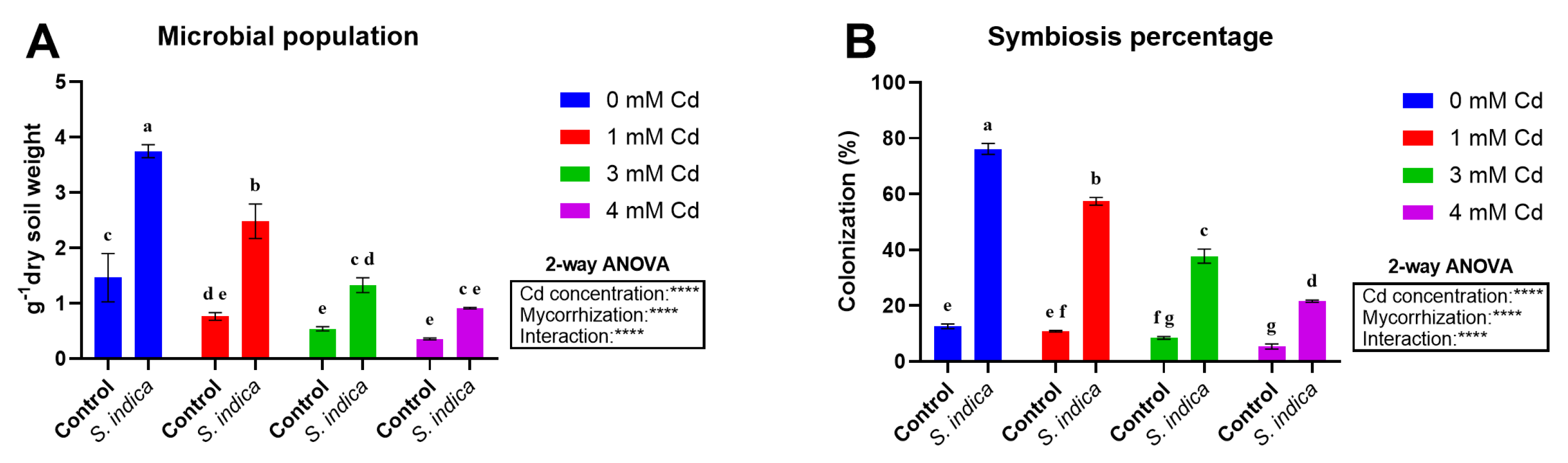
2.6. Microbial Population
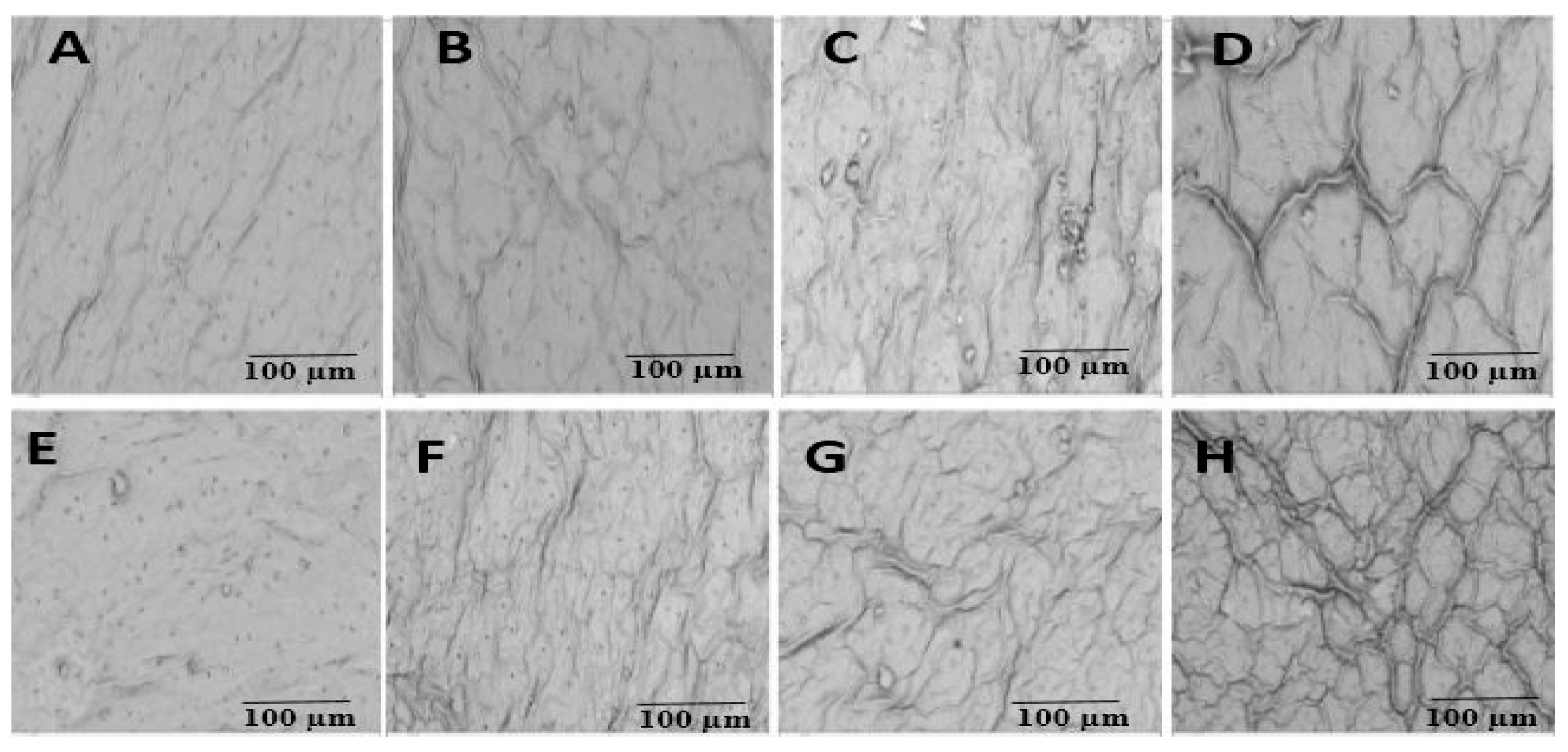
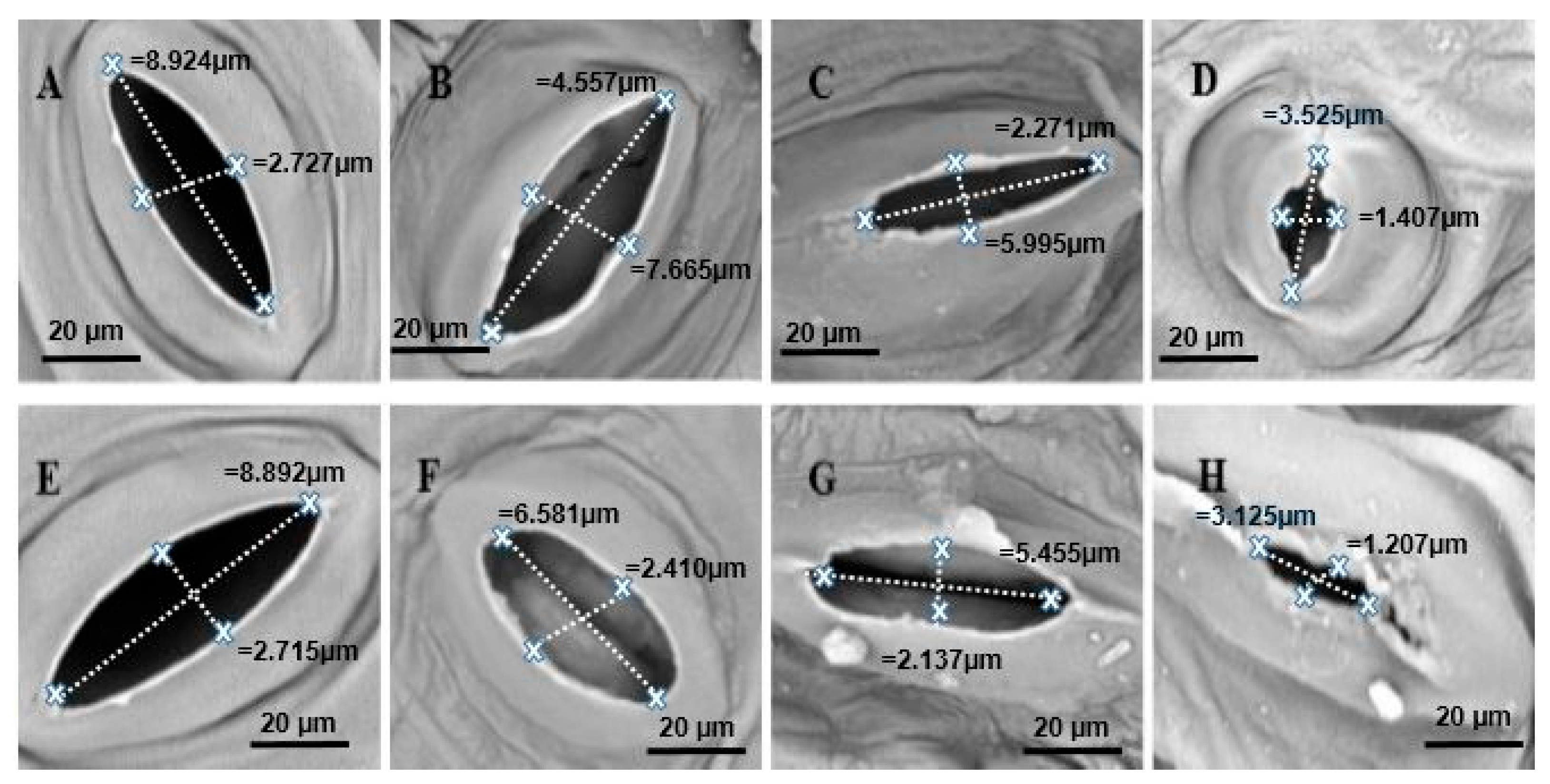
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Observations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
4.2. Seedbed Preparation
4.3. Measurement of Morphological Traits
4.4. Relative Water Content (RWC)
4.5. Electrolyte Leakage (EL)
4.6. Soluble Carbohydrates
4.7. Proline Content
4.8. Glycine Betaine
4.9. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
4.9.1. Protein Extraction
4.9.2. Catalase (CAT) Enzyme Activity
4.9.3. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Enzyme Activity
4.10. Total Phenol and Flavonoid Contents
4.11. Analysis of Ion Contents in the Biomass
4.12. Fungal Colonization
4.13. Microbial Population Measurement
4.14. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Shaheen, S.M.; Chen, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hou, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yuan, C.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, H.; Gao, J. Metabolomics analysis reveals different mechanisms of cadmium response and functions of reduced glutathione in cadmium detoxification in the Chinese cabbage. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 98, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsdr, U. Toxicological Profile for Chromium. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service. 2012. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Wu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Li, X. Jasmonic acid negatively regulation of root growth in Japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.) under cadmium treatment. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 98, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Jiang, W.; Xiukang, W.; Hussain, S.; Ahmad, M.; Maqsood, M.F.; Ali, N.; Ishfaq, M.; Kaleem, M.; Haider, F.U. Cadmium phytotoxicity, tolerance, and advanced remediation approaches in agricultural soils; a comprehensive review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 773815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rasafi, T.; Oukarroum, A.; Haddioui, A.; Song, H.; Kwon, E.E.; Bolan, N.; Tack, F.M.; Sebastian, A.; Prasad, M.; Rinklebe, J. Cadmium stress in plants: A critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 675–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Q. An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: Technical progress over the last decade. Water Res. 2018, 147, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, D.; Kaur, T.; Devi, R.; Rana, K.L.; Yadav, N.; Rastegari, A.A.; Yadav, A.N. Biotechnological applications of beneficial microbiomes for evergreen agriculture and human health. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 255–279. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, A.; Bakshi, M.; Lou, B.; Hartmann, A.; Oelmueller, R. Piriformospora indica: A novel plant growth-promoting mycorrhizal fungus. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.-A.; Liu, R.-C.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Alsayed, M.F.; Harsonowati, W.; Wu, Q.-S. Symbiotic fungi alter the acquisition of phosphorus in Camellia oleifera through regulating root architecture, plant phosphate transporter gene expressions and soil phosphatase activities. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; An, C.; Jiao, S.; Jia, F.; Liu, R.; Wu, Q.; Dong, Z. Impacts of the inoculation of Piriformospora indica on photosynthesis, osmoregulatory substances, and antioxidant enzymes of alfalfa seedlings under cadmium stress. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boorboori, M.R.; Zhang, H. The effect of cadmium on soil and plants, and the influence of Serendipita indica (Piriformospora indica) in mitigating cadmium stress. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Gill, R.; Trivedi, D.K.; Anjum, N.A.; Sharma, K.K.; Ansari, M.W.; Ansari, A.A.; Johri, A.K.; Prasad, R.; Pereira, E. Piriformospora indica: Potential and significance in plant stress tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabral, S.; Varma, A.; Choudhary, D.K.; Bahuguna, R.N.; Nath, M. Biopriming with Piriformospora indica ameliorates cadmium stress in rice by lowering oxidative stress and cell death in root cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, V.A.J.M.; Sepehri, M.; Khatabi, B.; Rezaei, M. Alleviation of zinc deficiency in wheat inoculated with root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica and rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida. Rhizosphere 2021, 17, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-J.; Shao, K.-H.; Chan, M.-T.; Cheng, C.-P.; Yeh, K.-W.; Oelmüller, R.; Wang, S.-J. Piriformospora indica symbiosis improves water stress tolerance of rice through regulating stomata behavior and ROS scavenging systems. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1722447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Kumar, M.; Deep, D.K.; Kumar, H.; Sharma, R.; Tripathi, T.; Tuteja, N.; Saxena, A.K.; Johri, A.K. A phosphate transporter from the root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica plays a role in phosphate transport to the host plant. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 26532–26544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Fard, E.M.; Ghabooli, M. Piriformospora indica affect drought tolerance by regulation of genes expression and some morphophysiological parameters in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 287, 110260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of proline under changing environments: A review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivedita; Rawoof, A.; Ramchiary, N.; Abdin, M.Z. A high-throughput RNA-Seq approach to elucidate the transcriptional response of Piriformospora indica to high salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyens, N.; van der Lelie, D.; Taghavi, S.; Vangronsveld, J. Phytoremediation: Plant–endophyte partnerships take the challenge. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, H.; Luo, C.; Wang, M.; Yin, H. Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide CPS-2 protects human mesangial cells from PDGF-BB-induced proliferation through the PDGF/ERK and TGF-β1/Smad pathways. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mun, J.-H.; Bancroft, I.; Cheng, F. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawon, R.A.; Kang, B.S.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, H.J.; Katrich, E.; Gorinstein, S.; Ku, Y.G. Influence of drought stress on bioactive compounds, antioxidant enzymes and glucosinolate contents of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa). Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, B.