Zinc Translocation from Coastal Soil to Wheat as Mediated by Zinc Supply Levels and Soil Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
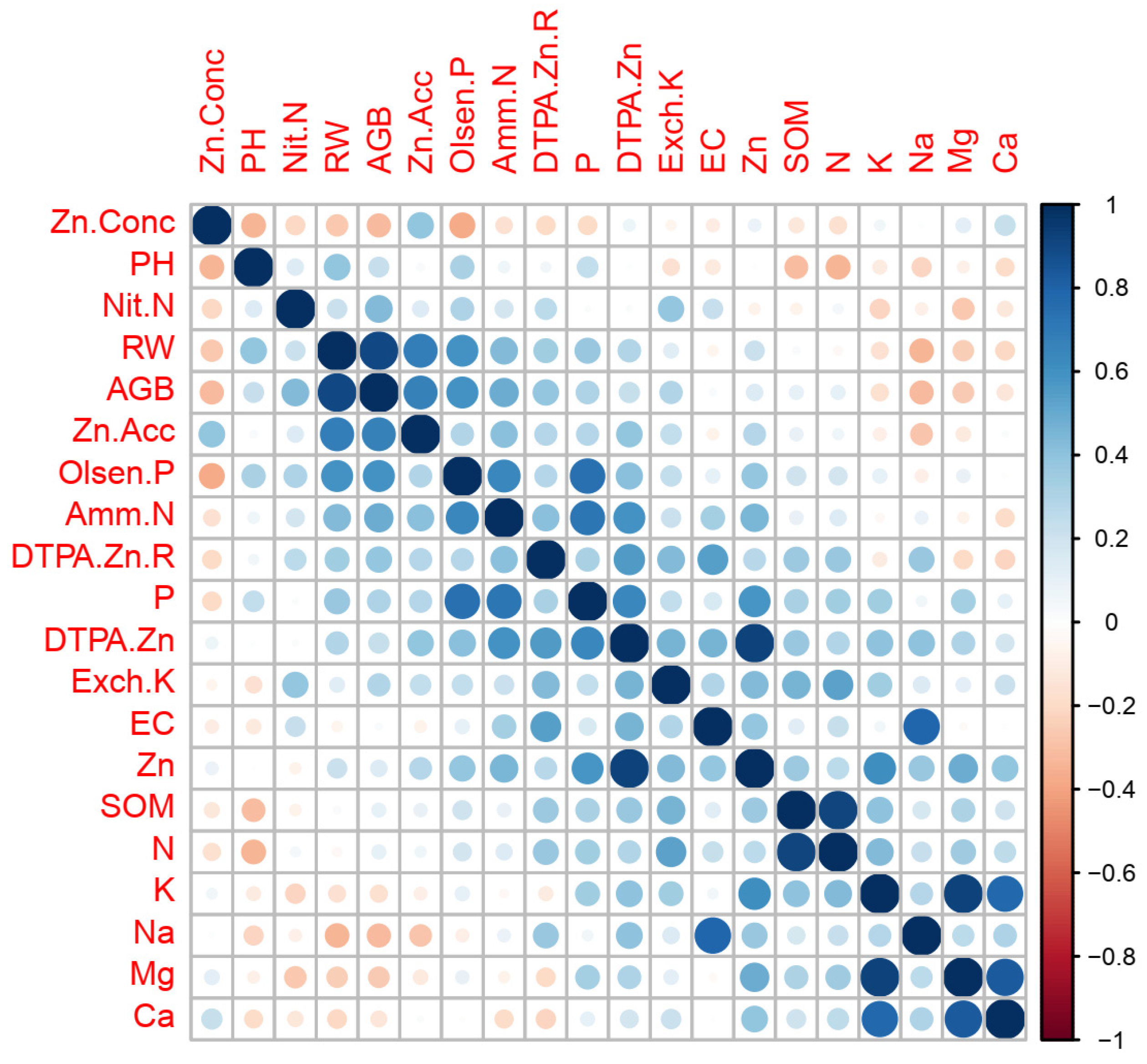
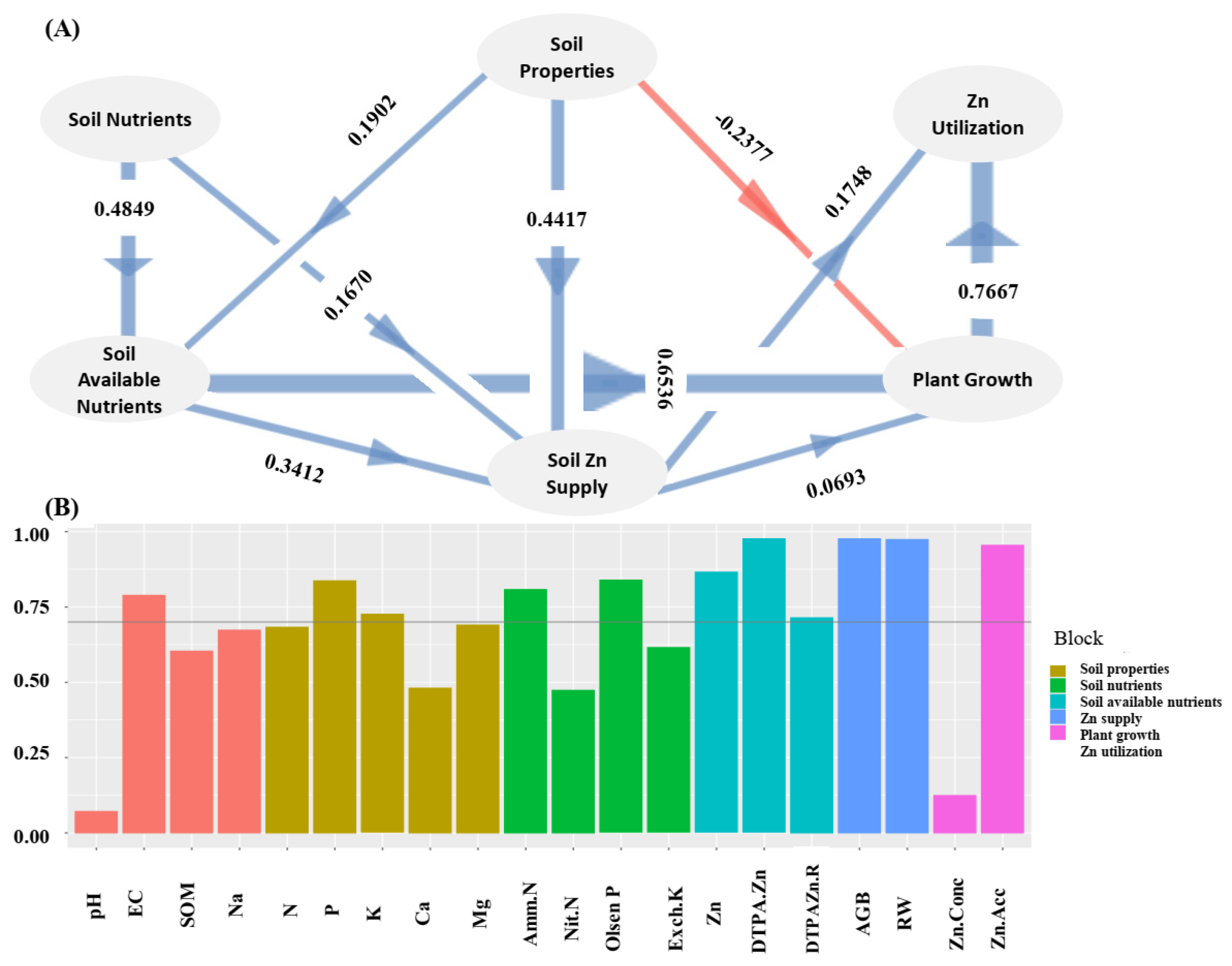
2.1. Zn Translocation from Soil to Wheat Plant as Mediated by Soil Properties
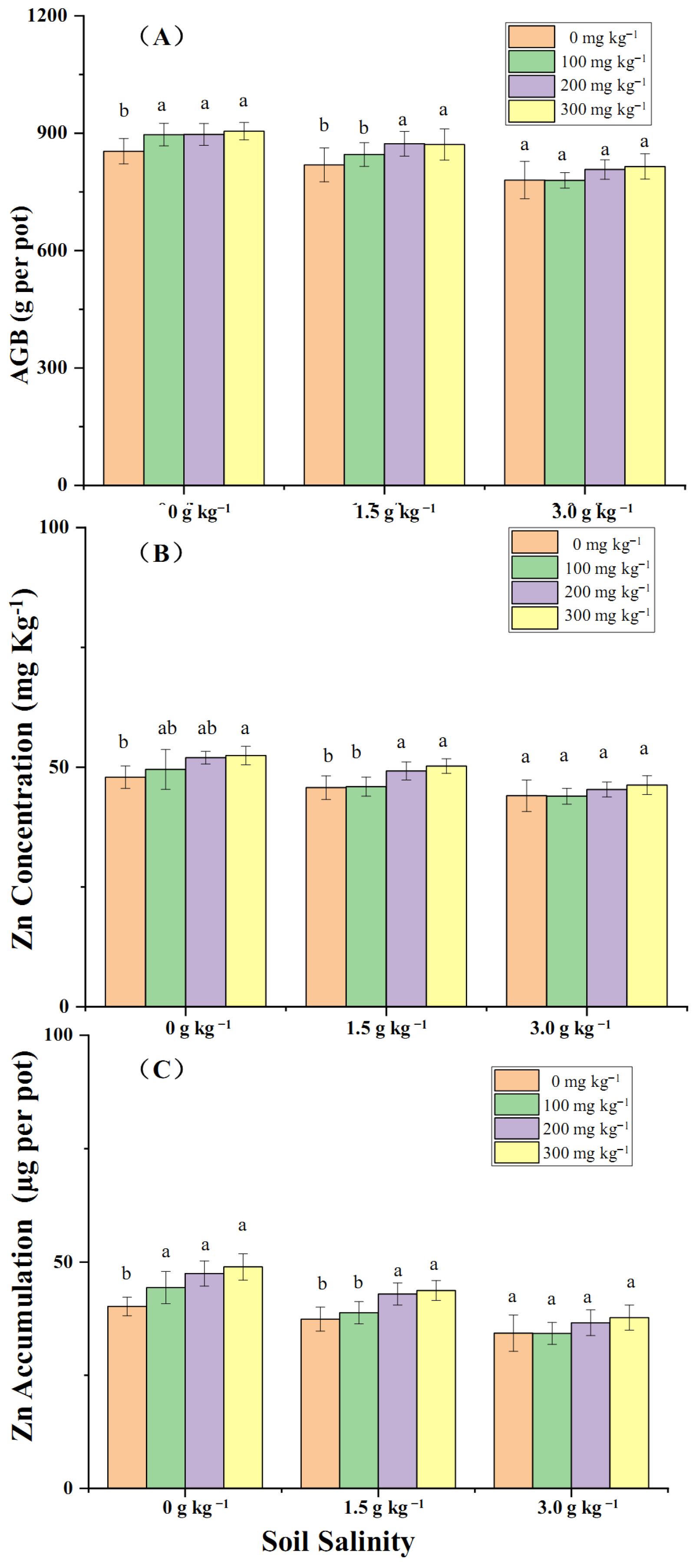
2.2. The Effects of Zn Application on Wheat Zn Accumulation Mediated by Soil Salinity
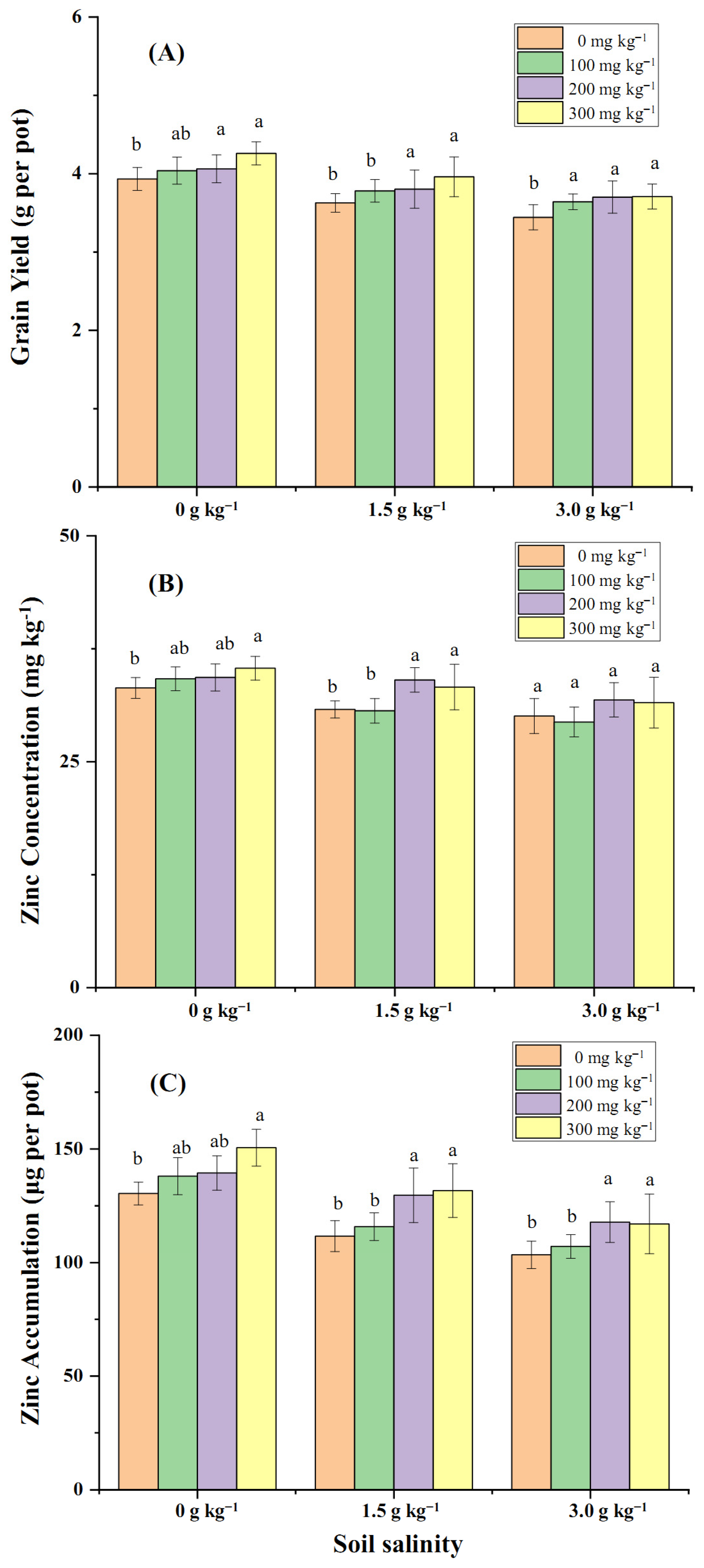
2.3. Effect of Soil and Foliar Zn Application on Wheat Grain Yield and Grain Zn Concentration in Coastal Saline Fields
3. Discussion
3.1. Zn Translocation from Soil to Wheat Mediated by Soil Properties
3.2. Effectiveness of Zn Application on Zn Translocation from Soil to Wheat Mediated by Salt Stress
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pot Study Using Soils from Different Locations
4.2. Pot Study Examining the Effects of Zn Application and Salinity
4.3. Field Trial
4.4. Measurement of Soil Chemical Indexes
4.5. Elemental Measurement of Soil and Plants
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stangoulis, J.C.R.; Knez, M. Biofortification of major crop plants with iron and zinc-achievements and future directions. Plant Soil. 2022, 474, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Li, K.; Yang, N.; Yang, Y.; Huang, D.; Liang, D.; Zhao, H.; Mao, H.; et al. Grain iron and zinc concentrations of wheat and their relationships to yield in major wheat production areas in China. Field Crop. Res. 2014, 156, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Kutman, U.B. Agronomic biofortifcation of cereals with zinc: A review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, C.; Kumar, S.; Ranjan, R.D.; Kumhar, S.R.; Govindan, V. Genomic approaches for improving grain zinc and iron content in wheat. