Introgression of Herbicide-Resistant Gene from Genetically Modified Brassica napus L. to Brassica rapa through Backcrossing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Hybridization Potential and Crossability of B. rapa with GM B. napus
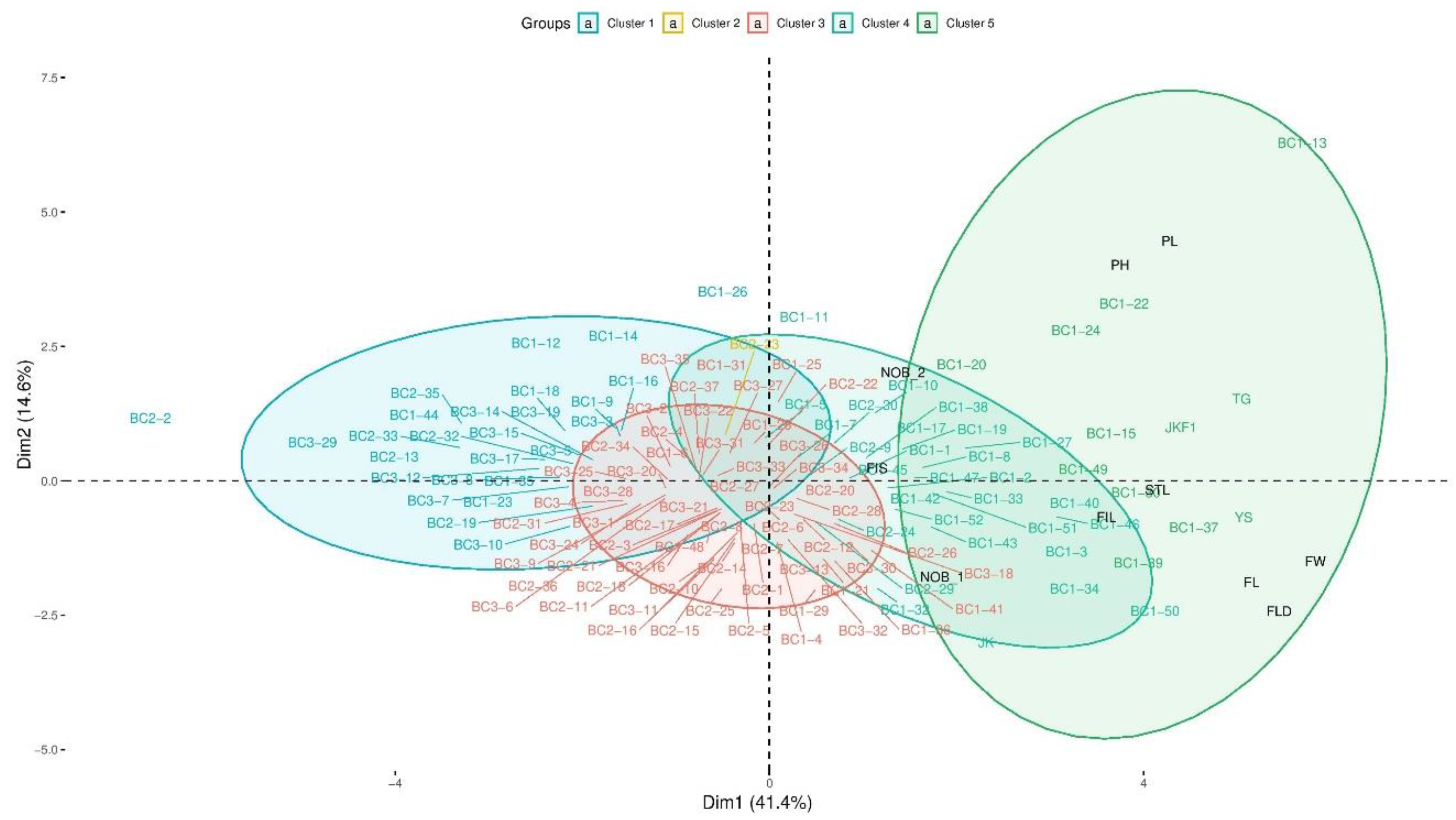
2.2. Morphological Variations among the Parental and Backcross Progenies
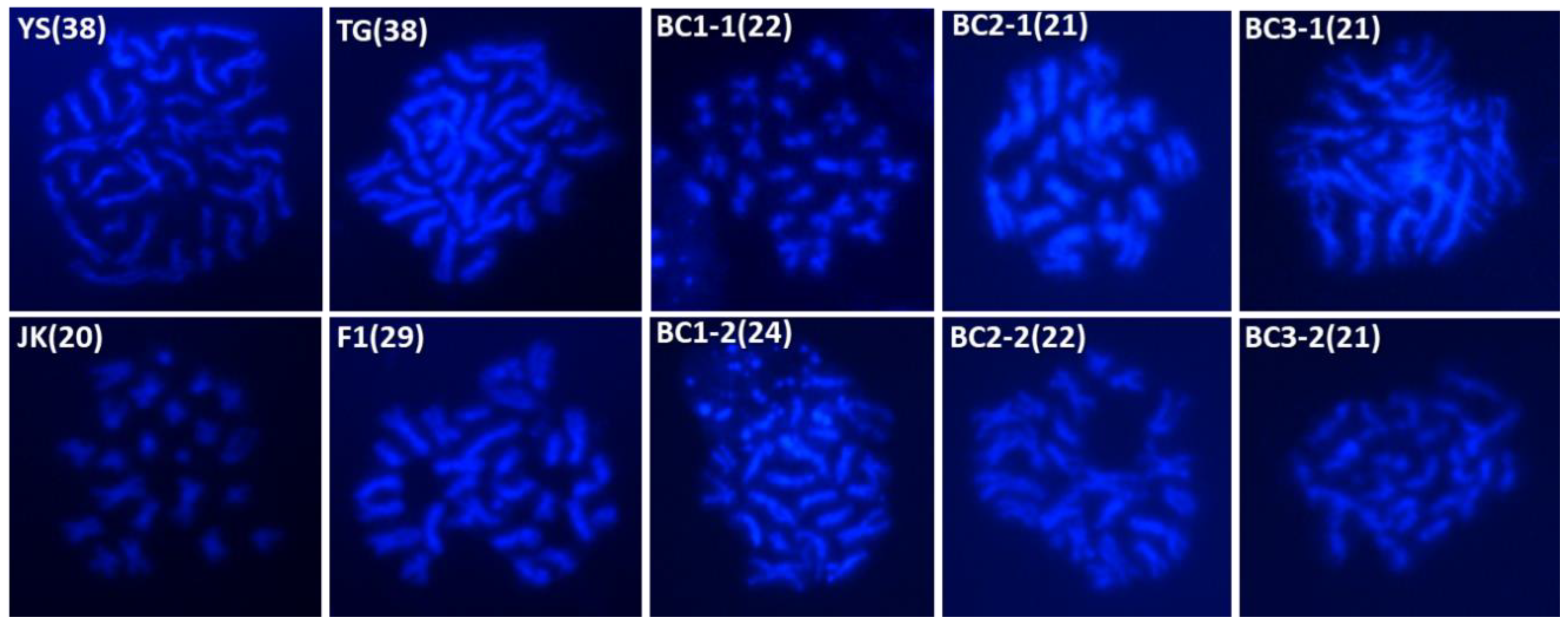
2.3. Cytological Analysis of Parental and Backcross Progenies
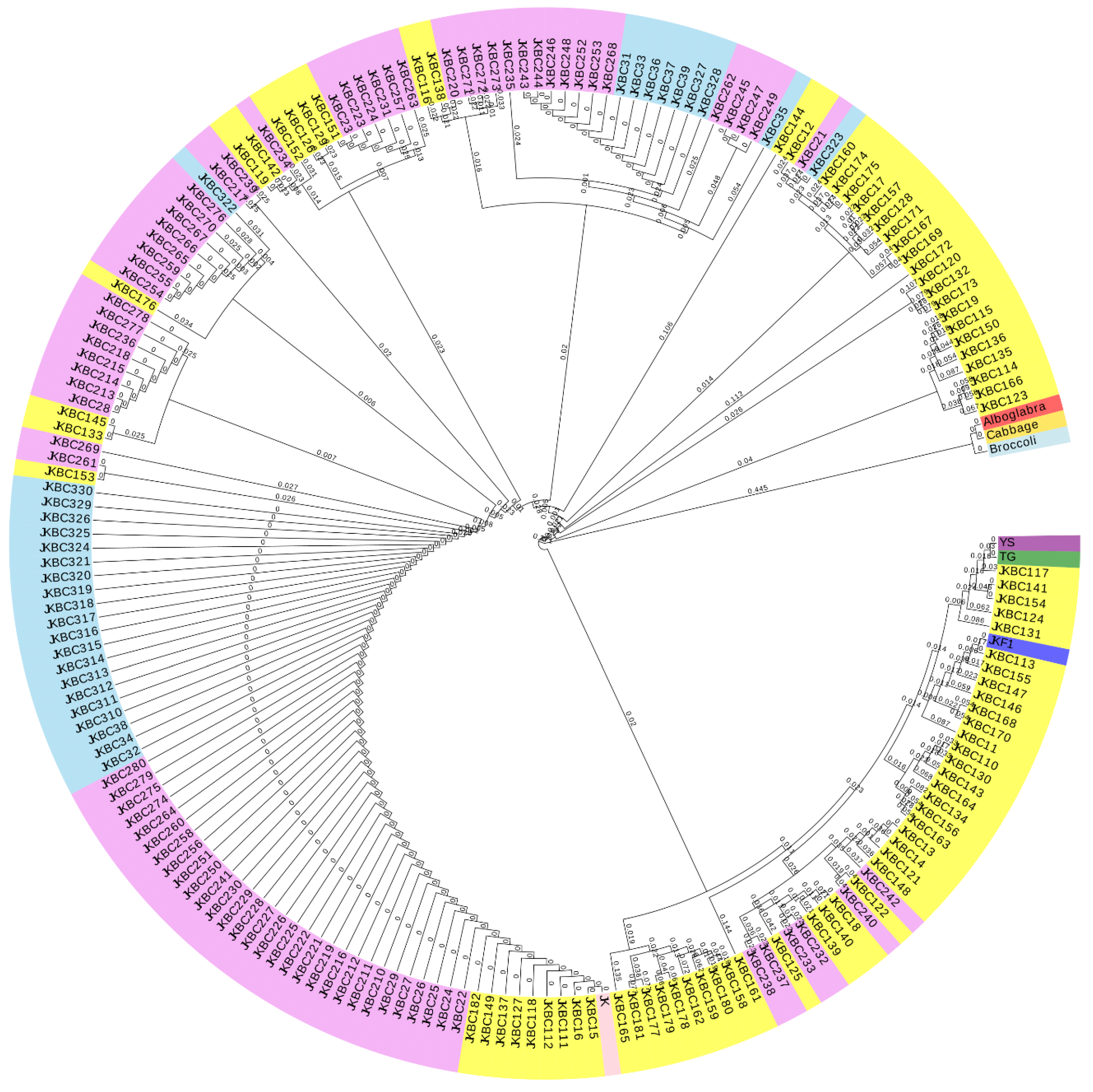
2.4. Molecular Marker Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Hybridization
4.2. Morphological Characteristics
4.3. Cytological Observations
4.4. SSR Marker Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sohn, S.I.; Oh, Y.J.; Lee, K.R.; Ko, H.C.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Chang, A. Characteristics analysis of F1 hybrids between genetically modified Brassica napus and B. Rapa. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaharu, U.; Nagaharu, N. Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn. J. Bot. 1935, 7, 389–452. [Google Scholar]
- Chalhoub, B.; Denoeud, F.; Liu, S.; Parkin, I.A.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Chiquet, J.; Belcram, H.; Tong, C.; Samans, B.; et al. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 2014, 345, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bus, A.; Körber, N.; Snowdon, R.J.; Stich, B. Patterns of molecular variation in a species-wide germplasm set of Brassica napus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.J.; Elliott, L.J.; Allainguillaume, J.; Shaw, M.W.; Norris, C.; Welters, R.; Alexander, M.; Sweet, J.; Mason, D.C. Hybridization between Brassica napus and B. rapa on a national scale in the United Kingdom. Science 2003, 302, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. Biotechnology: Herbicide-resistant crops. In Encyclopedia of Agriculture and Food Systems; van Alfen, M., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 94–116. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, S.-I.; Pandian, S.; Oh, Y.-J.; Kang, H.-J.; Ryu, T.-H.; Cho, W.-S.; Shin, E.-K.; Shin, K.