The Influence of Sodium Humate on the Biosynthesis and Contents of Flavonoid Constituents in Lemons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
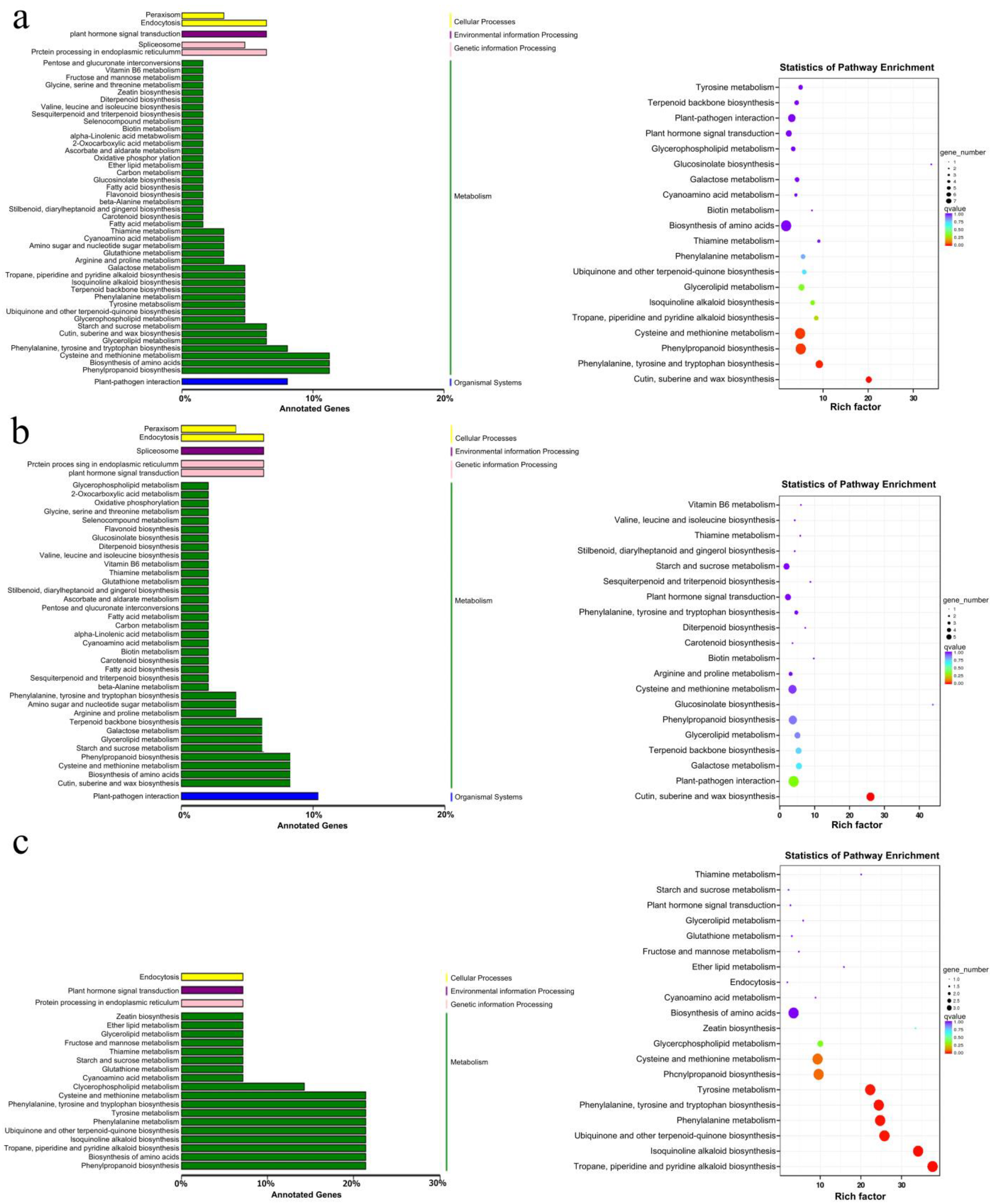
2.1. Analysis of the Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) between the Distilled-Water-Treated and Sodium-Humate-Treated Groups
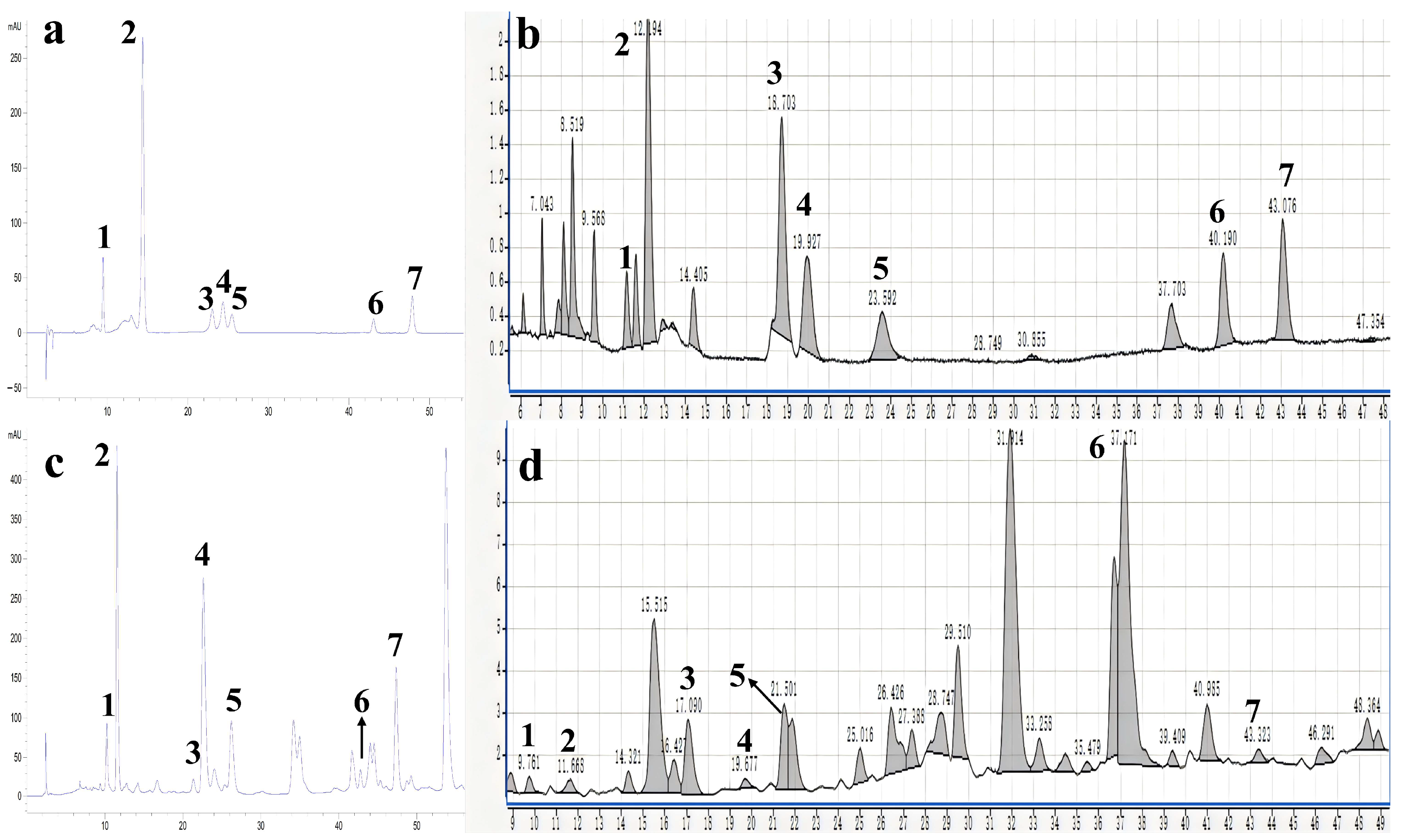
2.2. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis on Flavonoids from the Lemon Peels
2.3. Method Evaluation
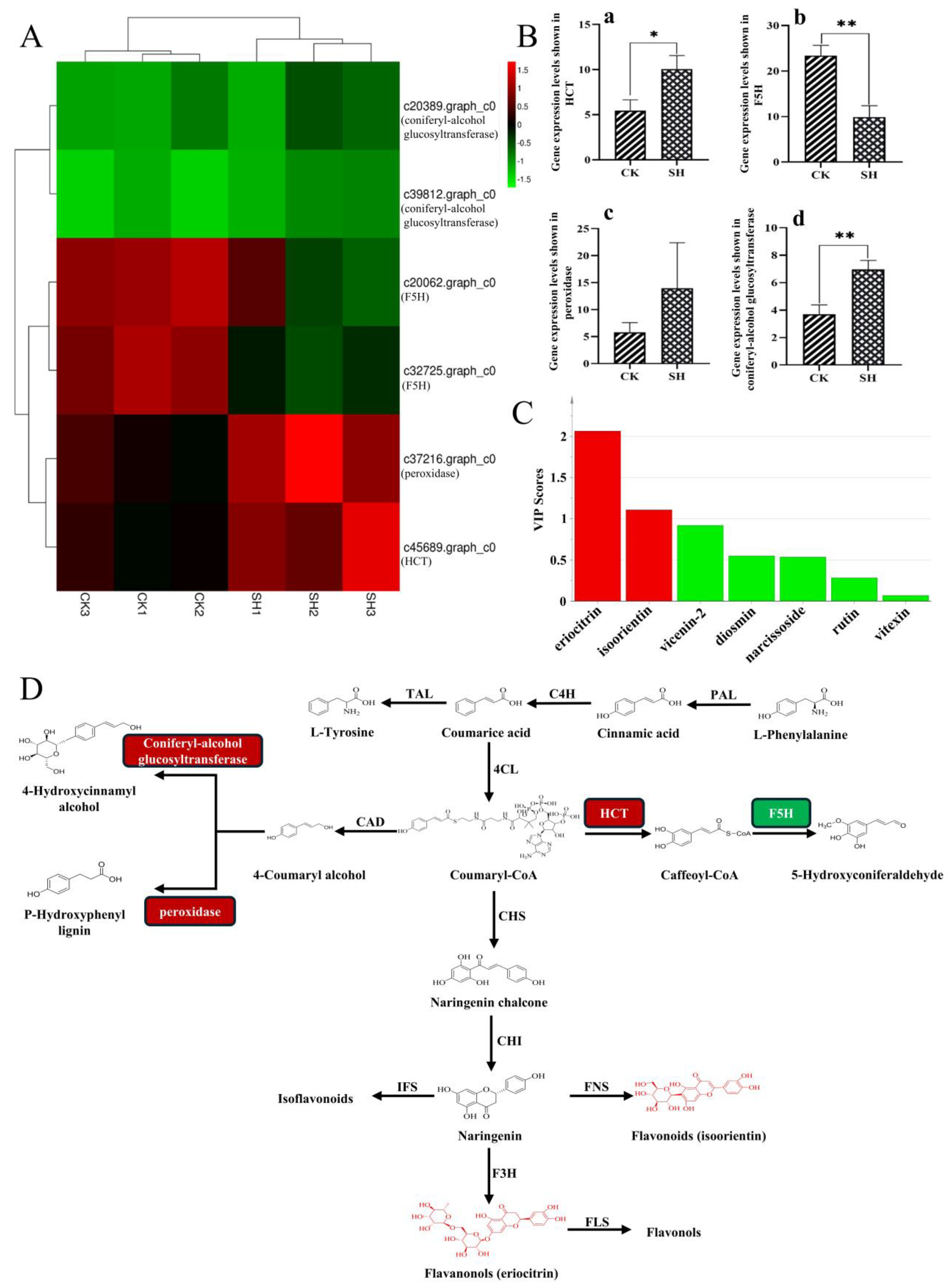
2.4. Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Data on Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Lemon
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Processing Method and Sampling Method
4.3. Transcriptome Sequencing and Data Analysis
4.4. Flavonoid Metabolite Analysis
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Gao, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Yi, C. Linking plant secondary metabolites and plant microbiomes: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 621276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubair, A.R.; Waquar, A.; Alexander, S.L.; Saad, B.J. From nature to lab: A review of secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways, environmental influences, and in vitro approaches. Metabolites 2023, 13, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, M.; Kliebenstein, D.J. Plant secondary metabolites as defenses, regulators, and primary metabolites: The blurred functional trichotomy. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divekar, P.A.; Narayana, S.; Divekar, B.A.; Kumar, R.; Gadratagi, B.G.; Ray, A.; Singh, A.K.; Rani, V.; Singh, V.; Singh, A.K.; et al. Plant secondary metabolites as defense tools against herbivory for sustainable crop protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Dickinson, A.J. A century of plant secondary metabolism research: From ‘what?’ to ‘where, how, and why?’. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, L.Â.M.; Neto, R.N.M.; Ataíde, A.C.S.; Fonseca, D.C.S.C.; Soares, E.F.A.; Sousa, J.C.S.; Mondego-Oliveira, R.