An Investigation into the Evolutionary Characteristics and Expression Patterns of the Basic Leucine Zipper Gene Family in the Endangered Species Phoebe bournei Under Abiotic Stress Through Bioinformatics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material, Data Sources, and Conditions for Growth
2.2. The PbbZIP Gene Identification and Physicochemical Characteristics
2.3. PbbZIP Gene Family Chromosomal Distribution
2.4. Construction and Analysis of Evolutionary Tree and Collinearity Analysis
2.5. Motif Analysis and Gene Structure of the PbbZIPs
2.6. Examination of Cis-Elements in the Promoters of PbbZIP Genes
2.7. Transcriptome Data Acquisition and Abiotic Stress Treatment of Different Plant Tissues
2.8. Abiotic Stress Experiment and qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Physicochemical Characteristics of the PbbZIP Gene
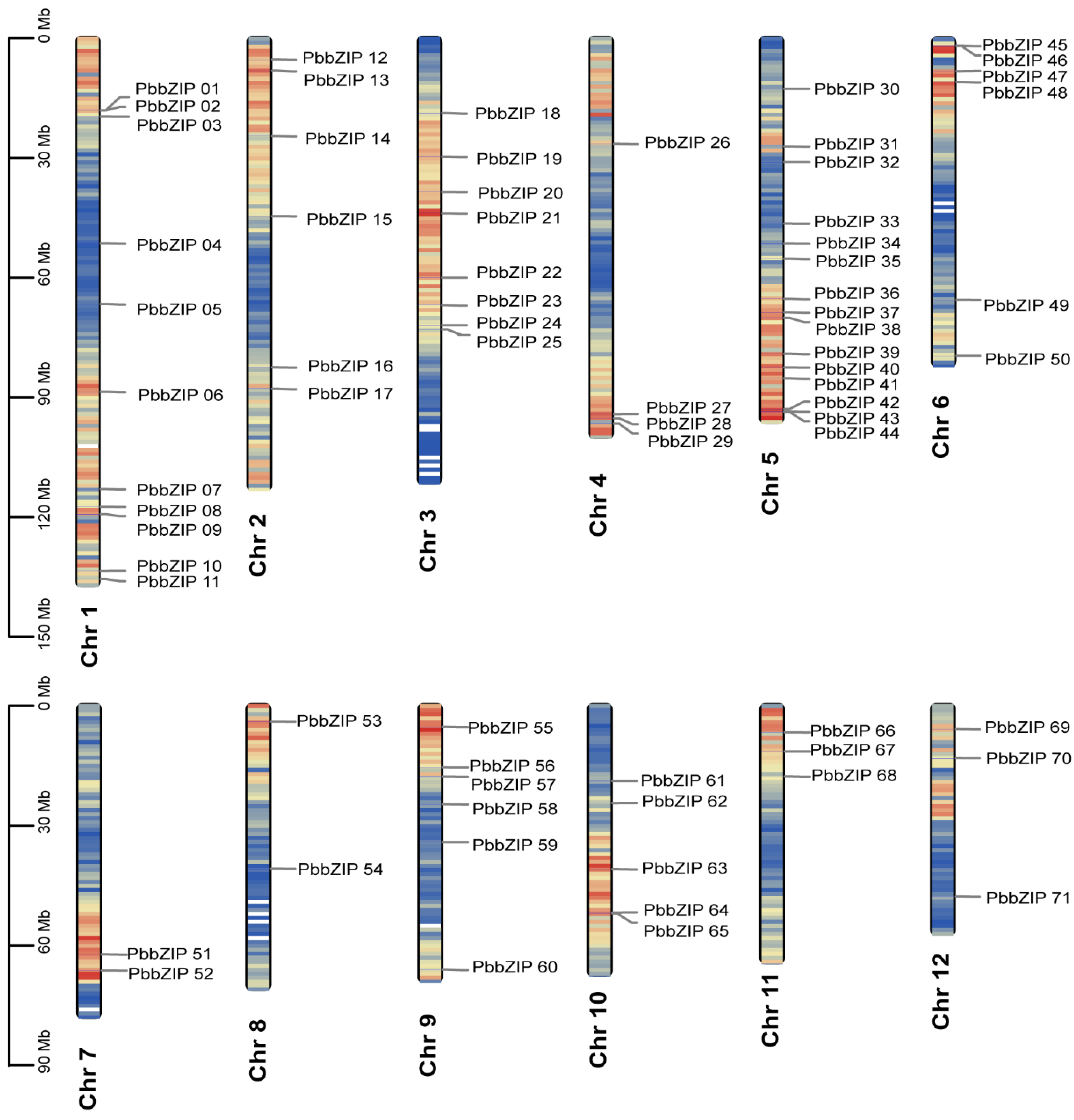
3.2. Chromosomal Localization of bZIP Genes in P. bournei
3.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment Analysis of the PbbZIP Gene Family
3.4. Phylogenetic and Co-Linearity Analysis of the PbbZIP Genes
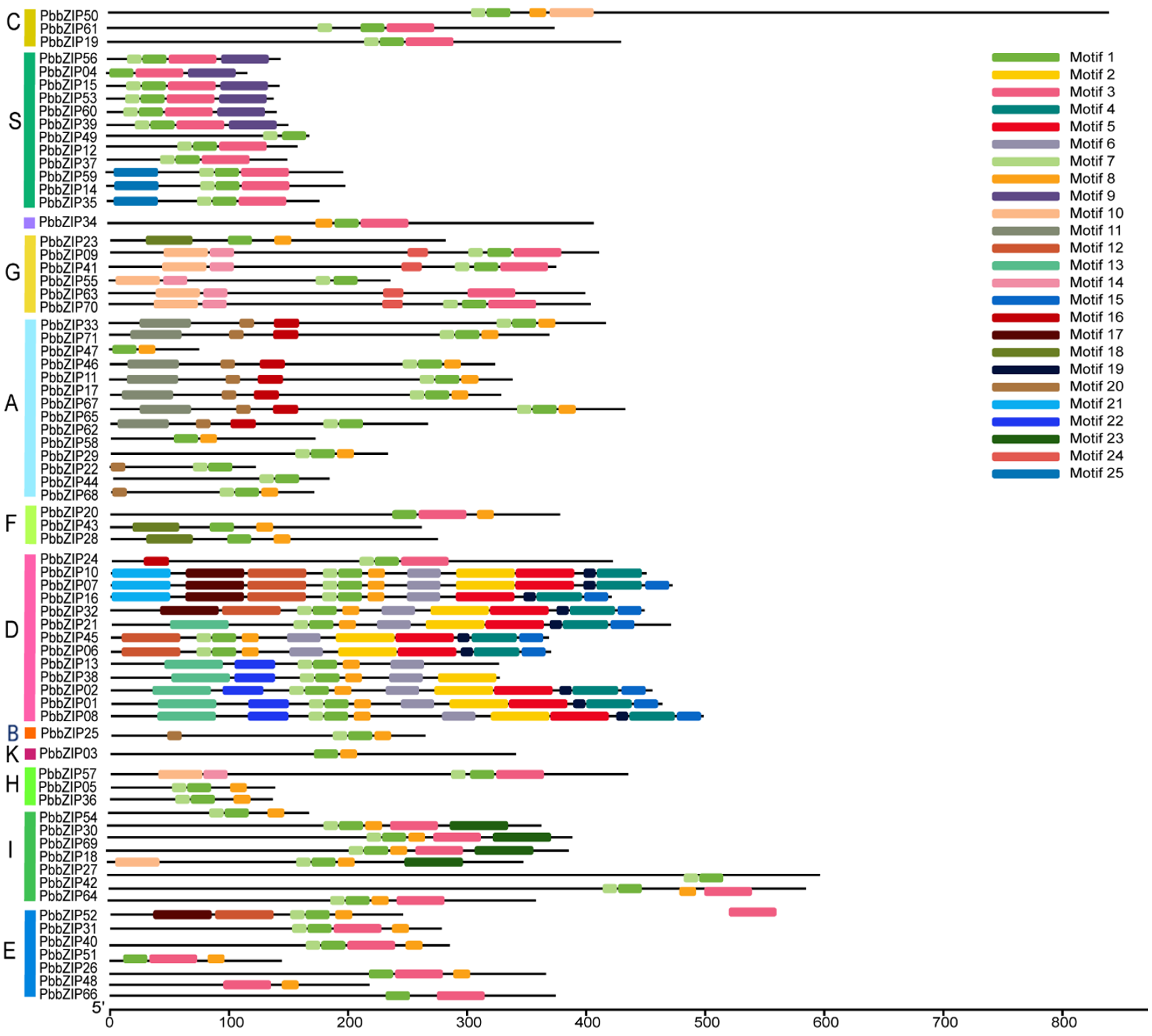
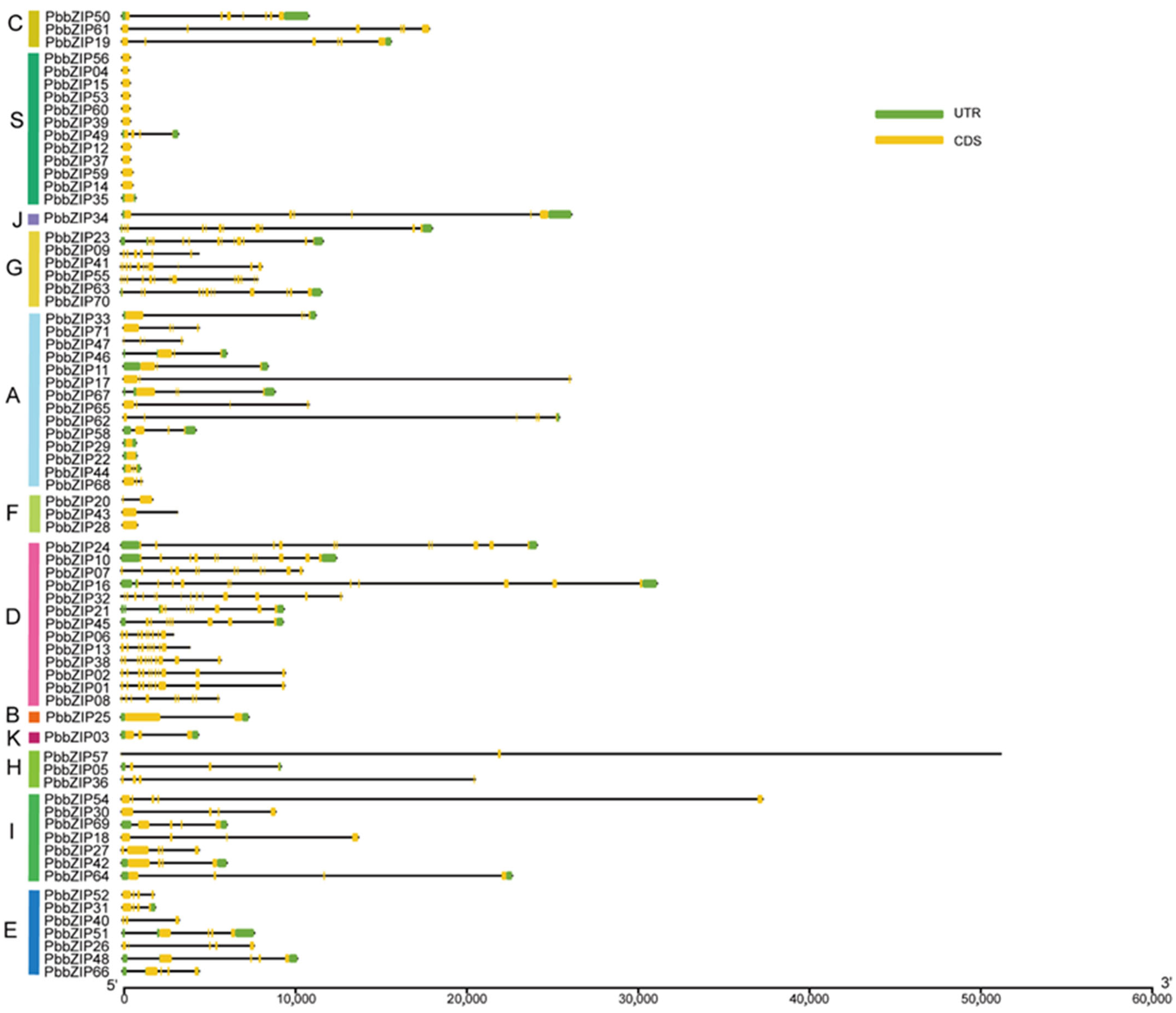
3.5. Protein Motif and Exon–Intron Structure Analysis of the PbbZIP Genes
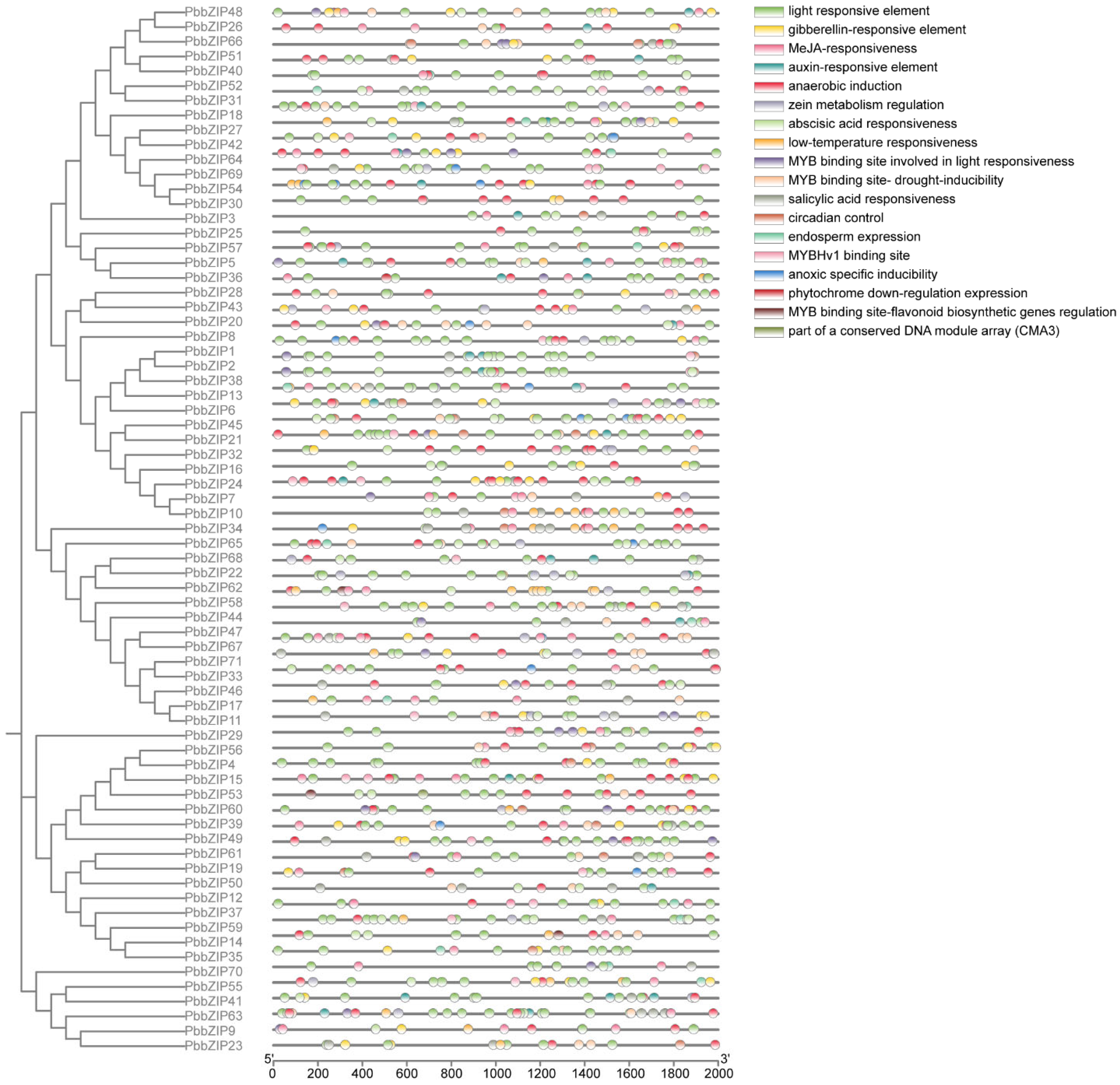
3.6. Cis-Acting Elements Analysis of PbbZIP Genes
3.7. Expression Analysis of PbbZIP Genes in Different Tissues
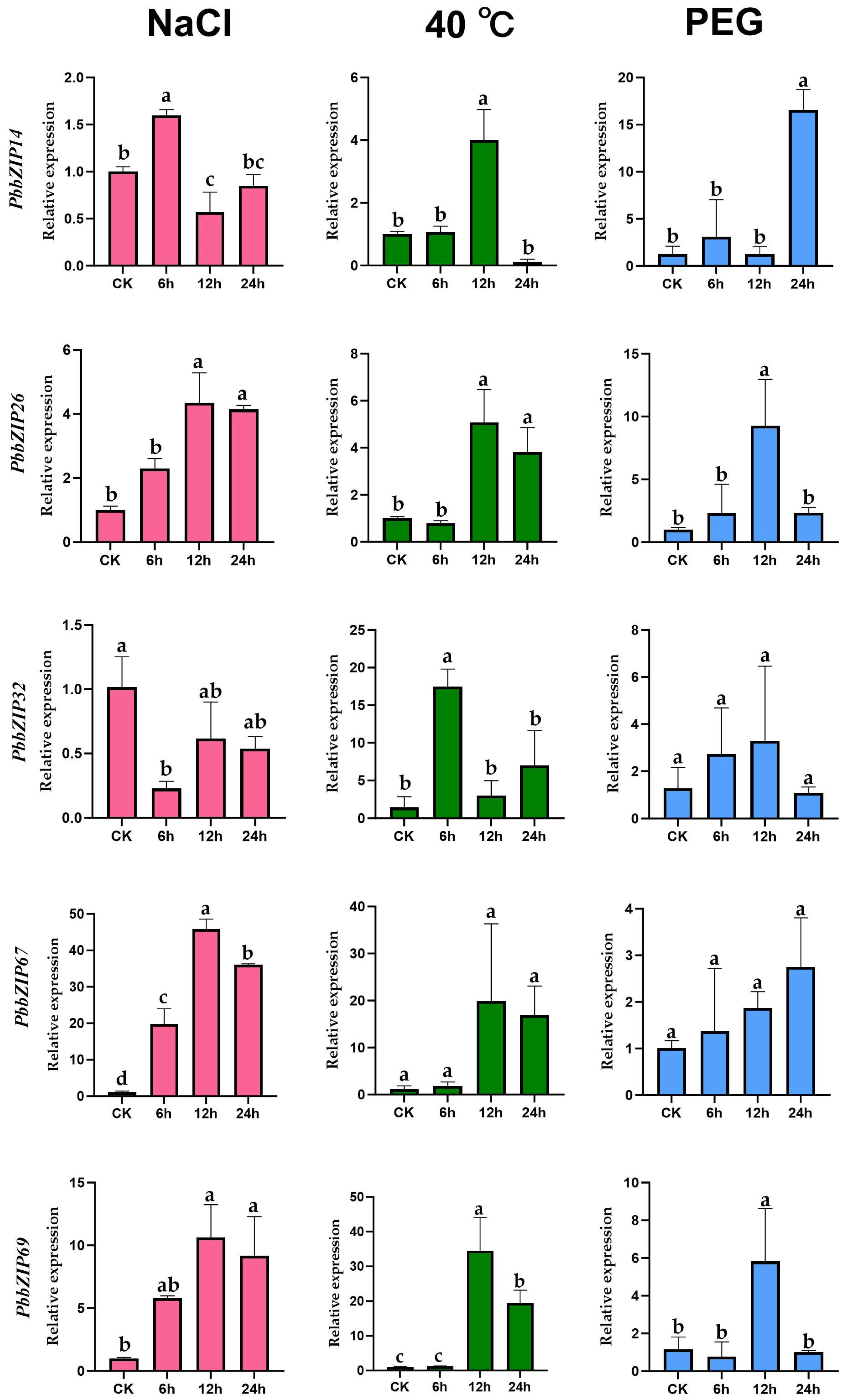
3.8. The Expression Profile of PbbZIP Genes Under Abiotic Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.M.; Zhu, J.H.; Gong, Z.Z.; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamalakshmi Devi, E.; Kumar, S.; Basanta Singh, T.; Sharma, S.K.; Beemrote, A.; Premabati Devi, C.; Chongtham, S.K.; Singh, C.H.; Yumlembam, R.A.; Haribhushan, A.; et al. Adaptation Strategies and Defence Mechanisms of Plants During Environmental Stress; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 359–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.Y.; Ding, Y.F.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, F.J.; Sun, J.W.; Zhu, C. The role of receptor-like protein kinases (RLKs) in abiotic stress response in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Zhou, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.H.; Xu, T.D. Protein phosphorylation: A molecular switch in plant signaling. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Huang, S.S.C.; Wise, A.; Castanon, R.; Nery, J.R.; Chen, H.M.; Watanabe, M.; Thomas, J.; Bar-Joseph, Z.; Ecker, J.R. A transcription factor hierarchy defines an environmental stress response network. Science 2016, 354, aag1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.Y.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.S.; Chen, Y.F.; Li, L.C.; Yu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.N.; Ma, Y.Z. Isolation and Functional Analysis of the bZIP Transcription Factor Gene TaABP1 from a Chinese Wheat Landrace. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawan, A.; Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dröge-Laser, W.; Snoek, B.L.; Snel, B.; Weiste, C. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor family—An update. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhong, X.J.; Xie, D. Genome-Wide Analysis of bZIP-Encoding Genes in Maize. DNA Res. 2012, 19, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.R.; Quan, S.W.; Niu, J.X.; Guo, C.H.; Kang, C.; Liu, J.M.; Yuan, X. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, Expression and Duplication Analysis of bZIP Family Genes in Juglans regia L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, S.; Yao, W.J.; Cheng, Z.H.; Zhou, B.R.; Jiang, T.B. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP gene family in poplar. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.L.; Li, H.T.; Wang, Y.K.; Li, D.K.; Xue, C.L.; Liu, Z.G.; Liu, M.J.; Zhao, J. Genome-wide analysis of the bZIP gene family in Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Li, L.X.; ShangGuan, G.D.; Jia, C.; Deng, S.N.; Noman, M.; Liu, Y.L.; Guo, Y.X.; Han, L.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of bZIP gene family in Carthamus tinctorius L. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.; Baek, W.; Lim, C.W.; Lee, S.C. Post-translational Modifications of bZIP Transcription Factors in Abscisic Acid Signaling and Drought Responses. Curr. Genom. 2021, 22, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, M.J.; Wang, J.J.; Lu, H.P.; Liu, J.X. bZIP17 regulates heat stress tolerance at reproductive stage in Arabidopsis. aBIOTECH 2021, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.L.; Dzinyela, R.; Yang, L.M.; Hwarari, D. bZIP Transcription Factors: Structure, Modification, Abiotic Stress Responses and Application in Plant Improvement. Plants 2024, 13, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.R.B.; Serrão, C.P.; Barros, N.L.F.; Reis, S.P.D.; Marques, D.N. Plant bZIP Proteins: Potential use in Agriculture-A Review. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2023, 25, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.L.; Xu, N.; Wu, Q.; Yu, B.; Li, X.X.; Chen, R.R.; Huang, J.L. Rice transcription factor OsMADS57 regulates plant height by modulating gibberellin catabolism. Rice 2019, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsai, R.; Castleden, I.; Whelan, J. Common and distinct organ and stress responsive transcriptomic patterns in Oryza sativa and A. thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inukai, S.; Kock, K.H.; Bulyk, M.L. Transcription factor–DNA binding: Beyond binding site motifs. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2017, 43, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, A.J.; Steinbachová, L.; Timofejeva, L.; Čermák, V.; Klodová, B.; Ganji, R.S.; Limones-Mendez, M.; Bokvaj, P.; Hafidh, S.; Potěšil, D.; et al. Arabidopsis bZIP18 and bZIP52 Accumulate in Nuclei Following Heat Stress where They Regulate the Expression of a Similar Set of Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindbäck, L.N.; Ji, Y.; Cervela-Cardona, L.; Jin, X.; Pedmale, U.V.; Strand, Å. An interplay between bZIP16, bZIP68, and GBF1 regulates nuclear photosynthetic genes during photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 1082–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Song, W.; Chen, Z.; Cai, H.; Gong, Q.; Liu, J.; Shi, C.; Wang, S. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of diverse Phoebe (Lauraceae) species endemic to China provide insight into their phylogeographical origin. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.B.; Liang, J.Y.; Chen, M.Y.; Zheng, S.Q.; Xu, J.Y. Study on the Structural Characteristics and Physical and Mechanical Properties of P. bournei Thinning Wood. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 3025–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Shen, A.H.; Lin, X.C. Fengshui forests conserve genetic diversity: A case study of P. bournei (Hemsl.) Yang in southern China. Genet. Mol. Res. GMR 2015, 14, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.M.; Li, J.P.; Tang, T. Determining the Optimal Density of P. bournei Plantations Based on Dynamic Programming under Close-to-Nature Management Measures. Sustainability 2022, 14, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, X.H.; Lu, Y.F.; Hu, X.G.; Lou, L.H.; Tong, Z.K.; Zhang, J.H. Assessing the current genetic structure of 21 remnant populations and predicting the impacts of climate change on the geographic distribution of Phoebe sheareri in southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waadt, R.; Seller, C.A.; Hsu, P.K.; Takahashi, Y.; Munemasa, S.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartas, M. Abiotic Stresses in Plants: From Molecules to Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Liu, L.L.; Sun, S.X.; Li, Y.M.; Jia, L.; Ye, S.L.; Yu, Y.X.; Dossa, K.; Luan, Y.P. Leaf-transcriptome profiles of P. bournei provide insights into temporal drought stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1010314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.; Yin, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Han, X.; Tong, Z.K. Co-expression network analysis reveals PbTGA4 and PbAPRR2 as core transcription factors of drought response in an important timber species P. bournei. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1297235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.N.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.L.; Wang, Q.G.; Zhang, Y.T.; Han, X.; Yang, Q.; Ma, W.J.; Tong, Z.K.; Zhang, J.H. Genome-wide identification of the bHLH transcription factor family and the regulatory roles of PbbHLH74 in response to drought stress in P. bournei. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.H.; Tang, X.H.; Li, J.S.; Zheng, Q.M.; Wang, T.; Cheng, S.Z.; Chen, S.P.; Cao, S.J.; Cao, G.Q. Genome wide investigation of Hsf gene family in P bournei: Identification, evolution, and expression after abiotic stresses. J. For. Res. 2023, 35, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Liao, W.H.; Li, J.S.; Pan, J.X.; Yang, S.J.; Chen, S.P.; Cao, S.J. Genome-Wide Identification of GATA Family Genes in P. bournei and Their Transcriptional Analysis under Abiotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.H.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.C.; He, C.Y.; Wu, Z.K.; Tong, Z.K.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Cao, S.J. The Vital Role of the CAMTA Gene Family in P. bournei in Response to Drought, Heat, and Light Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Doerks, T.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2015. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1, D257–D260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Shamloo, S.; Butler, G. TportHMM: Predicting the substrate class of transmembrane transport proteins using profile Hidden Markov Models. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 16–19 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.Q.; Wang, J.; Wong, G.K.S.; Yu, J. KaKsCalculator: Calculating Ka and Ks Through Model Selection and Model Averaging. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2006, 4, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, J.J.; Mosqueiro, T.; Rotman, J.; Xue, V.; Chapski, D.J.; Hoz, J.D.; Matias, P.; Martin, L.S.; Zelikovsky, A.; Pellegrini, M.; et al. Telescope: An interactive tool for managing large-scale analysis from mobile devices. GigaScience 2020, 9, giz163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.L.; Guo, Y.; Sheng, Q.H.; Shyr, Y. Advanced heat map and clustering analysis using heatmap3. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 986048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mravec, J.; Skůpa, P.; Bailly, A.; Hoyerová, K.; Krecek, P.; Bielach, A.; Petrásek, J.; Zhang, J.; Gaykova, V.; Stierhof, Y.D.; et al. Subcellular homeostasis of phytohormone auxin is mediated by the ER-localized PIN5 transporter. Nature 2009, 459, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.X.; Jia, L.D.; Huang, X.H.; Ma, G.Q.; Wang, S.X.; Zhu, M.C.; Zhang, A.X.; Guan, M.W.; Lu, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Structural Analysis of bZIP Transcription Factor Genes in Brassica napus. Genes 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Q.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, P.C.; Li, L. Dephosphorylation of bZIP59 by PP2A ensures appropriate shade avoidance response in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2025, 60, 551–566.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hir, H.; Nott, A.; Moore, M.J. How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, O.; Singh, P.C.; Bhatia, R. A review on drought stress in plants: Implications, mitigation and the role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.M.; Zhong, M.C.; Li, J.S.; Jiang, Y.M.; Zhou, X.R.; Justice Ijeoma, C.; Tang, X.H.; Chen, S.P.; Cao, S.J. Genome Identification and Evolutionary Analysis of LBD Genes and Response to Environmental Factors in P. bournei. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.T.; Norris, A.; Jiang, C.Z. S1-bZIP Transcription Factors Play Important Roles in the Regulation of Fruit Quality and Stress Response. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 802802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulraheem, M.I.; Xiong, Y.; Moshood, A.Y.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J. Mechanisms of Plant Epigenetic Regulation in Response to Plant Stress: Recent Discoveries and Implications. Plants 2024, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.A.; Manzoor, M.M.; Li, G.H.; Abdullah, M.; Han, W.; Wenlong, H.; Shakoor, A.; Riaz, M.W.; Rehman, S.; Cai, Y.P. Genome-wide identification and characterization of bZIP transcription factors and their expression profile under abiotic stresses in Chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeo, K.; Ito, T. Subcellular localization of VIP1 is regulated by phosphorylation and 14-3-3 proteins. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 1972–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.L.; Mo, Z.J.; Fan, Y.; Li, K.Y.; Yang, M.F.; Li, D.C.; Ke, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.Y.; Fan, Y.; et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bZIP transcription factor family genes in response to abiotic stress in Nicotiana tabacum L. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Song, K.K.; Li, B.; Song, Y.R.; Zhang, X.H.; Li, H.Z.; Yang, L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of NF-Y gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.C.; Purugganan, M.D. The early stages of duplicate gene evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15682–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuel, B.S.; Shaikh, T.H. Segmental duplications: An ‘expanding’ role in genomic instability and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemayel, R.; Vinces, M.D.; Legendre, M.; Verstrepen, K.J. Variable tandem repeats accelerate evolution of coding and regulatory sequences. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 445–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuskan, G.A.; Difazio, S.; Jansson, S.; Bohlmann, J.; Grigoriev, I.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; Ralph, S.; Rombauts, S.; Salamov, A.; et al. The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 2006, 313, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vision, T.J.; Brown, D.G.; Tanksley, S.D. The origins of genomic duplications in Arabidopsis. Science 2000, 290, 2114–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.P.; Amir, A. Exploring the effect of network topology, mRNA and protein dynamics on gene regulatory network stability. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Ru, Y.Y.; Hong, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zuo, R.F.; Guo, X.X.; Wang, J.Z.; Zhang, H.F.; Zheng, X.B.; Wang, P.; et al. System-wide characterization of bZIP transcription factor proteins involved in infection-related morphogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Cai, H.Y.; Bai, M.Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, F.Q.; Huang, Y.M.; Priyadarshani, S.V.G.N.; Chai, M.N.; Liu, L.P.; Liu, Y.H.; et al. A Soybean bZIP Transcription Factor GmbZIP19 Confers Multiple Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses in Plant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Long, Y.; Si, W.N.; Cheng, B.J.; Jiang, H.Y. A Novel Heat Shock Transcription Factor (ZmHsf08) Negatively Regulates Salt and Drought Stress Responses in Maize. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| PbZIP14 | GCAGCCTGGTGAGGTAGC | GTGGACGTGGGGTAAGGC |
| PbZIP26 | AGAGGTCCGAGTCCGCAA | CGTTCAACCCTTCCGCCT |
| PbZIP32 | GACGAGCACCACAGGCAT | TCGGACTTGGCGGCAATT |
| PbZIP67 | TCGGCATGCCTGATGGTG | TGACTCAGAGTCCGCGGA |
| PbZIP69 | CATGGCCCCTGCAAGTGT | GGCACCACTCCACTTGCT |
| PbEF1α | CATTCAAGTATGCGTGGGT | ACGGTGACCAGGAGCA |
| Gene Accession | ID | AA/aa | MW/Da | Theoretical pI | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OF19974-RA | PbbZIP1 | 399 | 41,600.65 | 5.89 | 51.93 | −0.67 | Nucleus |
