Straw and Green Manure Return Can Improve Soil Fertility and Rice Yield in Long-Term Cultivation Paddy Fields with High Initial Organic Matter Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
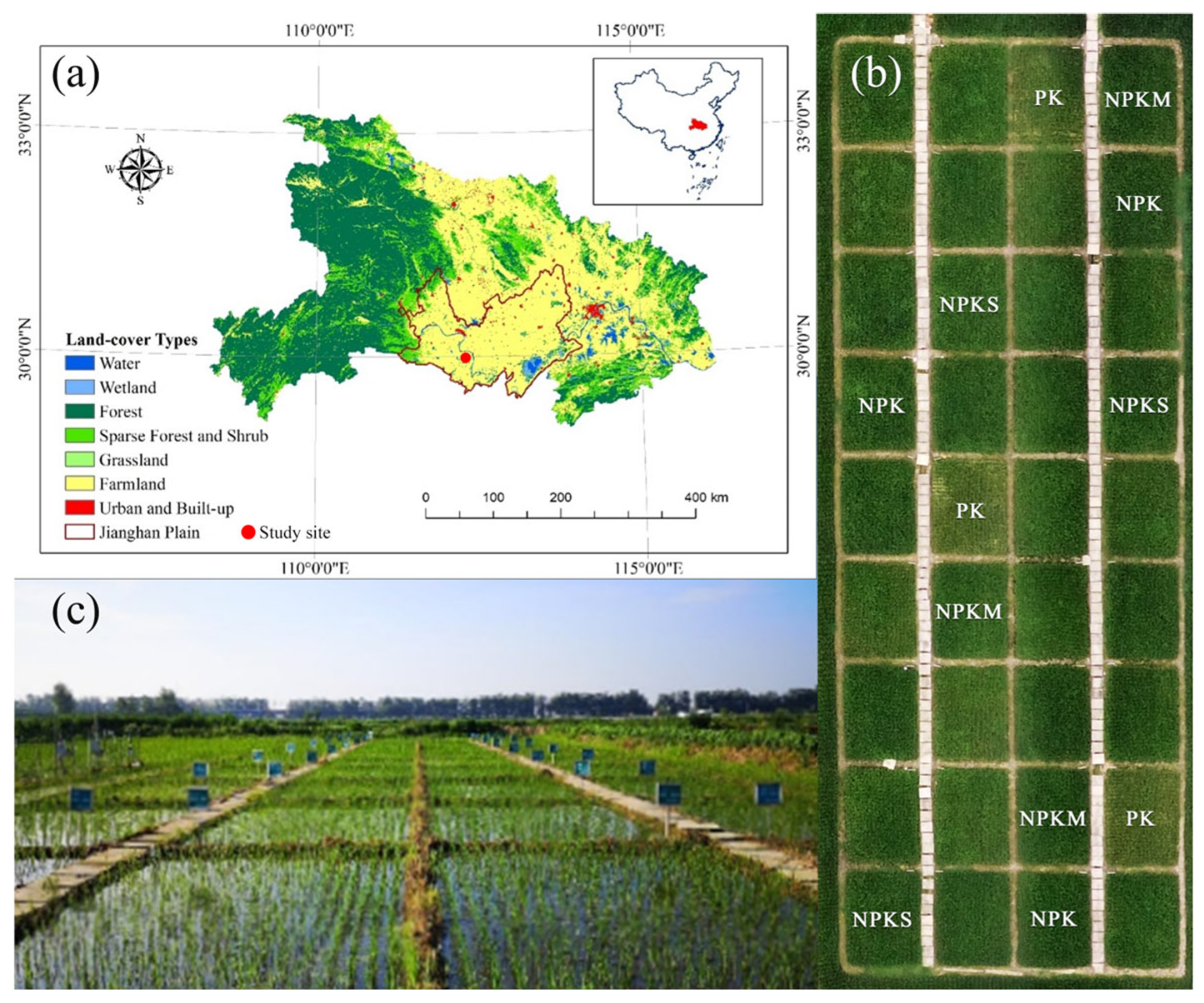
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Rice Growth Indexes Measurement
2.4. Soil and Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
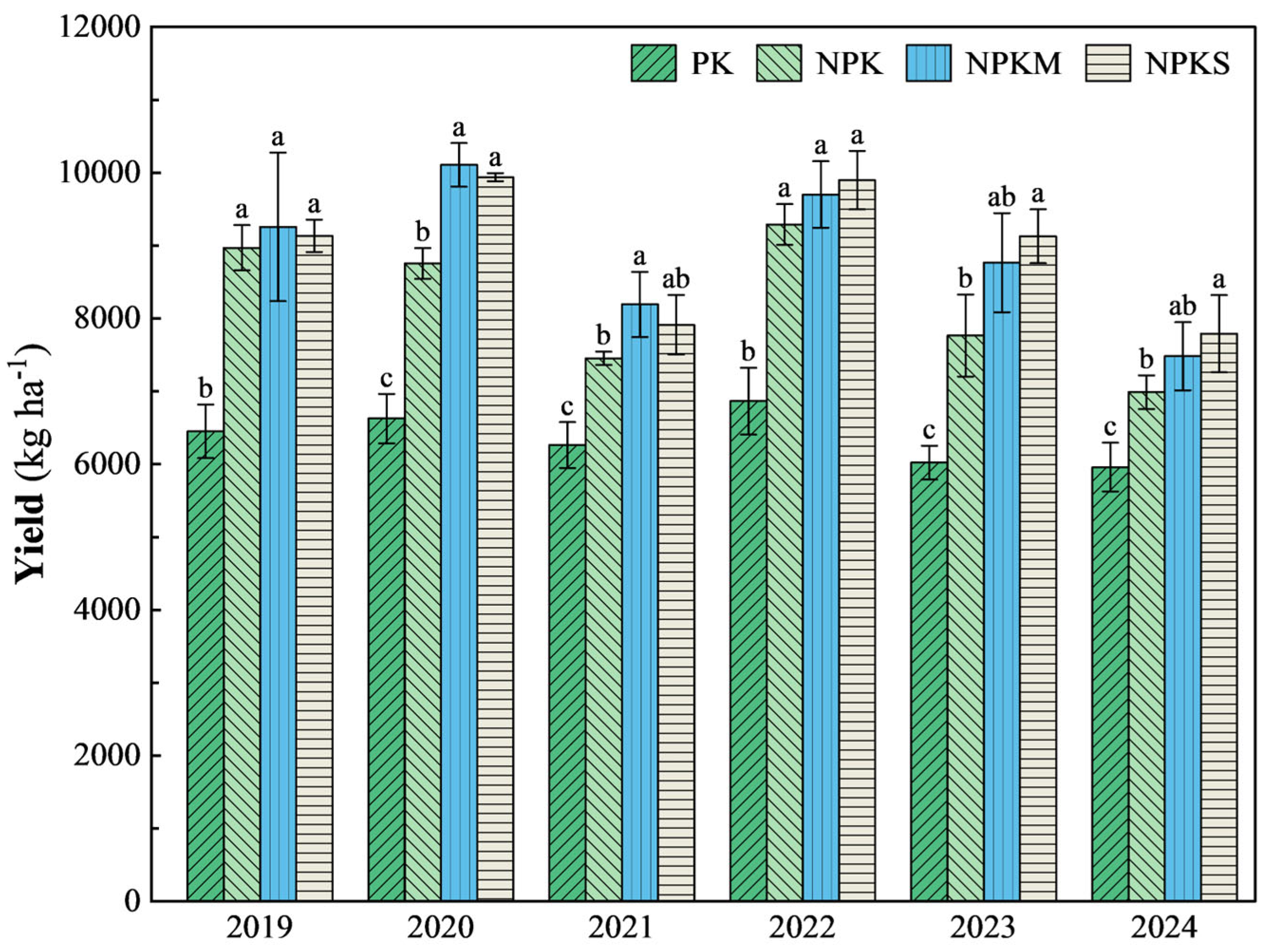
3.1. Rice Yield and Its Components
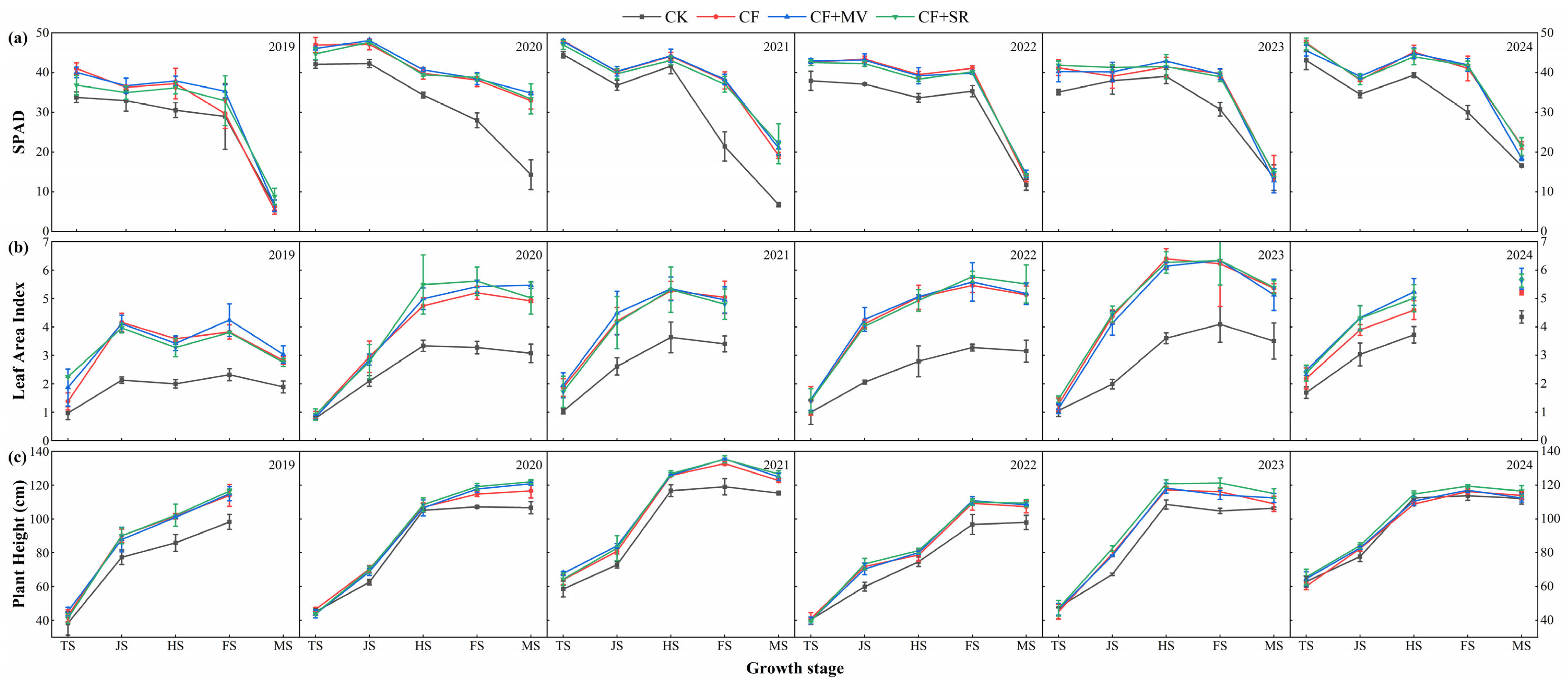
3.2. Rice Growth Index Measurement
3.3. Properties of Topsoil After 2024 Harvest
3.4. Dynamics of NN and AN in Topsoil During the Rice Growth Period
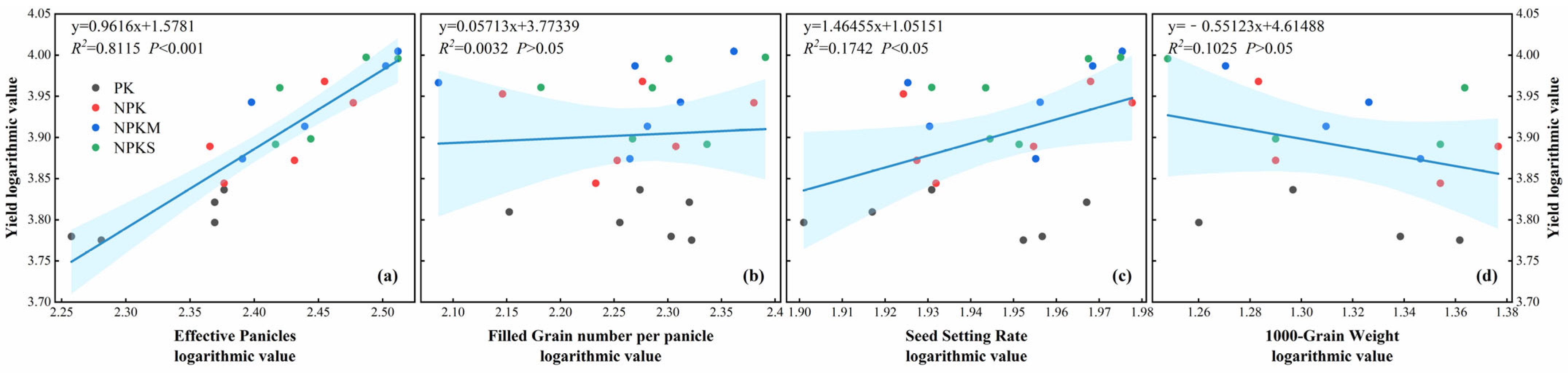
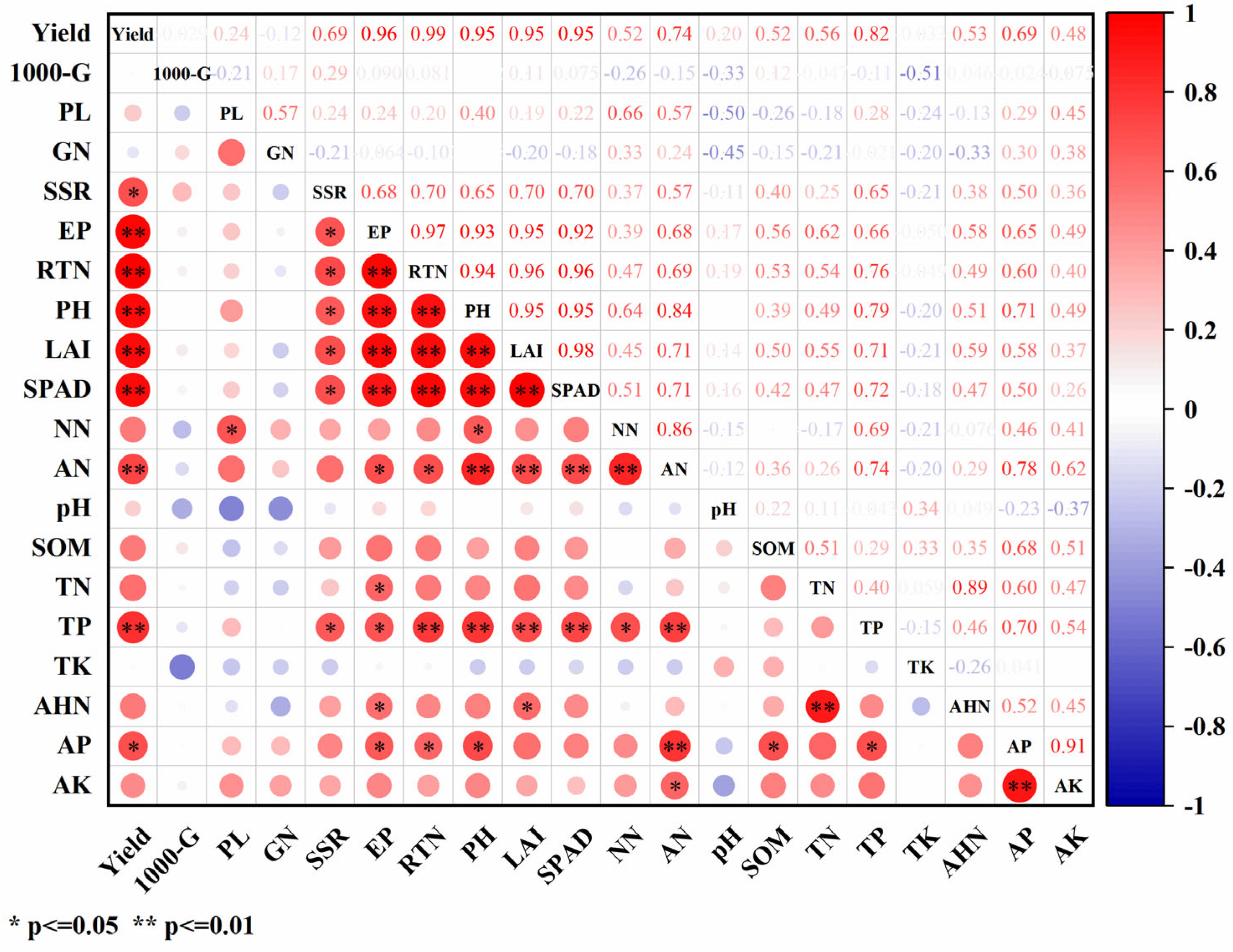
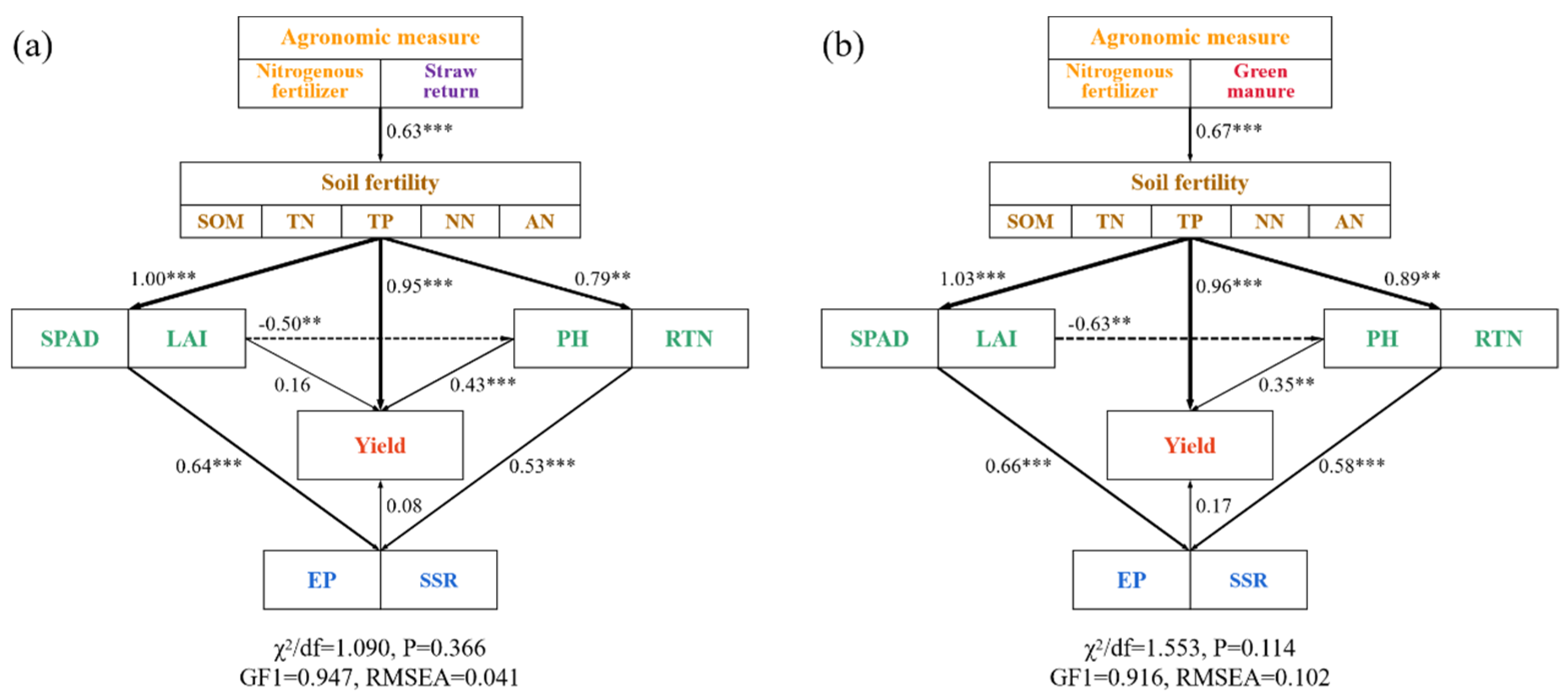
3.5. Comprehensive Analysis of Rice Yield and Its Components, Growth Index, and Topsoil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Soil Organic Matter Content to Straw Returning to the Field and Winter Green Manure
4.2. The Different Effects of Straw and Winter Green Manure on Topsoil Properties
4.3. Effects of Straw Return and Winter Green Manure on Rice Growth and Yield
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2024; FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, N.; Grassini, P.; Yang, H.; Huang, J.; Cassman, K.G.; Peng, S. Closing yield gaps for rice self-sufficiency in China. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.Z.; Wang, P.; Tao, F.L. Future extreme temperature and its impact on rice yield in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4814–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, R.; Jagadish, S.; Sumfleth, K.; Pathak, H.; Howell, G.; Ismail, A.; Serraj, R.; Redona, E.; Singh, R.; Heuer, S. Regional vulnerability of climate change impacts on Asian rice production and scope for adaptation. Adv. Agron. 2009, 102, 91–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretty, J.; Benton, T.G.; Bharucha, Z.P.; Dicks, L.V.; Flora, C.B.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Goulson, D.; Hartley, S.; Lampkin, N.; Morris, C.; et al. Global assessment of agricultural system redesign for sustainable intensification. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, C.; Blanco-Canqui, H.; DeClerck, F.; Gatere, L.; Grace, P. Conservation agriculture and ecosystem services: An overview. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 187, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergtold, J.S.; Ramsey, S.; Maddy, L.; Williams, J.R. A review of economic considerations for cover crops as a conservation practice. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2019, 34, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, C.M.; Liang, X.Q.; Linquist, B.A.