-S. A Review of the Unintentional Release of Feral Genetically Modified Rapeseed into the Environment. Biology 2021, 10, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckie, H.J.; Warwick, S.I.; Nair, H.; Séguin-Swartz, G. Gene flow in commercial fields of herbicide-resistant canola (Brassica napus). Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 1276–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellstrand, N.C.; Meirmans, P.; Rong, J.; Bartsch, D.; Ghosh, A.; de Jong, T.J.; Haccou, P.; Lu, B.; Snow, A.A.; Stewart, C.N., Jr.; et al. Introgression of crop alleles into wild or weedy populations. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2013, 44, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.; Thamilarasan, S.K.; Pandian, S.; Oh, Y.; Ryu, T.; Lee, G.; Shin, E. Interspecific Hybridization of Transgenic Brassica napus and Brassica rapa—An Overview. Genes 2022, 13, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, C.; Lillemo, M.; Hvoslef-Eide, T.A. Global regulation of genetically modified crops amid the gene edited crop boom—A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 630396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijten, S.H.; Schidlo, N.S.; Meirmans, P.G.; de Jong, T.J. Hybridisation and introgression between Brassica napus and B. rapa in the Netherlands. Plant Biol. 2015, 17, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devos, Y.; Hails, R.S.; Messéan, A.; Perry, J.N.; Squire, G.R. Feral genetically modified herbicide tolerant oilseed rape from seed import spills: Are concerns scientifically justified? Trans. Res. 2012, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Ma, K.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Darmency, H. Consequences of gene flow between oilseed rape (Brassica napus) and its relatives. Plant Sci. 2013, 211, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbach, N. How to model and simulate the effects of cropping systems on population dynamics and gene flow at the landscape level: Example of oilseed rape volunteers and their role for co-existence of GM and non-GM crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooftman, D.A.; Oostermeijer, J.G.B.; Marquard, E.; Den Nijs, H.J.C. Modelling the consequences of crop–wild relative gene flow: A sensitivity analysis of the effects of outcrossing rates and hybrid vigour breakdown in Lactuca. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.-I.; Thamilarasan, S.K.; Pandian, S.; Oh, Y.-J.; Kang, H.-J.; Shin, E.-K. Characteristics and Fitness Analysis through Interspecific Hybrid Progenies of Transgenic Brassica napus and B. rapa L. ssp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, A.A.; Andersen, B.; Jørgensen, R.B. Costs of transgenic herbicide resistance introgressed from Brassica napus into weedy B. Rapa. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.; Topinka, K.; Huffman, J.; Davis, L.; Good, A. Pollen flow between herbicide-resistant Brassica napus is the cause of multiple-resistant B. napus volunteers. Weed Sci. 2000, 48, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renno, J.F.; Winkel, T. Phenology and reproductive effort of cultivated and wild forms of Pennisetum glaucum under experimental conditions in the Sahel: Implications for the maintenance of polymorphism in the species. Can. J. Bot. 1996, 74, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, J.; Kotlarski, S.; Wojciechowski, A. The evaluation of self-incompatibility and crossability in choosen Brassica species based on the observation of pollen tubes growth and seed set. Acta Sci. Pol. Agric. 2014, 13, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Tonosaki, K.; Osabe, K.; Kawanabe, T.; Fujimoto, R. The importance of reproductive barriers and the effect of allopolyploidization on crop breeding. Breed. Sci. 2016, 66, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Lu, C.; Zhang, B.; Bo, H.; Wu, Y.; Wu, G.; Cao, Y.; Yu, D. Gene transferability from transgenic Brassica napus L. to various subspecies and varieties of Brassica rapa. Transgenic Res. 2009, 18, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, J.; Huangfu, C.; Qiang, S. Potential gene flow of two herbicide-tolerant transgenes from oilseed rape to wild B. juncea