Composted PBST Biodegradable Mulch Film Residues Enhance Crop Development: Insights into Microbial Community Assembly, Network Interactions, and Soil Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Understanding the impact of PBST-BDM raw material, PBST-BDM residues, and PBST-BDM composting product on Chinese cabbage growth;
- (2)
- Analyzing the varying responses of soil to these materials;
- (3)
- Uncovering the relationships between different factors.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Growth Index of Chinese Cabbage
2.1.1. Emergence Rates
2.1.2. Plant Height, Leaf Area, and Fresh Biomass Production
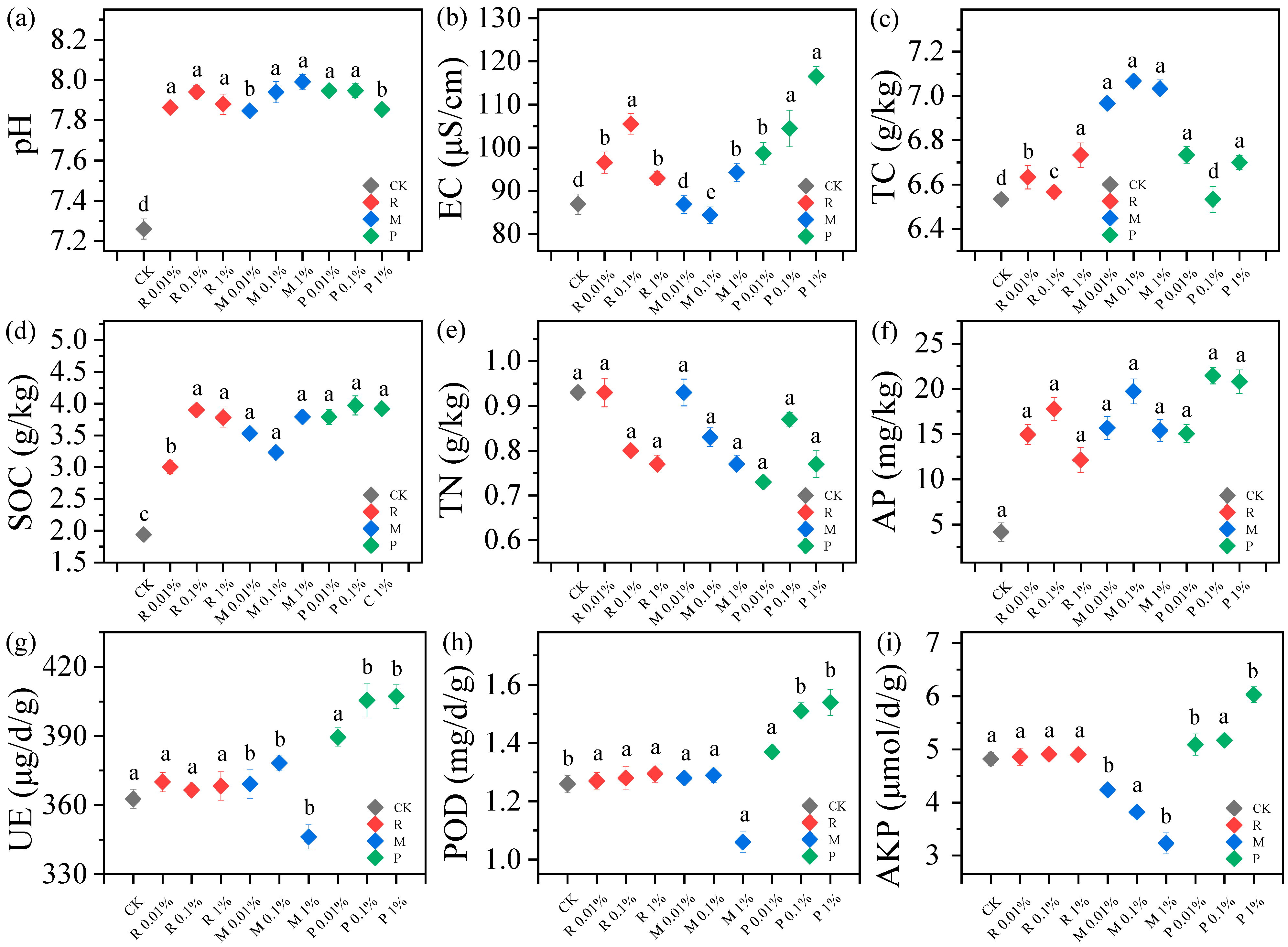
2.2. Variations of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Soil Bacterial Community Dynamics in Response to Different Treatments
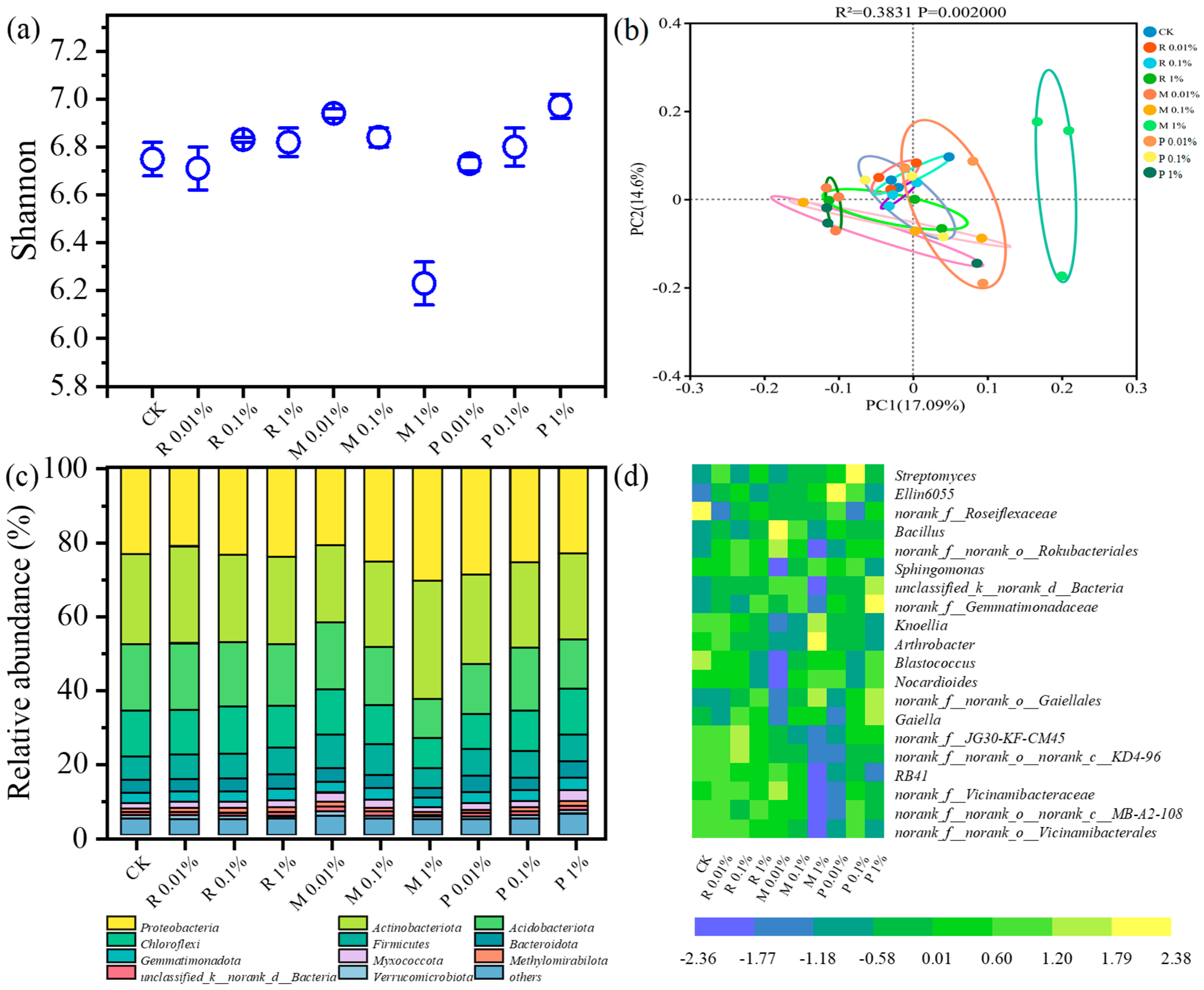
2.3.1. Diversity and Structure
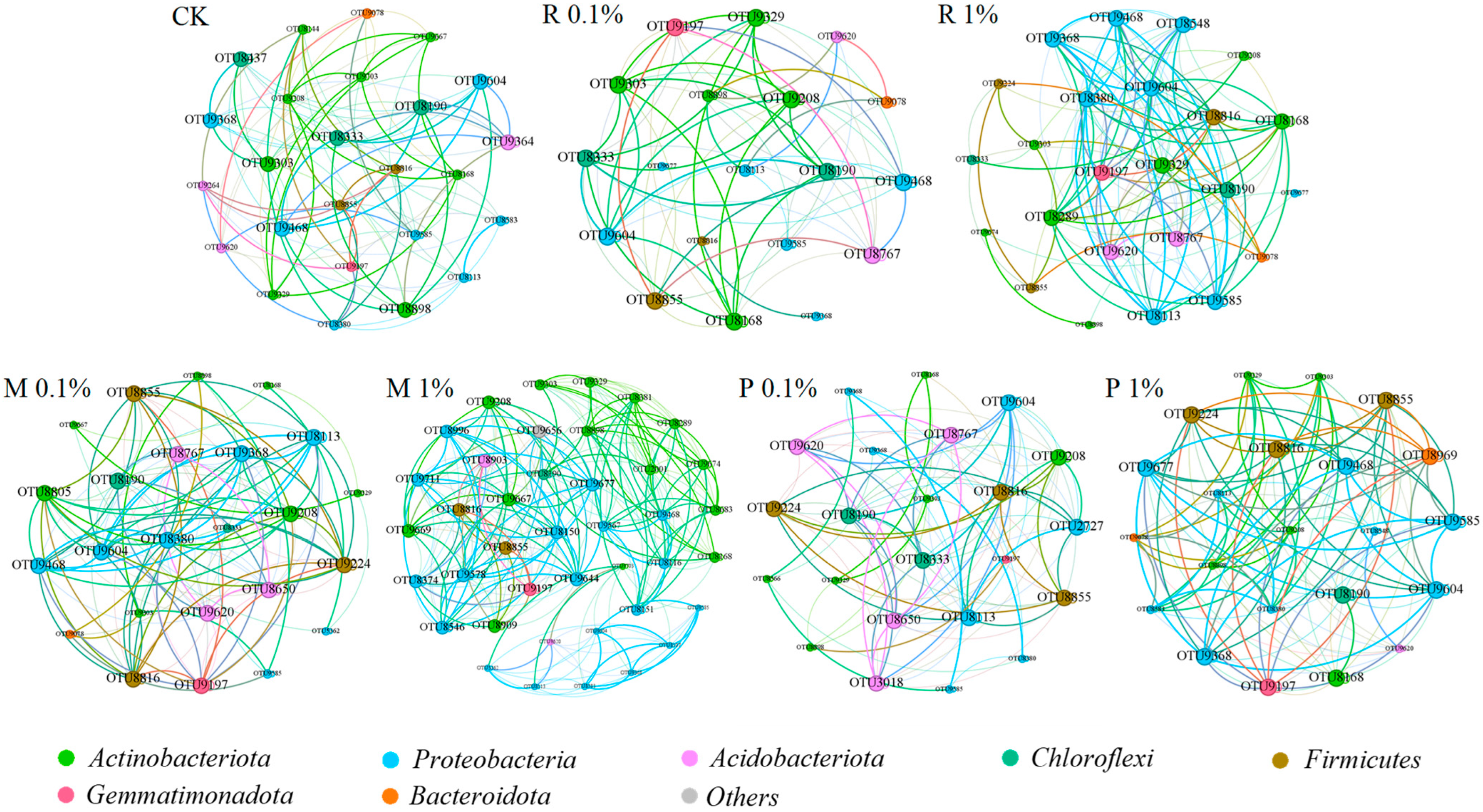
2.3.2. Examination of the Topological Characteristics of Co-Occurrence Networks in Bacterial Populations
2.3.3. Sensitive Bacterial Populations
2.4. Responses of Soil Metabolism to the Treatments of PBST Raw Material, PBST Residues, and PBST Composting Product
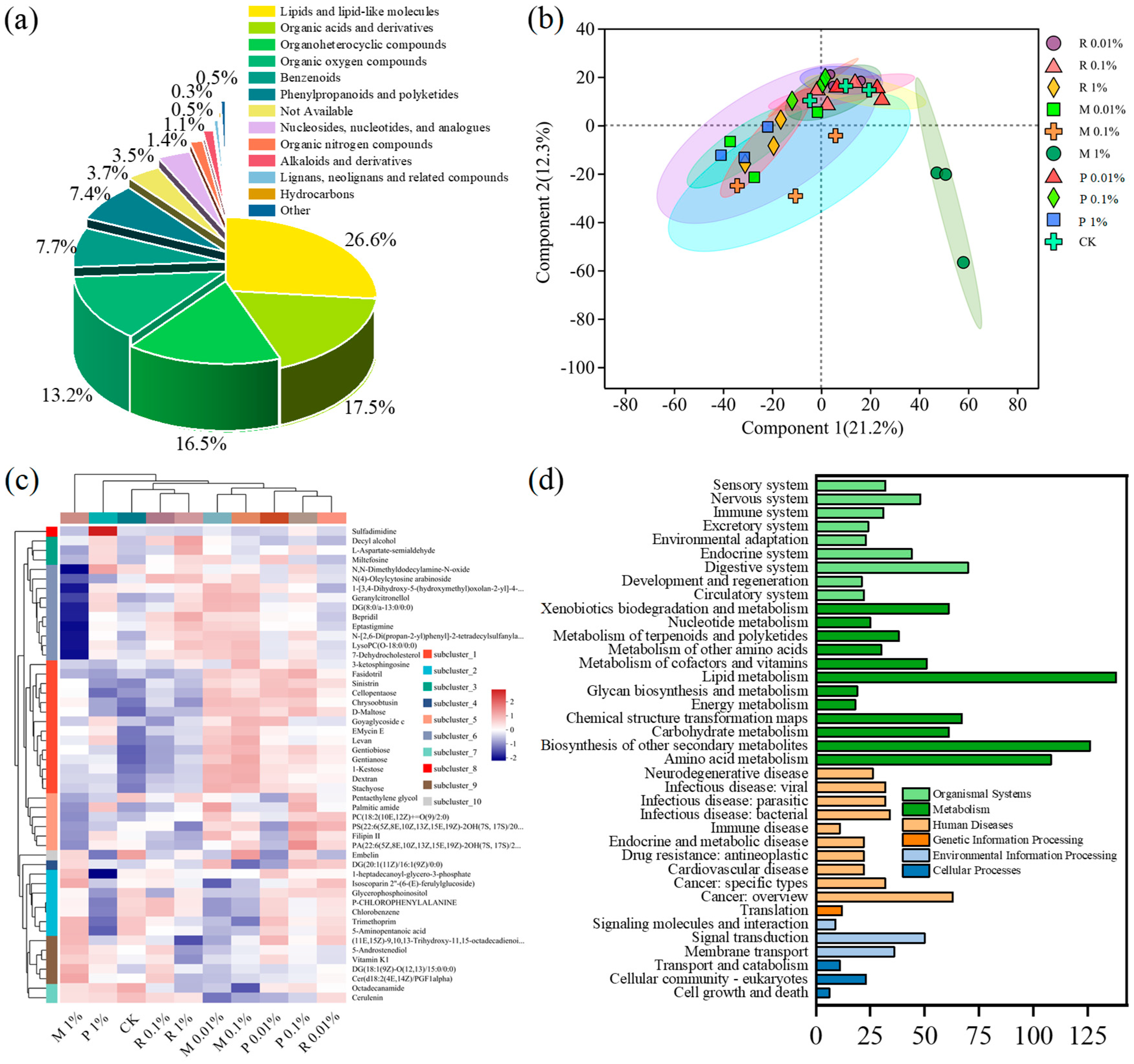
2.4.1. Advanced Multivariate Evaluation of Metabolites
2.4.2. Soil Differential Metabolites Analysis
2.4.3. Differential Pathway Enrichment
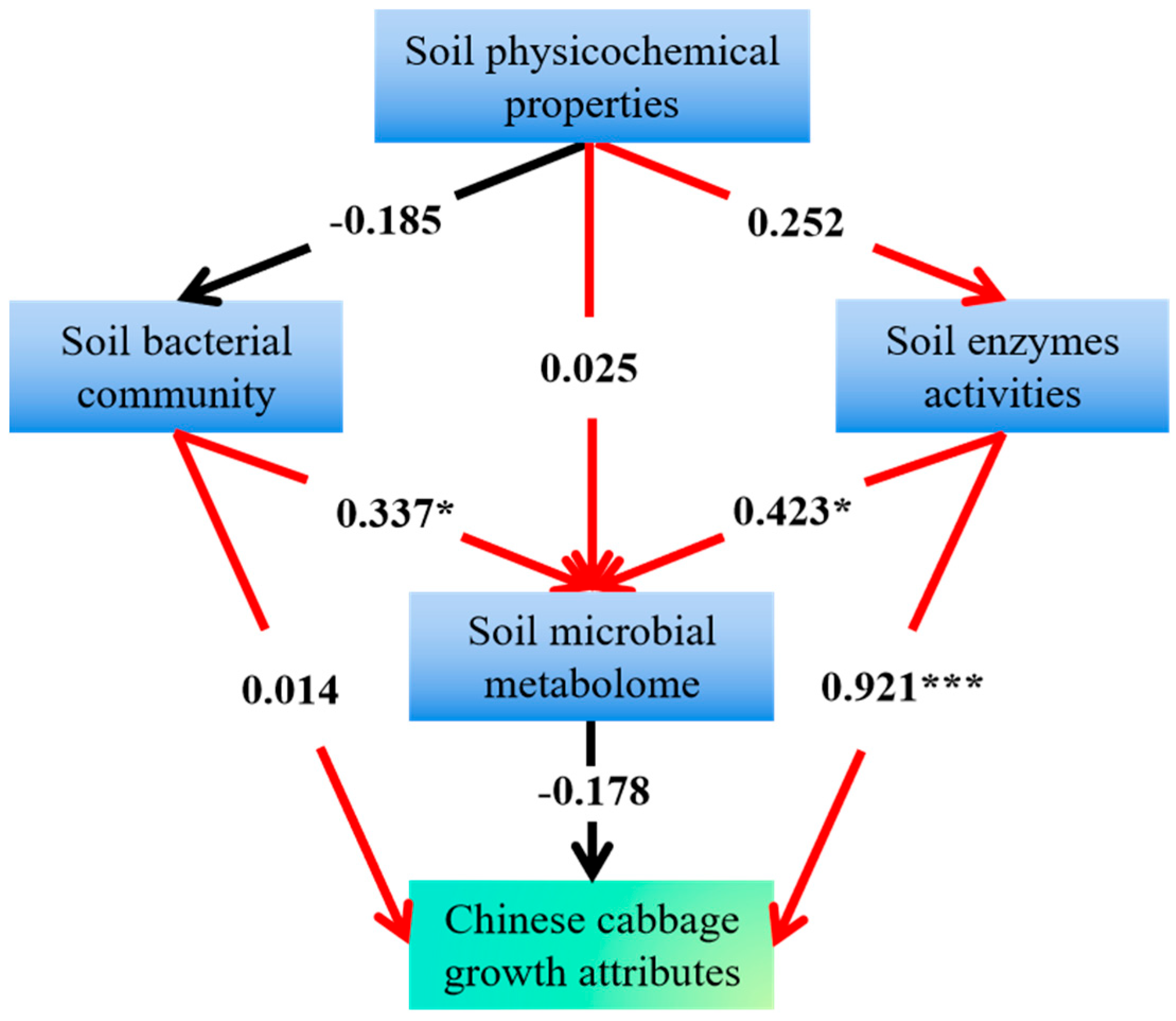
2.4.4. Comprehensive Effects of Soil Physicochemical Properties, Microbial Communities, Enzyme Activities, and Microbial Metabolism on Chinese Cabbage Growth
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Soil Preparation and Experiment Materials
3.2. Experiment Procedure
3.3. Analytical Methods
3.3.1. Growth Parameters of Chinese Cabbage
3.3.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.4. Microbiological Analysis
3.5. Non-Specific Soil Metabolic Profiling
3.6. Statistical Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Are biodegradable mulch films a sustainable solution to microplastic mulch film pollution? A biogeochemical perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemlou, M.; Daver, F.; Murdoch, B.J.; Ball, A.S.; Ivanova, E.P.; Adhikari, B. Biodegradation of novel bioplastics made of starch, polyhydroxyurethanes and cellulose nanocrystals in soil environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Zuo, Q.; Gu, J.; Zhou, J.; Du, L.; Liu, D. Large mulch film residues are more unfavourable to the reduction of soil antibiotic resistance genes induced by organic fertilisation than small mulch film residues. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Liu, C.; Lin, S.; Zuo, Q.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Improving rice production sustainability by reducing water demand and greenhouse gas emissions with biodegradable films. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, M.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.; Ge, M.; Li, N.; Ning, Z.; Gao, W.; Fan, C.; et al. Molecular insights into effects of PBAT microplastics on latosol microbial diversity and DOM chemodiversity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sintim, H.Y.; Bary, A.I.; Hayes, D.G.; Wadsworth, L.C.; Anunciado, M.B.; English, M.E.; Bandopadhyay, S.; Schaeffer, S.M.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Miles, C.A.; et al. In situ degradation of biodegradable plastic mulch films in compost and agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zou, G.; Zuo, Q.; Li, C.; Gu, J.; Kang, L.; Ma, M.; Liang, K.; Liu, D.; Du, L. Soil bacterial community and metabolism showed a more sensitive response to PBAT biodegradable mulch residues than that of LDPE mulch residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fan, B.; Hou, J.; Dang, Q.; Cui, D.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Inhibitory effect of microplastics on soil extracellular enzymatic activities by changing soil properties and direct adsorption: An investigation at the aggregate-fraction level. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Kim, S.W.; Zhu, Y.G. The soil plastisphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ding, F.; Flury, M.; Wang, J. Dynamics of macroplastics and microplastics formed by biodegradable mulch film in an agricultural field. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Di, H.H.; He, X.S.; Sun, Y.; Xiang, S.; Huang, Z.B. The mechanism of microbial community succession and microbial co-occurrence network in soil with compost application. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Mohamed, T.A.