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Lee, J.; Lundy, M.E.; van Gestel, N.; Six, J.; Venterea, R.T.; van Kessel, C. Productivity limits and potentials of the principles of conservation agriculture. Nature 2015, 517, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirzel, J.; Undurraga, P.; Vera, C.; Matus, I.; Michelow, P. Three Biannual Rotations Cycles with Residue Incorporation Affect Wheat Production and Chemical Soil Properties. Plants 2023, 12, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Shen, Y.; Kong, X.; Ge, B.; Sun, X.; Cao, M. Effects of Diverse Crop Rotation Sequences on Rice Growth, Yield, and Soil Properties: A Field Study in Gewu Station. Plants 2024, 13, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Yi, J.; Yang, Q.; Ding, F. Preferential flow influences the profile partition patterns of rainwater infiltration in a steep forested headwater catchment. J. Hydrol. 2025, 661, 133541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiu, T.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Tan, W.; Wei, X.; Cui, Y.; Cui, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, L. Crop residue return sustains global soil ecological stoichiometry balance. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2203–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablimit, R.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, M.; Meng, X.; An, L.; Chen, Y. Altering microbial community for improving soil properties and agricultural sustainability during a 10-year maize-green manure intercropping in Northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Yakov, K.; Liu, S.; Li, F.-M. Effects of tillage on soil organic carbon and crop yield under straw return. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 354, 108543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Li, S.; Xing, Z.; Cheng, S.; Guo, B.; Hu, Y.; Wei, H.; Gao, H.; Liao, P.; Wei, H. Differences in rice yield and biomass accumulation dynamics for different direct seeding methods after wheat straw return. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, e425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yin, L.; Ju, W.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, S. Meta-analysis of green manure effects on soil properties and crop yield in northern China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 266, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.E.; Paustian, K.; Conant, R.T.; Plante, A.F.; Six, J. Soil carbon saturation: Evaluation and corroboration by long-term incubations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: Implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant Soil 2002, 241, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- McLeod, S. Determination of total soil and plant nitrogen using a micro-distillation unit in a continuous flow analyzer. Anal. Chim. Acta 1992, 266, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Wen, X.; Hu, S.; Yang, Z.; Guo, B.