Parental Reconstruction from a Half-Sib Population of Stoneless Jujube Ziziphus jujuba Mill. Based on Individual Specific SNP Markers Using Multiplex PCR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Selection of JingZao 39 Male Trees for Parental Reconstruction of Half-Sib Population
2.2. Selection of Individual Specific SNPs of JingZao 39
2.3. Confirmation of Male Parents of Half-Sib Plants Using SNPs and Identity by the Descent Method
2.4. Two-Round PCR
Multiplex PCR Data Description
3. Discussion
3.1. Development of a Two-Round Multiplex PCR Assay
3.2. Multiplex PCR-Based Target SNP-Seq Technology
3.3. SNPs and Whole Genomes Resequencing-Based Paternity Analysis
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Selection of Genome-Wide Perfect SNPs in Z. jujuba (JingZao 39)
4.2. Primer Design for Multiplex PCR
4.3. Construction of the Target SNP-Seq PCR Free Library
4.4. Data Analysis
4.5. Parentage Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, B.; Yang, S.; Tahir, M.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, M.; Kong, D.; Bo, W.; Pang, X. Integrative metabolome and transcriptome profiling reveal key metabolic regulatory networks in Ziziphus jujuba cv. Dongzao pulp. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.H.; Wu, C.S.; Wang, M. The jujube (Ziziphus jujuba mill.) fruit: A review of current knowledge of fruit composition and health benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3351–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Mohamed, M.N.; Singh, A.; Tiwari, D. Fruit Breeding: Approaches and Achievements; New India Publishing Agency: New Delhi, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, T.M.; Aranzana, M.J. Attention sports fans! The far-reaching contributions of bud sport mutants to horticulture and plant biology. Hortic. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Wang, J.; Miao, L.; Zhao, J.; Ke, Q.; Chen, B.; Qu, Q.; Zhou, T.; Xu, P. Development of an informative snp panel for molecular parentage analysis in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ren, J.; Tao, J. A snp in the promoter region of the vvmyba1 gene is responsible for differences in grape berry color between two related bud sports of grape. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 82, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichoux, E.; Lagache, L.; Wagner, S.; Chaumeil, P.; Léger, P.; Lepais, O.; Lepoittevin, C.; Malausa, T.; Revardel, E.; Salin, F. Current trends in microsatellite genotyping. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, M.J.; Dierens, L.; McWilliam, S.; Little, B.; Murphy, B.; Coman, G.J.; Barendse, W.; Henshall, J. Comparison of microsatellite and snp DNA markers for pedigree assignment in b lack t iger shrimp, p enaeus monodon. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D.W.; Pearson, J.V.; Szelinger, S.; Sekar, A.; Redman, M.; Corneveaux, J.J.; Pawlowski, T.L.; Laub, T.; Nunn, G.; Stephan, D.A. Identification of genetic variants using bar-coded multiplexed sequencing. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnirke, A.; Melnikov, A.; Maguire, J.; Rogov, P.; LeProust, E.M.; Brockman, W.; Fennell, T.; Giannoukos, G.; Fisher, S.; Russ, C. Solution hybrid selection with ultra-long oligonucleotides for massively parallel targeted sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wen, C. A new snp genotyping technology target snp-seq and its application in genetic analysis of cucumber varieties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biezuner, T.; Brilon, Y.; Arye, A.B.; Oron, B.; Kadam, A.; Danin, A.; Furer, N.; Minden, M.D.; Kim, D.D.H.; Shapira, S. An improved molecular inversion probe based targeted sequencing approach for low variant allele frequency. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2022, 4, lqab125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfer, E.J.; Stovold, G.T.; Li, Y.; Silva-Junior, O.B.; Grattapaglia, D.G.; Dungey, H.S. Parentage reconstruction in eucalyptus nitens using snps and microsatellite markers: A comparative analysis of marker data power and robustness. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laucou, V.; Launay, A.; Bacilieri, R.; Lacombe, T.; Adam-Blondon, A.-F.; Berard, A.; Chauveau, A.; de Andrés, M.T.; Hausmann, L.; Ibanez, J. Extended diversity analysis of cultivated grapevine vitis vinifera with 10k genome-wide snps. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, C.; Tumino, G.; Gardiman, M.; Crespan, M.; Bignami, C.; De Palma, L.; Barbagallo, M.G.; Muganu, M.; Morcia, C.; Novello, V. Parentage atlas of italian grapevine varieties as inferred from snp genotyping. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 605934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, S.; Wei, S.; Langer, C.; Knop, S.; Pischimarov, J.; Kull, M.; Stühmer, T.; Steinbrunn, T.; Bargou, R.; Einsele, H. Rare snps in receptor tyrosine kinases are negative outcome predictors in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, F. Analysis of Half-Sib Progeny Tests in Forestry; North Carolina State University and Departament of Forestry and Enviromental Resources: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, S.K.; Dhakad, A.K.; Sharma, R. Growth dynamics of different half-sib families of melia azedarach linn. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Gutiérrez, M.; Alonso, M.; Toval, G.; Díaz, R. Testing of selected pinus pinaster half-sib families for tolerance to pinewood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). For. Int. J. For. Res. 2018, 91, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, L.; Moutahir, H.; Cortina, J.; Vilagrosa, A. The role of population and half-sib family on driving suitable functional traits for quercus suber l. Forest restoration. Forests 2020, 11, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWoody, J.; Avise, J. Microsatellite variation in marine, freshwater and anadromous fishes compared with other animals. J. Fish Biol. 2000, 56, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodel, R.G.; Segovia-Salcedo, M.C.; Landis, J.B.; Crowl, A.A.; Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Douglas, N.A.; Germain-Aubrey, C.C.; Chen, S. The report of my death was an exaggeration: A review for researchers using microsatellites in the 21st century. Appl. Plant Sci. 2016, 4, 1600025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, Y.-x.; Li, K.; Qi, L.-x.; Zhang, Q.-f.; Wang, M.-c.; Xiao, J.-h. A novel three-round multiplex pcr for snp genotyping with next generation sequencing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4371–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Multiplex pcr-based next generation sequencing as a novel, targeted and accurate molecular approach for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1181348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migicovsky, Z.; Gardner, K.M.; Richards, C.; Chao, C.T.; Schwaninger, H.R.; Fazio, G.; Zhong, G.-Y.; Myles, S. Genomic consequences of apple improvement. Hortic. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnifro, E.M.; Ashshi, A.M.; Cooper, R.J.; Klapper, P.E. Multiplex pcr: Optimization and application in diagnostic virology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, T.M.; Marston, E.J.; Eagle, J.D.; Sthapit, S.R.; Hooker, M.A.; Skinner, D.Z.; See, D.R. Genotyping by multiplexed sequencing (gms): A customizable platform for genomic selection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D. and Zhang, C. Universal multiplex pcr: A novel method of simultaneous amplification of multiple DNA fragments. Plant Methods 2012, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, N.R.; Harmon, S.A.; Narum, S.R. Genotyping-in-thousands by sequencing (gt-seq): A cost effective snp genotyping method based on custom amplicon sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Fang, J.Z.; Duan, W.; Wu, L.R.; Zhang, A.W.; Dalchau, N.; Yordanov, B.; Petersen, R.; Phillips, A.; Zhang, D.Y. Predicting DNA hybridization kinetics from sequence. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewhey, R.; Warner, J.B.; Nakano, M.; Libby, B.; Medkova, M.; David, P.H.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Samuels, M.L.; Hutchison, J.B.; Larson, J.W. Microdroplet-based pcr enrichment for large-scale targeted sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Dumont, T.; Pope, B.J.; Hammet, F.; Southey, M.C.; Park, D.J. A high-plex pcr approach for massively parallel sequencing. Biotechniques 2013, 55, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, Y.; Takahagi, K.; Shimizu, M.; Inoue, K.; Mochida, K. Multiplex pcr targeted amplicon sequencing (mta-seq): Simple, flexible, and versatile snp genotyping by highly multiplexed pcr amplicon sequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 292952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchihashi, Z.; Dracopoli, N. Progress in high throughput snp genotyping methods. Pharmacogenom. J. 2002, 2, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Ren, Y.; Xu, C.; Wu, K.; Zou, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Development of multiple snp marker panels affordable to breeders through genotyping by target sequencing (gbts) in maize. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.J.; Nguyen, T.M.; Waterman, A.; Chalmers, K.J. Multiplex-ready pcr: A new method for multiplexed ssr and snp genotyping. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Fowler, N.; Walmsley, M.L.; Schmidt, T.; Scharrer, J.; Kowaleski, J.; Grimes, T.; Hoyos, S.; Chen, J. Analytical sensitivity comparison between singleplex real-time pcr and a multiplex pcr platform for detecting respiratory viruses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Long, J.; Zhang, B.; Shyr, Y. Steps to ensure accuracy in genotype and snp calling from illumina sequencing data. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, X.; Dong, J.; Cui, R.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; He, T.; Zheng, P.; Wang, R. A primary study of breeding system of ziziphus jujuba var. Spinosa. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, P.E.; Asfaw, A.; Tongoona, P.B.; Danquah, A.; Danquah, E.Y.; De Koeyer, D.; Asiedu, R. Pollination success in some white yam genotypes under polycross and nested mating designs. Int. J. Biol. Sci. Appl. 2018, 5, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.G.; Small, C.M.; Paczolt, K.A.; Ratterman, N.L. A practical guide to methods of parentage analysis. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, P.E.; Paterne, A.A.; Danquah, A.; Tongoona, P.B.; Danquah, E.Y.; De Koeyer, D.; Ikeogu, U.N.; Asiedu, R.; Asfaw, A. Paternity assignment in white guinea yam (Dioscorea rotundata) half-sib progenies from polycross mating design using snp markers. Plants 2020, 9, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momozawa, Y.; Mizukami, K. Unique roles of rare variants in the genetics of complex diseases in humans. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 66, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticca, E.L.; Belbin, G.M.; Gignoux, C.R. Current developments in detection of identity-by-descent methods and applications. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 722602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, E.A. Identity by descent: Variation in meiosis, across genomes, and in populations. Genetics 2013, 194, 301–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, S.R. Estimation of pairwise identity by descent from dense genetic marker data in a population sample of haplotypes. Genetics 2008, 178, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. High-resolution detection of identity by descent in unrelated individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The genome analysis toolkit: A mapreduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Fu, W.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kong, D.; Cao, M.; Pang, X.; Bo, W. Identification of key genes of fruit shape variation in jujube with integrating elliptic fourier descriptors and transcriptome. Plants 2024, 13, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenay-Greunke, Y.; Bohan, D.A.; Traugott, M.; Wallinger, C. Handling of targeted amplicon sequencing data focusing on index hopping and demultiplexing using a nested metabarcoding approach in ecology. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows–wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Summa, S.; Malerba, G.; Pinto, R.; Mori, A.; Mijatovic, V.; Tommasi, S. Gatk hard filtering: Tunable parameters to improve variant calling for next generation sequencing targeted gene panel data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J. Plink: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
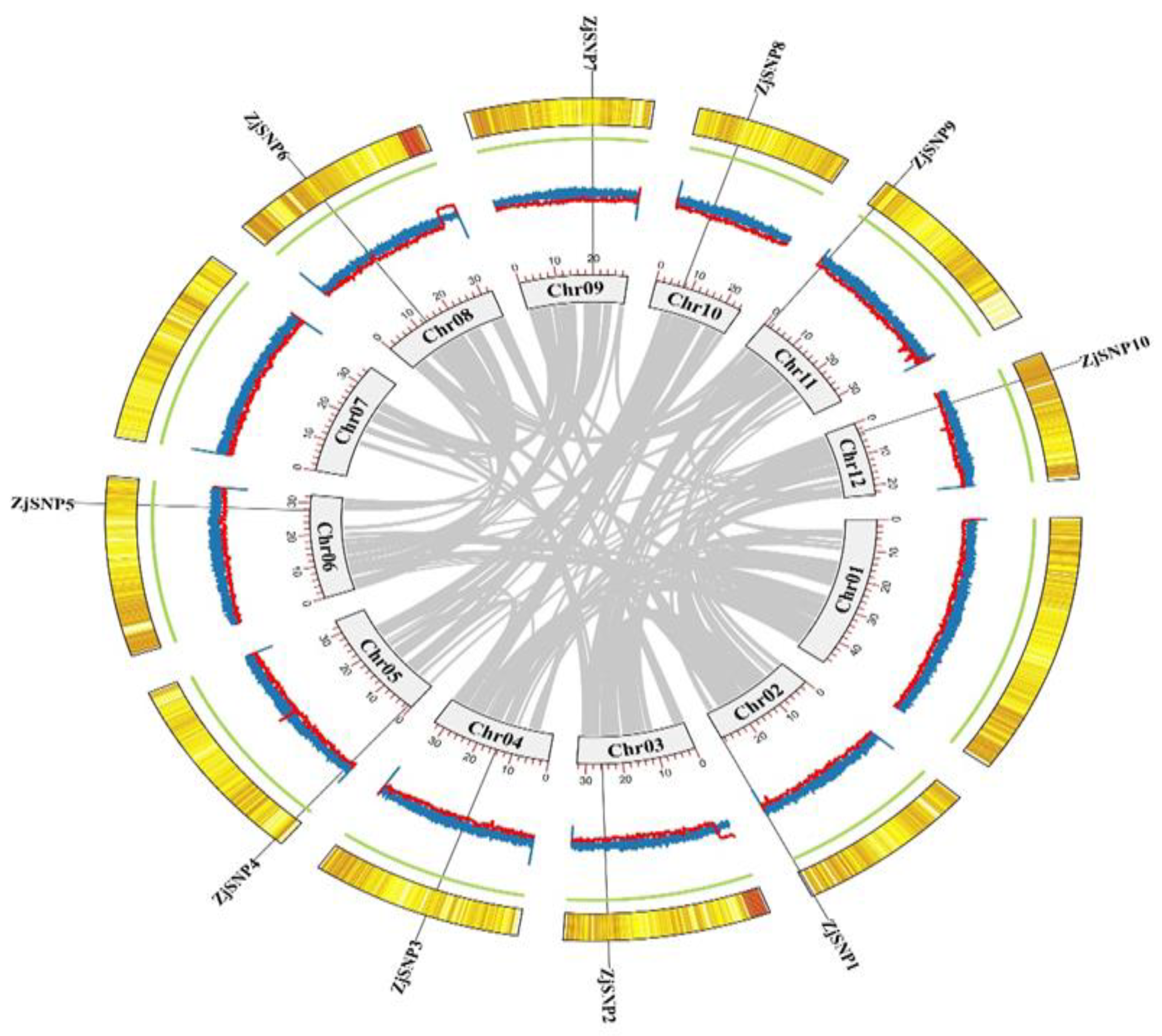
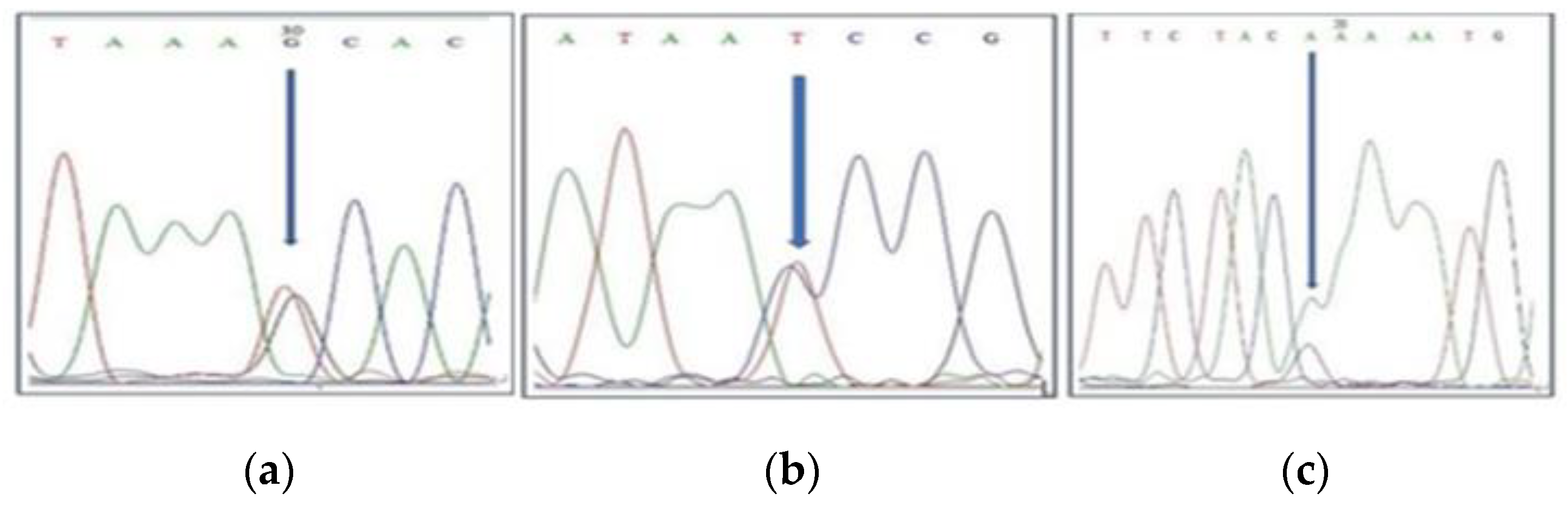


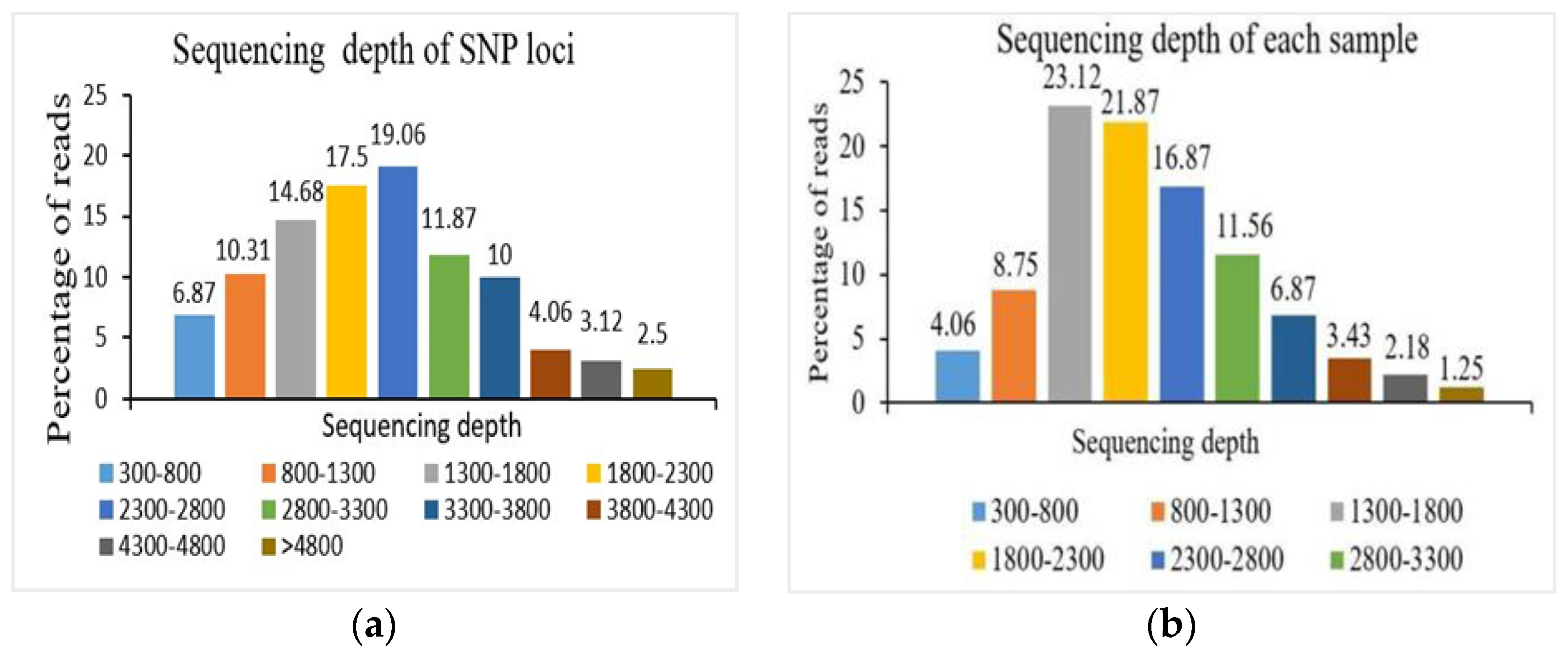
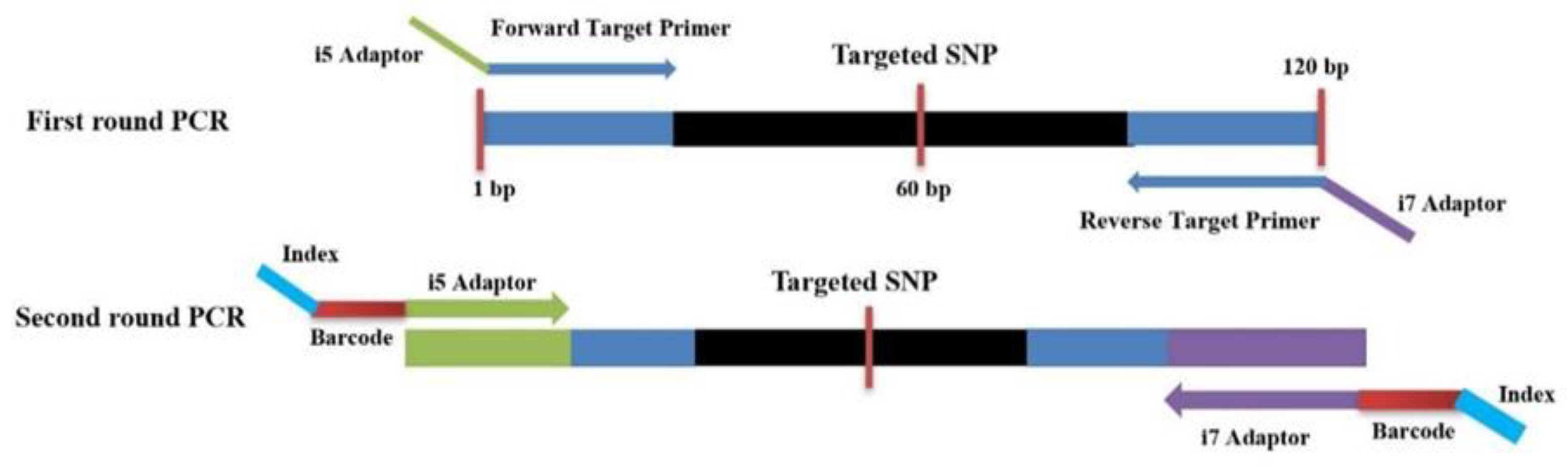
| Chromosome Number | SNP Position | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| CHR2 | 29727994 | TTGATGCATTATGAGAATAAGG | CAGTGTTTCCACATGATTCACAG |
