Genome-Wide Identification of PP2C Gene Family in Oat (Avena sativa L.) and Its Functional Analyses in Response to ABA and Abiotic Stresses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Treatments
2.2. Genome-Wide Identification of the PP2C Genes in Oat
2.3. Phylogenetic Construction, Conserved Motifs, and Exon–Intron Structure
2.4. Protein Features, Chromosome Location, and Cis-Acting Element Analysis of AsaPP2C Genes
2.5. Expression Pattern Analysis of AsaPP2Cs Obtained from Transcriptome Sequencing
2.6. RNA Extraction and Expression of AsaPP2Cs Under Different Stresses
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the PP2C Gene Family in Oat
3.2. Chromosomal Location of AsaPP2C Genes
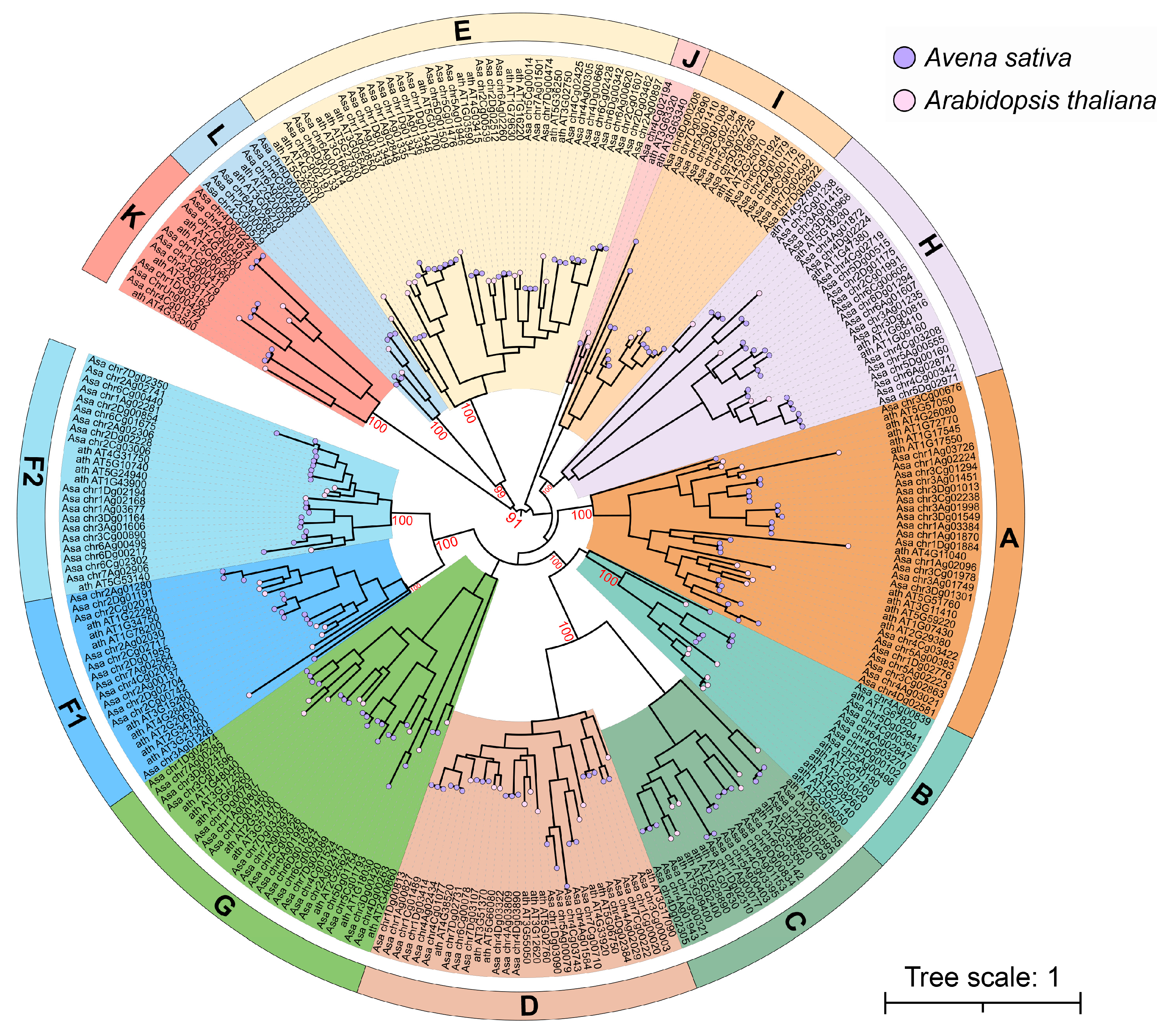
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis of AsaPP2C Genes
3.5. Cis-Element Analysis of the AsaPP2C Promoter in Oat
3.6. Analysis of AsaPP2C Gene Expression Patterns Under Drought Stress
3.7. Expression Profile Analysis of AsaPP2C Genes Under Abiotic Stresses and ABA Treatments in Leaves
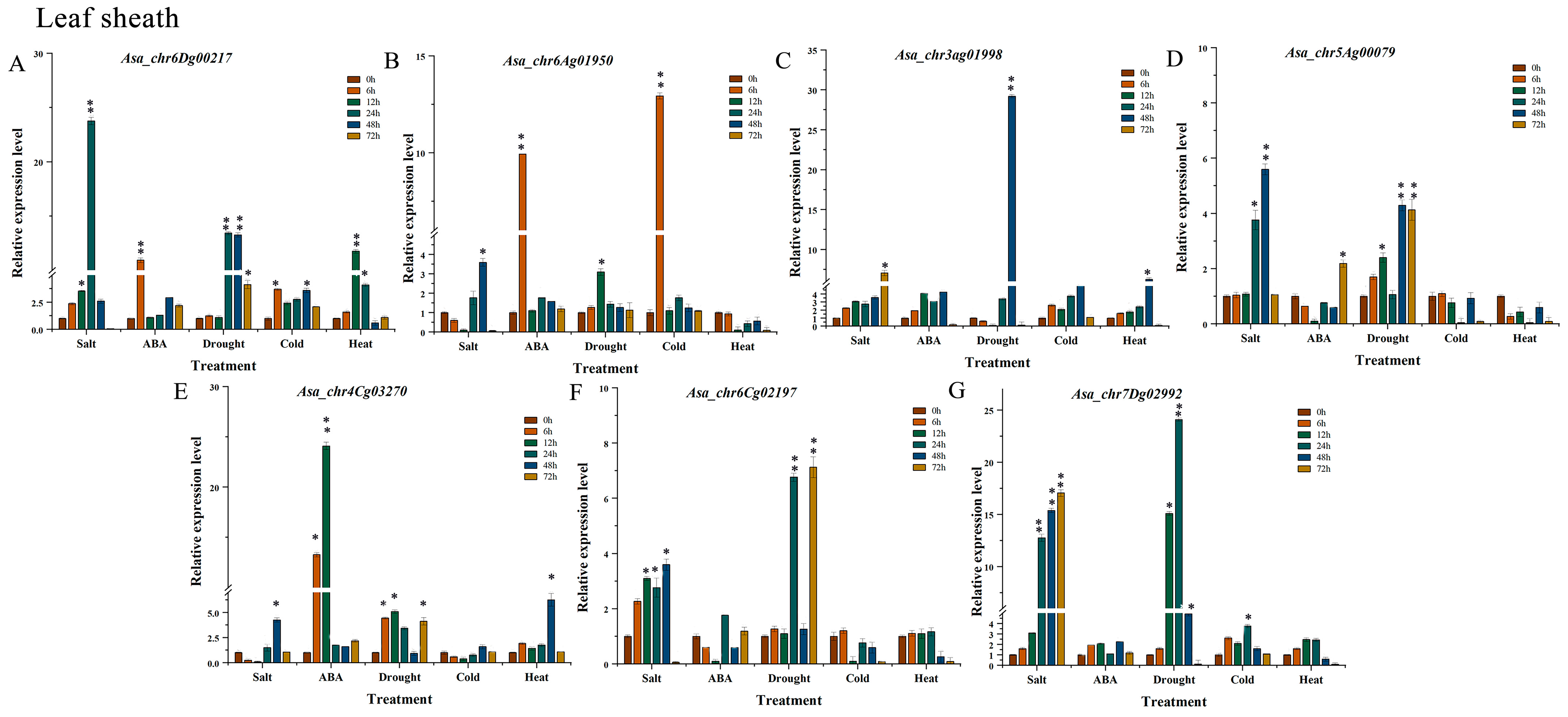
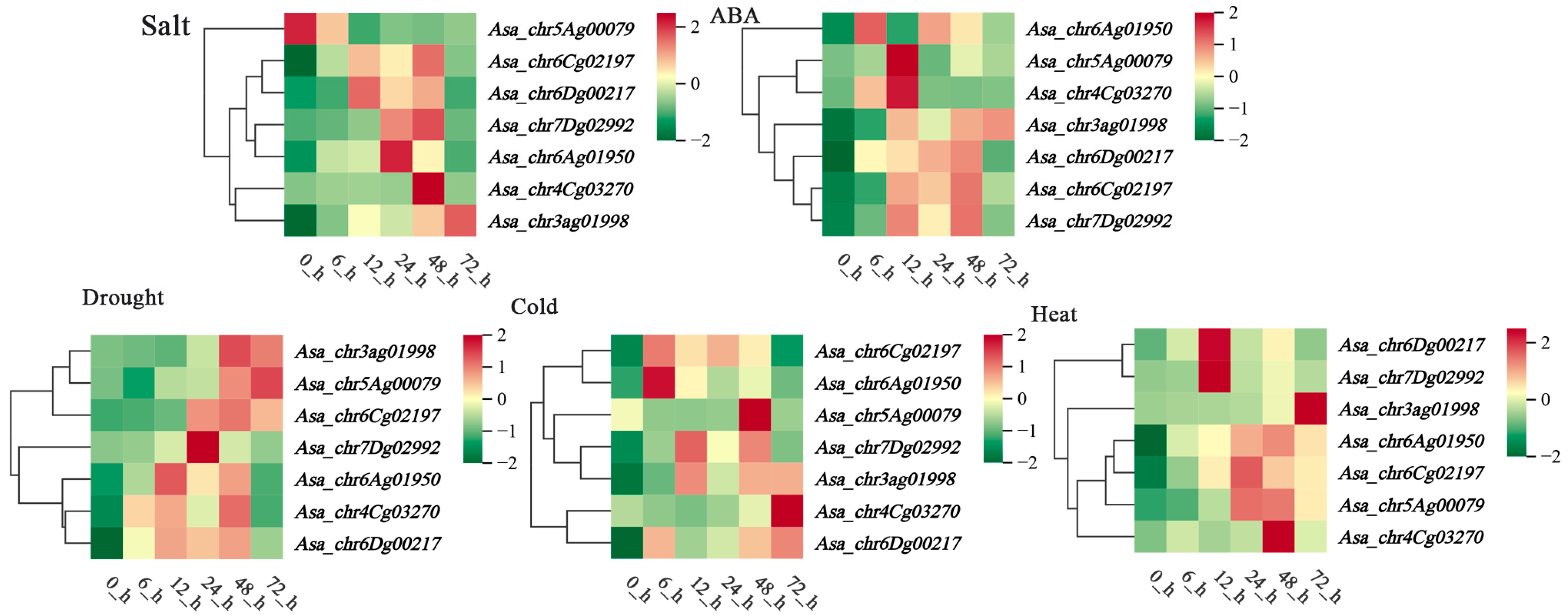
3.8. Expression Profile Analysis of AsaPP2C Genes Under Abiotic Stresses and ABA Treatments in Leaf Sheath
3.9. Expression Profile of AsaPP2C Genes Under Abiotic Stresses and ABA Treatments in Roots
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, Z.; Xiong, L.; Shi, H. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 635–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Cao, L.; Ye, F.; Ma, C.; Liang, X.; Song, Y.; Lu, X. Identification of the maize PP2C gene family and functional studies on the role of ZmPP2C15 in drought tolerance. Plants 2024, 13, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Islam, T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of glyoxalase gene families in soybean (Glycine max) indicate their development and abiotic stress specific response. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskara, G.; Wong, M.; Verslues, P. The flip side of phospho-signalling: Regulation of protein dephosphorylation and the protein phosphatase 2Cs. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 2913–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, H.; Kondo, S.; Tanaka, T.; Imamura, C.; Muramoto, N.; Hattori, E.; Ogawa, K.; Mitsukawa, N.; Ohto, C. Overexpression of a novel Arabidopsis PP2C isoform, AtPP2CF1, enhances plant biomass production by increasing inflorescence stem growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5385–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arter, C.; Trask, L.; Ward, S. Structural features of the protein kinase domain and targeted binding by small-molecule inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, B.; Plaxton, W. Multifaceted functions of post-translational enzyme modifications in the control of plant glycolysis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 55, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Zhao, C.-F.; Zhou, L.-H.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.-L. The Arabidopsis kinase-associated protein phosphatase KAPP, interacting with protein kinases SnRK2.2/2.3/2.6, negatively regulates abscisic acid signaling. Plant Mol. Biol 2020, 102, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Hu, L.; Ma, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, J. Importance of tyrosine phosphorylation in hormone-regulated plant growth and development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, M.; Pedrotti, L.; Krischke, M. The evolutionarily conserved kinase SnRK1 orchestrates resource mobilization during Arabidopsis seedling establishment. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 616–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, K.; Niu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, R. Genome-wide identification of PP2C genes and their expression profiling in response to drought and cold stresses in Medicago truncatula. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qin, Q.; Su, M. Type one protein phosphatase regulates fixed-carbon starvation-induced autophagy in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 4531–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Nan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, X. Genome-wide identification, expression and interaction analysis of GmSnRK2 and type A PP2C Genes in response to abscisic acid treatment and drought stress in soybean plant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Huang, X.; He, Z. Phosphorylation of OsTGA5 by casein kinase II compromises its suppression of defense-related gene transcription in rice. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3425–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Genome-wide and expression analysis of protein phosphatase 2C in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. The maize clade A PP2C phosphatases play critical roles in multiple abiotic stress responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Ke, H.; Hu, M. Genome-wide identification, evolution, and transcriptional profiling of PP2C gene family in Brassica rapa. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2965035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.; Khan, N.; Pervaiz, T. Genome-wide identification, evolution, and molecular characterization of the PP2C gene family in woodland strawberry. Gene 2019, 702, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ni, L.; Xia, X. Genome-wide analysis of the protein phosphatase 2C genes in tomato. Genes 2022, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Pan, S. Maize protein phosphatase gene family: Identifcation and molecular characterization. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Giri, J.; Kapoor, S.; Tyagi, A.; Pandey, G. Protein phosphatase complement in rice: Genome-wide identifcation and transcriptional analysis under abiotic stress conditions and reproductive development. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, S.; Li, X.; Lyu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wan, Z.; Yu, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the cucumber PP2C gene family. BMC Genom. 2022, 6, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Han, J.; Wang, E.; Xiao, J.; Hu, R.; Yang, G. Genome-wide identifcation and homoeologous expression analysis of PP2C genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Blacquiere, G.; Leus, G. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yin, D.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Z.; Tuluhong, M.; Li, X. Validation of appropriate reference genes for qRT-PCR normalization in Oat (Avena sativa L.) under UV-B and high-light stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Shan, X.; Si, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, M. Identification of PP2C gene family in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) and function analysis of PhePP2CA13. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2025, 109929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazadee, H.; Khan, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Zeng, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X. Identification and expression profiling of protein phosphatases (PP2C) gene family in Gossypium hirsutum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yan, H.; Guo, L.; Deng, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Kang, L.; Zhou, P.; Yu, K.; Dong, X.; et al. Reference genome assemblies reveal the origin and evolution of allohexaploid oat. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.; Grill, E.; Meskiene, I.; Schweighofer, A. Type 2C protein phosphatases in plants. Febs J. 2012, 280, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogozin, B.; Sverdlov, A.; Babenko, V.; Koonin, E. Analysis of evolution of exon-intron structure of eukaryotic genes. Brief. Bioinform. 2005, 6, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Jiang, M.; Li, P.; Chu, Z. Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analyses of the PP2C gene family with their expression profiling in response to multiple stresses in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecharny, A.; Boudet, N.; Gy, I.; Aubourg, S.; Kreis, M. Introns in, introns out in plant gene families: A genomic approach of the dynamics of gene structure. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2003, 3, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Serine/threonine phosphatases: Mechanism through structure. Cell 2009, 139, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Conery, J.S. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 2000, 290, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhu, L.; Cai, G.; Lv, C.; Yang, H.; Ren, X.; Lan, H. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the PP2C family from zea mays and its role in long-distance signaling. Plants 2023, 12, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, N.; Sarkeshik, A.; Nito, K.; Park, S.; Wang, A.; Carvalho, P. PYR/PYL/RCAR family members are major in-vivo ABI1 protein phosphatase 2C-interacting proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2010, 61, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, M.; Luo, D. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic, structural and functional evolution of the core components of ABA signaling in plant species: A focus on rice. Planta 2024, 260, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J. The U-box family genes in Medicago truncatula: Key elements in response to salt, cold, and drought stresses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, S.; Rodrigues, A.; Saez, A.; Dizon, M.; Galle, A.; Kim, T.; Santiago, J.; Flexas, J.; Schroeder, J.; Rodriguez, P. Triple Loss of Function of Protein Phosphatases Type 2C Leads to Partial Constitutive Response to Endogenous Abscisic Acid. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Ding, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D. Identification of an important site for function of the type 2C protein phosphatase ABI2 in abscisic acid signalling in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 5713–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskara, G.; Nguyen, T.; Verslues, P. Unique drought resistance functions of the highly ABA-induced Clade A protein phosphatase 2Cs. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweighofer, A. The PP2C-type phosphatase AP2C1, which negatively regulates MPK4 and MPK6, modulates innate immunity, jasmonic acid, and ethylene levels in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2213–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pri-Tal, O.; Sun, Y.; Dadras, A.; Fürst-Jansen, J.; Zimran, G.; Michaeli, D.; Mosquna, A. Constitutive activation of ABA receptors in Arabidopsis reveals unique regulatory circuitries. New Physiol. 2024, 241, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Gao, G.; Zhu, A.; Chen, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of BnPP2C Gene Family in Response to Multiple Stresses in Ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Gao, L.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Y. DIW1 encoding a clade I PP2C phosphatase negatively regulates drought tolerance by de-phosphorylating TaSnRK1. 1 in wheat. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 1918–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, P.; Niu, K.; Chai, J.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, G. Genome-Wide Identification of PP2C Gene Family in Oat (Avena sativa L.) and Its Functional Analyses in Response to ABA and Abiotic Stresses. Plants 2025, 14, 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14132062
Huang P, Niu K, Chai J, Wang W, Ma Y, Cao Y, Zhao G. Genome-Wide Identification of PP2C Gene Family in Oat (Avena sativa L.) and Its Functional Analyses in Response to ABA and Abiotic Stresses. Plants. 2025; 14(13):2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14132062
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Panpan, Kuiju Niu, Jikuan Chai, Wenping Wang, Yanming Ma, Yanan Cao, and Guiqin Zhao. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification of PP2C Gene Family in Oat (Avena sativa L.) and Its Functional Analyses in Response to ABA and Abiotic Stresses" Plants 14, no. 13: 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14132062
APA StyleHuang, P., Niu, K., Chai, J., Wang, W., Ma, Y., Cao, Y., & Zhao, G. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification of PP2C Gene Family in Oat (Avena sativa L.) and Its Functional Analyses in Response to ABA and Abiotic Stresses. Plants, 14(13), 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14132062