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y.; Mao, M.; Yao, L. The impact of greenhouse vegetable farming duration and soil types on phytoavailability of heavy metals and their health risk in eastern China. Chemosphere 2014, 103, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Saeed, U.-R.; Haoxin, T.; Lantian, S.; Pei, Z.; Nan, H. Mutualistic fungus Piriformospora indica modulates cadmium phytoremediation properties of host plant via concerted action of enzymatic and non-enzymatic biochemicals. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, U.; Malik, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Ok, Y.S.; Shah, M.H.R.; Rehman, R.A.; Ahmad, N. Biochar enhances the cadmium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) through modification of Cd uptake and physiological and biochemical attributes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21385–21394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komárková, M.; Kovalíková, Z.; Šimek, J.; Skarka, A.; Tůma, J. Physiological and biochemical responses of Brassica napus L. cultivars exposed to Cd stress. Plant Soil Environ. 2022, 68, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, N.; Mondal, S.C.; Farooq, M.; Gogoi, N. Influence of heavy metals on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat, pea, and tomato. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabivand, S.; Parvaneh, A.; Aliloo, A.A. The cadmium toxicity in Helianthus annuus can be modulated by endosymbiotic fungus (Piriformospora indica). J. Genet. Resour. 2018, 4, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.; Perumal, A.B.; Zhu, J.; Lu, X.; Dai, M.; Liu, X.; Lin, F. The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica-assisted alleviation of cadmium in tobacco. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucińska-Sobkowiak, R. Water relations in plants subjected to heavy metal stresses. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.; Alqarawi, A.; Al Huqail, A.A.; Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S. Alleviation of cadmium stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi via induction of acquired systemic tolerance. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhalipour, M.; Esmaielpour, B.; Gohari, G.; Haghighi, M.; Jafari, H.; Farhadi, H.; Kulak, M.; Kalisz, A. Salt stress mitigation via the foliar application of chitosan-functionalized selenium and anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles in stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni). Molecules 2021, 26, 4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Manchanda, G. Role of arbuscular mycorrhizae in the alleviation of ionic, osmotic and oxidative stresses induced by salinity in Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.(pigeonpea). J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2009, 195, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.-T.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Feng, X.-C.; Zhou, N.; Feng, H.-D.; Liu, Y.-M.; Harsonowati, W.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Wu, Q.-S. Endophytic fungi accelerate leaf physiological activity and resveratrol accumulation in Polygonum cuspidatum by up-regulating expression of associated genes. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Wang, Q.; Fazal, A.; Wang, L.-J.; Song, S.; Kong, M.