Effects of Stumping on Ecological Stoichiometry and Allometric Growth in Leaf, Absorptive Root, and Rhizosphere Soil of Hippophae rhamnoides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
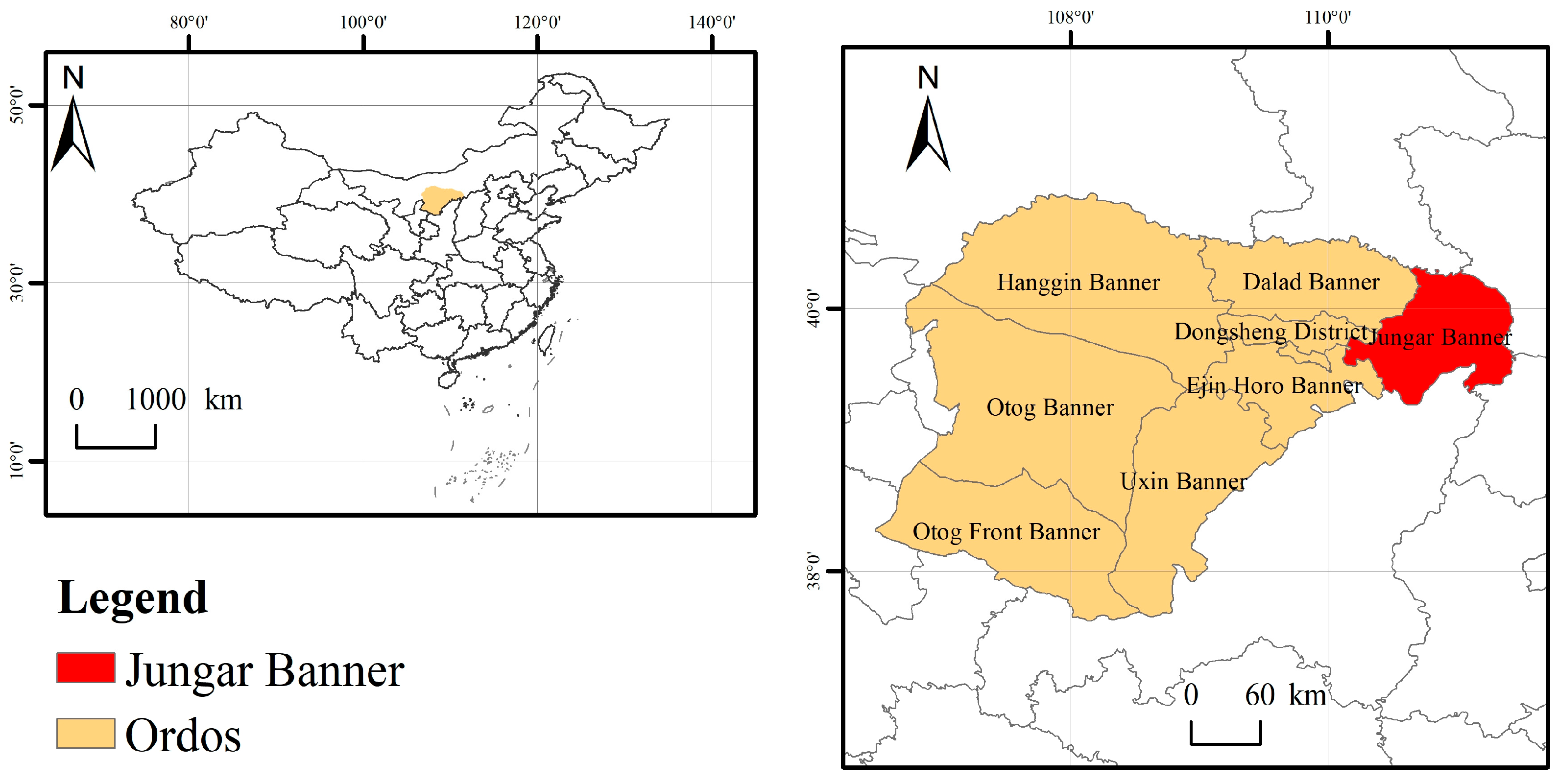
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Contents and Stoichiometric Changes of C, N, and P in Leaves and Absorptive Roots of H. rhamnoides
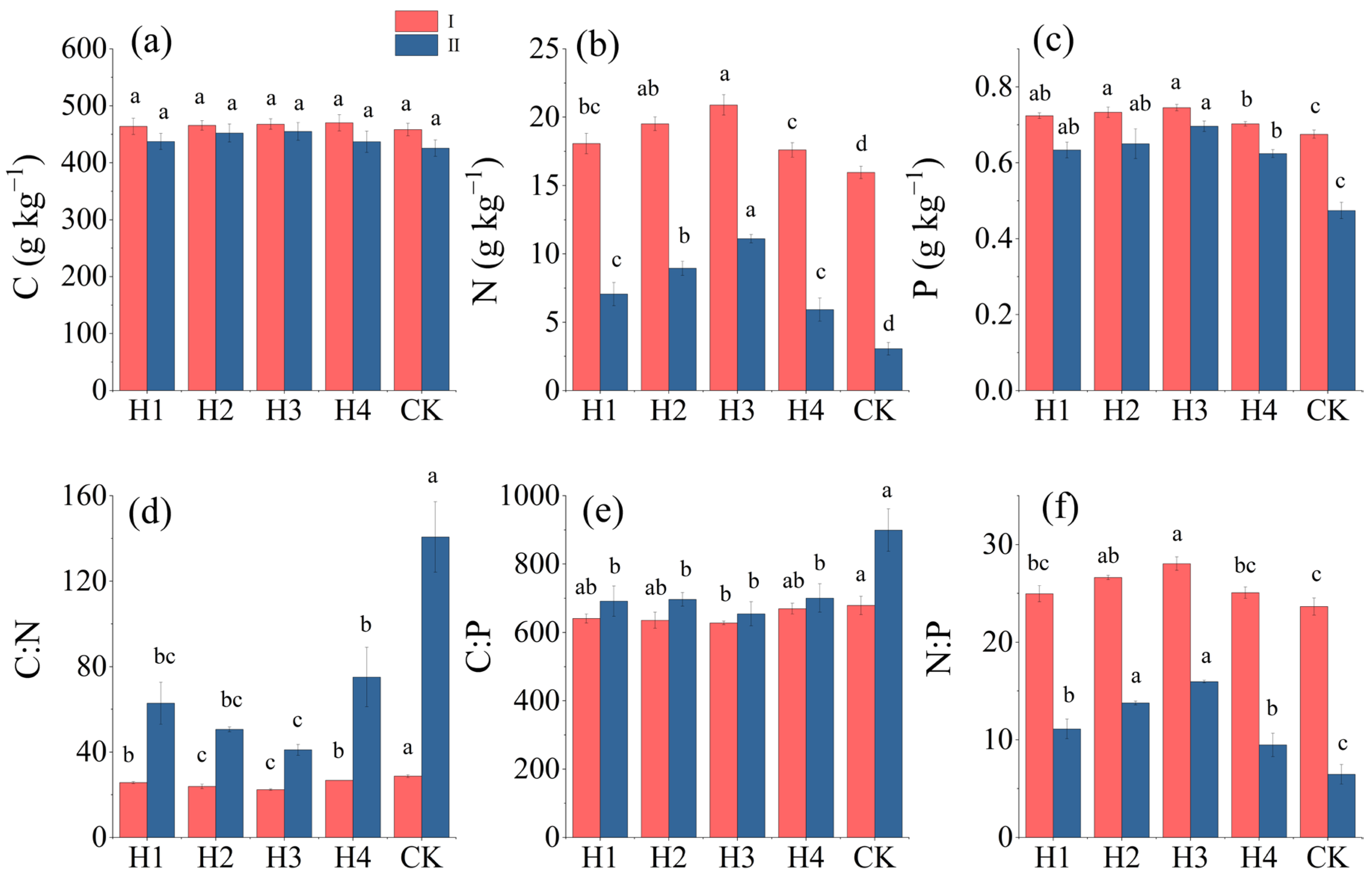
3.2. Contents of and Stoichiometric Changes in C, N, and P in Rhizosphere Soils of H. rhamnoides
3.3. Allometric Growth Relationship of C, N, and P Between Leaves and Absorptive Roots of H. rhamnoides
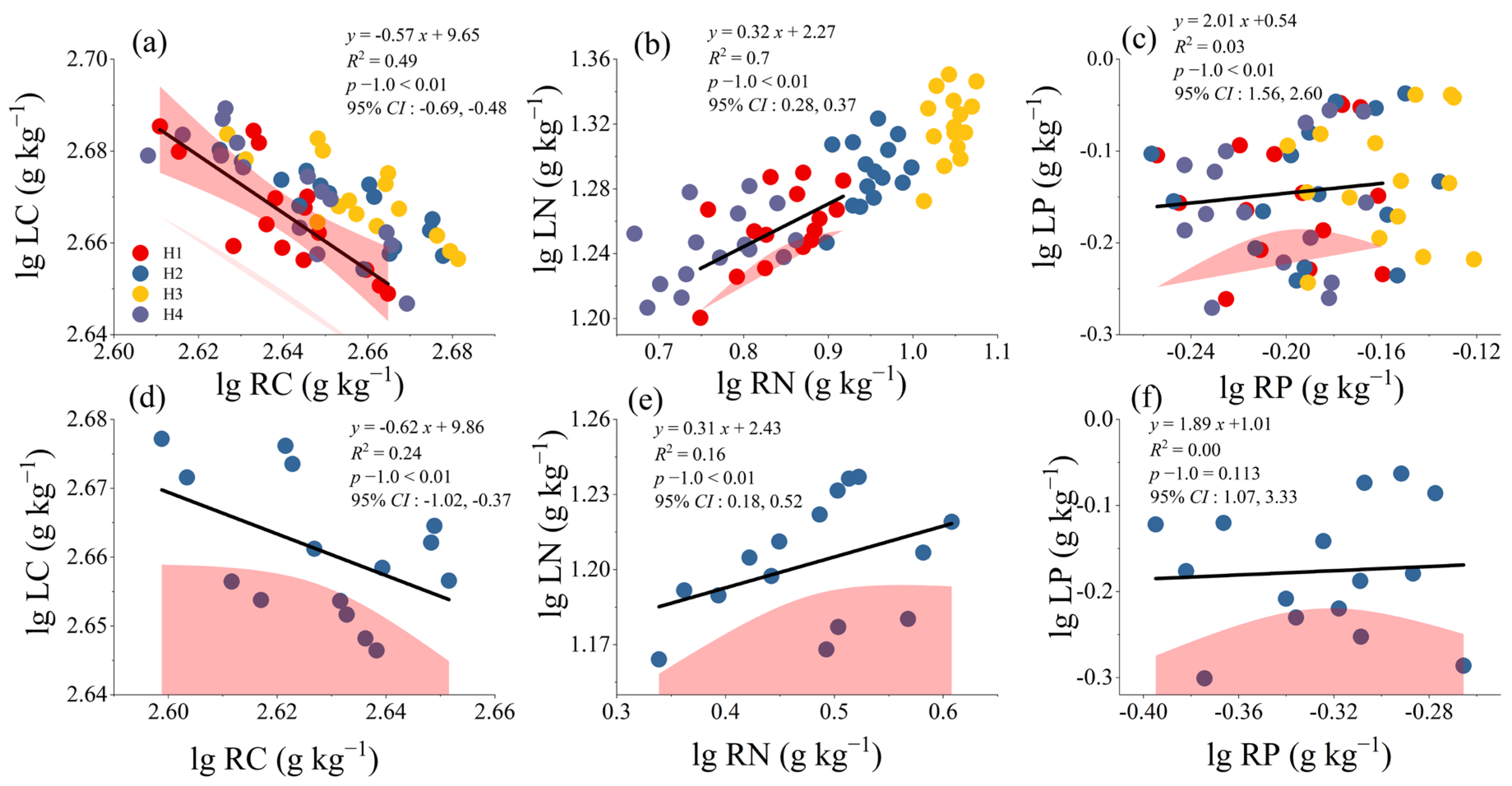
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Allometric Data for Leaves, Absorptive Roots, and Rhizosphere Soils of H. rhamnoides
4. Discussion
4.1. C, N, and P Contents and Stoichiometric Changes in Leaves, Absorptive Roots, and Rhizosphere Soils of H. rhamnoides
4.2. Correlation Between Stoichiometric Ratios and Allometric Growth in Leaves, Absorptive Roots, and Rhizosphere Soils of H. rhamnoides
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.R.; An, S.S. Ecological stoichiometry in leaves, roots, litters and soil among different plant communities in a desertified region of Northern China. Catena 2018, 166, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooshammer, M.; Wanek, W.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Richter, A. Stoichiometric imbalances between terrestrial decomposer communities and their resources: Mechanisms and implications of microbial adaptations to their resources. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 00022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.H.; Ma, X.C.; Peng, F.X.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Q.; Xu, D.D.; Ruan, H.H.; Xu, X. Consistent responses of the C:N:P stoichiometry of green leaves and fine roots to N addition in poplar plantations in eastern coastal China. Plant Soil 2023, 485, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Chen, H.Y.H. Plant mixture balances terrestrial ecosystem C:N:P stoichiometry. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Yu, G.R.; Wang, Q.F.; Wang, R.L.; Zhang, J.H.; Liu, C.C.; He, N.P. Conservative allocation strategy of multiple nutrients among major plant organs: From species to community. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, M.L.; Dickie, I.A.; Eissenstat, D.M.; Fahey, T.J.; Fernandez, C.W.; Guo, D.L.; Helmisaari, H.S.; Hobbie, E.A.; Iversen, C.M.; Jackson, R.B.; et al. Redefining fine roots improves understanding of below-ground contributions to terrestrial biosphere processes. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, J.; Weigelt, A.; van der Plas, F.; Laughlin, D.C.; Kuyper, T.W.; Guerrero-Ramirez, N.; Valverde-Barrantes, O.J.; Bruelheide, H.; Freschet, G.T.; Iversen, C.M.; et al. The fungal collaboration gradient dominates the root economics space in plants. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.P.; Jian, J.N.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Yang, G.H.; Han, X.H.; Ren, C.J. Response of root nutrient resorption strategies to rhizosphere soil microbial nutrient utilization along Robinia pseudoacacia plantation chronosequence. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 489, 119053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Qiu, X.R.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.N.; Hu, H.L.; Xie, J.L.; Chen, G.; Xiao, Y.L.; Tang, Y.; Tu, L.H. C:N:P stoichiometry responses to 10 years of nitrogen addition differ across soil components and plant organs in a subtropical Pleioblastus amarus forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Elser, J.J.; He, N.P.; Wu, H.H.; Chen, Q.S.; Zhang, G.M.; Han, X.G. Stoichiometric homeostasis of vascular plants in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Oecologia 2011, 166, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorter, H.; Jagodzinski, A.M.; Ruiz-Peinado, R.; Kuyah, S. How does biomass distribution change with size and differ among species? An analysis for 1200 plant species from five continents. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, J. Allocation, plasticity and allometry in plants. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 6, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, Z.; Gheyret, G.; Zhou, G.; Xie, Z.; Tang, Z. The community-level scaling relationship between leaf nitrogen and phosphorus changes with plant growth, climate and nutrient limitation. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Gou, X.H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.Z.; Xia, J.Q.; Wang, Y.F. Nutrient allocation strategies of four conifers from semiarid to extremely arid environments. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 186, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.S.; Bi, C.F.; Cao, M.M.; Li, H.E.; Wang, X.H.; Wu, W. Simulation of sediment retention effects of the double seabuckthorn plant flexible dams in the Pisha Sandstone area of China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.L.; Li, T.J.; Li, G.Q.; Liu, C.H.; Gao, H.Y.; Dai, G.H.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Li, S.L. Modular growth and clonal propagation of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis in response to irrigation intensity. J. For. Res. 2016, 27, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Giambalvo, D.; Amato, G.; Stringi, L. Effects of stubble height and cutting frequency on regrowth of Berseem clover in a Mediterranean semiarid environment. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Minggagud, H.; Baoyin, T.G.T.; Li, F.Y.H. Plant production decreases whereas nutrients concentration increases in response to the decrease of mowing stubble height. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langworthy, A.D.; Rawnsley, R.P.; Freeman, M.J.; Corkrey, R.; Harrison, M.T.; Pembleton, K.G.; Lane, P.A.; Henry, D.A. Effect of stubble-height management on crown temperature of perennial ryegrass, tall fescue and chicory. Crop Pasture Sci. 2019, 70, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.W.; Wang, X.Z.; Li, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, G. Responses of Caragana korshinskii to different aboveground shoot removal: Combining defence and tolerance strategies. Ann. Bot. 2006, 98, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Bao, W.K.; Wu, N.; Hu, H.; Yang, T.H. Environmental aridity driving latitudinal pattern of biomass allocation fractions in root systems of 63 shrub species in dry valleys. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, W.S.; Chen, F.S.; Wang, F.C.; Fang, X.M.; Mao, R.; Wang, H.M. The species-specific responses of nutrient resorption and carbohydrate accumulation in leaves and roots to nitrogen addition in a subtropical mixed plantation. Can. J. For. Res. 2019, 49, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; Carrillo, Y.; Boot, C.M.; Rocca, J.D.; Pendall, E.; Wallenstein, M.D. Rhizosphere stoichiometry: Are C:N:P ratios of plants, soils, and enzymes conserved at the plant species-level? New Phytol. 2014, 201, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.F.; Freschet, G.T.; Pan, X.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Li, Y.; Dong, M. Coordinated variation in leaf and root traits across multiple spatial scales in Chinese semi-arid and arid ecosystems. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Kou, L.; Sheng, L.G. Decomposition of leaf mixtures and absorptive-root mixtures synchronously changes with deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 107602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Kerkhoff, A.J.; Enquist, B.J. Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, N.R.; TumberDávila, S.J.; Phillips, R.P.; Bauerle, T.L.; Brunn, M.; Hafner, B.D. Estimating the global root exudate carbon flux. Biogeochemistry 2024, 167, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Peng, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, F.; Yang, G. Linking microbial C:N:P stoichiometry to microbial community and abiotic factors along a 3500-km grassland transect on the Tibetan plateau. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daufresne, T. Optimal nitrogen-to-phosphorus stoichiometry of phytoplankton. Nature 2004, 429, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, J.; Clark, C.M.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Han, X. Grazing alters ecosystem functioning and C:N:P stoichiometry of grasslands along a regional precipitation gradient. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Zhou, H.X.; Wang, G.L.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.B.; Duan, M.C. Nitrogen Addition Changes the Stoichiometry and Growth Rate of Different Organs in Pinus tabuliformis Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.P.; Shen, Z.J.; Zhang, Z. Phosphorus Speciation and Nutrient Stoichiometry in the Soil-Plant System During Primary Ecological Restoration of Copper Mine Tailings. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Y.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Yao, Y.F.; Qi, W. Stump height after regenerative cutting of sea-buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) affects fine root architecture and rhizosphere soil stoichiometric properties. Rhizosphere 2022, 24, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.D.; Luo, Y.; Tu, W.G.; Wan, T. Drought differently affects growth properties, leaf ultrastructure, nitrogen absorption and metabolism of two dominant species of Hippophae on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.Q.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Tang, M.; Ren, Y.Z.; Hu, J. Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) plantation degradation aggravates microbial metabolic C and P limitations on the Northern Loess Plateau in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; He, F.K.