Effects of Micro-Topography on Soil Nutrients and Plant Diversity of Artificial Shrub Forest in the Mu Us Sandy Land
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Species Composition of Different Types of Artificial Shrub Plant Communities Under the Influence of Micro-Topography
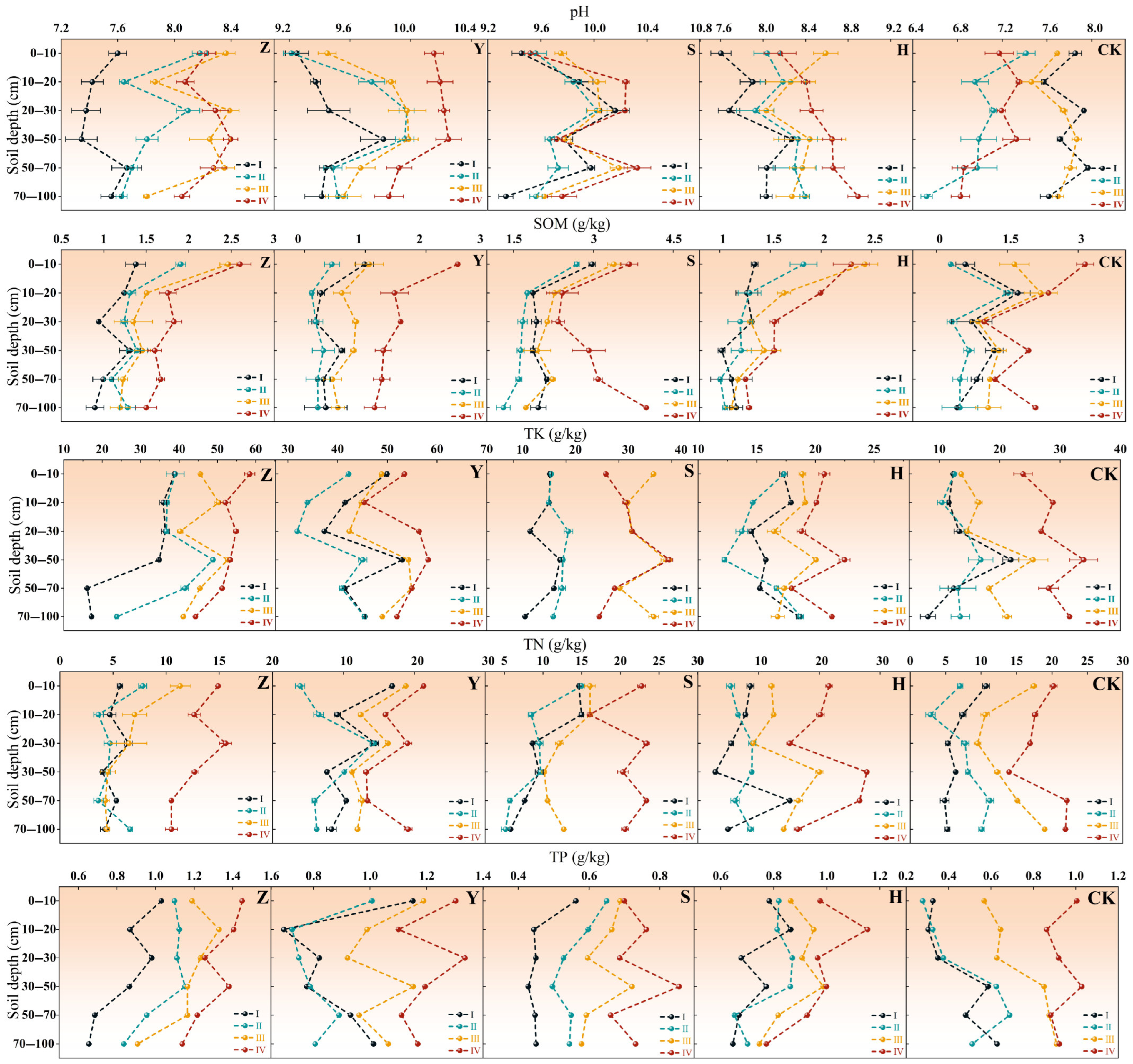
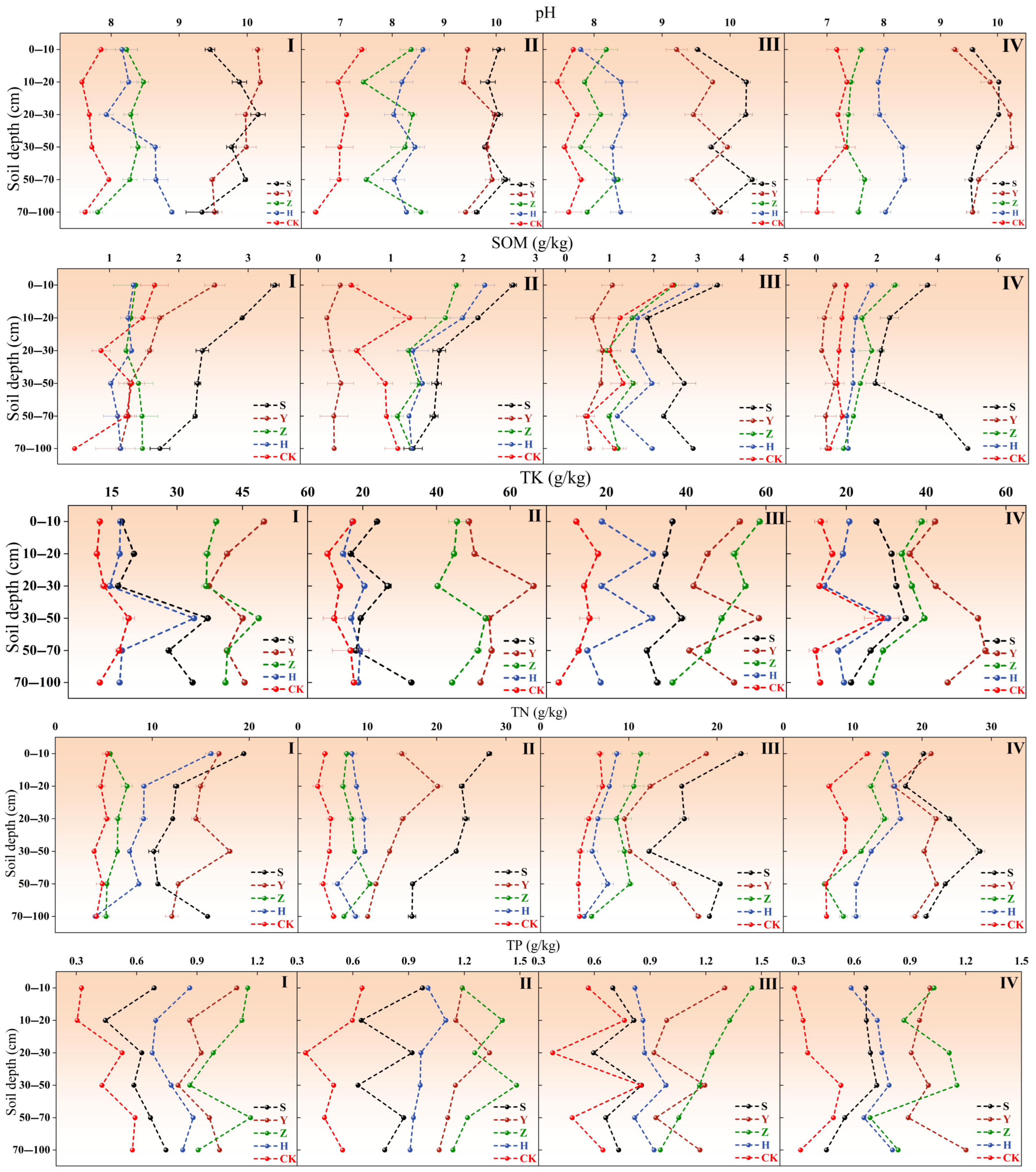
2.2. Soil Nutrient Variations Across Micro-Topographies in Different Types of Shrub Plantations
2.3. Soil Nutrient Variations in Shrub Plantations Across Different Micro-Topographies
2.4. Correlation Analysis Between Plant Diversity and Soil Nutrients
3. Discussion
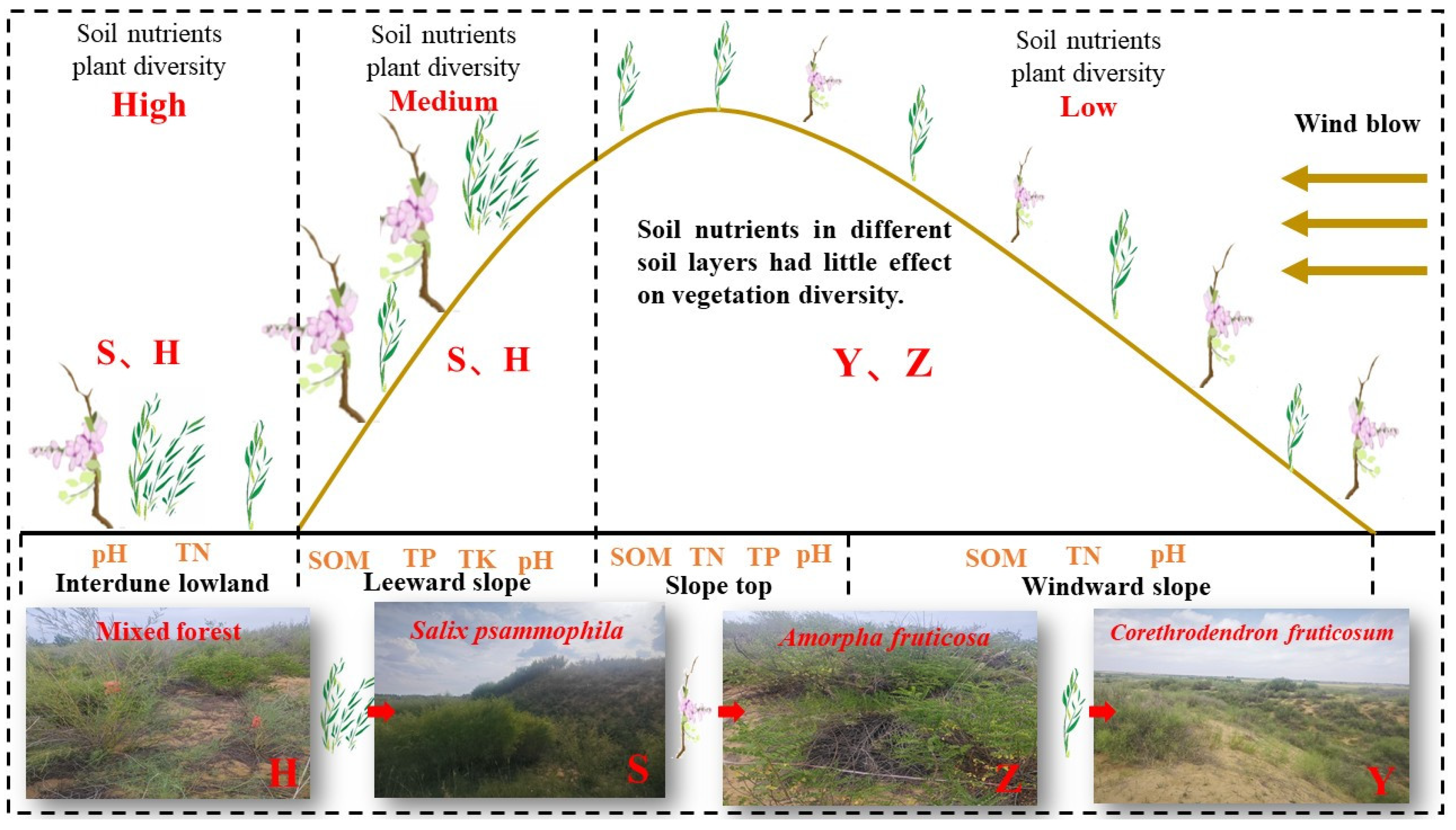
3.1. Impacts of Micro-Topography on Soil Nutrients and Plant Diversity
3.2. Impacts of Stand Types on Soil Nutrients and Plant Diversity
3.3. Correlations Between Soil Nutrients and Vegetation Types
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Location and Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Sample Plot Setting and Investigation
4.2.2. Soil Sample Collection and Determination
- (1)
- pH
- (2)
- Soil organic matter (SOM)
- (3)
- Total nitrogen (TN)
- (4)
- Total phosphorus (TP)
- (5)
- Total potassium (TK)
4.2.3. Plant Diversity Index Calculation
- (1)
- Margalef species richness index (R)
- (2)
- Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H)
- (3)
- Pielou evenness index (J)
4.2.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, W.; Bezemer, T.M.; Berendse, F. Soil heterogeneity and plant species diversity in experimental grassland communities: Contrasting effects of soil nutrients and pH at different spatial scales. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Rillig, M.C.; Yu, M.F.; Hu, J.N.; Huang, L.; Yu, F.H. Soil nutrient heterogeneity alters productivity and diversity of experimental plant communities under multiple global change factors. Oikos 2023, 2023, e10189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tan, N.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, J. Plant diversity and species turnover co-regulate soil nitrogen and phosphorus availability in Dinghushan forests, southern China. Plant Soil 2021, 464, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.J.; Li, Y.L.; Cheng, J.W.; Zhang, T.R.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.H. Spatial heterogeneity of plant and soil systems at the patch scale in a typical steppe in Inner Mongolia. Pratacultural Sci. 2019, 36, 1498–1507. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.R.; Xin, Z.M.; Gegen, B.T.; Li, X.L.; Luo, F.M.; Xu, J.; Liu, F.; Hao, Y.G.; Yao, B. Correlation of Typical Shrub Community Diversity and Soil Nutrient in Northeast Ulanbuh Desert. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 95–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J. Key ecological issues in plant-soil feedback: Pattern, process and mechanism. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2020, 44, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, K.; Wei, T.; Sha, G.; Yu, H.; Fan, D.; Zhou, W.; Ding, X.; Feng, H. Response of understory plant species diversity to plant mixture on the Loess Plateau: A case study of Hippophae rhamnoides. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumilamba, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhan, Y.; Lu, X. Understory biodiversity in Karst forests: A comparison of pure (Pinus massoniana) and mixed forests in Guiyang, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 588, 122753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xiao, K.; Zheng, H.; Gao, Y.; Miao, Z.; Ge, Z. The Effects of Nutrient and Water Use Efficiency on Plant Species Diversity in the Understory of Broad-Leaved Evergreen Forests. Diversity 2025, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, P.; Eisenhauer, N.; Roscher, C. Linking plant diversity–productivity relationships to plant functional traits of dominant species and changes in soil properties in 15-year-old experimental grasslands. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Pan, Y.; Bao, H.; Liang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, H.; Huang, W. Variations in soil physico-chemical properties along slope position gradient in secondary vegetation of the hilly region, Guilin, Southwest China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.M. Effects of Dune Micro-Topography on Plant Distribution Characteristics in Hunshandake Sandy Land. Doctoral Dissertation, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, H.; Shan, L.; Chen, G.; Ning, T. Effects of Micro-Topography and Vegetation on Soil Moisture on Fixed Sand Dunes in Tengger Desert, China. Plants 2024, 13, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.Q.; Ren, J.J.; Zhang, Y.M. Effect of slope aspect and terrain of sand dune on herbaceous diversity in Gurbantunggut desert. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Šilc, U.; Caković, D.; Küzmič, F.; Stešević, D. Trampling impact on vegetation of embryonic and stabilised sand dunes in Montenegro. J. Coast. Conserv. 2017, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z. Influence of Soil Moisture in Semi-Fixed Sand Dunes of the Tengger Desert, China, Based on PLS-SEM and SHAP Models. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Kang, H.; Liu, Z.; Tuo, F.; Hu, G. Microtopography Affects the Diversity and Stability of Vegetation Communities by Regulating Soil Moisture. Water 2025, 17, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, K.; Hong, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, F. Soil Microbial Communities and Their Relationship with Soil Nutrients in Different Density Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Forests 2025, 16, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.F.; Bian, Z.H.; Xi, J.J.; Zhao, J.B. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil moisture in different types of sand dune in the Mu Us Sandy Land, adjacent to north of Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Ge, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Goudie, A.S.; Hu, S. Contributions of ecological programs to vegetation restoration in arid and semiarid China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Yan, C.; Li, X.; Qian, D.; Feng, K. Monitoring the response of vegetation dynamics to ecological engineering in the Mu Us Sandy Land of China from 1982 to 2014. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Pei, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Bu, C.; Zhang, Q. Multisource remote sensing monitoring and analysis of the driving forces of vegetation restoration in the Mu Us sandy land. Land 2022, 11, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Svenning, J.C. Ecological restoration is the dominant driver of the recent reversal of desertification in the Mu Us Desert (China). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lei, J.; Xu, X.; Gao, P.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhong, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, G. Spatial pattern for soil water and chemical properties in Gurbantunggut Desert. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 4380–4389. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Gongadze, K.; Wu, L. Soil nutrients of different land-use types and topographic positions in the water-wind erosion crisscross region of China’s Loess Plateau. Catena 2020, 184, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Jia, R.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, G. Carbon sequestration capacity of shifting sand dune after establishing new vegetation in the Tengger Desert, northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 478, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Lian, J. Scale dependence of plant species richness and vegetation-environment relationship along a gradient of dune stabilization in Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China. J. Arid Land 2014, 6, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; He, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Lv, X.; Pu, X.; Zhuang, L. Responses and comprehensive evaluation of growth characteristics of ephemeral plants in the desert–oasis ecotone to soil types. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Gou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, M. Succession of a natural desert vegetation community after long-term fencing at the edge of a desert oasis in northwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1091446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.Y.; Chen, Y.Y. Relationship between micro-topographic units of fixed dunes and aboveground vegetation in desert steppe of Ningxia. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2014, 42, 348–350. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, W.X. Distribution characteristics of aboveground vegetation, soil seed bank and soil water content in fixed dunes with different microtopography. Pratacultural Sci. 2014, 31, 1825–1832. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Die, C.; Feng, X.; Ren, K.; Brevik, E.C.; Yu, Y. Assessment of the impact of different vegetation patterns on soil erosion processes on semiarid loess slopes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, D.; Shi, F.; Dong, Y.; Liu, N.; Liang, Y. Species-abundance distribution patterns of plant communities in the Gurbantünggüt desert, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Knighton, J.; Evaristo, J.; Wassen, M. Contrasting adaptive strategies by Caragana korshinskii and Salix psammophila in a semiarid revegetated ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 300, 108323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ri, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, L.Q.; Qing, H.; Yao, Z.Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Tian, J.-B.; Cao, X.-P.; Yang, L.; et al. Establishment, development, and decline of Salix psammophila communities: Changes in soil conditions and floristic composition in dune slacks. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.J.; Hong, G.Y.; Wu, Y.Z.; Li, Z.F.; Hai, L.; Wang, P.P.; Gao, X.W.; Yang, J. Root distribution characteristics of Hedysarum leave with different aerial seeding years in Mu Us Sandy Land. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 29–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Guan, W. The effect of slope aspect on vegetation attributes in a mountainous dry valley, Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Q. Interaction Between Different Sand-Fixing Shrubs and Micro-Topography on Soil Characteristics in the Wind-Sand Area of Eastern Ningxia. Masteral Dissertation, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Chen, L.; Su, X.; Liu, D.; Jin, T.; Shi, S.; Li, T.; Liu, G. Effects of soil physico-chemical properties on plant species diversity along an elevation gradient over alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 822268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L. Spatial Variability of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in the Gurbantunggut Desert and Its Impact on Plant Diversity. Doctoral Dissertation, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, Q.X.; Ma, Y.; Xie, L.; Song, N.P. Relationship between restoration of plant diversity and soil habitat in desert steppe. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.M.; Li, G.; t Ma, J.J.; Li, Y.J.; Liang, T.Y. Analysis of micro-topographic vegetation characteristics in Hunshandake Sandy Land. North. Hortic. 2015, 53–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.W. Study on the Ecological Process of Vegetation and Its Response Mechanism to Hydrology in Semi-Arid Watersheds. Doctoral Dissertation, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Laxton, R.R. The measure of diversity. J. Theor. Biol. 1978, 70, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohlgren, T.J. Measuring Plant Diversity: Lessons from the Field; OUP USA: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Šmilauer, P.; Lepš, J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO5; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]




| Micro-Topography | Species | Families | Form | Shrub Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windward slope | Aster altaicus Willd. | Asteraceae | HP | S, Z, H |
| Stipa capillata L. | Poaceae | HP | S, Y, Z, H | |
| Lactuca tatarica L. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Corispermum hyssopifolium L. | Amaranthaceae | AH | H | |
| Setaria viridis L. | Poaceae | AH | S | |
| Cynanchum chinense R. Br. | Apocynaceae | FU | S | |
| Inula linariifolia Turcz. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Agriophyllum pungens Vahl. | Amaranthaceae | AH | Y, CK | |
| Slope top | Aster altaicus Willd. | Asteraceae | HP | S, Y, Z, H |
| Stipa capillata L. | Poaceae | HP | S, Y, Z, H | |
| Lactuca tatarica L. | Asteraceae | HP | S, H | |
| Corispermum hyssopifolium L. | Amaranthaceae | AH | Z, H | |
| Setaria viridis L. | Poaceae | AH | S, Y | |
| Cynanchum chinense R. Br. | Apocynaceae | FU | S | |
| Echinops gmelinii Turcz. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Grubovia dasyphylla Fisch. & C. A. Mey. | Amaranthaceae | AH | S | |
| Setaria faberi R. A. W. Herrmann | Poaceae | AH | S | |