| OF19973-RA | PbbZIP2 | 144 | 16,506.95 | 6.28 | 82.64 | −0.585 | Nucleus |
| OF19914-RA | PbbZIP3 | 136 | 15,566.31 | 9.52 | 55.96 | −1.396 | Nucleus |
| OF10270-RA | PbbZIP4 | 231 | 25,909.15 | 8.5 | 58.74 | −0.698 | Nucleus |
| OF18209-RA | PbbZIP5 | 198 | 22,954.6 | 6.71 | 72.47 | −0.855 | Nucleus |
| OF02523-RA | PbbZIP6 | 141 | 16,414.99 | 7.8 | 82.34 | −0.684 | Nucleus |
| OF11694-RA | PbbZIP7 | 159 | 18,344.72 | 10.29 | 76.73 | −0.76 | Nucleus |
| OF11818-RA | PbbZIP8 | 325 | 36,545.42 | 9.25 | 69.05 | −0.674 | Nucleus |
| OF11930-RA | PbbZIP9 | 199 | 23,154.87 | 6.05 | 79.4 | −0.855 | Nucleus |
| OF28301-RA | PbbZIP10 | 144 | 16,675.1 | 6.19 | 75.83 | −0.704 | Nucleus |
| OF28225-RA | PbbZIP11 | 447 | 49,195.23 | 6.28 | 78.68 | −0.46 | Nucleus |
| OF04812-RA | PbbZIP12 | 327 | 36,606.14 | 8.68 | 64.68 | −0.878 | Nucleus |
| OF04669-RA | PbbZIP13 | 368 | 41,352.8 | 6.73 | 80.92 | −0.451 | Nucleus |
| OF06905-RA | PbbZIP14 | 322 | 35,902.66 | 7.96 | 79.97 | −0.577 | Nucleus |
| OF08770-RA | PbbZIP15 | 74 | 8813.28 | 10.34 | 59.46 | −1.295 | Nucleus |
| OF03422-RA | PbbZIP16 | 373 | 41,747.12 | 6.88 | 63.06 | −0.914 | Nucleus |
| OF22080-RA | PbbZIP17 | 169 | 19,451.17 | 9.23 | 70.89 | −0.337 | Nucleus |
| OF12918-RA | PbbZIP18 | 374 | 41,217.7 | 5.51 | 70.43 | −0.613 | Nucleus |
| OF09866-RA | PbbZIP19 | 387 | 42,269.25 | 6.38 | 61.4 | −0.716 | Nucleus |
| OF05546-RA | PbbZIP20 | 433 | 45,888.29 | 9.01 | 64.09 | −0.659 | Nucleus |
| OF25842-RA | PbbZIP21 | 368 | 40,364.2 | 8.74 | 57.61 | −0.713 | Nucleus |
| OF24005-RA | PbbZIP22 | 365 | 41,331.5 | 8.37 | 83.64 | −0.368 | Nucleus |
| OF23680-RA | PbbZIP23 | 277 | 31,093.66 | 5.51 | 76.03 | −0.716 | Nucleus |
| OF23482-RA | PbbZIP24 | 496 | 55,948.95 | 6.42 | 81.47 | −0.393 | Nucleus |
| OF23448-RA | PbbZIP25 | 461 | 52,301.17 | 5.78 | 76.68 | −0.558 | Nucleus |
| OF10424-RA | PbbZIP26 | 339 | 38,460.28 | 4.78 | 81.36 | −0.556 | Nucleus |
| OF01790-RA | PbbZIP27 | 117 | 13,424.64 | 6.72 | 90.85 | −0.318 | Nucleus |
| OF01865-RA | PbbZIP28 | 135 | 15,157 | 6.19 | 67.19 | −0.977 | Nucleus |
| OF01905-RA | PbbZIP29 | 324 | 35,867.17 | 7.19 | 65.12 | −0.762 | Nucleus |
| OF01159-RA | PbbZIP30 | 419 | 45,724.98 | 7.83 | 74.61 | −0.562 | Nucleus |
| OF00429-RA | PbbZIP31 | 244 | 26,831.46 | 5.51 | 67.99 | −0.641 | Nucleus |
| OF29773-RA | PbbZIP32 | 374 | 39,382.74 | 5.96 | 47.83 | −0.74 | Nucleus |
| OF27741-RA | PbbZIP33 | 470 | 51,343.31 | 6.89 | 76.47 | −0.514 | Nucleus |
| OF15721-RA | PbbZIP34 | 337 | 37,502.44 | 7.03 | 68.31 | −0.788 | Nucleus |
| OF15812-RA | PbbZIP35 | 217 | 24,620.4 | 7.03 | 76.45 | −0.745 | Nucleus |
| OF11162-RA | PbbZIP36 | 597 | 65,168.15 | 8.83 | 56.52 | −0.898 | Nucleus |
| OF10986-RA | PbbZIP37 | 280 | 29,704.17 | 5.45 | 67.93 | −0.514 | Nucleus |
| OF10903-RA | PbbZIP38 | 121 | 14,142.05 | 8.54 | 57.27 | −1.001 | Nucleus |
| OF09410-RA | PbbZIP39 | 139 | 16,192.43 | 6.83 | 73.74 | −0.831 | Nucleus |
| OF09226-RA | PbbZIP40 | 363 | 39,949.87 | 6.19 | 74.71 | −0.599 | Nucleus |
| OF07945-RA | PbbZIP41 | 389 | 42,749.74 | 5.97 | 68.71 | −0.666 | Nucleus |
| OF05157-RA | PbbZIP42 | 284 | 31,775.42 | 6.51 | 69.75 | −0.744 | Nucleus |
| OF05208-RA | PbbZIP43 | 468 | 52,189.65 | 6.52 | 74.49 | −0.58 | Nucleus |
