Biochar and Melatonin Partnership Mitigates Arsenic Toxicity in Rice by Modulating Antioxidant Defense, Phytochelatin Synthesis, and Down-Regulating the Transporters Involved in Arsenic Uptake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biochar Characterization
2.2. Physiological Traits
2.3. Oxidative Markers and Antioxidant Activities
2.4. Osmolytes, Endogenous Melatonin and Phytochelatin Synthesis
2.5. Soil Properties and Arsenic Fractions
2.6. Growth and Yield Traits and Element Accumulation in Rice Seedlings
2.7. Gene Expression
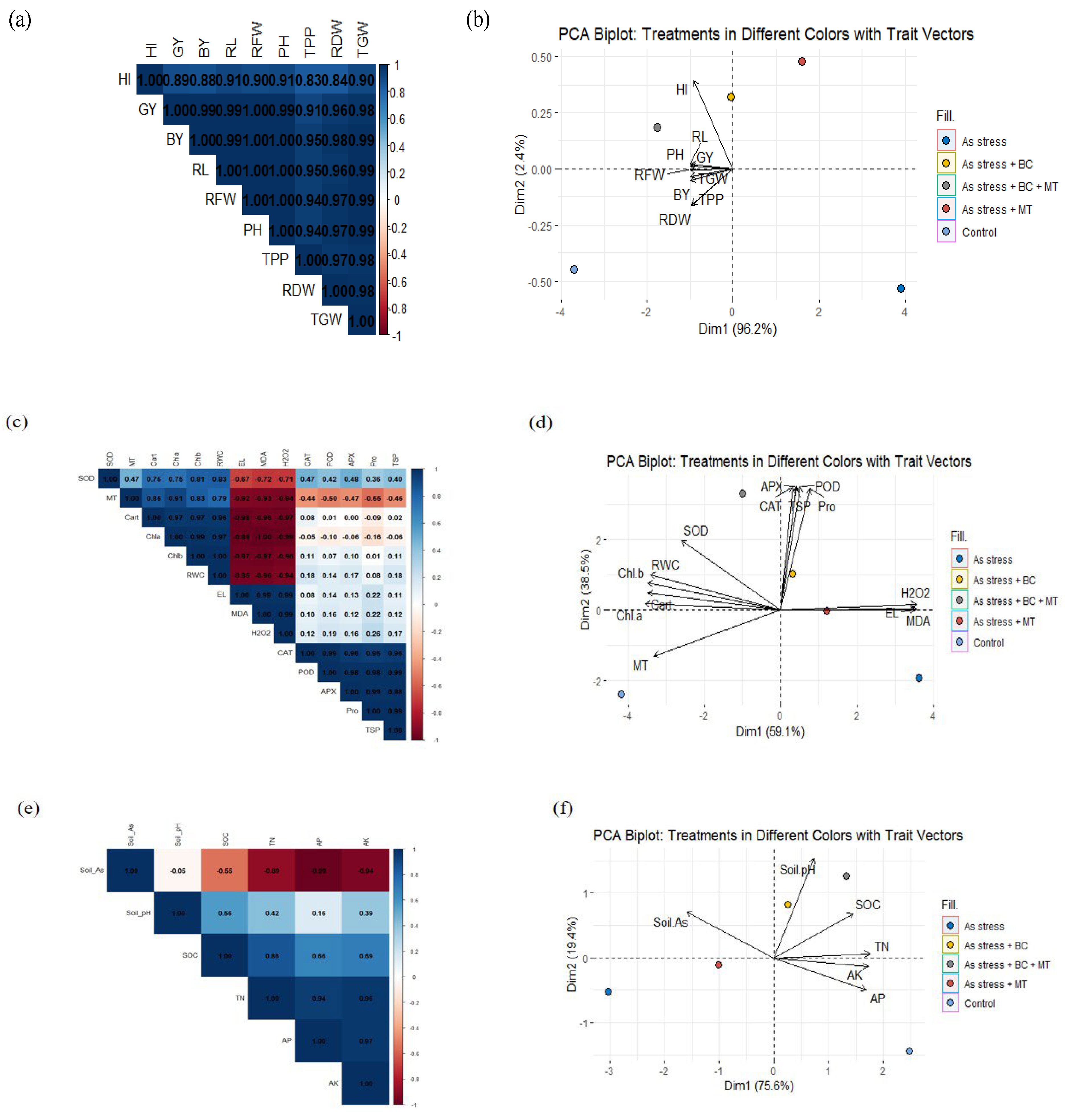
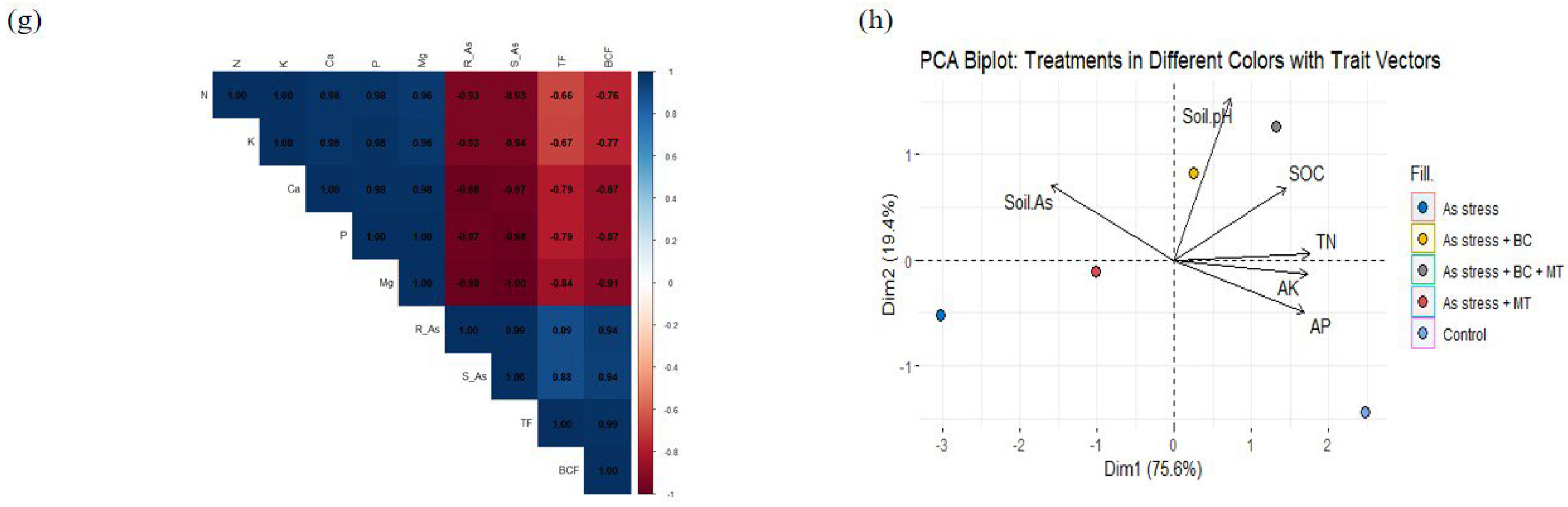
2.8. Principal Component Analysis
2.9. Correlation Between Different Traits
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experiment Site and Biochar Preparation
4.2. Experimental Details
4.3. Determination of Chlorophyll Synthesis, Leaf Water Contents and Oxidative Markers
4.4. Determination of Leaf Osmolytes, Endogenous Melatonin and Antioxidants
4.5. Tissue Nutrient and Arsenic Concentration
4.6. Determination of Soil Properties
4.7. Agronomic Parameters
4.8. RNA Preparation and Gene Expression Analysis
4.9. Determination of Phytochelatin Synthesis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Sun, L.; Zhang, P.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles alleviate cadmium stress by modulating plant metabolism and decreasing cadmium accumulation in Perilla frutescents. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 100, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.-H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, P. Assessing the arsenic-saturated biochar recycling potential of vermitechnology: Insights on nutrient recovery, metal benignity, and microbial activity. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeuren, A.; Pereira, B.; Kaba, A.J.; Titeux, H.; Delmelle, P. Environmental bioavailability of arsenic, nickel and chromium in soils impacted by high geogenic and anthropogenic background contents. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath Barbhuiya, S.; Warisa, R.; Barhoi, D.; Das, J.; Giri, S. Consequences of arsenic exposure in Plant-health status: An overview. In Arsenic in the Environment Sources, Impacts and Remedies; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Castillo, J.I.; Saldaña-Robles, A.; Ozuna, C. Arsenic stress in plants: A metabolomic perspective. Plant Stress 2022, 3, 100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.H.; Chandrasekharam, D.; Dhanachandra, W.; Ram, K. Relationship of arsenic accumulation with irrigation practices and crop type in agriculture soils of Bengal Delta, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, J.A.; Ahmad, P.; Corpas, F.J. Main nitric oxide (NO) hallmarks to relieve arsenic stress in higher plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Sher, A.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Ijaz, M.; Nawaz, M.; Ul-Allah, S.; Abbas, T.; Shah, A.N.; Imam, M.S.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; et al. Application of silicon and biochar alleviates the adversities of arsenic stress in maize by triggering the morpho-physiological and antioxidant defense mechanisms. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 979049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, E.F.; Reid, B.J.; Sun, G.-X.; Yuan, H.-Y.; Li, X.-M.; Zhu, Y.