Non-Canonical Inter-Protein Interactions of Key Proteins Belonging to Cytokinin Signaling Pathways
Abstract
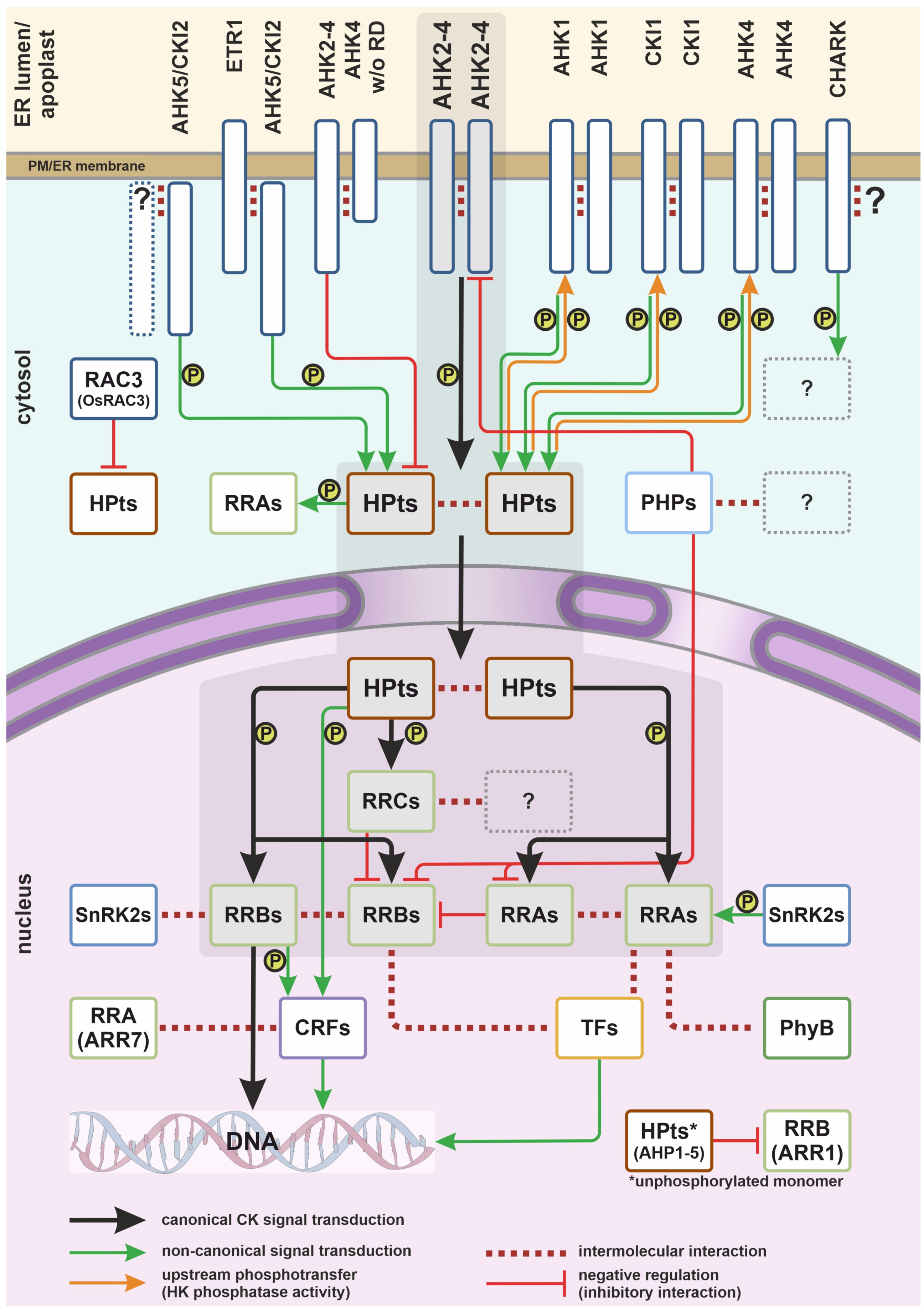
1. Introduction
2. Cytokinin Receptors
2.1. Negative Regulation of Cytokinin Signaling by Cytokinin Receptors
2.2. Interaction of Cytokinin Receptors with Other Histidine Kinases
2.3. Non-Canonical Interactions of Cytokinin Receptors with Other MSP Members
2.4. Non-Canonical Cytokinin Receptor
3. Phosphotransmitters
3.1. Negative Regulation of Cytokinin Signaling by Phosphotransmitters
3.2. Dimerization of Phosphotransmitters
4. Interactions of Phosphotransmitters with Non-Cytokinin Histidine Kinases
4.1. Interactions of Phosphotransmitters with ETR1
4.2. Interactions of Phosphotransmitters with AHK1
4.3. Interactions of Phosphotransmitters with CKI1
4.4. Interactions of Phosphotransmitters with AHK5/CKI2
4.5. Interactions of Phosphotransmitters with CRFs
4.6. Interactions of Phosphotransmitters with Molecular Switches
5. Response Regulators
5.1. Dimerization of Type-A Response Regulators
5.2. Interactions of Response Regulators with Kinases
5.3. Interactions of Response Regulators with Other Transcriptional Factors and Transcriptional Modulators
5.4. Interactions of Response Regulators with Phytochromes
5.5. Signal Overlap and Non-Canonical Interactions of CK-Related Proteins
- (1)
- Why does the CK signaling system need such a redundancy of components? For example, there are 3/5 CHKs, 5/2 HPts, 10/13 RRAs, and 11/13 RRBs in Arabidopsis and rice, respectively. Such signal overlap seems unnecessary simply to create a failsafe system [56].
- (2)
- How does a plant differentiate the source of a signal and form an adequate response? In other words, what is the basis for CK specificity? CKs affect a wide range of aspects of plant growth and development and regulate responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. The roles of these hormones can be different, and sometimes opposite, depending not only on the age of the plant and its stage of development but also on the type of organ and tissue where they work (reviewed, for example, in [8,172,173].