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1045955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Hui, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Shi, M. Selecting high zinc wheat cultivars increases grain zinc bioavailability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11196–11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senguttuvel, P.; Padmavathi, G.; Jasmine, C.; Sanjeeva Rao, D.; Neeraja, C.N.; Jaldhani, V.; Beulah, P.; Gobinath, R.; Aravind Kumar, J.; Sai Prasad, S.V.; et al. Rice biofortification: Breeding and genomic approaches for genetic enhancement of grain zinc and iron contents. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1138408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tian, J.; Liang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, G.; Du, Q.; Cheng, D.; Cai, H.; et al. A high activity zinc transporter oszip9 mediates zinc uptake in rice. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, M.; Liu, S.J.; Deng, F.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Che, J.; Yamaji, N.; Hu, F.; Lei, G.J. A vacuolar transporter plays important roles in zinc and cadmium accumulation in rice grain. New Phytol. 2023, 239, 1919–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, A.; Ghazanfar, M.; Khan, J.S.; Pervaiz, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Alamri, S. Zinc Absorption through Leaves and Subsequent Translocation to the Grains of Bread Wheat after Foliar Spray. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Amanullah; Ahmed, I. Enhancing Zinc Biofortification of Wheat through Integration of Zinc, Compost, and Zinc-Solubilizing Bacteria. Agriculture 2022, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, K.; Hafez, E.M.; Omara, A.E.D.; Rashwan, E.; Alshaal, T. Zinc oxide nanoparticles and PGPR strengthen salinity tolerance and productivity of wheat irrigated with saline water in sodic-saline soil. Plant Soil. 2023, 493, 475–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and humans. Environ. Geochem. HLTH 2009, 31, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.; Guppy, C.; Nachimuthu, G.; Hulugalle, N. Changes in micronutrient concentrations under minimum tillage and cotton-based crop rotations in irrigated vertisols. Soil Till. Res. 2023, 228, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich No. 