Genetic Diversity and Connectivity of Reef-Building Halimeda macroloba in the Indo-Pacific Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
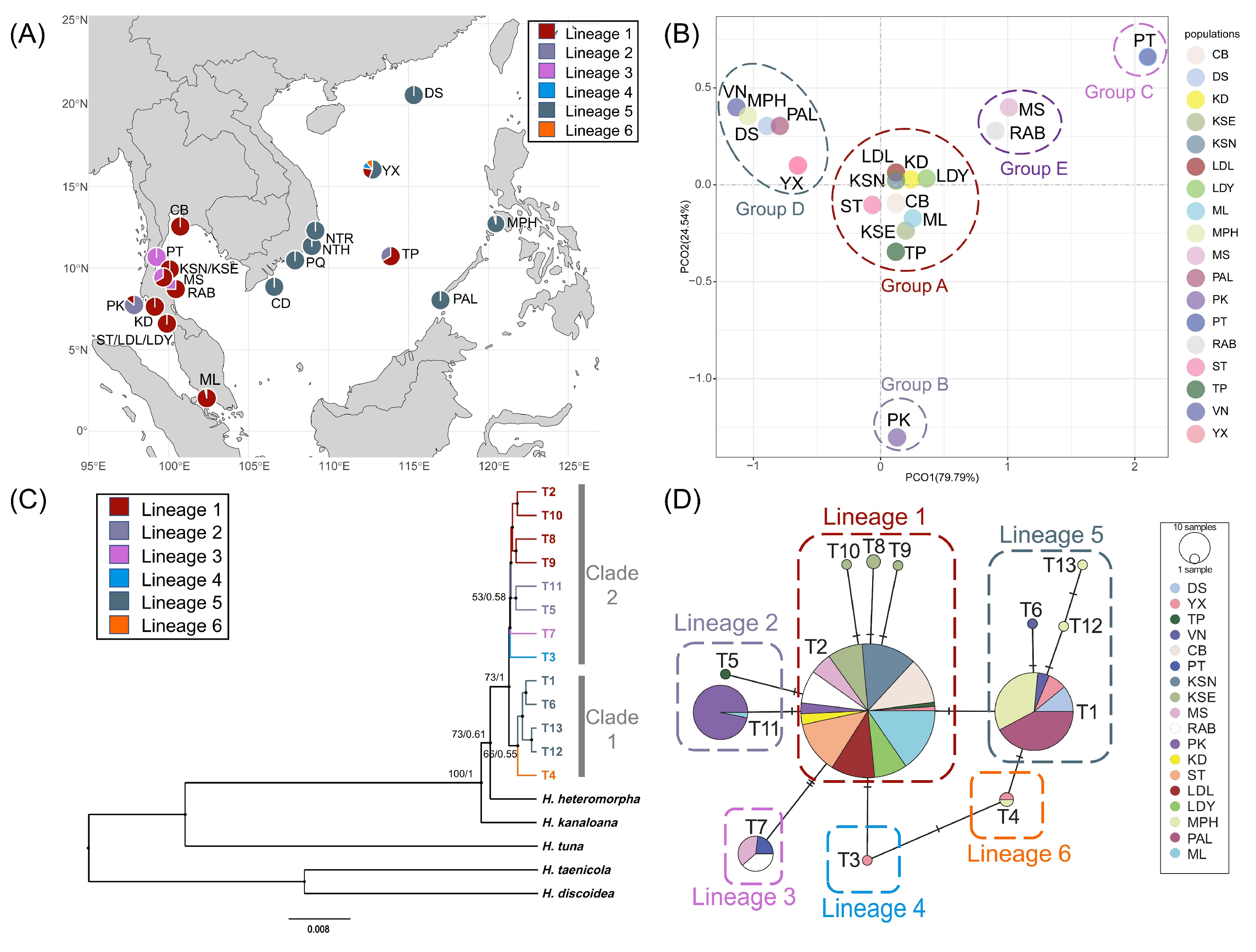
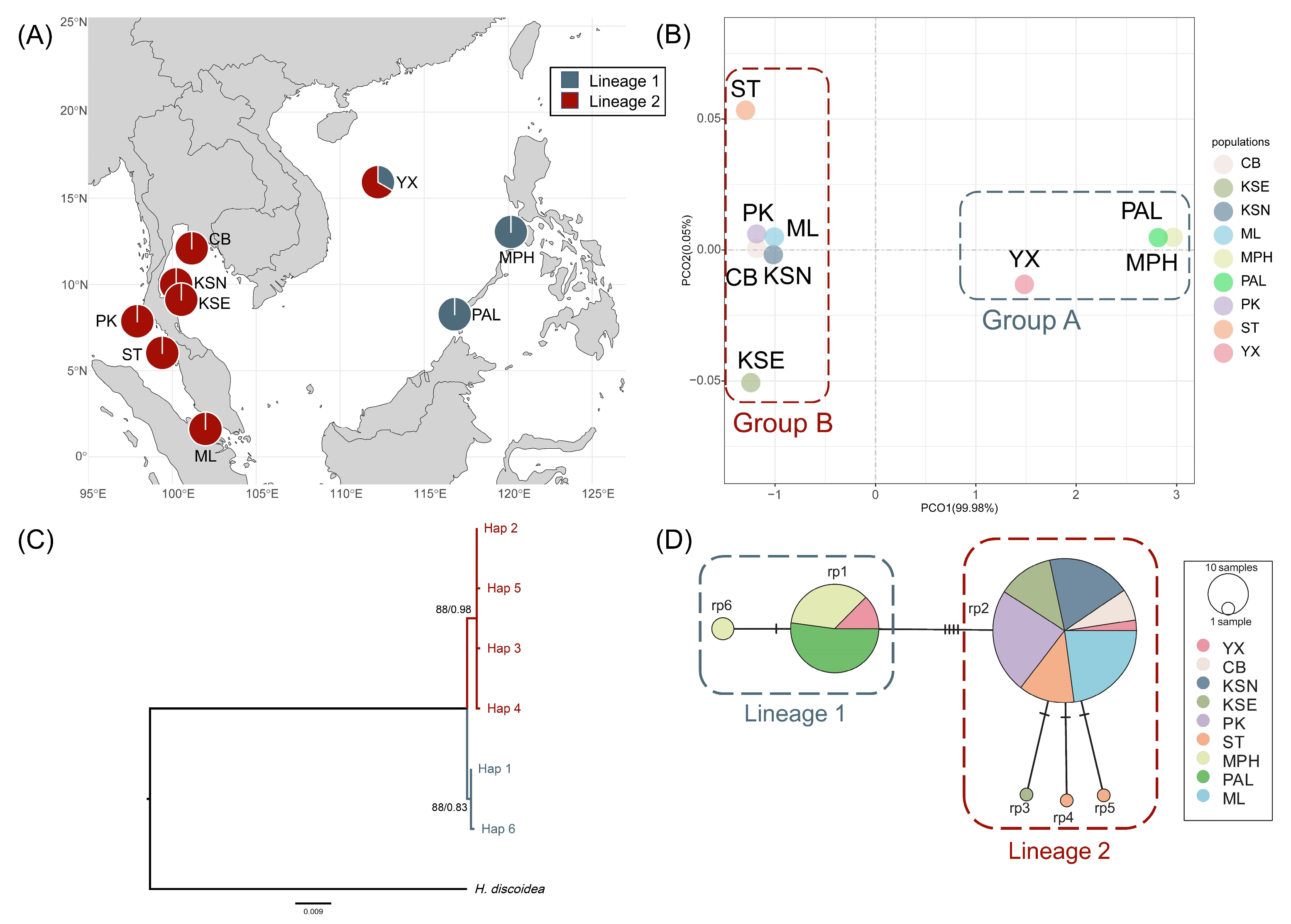
2.1. Genetic Diversity and Population Genetic Structure
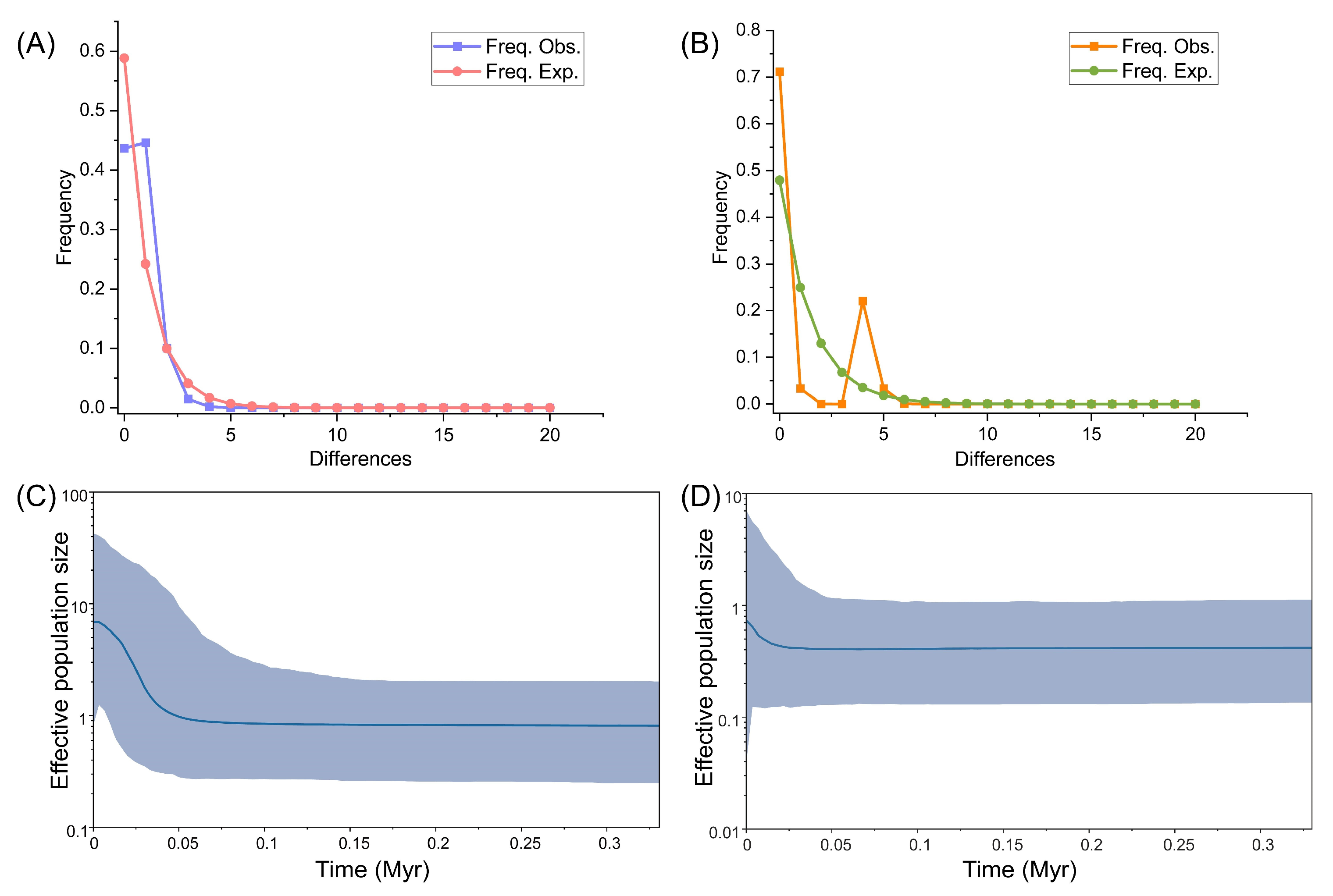
2.2. Demographical Population History
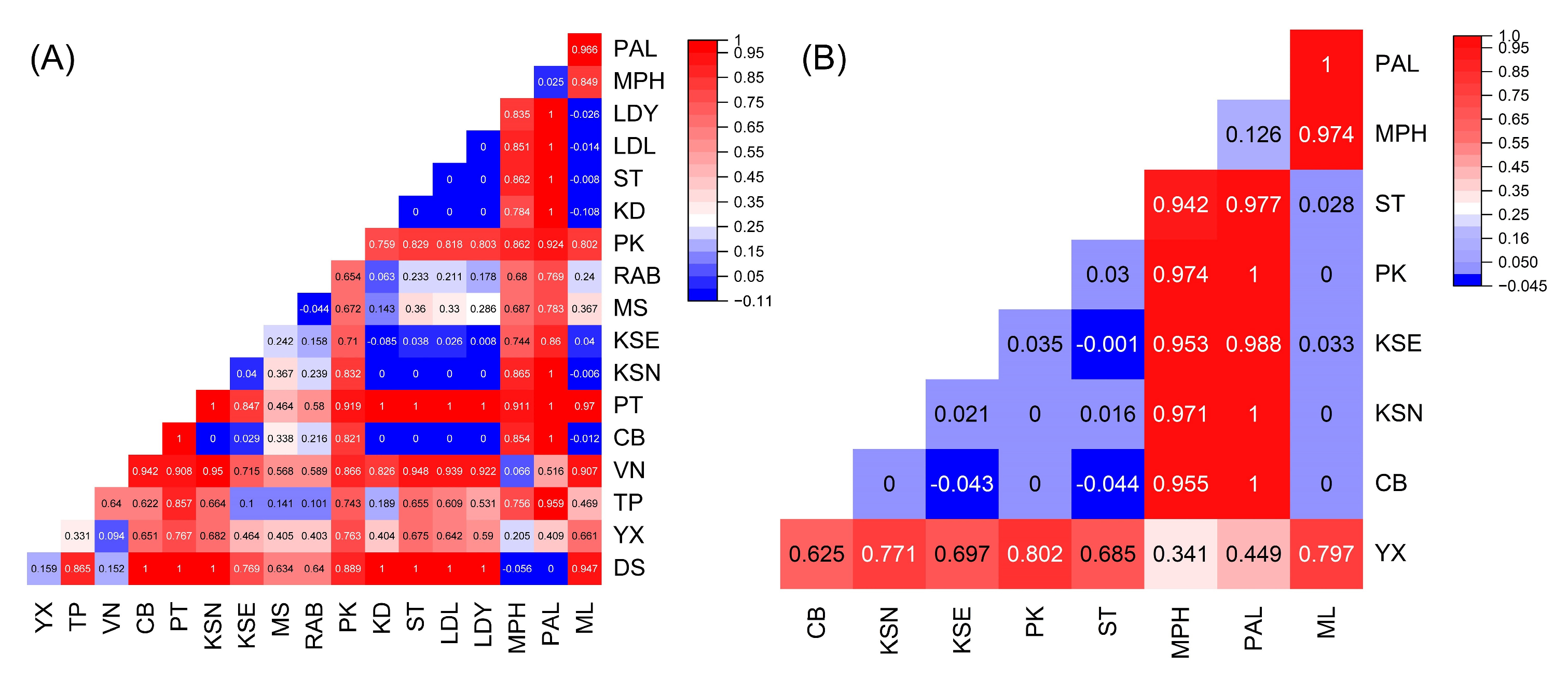
2.3. Population Gene Flow
3. Discussion
3.1. Genetic Connectivity Derived by Ocean Currents
3.2. Intraspecific Phylogeographical Pattern of H. macroloba
3.3. Conservation and Management
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and Amplification
4.2. Molecular Diversity and Phylogenetic Relationship
4.3. Population Genetic Structure and Differentiation
4.4. Divergence Time and Demographic History
4.5. Intraspecific Genetic Connectivity
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AICc | Akaike Information Criterion |
| ML | Maximum likelihood |
| BI | Bayesian inference |
| ESS | Effective sample size |
| PCoA | Principal component analysis |
| AMOVA | Analysis of molecular variance |
| Fst | Fixation index |
| BSP | Bayesian skyline plot |
| HPD | Highest posterior density |
| Nm | Migration rates |
| Myr | Million years |
| SCSTF | South China Sea throughflow |
| MU | Management unit |
References
- Jones, G.P.; Srinivasan, M.; Almany, G.R. Population connectivity and conservation of marine biodiversity. Oceanography 2007, 20, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN-WCPA. Guidelines for Conserving Connectivity Through Ecological Networks and Corridors. 2020. Available online: https://iucn.org/resources/publication/guidelines-conserving-connectivity-through-ecological-networks-and-corridors (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Krosby, M.; Tewksbury, J.; Haddad, N.M.; Hoekstra, J. Ecological connectivity for a changing climate. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 1686–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.H.; Brink, K.H.; Scott, B.E. Comparison of marine and terrestrial ecosystems: Suggestions of an evolutionary perspective influenced by environmental variation. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Baird, A.H.; Bellwood, D.R.; Card, M.; Connolly, S.R.; Folke, C.; Grosberg, R.