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J. Microhabitat drive microbial anabolism to promote carbon sequestration during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guliyev, V.; Tanunchai, B.; Noll, M.; Buscot, F.; Purahong, W.; Blagodatskaya, E. Links among microbial communities, soil properties and functions: Are fungi the sole players in decomposition of bio-based and biodegradable plastic? Polymers 2022, 14, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, P.; Wu, L.; Li, B.; Li, N.; Pan, X.; Dai, J. Superior gas barrier properties of biodegradable PBST vs. PBAT copolyesters: A comparative study. Polymers 2021, 13, 3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Xi, Y.; Shi, X.; Guo, C.; Zhong, Y.; Song, C.; Guan, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, Q.; Li, F. Effects of residual plastic film on crop yield and soil fertility in a dryland farming system. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskei, K.; Munyasya, A.N.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhou, R.; Indoshi, S.N.; Wang, W.; Cheruiyot, W.K.; Mburu, D.M.; Nyende, A.B.; et al. Effects of increased plastic film residues on soil properties and crop productivity in agro-ecosystem. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chen, P.; Gao, X.; Zou, Q.; Fang, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Effects of plastic film residue and emitter flow rate on soil water infiltration and redistribution under different initial moisture content and dry bulk density. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, I.K.; Diekötter, T.; Troegel, S.; Lenz, M. Amount, distribution and composition of large microplastics in typical agricultural soils in Northern Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.F.; Antonio, J.C.; Cui, Y.X.; Li, L.W.; Aron, H.; Liu, B.C.; Mikael, S.H. Millions of microplastics released from a biodegradable polymer during biodegradation/enzymatic hydrolysis. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, F.; Yang, G.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. The impact of ammonifying microorganisms on the stabilization and carbon conversion of cow manure and wheat husk co-composting. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Yang, X.M.; Amalia, M.P.; Esperanza, H.L.; Nicolas, B.; Henny, G.; Paolina, G.; Violette, G. Macro- and micro- plastics in soil-plant system: Effects of plastic mulch film residues on wheat (triticum aestivum) growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayyab, M.; Kazmi, S.S.U.H.; Pastorino, P.; Saqib, H.S.A.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Hanif, M.S.; Islam, W. Microplastics in agroecosystems: Soil-plant dynamics and effective remediation approaches. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciarelli, E.; Casorri, L.; Luigi, M.D.; Beni, C.; Valentini, M.; Costantini, E.; Aielli, L.; Reale, M. Microplastics in agricultural crops and their possible impact on farmers’ health: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A.; Rizvi, Z.F. Impact of plastic mulching as a major source of microplastics in agroecosystems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosni, A.S.A.; Pittman, J.K.; Robson, G.D. Microbial degradation of four biodegradable polymers in soil and compost demonstrating polycaprolactone as an ideal compostable plastic. Waste Manag. 2019, 97, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Anoopkumar, A.N.; Madhavan, A.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A.; Sindhu, R.; Awasthi, M.K. Degradation mechanism of microplastics and potential risks during sewage sludge co-composting: A comprehensive review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.Q.; Xing, R.Z.; Xie, S.G.; Yang, X.G.; Gui, P.; Lü, J.; Liao, H.P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S.H.; et al. Enhanced in situ biodegradation of microplastics in sewage sludge using hyperthermophilic composting technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 384, 121271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Shen, W.L.; Feng, K.; Feng, Y.Z.; He, Z.L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Deng, Y. Organic fertilizer potentiates the transfer of typical antibiotic resistance gene among special bacterial species. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Hartemink, A.E. The efects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant Soil 2023, 487, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, S.; Martin-Closas, L.; Pelacho, A.; DeBruyn, J.M. Biodegradable plastic mulch films: Impacts on soil microbial communities and ecosystem functions. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, G.; Li, Z.; Fu, P. Formulation, performance and environmental/agricultural benefit analysis of biomass-based biodegradable mulch films: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 203, 112663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.J.; Li, G.; Cui, Y.R.; Xie, J.; Liang, Z.W.; Guan, F.C.; Li, Z.H. Response of alfalfa leaf traits and rhizosphere fungal communities to compost application in saline-sodic soil. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Microbes drive metabolism, community diversity, and interactions in response to microplastic-induced nutrient imbalance. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xu, Y.; Lei, F.; Yu, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jia, H.; Guo, X. Degradation of polyethylene plastic in soil and effects on microbial community composition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 15, 126173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Pan, S.Q.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lin, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, S.H. Effects of the feeding ratio of food waste on fed-batch aerobic composting and its microbial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, S.; González, J.E.L.Y.; Henderson, K.B.; Anunciado, M.B.; Debruyn, J.M. Soil microbial communities associated with biodegradable plastic mulch films. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Zaidi, M.G.H.; Soni, R.; Lata, K.; Shouche, Y.S. Implication of arthrobacter and enterobacter species for polycarbonate degradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegr. 2008, 61, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatheru, W.M.; Sun, K.; Gao, Y.Z. Sphingomonas in microbe-assisted phytoremediation: Tackling soil pollution. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshafi, M.H.; Forootanfar, H.; Ameri, A.; Shakibaie, M.; Dehghan-Noudeh, G.; Razavi, M. Antimicrobial activity of Bacillus sp. strain FAS1 isolated from soil. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 24, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Qin, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yin, Y. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on carbon components and microbial functional metabolism during cow manure-straw composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Park, L.S.