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich No. 2. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Barrow, N.J. Soil pH-nutrient relationships: The diagram. Plant Soil. 2023, 486, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Hartemink, A.E. The efects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant Soil. 2023, 487, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eynde, E.; Groenenberg, J.E.; Hofand, E.; Comans, R.N.J. Solid-solution partitioning of micronutrients Zn, Cu and B in tropical soils: Mechanistic and empirical models. Geoderma 2022, 414, 115773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Soriano, M.C.; Peña, A.; Mingorance, M.D. Soluble metal pool as afected by soil addition with organic inputs. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tella, M.; Bravin, M.N.; Thuriès, L.; Cazevieille, P.; Chevassus-Rosset, C.; Collin, B.; Chaurand, P.; Legros, S.; Doelsch, E. Increased zinc and copper availability in organic waste amended soil potentially involving distinct release mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Khoshgoftarmanesh, A.H.; Afyuni, M.; Shrivani, M.; Schulin, R. The effect of preceding crop on wheat grain zinc concentration and its relationship to total amino acids and dissolved organic carbon in rhizosphere soil solution. Biol. Fert. Soils 2014, 50, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.; Bravin, M.N.; Crouzet, O.; Lamy, I. Does a decade of soil organic fertilization promote copper and zinc phytoavailability? Evidence from a laboratory biotest with field-collected soil samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawar, K.; Ali, W.; Bibi, H.; Mian, I.