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Q. Effects of wheat straw derived biochar on cadmium availability in a paddy soil and its accumulation in rice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-C.; Zhao, Y.-W.; Wang, J.-Z.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Han, X.-Z.; Xu, M.-G.; Lu, C.-A. The efficiency of long-term straw return to sequester organic carbon in Northeast China’s cropland. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, G. Effects of long-term winter cropping on paddy rice yield, soil properties and rhizosphere bacterial community in Southern China. Field Crops Res. 2025, 322, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Gao, S.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Yan, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Hu, T.-X.; Gong, Y.-B. Long-term manuring and fertilization effects on soil organic carbon pools under a wheat–maize cropping system in North China Plain. Plant Soil 2009, 314, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltas, A.; Kebli, H.; Oberholzer, H.R.; Weisskopf, P.; Sinaj, S. The effects of organic and mineral fertilizers on carbon sequestration, soil properties, and crop yields from a long-term field experiment under a Swiss conventional farming system. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-J.; Xie, D.-T. Combining Ridge with No-Tillage in Lowland Rice-Based Cropping System: Long-Term Effect on Soil and Rice Yield. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Jia, R.; Zhou, J.; Zamanian, K.; Yang, Y.; Mganga, K.Z.; Zeng, Z.; Zang, H. Soybean inclusion reduces soil organic matter mineralization despite increasing its temperature sensitivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, J.; Bai, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Kumar, M.; Zeng, X. Influence of green manure and rice straw management on soil organic carbon, enzyme activities, and rice yield in red paddy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.E.; Paustian, K.; Conant, R.T.; Plante, A.F.; Six, J. Soil carbon saturation: Implications for measurable carbon pool dynamics in long-term incubations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C. Effects of straw carbon input on carbon dynamics in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, Q.; He, Y.; Liu, J. Is green manure a viable substitute for inorganic fertilizer to improve grain yields and advance carbon neutrality in paddy agriculture? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 359, 108762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paustian, K.; Lehmann, J.; Ogle, S.; Reay, D.; Robertson, G.P.; Smith, P. Climate-smart soils. Nature 2016, 532, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbuthia, L.W.