| OF05212-RA | PbbZIP44 | 416 | 45,110 | 8.78 | 59.59 | −0.779 | Nucleus |
| OF19397-RA | PbbZIP45 | 407 | 46,959.1 | 8.7 | 63.51 | −0.926 | Nucleus |
| OF19394-RA | PbbZIP46 | 177 | 20,625.17 | 6.44 | 80.96 | −0.801 | Nucleus |
| OF18693-RA | PbbZIP47 | 167 | 18,448.37 | 9.74 | 60.78 | −1.117 | Nucleus |
| OF18548-RA | PbbZIP48 | 150 | 17,606.19 | 11.45 | 94.87 | −0.687 | Nucleus` |
| OF28795-RA | PbbZIP49 | 453 | 50,318.03 | 6.55 | 78.9 | −0.482 | Nucleus |
| OF26318-RA | PbbZIP50 | 151 | 17,332.69 | 6.59 | 79.47 | −0.643 | Nucleus |
| OF26807-RA | PbbZIP51 | 143 | 16,152.73 | 9.71 | 83.15 | −0.45 | Nucleus |
| OF24581-RA | PbbZIP52 | 235 | 25,001.1 | 9.56 | 57.74 | −0.487 | Nucleus |
| OF06079-RA | PbbZIP53 | 584 | 64,394.12 | 6.65 | 58.18 | −0.9 | Nucleus |
| OF29662-RA | PbbZIP54 | 273 | 29,723.97 | 6.55 | 62.89 | −0.756 | Nucleus |
| OF16038-RA | PbbZIP55 | 169 | 19,301.84 | 9.62 | 61.83 | −0.872 | Nucleus |
| OF02992-RA | PbbZIP56 | 376 | 42,234.62 | 7.68 | 60.51 | −0.903 | Nucleus |
| OF03083-RA | PbbZIP57 | 431 | 46,862.33 | 9.61 | 63.34 | −0.757 | Nucleus |
| OF03232-RA | PbbZIP58 | 262 | 29,182.16 | 9.59 | 47.33 | −0.919 | Nucleus |
| OF01374-RA | PbbZIP59 | 430 | 46,845.64 | 5.57 | 64.02 | −0.78 | Nucleus |
| OF10634-RA | PbbZIP60 | 170 | 20,349.2 | 7.74 | 68.82 | −1.127 | Nucleus |
| OF29018-RA | PbbZIP61 | 403 | 43,556.63 | 6.61 | 56.23 | −0.771 | Nucleus |
| OF28905-RA | PbbZIP62 | 358 | 39,138.26 | 6.5 | 62.23 | −0.794 | Nucleus |
| OF18055-RA | PbbZIP63 | 265 | 29,261.84 | 6.38 | 60.75 | −0.774 | Nucleus |
| OF20655-RA | PbbZIP64 | 348 | 38,339.97 | 5.89 | 62.61 | −0.615 | Nucleus |
| OF20635-RA | PbbZIP65 | 419 | 45,891.11 | 5.39 | 63.56 | −0.692 | Nucleus |
| OF14232-RA | PbbZIP66 | 260 | 28,706.32 | 6.82 | 71.69 | −0.58 | Nucleus |
| OF17740-RA | PbbZIP67 | 366 | 41,515.21 | 8.39 | 80.25 | −0.485 | Nucleus |
| OF17491-RA | PbbZIP68 | 180 | 19,918.45 | 8.68 | 71.56 | −0.411 | Nucleus |
| OF12212-RA | PbbZIP69 | 409 | 43,379.93 | 6.18 | 49.24 | −0.838 | Nucleus |
| OF07610-RA | PbbZIP70 | 448 | 48,779.58 | 7.18 | 78.04 | −0.485 | Nucleus |
| OF26090-RA | PbbZIP71 | 839 | 88,864.94 | 6.41 | 68.1 | −0.464 | Nucleus |
| A. Thaliana Gene ID | A. Thaliana Gene Name | CLASS | P. bournei Gene ID | P. bournei Gene Name | CLASS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT5G49450 | ATbZIP1 | S | OF08770-RA | PbbZIP15 | S |
| AT5G49450 | ATbZIP1 | S | OF06079-RA | PbbZIP53 | S |
| AT2G18160 | ATbZIP2 | S | OF09410-RA | PbbZIP39 | S |
| AT5G15830 | ATbZIP3 | S | OF15812-RA | PbbZIP35 | S |
| AT3G49760 | ATbZIP5 | S | OF04812-RA | PbbZIP12 | S |
| AT3G49760 | ATbZIP5 | S | OF10986-RA | PbbZIP37 | S |
| AT2G22850 | ATbZIP6 | S | OF04812-RA | PbbZIP12 | S |
| AT2G22850 | ATbZIP6 | S | OF10986-RA | PbbZIP37 | S |
| AT4G37730 | ATbZIP7 | S | OF04812-RA | PbbZIP12 | S |
| AT4G37730 | ATbZIP7 | S | OF10986-RA | PbbZIP37 | S |
| AT4G34590 | ATbZIP11 | S | OF09410-RA | PbbZIP39 | S |
| AT4G35900 | ATbZIP14 | A | OF24005-RA | PbbZIP22 | A |
| AT4G35900 | ATbZIP14 | A | OF05212-RA | PbbZIP44 | A |
| AT4G35900 | ATbZIP14 | A | OF17491-RA | PbbZIP68 | A |
| AT5G42910 | ATbZIP15 | A | OF17740-RA | PbbZIP67 | A |
| AT2G40950 | ATbZIP17 | B | OF23448-RA | PbbZIP25 | B |
| AT2G40620 | ATbZIP18 | I | OF12918-RA | PbbZIP18 | I |