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Hussain, M.B.; Ali, M.; Ali, S.; Fahad, S.; Rehman, S.u.; et al. Effect of Different Levels of Zinc and Compost on Yield and Yield Components of Wheat. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eynde, E.; Fendrich, A.N.; Ballabio, C.; Panagos, P. Spatial assessment of topsoil zinc concentrations in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wu, M.; Su, R.; Zhang, K.; Chang, C.; Peng, Q.; Dong, Z.; Pang, J.; Lambers, H. Strong phosphorus (P)-zinc (Zn) interactions in a calcareous soil-alfalfa system suggest that rational P fertilization should be considered for Zn biofortification on Zn-deficient soils and phytoremediation of Zn-contaminated soils. Plant Soil 2021, 461, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Watts-Williams, S.J.; Smith, F.A.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Patti, A.F.; Cavagnaro, T.R. How important is the mycorrhizal pathway for plant Zn uptake? Plant Soil 2015, 390, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Zou, C. Zinc uptake by roots and accumulation in maize plants as affected by phosphorus application and arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization. Plant Soil 2017, 413, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccina, A.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Pellegrino, E.; Ercoli, L.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Watts-Williams, S.J. The mycorrhizal pathway of zinc uptake contributes to zinc accumulation in barley and wheat grain. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Shi, L.; Xu, F.; Cai, H. High level of zinc triggers phosphorus starvation by inhibiting root-to-shoot translocation and preferential distribution of phosphorus in rice plants. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, X.W.; Tian, X.H.; Wang, S.X.; Chen, Y.L. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Foliar Zinc Application at Different Growth Stages on Zinc Translocation and Utilization Efficiency in Winter Wheat. Cereal Res. Commun. 