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; DeBruyn, J.; Schaeffer, S.; Tyler, D.; Odoi, E.; Mpheshea, M.; Walker, F.; Eash, N. Long term tillage, cover crop, and fertilization effects on microbial community structure, activity: Implications for soil quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Lin, X.; Zhu, J.; Cai, Z.; Jia, Z. Nitrification of archaeal ammonia oxidizers in acid soils is supported by hydrolysis of urea. ISME J 2012, 6, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Co-incorporation of Rice Straw and Green Manure Benefits Rice Yield and Nutrient Uptake. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Wei, T.; Yang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Yang, B.; Han, Q.; Ren, X. Effects of straw incorporation on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and crop yield in a semiarid region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Lin, X. Effects of different genotypes of Astragalus sinicus on uptake and utilization of sparingly soluble phosphorus. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 20, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shar, A.G.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, X. Effect of straw return mode on soil aggregation and aggregate carbon content in an annual maize-wheat double cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, K.; Zhou, W.; Qiu, S.; Huang, S.; He, P. Changes in soil microbial community, enzyme activities and organic matter fractions under long-term straw return in north-central China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 216, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Zhi, M.; Zhao, W.; Pang, J.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y. Straw retention combined with phosphorus fertilizer promotes soil phosphorus availability by enhancing soil P-related enzymes and the abundance of phoC and phoD genes. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, R.; Wu, K.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, R.; Wu, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Long-Term Straw Returning Enhances Phosphorus Uptake by Zea mays L. through Mediating Microbial Biomass Phosphorus Turnover and Root Functional Traits. Plants 2024, 13, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wu, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. Long-term straw returning improve soil K balance and potassium supplying ability under rice and wheat cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yan, S.-S.; Jia, T.-Y.; Dong, S.-K.; Ma, C.-M.; Gong, Z.