Nomenclature and Typification of the Goat Grass Aegilops tauschii Coss. (Poaceae: Triticeae): A Key Species for the Secondary Gene Pool of Common Wheat Triticum aestivum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nomenclatural Background
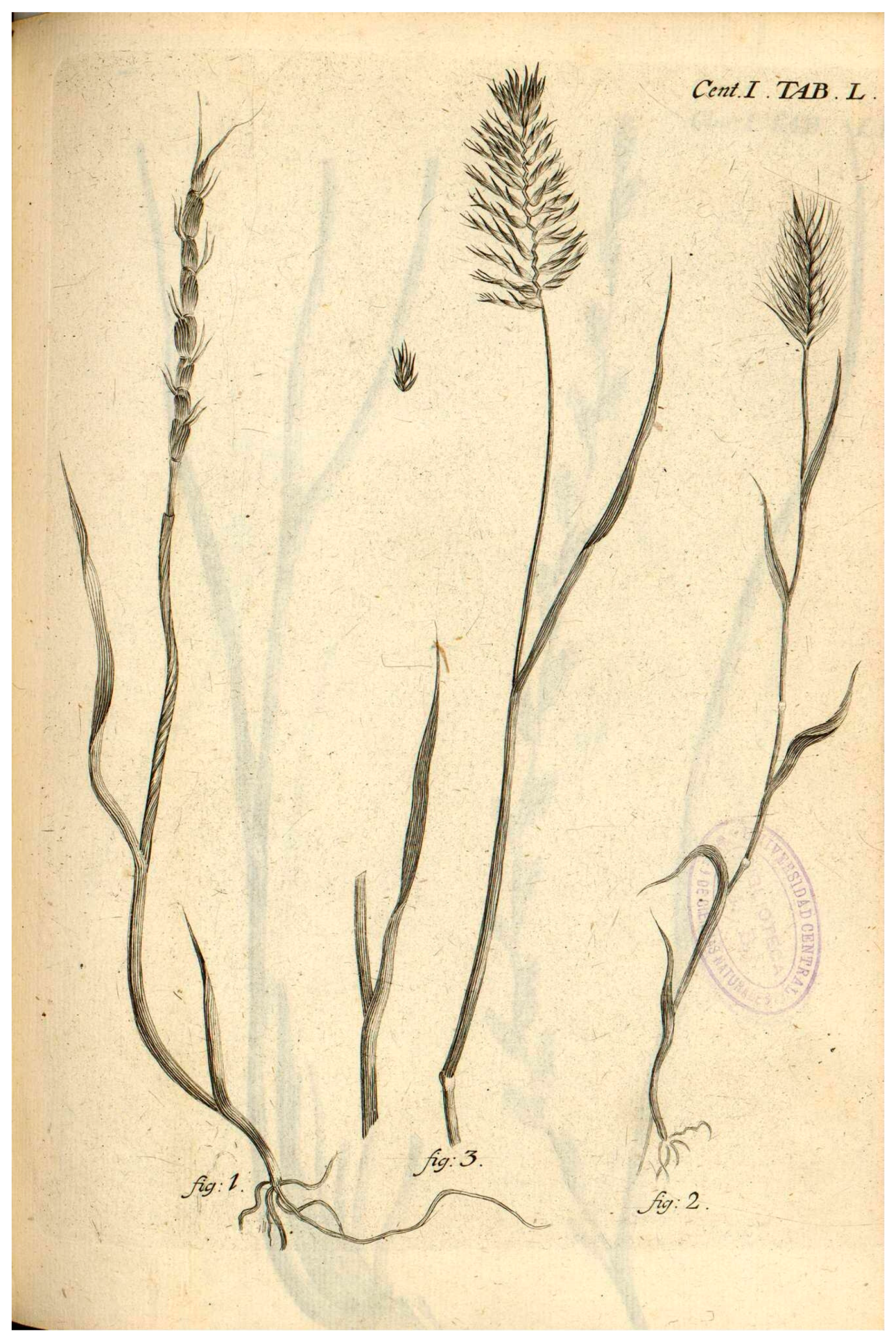
2.2. Typification of the Name
3. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gandhi, H.T.; Vales, M.I.; Mallory-Smith, C.; Riera-Lizarazu, O. Genetic Structure of Aegilops cylindrica Host in Its Native Range and in the United States of America. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvelev, N.N. The System of the Grasses (Poaceae) and Their Evolution. Bot. Rev. 1989, 55, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, I.; Vrána, J.; Burešová, V.; Cápal, P.; Farkas, A.; Darkó, É.; Cseh, A.; Kubaláková, M.; Molnár-Láng, M.; Doležel, J. Dissecting the U, M, S and C Genomes of Wild Relatives of Bread Wheat (Aegilops spp.) into Chromosomes and Exploring Their Synteny with Wheat. Plant J. 2016, 88, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ning, S.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Hao, M.; Liu, D. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization Karyotyping Reveals the Presence of Two Distinct Genomes in the Taxon Aegilops tauschii. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, R.; Arzani, A.; Mirmohammady Maibody, S.A.M. Polyphenols, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Activity Involved in Salt Tolerance in Wheat, Aegilops cylindrica and Their Amphidiploids. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 646221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qi, G.; Ren, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wu, X. Analysis of PYL Genes and Their Potential Relevance to Stress Tolerance and Berry Ripening in Grape. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2020, 145, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yoo, E.; Lee, S.; Cho, G.-T.; Lee, G.-A.; Yi, J.Y.; Du, X.; Han, S.; Hyun, D.Y.; Ro, N.; et al. Classification of 17 Species Aegilops Using DNA Barcoding and SNPs, Reveals Gene Flow among Aegilops biuncialis, Aegilops juvenalis, and Aegilops columnaris. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 984825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Slageren, M.W. Wild Wheats: A Monograph of Aegilops L. and Amblyopyrum (Jaub. & Spach) Eig (Poaceae); Wageningen Agricultural University Papers 94–7; Wageningen Agricultural University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- POWO Plant of the World Online. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:384652-1 (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Zhukovsky, P.M. A Critical-Systematical Survey of the Species of the Genus Aegilops L. Bull. Appl. Bot. Genet. Plant Breed 1928, 18, 417–609. [Google Scholar]