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishimura, C.; Ohashi, Y.; Sato, S.; Kato, T.; Tabata, S.; Ueguchi, C. Histidine kinase homologs that act as cytokinin receptors possess overlapping functions in the regulation of shoot and root growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartrina, I.; Otto, E.; Strnad, M.; Werner, T.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin regulates the activity of reproductive meristems, flower organ size, ovule formation, and thus seed yield in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dello Ioio, R.; Linhares, F.S.; Sabatini, S. Emerging role of cytokinin as a regulator of cellular differentiation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Leyser, O. Auxin, cytokinin and the control of shoot branching. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Ramireddy, E.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin as a positional cue regulating lateral root spacing in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4759–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cortijo, S.; Korsbo, N.; Roszak, P.; Schiessl, K.; Gurzadyan, A.; Wightman, R.; Jönsson, H.; Meyerowitz, E. Molecular mechanism of cytokinin-activated cell division in Arabidopsis. Science 2021, 371, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin action in plant development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Cytokinin signaling in plant development. Development 2018, 145, dev149344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortleven, A.; Leuendorf, J.E.; Frank, M.; Pezzetta, D.; Bolt, S.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin Action in response to abiotic and biotic stresses in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 998–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira-Rodado, V. New insights into Multistep-Phosphorelay (MSP)/Two-Component System (TCS) regulation: Are plants and bacteria that different? Plants 2019, 8, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, M.; Dabi, T.; Chory, J. Structural basis for cytokinin recognition by Arabidopsis thaliana histidine kinase 4. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steklov, M.Y.; Lomin, S.N.; Osolodkin, D.I.; Romanov, G.A. Structural basis for cytokinin receptor signaling: An evolutionary approach. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomin, S.N.; Krivosheev, D.M.; Steklov, M.Y.; Arkhipov, D.V.; Osolodkin, D.I.; Schmülling, T.; Romanov, G.A. Plant membrane assays with cytokinin receptors underpin the unique role of free cytokinin bases as biologically active ligands. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, A.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin signal perception and transduction. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, G.A. How do cytokinins affect the cell? Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 56, 268–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, G.E.; Shiu, S.-H.; Armitage, J.P. Two-component systems and their co-option for eukaryotic signal transduction. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R320–R330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipov, D.V.; Lomin, S.N.; Myakushina, Y.A.; Savelieva, E.M.; Osolodkin, D.I.; Romanov, G.A. Modeling of protein–protein interactions in cytokinin signal transduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipov, D.V.; Lomin, S.N.; Romanov, G.A. A Model of the Full-Length Cytokinin Receptor: New Insights and Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Wang, M.; An, Y. Overexpression of a B-type cytokinin response regulator (OsORR2) reduces plant height in rice. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1780405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, W.G.; Romanov, G.A.; Köllmer, I.; Bürkle, L.; Schmülling, T. Immediate-early and delayed cytokinin response genes of Arabidopsis thaliana identified by genome-wide expression profiling reveal novel cytokinin-sensitive processes and suggest cytokinin action through transcriptional cascades. Plant J. 2005, 44, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, W.G.; Schmülling, T. Transcript profiling of cytokinin action in Arabidopsis roots and shoots discovers largely similar but also organ-specific responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschiedrich, C.P.; Keidel, V.; Szurmant, H. Molecular Mechanisms of Two-Component Signal Transduction. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 3752–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuendorf, J.E.; Schmülling, T. Meeting at the DNA: Specifying cytokinin responses through transcription factor complex formation. Plants 2021, 10, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Sheen, J. Two-component circuitry in Arabidopsis cytokinin signal transduction. Nature 2001, 413, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, J.P.; Deruère, J.; Maxwell, B.B.; Morris, V.F.; Hutchison, C.E.; Ferreira, F.J.; Schaller, G.E.; Kieber, J.J. Cytokinin regulates type-A Arabidopsis Response Regulator activity and protein stability via two-component phosphorelay. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3901–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, A.; Brault, M.; Frugier, F.; Kuderova, A.; Lindner, A.C.; Motyka, V.; Rashotte, A.M.; Schwartzenberg, K.V.; Vankova, R.; Schaller, G.E. Nomenclature for members of the two-component signaling pathway of plants. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallmeroth, N.; Jeschke, D.; Slane, D.; Nägele, J.; Veerabagu, M.; Mira-Rodado, V.; Berendzen, K.W. ARR22 overexpression can suppress plant Two-Component Regulatory Systems. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Sakurai, K.; Imamura, A.; Nakamura, A.; Ueguchi, C.; Mizuno, T. Compilation and characterization of histidine-containing phosphotransmitters implicated in His-to-Asp phosphorelay in plants: AHP signal transducers of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 2486–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mähönen, A.P.; Bishopp, A.; Higuchi, M.; Nieminen, K.M.; Kinoshita, K.; Törmäkangas, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Oka, A.; Kakimoto, T.; Helariutta, Y. Cytokinin signaling and its inhibitor AHP6 regulate cell fate during vascular development. Science 2006, 311, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, A.; Soni, P.; Nongpiur, R.C.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Mapping the ‘Two-component system’ network in rice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, C.; Rawat, N.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Knockdown of OsPHP1 Leads to Improved Yield Under Salinity and Drought in Rice via Regulating the Complex Set of TCS Members and Cytokinin Signalling. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 48, 2769–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougel, C.; Zhulin, I.B. CHASE: An extracellular sensing domain common to transmembrane receptors from prokaryotes, lower eukaryotes and plants. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekárová, B.; Szmitkowska, A.; Dopitová, R.; Degtjarik, O.; Žídek, L.; Hejátko, J. Structural aspects of multistep phosphorelay-mediated signaling in plants. Mol. Plant 2016, 29, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomin, S.N.; Myakushina, Y.A.; Arkhipov, D.V.; Leonova, O.G.; Popenko, V.I.; Schmülling, T.; Romanov, G.A. Studies of cytokinin receptor-phosphotransmitter interaction provide evidences for the initiation of cytokinin signalling in the endoplasmic reticulum. Funct Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Miwa, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Yamada, H.; Aiba, H.; Mizuno, T. The Arabidopsis sensor His-kinase, AHk4, can respond to cytokinins. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Higuchi, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Seki, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Kato, T.; Tabata, S.; Shinozaki, K.; Kakimoto, T. Identification of CRE1 as a cytokinin receptor from Arabidopsis. Nature 2001, 409, 1060–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimoto, T. Perception and signal transduction of cytokinins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomin, S.N.; Myakushina, Y.A.; Kolachevskaya, O.O.; Getman, I.A.; Arkhipov, D.V.; Savelieva, E.M.; Osolodkin, D.I.; Romanov, G.A. Cytokinin perception in potato: New features of canonical players. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 3839–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomin, S.N.; Krivosheev, D.M.; Steklov, M.Y.; Osolodkin, D.I.; Romanov, G.A. Receptor properties and features of cytokinin signaling. Acta Naturae 2012, 4, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Chen, H.-C.; Sheen, J. Two-component signal transduction pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, B.N.; Agustoni, E.; Böhm, R.; Kaczmarczyk, A.; Mangia, F.; von Arx, C.; Jenal, U.; Hiller, S.; Plaza-Menacho, I.; Schirmer, T. Hybrid histidine kinase activation by cyclic di-GMP-mediated domain liberation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mähönen, A.P.; Higuchi, M.; Törmäkangas, K.; Miyawaki, K.; Pischke, M.S.; Sussman, M.R.; Helariutta, Y.; Kakimoto, T. Cytokinins regulate a bidirectional phosphorelay network in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Kakimoto, T.; Imamura, A.; Suzuki, T.; Ueguchi, C.; Mizuno, T. Biochemical characterization of a putative cytokinin-responsive His-kinase, CKI1, from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 1627–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.; Müller, S.; Drechsler, T.; Berleth, M.; Caesar, K.; Rohr, L.; Harter, K.; Groth, G. High-level expression, purification and initial characterization of recombinant Arabidopsis histidine kinase AHK1. Plants 2020, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Králová, M.; Kubalová, I.; Hajný, J.; Kubiasová, K.; Vagaská, K.; Ge, Z.; Gallei, M.; Semerádová, H.; Kuchařová, A.; Hönig, M.; et al. A decoy receptor derived from alternative splicing fine-tunes cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 1850–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleecker, A.B.; Estelle, M.A.; Somerville, C.; Kende, H. Insensitivity to ethylene conferred by a dominant mutation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 1988, 241, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ždárská, M.; Cuyacot, A.R.; Tarr, P.T.; Yamoune, A.; Szmitkowska, A.; Hrdinová, V.; Gelová, Z.; Meyerowitz, E.M.; Hejátko, J. ETR1 Integrates Response to Ethylene and Cytokinins into a Single Multistep Phosphorelay Pathway to Control Root Growth. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grefen, C.; Städele, K.; Růzicka, K.; Obrdlik, P.; Harter, K.; Horák, J. Subcellular localization and in vivo interactions of the Arabidopsis thaliana ethylene receptor family members. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, G.A.; Lomin, S.N.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin signaling: From the ER or from the PM? That is the question! New Phytol. 2018, 218, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiasová, K.; Montesinos, J.C.; Šamajová, O.; Nisler, J.; Mik, V.; Semerádová, H.; Plíhalová, L.; Novák, O.; Marhavý, P.; Cavallari, N.; et al. Cytokinin fluoroprobe reveals multiple sites of cytokinin perception at plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmitkowska, A.; Cuyacot, A.R.; Pekárová, A.; Ždárská, M.; Houser, J.; Komárek, J.; Jaseňáková, Z.; Jayasree, A.; Heunemann, M.; Ubogoeva, E.; et al. AHK5 mediates ETR1-initiated multistep phosphorelay in Arabidopsis. bioRxiv 2021, 460643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Duan, K.X.; Ma, B.; Yin, C.C.; Hu, Y.; Tao, J.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Cao, W.Q.; Chen, H.; Yang, C.; et al. Histidine kinase MHZ1/OsHK1 interacts with ethylene receptors to regulate root growth in rice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortay, H.; Mehnert, N.; Bürkle, L.; Schmülling, T.; Heyl, A. Analysis of protein interactions within the cytokinin-signaling pathway of Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 4631–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Aoyama, T.; Oka, A. Arabidopsis ARR1 and ARR2 response regulators operate as transcriptional activators. Plant J. 2000, 24, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortay, H.; Gruhn, N.; Pfeifer, A.; Schwerdtner, M.; Schmülling, T.; Heyl, A. Toward an interaction map of the two-component signaling pathway of Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3649–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshishian, E.A.; Rashotte, A.M. Plant cytokinin signalling. Essays Biochem. 2015, 58, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawa, M.; Cortleven, A.; Schmülling, T.; Heyl, A. Characterization of CHARK, an unusual cytokinin receptor of rice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berleth, M.; Berleth, N.; Minges, A.; Hänsch, S.; Burkart, R.C.; Stork, B.; Stahl, Y.; Weidtkamp-Peters, S.; Simon, R.; Groth, G. Molecular analysis of protein-protein interactions in the ethylene pathway in the different ethylene receptor subfamilies. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, R.L.; Coonfield, M.L.; Schaller, G.E. Histidine kinase activity of the ETR1 ethylene receptor from Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7825–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussatche, P.; Klee, H.J. Autophosphorylation activity of the Arabidopsis ethylene receptor multigene family. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48734–48741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Zhou, H.L.; Chen, T.; Gong, Y.; Cao, W.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y. Evidence for serine/threonine and histidine kinase activity in the tobacco ethylene receptor protein NTHK2. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerny, M.; Dycka, F.; Bobál’ová, J.; Brzobohatý, B. Early cytokinin response proteins and phosphoproteins of Arabidopsis thaliana identified by proteome and phosphoproteome profiling. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Kurata, N. Identification and characterization of cytokinin-signalling gene families in rice. Gene 2006, 382, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.E.; Li, J.; Argueso, C.; Gonzalez, M.; Lee, E.; Lewis, M.W.; Maxwell, B.B.; Perdue, T.D.; Schaller, G.E.; Alonso, J.M.; et al. The Arabidopsis histidine phosphotransfer proteins are redundant positive regulators of cytokinin signaling. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3073–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punwani, J.A.; Kieber, J.J. Localization of the Arabidopsis histidine phosphotransfer proteins is independent of cytokinin. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Yamashino, T.; Mizuno, T. Comparative studies of the AHP histidine-containing phosphotransmitters implicated in His-to-Asp phosphorelay in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.E.; Kieber, J.J. Signaling via histidine-containing phosphotransfer proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.; Bitto, E.; Bingman, C.A.; Allard, S.T.; Wesenberg, G.E.; Wrobel, R.L.; Fox, B.G.; Phillips, G.N. Crystal structure of a putative histidine-containing phosphotransfer protein from Oryza sativa. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2010, 53, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruszkowski, M.; Brzezinski, K.; Jedrzejczak, R.; Dauter, M.; Dauter, Z.; Sikorski, M.; Jaskolski, M. Medicago truncatula histidine-containing phosphotransfer protein: Structural and biochemical insights into the cytokinin transduction pathway in plants. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 3709–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, J.P.; Haberer, G.; Ferreira, F.J.; Deruère, J.; Mason, M.G.; Schaller, G.E.; Alonso, J.M.; Ecker, J.R.; Kieber, J.J. Type-A Arabidopsis response regulators are partially redundant negative regulators of cytokinin signaling. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyros, R.D.; Mathews, D.E.; Chiang, Y.H.; Palmer, C.M.; Thibault, D.M.; Etheridge, N.; Argyros, D.A.; Mason, M.G.; Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Type B response regulators of Arabidopsis play key roles in cytokinin signaling and plant development. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2102–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareek, A.; Singh, A.; Kumar, M.; Kushwaha, H.R.; Lynn, A.M.; Singla-Pareek, S.L. Whole genome analysis of Oryza sativa L. reveals similar architecture of two-component-signaling-machinery with Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 380–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, G.E.; Doi, K.; Hwang, I.; Kieber, J.J.; Khurana, J.P.; Kurata, N.; Mizuno, T.; Pareek, A.; Shiu, S.H.; Wu, P.; et al. Nomenclature for two-component signaling elements of rice. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Weir, N.R.; Hill, K.; Zhang, W.; Kim, H.J.; Shiu, S.H.; Schaller, G.E.; Kieber, J.J. Characterization of genes involved in cytokinin signaling and metabolism from rice. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1666–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.Y.; Cho, C.; Kim, J. Inducible expression of Arabidopsis response regulator 22 (ARR22), a type-C ARR, in transgenic Arabidopsis enhances drought and freezing tolerance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argueso, C.T.; Kieber, J.J. Cytokinin: From autoclaved DNA to two-component signaling. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 1429–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, G.E.; Kieber, J.J.; Shiu, S.H. Two-component signaling elements and histidyl-aspartyl phosphorelays. Arabidopsis Book 2008, 6, e0112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horák, J.; Janda, L.; Pekárová, B.; Hejátko, J. Molecular mechanisms of signalling specificity via phosphorelay pathways in Arabidopsis. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2011, 12, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan-Hirsch, J.; Tallerday, E.J.; Burr, C.A.; Hodgens, C.; Boeshore, S.L.; Beaver, K.; Melling, A.; Sari, K.; Kerr, I.D.; Šimura, J.; et al. Function of the pseudo phosphotransfer proteins has diverged between rice and Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2021, 106, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.I.; Ruszkowski, M. ARR1 and AHP interactions in the multi-step phosphorelay system. Front Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1537021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punwani, J.A.; Hutchison, C.E.; Schaller, G.E.; Kieber, J.J. The subcellular distribution of the Arabidopsis histidine phosphotransfer proteins is independent of cytokinin signaling. Plant J. 2010, 62, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharein, B.; Groth, G. Phosphorylation alters the interaction of the Arabidopsis phosphotransfer protein AHP1 with its sensor kinase ETR1. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, H.; Liang, W.L.; Liu, J.J.; Tian, H.Y.; Wang, L.H.; Wei, Y.H. Identification of the AHP family reveals their critical response to cytokinin regulation during adventitious root formation in apple rootstock. Front Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1511713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urao, T.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Plant histidine kinases: An emerging picture of two-component signal transduction in hormone and environmental responses. Sci. STKE 2001, 2001, re18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Kwok, S.F.; Bleecker, A.B.; Meyerowitz, E.M. Arabidopsis ethylene-response gene ETR1, similarity of product to two-component regulators. Science 1993, 262, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Sakai, H.; Nourizadeh, S.; Chen, Q.G.; Bleecker, A.B.; Ecker, J.R.; Meyerowitz, E.M. EIN4 and ERS2 are members of the putative ethylene receptor gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Hua, J.; Chen, Q.G.; Chang, C.; Medrano, L.J.; Bleecker, A.B.; Meyerowitz, E.M. ETR2 is an ETR1-like gene involved in ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5812–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urao, T.; Yakubov, B.; Satoh, R.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Seki, M.; Hirayama, T.; Shinozaki, K. A transmembrane hybrid-type histidine kinase in Arabidopsis functions as an osmosensor. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, R.; Horák, J.; Chaban, C.; Mira-Rodado, V.; Witthöft, J.; Elgass, K.; Grefen, C.; Cheung, M.K.; Meixner, A.J.; Hooley, R.; et al. The histidine kinase AHK5 integrates endogenous and environmental signals in Arabidopsis guard cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira-Rodado, V.; Veerabagu, M.; Witthöft, J.; Teply, J.; Harter, K.; Desikan, R. Identification of two-component system elements downstream of AHK5 in the stomatal closure response of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Guo, B.; Xie, X.; Yao, Y.; Peng, H.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ni, Z. A novel histidine kinase gene, ZmHK9, mediate drought tolerance through the regulation of stomatal development in Arabidopsis. Gene 2012, 501, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.; Jane, W.N.; Verslues, P.E. Role of the putative osmosensor Arabidopsis histidine kinase1 in dehydration avoidance and low-water-potential response. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.S.; Urao, T.; Qin, F.; Maruyama, K.; Kakimoto, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Functional analysis of AHK1/ATHK1 and cytokinin receptor histidine kinases in response to abscisic acid, drought, and salt stress in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20623–20628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, J.; Liu, J.; Bennett, M.H.; Mansfield, J.W.; Desikan, R. Arabidopsis histidine kinase. 