-P. Decomposition characteristics of rice straw returned to the soil in northeast China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 114, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xie, J.; Du, J.; Ge, H.; Wei, C.; Qian, H.; Liang, H.; Nie, J.; Hu, F.; Gao, S.; et al. Rice straw nitrogen can be utilized by rice more efficiently when co-incorporating with milk vetch. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gan, G.; Chen, X.; Zou, J. Effects of Long-Term Straw Management and Potassium Fertilization on Crop Yield, Soil Properties, and Microbial Community in a Rice–Oilseed Rape Rotation. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, S.; Han, S.; Li, M.; Cheng, W.; Bu, R.; Cao, W.; Wu, J. Effects of long-term substitution of chemical fertilizer with Chinese milk vetch on soil phosphorus availability and leaching risk in the double rice systems of Eastern China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Xu, J.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J.; Brookes, P.C. Differences in carbon and nitrogen mineralization in soils of differing initial pH induced by electrokinesis and receiving crop residue amendments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 67, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Liu, X.M.; Butterly, C.; Tang, C.X.; Xu, J.M. pH change, carbon and nitrogen mineralization in paddy soils as affected by Chinese milk vetch addition and soil water regime. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, F.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, J. Meta-analysis reveals that returning crop straw to arable land causes soil acidification at the global scale. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Li, B.; Vogt, R.D.; Mulder, J.; Song, H.; Chen, J.; Guo, J. Straw return exacerbates soil acidification in major Chinese croplands. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Kapoor, K.K.; Kundu, B.S.; Mehta, R.K. Identification of organic acids produced during rice straw decomposition and their role in rock phosphate solubilization. Plant Soil Environ. 2008, 54, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Xie, J.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Hu, F.; Gao, S.; Cao, W. Application of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) with reduced chemical fertilizer improves rice yield and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium use efficiency in southern China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 144, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Effects of Straw Return Rate on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Yield in Paddy Fields. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cao, W. Effects of different soil moisture on growth and physiological characteristics of Astragalus sinicus. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2012, 21, 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, B.; Feng, X.; Tian, G.; Hu, X.