-G. Silicon (Si) biochar for the mitigation of arsenic (As) bioaccumulation in spinach (Spinacia oleracean) and improvement in the plant growth. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Du, H.; Tie, B.; Lu, X.; Qin, S.; Lei, M. The ignored risk: Heavy metal pollution of medicine and food homologous substances. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 18577–18587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.S.; Mise, N.; Ichihara, S. Arsenic contamination in food chain in Bangladesh: A review on health hazards, socioeconomic impacts and implications. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2022, 2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ghorbani, A.; Pehlivan, N.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Elshikh, M.S.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Barker, J.; Zargar, M.; Chen, M. Co-application of melatonin and zeolite boost bamboo tolerance under cadmium by enhancing antioxidant capacity, osmolyte accumulation, plant nutrient availability, and decreasing cadmium absorption. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 322, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Emamverdian, A.; Chen, M.-X.; Naz, S.; Muhammad, H.M.D.; Altaf, M.A.; Ahmad, R. Illustrating recent development in melatonin-heavy metal research in plant. In Melatonin in Plants: A Pleiotropic Molecule for Abiotic Stresses and Pathogen Infection; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Emamverdian, A.; Pishkar, L.; Chashmi, K.A.; Salavati, J.; Zargar, M.; Chen, M. Melatonin-mediated nitric oxide signaling enhances adaptation of tomato plants to aluminum stress. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 162, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, V.; Namdjoyan, S.; Soorki, A.A. Interactive effects of exogenous melatonin and hydrogen sulfide in alleviating lead toxicity in safflower seedlings. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdjoyan, S.; Soorki, A.A.; Elyasi, N.; Kazemi, N.; Simaei, M. Melatonin alleviates lead-induced oxidative damage in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) seedlings. Ecotoxicology 2019, 29, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ahammed, G.J.; Zhang, X.-N.; Zhang, L.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Fu, J.-Y.; Han, W.-Y. Melatonin-mediated regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis and antioxidant defense confer tolerance to arsenic stress in Camellia sinensis L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhat, H.F.; Zia, Z.; Fahad, S.; Abbas, S.; Hammad, H.M.; Shahzad, A.N.; Abbas, F.; Alharby, H.; Shahid, M. Arsenic uptake, accumulation and toxicity in rice plants: Possible remedies for its detoxification: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9142–9158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armynah, B.; Atika; Djafar, Z.; Piarah, W.H.; Tahir, D. Analysis of chemical and physical properties of biochar from rice husk biomass. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 979, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Kang, C.; Ren, D.; Zhang, L. Assessment of the variation of heavy metal pollutants in soil and crop plants through field and laboratory tests. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, S.; Abbas, G.; Shahid, M.; Amjad, M.; Hussain, M.; Asad, S.A.; Imran, M.; Naeem, M.A. Effect of salinity on physiological, biochemical and photostabilizing attributes of two genotypes of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) exposed to arsenic stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilachi, I.C.; Stoleru, V.; Gavrilescu, M. Analysis of heavy metal impacts on cereal crop growth and development in contaminated soils. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.H.; Alamri, S.; Nasir Khan, M.; Corpas, F.J.; Al-Amri, A.A.; Alsubaie, Q.D.; Ali, H.M.; Kalaji, H.M.; Ahmad, P. Melatonin and calcium function synergistically to promote the resilience through ROS metabolism under arsenic-induced stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Hong, Z.; Islam, F.; Noor, Y.; Hannan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ayyaz, A.; Mwamba, T.M.; Zhou, W.; Song, W. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of arsenic induced toxicity reveals the mechanism of multilevel coordination of efficient defense and energy metabolism in two Brassica napus cultivars. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Amjad, M.; Saqib, M.; Murtaza, B.; Asif Naeem, M.; Shabbir, A.; Murtaza, G. Soil sodicity is more detrimental than salinity for quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): A multivariate comparison of physiological, biochemical and nutritional quality attributes. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2020, 207, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshir, F.; Abbas, G.; Amjad, M.; Rizwan, M.; Akram, M.; Ahmad, S.; Tahir, M.; Ali, S.; Farooq, A.B.U. Physiological and biochemical characterization of Kalongi (Nigella sativa) against arsenic stress: Implications for human health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 298, 118829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, M.A.; Abdullah, M.; Imran, M.; Shahid, M.; Abbas, G.; Amjad, M.; Natasha; Shah, G.M.; Khan, W.-u.-D.; Alamri, S.; et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles doped biochar ameliorates trace elements induced phytotoxicity in tomato by modulation of physiological and biochemical responses: Implications for human health risk. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, E.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Sarkar, B.; Xu, S.; Song, H.; Liang, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Hou, D.; et al. Iron-modified biochar and water management regime-induced changes in plant growth, enzyme activities, and phytoavailability of arsenic, cadmium and lead in a paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, R.; Asif, S.; Asaf, S.; Lubna; Du, X.-X.; Park, J.-R.; Nari, K.; Bhatta, D.; Lee, I.-j.; Kim, K.-M. Melatonin alleviates arsenic (As) toxicity in rice plants via modulating antioxidant defense system and secondary metabolites and reducing oxidative stress. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, W.; Qin, J.; Li, H.; Chen, G. Hydrous zirconium oxide modified biochar for in situ remediation of arsenic contaminated agricultural soil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, C.; Lim, K.-J.; Wang, Z. The additive effect of biochar amendment and simulated nitrogen deposition stimulates the plant height, photosynthesis and accumulation of NPK in pecan (Carya illinoinensis) seedlings. AoB Plants 2020, 12, plaa035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, K.; Kumar, B.