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Xiao, H.X.; Hoang, D.T.T.; Pu, S.Y.; Razavi, B.S. Nutrients in the rhizosphere: A meta-analysis of content, availability, and influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 153908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Y.; Ma, Z.L.; Chen, H.Y.H. Intensive plantations decouple fine root C:N:P in subtropical forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 505, 119901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.J.; Yao, X.; Liu, G.B.; Wang, G.L. Effect of nitrogen addition on the decomposition and release of compounds from fine roots with different diameters: The importance of initial substrate chemistry. Plant Soil 2019, 438, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.J.; Sheng, M.Y.; Bai, Y.X.; Jie, Y.; Xiao, H.L. Response of C, N, and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem, SW China. Plant Soil 2020, 475, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latati, M.; Dokukin, P.; Aouiche, A.; Rebouh, N.Y.; Takouachet, R.; Hafnaoui, E.; Hamdani, F.Z.; Bacha, F.; Ounane, S.M. Species Interactions Improve Above-Ground Biomass and Land Use Efficiency in Intercropped Wheat and Chickpea under Low Soil Inputs. Agronomy 2022, 9, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; He, N.P.; Liu, C.C.; Xu, L.; Yu, Q.; Yu, G.R. Allocation strategies for nitrogen and phosphorus in forest plants. Oikos 2018, 127, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Tan, T.; Wu, D.; Li, C.; Jing, H.; Wu, J. Seasonal variations in carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus of Pinus yunnanensis at different stand ages. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Y.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Yao, Y.F.; Qi, W. Hippophae rhamnoides treated at different stump heights in feldspathic sandstone areas of Inner Mongolia. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1104632. [Google Scholar]
- Tilman, D. Niche trade-offs, neutrality, and community structure: A stochastic theory of resource competition, invasion, and community assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10854–10861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Ubach, A.; Sardansa, J.; Pérez-Trujillob, M.; Estiarte, M.; Peñuelas, J. Strong relationship between elemental stoichiometry and metabolome in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4181–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Fang, Y.; An, S. Ecological stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and C:N:P in shoots and litter of plants in grassland in Yunwu Mountain. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2016, 53, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Kerkhoff, A.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Elser, J.J.; Enquist, B.J. Phylogenetic and growth form variation in the scaling of nitrogen and phosphorus in the seed plants. Am. Nat. 2006, 168, E103–E122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausch, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Carbon input by roots into the soil: Quantification of rhizodeposition from roots to ecosystem scale. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Traits | df (Degrees of Freedom) | SS (Sum of Squares) | MS (Mean Square) | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC (leaf C content, g kg−1) | 4 | 250.77 | 62.69 | 0.46 | 0.766 |
| LN (leaf N content, g kg−1) | 4 | 42.43 | 10.61 | 28.79 | 0.0001 |
| LP (leaf P content, g kg−1) | 4 | 0.0092 | 0.0023 | 24.77 | 0.0001 |
| LC:LN (leaf LC:LN ratio) | 4 | 72.14 | 18.035 | 47.78 | 0.0001 |
| LC:LP (leaf LC:LP ratio) | 4 | 5991.52 | 1497.885 | 4.38 | 0.0264 |
| LN:LP (leaf LN:LP ratio) | 4 | 34.41 | 8.60 | 18.39 | 0.0001 |
| RC (absorptive root C content, g kg−1) | 4 | 1765.67 | 441.42 | 1.77 | 0.212 |
| RN (absorptive root N content, g kg−1) | 4 | 111.38 | 27.84 | 69.15 | 0.0001 |
| RP (absorptive root P content, g kg−1) | 4 | 0.084 | 0.021 | 38.53 | 0.0001 |
| RC:RN (absorptive root LC:LN ratio) | 4 | 18,614.59 | 4653.65 | 40.93 | 0.0001 |
| RC:RP (absorptive root LC:LP ratio) | 4 | 113,709.42 | 28,427.36 | 15.43 | 0.0003 |
| RN:RP (absorptive root LN:LP ratio) | 4 | 163.66 | 40.91 | 58.095 | 0.0001 |
| Traits | df (Degrees of Freedom) | SS (Sum of Squares) | MS (Mean Square) | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (rhizosphere soil C content, g kg−1) | 4 | 22.91 | 5.73 | 5.30 | 0.0149 |
| N (rhizosphere soil N content, g kg−1) | 4 | 0.13 | 0.032 | 5.43 | 0.0138 |
| P (rhizosphere soil P content, g kg−1) | 4 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 11.46 | 0.0009 |
| C:N (rhizosphere soil C:N ratio) | 4 | 6.66 | 1.67 | 3.63 | 0.0446 |
| C:P (rhizosphere soil C:P ratio) | 4 | 880.0021 | 220.0005 | 6.63 | 0.0071 |
| N:P (rhizosphere soil N:P ratio) | 4 | 5.46 | 1.37 | 6.99 | 0.0059 |