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Optimizing nitrogen supply increases rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency by regulating yield formation factors. Field Crops Res. 2013, 150, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, T.S.; Gardiner, E.S.; Comer, G.S. Modeling the relationship between extractable chlorophyll and SPAD-502 readings for endangered plant species research. J. Nat. Conserv. 2009, 17, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Zheng, G.; Hamdani, S.; Essemine, J.; Song, Q.; Wang, H.; Chu, C.; Sirault, X.; Zhu, X.-G. Leaf photosynthetic parameters related to biomass accumulation in a global rice diversity survey. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yu, J.; Tao, G.C.; Vos, J.; Bouman, B.; Xie, G.H.; Meinke, H. Yield formation and tillering dynamics of direct-seeded rice in flooded and nonflooded soils in the Huai River Basin of China. Field Crops Res. 2010, 116, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.-H.; Zhao, Z.-K.; Pan, X.-H.; Huang, S.; Tan, X.-M.; Wu, J.-F.; Shi, Q.-H. Integration of Growing Milk Vetch in Winter and Reducing Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Can Improve Rice Yield in Double-Rice Cropping System. Rice Sci. 2016, 23, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Li, C.; Yao, L.; Cui, H.; Tian, Y.; Sun, X.; Yu, T.; He, J.; Wang, S. Effects of dynamic nitrogen application on rice yield and quality under straw returning conditions. Environ. Res. 2024, 243, 117857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Evgenia, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Hu, Q.-J.; Zhang, C.-M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Shi, X.-J. Substituting nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer with optimal amount of crop straw improves rice grain yield, nutrient use efficiency and soil carbon sequestration. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3345–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Gao, D.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Bai, T.; Shao, X.; Geng, Y. Straw and nitrogen amendments improve soil, rice yield, and roots in a saline sodic soil. Rhizosphere 2022, 24, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Treatment | Effective Panicles (104·ha−1) | Filled Grain Number per Panicle | Seed Setting Rate (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | PK | - | 141 ± 21 a | 82.6 ± 5.2 a | - |
| NPK | - | 140 ± 33 a | 84.0 ± 5.6 a | - | |
| NPKM | - | 122 ± 47 a | 84.2 ± 7.2 a | - | |
| NPKS | - | 152 ± 15 a | 85.1 ± 2.4 a | - | |
| 2020 | PK | 234 ± 26 b | 209 ± 32 a | 92.7 ± 3.9 a | - |
| NPK | 300 ± 27 ab | 240 ± 13 a | 95.0 ± 3.3 a | - | |
| NPKM | 325 ± 32 a | 230 ± 2 a | 94.5 ± 3.8 a | - | |