| Agriophyllum pungens Vahl. | Amaranthaceae | AH | Y, CK | |
| Leeward slope | Aster altaicus Willd. | Asteraceae | HP | S, Y, H |
| Stipa capillata L. | Poaceae | HP | S, Y, Z, H | |
| Corispermum hyssopifolium L. | Amaranthaceae | AH | Z, H | |
| Setaria viridis L. | Poaceae | AH | S | |
| Cynanchum chinense R. Br. | Apocynaceae | FU | S, Z | |
| Inula linariifolia Turcz. | Asteraceae | HP | H | |
| Echinochloa crus-galli var. | Poaceae | AH | S | |
| Salsola collina Pall. | Amaranthaceae | AH | S, Y, H | |
| Teloxys aristata L. | Amaranthaceae | AH | S | |
| Suaeda glauca Bunge. | Amaranthaceae | AH | S | |
| Agriophyllum pungens Vahl. | Amaranthaceae | AH | S, CK | |
| Interdune lowland | Aster altaicus Willd. | Asteraceae | HP | S, Y, Z, H |
| Stipa capillata L. | Poaceae | HP | S, Y, Z, H | |
| Lactuca tatarica L. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Corispermum hyssopifolium L. | Amaranthaceae | AH | S, Z, H | |
| Setaria viridis L. | Poaceae | AH | Y, Z | |
| Inula linariifolia Turcz. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Thermopsis lanceolata R. Br. | Fabaceae | HP | S | |
| Grubovia dasyphylla Fisch. & C. A. Mey. | Amaranthaceae | AH | S | |
| Echinochloa crus-galli var. | Poaceae | AH | Z, H | |
| Salsola collina Pall. | Amaranthaceae | AH | S, Y, H | |
| Astragalus laxmannii Jacq. | Fabaceae | HP | S | |
| Sonchus brachyotus DC. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Oxytropis myriophylla Pall. | Fabaceae | HP | S | |
| Ixeris chinensis Thunb. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Astragalus melilotoides Pall. | Fabaceae | HP | Z | |
| Euphorbia humifusa Willd. ex Schltdl. | Euphorbiaceae | AH | S | |
| Onopordum acanthium L. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Saussurea amara L. | Asteraceae | HP | S | |
| Cynanchum chinense R. Br. | Apocynaceae | FU | S | |
| Agriophyllum pungens Vahl. | Amaranthaceae | AH | CK |
| Index | Variance Source | Sum of Squares (SS) | df | Mean Square (MS) | F | p | Post Hoc Test * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | MT | 2.200 | 3 | 0.733 | 9.62 | 0.000 ** | I > II, I > IV, III > IV |
| Veg | 116.625 | 4 | 29.156 | 382.38 | 0.000 ** | S > Z, S > H, S > CK, Y > Z, Y > H, Y > CK, H > Z, Z > CK, H > CK | |
| MT × Veg | 3.049 | 12 | 0.254 | 3.33 | 0.000 ** | ||
| SOM | MT | 2.763 | 3 | 0.921 | 3.72 | 0.014 * | I > II, III > II |
| Veg | 44.459 | 4 | 11.115 | 44.92 | 0.000 ** | S > Y, S > Z, S > H, S > CK, Z > Y, H > Y, CK > Y, Z > CK, H > CK | |
| MT × Veg | 12.406 | 12 | 1.034 | 4.18 | 0.000 ** | ||
| TN | MT | 512.086 | 3 | 170.695 | 22.30 | 0.000 ** | II > I, IV > I, IV > II, IV > III |