| AT4G35040 | ATbZIP19 | F | OF01865-RA | PbbZIP28 | F |
| AT4G35040 | ATbZIP19 | F | OF05208-RA | PbbZIP43 | F |
| AT5G06950 | ATbZIP20 | D | OF10903-RA | PbbZIP38 | D |
| AT1G22070 | ATbZIP22 | D | OF25842-RA | PbbZIP21 | D |
| AT2G16770 | ATbZIP23 | F | OF01865-RA | PbbZIP28 | F |
| AT2G16770 | ATbZIP23 | F | OF05208-RA | PbbZIP43 | F |
| AT2G17770 | ATbZIP27 | A | OF24005-RA | PbbZIP22 | A |
| AT2G17770 | ATbZIP27 | A | OF17491-RA | PbbZIP68 | A |
| AT4G38900 | ATbZIP29 | I | OF01790-RA | PbbZIP27 | I |
| AT4G38900 | ATbZIP29 | I | OF05157-RA | PbbZIP42 | I |
| AT2G21230 | ATbZIP30 | I | OF01790-RA | PbbZIP27 | I |
| AT2G21230 | ATbZIP30 | I | OF05157-RA | PbbZIP42 | I |
| AT2G42380 | ATbZIP34 | E | OF00429-RA | PbbZIP31 | E |
| AT3G19290 | ATbZIP38 | A | OF17740-RA | PbbZIP67 | A |
| AT4G36730 | ATbZIP41 | G | OF16038-RA | PbbZIP55 | H |
| AT1G75390 | ATbZIP44 | S | OF09410-RA | PbbZIP39 | S |
| AT5G65210 | ATbZIP47 | D | OF19397-RA | PbbZIP45 | D |
| AT3G56660 | ATbZIP49 | B | OF23448-RA | PbbZIP25 | B |
| AT1G77920 | ATbZIP50 | D | OF19397-RA | PbbZIP45 | D |
| AT3G62420 | ATbZIP53 | S | OF08770-RA | PbbZIP15 | S |
| AT3G62420 | ATbZIP53 | S | OF06079-RA | PbbZIP53 | S |
| AT3G62420 | ATbZIP53 | S | OF10634-RA | PbbZIP60 | S |
| AT5G11260 | ATbZIP56 | H | OF11162-RA | PbbZIP36 | H |
| AT5G10030 | ATbZIP57 | D | OF25842-RA | PbbZIP21 | D |
| AT3G17609 | ATbZIP64 | H | OF03083-RA | PbbZIP57 | H |
| AT5G06839 | ATbZIP65 | D | OF02523-RA | PbbZIP6 | D |
| AT5G06839 | ATbZIP65 | D | OF19974-RA | PbbZIP1 | D |
| AT1G32150 | ATbZIP68 | G | OF18055-RA | PbbZIP63 | G |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Bakari, A.; Guan, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Nyoni, M.; Cao, S.; Zhang, Z. An Investigation into the Evolutionary Characteristics and Expression Patterns of the Basic Leucine Zipper Gene Family in the Endangered Species Phoebe bournei Under Abiotic Stress Through Bioinformatics. Plants 2025, 14, 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152292
Feng Y, Bakari A, Guan H, Wang J, Zhang L, Xu M, Nyoni M, Cao S, Zhang Z. An Investigation into the Evolutionary Characteristics and Expression Patterns of the Basic Leucine Zipper Gene Family in the Endangered Species Phoebe bournei Under Abiotic Stress Through Bioinformatics. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152292
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yizhuo, Almas Bakari, Hengfeng Guan, Jingyan Wang, Linping Zhang, Menglan Xu, Michael Nyoni, Shijiang Cao, and Zhenzhen Zhang. 2025. "An Investigation into the Evolutionary Characteristics and Expression Patterns of the Basic Leucine Zipper Gene Family in the Endangered Species Phoebe bournei Under Abiotic Stress Through Bioinformatics" Plants 14, no. 15: 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152292
APA StyleFeng, Y., Bakari, A., Guan, H., Wang, J., Zhang, L., Xu, M., Nyoni, M., Cao, S., & Zhang, Z. (2025). An Investigation into the Evolutionary Characteristics and Expression Patterns of the Basic Leucine Zipper Gene Family in the Endangered Species Phoebe bournei Under Abiotic Stress Through Bioinformatics. Plants, 14(15), 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152292