-J.; Mahmood, T.; Lu, S. The DnaJ-like zinc finger protein ORANGE promotes proline biosynthesis in drought-stressed Arabidopsis seedlings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Alam, P.; Bhardwaj, R.; Siddique, K.H. Exogenous application of calcium to 24-epibrassinosteroid pre-treated tomato seedlings mitigates NaCl toxicity by modifying ascorbate–glutathione cycle and secondary metabolites. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Ali, M.M.; Eaton, D.W. Health risk assessment due to heavy metal exposure from commonly consumed fish and vegetables. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2016, 36, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, B.; Nasim, S.; Samantary, S.; Srivastava, S. Assessment of osmolyte accumulation in heavy metal exposed Salvinia natans. Int. J. Bot. 2012, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Prado, C.; Podazza, G.; Interdonato, R.; González, G.A.; Hilal, M.; Pardo, F.E. Soluble sugars: Metabolism, sensing and abiotic stress: A complex network in the life of plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.P.; Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Unraveling the role of fungal symbionts in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, F.; Liu, J.; Gao, Q.; Lou, B. Piriformospora indica confers cadmium tolerance in Nicotiana tabacum. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Ayub, A.; Hussain, S.; Waraich, E.A.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Ishfaq, M.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, N.; Maqsood, M.F. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Recent progress on morpho-physiological effects and remediation strategies. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 212–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Murata, N. Glycinebetaine protects plants against abiotic stress: Mechanisms and biotechnological applications. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Ali, S.; Hameed, A.; Bharwana, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ishaque, W.; Farid, M.; Mahmood, K.; Iqbal, Z. Cadmium stress in cotton seedlings: Physiological, photosynthesis and oxidative damages alleviated by glycinebetaine. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 104, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Chadd, R.P.; Kumar, A. Trace elements in soil-vegetables interface: Translocation, bioaccumulation, toxicity and amelioration-a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2927–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Biochemistry of oxidative stress. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, A.; Fatemi, H.; Esmaiel Pour, B.; Rizwan, M.; Soltani, A.-A. Lead (Pb)-resistant bacteria inhibit Pb accumulation in dill (Anethum graveolens L.) by improving biochemical, physiological, and antioxidant enzyme response of plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5704–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, N.A.; Ahmad, I.; Mohmood, I.; Pacheco, M.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E.; Umar, S.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, N.A.; Iqbal, M. Modulation of glutathione and its related enzymes in plants’ responses to toxic metals and metalloids—A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 75, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.F.; Moursi, Y.S.; Amro, A.; Baenziger, P.S.; Sallam, A. Investigation of heat-induced changes in the grain yield and grains metabolites, with molecular insights on the candidate genes in barley. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, I.; Chtourou, Y.; Djebali, W. Selenium alleviates cadmium toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seedlings. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.C.; Carvalho, R.F.; Gratão, P.L.; Carvalho, G.; Tezotto, T.; Medici, L.O.; Peres, L.E.; Azevedo, R.A. Biochemical responses of the ethylene-insensitive Never ripe tomato mutant subjected to cadmium and sodium stresses. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 71, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Hassani, D.; Liao, J.; Xiong, X.; Bilal, M.; Huang, D. An endosymbiont Piriformospora indica reduces adverse effects of salinity by regulating cation transporter genes, phytohormones, and antioxidants in Brassica campestris ssp. Chinensis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 153, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.E.; Abdelsattar, M.; Abdeldaym, E.A.; Atia, M.A.; Mahmoud, A.W.M.; Saad, M.M.; Hirt, H. Piriformospora indica alters Na+/K+ homeostasis, antioxidant enzymes and LeNHX1 expression of greenhouse tomato grown under salt stress. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Tiwari, N. Microbial amelioration of salinity stress in HD 2967 wheat cultivar by up-regulating antioxidant defense. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2021, 14, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohari, G.; Safai, F.; Panahirad, S.; Akbari, A.; Rasouli, F.; Dadpour, M.R.; Fotopoulos, V. Modified multiwall carbon nanotubes display either phytotoxic or growth promoting and stress protecting activity in Ocimum basilicum L. in a concentration-dependent manner. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak-Sprada, S.; Stobiecki, M.; Deckert, J. Activation of phenylpropanoid pathway in legume plants exposed to heavy metals. Part II. Profiling of isoflavonoids and their glycoconjugates induced in roots of lupine (Lupinus luteus) seedlings treated with cadmium and lead. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2011, 58, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, P.; Meng, D.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J. Isolation, characterization and inoculation of Cd tolerant rice endophytes and their impacts on rice under Cd contaminated environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Feng, Y.; Qi, F.; Hao, R. Research progress of Piriformospora indica in improving plant growth and stress resistance to plant. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damam, M.; Kaloori, K.; Gaddam, B.; Kausar, R. Plant growth promoting substances (phytohormones) produced by rhizobacterial strains isolated from the rhizosphere of medicinal plants. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2016, 37, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mancy, A.G.; Alnaggar, A.E.A.M.; Refaey, E.E.; Mohamed, H.I.; Elnosary, M.E. A polishing the harmful effects of Broad Bean Mottle Virus infecting broad bean plants by enhancing the immunity using different potassium concentrations. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2022, 50, 12654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.F.; Sehar, S.; Han, Z.; Lwalaba, J.L.W.; Jilani, G.; Zeng, F.; Chen, Z.