Phosphorylation of Plant Ferredoxin-like Protein Is Required for Intensifying PAMP-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Preparation of HrpN Protein and flg22Pst
2.3. Preparation of Recombinant PFLP Proteins
2.4. Analysis of Hypersensitive Response Ratio in Arabidopsis thaliana
2.5. Rapid Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Callose Deposition Assay
2.6. Disease Severity Assay
2.7. Analysis of Defense Gene Expression Involved in the MAPK Signaling Pathway
3. Results
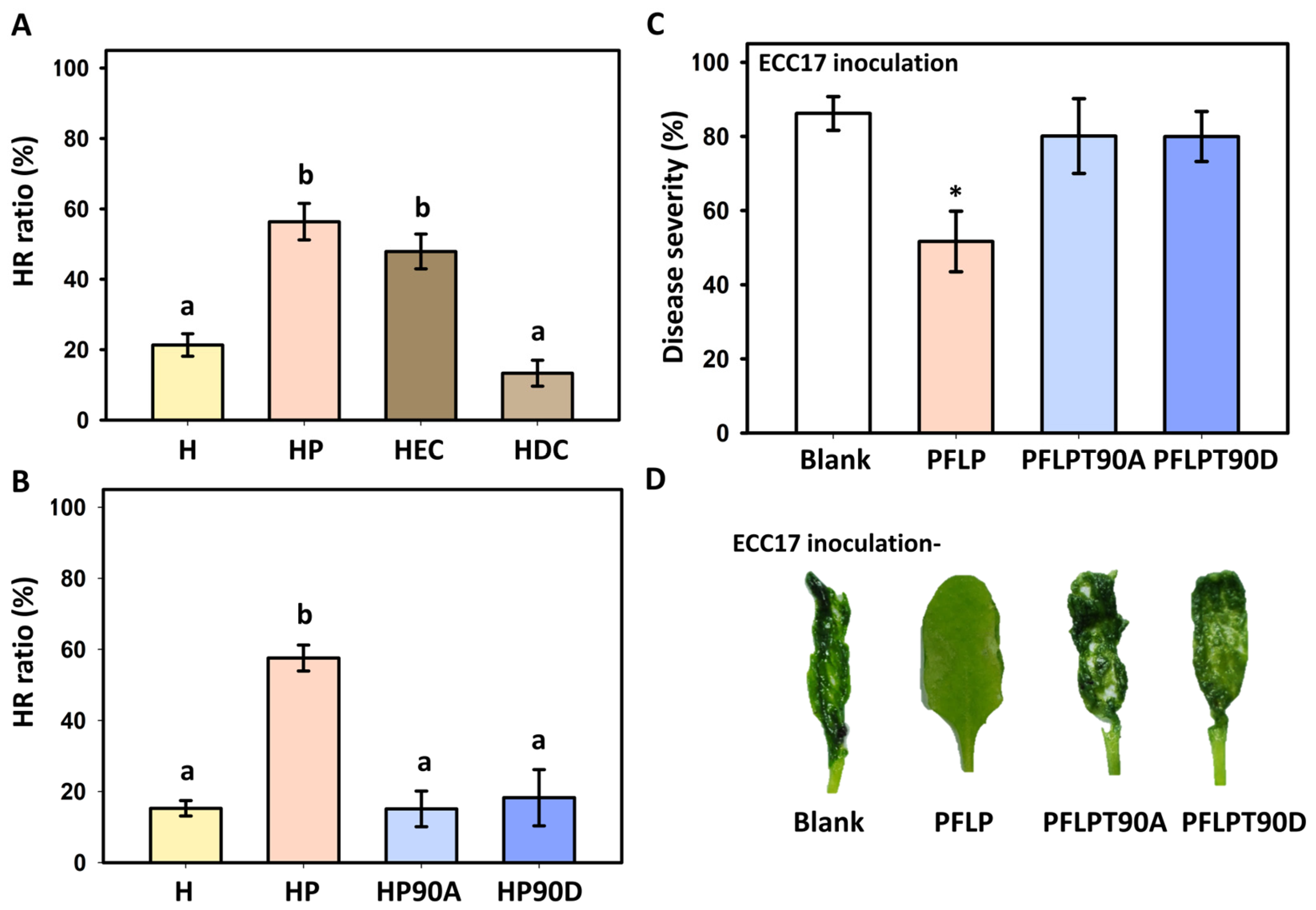
3.1. Effect of PFLP Recombinant Protein on the Occurrence of Hypersensitive Reaction (HR) and Its Effect on Controlling Bacterial Soft Rot Disease
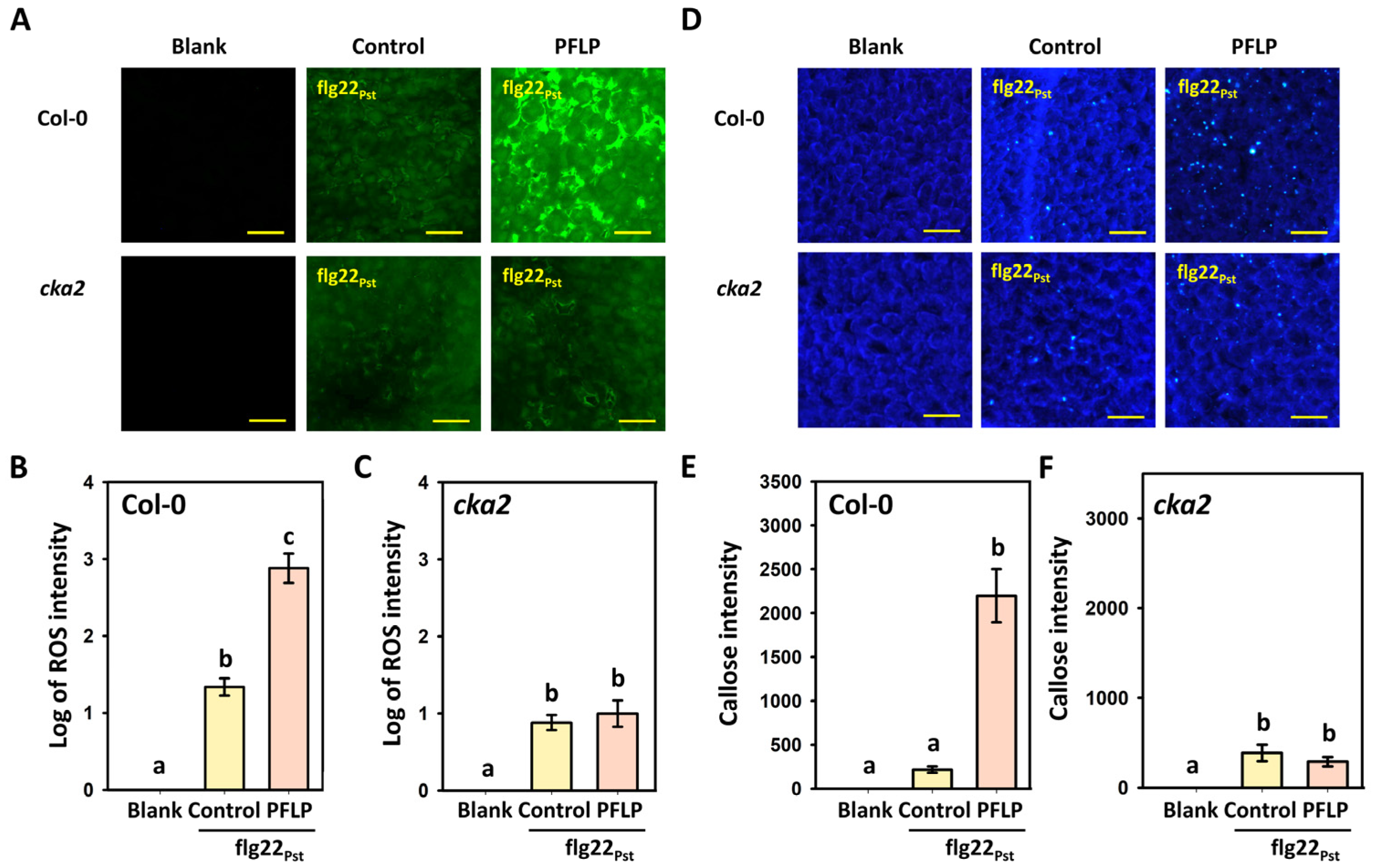
3.2. Effect of PFLP Recombinant Protein on Enhancing PTI Defense Response in the cka2 Mutant
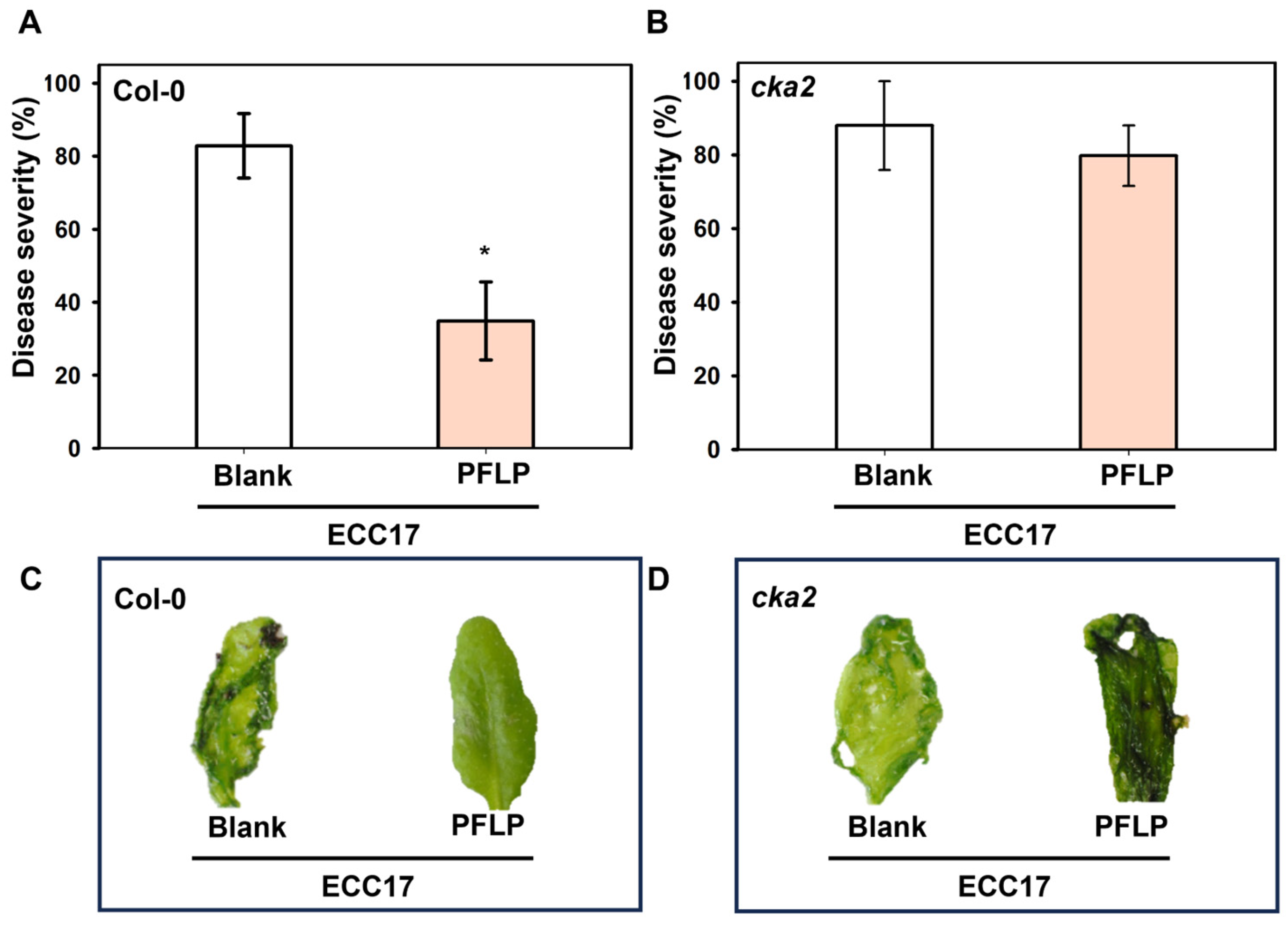
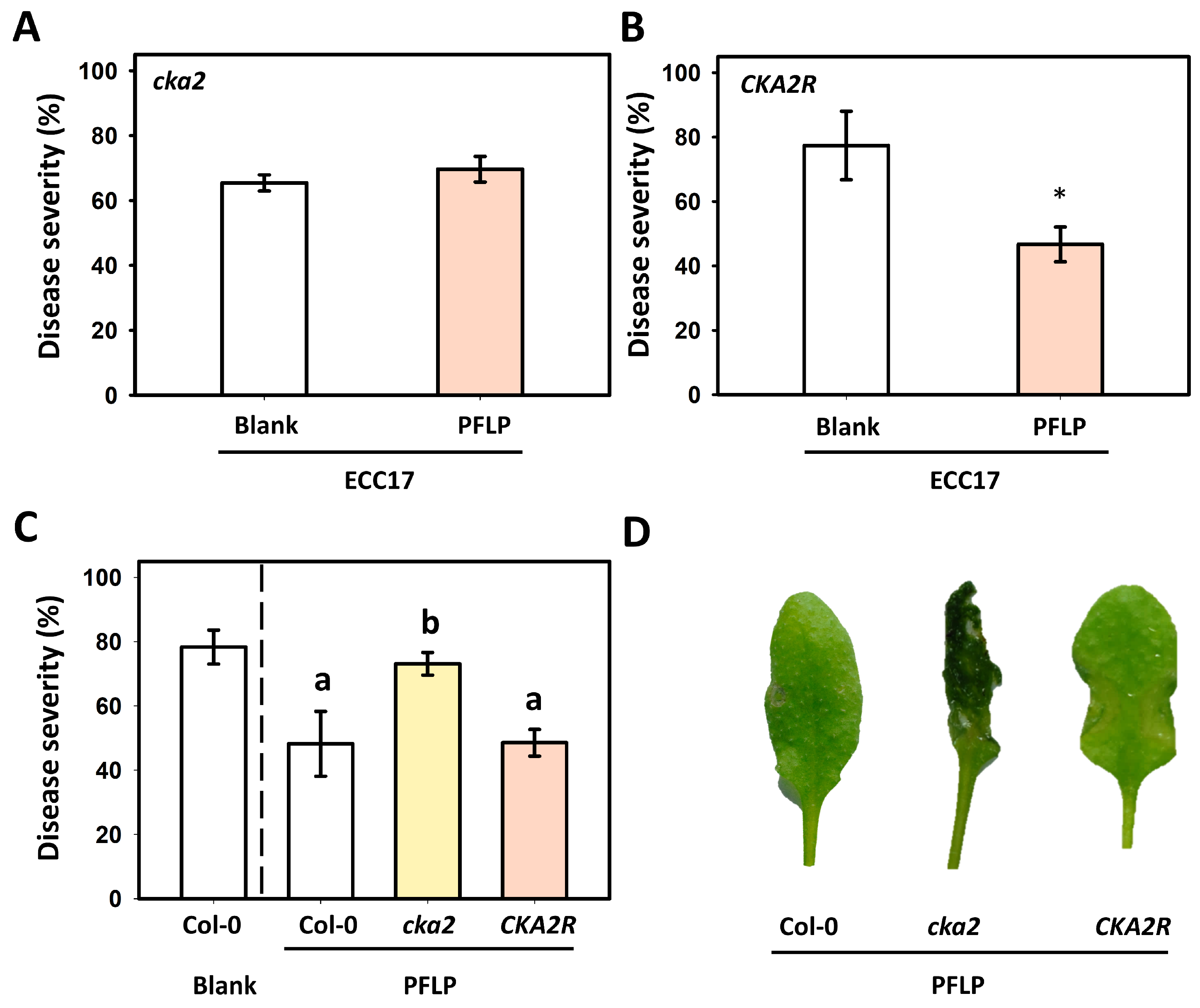
3.3. Disease Control of PFLP Recombinant Protein in cka2 Mutant
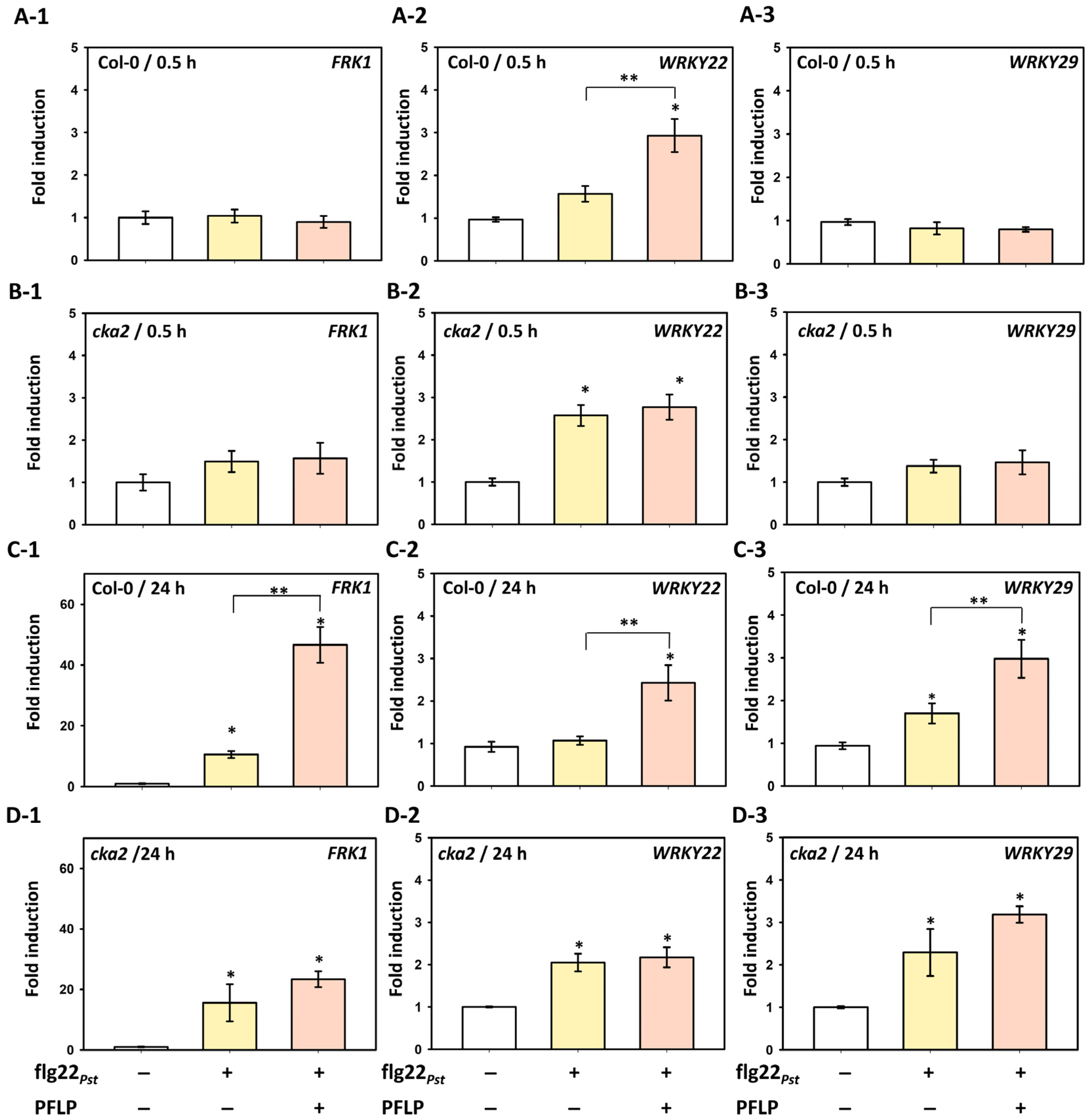
3.4. Relationship Between PFLP-Mediated Enhancement of Disease Resistance and MAPK Pathway Signaling in the cka2 Mutant
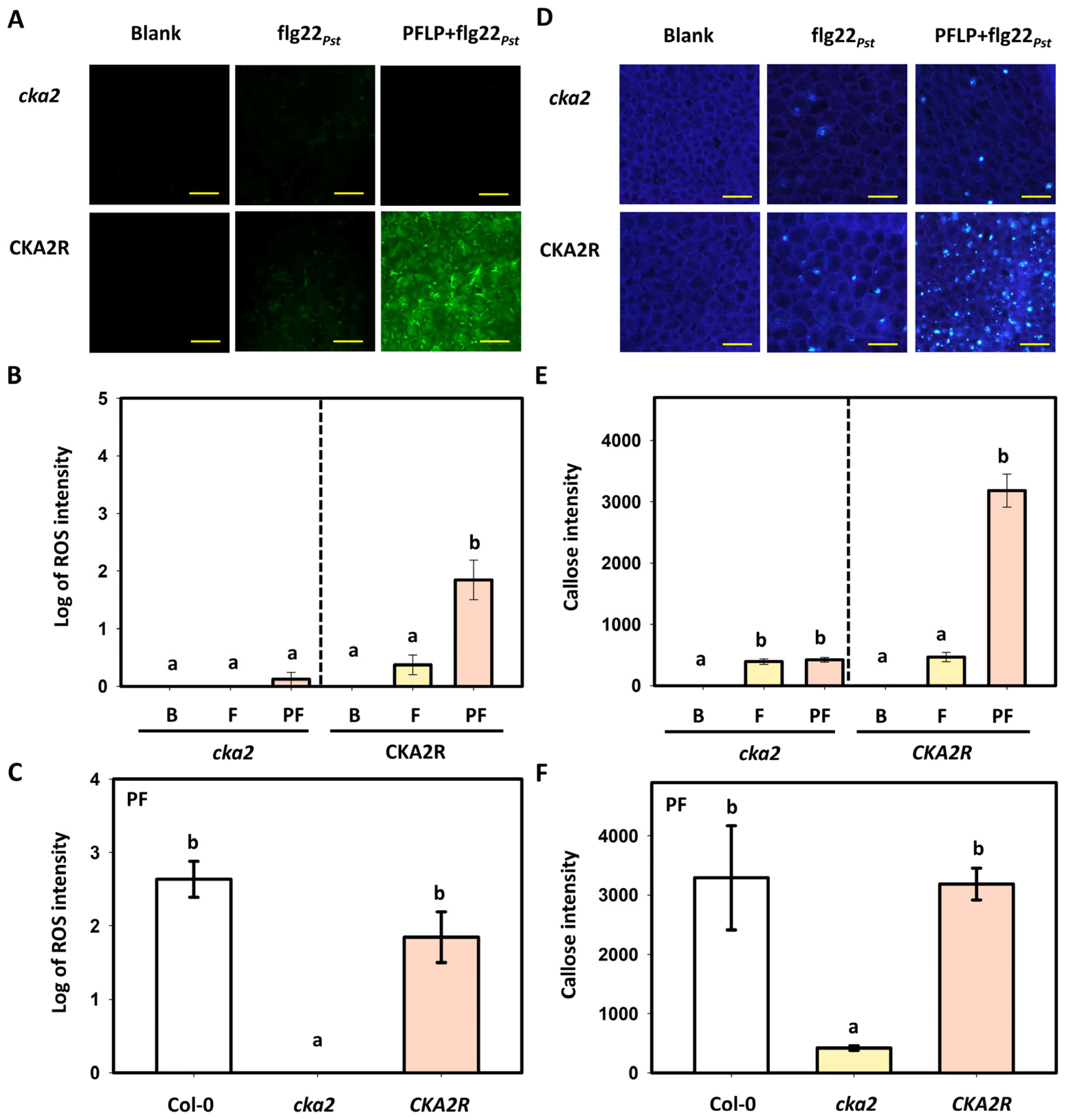
3.5. Effects of PFLP on flg22Pst-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Callose Deposition in the CKA2R Complementation Line
3.6. Assay of PFLP-Mediated Control of Bacterial Soft Rot in the CKA2R Complementation Line