| Index (lg y − lg x) | Treatment | n | R2 | p | Slope | 95% CI | Intercept | p − 1.0 | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN–RC | H1 | 15 | 0.30 | <0.001 ** | −1.59 | −2.59, −0.98 | 12.58 | <0.001 ** | A |
| H2 | 15 | 0.02 | <0.01 ** | −1.24 | −2.19, −0.71 | 10.57 | <0.001 ** | A | |
| H3 | 15 | 0.32 | <0.001 ** | −1.34 | −2.16, −0.83 | 11.26 | <0.001 ** | A | |
| H4 | 15 | 0.25 | <0.01 ** | −1.21 | −1.99, −0.74 | 10.22 | <0.01 ** | A | |
| CK | 15 | 0.19 | <0.01 ** | −1.48 | −2.49, −0.89 | 11.75 | <0.001 ** | A | |
| LP–RC | H1 | 15 | 0.01 | <0.01 ** | −4.49 | −7.92, −2.55 | 26.98 | <0.001 ** | A |
| H2 | 15 | 0.03 | <0.01 ** | −4.26 | −7.45, −2.43 | −26.36 | <0.05 * | A | |
| H3 | 15 | 0.01 | <0.01 ** | −4.26 | −7.51, −2.42 | 25.79 | <0.001 ** | A | |
| H4 | 15 | 0.00 | <0.01 ** | −3.86 | −6.80, −2.19 | 23.09 | <0.001 ** | A | |
| CK | 15 | 0.00 | <0.01 ** | −4.63 | −8.17, −2.62 | 27.63 | <0.001 ** | A | |
| LP–RN | H1 | 15 | 0.04 | <0.01 ** | 1.35 | 0.77, 2.36 | −2.96 | 0.359 | I |
| H2 | 15 | 0.08 | <0.01 ** | 2.41 | 1.39, 4.17 | 5.60 | <0.05 * | A | |
| H3 | 15 | 0.09 | <0.01 ** | 3.70 | 2.15, 6.37 | −9.21 | <0.05 * | A | |
| H4 | 15 | 0.03 | <0.01 ** | 1.20 | 0.68, 2.09 | −2.48 | 0.551 | I | |
| CK | 15 | 0.04 | <0.01 ** | 0.96 | 0.55, 1.67 | −1.46 | 0.88 | I |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, W.; Ba, D.; Feng, F. Effects of Stumping on Ecological Stoichiometry and Allometric Growth in Leaf, Absorptive Root, and Rhizosphere Soil of Hippophae rhamnoides. Plants 2025, 14, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101513
Liu L, Guo Y, Liu W, Ba D, Feng F. Effects of Stumping on Ecological Stoichiometry and Allometric Growth in Leaf, Absorptive Root, and Rhizosphere Soil of Hippophae rhamnoides. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101513
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu, Yuefeng Guo, Wangsuo Liu, Darifu Ba, and Fei Feng. 2025. "Effects of Stumping on Ecological Stoichiometry and Allometric Growth in Leaf, Absorptive Root, and Rhizosphere Soil of Hippophae rhamnoides" Plants 14, no. 10: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101513
APA StyleLiu, L., Guo, Y., Liu, W., Ba, D., & Feng, F. (2025). Effects of Stumping on Ecological Stoichiometry and Allometric Growth in Leaf, Absorptive Root, and Rhizosphere Soil of Hippophae rhamnoides. Plants, 14(10), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101513