-H.; Shamsi, I.H. Zinc alleviates cadmium toxicity by modulating photosynthesis, ROS homeostasis, and cation flux kinetics in rice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Vadassery, J. Molecular mechanisms of Piriformospora indica mediated growth promotion in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2022, 17, 2096785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shahba, M.S.; Mansour, M.M.; Mohamed, H.I.; Sofy, M.R. Effect of biosorptive removal of cadmium ions from hydroponic solution containing indigenous garlic peel and mercerized garlic peel on lettuce productivity. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaithloul, H.A.; Soliman, M.H.; Ameta, K.L.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Elkelish, A. Changes in ecophysiology, osmolytes, and secondary metabolites of the medicinal plants of Mentha piperita and Catharanthus roseus subjected to drought and heat stress. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, M.T.; Sgherri, C.; Clijsters, H.; Navari-Izzo, F. Antioxidative responses of wheat treated with realistic concentration of cadmium. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2003, 50, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagonda, T.; Adil, M.F.; Sehar, S.; Rasheed, A.; Joan, H.I.; Ouyang, Y.; Shamsi, I.H. Physio-ultrastructural footprints and iTRAQ-based proteomic approach unravel the role of Piriformospora indica-colonization in counteracting cadmium toxicity in rice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiyu, Q.; Hongen, L.; Zhaojun, N.; Wei, G.; Chang, L.; Peng, Z. Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: A review. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibril, S.A.; Hassan, S.A.; Ishak, C.F.; Megat Wahab, P.E. Cadmium toxicity affects phytochemicals and nutrient elements composition of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Adv. Agric. 2017, 2017, 1236830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, J.; Rahnama, K.; Babaeizad, V.; Ramezanpour, S.S.; Keel, C. Induction of Wheat Resistance to STB by the Endophytic Fungus Serendipita indica and Pseudomonas protegens. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, e2762. [Google Scholar]
- Anith, K.; Sreekumar, A.; Sreekumar, J. The growth of tomato seedlings inoculated with co-cultivated Piriformospora indica and Bacillus pumilus. Symbiosis 2015, 65, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, D.R.; Arnon, D.I. The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circular. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. 1938, 347, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, S.W.; Nguyen, H.T.; Holaday, A.S. Leaf water content and gas-exchange parameters of two wheat genotypes differing in drought resistance. Crop Sci. 1990, 30, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hniličková, H.; Hniličk, F.; Orsák, M.; Hejnák, V. Effect of salt stress on growth, electrolyte leakage, Na+ and K+ content in selected plant species. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irigoyen, J.; Einerich, D.; Sánchez-Díaz, M. Water stress induced changes in concentrations of proline and total soluble sugars in nodulated alfalfa (Medicago sativa) plants. Physiol. Plant. 1992, 84, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ls, B. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, C.; Grattan, S. Rapid assay for determination of water soluble quaternary ammonium compounds. Plant Soil 1983, 70, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, B.; Maehly, A. Assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 2, 764–775. [Google Scholar]