| NPKS | 307 ± 34 ab | 246 ± 17 a | 94.4 ± 3.1 a | - | |
| 2021 | PK | 234 ± 15 b | 180 ± 17 a | 79.8 ± 6.9 a | 18.2 ± 0.1 a |
| NPK | 270 ± 12 ab | 179 ± 40 a | 84.6 ± 5.7 a | 19.5 ± 0.6 a | |
| NPKM | 275 ± 24 ab | 191 ± 39 a | 85.2 ± 4.0 a | 20.4 ± 2.1 a | |
| NPKS | 278 ± 24 a | 185 ± 13 a | 88.0 ± 5.3 a | 19.5 ± 0.6 a | |
| 2022 | PK | 238 ± 12 b | 188 ± 8 a | 85.1 ± 4.4 b | 19.8 ± 3.4 a |
| NPK | 285 ± 6 ab | 189 ± 18 a | 92.9 ± 1.6 a | 19.2 ± 0.3 a | |
| NPKM | 318 ± 35 a | 186 ± 11 a | 93.0 ± 1.7 a | 18.6 ± 0.4 a | |
| NPKS | 323 ± 25 a | 200 ± 21 a | 92.8 ± 2.2 a | 17.7 ± 1.5 a | |
| 2023 | PK | 181 ± 28 b | 201 ± 17 a | 90.5 ± 0.7 a | 21.8 ± 0.5 a |
| NPK | 232 ± 24 ab | 203 ± 22 a | 90.1 ± 2.0 a | 23.8 ± 1.5 a | |
| NPKM | 250 ± 16 ab | 205 ± 17 a | 90.6 ± 1.9 a | 21.2 ± 0.5 a | |
| NPKS | 263 ± 62 a | 193 ± 15 a | 87.8 ± 3.5 a | 23.1 ± 2.4 a | |
| 2024 | PK | 191 ± 29 b | 210 ± 31 a | 89.6 ± 2.8 ab | 23.0 ± 1.3 a |
| NPK | 238 ± 40 ab | 171 ± 33 a | 85.5 ± 2.5 b | 22.6 ± 0.8 a | |
| NPKM | 246 ± 28 ab | 184 ± 14 a | 90.4 ± 1.8 a | 22.2 ± 0.1 a | |
| NPKS | 261 ± 8 a | 217 ± 18 a | 89.4 ± 1.2 ab | 22.6 ± 1.1 a |
| Year | Treatments | Tillering Stage | Jointing Stage | Heading Stage | Filling Stage | Maturity Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | PK | 11.9 ± 0.8 b | - | 12.1 ± 1.3 b | - | - |
| NPK | 17.8 ± 2.1 a | - | 14.3 ± 1.1 ab | - | - | |
| NPKM | 18.8 ± 0.5 a | - | 16.7 ± 1.6 a | - | - | |
| NPKS | 17.5 ± 1.3 a | - | 15.8 ± 1.7 a | - | - | |
| 2021 | PK | 9.3 ± 2.3 b | - | 10.7 ± 0.4 b | 8.9 ± 1.1 b | 9.7 ± 0.6 b |
| NPK | 12.1 ± 2.4 ab | - | 15.7 ± 1.0 ab | 12.7 ± 0.3 a | 11.1 ± 0.5 ab | |
| NPKM | 12.6 ± 1.6 ab | - | 14.2 ± 3.3 a | 12.5 ± 1.4 a | 11.3 ± 1.0 ab | |
| NPKS | 13.8 ± 1.1 a | - | 15.4 ± 0.2 a | 12.3 ± 2.6 a | 11.5 ± 1.0 a | |
| 2022 | PK | 13.1 ± 2.5 a | 15.9 ± 1.6 b | 12.5 ± 2.0 b | 12.3 ± 0.6 b | |
| NPK | 13.7 ± 4.4 a | 25.6 ± 2.4 ab | 17.2 ± 2.7 a | 14.7 ± 0.3 ab | ||
| NPKM | 15.5 ± 1.6 a | 28.9 ± 2.6 a | 17.9 ± 1.3 a | 16.4 ± 1.8 a | ||
| NPKS | 14.6 ± 2.3 a | 23.8 ± 8.1 ab | 18.0 ± 2.1 a | 16.7 ± 1.3 a | ||
| 2023 | PK | 7.5 ± 0.8 a | 11.5 ± 1.0 b | 10.6 ± 0.9 b | 9.3 ± 1.4 b | |
| NPK | 10.8 ± 2.3 a | 19.2 ± 2.6 a | 15.3 ± 0.8 a | 11.9 ± 1.2 ab | ||
| NPKM | 9.7 ± 3.2 a | 18.4 ± 4.4 a | 16.1 ± 1.6 a | 12.9 ± 0.8 ab | ||
| NPKS | 11.5 ± 1.6 a | 20.1 ± 2.6 a | 16.7 ± 1.2 a | 13.5 ± 3.2 a | ||
| 2024 | PK | 9.6 ± 3.1 a | 11.9 ± 2.5 b | 11.0 ± 1.4 a | 9.1 ± 1.1 b | 9.9 ± 1.5 b |
| NPK | 11.7 ± 1.1 a | 14.1 ± 3.2 ab | 15.3 ± 2.3 a | 13.7 ± 0.5 a | 12.3 ± 2.0 ab | |
| NPKM | 15.9 ± 6.0 a | 18.1 ± 1.9 a | 14.7 ± 2.3 a | 13.7 ± 1.1 a | 12.7 ± 1.5 ab | |
| NPKS | 16.3 ± 1.2 a | 17.4 ± 2.3 a | 14.9 ± 3.3 a | 14.0 ± 1.8 a | 13.5 ± 0.4 a |