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Cartágenes, M.S.S.; Lima-Neto, L.G.; et al. Flavonoids, alkaloids and saponins: Are these plant-derived compounds an alternative to the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis? A literature review. Clin. Phytosci. 2021, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seca, A.M.L.; Trendafilova, A. Secondary metabolites in edible species: Looking beyond nutritional. Foods 2021, 10, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Pandey, S.; Acqua, S.D. The influence of environmental conditions on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants: A literature review. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, U.; Ullah, S.; Tang, Z.H.; Elateeq, A.A.; Khan, Y.; Khan, J.; Khan, A.; Ali, S. Plant metabolomics: An overview of the role of primary and secondary metabolites against different environmental stress factors. Life 2023, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fernie, A.R. Plant secondary metabolism in a fluctuating world: Climate change perspectives. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuss, L.; Feng, S.; Hung, W.L.; Yu, Q.; Jr, F.G.G.; Wang, Y. Analysis of flavor and other metabolites in lemon juice (citrus limon) from huanglongbing-affected trees grafted on different rootstocks. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsouna, A.B.; Halima, N.B.; Smaoui, S.; Hamdi, N. Citrus lemon essential oil: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities with its preservative effect against listeria monocytogenes inoculated in minced beef meat. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek-Szczykutowicz, M.; Szopa, A.; Ekiert, H. Citrus limon (lemon) phenomenon-a review of the chemistry, pharmacological properties, applications in the modern pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics industries, and biotechnological studies. Plants 2020, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Bautista, R.J.H.; Sandhu, M.A.; Hussein, O.E. Beneficial effects of citrus flavonoids on cardiovascular and metabolic health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Shu, G.; Li, J. Antihypertensive potential of plant foods: Research progress and prospect of plant-derived angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5297–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, H.