- Eig, A. Monographisch-Kritische Übersicht Der Gattung Aegilops. Feddes Reper. 1929, 55, 1–228. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, L.A. Reevaluation of Systematic Relationships in Triticum L. and Aegilops L. Based on Comparative Morphological and Anatomical Investigations of Dispersal Mechanisms. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.K.; Baum, B.R. Stable Classification and Nomenclature in the Triticeae: Desirability, Limitations and Prospects. Euphytica 1989, 41, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhao, S.; Kong, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; He, W.; Appels, R.; Pfeifer, M.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Aegilops tauschii Draft Genome Sequence Reveals a Gene Repertoire for Wheat Adaptation. Nature 2013, 496, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalet-Giorsa, E.; González-Muñoz, A.; Athiyannan, N.; Holden, S.; Salhi, A.; Gardener, C.; Quiroz-Chávez, J.; Rustamova, S.M.; Elkot, A.F.; Patpour, M.; et al. Origin and Evolution of the Bread Wheat D Genome. Nature 2024, 633, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunewaki, K. Plasmon Analysis in the Triticum-Aegilops Complex. Breed. Sci. 2009, 470, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, H. Discovery of the DD-Analyser, One of the Ancestors of Triticum vulgare. Agric. Hort. 1944, 19, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mcfadden, E.S.; Sears, E.R. The Origin of Triticum spelta and Its Free-Threshing Hexaploid Relatives. J. Hered. 1946, 37, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, G.; Seberg, O.; Yde, M.; Berthelsen, K. Phylogenetic Relationships of Triticum and Aegilops and Evidence for the Origin of the A, B, and D Genomes of Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 39, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Luo, M.-C.; Chen, Z.; You, F.M.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Dvorak, J. Aegilops tauschii Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Shed Light on the Origins of Wheat D-Genome Genetic Diversity and Pinpoint the Geographic Origin of Hexaploid Wheat. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, M.S.; Rao, M.V. Macro-Mutations and Subspecific Differentiation in Triticum. Wheat Inf. Serv. 1961, 13, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak, J.; Luo, M.-C.; Yang, Z.-L.; Zhang, H.-B. The Structure of the Aegilops tauschii Genepool and the Evolution of Hexaploid Wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, N.P.; Golovnina, K.A.; Kondratenko, E.Y. Taxonomy and Molecular Phylogeny of Natural and Artificial Wheat Species. Breed. Sci. 2009, 498, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, Y. Evolution of Polyploid Triticum Wheats under Cultivation: The Role of Domestication, Natural Hybridization and Allopolyploid Speciation in Their Diversification. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, T.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Deal, K.R.; Dubcovsky, J.; McGuire, P.E.; Lux, T.; Spannagl, M.; Mayer, K.F.X.; Baldrich, P.; et al. Aegilops tauschii Genome Assembly Aet v5.0 Features Greater Sequence Contiguity and Improved Annotation. G3 2021, 11, jkab325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, P.I. Genetics of Wheat Storage Proteins and the Effect of Allelic Variation on Bread-Making Quality. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1987, 38, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepurnov, G.Y.; Ovchinnikova, E.S.; Blinov, A.G.; Chikida, N.N.; Belousova, M.K.; Goncharov, N.P. Analysis of the Structural Organization and Expression of the Vrn-D1 Gene Controlling Growth Habit (Spring vs. Winter) in Aegilops tauschii Coss. Plants 2023, 12, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, B.S.; Raupp, W.J.; Sharma, H.C.; Browder, L.E.; Hatchett, J.H.; Cook, D.L.S.; Hetz, J.H.W.L.; Anderson, M.M. Resistance in Aegilops squarrosa to Wheat Leaf Rust, Wheat Powdery Mildew, Greenbug, and Hessian Fly. Plant Dis. 1986, 70, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohary, D.; Feldman, M. Hybridization between Amphidiploids and the Evolution of Polyploids in the Wheat (Aegilops-Triticum) Group. Evolution 1962, 16, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, N.P. Genus Triticum L. Taxonomy: The Present and the Future. Plant Syst. Evol. 2011, 295, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, N.P. Comparative Genetics of Wheats and Their Related Species; Publishing House of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2002. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Goncharov, N.P. Opredelitel’ Raznovidnostey Myagkoy I Tverdoy Pshenits; Manual Book of Common and Hard Wheat Varieties; Publishing House of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2009. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- MacKey, J. Wheat: Its Concept, Evolution, and Taxonomy, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kislev, M.E. Triticum parvicoccum sp. Nov., the Oldest Naked Wheat. Isr. J. Bot. 1979, 28, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udachin, R.A. On the Possible Current Existence of Triticum antiquorum Heer. Nauch.-Tekhn. Byul. 1982, 119, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Udachin, R.A.N.I. Vavilov and Studies of Wheats from Central Asia. Tr. Prikl. Bot. Genet. Sel. 1991, 140, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Goncharov, N.P.; Gaidalenok, R.F. Localization of Genes Controlling Spherical Grain and Compact Ear in Triticum antiquorum Heer Ex Udacz. Russ. J. Genet. 2005, 41, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, D.; Ferrer-Gallego, P.P.; Obón, C.; Alcaraz, F.; Laguna, E.; Goncharov, N.P. Exploring the Origins of Hexaploid Wheats: Typification of Archaeological Triticum vulgare Var. Antiquorum and Description of Modern Triticum sphaerococcum subsp. Antiquorum (Poaceae: Triticeae). Taxonomy 2024, 4, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, M. When and Where Did Domesticated Cereals First Occur in Southwest Asia? In The Dawn of Farming in the Near East; Cappers, R.T.J., Bottema, S., Eds.; Ex Oriente: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Arzani, A.; Ashraf, M. Cultivated Ancient Wheats (Triticum spp.): A Potential Source of Health-Beneficial Food Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, K. Vorarbeiten Zur Monographischen Darstellung von Wildpflanzensortimenten: Aegilops L.—Resistenzuntersuchungen. Die Kult. 1985, 33, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbers, E.L.; Gill, K.S.; Cox, T.S.; Gill, B.S. Variation of Molecular Markers among Geographically Diverse Accessions of Triticum tauschii. Genome 1991, 34, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudnikov, A.J.; Goncharov, N.P. Allozyme Variation in Aegilops squarrosa. Hereditas 1993, 119, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, J.; Luo, M.; Akhunov, E.D.N.I. Vavilov’s Theory of Centres of Diversity in the Light of Current Understanding of Wheat Diversity, Domestication and Evolution. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2011, 47, S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, H.; Tanaka, M. Morphological and Physiological Variation among Aegilops squarrosa Strains Collected in Pakistan, Afganistan and Iran. Preslia 1958, 30, 241–251. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wong, D.; Forrest, K.; Allen, A.; Chao, S.; Huang, B.E.; Maccaferri, M.; Salvi, S.; Milner, S.G.; Cattivelli, L.; et al. Characterization of Polyploid Wheat Genomic Diversity Using a High-Density 90,000 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Array. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K. Vorarbeiten Zur Monographischen Darstellung von Wildpflanzensortimenten: Aegilops L. Die Kult. 1980, 28, 33–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, H.; Yamashita, K.; Tanaka, M. Morphological, Physiological, Genetic and Cytological Studies in Aegilops and Triticum Collected from Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iran. In Results of the Kyoto University Scientific Expedition to the Karakoram and Hindukush; Yamashita, K., Ed.; Kyoto University: Kyoto, Japan, 1965; pp. 1–118. [Google Scholar]
- Tzvelev, N.N.; Probatova, N.S. Grasses of Russia; KMK: Moscow, Russia, 2019. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Nishioka, E.; Kawahara, T.; Takumi, S. Genealogical Analysis of Subspecies Divergence and Spikelet-Shape Diversification in Central Eurasian Wild Wheat Aegilops tauschii Coss. Plant Syst. Evol. 2009, 279, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.; Mohammad, T.Æ.; Naghavi, R. Distribution and Diversity of Aegilops tauschii in Iran. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008, 55, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaska, V. Electrophoretic Survey of Seedling Esterases in Wheats in Relation to Their Phylogeny. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1980, 56, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.; Furuta, Y.; Wada, T. Genetics Studies on Alpha-Amylase Isozymes in Wheat. III. Jpn. J. Genet. 1980, 55, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y. Isozyme Variations in Aegilops and Triticum, IV. The Origin of the Common Wheats Revealed from the Study on Esterase Isozymes in Synthesized Hexaploid Wheats. Jpn. J. Genet. 1979, 54, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, J.; Deal, K.R.; Luo, M.-C.; You, F.M.; von Borstel, K.; Dehghani, H. The Origin of Spelt and Free-Threshing Hexaploid Wheat. J. Hered. 2012, 103, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, K. Alpha-Amylase Isozymes and Phylogeny of Hexaploid Wheat. In Proceedings of the 4th International Wheat Genetics Symposium; Sears, E.R., Sears, L.M., Eds.; Missouri Agricultural Experiment Station: Columbia, MO, USA, 1973; pp. 851–855. [Google Scholar]
- Lelley, T.; Stachel, M.; Grausgruber, H.; Vollmann, J. Analysis of Relationships between Aegilops tauschii and the D Genome of Wheat Utilizing Microsatellites. Genome 2000, 43, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, N.; Yamasaki, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Kawahara, T.; Takumi, S. Population Structure of Wild Wheat D-Genome Progenitor Aegilops tauschii Coss.: Implications for Intraspecific Lineage Diversification and Evolution of Common Wheat. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosson, E.-C. Notes Sur Quelques Plantes de France Critiques; Librairie de Victor Masson, Place de l’École-de-Médecine 1: Paris, France, 1849. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, P.H. Aegilops. In Flora of Turkey and the East Aegean Islands; Davis, P., Ed.; Edinburgh University Press: Edinburgh, Scotland, 1985; pp. 163, 232–233, 237, 239, 241, 243. [Google Scholar]