5 regulates salt sensitivity and resistance against bacterial and fungal infection. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwama, A.; Yamashino, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakakibara, H.; Kakimoto, T.; Sato, S.; Kato, T.; Tabata, S.; Nagatani, A.; Mizuno, T. AHK5 histidine kinase regulates root elongation through an ETR1-dependent abscisic acid and ethylene signaling pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, K.; Wu, S.; Zhai, J.; Fang, L.; Zeng, S. A Comparative transcriptome analysis revealing the mechanism underlying the effect of maternal plant age on adventitious rooting of Euryodendron excelsum cuttings. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlbach, D.J.; Quirino, B.F.; Sussman, M.R. Analysis of the Arabidopsis histidine kinase ATHK1 reveals a connection between vegetative osmotic stress sensing and seed maturation. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, M.S.; Jones, L.G.; Otsuga, D.; Fernandez, D.E.; Drews, G.N.; Sussman, M.R. An Arabidopsis histidine kinase is essential for megagametogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15800–15805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejátko, J.; Pernisová, M.; Eneva, T.; Palme, K.; Brzobohatý, B. The putative sensor histidine kinase CKI1 is involved in female gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2003, 269, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Dong, H.; Mu, J.; Ren, B.; Zheng, B.; Ji, Z.; Yang, W.-C.; Liang, Y.; Zuo, J. Arabidopsis histidine kinase CKI1 acts upstream of HISTIDINE PHOSPHOTRANSFER PROTEINS to regulate female gametophyte development and vegetative growth. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1232–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.M. Ethylene signaling in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7710–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urao, T.; Miyata, S.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Possible His to Asp phosphorelay signaling in an Arabidopsis two-component system. FEBS Lett. 2000, 478, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharein, B.; Voet-van-Vormizeele, J.; Harter, K.; Groth, G. Ethylene signaling: Identification of a putative ETR1-AHP1 phosphorelay complex by fluorescence spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 377, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, C.; Lohrmann, J.; Albrecht, V.; Sweere, U.; Hummel, F.; Yoo, S.D.; Hwang, I.; Zhu, T.; Schäfer, E.; Kudla, J.; et al. The response regulator 2 mediates ethylene signalling hormone signal integration in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3290–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, I.H.; Aman, S.; Zubo, Y.; Ramzan, A.; Wang, X.; Shakeel, S.N.; Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Ethylene Inhibits Cell Proliferation of the Arabidopsis Root Meristem. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.M.; Kim, H.J.; Mathews, D.E.; Hutchison, C.E.; Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. A role for two-component signaling elements in the Arabidopsis growth recovery response to ethylene. Plant Direct 2018, 2, e00058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héricourt, F.; Chefdor, F.; Bertheau, L.; Tanigawa, M.; Maeda, T.; Guirimand, G.; Courdavault, V.; Larcher, M.; Depierreux, C.; Bénédetti, H.; et al. Characterization of histidine-aspartate kinase HK1 and identification of histidine phosphotransfer proteins as potential partners in a Populus multistep phosphorelay. Physiol. Plant 2013, 149, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertheau, L.; Miranda, M.; Foureau, E.; Rojas Hoyos, L.F.; Chefdor, F.; Héricourt, F.; Depierreux, C.; Morabito, D.; Papon, N.; Clastre, M.; et al. In planta validation of HK1 homodimerization and recruitment of preferential HPt downstream partners involved in poplar multistep phosphorelay systems. Plant Biosyst. 2013, 147, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertheau, L.; Chefdor, F.; Guirimand, G.; Courdavault, V.; Depierreux, C.; Morabito, D.; Brignolas, F.; Héricourt, F.; Carpin, S. Identification of five B-type response regulators as members of a multistep phosphorelay system interacting with histidine-containing phosphotransfer partners of Populus osmosensor. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertheau, L.; Djeghdir, I.; Foureau, E.; Chefdor, F.; Glevarec, G.; Oudin, A.; Depierreux, C.; Morabito, D.; Brignolas, F.; Courdavault, V.; et al. Insights into B-type RR members as signaling partners acting downstream of HPt partners of HK1 in the osmotic stress response in Populus. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 94, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeghdir, I.; Chefdor, F.; Bertheau, L.; Koudounas, K.; Carqueijeiro, I.; Lemos Cruz, P.; Courdavault, V.; Depierreux, C.; Larcher, M.; Lamblin, F.; et al. Evaluation of type-B RR dimerization in poplar: A mechanism to preserve signaling specificity? Plant Sci. 2012, 313, 111068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefdor, F.; Héricourt, F.; Koudounas, K.; Carqueijeiro, I.; Courdavault, V.; Mascagni, F.; Bertheau, L.; Larcher, M.; Depierreux, C.; Lamblin, F.; et al. Highlighting type A RRs as potential regulators of the dkHK1 multi-step phosphorelay pathway in Populus. Plant Sci. 2018, 277, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Héricourt, F.; Larcher, M.; Chefdor, F.; Koudounas, K.; Carqueijeiro, I.; Lemos Cruz, P.; Courdavault, V.; Tanigawa, M.; Maeda, T.; Depierreux, C.; et al. New Insight into HPts as Hubs in Poplar Cytokinin and Osmosensing Multistep Phosphorelays: Cytokinin Pathway Uses Specific HPts. Plants 2019, 8, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakimoto, T. CKI1, a histidine kinase homolog implicated in cytokinin signal transduction. Science 1996, 274, 982–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Suzuki, T.; Terada, K.; Takei, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Miwa, K.; Yamashino, T.; Mizuno, T. The Arabidopsis AHK4 histidine kinase is a cytokinin-binding receptor that transduces cytokinin signals across the membrane. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekárová, B.; Klumpler, T.; Třísková, O.; Horák, J.; Jansen, S.; Dopitová, R.; Borkovcová, P.; Papoušková, V.; Nejedlá, E.; Sklenář, V.; et al. Structure and binding specificity of the receiver domain of sensor histidine kinase CKI1 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2011, 67, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejátko, J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, G.T.; Dobesová, R.; Choi, S.; Choi, S.M.; Soucek, P.; Horák, J.; Pekárová, B.; Palme, K.; et al. The histidine kinases CYTOKININ-INDEPENDENT1 and ARABIDOPSIS HISTIDINE KINASE2 and 3 regulate vascular tissue development in Arabidopsis shoots. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2008–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimoto, T. Biosynthesis of cytokinins. J. Plant Res. 2003, 116, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grefen, C.; Harter, K. Plant two-component systems: Principles, functions, complexity and cross talk. Planta 2004, 219, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Reiss, K.; Veerabagu, M.; Heunemann, M.; Harter, K.; Stehle, T. Structure-function analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana histidine kinase AHK5 bound to its cognate phosphotransfer protein AHP1. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashotte, A.; Carson, S.; To, J.; Kieber, J. Expression profiling of cytokinin action in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutcliffe, J.W.; Hellmann, E.; Heyl, A.; Rashotte, A.M. CRFs form protein-protein interactions with each other and with members of the cytokinin signalling pathway in Arabidopsis via the CRF domain. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4995–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashotte, A.M.; Mason, M.G.; Hutchison, C.E.; Ferreira, F.J.; Schaller, G.E.; Kieber, J.J. A subset of Arabidopsis AP2 transcription factors mediates cytokinin responses in concert with a two-component pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11081–11085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Cho, C.; Lee, M.R.; Van Binh, N.; Kim, J. CYTOKININ RESPONSE FACTOR2 (CRF2) and CRF3 regulate lateral root development in response to cold stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1828–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmark, H.T.; Rashotte, A.M. Review—Cytokinin Response Factors: Responding to more than cytokinin. Plant Sci. 2019, 289, 110251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimášková, M.; O’Brien, J.A.; Khan, M.; Van Noorden, G.; Ötvös, K.; Vieten, A.; De Clercq, I.; Van Haperen, J.M.A.; Cuesta, C.; Hoyerová, K.; et al. Cytokinin response factors regulate PIN-FORMED auxin transporters. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucinotta, M.; Manrique, S.; Guazzotti, A.; Quadrelli, N.E.; Mendes, M.A.; Benkova, E.; Colombo, L. Cytokinin response factors integrate auxin and cytokinin pathways for female reproductive organ development. Development 2016, 143, 4419–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, C.K.; Brenner, W.G. Cytokinin Signaling downstream of the His-Asp phosphorelay network: Cytokinin-regulated genes and their functions. Front Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 604489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, P.J.; Compton, M.A.; Adams, C.I.; Rashotte, A.M. Cytokinin response factor 4 (CRF4) is induced by cold and involved in freezing tolerance. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Liang, W.; Zhu, G.; Dong, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; et al. The RAC/ROP GTPase activator OsRopGEF10 functions in crown root development by regulating cytokinin signaling in rice. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, S.; Kiba, T.; Imamura, A.; Hanaki, N.; Nakamura, A.; Suzuki, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Ueguchi, C.; Sugiyama, T.; Mizuno, T. Genes encoding pseudo-response regulators: Insight into His-to-Asp phosphorelay and circadian rhythm in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2000, 41, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T. Plant response regulators implicated in signal transduction and circadian rhythm. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Nakamichi, N. Pseudo-response regulators (PRRs) or true oscillator components (TOCs). Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClung, C.R. Plant circadian rhythms. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiba, T.; Naitou, T.; Koizumi, N.; Yamashino, T.; Sakakibara, H.; Mizuno, T. Combinatorial microarray analysis revealing arabidopsis genes implicated in cytokinin responses through the His->Asp Phosphorelay circuitry. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Jiao, F.; Chu, J.; Jin, G.; Chen, M.; Wu, P. The two-component signal system in rice (Oryza sativa L.): A genome-wide study of cytokinin signal perception and transduction. Genomics 2007, 89, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, I.B.; Deruere, J.; Kieber, J.J. Characterization of the response of the Arabidopsis response regulator gene family to cytokinin. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiba, T.; Yamada, H.; Sato, S.; Kato, T.; Tabata, S.; Yamashino, T.; Mizuno, T. The type-A response regulator, ARR15, acts as a negative regulator in the cytokinin-mediated signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, A.; Yoshino, Y.; Mizuno, T. Cellular localization of the signaling components of Arabidopsis His-to-Asp phosphorelay. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 2113–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Koizumi, N.; Nakamichi, N.; Kiba, T.; Yamashino, T.; Mizuno, T. Rapid response of Arabidopsis T87 cultured cells to cytokinin through His-to-Asp phosphorelay signal transduction. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 1966–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiba, T.; Aoki, K.; Sakakibara, H.; Mizuno, T. Arabidopsis response regulator, ARR22, ectopic expression of which results in phenotypes similar to the wol cytokinin-receptor mutant. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pils, B.; Heyl, A. Unraveling the evolution of cytokinin signaling. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horák, J.; Grefen, C.; Berendzen, K.W.; Hahn, A.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Stadelhofer, B.; Stahl, M.; Koncz, C.; Harter, K. The Arabidopsis thaliana response regulator ARR22 is a putative AHP phospho-histidine phosphatase expressed in the chalaza of developing seeds. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 15, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallmeroth, N.; Anastasia, A.K.; Harter, K.; Berendzen, K.W.; Mira-Rodado, V. Arabidopsis response regulator. 22 inhibits cytokinin-regulated gene transcription in vivo. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T. Two-component phosphorelay signal transduction systems in plants: From hormone responses to circadian rhythms. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 6912, 2263–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Sakurai, K.; Ueguchi, C.; Mizuno, T. Two types of putative nuclear factors that physically interact with histidine-containing phosphotransfer (Hpt) domains, signaling mediators in His-to-Asp phosphorelay, in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrmann, J.; Sweere, U.; Zabaleta, E.; Bäurle, I.; Keitel, C.; Kozma-Bognar, L.; Brennicke, A.; Schäfer, E.; Kudla, J.; Harter, K. The response regulator ARR2, a pollen-specific transcription factor involved in the expression of nuclear genes for components of mitochondrial complex I in Arabidopsis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2001, 265, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, K.; Imamura, A.; Katoh, E.; Hatta, T.; Tachiki, M.; Yamada, H.; Mizuno, T.; Yamazaki, T. Molecular structure of the GARP family of plant Myb-related DNA binding motifs of the Arabidopsis response regulators. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2015–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubo, Y.O.; Schaller, G.E. Role of the Cytokinin-Activated Type-B Response Regulators in Hormone Crosstalk. Plants 2020, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, M.G.; Mathews, D.E.; Argyros, D.A.; Maxwell, B.B.; Kieber, J.J.; Alonso, J.M.; Ecker, J.R.; Schaller, G.E. Multiple type-B response regulators mediate cytokinin signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 3007–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Roman, A.; Mack, T.R.; Stock, A.M. Structural analysis and solution studies of the activated regulatory domain of the response regulator ArcA: A symmetric dimer mediated by the alpha4-beta5-alpha5 face. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 349, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, T.R.; Gao, R.; Stock, A.M. Probing the roles of the two different dimers mediated by the receiver domain of the response regulator, PhoB. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 389, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capra, E.J.; Laub, M.T. Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerabagu, M.; Elgass, K.; Kirchler, T.; Huppenberger, P.; Harter, K.; Chaban, C.; Mira-Rodado, V. The Arabidopsis B-type response regulator. 18 homomerizes and positively regulates cytokinin responses. Plant J. 2012, 72, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.M.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, T.Q.; Xu, Z.G.; Ma, M.L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.W. The structure of B-ARR reveals the molecular basis of transcriptional activation by cytokinin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319335121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramireddy, E.; Brenner, W.G.; Pfeifer, A.; Heyl, A.; Schmülling, T. In planta analysis of a cis-regulatory cytokinin response motif in Arabidopsis and identification of a novel enhancer sequence. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, X.; Ljung, K.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Yang, F.; Wang, M.; Tao, Y. Type B Response Regulators Act As Central Integrators in Transcriptional Control of the Auxin Biosynthesis Enzyme TAA1. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1438–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Izawa, T.; Fuse, T.; Yamanouchi, U.; Kubo, T.; Shimatani, Z.; Yano, M.; Yoshimura, A. Ehd1, a B-type response regulator in rice, confers short-day promotion of flowering and controls FT-like gene expression independently of Hd1. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, L.H.; Yoon, J.; Pasriga, R.; An, G. Homodimerization of Ehd1 is required to induce flowering in rice. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hou, L.; Meng, J.; You, H.; Li, Z.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S.; Shi, Y. The antagonistic action of abscisic acid and cytokinin signaling mediates drought stress response in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgunova, E.; Taipale, J. Structural perspective of cooperative transcription factor binding. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-de la Rosa, N.; Sotillo, B.; Miskolczi, P.; Gibbs, D.J.; Vicente, J.; Carbonero, P.; Oñate-Sánchez, L.; Holdsworth, M.J.; Bhalerao, R.; Alabadí, D.; et al. Large-scale identification of gibberellin-related transcription factors defines group VII ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTORS as functional DELLA partners. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-de la Rosa, N.; Pfeiffer, A.; Hill, K.; Locascio, A.; Bhalerao, R.P.; Miskolczi, P.; Grønlund, A.L.; Wanchoo-Kohli, A.; Thomas, S.G.; Bennett, M.J.; et al. Genome Wide Binding Site Analysis Reveals Transcriptional Coactivation of Cytokinin-Responsive Genes by DELLA Proteins. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Guo, D.; Wei, B.; Zhang, F.; Pang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, T.; Gu, H.; Qu, L.J.; et al. The TIE1 transcriptional repressor links TCP transcription factors with TOPLESS/TOPLESS-RELATED corepressors and modulates leaf development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yuan, R.; Zhang, T.; An, F.; Wang, N.; Lan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Arabidopsis TIE1 and TIE2 transcriptional repressors dampen cytokinin response during root development. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ye, T.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.Q.; Wu, Y. Cytokinin antagonizes ABA suppression to seed germination of Arabidopsis by downregulating ABI5 expression. Plant J. 2011, 68, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, C.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Hong, S.; Liang, Y.; Ren, B.; Zuo, J. Cytokinin antagonizes abscisic acid-mediated inhibition of cotyledon greening by promoting the degradation of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE5 protein in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, C.M.; Hecker, A.; Cheng, C.Y.; Brand, L.; Collani, S.; Schmid, M.; Schaller, G.E.; Wanke, D.; Harter, K.; Kieber, J.J. Role of BASIC PENTACYSTEINE transcription factors in a subset of cytokinin signaling responses. Plant J. 2018, 95, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweere, U.; Eichenberg, K.; Lohrmann, J.; Mira-Rodado, V.; Bäurle, I.; Kudla, J.; Nagy, F.; Schafer, E.; Harter, K. Interaction of the response regulator ARR4 with phytochrome B in modulating red light signaling. Science 2001, 294, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomé, P.A.; To, J.P.; Kieber, J.J.; McClung, C.R. Arabidopsis response regulators ARR3 and ARR4 play cytokinin-independent roles in the control of circadian period. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira-Rodado, V.; Sweere, U.; Grefen, C.; Kunkel, T.; Fejes, E.; Nagy, F.; Schäfer, E.; Harter, K. Functional cross-talk between two-component and phytochrome B signal transduction in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2595–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wybouw, B.; De Rybel, B. Cytokinin—A Developing Story. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Meng, Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, M. Research Progress on the Roles of Cytokinin in Plant Response to Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Pischke, M.S.; Mähönen, A.P.; Miyawaki, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Seki, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Kato, T.; Tabata, S.; et al. In planta functions of the Arabidopsis cytokinin receptor family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8821–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.W.; Oh, S.I.; Kim, Y.Y.; Yoo, K.S.; Cui, M.H.; Shin, J.S. Arabidopsis histidine-containing phosphotransfer factor 4 (AHP4) negatively regulates secondary wall thickening of the anther endothecium during flowering. Mol. Cells 2008, 25, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, M.G.; Li, J.; Mathews, D.E.; Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Type-B response regulators display overlapping expression patterns in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattolin, S.; Alandete-Saez, M.; Elliott, K.; Gonzalez-Carranza, Z.; Naomab, E.; Powell, C.; Roberts, J.A. Spatial and temporal expression of the response regulators ARR22 and ARR24 in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 4225–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hradilová, J.; Brzobohatý, B. Expression pattern of the AHP gene family from Arabidopsis thaliana and organ specific alternative splicing in the AHP5 gene. Biol. Plant 2007, 51, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, Y.; Imamura, A.; Kiba, T.; Amano, Y.; Yamashino, T.; Mizuno, T. Comparative studies on the type-B response regulators revealing their distinctive properties in the His-to-Asp phosphorelay signal transduction of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, G.E.; Ladd, A.N.; Lanahan, M.B.; Spanbauer, J.M.; Bleecker, A.B. The ethylene response mediator ETR1 from Arabidopsis forms a disulfide-linked dimer. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12526–12530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caesar, K.; Thamm, A.M.; Witthöft, J.; Elgass, K.; Huppenberger, P.; Grefen, C.; Horak, J.; Harter, K. Evidence for the localization of the Arabidopsis cytokinin receptors AHK3 and AHK4 in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 5571–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfetange, K.; Lomin, S.N.; Romanov, G.A.; Stolz, A.; Heyl, A.; Schmülling, T. The cytokinin receptors of Arabidopsis are located mainly to the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1808–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daudu, D.; Allion, E.; Liesecke, F.; Papon, N.; Courdavault, V.; Dugé de Bernonville, T.; Mélin, C.; Oudin, A.; Clastre, M.; Lanoue, A.; et al. CHASE-containing histidine kinase receptors in apple tree: From a common receptor structure to divergent cytokinin binding properties and specific functions. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, A.; Piya, S.; Fernandez, J.C.; Chervin, C.; Hewezi, T.; Binder, B.M. Ethylene receptors signal via a noncanonical pathway to regulate abscisic acid responses. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 910–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, X.L.T.; Prerostova, S.; Thu, N.B.A.; Thao, N.P.; Vankova, R.; Tran, L.P. Histidine kinases: Diverse functions in plant development and responses to environmental conditions. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 297–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xie, Y. OsPHP1 as a Negative Regulator of Cytokinin Signaling in Rice Stress Responses. Plant Cell Environ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, R.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, Z. The Interaction Network and Signaling Specificity of Two-Component System in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CK-Related Protein | Interaction Details | Interaction Partner | Role of Interaction | Experimental Evidence (Assay, Method) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHK2-4 | heterodimerization | CRE1int7 (AHK4 w/o RD) | Negative regulation of CK signaling. | BiFC | [44] |
| AHK4 | ← phosphate | AHP1-3,5 | Negative regulation of CK signaling. | Phosphotransfer in vitro, yeast system | [41] |
| AHK2 | phosphate → | ARR12,14 (type-B), | Unknown. | Y2H | [52] |
| AHP1-5 | complex formation in the absence of phosphate | ARR1 | Negative regulation of CK signaling. | BLI | [79] |
| Unknown | complex formation | CHARK | Branch of the cytokinin signaling pathway. | No | [56] |
| AHP2-3,5 | homo- and heterodimerization | AHP5 | Unknown. | Y2H | [52] |
| AHP2 | homodimerization | AHP2 | Unknown. | BiFC | [80] |
| AHP1 | homodimerization | AHP1 | Unknown. | Protein electrophoresis in vitro | [81] |
| AHP1-3 | homodimerization | AHP1-3 | Unknown. | BiFC | [33] |
| MdAHP1,6 | heterodimerization | MdAHP3 | Regulation of adventitious root formation. | BiFC Y2H | [83] |
| AHP1-3, StHP1a | homodimerization | AHP1-3, StHP1a | Unknown. | In silico methods | [17] |
| AHP1-3,5 | ← phosphate | ETR1 | Crosstalk between CK and ethylene signaling pathways. | BiFC Y2H | [46,81,102,103] |
| AHP2 HPt2,7 and 9 of poplar | ← phosphate | AHK1 (and orthologs) | Positive regulation of AHK1 signaling Crosstalk between CK, osmosensing and ABA signaling pathways. | Microscale thermophoresis in vitro, Y2H BiFC | [44,102,107] |
| AHP2 | phosphate → | AHK1 | Negative regulation of AHK1 signaling. | Microscale thermophoresis in vitro | [43] |
| AHP1,2,3,5 | ← phosphate | CKI1 | Positive regulation of CKI1 signaling. | Y2H, BiFC, Microscale thermophoresis in vitro | [41,100,102,116,117] |
| AHP1,2 | phosphate → | CKI1 | Negative regulation of CKI1 signaling. | Phosphotransfer in vitro | [43] |
| AHP1-3,5,6 | ← phosphate | AHK5/CKI2 | Positive regulation of AHK5 signaling. Crosstalk between CK, ethylene and ABA signaling pathways. | Y2H, BiFC, SPR | [89,90,95,120] |
| AHP1-5 | phosphate → | CRF1-8 | Branch of the cytokinin signaling pathway. Crosstalk between CK and auxin signaling (for CRF2,3,6). | Y2H, BiFC | [122,124] |
| ARR10,12 (RRBs) ARR7 (RRA) | complex formation | CRF1,2,6 | |||
| OsHP1,2 | complex formation | OsRAC3 | Inhibition of CK signal transduction. Crosstalk between CK and auxin signaling pathways. | Y2H Pull down assay and Co-IP in vitro | [130] |
| ARR5 (RRA) | homodimerization | ARR5 | Maintenance of the protein stability. Interaction with working partners. | Co-IP in vitro, LCI | [160] |
| ARR2 (RRB) | ← phosphate | ETR1 | Crosstalk between CK and ethylene signaling pathways. | Phosphotransfer in vitro | [104] |
| ARR5 (RRA) 1,11,12 (RRBs) | ← phosphate | SnRK2.2, SnRK2.3, SnRK2.6 | Crosstalk between CK and ABA signaling pathways. Maintenance of the ARR5 stability. Suppressing the activity of the kinases (for RRBs). | BiFC, LCI | [160] |
| ARR1 (RRB) | complex formation | DELLAs | Increase in the ARR1 transcriptional activity. Crosstalk between CK, auxin and gibberellin signaling pathways. | Co-IP in vitro, Y2H | [155,162,163] |
| ARR1 (RRB) | complex formation | EIN3 | Increase in the ARR1 transcriptional activity. Crosstalk between CK and ethylene signaling pathways. | BiFC | [155] |
| ARR4-6 (RRAs) | complex formation | ABI5 | Crosstalk between CK and ABA signaling pathways. | Pull down assay in vitro, Y2H, BiFC | [166,167] |
| ARR4,5 (RRAs) | complex formation | BPC1,6 | Regulation (positive/negative) of CK signaling. | Y2H | [168] |
| ARR11 (RRB) | complex formation | TIE1 | Transcriptional suppression of CK target gene(s). | Y2H | [164,165] |
| ARR1,2,10,11,12,14,18 (RRBs) | complex formation | TIE2 | Transcriptional suppression of CK target gene(s). | Y2H, LCI, Co-IP in vitro | |
| ARR3, ARR4 (RRAs) | complex formation | phyB | PhyB active form stabilization. Positive regulation of red light signaling. Crosstalk between CK and red light signaling. | Pull down assay in vitro, Y2H | [169,170] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savelieva, E.M.; Arkhipov, D.V.; Kozinova, A.V.; Romanov, G.A.; Lomin, S.N. Non-Canonical Inter-Protein Interactions of Key Proteins Belonging to Cytokinin Signaling Pathways. Plants 2025, 14, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101485
Savelieva EM, Arkhipov DV, Kozinova AV, Romanov GA, Lomin SN. Non-Canonical Inter-Protein Interactions of Key Proteins Belonging to Cytokinin Signaling Pathways. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101485
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavelieva, Ekaterina M., Dmitry V. Arkhipov, Anna V. Kozinova, Georgy A. Romanov, and Sergey N. Lomin. 2025. "Non-Canonical Inter-Protein Interactions of Key Proteins Belonging to Cytokinin Signaling Pathways" Plants 14, no. 10: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101485
APA StyleSavelieva, E. M., Arkhipov, D. V., Kozinova, A. V., Romanov, G. A., & Lomin, S. N. (2025). Non-Canonical Inter-Protein Interactions of Key Proteins Belonging to Cytokinin Signaling Pathways. Plants, 14(10), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101485