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Protective mechanisms of sulfur against arsenic phytotoxicity in Brassica napus by regulating thiol biosynthesis, sulfur-assimilation, photosynthesis, and antioxidant response. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 188, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrakar, V.; Pandey, N.; Keshavkant, S. Plant Responses to Arsenic Toxicity: Morphology and Physiology. In Mechanisms of Arsenic Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofroňová, M.; Hrdinová, A.; Mašková, P.; Tremlová, J.; Soudek, P.; Petrová, Š.; Pinkas, D.; Lipavská, H. Multi-component antioxidative system and robust carbohydrate status, the essence of plant arsenic tolerance. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; Huang, L.; Riaz, M.; Bashir, S.; Mustafa, A.; Abbasi, G.H.; Xue, B.; Ali, U. Ameliorative effects of biochar on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and heavy metal immobilization in soil irrigated with untreated wastewater. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 39, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ji, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhou, G.; Liu, R.; Shao, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, N.; Zhou, X.; et al. Biochar amendment boosts photosynthesis and biomass in C3 but not C4 plants: A global synthesis. GCB Bioenergy 2020, 12, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Ha, C.V.; Rahman, M.M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Keya, S.S.; Watanabe, Y.; Itouga, M.; Hashem, A.; Abd Allah, E.F.; Fujita, M.; et al. Strigolactones modulate cellular antioxidant defense mechanisms to mitigate arsenate toxicity in rice shoots. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species signalling in plant stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.Z.; McGee, R.; Hoque, M.A.; Ahammed, G.J.; Carpenter-Boggs, L. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, selenium and biochar on photosynthetic pigments and antioxidant enzyme activity under arsenic stress in mung bean (Vigna radiata). Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, S.; Al-Amri, S.M. Exogenous melatonin-mediated modulation of arsenic tolerance with improved accretion of secondary metabolite production, activating antioxidant capacity and improved chloroplast ultrastructure in rosemary herb. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulick, D.; Ghosh, D.; Chandra Santra, S. Evaluation of effectiveness of seed priming with selenium in rice during germination under arsenic stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 109, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Rahman, A.; Ansary, M.M.U.; Watanabe, A.; Fujita, M.; Tran, L.-S.P. Hydrogen sulfide modulates cadmium-induced physiological and biochemical responses to alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Cheng, Y.; Kanwar, M.K.; Chu, X.-Y.; Ahammed, G.J.; Qi, Z.-Y. Responses of plant proteins to heavy metal stress—A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ahammed, G.J.; Yin, L.; Shi, K.; Xia, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, J. Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Alam, P.; Hussain, A.; Karabulut, F.; Tonny, S.H.; Cheng, S.H.; Yusuf, M.; Adil, M.F.; Sehar, S.; Alomrani, S.O.; et al. Phytochelatins: Key regulator against heavy metal toxicity in plants. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Ghassemi-Golezani, K. The modified biochars influence nutrient and osmotic statuses and hormonal signaling of mint plants under fluoride and cadmium toxicities. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1064409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.T.F.; Chow, K.L.; Chen, X.W.; Ng, C.W.W.; Wong, M.H. Effects of biochar on soil water retention curves of compacted clay during wetting and drying. Biochar 2022, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Rahman, M.M.; Ghosh, T.K.; Kabir, A.H.; Abdelrahman, M.; Rahman Khan, M.A.; Mochida, K.; Tran, L.-S.P. Potassium in plant physiological adaptation to abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 186, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Bhat, J.A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Moustakas, M.; Ahmad, P. Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles (MgO-NPs) Alleviate arsenic toxicity in soybean by modulating photosynthetic function, nutrient uptake and antioxidant potential. Metals 2022, 12, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therby-Vale, R.; Lacombe, B.; Rhee, S.Y.; Nussaume, L.; Rouached, H. Mineral nutrient signaling controls photosynthesis: Focus on iron deficiency-induced chlorosis. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Exogenous melatonin regulates endogenous phytohormone homeostasis and thiol-mediated detoxification in two indica rice cultivars under arsenic stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1585–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, M.S.; Guo, S.; Baloch, A.R.; Sun, J.; Shu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ahammed, G.J.; Kabir, K.; Roy, R. Melatonin alleviates nickel phytotoxicity by improving photosynthesis, secondary metabolism and oxidative stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lian, W.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Q.; Jia, Y.; Jia, H.; Xie, L. NtIAA26 positively regulates salt tolerance in tobacco by modulating potassium uptake and antioxidant activity. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 97, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.-S.; Tang, C.-S.; Gu, K.; Shi, B. Remediation of heavy-metal-contaminated soils by biochar: A review. Environ. Geotech. 2020, 9, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Su, Q.; Guoqin, H.; Du, Z.; Noor, M.A.; Asseri, T.A.Y.; Hassan, M.U. Integrative biochar and melatonin application mitigates lead toxicity in rice by modulating antioxidant activities and iron plaque formation and downregulating the expression of metal uptake genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1609825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, M.; Zhang, C.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, J. Melatonin application enhances the remediation of cadmium-contaminated soils by Cinnamomum camphora. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 968, 178912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arco-Lázaro, E.; Pardo, T.; Clemente, R.; Bernal, M.P. Arsenic adsorption and plant availability in an agricultural soil irrigated with As-rich water: Effects of Fe-rich amendments and organic and inorganic fertilisers. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 209, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronzan, M.; Piacentini, D.; Fattorini, L.; Della Rovere, F.; Eiche, E.; Riemann, M.; Altamura, M.M.; Falasca, G. Cadmium and arsenic affect root development in Oryza sativa L. negatively interacting with auxin. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 151, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Khan, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Sun, T.-R.; Tang, J.-F.; Cotner, J.B.; Xu, Y.-Y. Biochars induced modification of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in soil and its impact on mobility and bioaccumulation of arsenic and cadmium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 348, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.; Shaheen, S.M.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Wang, S.-L.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J. Release dynamics of As, Co, and Mo in a biochar treated soil under pre-definite redox conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, W. Insight into interaction between biochar and soil minerals in changing biochar properties and adsorption capacities for sulfamethoxazole. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Upadhyay, M.K.; Giri, B.; Karwadiya, J.; Bose, S.; Jaiswal, M.K. Iron oxide doped rice biochar reduces soil-plant arsenic stress, improves nutrient values: An amendment towards sustainable development goals. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, J.Z.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Patinha, C.; Durães, N.; Vieira, E.M.; Rodrigues, V.G.S. Sorption of arsenic by composts and biochars derived from the organic fraction of municipal solid wastes: Kinetic, isotherm and oral bioaccessibility study. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, X.; Meng, J.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. Remediation of As(III) and Cd(II) co-contamination and its mechanism in aqueous systems by a novel calcium-based magnetic biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 348, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. Vacuolar transporters for cadmium and arsenic in plants and their applications in phytoremediation and crop development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Islam, F.; Ali, B.; Najeeb, U.; Mao, B.; Gill, R.A.; Yan, G.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Zhou, W. Arsenic toxicity in plants: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of its transport and metabolism. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 132, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Harris, W.G.; Migliaccio, K.W. Removal of arsenic by magnetic biochar prepared from pinewood and natural hematite. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Shan, X.-Q.; McLaren, R.; Duan, J. The ageing effect on the bioaccessibility and fractionation of arsenic in soils from China. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.; Kasuga, J.; Makino, T.; Arao, T. Evaluation of the effects of application of iron materials on the accumulation and speciation of arsenic in rice grain grown on uncontaminated soil with relatively high levels of arsenic. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 125, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, R.R.; Trugilho, P.F.; Silva, C.A.; Melo, I.C.N.A.d.; Melo, L.C.A.; Magriotis, Z.M.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. Properties of biochar derived from wood and high-nutrient biomasses with the aim of agronomic and environmental benefits. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, J.W.; Steiner, C.; Harris, K.; Das, K.C.; Bibens, B. Effect of low-temperature pyrolysis conditions on biochar for agricultural use. Trans. ASABE 2008, 51, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. [34] Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 350–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, L.; Tonini, M.; Soldatini, G.F. Effects of high light and ozone fumigation on photosynthesis in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 38, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, V.; Yordanov, I.; Edreva, A. Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants. Plant Sci. 2000, 151, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, Y.; Back, K. An increase in melatonin in transgenic rice causes pleiotropic phenotypes, including enhanced seedling growth, delayed flowering, and low grain yield. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Oxygen Radicals in Biological Systems. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, B.; Maehly, A.C. [136] Assay of catalases and peroxidases. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1955; pp. 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa, R.S.; Plumb-Dhindsa, P.; Thorpe, T.A. Leaf senescence: Correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J. Exp. Bot. 1981, 32, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Case, V.W. Sampling, Handling, and Analyzing Plant Tissue Samples. In SSSA Book Series; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 389–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Xiong, H.; Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Al-Khalaf, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Ahmed, W. Biochar and trehalose co-application: A sustainable strategy for alleviating lead toxicity in rice. Plants 2025, 14, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.N.; Husain, S.Z.; Nazir, I. Heavy metal contamination and accumulation in soil and wild plant species from industrial area of Islamabad, Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Agronomy Monographs; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmke, P.A.; Sparks, D.L. Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, and Cesium. In SSSA Book Series; Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 551–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Hasan, M.K.; Li, Z.; Yang, T.; Jin, W.; Qi, Z.; Yang, P.; Wang, G.; Ahammed, G.J.; Zhou, J. Melatonin-induced plant adaptation to cadmium stress involves enhanced phytochelatin synthesis and nutrient homeostasis in Solanum lycopersicum L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minocha, R.; Thangavel, P.; Dhankher, O.P.; Long, S. Separation and quantification of monothiols and phytochelatins from a wide variety of cell cultures and tissues of trees and other plants using high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1207, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
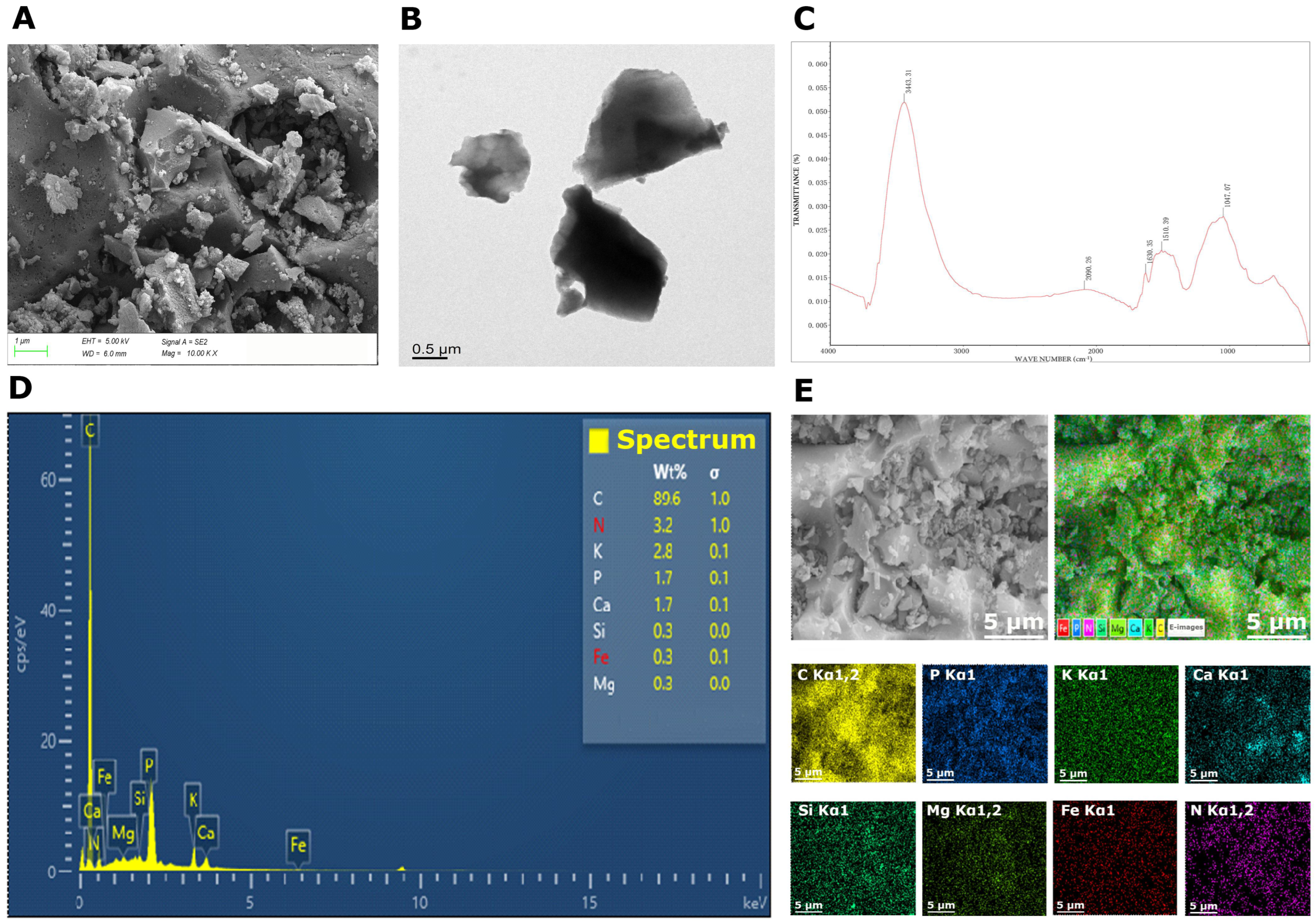


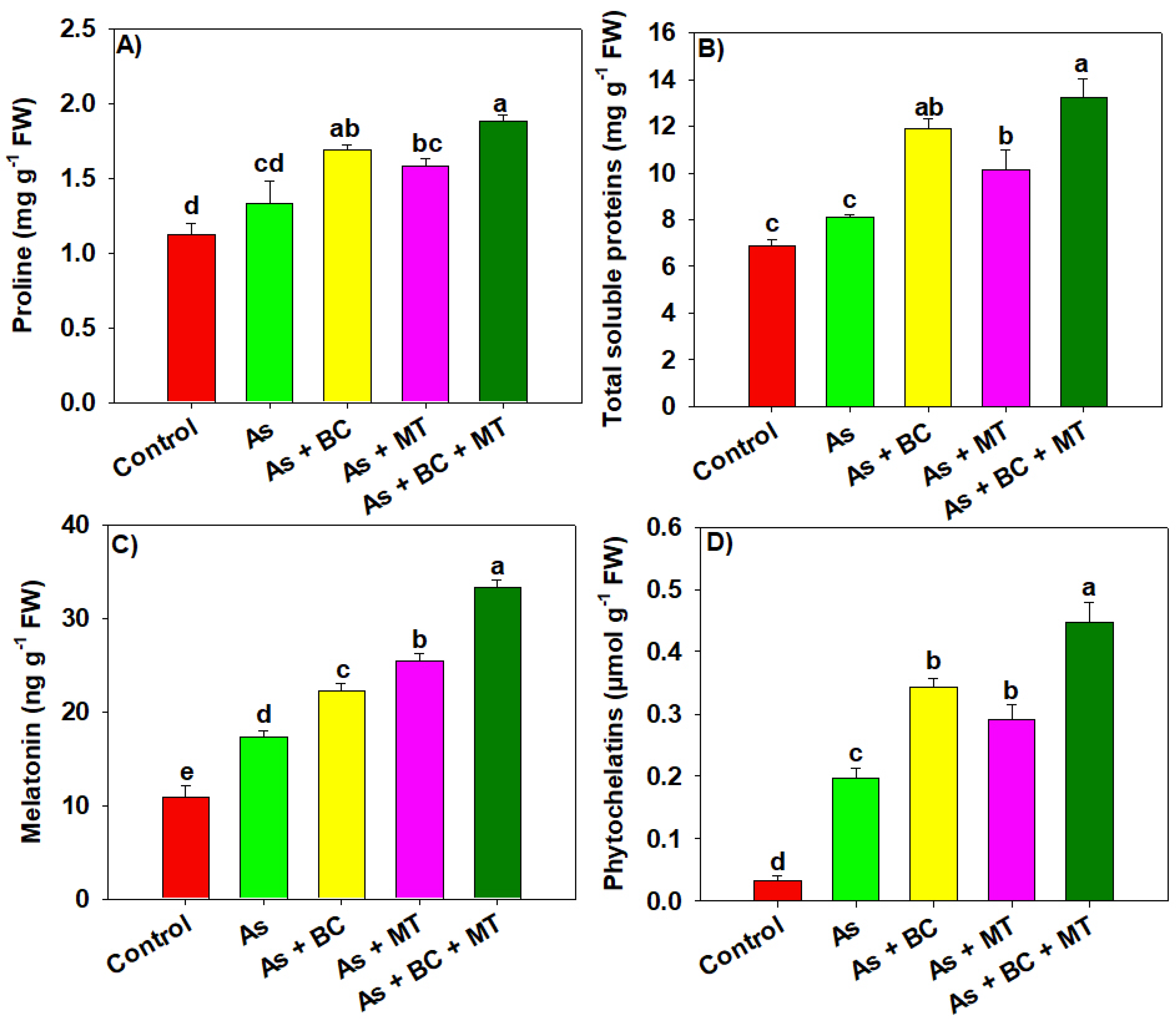
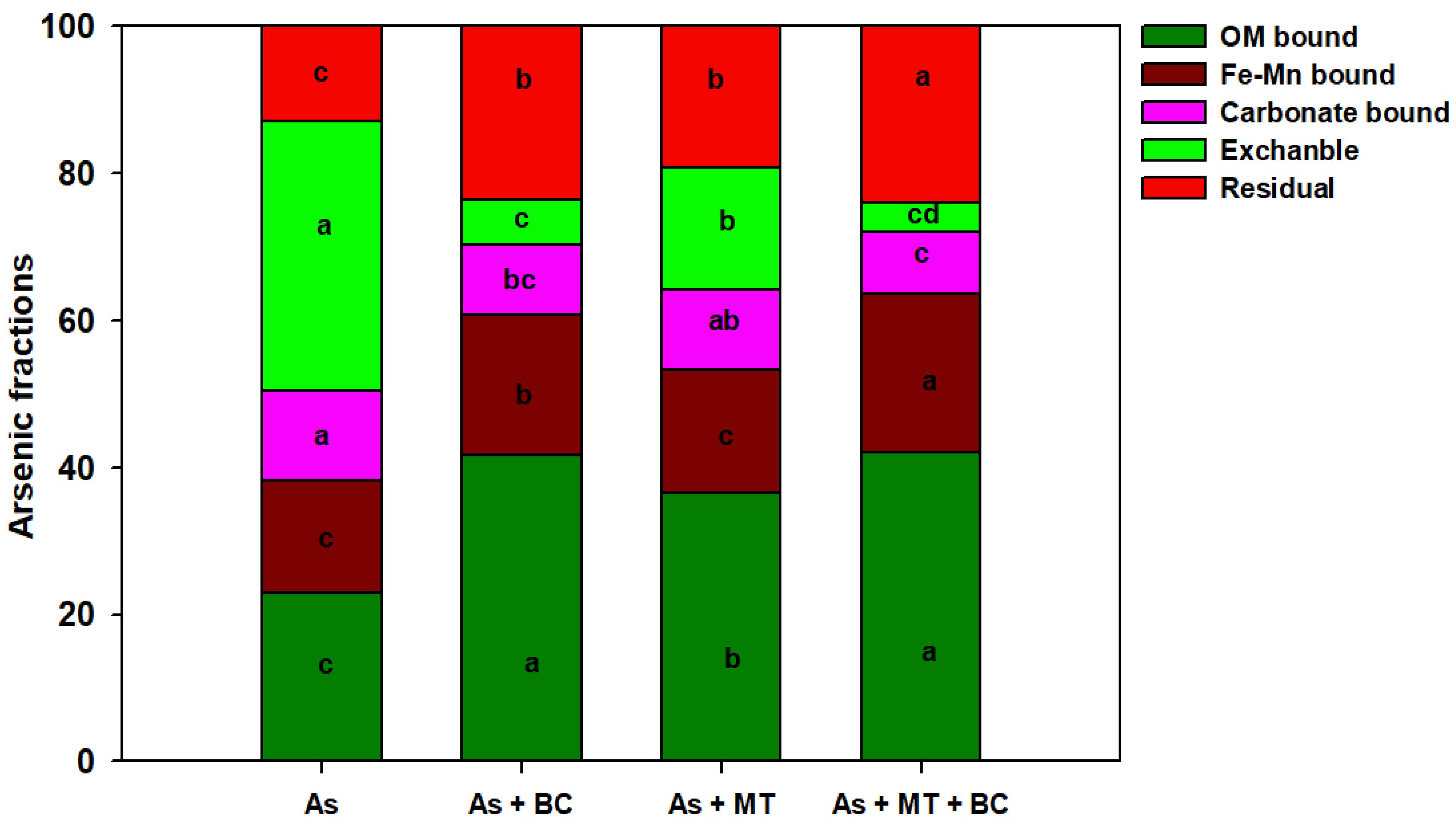

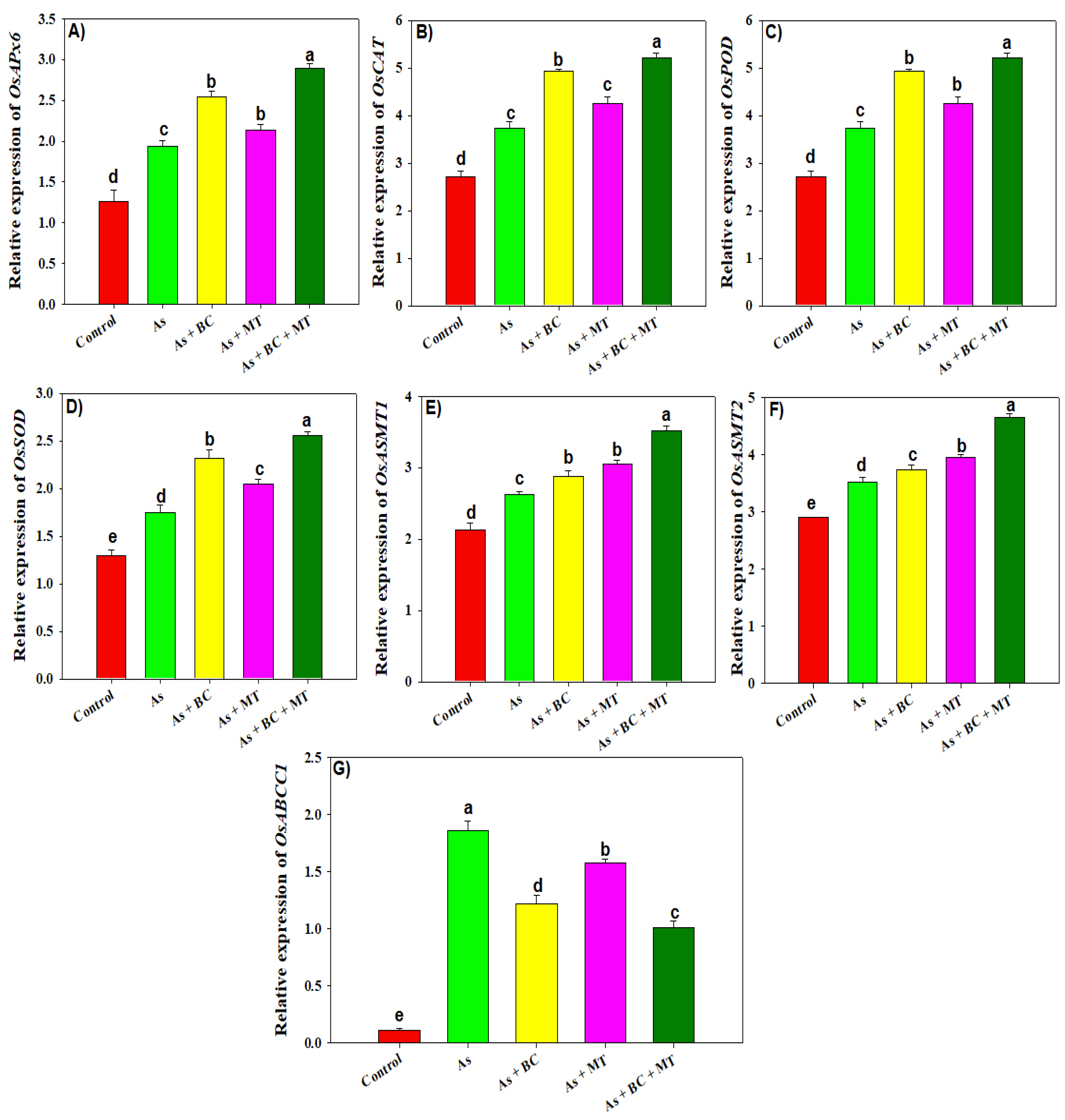
| Treatments | Soil As (mg kg−1) | Soil pH | TN (g kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 5.62 ± 0.021 c | 1.72 ± 0.07 a | 53.70 ± 1.81 a | 128.63 ± 2.36 a |