- Giannopolitis, C.N.; Ries, S.K. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1977, 59, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Gálvez, A.; Di Scala, K.; Rodríguez, K.; Lemus-Mondaca, R.; Miranda, M.; López, J.; Perez-Won, M. Effect of air-drying temperature on physico-chemical properties, antioxidant capacity, colour and total phenolic content of red pepper (Capsicum annuum, L. var. Hungarian). Food Chem. 2009, 117, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldahl, C. A new method for the determination of nitrogen in organic matter. Z. Anal. Chem. 1883, 22, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.; Sommers, E. Phosphorus soluble in sodium bicarbonate. Methods Soil Anal. Part 1982, 2, 404–430. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.; Estefan, G.; Rashid, A. Soil and Plant Analysis Laboratory Manual; ICARDA: Beirut, Lebanon, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, R.; Chanana, Y.; Gurcharan Singh, G.S. Crop regulation effects on the cold storage of peaches. I. Effect on physical characteristics of fruits. Haryana J. Hortic. Sci. 2001, 30, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Westerman, R. Soil Testing and Plant Analysis. Soil Sci. 1991, 152, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormanik, P.; Mc Graw, A. Quantification of Vesicular-Arbuscular Mycorrhizal in Plant Roots. In Methods and Principles of Mycorrhizal Research; Schenck, N.C., Ed.; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1982; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wollum, A. Cultural methods for soil microorganisms. Methods Soil Anal. Part 2 Chem. Microbiol. Prop. 1982, 9, 781–802. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, A.; Demirci, B.; Baser, K. Micromorphology of glandular trichomes of Nepeta congesta Fisch. & Mey. var. congesta (Lamiaceae) and chemical analysis of the essential oils. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2007, 73, 29–34. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahbari, A.; Esmaielpour, B.; Azarmi, R.; Fatemi, H.; Lajayer, H.M.; Panahirad, S.; Gohari, G.; Vita, F. Symbiotic Fungus Serendipita indica as a Natural Bioenhancer Against Cadmium Toxicity in Chinese Cabbage. Plants 2025, 14, 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172773
Rahbari A, Esmaielpour B, Azarmi R, Fatemi H, Lajayer HM, Panahirad S, Gohari G, Vita F. Symbiotic Fungus Serendipita indica as a Natural Bioenhancer Against Cadmium Toxicity in Chinese Cabbage. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172773
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahbari, Akram, Behrooz Esmaielpour, Rasoul Azarmi, Hamideh Fatemi, Hassan Maleki Lajayer, Sima Panahirad, Gholamreza Gohari, and Federico Vita. 2025. "Symbiotic Fungus Serendipita indica as a Natural Bioenhancer Against Cadmium Toxicity in Chinese Cabbage" Plants 14, no. 17: 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172773
APA StyleRahbari, A., Esmaielpour, B., Azarmi, R., Fatemi, H., Lajayer, H. M., Panahirad, S., Gohari, G., & Vita, F. (2025). Symbiotic Fungus Serendipita indica as a Natural Bioenhancer Against Cadmium Toxicity in Chinese Cabbage. Plants, 14(17), 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172773