| Veg | 2867.848 | 4 | 716.962 | 93.66 | 0.000 ** | S > Y, S > Z, S > H, S > CK, Y > Z, Y > H, Y > CK, Z > CK, H > CK | |
| MT × Veg | 251.647 | 12 | 20.971 | 2.74 | 0.003 ** | ||
| TP | MT | 0.962 | 3 | 0.321 | 21.19 | 0.000 ** | II > I, III > I, II > IV, III > IV |
| Veg | 6.262 | 4 | 1.565 | 103.47 | 0.000 ** | Y > S, Z > S, H > S, S > CK, Y > H, Y > CK, Z > H, Z > CK, H > CK | |
| MT × Veg | 0.173 | 12 | 0.014 | 0.96 | 0.496 | ||
| TK | MT | 487.728 | 3 | 162.576 | 5.04 | 0.002 ** | III > I, III > IV |
| Veg | 19,722.929 | 4 | 4930.732 | 152.83 | 0.000 ** | Y > S, Z > S, S > H, S > CK, Y > Z, Y > H, Y > CK, Z > H, Z > CK, H > CK | |
| MT × Veg | 1276.143 | 12 | 106.345 | 3.30 | 0.001 ** |
| Plot Type | Longitude/° | Latitude/° | Elevation/m | Gradient/° | Windward Slope Direction | Height of Sand Dunes/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. psammophila (S) | 109.247885 | 38.880868 | 1273.50 | 10 | SW | 7 |
| C. fruticosum (Y) | 109.202737 | 38.892425 | 1270.49 | 11 | W | 9 |
| A. fruticose (Z) | 109.235263 | 38.872782 | 1310.00 | 9 | W | 8 |
| Mixed plantation (H) | 109.235801 | 38.873037 | 1312.00 | 10 | W | 8 |
| Bare sandy land (CK) | 109.293522 | 38.808715 | 1276.68 | 11 | SW | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, K.; Hai, L.; Qin, F.; Liu, L.; Hong, G.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Yue, Y.; Dong, X.; He, R.; et al. Effects of Micro-Topography on Soil Nutrients and Plant Diversity of Artificial Shrub Forest in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Plants 2025, 14, 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14142163
Zhao K, Hai L, Qin F, Liu L, Hong G, Li Z, Li L, Yue Y, Dong X, He R, et al. Effects of Micro-Topography on Soil Nutrients and Plant Diversity of Artificial Shrub Forest in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Plants. 2025; 14(14):2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14142163
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Kai, Long Hai, Fucang Qin, Lei Liu, Guangyu Hong, Zihao Li, Long Li, Yongjie Yue, Xiaoyu Dong, Rong He, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Micro-Topography on Soil Nutrients and Plant Diversity of Artificial Shrub Forest in the Mu Us Sandy Land" Plants 14, no. 14: 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14142163
APA StyleZhao, K., Hai, L., Qin, F., Liu, L., Hong, G., Li, Z., Li, L., Yue, Y., Dong, X., He, R., & Shi, D. (2025). Effects of Micro-Topography on Soil Nutrients and Plant Diversity of Artificial Shrub Forest in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Plants, 14(14), 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14142163