2014, 42, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. Zinc Uptake, Translocation, and Remobilization in Winter Wheat as Affected by Soil Application of Zn Fertilizer. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.X.; Xu, S.J.; Zou, C.Q. Zinc fractions in soils and uptake in winter wheat as affected by repeated applications of zinc fertilizer. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 200, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yuan, Y.R.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhao, W.F.; Li, X.P.; Wang, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Accumulation of zinc, iron and selenium in wheat as affected by phosphorus supply in salinised condition. Crop Pasture Sci. 2022, 73, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.K.; Wang, X.S.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, R.Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, J.S.; Tian, H.; Wang, Z.H.; Shi, M. Rhizosphere microbiome-related changes in soil zinc and phosphorus availability improve grain zinc concentration of wheat. Plant Soil 2023, 490, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.D.; Bullen, J.C.; Plancherel, Y.; Kirby, M.; Kirk, G.J.D.; Weiß, D.J. Significant effect of salinity on zinc adsorption on tropical coastal and floodplain soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 75, e13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gao, W.W.; Zhao, J.L.; Chen, Q.; Liang, D.; Xu, C.; Huang, L.S.; Ruan, L.M. Analysis of influencing factors on soil Zn content using generalized additive model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrador, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Lopez-Valdivia, L.M.; Gonzalez, D.; Novillo, J.; Rico, M.I. Relationships of soil properties with Mn and Zn distribution in acidic soils and their uptake by a barley crop. Geoderma 2007, 137, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, M.; Zhang, D.; Malhi, S.S.