Impact of Water Deficit Stress on Brassica Crops: Growth and Yield, Physiological and Biochemical Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Effects of Drought Stress on Brassica Crops
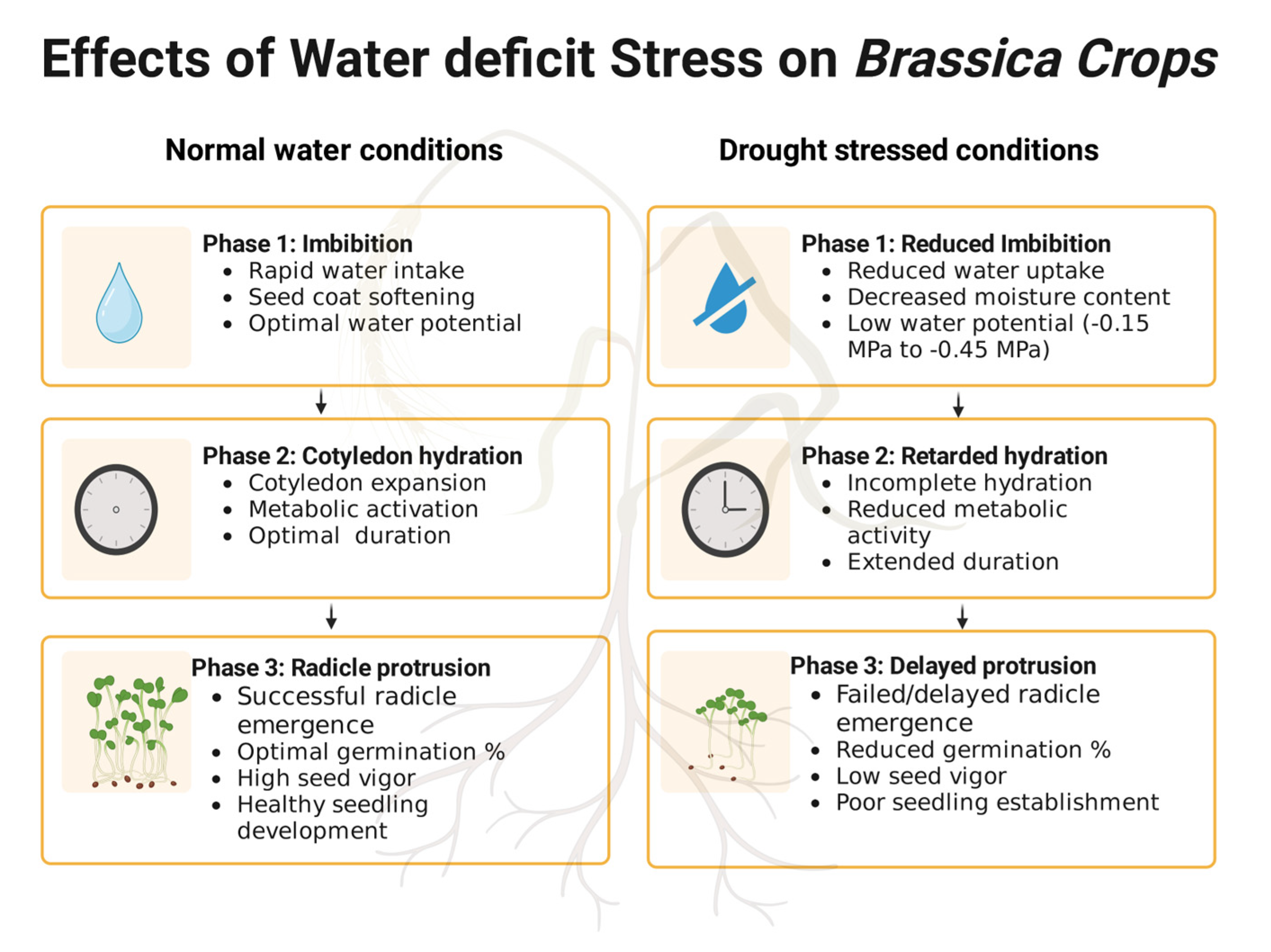
2.1. Effects of Drought Stress on Germination
2.2. Effects of Drought Stress on Physiological Characteristics
2.3. Effects of Drought Stress on Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense Systems
2.4. Effects of Drought Stress on Proline
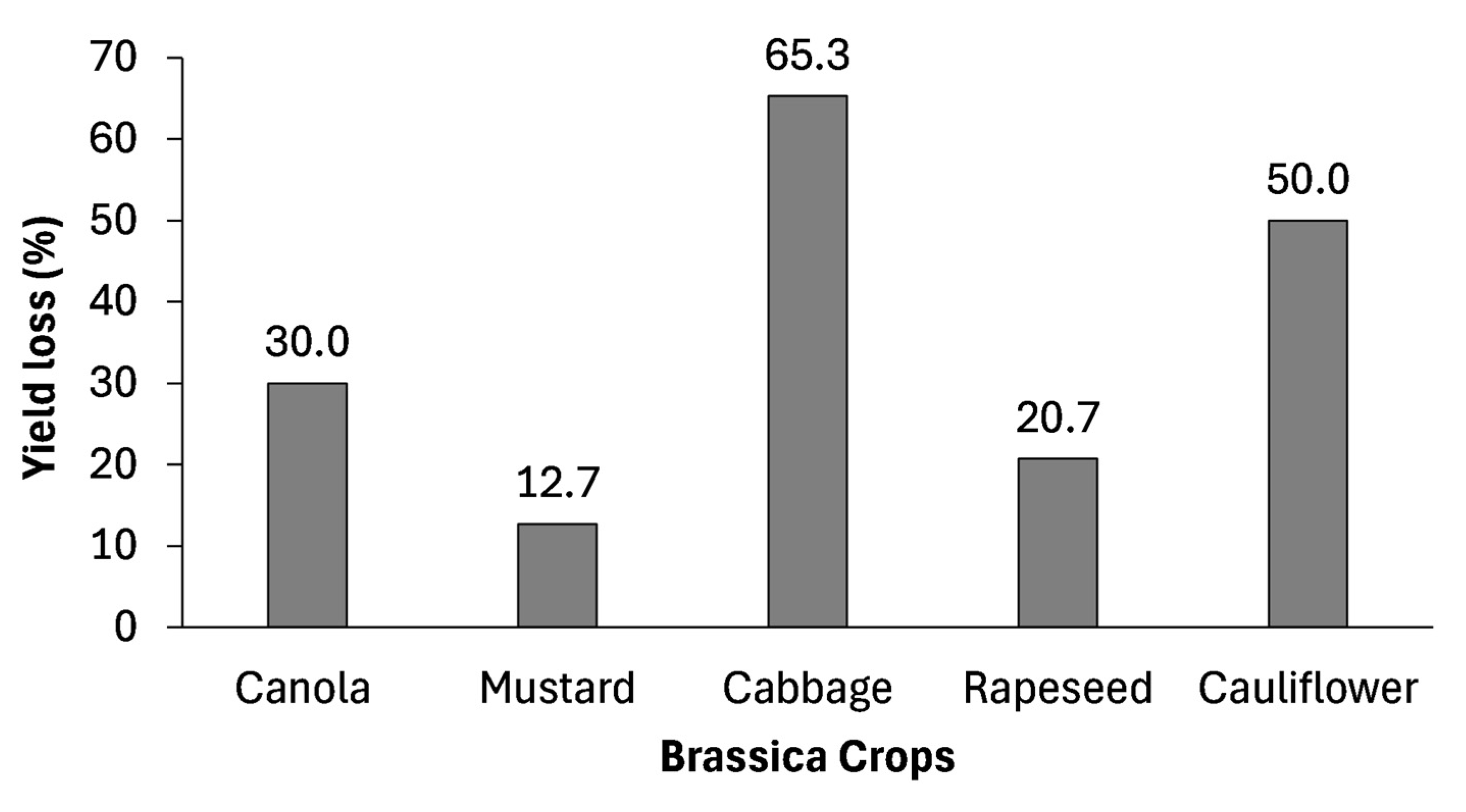
2.5. Effects of Drought Stress on Yield Characteristics
3. Research Gaps and Future Perspectives
3.1. Agronomic Practices
3.2. Soil and Water Management
3.3. Crop Selection and Breeding
3.4. Technological Interventions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ilahy, R.; Imen, T.; Pék, Z.; Montefusco, A.; Siddiqui, M.; Homa, F.; Hdider, C.; R’him, T.; Helyes, L.; Lenucci, M. Pre-and Post-Harvest Factors Affecting Glucosinolate Content in Broccoli. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aires, A. Brassica-Composition and Food Processing. In Processing and Impact on Active Components in Food; Preedy, V., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 17–25. ISBN 978-0-12-404699-3. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.-F.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.H. Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Activities of Common Vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6910–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.H.; Kristal, A.R.; Stanford, J.L. Fruit and Vegetable Intakes and Prostate Cancer Risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, D.T.; Verhagen, H.; Goldbohm, R.A.; van den Brandt, P.A.; van Poppel, G. A Review of Mechanisms Underlying Anticarcinogenicity by Brassica Vegetables. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 1997, 103, 79–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.; Abellán-Victorio, A.; Beretta, V.; Camargo, A.; Moreno, D.A. Functional Ingredients From Brassicaceae Species: Overview and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, G.; Long, W.; Zou, X.; Li, F.; Nishio, T. Recent Progress in Drought and Salt Tolerance Studies in Brassica Crops. Breed. Sci. 2014, 64, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Nizam, S.; Verma, P.K. Biotic and Abiotic Stress Signaling in Plants. In Stress Signaling in Plants: Genomics and Proteomics Perspective, Volume 1; Sarwat, M., Ahmad, A., Abdin, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 25–49. ISBN 978-1-4614-6372-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. The Stress Concept in Plants: An Introduction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 851, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarah, N.H. Effects of Drought Stress on Growth and Yield of Barley. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 25, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Functional Genomics in Plant Abiotic Stress Responses and Tolerance: From Gene Discovery to Complex Regulatory Networks and Their Application in Breeding. Proc. Jpn. Academy. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2022, 98, 470–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, X. Reprogramming of Plant Central Metabolism in Response to Abiotic Stresses: A Metabolomics View. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sengar, R.S.; Sahi, S.V. Chapter 14: Acclimation and Adaptation of Plants to Different Environmental Abiotic Stresses. In Crop Modeling for Agricultural Production and Management; CRC Press of Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2014; p. 356. ISBN 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, I.S.; De Cian, E.; Mistry, M.N. Global Vulnerability of Crop Yields to Climate Change. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2021, 109, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; van der Schrier, G.; Jones, P.D.; Barichivich, J.; Briffa, K.R.; Sheffield, J. Global Warming and Changes in Drought. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, F.; Mazdiyasni, O.; AghaKouchak, A. Evidence of Anthropogenic Impacts on Global Drought Frequency, Duration, and Intensity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, K.-J.; Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C.-M. Drought and Crop Yield. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.W.; Van Loon, A.F. Droughts Are Coming on Faster. Science 2023, 380, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overpeck, J.T.; Udall, B. Climate Change and the Aridification of North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11856–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Mankin, J.S.; Marvel, K.; Williams, A.P.; Smerdon, J.E.; Anchukaitis, K.J. Twenty-First Century Drought Projections in the CMIP6 Forcing Scenarios. Earth’s Future 2020, 8, e2019EF001461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Kuromori, T.; Urano, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Drought Stress Responses and Resistance in Plants: From Cellular Responses to Long-Distance Intercellular Communication. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 556972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S. Crop Failures More Likely in Warmer, Dryer World. Available online: https://www.woodwellclimate.org/climate-change-food-security-crop-failures/ (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Lisar, S.Y.; Motafakkerazad, R.; Hossain, M.M.; Rahman, I.M. Causes, Effects and Responses. Water Stress. 2012, 25, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Namias, J. Some Causes of United States Drought. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, O.; Singh, P.C.; Bhatia, R. A Review on Drought Stress in Plants: Implications, Mitigation and the Role of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 5, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Rivero, R.M.; Shulaev, V.; Blumwald, E.; Mittler, R. Abiotic and Biotic Stress Combinations. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abobatta, W.F. Plant Responses and Tolerance to Combined Salt and Drought Stress. In Salt and Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants: Signaling Networks and Adaptive Mechanisms; Hasanuzzaman, M., Tanveer, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 17–52. ISBN 978-3-030-40277-8. [Google Scholar]
- Galmés, J.; Medrano, H.; Flexas, J. Photosynthetic Limitations in Response to Water Stress and Recovery in Mediterranean Plants with Different Growth Forms. New Phytol. 2007, 175, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Response Mechanism of Plants to Drought Stress. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.R.; Chaitanya, K.V.; Vivekanandan, M. Drought-Induced Responses of Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Metabolism in Higher Plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 161, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, F.K.; Rivero, R.M.; Blumwald, E.; Mittler, R. Reactive Oxygen Species, Abiotic Stress and Stress Combination. Plant J. 2017, 90, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Sultan, M.A.R.F.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, F.; Zhao, H.X. Physiological and Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Different Drought Responses in Roots and Leaves of Drought-Tolerant Wild Wheat (Triticum Boeoticum). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.-J.; Hwang, Y.; Koh, Y.-M.; Zhu, F.; Deshpande, A.S.; Bechard, T.; Andreescu, S. Physiological and Molecular Modulations to Drought Stress in the Brassica Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-Q.; Huang, J.; Guo, S.