| As | 54.46 ± 2.21 a | 5.58 ± 0.026 c | 1.12 ± 0.03 d | 35.43 ± 0.86 d | 92.27 ± 1.72 d |
| As + BC | 37.23 ± 1.78 c | 5.94 ± 0.028 b | 1.49 ± 0.04 bc | 42.73 ± 1.25 bc | 109.54 ± 1.24 c |
| As + MT | 45.43 ± 3.27 b | 5.60 ± 0.041 c | 1.38 ± 0.02 c | 40.30 ± 0.74 c | 98.37 ± 2.05 d |
| As+ BC + MT | 31.27 ± 0.78 c | 6.12 ± 0.021 a | 1.61 ± 0.05 ab | 45.50 ± 0.90 b | 119.26 ± 2.80 b |
| Treatments | RL (cm) | RFW (g) | RDW (g) | PH (cm) | TPP | TGW (g) | BYP (g) | GYP (g) | HI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 35.04 ± 2.55 a | 14.74 ± 0.47 a | 5.38 ± 0.09 a | 101.67 ± 2.87 a | 11 ± 1.25 a | 28.32 ± 0.85 a | 156.81 ± 2.58 a | 18.06 ± 0.81 a | 21.61 ± 1.94 a |
| As | 15.47 ± 0.86 d | 7.63 ± 0.43 c | 2.40 ± 0.13 d | 79.33 ± 2.49 d | 9 ± 0.94 b | 16.63 ± 1.23 d | 117.65 ± 2.62 c | 13.36 ± 0.79 d | 16.33 ± 0.35 b |
| As + BC | 26.40 ± 0.70 b | 11.20 ± 0.82 b | 3.45 ± 0.19 c | 91.00 ± 2.45 bc | 10 ± 0.47 ab | 22.69 ± 0.47 bc | 135.67 ± 2.49 b | 15.67 ± 0.86 bc | 20.57 ± 0.90 a |
| As + MT | 21.10 ± 0.95 c | 9.67 ± 0.41 bc | 3.10 ± 0.09 c | 86.00 ± 1.41 cd | 10 ± 0.49 ab | 19.88 ± 1.26 c | 127.33 ± 4.11 bc | 14.71 ± 0.38 cd | 19.83 ± 0.45 ab |
| As+ BC + MT | 31.31 ± 0.82 a | 13.33 ± 0.90 a | 4.19 ± 0.16 b | 97.33 ± 1.70 ab | 11 ± 1.25 ab | 24.66 ± 0.63 b | 148.31 ± 3.23 a | 17.56 ± 0.30 ab | 20.93 ± 1.27 a |
| Treatments | Nitrogen (mg kg−1) | Phosphorous (mg kg−1) | Potassium (mg kg−1) | Calcium (mg kg−1) | Magnesium (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 42.00 ± 1.73 a | 25.50 ± 0.78 a | 61.70 ± 1.24 a | 66.90 ± 1.28 a | 62.07 ± 1.67 a |
| As | 26.30 ± 0.80 d | 14.33 ± 0.17 e | 33.70 ± 1.36 e | 37.10 ± 1.61 d | 36.58 ± 0.85 e |
| As + BC | 36.20 ± 0.50 bc | 20.20 ± 0.82 c | 51.97 ± 0.56 c | 51.50 ± 0.82 c | 47.81 ± 1.16 c |
| As + MT | 34.00 ± 0.72 c | 17.67 ± 0.41 d | 46.83 ± 0.43 d | 49.80 ± 4.80 c | 43.03 ± 1.24 d |
| As+ BC + MT | 39.70 ± 1.28 ab | 22.63 ± 0.48 b | 56.83 ± 1.25 b | 57.50 ± 0.82 b | 54.07 ± 1.33 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor, M.A.; Hassan, M.U.; Khan, T.A.; Zhou, B.; Huang, G. Biochar and Melatonin Partnership Mitigates Arsenic Toxicity in Rice by Modulating Antioxidant Defense, Phytochelatin Synthesis, and Down-Regulating the Transporters Involved in Arsenic Uptake. Plants 2025, 14, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152453
Noor MA, Hassan MU, Khan TA, Zhou B, Huang G. Biochar and Melatonin Partnership Mitigates Arsenic Toxicity in Rice by Modulating Antioxidant Defense, Phytochelatin Synthesis, and Down-Regulating the Transporters Involved in Arsenic Uptake. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152453
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor, Mehmood Ali, Muhammad Umair Hassan, Tahir Abbas Khan, Baoyuan Zhou, and Guoqin Huang. 2025. "Biochar and Melatonin Partnership Mitigates Arsenic Toxicity in Rice by Modulating Antioxidant Defense, Phytochelatin Synthesis, and Down-Regulating the Transporters Involved in Arsenic Uptake" Plants 14, no. 15: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152453
APA StyleNoor, M. A., Hassan, M. U., Khan, T. A., Zhou, B., & Huang, G. (2025). Biochar and Melatonin Partnership Mitigates Arsenic Toxicity in Rice by Modulating Antioxidant Defense, Phytochelatin Synthesis, and Down-Regulating the Transporters Involved in Arsenic Uptake. Plants, 14(15), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152453