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Teng, H. Absorption, metabolism, and bioavailability of flavonoids: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 62, 7730–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, C.L.; Duclos, Q.; Blesso, C.N. Effects of dietary flavonoids on reverse cholesterol transport, hdl metabolism, and hdl function. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Dai, W.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, M. The positive effects of humic/fulvic acid fertilizers on the quality of lemon fruits. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Effect and mechanism of humic acids on volatile oils and flavonoids in lemon leaves. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X. Research progress on extraction and detection technologies of flavonoid compounds in foods. Foods 2024, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisshaar, B.; Jenkins, G.I. Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and its regulation in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 1998, 1, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Guo, K.; Liu, L.; Tian, W.; Xie, X.; Wen, S.; Wen, C. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic data reveal the flavonoid biosynthesis metabolic pathway in Perilla frutescens (L.) leaves. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Wu, W.; Ma, Y. Phenylpropanoid metabolism pathway in plants. Chin. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 38, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, Y. Research progress on regulation of plant flavonoids biosynthesis. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lv, S.; Zhao, L.; Gao, T.; Yu, C.; Hu, J.; Ma, F. Advances in the study of the function and mechanism of the action of flavonoids in plants under environmental stresses. Planta 2023, 257, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Li, H.Q.; Chiang, V.C.L.; Fu, Y.J. Cooperative regulation of flavonoid and lignin biosynthesis