| Treatments | Depth (cm) | pH (-) | SOM (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | TK (g kg−1) | AHN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) | C/N (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PK | 0–10 | 7.41 ± 0.05 b | 57.1 ± 6.6 c | 1.82 ± 0.16 b | 0.93 ± 0.06 a | 15.3 ± 3.9 a | 106 ± 8 a | 9.4 ± 0.2 c | 91.0 ± 5.7 c | 18.3 ± 3.0 a |
| NPK | 7.38 ± 0.05 bc | 59.2 ± 4.4 bc | 1.94 ± 0.29 b | 1.05 ± 0.13 a | 13.0 ± 1.6 a | 110 ± 5 a | 10.2 ± 1.5 bc | 87.2 ± 4.2 c | 17.8 ± 3.4 a | |
| NPKM | 7.59 ± 0.02 a | 63.3 ± 1.8 ab | 2.15 ± 0.31 ab | 1.09 ± 0.28 a | 15.2 ± 1.2 a | 112 ± 11 a | 10.9 ± 0.3 b | 98.7 ± 1.5 b | 17.3 ± 2.6 a | |
| NPKS | 7.34 ± 0.06 c | 64.1 ± 4.0 a | 2.33 ± 0.47 a | 1.13 ± 0.09 a | 13.7 ± 2.4 a | 115 ± 7 a | 12.5 ± 1.0 a | 131 ± 4 a | 16.8 ± 2.9 a | |
| PK | 10–20 | 7.47 ± 0.08 b | 38.3 ± 1.8 a | 1.12 ± 0.27 a | 0.86 ± 0.18 a | 14.9 ± 2.9 a | 69.8 ± 6.0 a | 8.6 ± 0.4 b | 91.3 ± 8.1 bc | 20.0 ± 2.3 a |
| NPK | 7.45 ± 0.02 bc | 38.8 ± 2.6 a | 1.30 ± 0.29 a | 0.98 ± 0.30 a | 14.3 ± 1.3 a | 70.6 ± 6.8 a | 8.7 ± 0.6 b | 84.6 ± 5.8 c | 17.7 ± 2.6 a | |
| NPKM | 7.64 ± 0.02 a | 39.8 ± 2.0 a | 1.34 ± 0.09 a | 1.03 ± 0.03 a | 15.3 ± 2.4 a | 72.6 ± 13.8 a | 9.4 ± 1.0 b | 92.9 ± 1.7 b | 17.6 ± 2.1 a | |
| NPKS | 7.40 ± 0.07 c | 40.1 ± 2.5 a | 1.43 ± 0.29 a | 1.06 ± 0.06 a | 16.4 ± 1.6 a | 74.1 ± 4.1 a | 10.3 ± 1.1 a | 122 ± 1 a | 16.6 ± 1.9 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Qiu, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Fei, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Straw and Green Manure Return Can Improve Soil Fertility and Rice Yield in Long-Term Cultivation Paddy Fields with High Initial Organic Matter Content. Plants 2025, 14, 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131967
Zhang H, Chen L, Wang Y, Xu M, Qiu W, Liu W, Wang T, Li S, Fei Y, Liu M, et al. Straw and Green Manure Return Can Improve Soil Fertility and Rice Yield in Long-Term Cultivation Paddy Fields with High Initial Organic Matter Content. Plants. 2025; 14(13):1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131967
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hailin, Long Chen, Yongsheng Wang, Mengyi Xu, Weiwen Qiu, Wei Liu, Tingyu Wang, Shenglong Li, Yuanhang Fei, Muxing Liu, and et al. 2025. "Straw and Green Manure Return Can Improve Soil Fertility and Rice Yield in Long-Term Cultivation Paddy Fields with High Initial Organic Matter Content" Plants 14, no. 13: 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131967
APA StyleZhang, H., Chen, L., Wang, Y., Xu, M., Qiu, W., Liu, W., Wang, T., Li, S., Fei, Y., Liu, M., Nie, H., Li, Q., Ni, X., & Yi, J. (2025). Straw and Green Manure Return Can Improve Soil Fertility and Rice Yield in Long-Term Cultivation Paddy Fields with High Initial Organic Matter Content. Plants, 14(13), 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131967