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Wang, Z.H. Field-scale studies quantify limitations for wheat grain zinc biofortification in dryland areas. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.T.; Wiita, E.; Nghiem, A.A.; Liu, J.Y.; Haque, E.; Austin, R.N.; Seng, C.Y.; Phan, K.; Zheng, Y.; Bostick, B.C. Zinc localization and speciation in rice grain under variable soil zinc deficiency. Plant Soil 2023, 491, 605–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eynde, E.; Breure, M.S.; Chikowo, R.; Njoroge, S.; Comans, R.N.J.; Hoffland, E. Soil zinc fertilisation does not increase maize yields in 17 out of 19 sites in Sub-Saharan Africa but improves nutritional maize quality in most sites. Plant Soil 2023, 490, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, Z.; Shi, M.; Wang, R.; Lyons, G.; Chen, Y.; Cakmak, I.; et al. Wheat grain zinc concentration as affected by soil nitrogen and phosphorus availability and root mycorrhizal colonization. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 134, 126469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recena, R.; García-López, A.M.; Delgado, A. Zinc Uptake by Plants as Affected by Fertilization with Zn Sulfate, Phosphorus Availability, and Soil Properties. Agronomy 2021, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Lora, A.; Delgado, A. Factors determining Zn availability and uptake by plants in soils developed under Mediterranean climate. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nable, R.O.; Webb, M.J. Further evidence that zinc is required throughout the root zone for optimal plant growth and development. Plant Soil 1993, 150, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhao, H.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z. Different increases in maize and wheat grain zinc concentrations caused by soil and foliar applications of zinc in Loess Plateau, China. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 135, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Measured Soil Chemical Parameters | Average ± SD | Minimum Value | Median Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.32 ± 0.64 | 6.25 | 7.49 |