in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2021, 40, 109–123. Available online: https://www.medsci.cn/sci/show_paper.asp?id=7007412a99452e9c (accessed on 3 July 2024). [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; He, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Fu, C.; Xu, H.; Hu, R.; Li, S. A p1-like myb transcription factor boosts biosynthesis and transport of c-glycosylated flavones in duckweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseau, S.; Hoffmann, L.; Geoffroy, P.; Lapierre, C.; Pollet, B.; Legrand, M. Flavonoid accumulation in arabidopsis repressed in lignin synthesis affects auxin transport and plant growth. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, H.; Li, Q. Biosynthetic regulatory network of flavonoid metabolites in stems and leaves of salvia miltiorrhiza. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jiao, B. Advances on the analysis of content and detection technologies for lemon flavonoids. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 12, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, N.; Yang, F.; Dai, W.; Yuan, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, M. The Influence of Sodium Humate on the Biosynthesis and Contents of Flavonoid Constituents in Lemons. Plants 2024, 13, 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13202888
Xu N, Yang F, Dai W, Yuan C, Li J, Zhang H, Ren Y, Zhang M. The Influence of Sodium Humate on the Biosynthesis and Contents of Flavonoid Constituents in Lemons. Plants. 2024; 13(20):2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13202888
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Nianao, Fan Yang, Weifeng Dai, Cheng Yuan, Jinxue Li, Hanqi Zhang, Youdi Ren, and Mi Zhang. 2024. "The Influence of Sodium Humate on the Biosynthesis and Contents of Flavonoid Constituents in Lemons" Plants 13, no. 20: 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13202888
APA StyleXu, N., Yang, F., Dai, W., Yuan, C., Li, J., Zhang, H., Ren, Y., & Zhang, M. (2024). The Influence of Sodium Humate on the Biosynthesis and Contents of Flavonoid Constituents in Lemons. Plants, 13(20), 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13202888