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Kleypas, J.; et al. Climate change, human impacts, and the resilience of coral reefs. Science 2003, 301, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppainen, P.; van Nes, S.; Ceder, C.; Ceder, C.; Johannesson, K. Refuge function of marine algae complicates selection in an intertidal snail. Oecologia 2005, 143, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wefer, G. Carbonate production by algae Halimeda, Penicillus and Padina. Nature 1980, 285, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, S.A.; Opdyke, B.N.; Wilson, P.A.; Henstock, T.J. Significance of Halimeda bioherms to the global carbonate budget based on a geological sediment budget for the Northern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W.A. Calcified macroalgae—Critical to coastal ecosystems and vulnerable to change: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, H.; Tyberghein, L.; Pauly, K.; Vlaeminck, C.; Nieuwenhuyze, K.V.; Kooistra, W.H.C.F.; Leliaert, F.; De Clerck, O. Macroecology meets macroevolution: Evolutionary niche dynamics in the seaweed Halimeda. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Qu, M.; Yu, H.; Yin, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.; et al. Genome of Halimeda opuntia reveals differentiation of subgenomes and molecular bases of multinucleation and calcification in algae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2403222121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, T.Y.; Liu, W.W.; Liang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Liu, J.X.; Wu, W.; Yu, K.F.; et al. Multi-scale ocean dynamical processes in the Indo-Pacific Convergence Zone and their climatic and ecological effects. Earth Sci. Rev. 2023, 237, 104313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakun, J.; Prathep, A. Calcium carbonate productivity by Halimeda macroloba in the tropical intertidal ecosystem: The significant contributor to global carbonate budgets. Phycol. Res. 2019, 67, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, M.; Draisma, S.G.A.; Pongparadon, S.; Wichachucherd, B.; Noiraksar, T.; Hu, Z.M. Predicting macroalgal species distributions along the Thai-Malay Peninsula. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 267, 107760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongparadon, S.; Zuccarello, G.C.; Phang, S.M.; Kawai, H.; Hanyuda, T.; Prathep, A. Diversity of Halimeda (Chlorophyta) from the Thai-Malay Peninsula. Phycologia 2015, 54, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, N.N.T.; Nguyen, X.T.; Nguyen, X.V. Morphological variation and haplotype diversity of Halimeda macroloba and H. opuntia (Chlorophyta: Halimedaceae) from southern Vietnam. Vietnam J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2022, 22, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrick, R.C.; Bonatelli, I.A.; Hyseni, C.; Morales, A.; Pelletier, T.A.; Perez, M.F.; Rice, E.; Satler, J.D.; Symula, R.E.; Thomé, M.T.C.; et al. The evolution of phylogeographic data sets. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.; Shafer, H.L.; Leonard, O.R.; Kovach, M.J.; Schorr, M.; Morris, A.B. Chloroplast DNA sequence utility for the lowest phylogenetic and phylogeographic inferences in angiosperms: The tortoise and the hare IV. Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 1987–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, H.; Vlaeminck, C.; Sauvage, T.; Sherwood, A.R.; Leliaert, F.; De Clerck, O. Phylogenetic analysis of Pseudochlorodesmis strains reveals cryptic diversity above the family level in the Siphonous green algae (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijoux, L.; Verbruggen, H.; Mattio, L.; Duong, N.; Payri, C. Diversity of Halimeda (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta) in New Caledonia: A combined morphological and molecular study. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1465–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, R.; Hanyuda, T.; Kawai, H. Taxonomic re-examination of Japanese Halimeda species using genetic markers, and proposal of a new species Halimeda ryukyuensis (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta). Phycol. Res. 2015, 63, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, F.; Pasella, M.M.; Lee, M.E.; Verbruggen, H. Phylogeography of the Mediterranean green seaweed Halimeda tuna (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbruggen, H.; Ashworth, M.; LoDuca, S.T.; Vlaeminck, C.; Cocquyt, E.; Sauvage, T.; Zechman, F.W.; Littler, D.S.; Littler, M.; Leliaert, F.; et al. A multi-locus time-calibrated phylogeny of the siphonous green algae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 50, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Roches, S.; Pendleton, L.H.; Shapiro, B.; Palkovacs, E.P. Conserving intraspecific variation for nature’s contributions to people. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, T.; Fragkopoulou, E.; Vapillon, L.; Gouvêa, L.; Serrão, E.A.; Assis, J. Unravelling the role of oceanographic connectivity in the distribution of genetic diversity of marine forests at the global scale. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2024, 33, e13857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.; Selkoe, K.A.; Watson, J.; Siegel, D.A.; Zacherl, D.C.; Toonen, R.J. Ocean currents help explain population genetic structure. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, L.; Hays, G.C. Ocean currents, individual movements and genetic structuring of populations. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, S.; Wang, W.L.; Tseng, K.Y.; Draisma, S.G.A.; Dumilag, R.V.; Hu, Z.M.; Li, J.J.; Lai, P.H.; Mattio, L.; Sherwood, A.R.; et al. Seaweed diversification driven by Taiwan’s emergence and the Kuroshio Current: Insights from the cryptic diversity and phylogeography of Dichotomaria (Galaxauraceae, Rhodophyta). Front. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 12, 1346199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, L.; Faúndez, J.; Navarrete, S.A.; Broitman, B.R.; Aiken, C.M.; Saenz-Agudelo, P. Oceanographical-driven dispersal and environmental variation explain genetic structure in an upwelling coastal ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnaire, P.A.; Broquet, T.; Aurelle, D.; Viard, F.; Souissi, A.; Bonhomme, F.; Arnaud-Haond, S.; Bierne, N. Using neutral, selected, and hitchhiker loci to assess connectivity of marine populations in the genomic era. Evol. Appl. 2015, 8, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, L.J.; Smith, C.M.; Coyer, J.A.; Hunter, C.L.; Beach, K.S.; Vroom, P.S. Asexual propagation in the coral reef macroalga Halimeda (Chlorophyta, Bryopsidales): Production, dispersal and attachment of small fragments. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 278, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, W.H.C.F.; Verbruggen, H. Genetic patterns in the calcified tropical seaweeds Halimeda opuntia, H. distorta, H. hederacea, and H. minima (BRYOPSIDALES, CHLOROPHYTA) provide insights in species boundaries and interoceanic dispersal. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Kawamura, H.; Hong, H.; Qi, Y. A Review on the Currents in the South China Sea: Seasonal Circulation, South China Sea Warm Current and Kuroshio Intrusion. J. Oceanogr. 2000, 56, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Song, Y.T.; Yamagata, T. An introduction to the South China Sea throughflow: Its dynamics, variability, and application for climate. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2009, 47, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, M.E. The role of stepping-stone islands. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1980, 17, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasova, G.A.; Demenok, M.N.; Xuan, N.B.; Long, B.H. The role of atmospheric circulation in spatial and temporal variations in the structure of currents in the western South China Sea. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2016, 52, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Z.Z.; Yanagi, T. The influence of the Andaman Sea and the South China Sea on water mass in the Malacca Strait. La Mer 2006, 43, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.W.; Cheang, C.C.; Chirapart, A.; Gerung, G.; Tharith, C.; Ang, P. Homogeneous population of the brown alga Sargassum polycystum in Southeast Asia: Possible role of recent expansion and asexual propagation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Hu, Z.M.; Gao, X.; Sun, Z.M.; Choi, H.G.; Duan, D.L.; Endo, H. Oceanic currents drove population genetic connectivity of the brown alga Sargassum thunbergii in the north-west Pacific. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 44, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.S.; Zhang, S.S.; Yan, C.X.; Draisma, S.G.A.; Kantachumpoo, A.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.D.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Duan, D.L. Influence of Indo-Pacific ocean currents on the distribution and demographic patterns of the brown seaweed Sargassum polycystum in tropical east Asia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 895554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.D.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.S.; Liu, L.; Draisma, S.G.A.; Duan, D.L. Marine conditions in Andaman Sea shape the unique genetic structure of Sargassum plagiophyllum C. Agardh. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, G.H.; Leliaert, F.; Le Gall, L.; Coppejans, E.; De Clerck, O.; Nguyen, T.V.; Payri, C.E.; Miller, K.A.; Yoon, H.S. Ancient Tethyan vicariance and long-distance dispersal drive global diversification and cryptic speciation in the red seaweed Pterocladiella. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 849476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagourgue, L.; Leliaert, F.; Payri, C.E. Historical biogeographical analysis of the Udoteaceae (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta) elucidates origins of high species diversity in the Central Indo-Pacific, Western Indian Ocean and Greater Caribbean regions. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2022, 169, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichachucherd, B.; Prathep, A.; Zuccarello, G.C. Phylogeography of Padina boryana (Dictyotales, Phaeophyceae) around the Thai-Malay Peninsula. Eur. J. Phycol. 