-Q.; Yang, X.; Bao, Y.-M.; Tang, H.-J.; Zhang, H.-S. Overexpression of a TFIIIA-Type Zinc Finger Protein Gene ZFP252 Enhances Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Fujita, D.; Basra, S.M.A. Plant Drought Stress: Effects, Mechanisms and Management. In Sustainable Agriculture; Lichtfouse, E., Navarrete, M., Debaeke, P., Véronique, S., Alberola, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 153–188. ISBN 978-90-481-2666-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhite, D.; Glantz, M. Understanding: The Drought Phenomenon: The Role of Definitions. Water Int. 1985, 10, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonogaki, H.; Bassel, G.W.; Bewley, J.D. Germination—Still a Mystery. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Bassel, G.W. Seed Vigour and Crop Establishment: Extending Performance beyond Adaptation. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 567–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Mehmood, S. Response of Four Brassica Species to Drought Stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1990, 30, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, K.J. Manipulation of Seed Water Relations Via Osmotic Priming to Improve Germination Under Stress Conditions. HortScience 1986, 21, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okçu, G.; Kaya, M.D.; Atak, M. Effects of Salt and Drought Stresses on Germination and Seedling Growth of Pea (Pisum sativum L.). Turk. J. Agric. For. 2005, 29, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, G.L.; Donovan, L.A. Water Potential and Ionic Effects on Germination and Seedling Growth of Two Cold Desert Shrubs. Am. J. Bot. 1999, 86, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, M.; Al Tawaha, A.R.; Lee, K. Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Three Lentil Cultivars under Moisture Stress. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2004, 3, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, S.S.; Sethi, G.S.; Behl, R.K. Indices of Drought Tolerance in Wheat Genotypes at Early Stages of Plant Growth. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2004, 190, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzig, S.V.; Nuppenau, J.-N.; Snowdon, R.J.; Schießl, S.V. Drought Stress Has Transgenerational Effects on Seeds and Seedlings in Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Sami, A.; Xu, Q.Q.; Wu, L.L.; Zheng, W.Y.; Chen, Z.P.; Jin, X.Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; et al. Effects of Seed Priming Treatments on the Germination and Development of Two Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Varieties under the Co-Influence of Low Temperature and Drought. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Q.; Sami, A.; Zhang, H.; Jin, X.Z.; Zheng, W.Y.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Wu, L.L.; Lei, Y.H.; Chen, Z.P.; Li, Y.; et al. Combined Influence of Low Temperature and Drought on Different Varieties of Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 147, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, T. Seed and Seedling Biology. Available online: https://extension.psu.edu/seed-and-seedling-biology (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Yan, M. Seed Priming Stimulate Germination and Early Seedling Growth of Chinese Cabbage under Drought Stress. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 99, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.; Xie, X.; Wang, L.; Saleem, M.; Man, C.; Lei, W. Morphological, Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Plants to Drought Stress. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseynova, I.M.; Suleymanov, S.Y.; Rustamova, S.M.; Aliyev, J.A. Drought-Induced Changes in Photosynthetic Membranes of Two Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Cultivars. Biochemistry 2009, 74, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, R.A.; Ort, D.R. Photosynthesis|Photosynthetic Efficiency Improvement. In Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry III, 3rd ed.; Jez, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 256–267. ISBN 978-0-12-822040-5. [Google Scholar]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought Stress Impacts on Plants and Different Approaches to Alleviate Its Adverse Effects. Plants 2021, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flexas, J.; Bota, J.; Loreto, F.; Cornic, G.; Sharkey, T.D. Diffusive and Metabolic Limitations to Photosynthesis under Drought and Salinity in C3 Plants. Plant Biol. 2004, 6, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed Shawon, R.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, S.K.; Ku, Y. gyu Changes in Free Amino Acid, Carotenoid, and Proline Content in Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa Subsp. Pekinensis) in Response to Drought Stress. Korean J. Plant Resour. 2018, 31, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, M.; El-Badri, A.M.; Hassan, M.U.; Haiyun, Y.; Chunyun, W.; Zhenkun, Y.; Jie, K.; Wang, B.; Zhou, G. Drought Stress in Brassica Napus: Effects, Tolerance Mechanisms, and Management Strategies. J. Plant Growth Regultors 2023, 42, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Anwar, Y.; Hasan, M.M.; Iqbal, A.; Ali, M.; Alharby, H.F.; Hakeem, K.R.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Attenuation of Drought Stress in Brassica Seedlings with Exogenous Application of Ca2+ and H2O2. Plants 2017, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhythm; Sharma, P.; Sardana, V. Physiological and Biochemical Traits of Drought Tolerance in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern & Coss. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 146, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, I.; Petřík, I.; Tarkowská, D.; Lepeduš, H.; Vujčić Bok, V.; Radić Brkanac, S.; Novák, O.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Correlations between Phytohormones and Drought Tolerance in Selected Brassica Crops: Chinese Cabbage, White Cabbage and Kale. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshidi Zinab, A.; Hasanloo, T.; Naji, A.M.; Delangiz, N.; Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Hemati, A.; Shobbar, Z.-S.; Farooq, M. Physiological and Biochemical Evaluation of Commercial Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.) Cultivars Under Drought Stress. Gesunde Pflanz. 2023, 75, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issarakraisila, M.; Ma, Q.; Turner, D.W. Photosynthetic and Growth Responses of Juvenile Chinese Kale (Brassica Oleracea Var. Alboglabra) and Caisin (Brassica Rapa Subsp. Parachinensis) to Waterlogging and Water Deficit. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 111, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Jung, H.; Park, G.-H. Drought Tolerance Evaluation and Growth Response of Chinese Cabbage Seedlings to Water Deficit Treatment. Agronomy 2024, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupitu, A.; Moisa, C.; Bortes, F.; Peteleu, D.; Dochia, M.; Chambre, D.; Ciutină, V.; Copolovici, D.M.; Copolovici, L. The Impact of Increased CO2 and Drought Stress on the Secondary Metabolites of Cauliflower (Brassica Oleracea Var. Botrytis) and Cabbage (Brassica oleracea Var. Capitata). Plants 2023, 12, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Duan, L.; Zhang, M. Physiological Evaluation of Drought Stress Tolerance and Recovery in Cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L.) Seedlings Treated with Methyl Jasmonate and Coronatine. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 31, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevilly, S.; Dolz-Edo, L.; López-Nicolás, J.M.; Morcillo, L.; Vilagrosa, A.; Yenush, L.; Mulet, J.M. Physiological and Molecular Characterization of the Differential Response of Broccoli (Brassica oleracea Var. Italica) Cultivars Reveals Limiting Factors for Broccoli Tolerance to Drought Stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 10394–10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Chauhan, J.S.; Meena, S.S. Drought Induced Changes in Water Use Efficiency and Other Morpho-Physiological Characters in Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L.). In Proceedings of the 16th Australian Research Assembly on Brassicas, Ballarat, VIC, Australia, 14–16 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Guidi, L.; Lo Piccolo, E.; Landi, M. Chlorophyll Fluorescence, Photoinhibition and Abiotic Stress: Does It Make Any Difference the Fact to Be a C3 or C4 Species? Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N. Chlorophyll Fluorescence—A Practical Guide. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałużewicz, A.; Bączek-Kwinta, R.; Krzesiński, W.; Spiżewski, T.; Zaworska, A. Effect of Biostimulants on Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters of Broccoli (Brassica Oleracea Var. Italica) under Drought Stress and Rewatering. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2018, 17, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyaz, A.; Miao, Y.; Hannan, F.; Islam, F.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.; Farooq, M.A.; Zhou, W. Drought Tolerance in Brassica Napus Is Accompanied with Enhanced Antioxidative Protection, Photosynthetic and Hormonal Regulation at Seedling Stage. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenham, K.; Guadagno, C.R.; Gehan, M.A.; Mockler, T.C.; Weinig, C.; Ewers, B.E.; McClung, C.R. Temporal Network Analysis Identifies Early Physiological and Transcriptomic Indicators of Mild Drought in Brassica Rapa. eLife 2017, 6, e29655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podda, A.; Pollastri, S.; Bartolini, P.; Pisuttu, C.; Pellegrini, E.; Nali, C.; Cencetti, G.; Michelozzi, M.; Frassinetti, S.; Giorgetti, L.; et al. Drought Stress Modulates Secondary Metabolites in Brassica oleracea L. Convar. Acephala (DC) Alef, Var. Sabellica L. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5533–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackah, E.; Kotei, R. Effect of Drought Length on the Performance of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea Var Capitata) in the Forest-Savannah Transition Zone, Ghana. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2020, 26, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, J. Drought or Mechanical Stress Affects Broccoli Transplant Growth and Establishment but Not Yield. HortScience 1990, 25, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabha, B.K.; Uprety, D.C. Effects of Elevated CO2 and Moisture Stress on Brassica Juncea. Photosynthetica 1998, 35, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardestani, G.H.; Rad, A.H.S. Impact of Regulated Deficit Irrigation on the Physiological Characteristics of Two Rapeseed Varieties as Affected by Different Potassium Rates. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 6510–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, B.; Singh, V.V.; Singh, B.K.; Priyamedha; Kumar, A.; Singh, D. Comparative Tolerance and Sensitive Response of Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern and Coss) Genotypes to High Temperature Stress. SABRAO J. Breed. Genet. 2015, 47, 315–325. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, F.; Bano, A.; Nosheen, A. Effects of Plant Growth Regulators on Growth and Oil Quality of Canola (Brassica napus L.) under Drought Stress. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz de Carvalho, M.H. Drought Stress and Reactive Oxygen Species. Plant Signal. Behav. 