| EC (dS m−1) | 5.76 ± 5.17 | 1.02 | 3.42 |
| SOM (g kg−1) | 12.73 ± 6.86 | 3.70 | 12.40 |
| Na (g kg−1) | 0.52 ± 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.41 |
| N (g kg−1) | 0.75 ± 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.72 |
| P (g kg−1) | 0.84 ± 0.35 | 0.48 | 0.75 |
| K (g kg−1) | 2.37 ± 0.91 | 0.96 | 2.24 |
| Ca (g kg−1) | 32.80 ± 5.42 | 24.36 | 30.82 |
| Mg (g kg−1) | 8.60 ± 1.72 | 5.70 | 8.56 |
| NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | 120.00 ± 12.00 | 20.00 | 100.00 |
| NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | 53.49 ± 80.49 | 12.34 | 35.00 |
| Olsen-P (mg kg−1) | 40.46 ± 11.35 | 24.90 | 36.20 |
| Exch-K(mg kg−1) | 192.06 ± 71.88 | 68.64 | 186.75 |
| Zn (mg kg−1) | 58.14 ± 57.52 | 14.60 | 44.25 |
| DTPA-Zn (mg kg−1) | 3.29 ± 5.65 | 0.60 | 1.60 |
| DTPA/Zn R (%) | 4.88 ± 2.97 | 1.34 | 3.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Dong, J.; Li, Y. Zinc Translocation from Coastal Soil to Wheat as Mediated by Zinc Supply Levels and Soil Properties. Plants 2025, 14, 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131971
Zhao D, Dong J, Li Y. Zinc Translocation from Coastal Soil to Wheat as Mediated by Zinc Supply Levels and Soil Properties. Plants. 2025; 14(13):1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131971
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Deyong, Jie Dong, and Yan Li. 2025. "Zinc Translocation from Coastal Soil to Wheat as Mediated by Zinc Supply Levels and Soil Properties" Plants 14, no. 13: 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131971
APA StyleZhao, D., Dong, J., & Li, Y. (2025). Zinc Translocation from Coastal Soil to Wheat as Mediated by Zinc Supply Levels and Soil Properties. Plants, 14(13), 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131971