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Suh, M.J.; Ham, S.; Bhatia, K.S.; Gurav, R.; Park, H.S.; Park, K.; et al. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) degradation by the newly isolated marine Bacillus sp. JY14. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danczak, R.E.; Johnston, M.D.; Kenah, C.; Slattery, M.; Wilkins, M.J. Microbial community cohesion mediates community turnover in unperturbed aquifers. mSystems 2018, 3, e00066-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Jin, T.; Liu, H.; Men, J.; Cai, G.; Cernava, T.; Duan, G.; Jin, D. Biodegradable mulch films significantly affected rhizosphere microbial communities and increased peanut yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. New insights into the vertical distribution and microbial degradation of microplastics in urban river sediments. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Yang, Y.C.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Tian, Y. Effects of biodegradable (PBAT/PLA) and conventional (LDPE) mulch film residues on bacterial communities and metabolic functions in different agricultural soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkereit, J.; Geisseler, D.; Lazicki, P.; Settles, M.L.; Durbin-Johnson, B.P.; Hodson, A. Interactions between nitrogen availability, bacterial communities, and nematode indicators of soil food web function in response to organic amendments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 157, 103767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Tang, C.; Lian, T.; Adams, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Soil microbial metabolism on carbon and nitrogen transformation links the crop-residue contribution to soil organic carbon. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikoyi, I.; Fowler, A.; Schmalenberger, A. One-time phosphate fertilizer application to grassland columns modifies the soil microbiota and limits its role in ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Jin, Q.; Luo, Q.; He, H. Combined contamination of microplastic and antibiotic alters the composition of microbial community and metabolism in wheat and maize rhizosphere soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 473, 134618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.Y.; Pan, C.R.; Su, X.M.; Zhou, X.; Bao, Y.Y. Combined effects of oxytetracycline and microplastic on wheat seedling growth and associated rhizosphere bacterial communities and soil metabolite profiles. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 302, 119046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprivova, A. and Kopriva, S. Plant secondary metabolites altering root microbiome composition and function. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 67, 102227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Gonzalez, J.A.; Suarez-Estrella, F.; Vargas-Garcia, M.C.; Lopez, M.J.; Jurado, M.M.; Moreno, J. Dynamics of bacterial microbiota during lignocellulosic waste composting: Studies upon its structure, functionality and biodiversity. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortman, S.E.; Elizabeth, J.; Mitchell, B.S.; Rhae, D. A new method for detecting micro-fragments of biodegradable mulch films containing poly (butylene Adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) in soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2022, 51, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.V.; Luciana, S.C.; Rubia, F.G.; Liliane, M.F.L. An overview on properties and applications of poly (butylene Adipate-co-terephthalate)-PBAT based composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59 (Suppl. 2), E7–E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Jin, N.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y.; Luo, S.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J. Changes in the microbial structure of the root soil and the yield of Chinese Baby Cabbage by chemical fertilizer reduction with bio-organic fertilizer application. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0121522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Fu, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Yu, Z. Impact of Interaction between Biochar and Soil Microorganisms on Growth of Chinese Cabbage by Increasing Soil Fertility. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future Directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ye, L.; Mu, X.; Xu, L.; Shi, Z.; Luo, Y. Synergistic effects of earthworms and cow manure under reduced chemical fertilization modified microbial community structure to mitigate continuous cropping effects on Chinese flowering cabbage. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1285464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Fu, T.; He, G.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, M.; Lou, F.; He, T. Characteristics of rhizosphere and bulk soil microbial community of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris) grown in Karst area. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1241436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zou, G.; Li, Y.; Pan, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Li, C.; Chen, Y. Biodegradable microplastics coupled with biochar enhance Cd chelation and reduce Cd accumulation in Chinese cabbage. Biochar 2025, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Zhou, Q. Response of soil enzymes, functional bacterial groups, and microbial communities exposed to sudan I–IV. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Liu, L.; Zou, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, D. Composted PBST Biodegradable Mulch Film Residues Enhance Crop Development: Insights into Microbial Community Assembly, Network Interactions, and Soil Metabolism. Plants 2025, 14, 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131902
Li L, Liu L, Zou G, Wang X, Xu L, Yang Y, Liu J, Liu H, Liu D. Composted PBST Biodegradable Mulch Film Residues Enhance Crop Development: Insights into Microbial Community Assembly, Network Interactions, and Soil Metabolism. Plants. 2025; 14(13):1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131902
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Liuliu, Liyuan Liu, Guoyuan Zou, Xuexia Wang, Li Xu, Yong Yang, Jinfeng Liu, Huabo Liu, and Dongsheng Liu. 2025. "Composted PBST Biodegradable Mulch Film Residues Enhance Crop Development: Insights into Microbial Community Assembly, Network Interactions, and Soil Metabolism" Plants 14, no. 13: 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131902
APA StyleLi, L., Liu, L., Zou, G., Wang, X., Xu, L., Yang, Y., Liu, J., Liu, H., & Liu, D. (2025). Composted PBST Biodegradable Mulch Film Residues Enhance Crop Development: Insights into Microbial Community Assembly, Network Interactions, and Soil Metabolism. Plants, 14(13), 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131902