2008, 3, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Mostofa, M.G.; Fujita, M. Cross Protection by Cold-Shock to Salinity and Drought Stress-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mustard (Brassica campestris L.) Seedlings. Mol. Plant Breed. 2013, 4, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.-N.; Wu, Q.-S.; Kuča, K. Unravelling the Role of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Mitigating the Oxidative Burst of Plants under Drought Stress. Plant Biol. 2021, 23 (Suppl. S1), 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, C.; Dixon, R.A. The Oxidative Burst in Plant Disease Resistance. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1997, 48, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittler, R. Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants and Stress Tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, T.; Pakniyat, H. Antioxidant Enzymes Changes in Response to Drought Stress in Ten Cultivars of Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2010, 46, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Abbey, L.; MacDonald, M. Changes in Endogenous Carotenoids, Flavonoids, and Phenolics of Drought-Stressed Broccoli Seedlings After Ascorbic Acid Preconditioning. Plants 2024, 13, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, N.; Akram, N.A.; Fatima, K.; Noreen, S.; Akram, M.S.; Umer, S.; Ashraf, M.; Alsahli, A.A.; Mansoor, S. Drought-Induced Changes in Plant-Yield Interlinked Biochemistry of Cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L. Var. Botrytis) by Exogenously Applied Alpha-Tocopherol. J. King Saud. Univ.-Sci. 2024, 36, 103028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-N.; Khan, M.A.; Kang, S.-M.; Hamayun, M.; Lee, I.-J. Enhancement of Drought-Stress Tolerance of Brassica Oleracea Var. Italica L. by Newly Isolated Variovorax Sp. YNA59. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cai, D.; Wang, J.; Cao, J.; Wen, Y.; He, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Physiological and Anatomical Changes in Two Rapeseed (Brassica Napus L.) Genotypes under Drought Stress Conditions. Oil Crop Sci. 2021, 6, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, N.A.; Fatima, K.; Kong, H.; Zafar, N.; Mahmood, S.; Ashraf, M.; Abdel Latef, A.A.H. Interactive Effect of Drought Stress and L-Methionine on the Growth and Physio-Biochemical Changes in Broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. Var. Italica): Leaf and Head. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 1954–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhao, P.; Tan, Z.; Peng, Y.; Xu, L.; Jin, Y.; Fang, W.; Guo, L.; Yao, X. Combining Physio-Biochemical Characterization and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal the Responses to Varying Degrees of Drought Stress in Brassica napus L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajji, M.; Lutts, S.; Kinet, J.-M. Water Deficit Effects on Solute Contribution to Osmotic Adjustment as a Function of Leaf Ageing in Three Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) Cultivars Performing Differently in Arid Conditions. Plant Sci. 2001, 160, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voetberg, G.S.; Sharp, R.E. Growth of the Maize Primary Root at Low Water Potentials 1: III. Role of Increased Proline Deposition in Osmotic Adjustment. Plant Physiol. 1991, 96, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, L.; Demir, Y. In Vivo and in Vitro Protective Role of Proline. Plant Growth Regul. 2002, 38, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, A.; Miyazaki, S.; Veronese, P.; Fujita, T.; Ibeas, J.I.; Damsz, B.; Narasimhan, M.L.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Joly, R.J.; Bressan, R.A. Does Proline Accumulation Play an Active Role in Stress-Induced Growth Reduction? Plant J. 2002, 31, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartika; Fadilah, L.N.; Lakitan, B. Growth Responses and Yield of Cauliflower (Brassica oleracea Var. Botrytis L.) to the Delayed Transplanting and Drought Stress. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 306, 01007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Kaman, H.; Sönmez, İ.; Uçan, U.; Akgün, İ.H. Yield and Yield Parameters Response of Cabbage to Partial Root Drying and Conventional Deficit Irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.A.; Ebrahim, N.E.S.; Mohamed, G.Z. Mitigation of Water Stress in Broccoli by Soil Application of Humic Acid. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, I.; Thavarajah, P.; Siva, N.; Wickramasinghe, A.N.K.; Smith, P.; Thavarajah, D. Moisture Deficit Effects on Kale (Brassica oleracea L. Var. Acephala) Biomass, Mineral, and Low Molecular Weight Carbohydrate Concentrations. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 226, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, A.; Reddy, K.R.; Walne, C.H.; Barickman, T.C.; Brazel, S.; Chastain, D.; Gao, W. Climate Stressors on Growth, Yield, and Functional Biochemistry of Two Brassica Species, Kale and Mustard. Life 2022, 12, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Shahid, A.; Saleem, M.; Imran Haider, K.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, M.; Iqbal, R. Effects and Management Strategies to Mitigate Drought Stress in Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.): A Review. Zemdirb.-Agric. 2017, 104, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, L.B.; Neik, T.X.; Batley, J. The Use of Genetic and Gene Technologies in Shaping Modern Rapeseed Cultivars (Brassica napus L.). Genes 2020, 11, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, S.; Felemban, A.; Abdelrahim, A.; Al-Dakhil, M. Agricultural and Technology-Based Strategies to Improve Water-Use Efficiency in Arid and Semiarid Areas. Water 2024, 16, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wan, H.; Jie, L.; Cui, B.; Zong, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Combined Application of Biochar and Partial Root-Zone Drying Irrigation Improves Water Relations and Water Use Efficiency of Cotton Plants under Salt Stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 290, 108584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, A.; Granda, L.; Berdugo-Cely, J.A.; Šamajová, O.; Šamaj, J.; Cerkal, R. A Dual Strategy of Breeding for Drought Tolerance and Introducing Drought-Tolerant, Underutilized Crops into Production Systems to Enhance Their Resilience to Water Deficiency. Plants 2020, 9, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, S.; Patidar, O.P.; Chaudhary, R.; Saroj, R.; Chandra, K.; Meena, V.K.; Limbalkar, O.M.; Patel, M.K.; Pardeshi, P.P.; Vasisth, P.; et al. Rapeseed-Mustard Breeding in India: Scenario, Achievements and Research Needs. In Brassica Breeding and Biotechnology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-1-83968-697-9. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, M.; Chapman, S.; Crespo-Herrera, L.; Molero, G.; Mondal, S.; Pequeno, D.N.L.; Pinto, F.; Pinera-Chavez, F.J.; Poland, J.; Rivera-Amado, C.; et al. Breeder Friendly Phenotyping. Plant Sci. 2020, 295, 110396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjabi, P.; Yadava, S.K.; Kumar, N.; Bangkim, R.; Ramchiary, N. Breeding Brassica Juncea and B. Rapa for Sustainable Oilseed Production in the Changing Climate: Progress and Prospects. In Genomic Designing of Climate-Smart Oilseed Crops; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 275–369. ISBN 978-3-319-93536-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sami, A.; Xue, Z.; Tazein, S.; Arshad, A.; He Zhu, Z.; Ping Chen, Y.; Hong, Y.; Tian Zhu, X.; Jin Zhou, K. CRISPR–Cas9-Based Genetic Engineering for Crop Improvement under Drought Stress. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 5814–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, M.T.; Mohan, V.R. Chemical Seed Priming: Molecules and Mechanisms for Enhancing Plant Germination, Growth, and Stress Tolerance. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Ahmed, S.; Akram, W.; Li, G.; Yasin, N.A. Selenium Seed Priming Enhanced the Growth of Salt-Stressed Brassica Rapa L. through Improving Plant Nutrition and the Antioxidant System. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.T.; Kannan, R.; Jayaseelan, R. Ascorbic Acid Preconditioning Effect on Broccoli Seedling Growth and Photosynthesis under Drought Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.F.; Huda, S.; Yong, M.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.-H.; Ahmed, T. Alleviation of Drought and Salt Stress in Vegetables: Crop Responses and Mitigation Strategies. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 99, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Photosynthetic Parameter | Decrease (%) | Crops | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal CO2 concentration | 40–60% | Kale, Cauliflower, Mustard | [61,64,75] |
| Net CO2 assimilation rate | 50–70% | Cauliflower, Chinese Cabbage, Cabbage | [62,63,64] |
| Net photosynthesis | 30–80% | Kale, Broccoli, Cauliflower, Mustard | [61,64,65,66,75] |
| Stomatal conductance | 60–90% | Cauliflower, Chinese Cabbage, Cabbage, Kale, Broccoli, Mustard | [61,62,63,64,65,66] |
| Transpiration rate | 50–75% | Chinese Cabbage, Kale, Broccoli, Cauliflower, Mustard | [61,62,64,65,66,75] |
| Parameter | Effects | Crops | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions | Increased (47–275%) | Cabbage, Cauliflower | [63] |
| Total phenolic content | Increased (50–105%) | Cabbage, Broccoli, Cauliflower | [63,85,86] |
| Flavonoid content | Increased (85–95%) | Cabbage, Cauliflower, Broccoli | [63,85] |
| Chlorophyll a, b and carotenoid content | Decreased (13–45%) | Cabbage, Cauliflower, Broccoli, Rapeseed | [57,58,63,85,87,88] |
| Guaiacol peroxidase (GPX) | Increased (55–150%) | Rapeseed, Mustard, Cauliflower | [58,84,86] |
| Decreased (25%) | Broccoli | [87] | |
| Ascorbic acid (AA) | Increased (150–600%) | Broccoli, Chinese cabbage, White cabbage, Kale | [59,85] |
| Malondialdehyde (MDA) | Increased (92–130%) | Rapeseed, Chinese cabbage, White cabbage, Kale | [59,88] |
| Catalase (CAT) activity | Increased (11–75%) | Broccoli, Cauliflower, Chinese cabbage, White cabbage, Kale | [59,86,87,89] |
| Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity | Increased (14–110%) | Broccoli, Cauliflower, Chinese cabbage, White cabbage, Kale, Rapeseed | [59,84,86,87,89] |
| Abscisic acid (ABA) | Increased (230–400%) | Chinese cabbage, White cabbage, Kale, Rapeseed | [59,90] |
| Total cytokinins (CKs) | Increased (50–70%) | Chinese cabbage, White cabbage, Kale | [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohan, V.R.; MacDonald, M.T.; Abbey, L. Impact of Water Deficit Stress on Brassica Crops: Growth and Yield, Physiological and Biochemical Responses. Plants 2025, 14, 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131942
Mohan VR, MacDonald MT, Abbey L. Impact of Water Deficit Stress on Brassica Crops: Growth and Yield, Physiological and Biochemical Responses. Plants. 2025; 14(13):1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131942
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohan, Vijaya R., Mason T. MacDonald, and Lord Abbey. 2025. "Impact of Water Deficit Stress on Brassica Crops: Growth and Yield, Physiological and Biochemical Responses" Plants 14, no. 13: 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131942
APA StyleMohan, V. R., MacDonald, M. T., & Abbey, L. (2025). Impact of Water Deficit Stress on Brassica Crops: Growth and Yield, Physiological and Biochemical Responses. Plants, 14(13), 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131942