| CHR6 | 27699126 | TTATAAGAATGCATGGCAGGTA | TCGGTGTTGGTCAACCAGGCTCA |
| CHR4 | 14484283 | TCAAGATGCACCAATTCTAAAGC | GGATCGGTCACCAAACGAGTCTC |
| CHR3 | 25613213 | ACCAACAAAGGACATACCAAAG | TTAAACCCTATAAGTGATATG |
| CHR11 | 1081719 | GATGCTTTGTCATTGATTTATGCTC | TTAAGACAACCACAACAAAATTTGC |
| CHR12 | 3218647 | AGAACCCTGTACAACATGGAAG | CCGCAAGGTTCTCCTCTGAAT |
| CHR10 | 7524906 | AAGAGGAGCTAGCTGGTACCTCC | GAGCTAACATTCAAGTGAAAAC |
| CHR9 | 19998728 | AGCATACCTCAAACCCTCGGA | CATGAAAATTGAAAGGGAAGAAAG |
| CHR8 | 12945656 | TCTAATCACATGTTGGTTAGG | ATAAGCCTTTATGATACAAACC |
| CHR5 | 992412 | GTGCCCCTTGCATTTTAGTCTG | GCCATCTCAAGGAGTATAACTTTG |
| Forward Primer PCR1 | Reverse Primer PCR1 |
|---|---|
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTTGATGCATTATGAGAATAAGG | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTCCAGTGTTTCCACATGATTCACAG |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTTATAAGAATGCATGGCAGGTA | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTTCGGTGTTGGTCAACCAGGCTCA |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTCAAGATGCACCAATTCTAAAGC | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTGGATCGGTCACCAAACGAGTCTC |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGACCAACAAAGGACATACCAAAG | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTTTAAACCCTATAAGTGATATG |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGGATGCTTTGTCATTGATTTATGCTC | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTTTAAGACAACCACAACAAAATTTGC |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGAGAACCCTGTACAACATGGAAG | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTCCGCAAGGTTCTCCTCTGAAT |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGAAGAGGAGCTAGCTGGTACCTCC | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTGAGCTAACATTCAAGTGAAAAC |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGAGCATACCTCAAACCCTCGGA | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTCATGAAAATTGAAAGGGAAGAAAG |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTCTAATCACATGTTGGTTAGG | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTATAAGCCTTTATGATACAAACC |
| TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGGTGCCCCTTGCATTTTAGTCTG | TCTCACACATATTCTCTGTGCCATCTCAAGGAGTATAACTTTG |
| Forward Primer PCR2 | Reverse Primer PCR2 |
|---|---|
| AATATAGGTATCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTGGAGATCTCACACATA |
| AATATATGAATCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTCAAGATCTCACACATA |
| AATATTACCATCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTACCATCTCACACATA |
| AATATCAGAATCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTCAGAATCTCACACATA |
| AATATCAAGTTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTCAAGTTCTCACACATA |
| AATATTTCGTTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTTCGTTCTCACACATA |
| AATATTCCGATCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTCCGATCTCACACATA |
| AATATTGAGCTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTGAGCTCTCACACATA |
| AATATCTGACTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTCTGACTCTCACACATA |
| AATATCCTCGTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTCCTCGTCTCACACATA |
| AATATAGGTGTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTAGGTGTCTCACACATA |
| AATATTCTAATCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTCTAATCTCACACATA |
| AATATTTGGATCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTTGGATCTCACACATA |
| AATATTCTAGTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTCTAGTCTCACACATA |
| AATATTCTGGTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTCTGGTCTCACACATA |
| AATATCTATTTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTCTATTTCTCACACATA |
| AATATAGGCATCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTAGGCATCTCACACATA |
| AATATTTAGTTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTTTAGTTCTCACACATA |
| AATATATCCGTCGTCGGCAGC | CCTCTATCCGTCTCACACATA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tahir, M.; Ren, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, M.; Refaiy, M.; Cao, M.; Kong, D.; Pang, X. Parental Reconstruction from a Half-Sib Population of Stoneless Jujube Ziziphus jujuba Mill. Based on Individual Specific SNP Markers Using Multiplex PCR. Plants 2024, 13, 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13223163
Tahir M, Ren Y, Wu B, Li M, Refaiy M, Cao M, Kong D, Pang X. Parental Reconstruction from a Half-Sib Population of Stoneless Jujube Ziziphus jujuba Mill. Based on Individual Specific SNP Markers Using Multiplex PCR. Plants. 2024; 13(22):3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13223163
Chicago/Turabian StyleTahir, Muhammad, Yue Ren, Bo Wu, Meiyu Li, Mohamed Refaiy, Ming Cao, Decang Kong, and Xiaoming Pang. 2024. "Parental Reconstruction from a Half-Sib Population of Stoneless Jujube Ziziphus jujuba Mill. Based on Individual Specific SNP Markers Using Multiplex PCR" Plants 13, no. 22: 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13223163
APA StyleTahir, M., Ren, Y., Wu, B., Li, M., Refaiy, M., Cao, M., Kong, D., & Pang, X. (2024). Parental Reconstruction from a Half-Sib Population of Stoneless Jujube Ziziphus jujuba Mill. Based on Individual Specific SNP Markers Using Multiplex PCR. Plants, 13(22), 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13223163