2014, 49, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulan, J.; Maneekat, S.; Zuccarello, G.C.; Muangmai, N. Phylogeographic patterns in cryptic species Bostrychia tenella (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta) across the Thai-Malay Peninsula. Algae 2022, 37, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggs, C.A.; Castilho, R.; Foltz, D.; Henzler, C.; Jolly, M.T.; Kelly, J.; Olsen, J.; Perez, K.E.; Stam, W.; Väinölä, R.; et al. Evaluating signatures of glacial refugia for north Atlantic benthic marine taxa. Ecology 2008, 89, S108–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhong, J. The genetic structure and connectivity of eight fish species in the Indo-Pacific convergence region. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2025, 44, 9–23, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Molengraaff, G. Modern deep-sea research in the East Indian Archipelago. Geogr. J. 1921, 57, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, M.I.; Taylor, D.; Hunt, C. Palaeoenvironments of insular Southeast Asia during the Last Glacial Period: A savanna corridor in Sundaland? Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005, 24, 2228–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.X. Response of western Pacific marginal seas to glacial cycles: Paleoceanographic and sedimentological features. Mar. Geol. 1999, 156, 5–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, H.; De Clerck, O.; Schils, T.; Kooistra, W.H.C.F.; Coppejans, E. Evolution and phylogeography of Halimeda section Halimeda (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 37, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengkaew, J.; Muangmai, N.; Zuccarello, G.C. Cryptic diversity of the mangrove-associated alga Bostrychia (Rhodomelaceae, Rhodophyta) from Thailand. Bot. Mar. 2016, 59, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, G. The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature 2000, 405, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau, G.; Coyer, J.A.; Veldsink, J.H.; Stam, W.T.; Olsen, J.L. Glacial refugia and recolonization pathways in the brown seaweed. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 3606–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.M.; Kantachumpoo, A.; Liu, R.Y.; Sun, Z.M.; Yao, J.T.; Komatsu, T.; Uwai, S.; Duan, D.L. A late Pleistocene marine glacial refugium in the south-west of Hainan Island, China: Phylogeographical insights from the brown alga. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, K.E.; Barber, P.H.; Crandall, E.D.; Ablan-Lagman, C.A.; Ambariyanto; Mahardika, G.N.; Manjaji-Matsumoto, B.M.; Juinio-Meñez, M.A.; Santos, M.D.; Starger, C.J.; et al. Comparative phylogeography of the coral triangle and implications for marine management. J. Mar. Biol. 2011, 2011, 396982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famà, P.; Wysor, B.; Kooistra, W.H.C.F.; Zuccarello, G.C. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Caulerpa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) inferred from chloroplast tufA gene. J. Phycol. 2002, 38, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremen, M.C.M.; Huisman, J.M.; Marcelino, V.R.; Verbruggen, H. Taxonomic revision of Halimeda (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta) in south-western Australia. Aust. Syst. Bot. 2016, 29, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanyuda, T.; Arai, S.; Ueda, K. Variability in the rbcL introns of Caulerpalean algae (Chlorophyta, Ulvophyceae). J. Plant Res. 2000, 113, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, N.E.; Dawes, C.J.; Pierce, S.K. Phylogenetic analysis of the large subunit RUBISCO gene supports the exclusion of Avrainvillea and Cladocephalus from the Udoteaceae (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchene, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kuhnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerli, P.; Mashayekhi, S.; Sadeghi, M.; Khodaei, M.; Shaw, K. Population genetic inference with MIGRATE. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Yao, J.; Roleda, M.Y.; Liang, Y.; Xu, R.; Lin, Y.; Gonzaga, S.M.C.; Du, Y.; Duan, D. Genetic Diversity and Connectivity of Reef-Building Halimeda macroloba in the Indo-Pacific Region. Plants 2025, 14, 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101497
Song X, Yao J, Roleda MY, Liang Y, Xu R, Lin Y, Gonzaga SMC, Du Y, Duan D. Genetic Diversity and Connectivity of Reef-Building Halimeda macroloba in the Indo-Pacific Region. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101497
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xiaohan, Jianting Yao, Michael Y. Roleda, Yanshuo Liang, Rui Xu, Yude Lin, Shienna Mae C. Gonzaga, Yuqun Du, and Delin Duan. 2025. "Genetic Diversity and Connectivity of Reef-Building Halimeda macroloba in the Indo-Pacific Region" Plants 14, no. 10: 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101497
APA StyleSong, X., Yao, J., Roleda, M. Y., Liang, Y., Xu, R., Lin, Y., Gonzaga, S. M. C., Du, Y., & Duan, D. (2025). Genetic Diversity and Connectivity of Reef-Building Halimeda macroloba in the Indo-Pacific Region. Plants, 14(10), 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101497