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Staskawicz, B.J.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system: From discovery to deployment. Cell 2024, 187, 2095–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, N.S.; Epple, P.; Dangl, J.L. Programmed cell death in the plant immune system. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.N.; Li, Y.T.; Wu, Y.Z.; Li, T.; Geng, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Tan, X.L. Plant Disease Resistance-Related Signaling Pathways: Recent Progress and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaouannet, M.; Rodriguez, P.A.; Thorpe, P.; Lenoir, C.J.; MacLeod, R.; Escudero-Martinez, C.; Bos, J.I. Plant immunity in plant-aphid interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Ren, X.; Dai, X.; Liu, H. PopW activates PAMP-triggered immunity in controlling tomato bacterial spot disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.-L.; Li, J.-R.; Li, A.-T.; Li, S.-H.; Blanco, S.D.; Chen, S.-Y.; Lai, Y.-R.; Shi, M.-Q.; Lin, T.-C.; Su, J.-F.; et al. A rapid method for screening pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered Immunity-Intensifying microbes. Plants 2024, 13, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Goodman, R.E.; Tetteh, A.O.; Lu, M.; Tripathi, L. Bioinformatics analysis to assess potential risks of allergenicity and toxicity of HRAP and PFLP proteins in genetically modified bananas resistant to Xanthomonas wilt disease. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namukwaya, B.; Tripathi, L.; Tripathi, J.N.; Arinaitwe, G.; Mukasa, S.B.; Tushemereirwe, W.K. Transgenic banana expressing gene confers enhanced resistance to Xanthomonas wilt disease. Transgenic Res. 2012, 21, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimusiima, J.; Köberl, M.; Tumuhairwe, J.B.; Kubiriba, J.; Staver, C.; Berg, G. Transgenic banana plants expressing Xanthomonas wilt resistance genes revealed a stable non-target bacterial colonization structure. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Sun, X.; Hu, Q.; Wu, A.; Lin, C.-H.; Lin, H.-J.; Twyman, R.M.; Christou, P.; Feng, T.-Y. Transgenic rice plants expressing the ferredoxin-like protein (AP1) from sweet pepper show enhanced resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Sci. 2001, 160, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-E.; Liu, C.-A.; Lee, M.-J.; Kuo, C.-G.; Chen, H.-M.; Ger, M.-J.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-R.; Lin, M.-K.; Feng, T.-Y. Resistance enhancement of transgenic tomato to bacterial pathogens by the heterologous expression of sweet pepper ferredoxin-I protein. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liau, C.H.; Lu, J.C.; Prasad, V.; Hsiao, H.H.; You, S.J.; Lee, J.T.; Yang, N.S.; Huang, H.E.; Feng, T.Y.; Chen, W.H.; et al. The sweet pepper ferredoxin-like protein (pflp) conferred resistance against soft rot disease in Oncidium orchid. Transgenic Res. 2003, 12, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-H.; Hong, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H. Plant ferredoxin-like protein enhances resistance to bacterial soft rot disease through PAMP-triggered immunity in. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 140, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, M.-K.; Huang, H.-E.; Ger, M.-J.; Chiu, S.-H.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-I.; Feng, T.-Y. Production of soft rot resistant calla lily by expressing a ferredoxin-like protein gene (pflp) in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.-J.; Liau, C.-H.; Huang, H.-E.; Feng, T.-Y.; Prasad, V.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Lu, J.-C.; Chan, M.-T. Sweet pepper ferredoxin-like protein (pflp) gene as a novel selection marker for orchid transformation. Planta 2003, 217, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.-Y.; Zheng, J.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chao, H.-R.; Lin, Y.-H. PFLP-intensified disease resistance against bacterial soft rot through the MAPK pathway in PAMP-triggered immunity. Phytopathology 2018, 108, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayakar, B.V.; Lin, H.J.; Chen, C.H.; Ger, M.J.; Lee, B.H.; Pai, C.H.; Chow, D.; Huang, H.E.; Hwang, S.Y.; Chung, M.C.; et al. Ferredoxin from sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) intensifying harpin-mediated hypersensitive response shows an enhanced production of active oxygen species (AOS). Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 51, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-E.; Ger, M.-J.; Yip, M.-K.; Chen, C.-Y.; Pandeya, A.K.; Feng, T.-Y. A hypersensitive response was induced by virulent bacteria in transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing a plant ferredoxin-like protein (PFLP). Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2004, 64, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, K. Structure and function of plant-type ferredoxins. Photosynth. Res. 2004, 81, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-E.; Ger, M.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yip, M.-K.; Chung, M.-C.; Feng, T.-Y. Plant ferredoxin-like protein (PFLP) exhibits an anti-microbial ability against soft-rot pathogen Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora in vitro and in vivo. Plant Sci. 2006, 171, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Huang, H.-E.; Wu, F.-S.; Ger, M.-J.; Liao, P.-L.; Chen, Y.-R.; Tzeng, K.-C.; Feng, T.-Y. Plant ferredoxin-like protein (PFLP) outside chloroplast in Arabidopsis enhances disease resistance against bacterial pathogens. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.H.; Huang, H.E.; Chen, Y.R.; Liao, P.L.; Chen, C.L.; Feng, T.Y. C-Terminal Region of Plant Ferredoxin-Like Protein Is Required to Enhance Resistance to Bacterial Disease. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Gao, G.