- Bor, N.L. Gramineae. In Flora Iranica; Rechinger, K., Ed.; Akademische Druck-u. Verlagsanstalt: Graz, Austria, 1970; pp. 1–573. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, T. Poaceae. In Flora of Pakistan; Nasir, E., Ali, S.I., Eds.; Fakhri Printing Press: Karachi, Pakistan, 1982; pp. 595–596. [Google Scholar]
- Turland, N.J.; Wiersema, J.H.; Barrie, F.R.; Greuter, W.; Hawksworth, D.L.; Herendeen, P.S.; Knapp, S.; Kusber, W.-H.; Li, D.-Z.; Marhold, K.; et al. International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (Shenzhen Code); Koeltz Botanical: Glashütten, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum, J.C. Plantarum Minus Cognitarum Centuria I Complectens Plantas Circa Byzantium & in Oriente Observatas.; Ex typographia Academiae: Petropoli, Brazil, 1728. [Google Scholar]
- Trinius, C.B. Clavis Agrostographiae Antiquioris. Uebersicht des Zustandes der Agrostographie Bis Auf Linné; Und Versuch Einer Reduction der Alten Synonyme der Gräser Auf Die Heutigen Trivialnahmen; In der Biedermann’schen Hofbuchhandlung: Coburg, Germany, 1822. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.J. Aegilops. In Flora de China; Wu, Z., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Missouri Botanical Garden: Beijing, China; St. Louis, MO, USA, 2006; p. 444. [Google Scholar]
- Thiers, B. Index Herbariorum: A Global Directory of Public Herbaria and Associated Staff; New York Botanical Garden’s Virtual Herbarium: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrer-Gallego, P.P.; Ferrer-Gallego, R.; Rivera, D.; Obón, C.; Laguna, E.; Goncharov, N.P. Nomenclature and Typification of the Goat Grass Aegilops tauschii Coss. (Poaceae: Triticeae): A Key Species for the Secondary Gene Pool of Common Wheat Triticum aestivum. Plants 2025, 14, 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152375
Ferrer-Gallego PP, Ferrer-Gallego R, Rivera D, Obón C, Laguna E, Goncharov NP. Nomenclature and Typification of the Goat Grass Aegilops tauschii Coss. (Poaceae: Triticeae): A Key Species for the Secondary Gene Pool of Common Wheat Triticum aestivum. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152375
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrer-Gallego, P. Pablo, Raúl Ferrer-Gallego, Diego Rivera, Concepción Obón, Emilio Laguna, and Nikolay P. Goncharov. 2025. "Nomenclature and Typification of the Goat Grass Aegilops tauschii Coss. (Poaceae: Triticeae): A Key Species for the Secondary Gene Pool of Common Wheat Triticum aestivum" Plants 14, no. 15: 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152375
APA StyleFerrer-Gallego, P. P., Ferrer-Gallego, R., Rivera, D., Obón, C., Laguna, E., & Goncharov, N. P. (2025). Nomenclature and Typification of the Goat Grass Aegilops tauschii Coss. (Poaceae: Triticeae): A Key Species for the Secondary Gene Pool of Common Wheat Triticum aestivum. Plants, 14(15), 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152375