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Ma, P. Casein kinase CK2 structure and activities in plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 276, 153767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulekar, J.J.; Huq, E. Expanding roles of protein kinase CK2 in regulating plant growth and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2883–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viela, B.; Pagés, M.; Riera, M. Emerging roles of protein kinase CK2 in abscisic acid signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Lai, I.-L.; Zheng, J.-L.; Lin, Y.H. Using dynamic changes of chlorophyll fluorescence in Arabidopsis thaliana to evaluate plant immunity-intensifying Bacillus spp. strains. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, G.; Duran, J.D.; Volko, S.; Boller, T. Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant J. 1999, 18, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göhre, V.; Jones, A.M.E.; Sklenář, J.; Robatzek, S.; Weber, A.P.M. Molecular crosstalk between PAMP-triggered immunity and photosynthesis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudsocq, M.; Willmann, M.R.; McCormack, M.; Lee, H.; Shan, L.; He, P.; Bush, J.; Cheng, S.H.; Sheen, J. Differential innate immune signalling via Ca2+ sensor protein kinases. Nature 2010, 464, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-T.; Li, A.-T.; Li, S.-H.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB05 increases resistance to bacterial wilt by activating mitogen-activated protein kinase and reactive oxygen species pathway crosstalk in Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytopathology 2022, 112, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvick, L.; Barnes, J.; Ebner, B.; Agrawal, S.; Andresen, M.; Lim, J.; Giesler, G.J.; Zoghbi, H.Y.; Orr, H.T. SCA1-like disease in mice expressing wild-type ataxin-1 with a serine to aspartic acid replacement at residue 776. Neuron 2010, 67, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.; Waksman, T.; Paliogianni, D.; Henderson, L.; Lütkemeyer, M.; Suetsugu, N.; Christie, J.M. Regulation of plant phototropic growth by NPH3/RPT2-like substrate phorylation and 14-3-3 binding. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krick, R.; Aschrafi, A.; Hasgün, D.; Arnemann, J. CK2-dependent C-terminal phosphorylation at T300 directs the nuclear transport of TSPY protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Tena, G.; Plotnikova, J.; Willmann, M.R.; Chiu, W.L.; Gomez-Gomez, L.; Boller, T.; Ausubel, F.M.; Sheen, J. MAP kinase signaling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 2002, 415, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalmi, S.K.; Sinha, A.K. ROS mediated MAPK signaling in abiotic and biotic stress- striking similarities and differences. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Verma, P.K. Guiding the guards: MPK3/6–VLN3 module regulating stomatal defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.; Shimono, M.; Tian, M.; Day, B. Arabidopsis Actin-Depolymerizing Factor-4 links pathogen perception, defense activation and transcription to cytoskeletal dynamics. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.-Y.; Gong, R.-W.; Chen, B.-W.; Lin, Y.-H. Phosphorylation of Plant Ferredoxin-like Protein Is Required for Intensifying PAMP-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2025, 14, 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14132044
Chen T-Y, Gong R-W, Chen B-W, Lin Y-H. Phosphorylation of Plant Ferredoxin-like Protein Is Required for Intensifying PAMP-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants. 2025; 14(13):2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14132044
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tzu-Yi, Rui-Wen Gong, Bo-Wei Chen, and Yi-Hsien Lin. 2025. "Phosphorylation of Plant Ferredoxin-like Protein Is Required for Intensifying PAMP-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana" Plants 14, no. 13: 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14132044
APA StyleChen, T.-Y., Gong, R.-W., Chen, B.-W., & Lin, Y.-H. (2025). Phosphorylation of Plant Ferredoxin-like Protein Is Required for Intensifying PAMP-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants, 14(13), 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14132044