var. gracilis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chèvre, A.M.; Ammitzbøll, H.; Breckling, B.; Dietz-Pfeilstetter, A.; Eber, F.; Fargue, A.; Gomez-Campo, C.; Jenczewski, E.; Jørgensen, R.; Lavigne, C.; et al. A review on interspecific gene flow from oilseed rape to wild relatives. In Introgression from Genetically Modified Plants into Wild Relatives; CABI Publishing: Oxfordshire, UK, 2004; pp. 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Warwick, S.I.; Simard, M.-J.; Légère, A.; Beckie, H.J.; Braun, L.; Zhu, B.; Mason, P.; Séguin-Swartz, G.; Stewart, C.N. Hybridization between transgenic Brassica napus L. and its wild relatives: Brassica rapa L., Raphanus raphanistrum L., Sinapis arvensis L., and Erucastrum gallicum (Willd.) O.E. Schulz. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, R.B.; Andersen, B. Spontaneous hybridization between oilseed rape (Brassica napus) and weedy B. campestris (Brassicaceae): A risk of growing genetically modified oilseed rape. Am. J. Bot. 1994, 81, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzJohn, R.G.; Armstrong, T.T.; Newstrom-Lloyd, L.E.; Wilton, A.D.; Cochrane, M. Hybridisation within Brassica and allied genera: Evaluation of potential for transgene escape. Euphytica 2007, 158, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Cowling, W.A. Center of Origin and Centers of Diversity in an Ancient Crop, Brassica rapa (Turnip Rape). J. Hered. 2014, 105, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; Duan, M.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Shen, D. Interspecific hybridization, polyploidization and backcross of Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra with B. rapa var. purpurea morphologically recapitulate the evolution of Brassica vegetables. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.W.; Bergman, A.; Pollock, D.D.; Goldstein, D.B. Microsatellite genetic distances with range constraints: Analytic description and problems of estimation. Genetics 1997, 145, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Tan, Y.; Shi, M.; Xu, Y.; Aryamanesh, N.; Yan, G. Interspecific introgression of male sterility from tetraploid oilseed Brassica napus to diploid vegetable B. rapa through hybridisation and backcrossing. Crop Pasture Sci. 2013, 64, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, S.I.; Lee, Y.H. Overexpression of a Brassica rapa MADS-box gene, BrAGL20, induces early flowering time phenotypes in Brassica napus. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2013, 7, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.H. Descriptors for Brassica & Raphanus; IBPGR: Rome, Italy, 1990; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Tagashira, N.; Hoshi, Y.; Yagi, K.; Pląder, W.; Malepszy, S. Cytogenetic comparison among three cultivars of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) by using post-heated DAPI band, 45S and 5S rDNA sites. Chromosom. Bot. 2009, 4, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hoshi, Y.; Mori, M.; Matoba, H.; Murata, T.; Plader, W.; Malepszy, S. Cucumbers (Cucumis sativus L.) Revealed by Fluorescent Staining with CMA and DAPI. Cytologia 2008, 73, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Doyle, J. DNA Protocols for Plants BT. In Molecular Techniques in Taxonomy; Hewitt, G.M., Johnston, A.W.B., Young, J.P.W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 283–293. ISBN 978-3-642-83962-7. [Google Scholar]
- Perrier, X. DARwin Software; Version 6.0.021; CIRAD: Paris, France, 2006; Available online: https://darwin.cirad.fr/product.php (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.-H. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cross Combination | Progeny | No. of Pollinated Flowers | No. of Pods | Pod-Setting Ratio (%) | Total No. of Seeds | Vivipary (%) | Empty Seeds (%) | Crossability Index (No. of Seeds/Pods) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. napus | Parental | 410 | 282 | 68.8 | 6073 | 89 (1.47) | 249 (4) | 21.5 ± 4.5 |
| B. rapa ssp. pekinensis | Parental | 268 | 159 | 59.4 | 1657 | 12 (0.72) | 454 (27) | 10.4 ± 3.1 |
| B. rapa ssp. pekinensis (♀) X GM B. napus (TG#19) (♂) | F1 hybrid | 123 | 61 | 49.5 | 480 | 152 (68.2) | 54 (24.2) | 11.2 ± 1.3 |
| B. rapa ssp. pekinensis (♀) X GM B. napus (TG#39) (♂) | F1 hybrid | 1282 | 540 | 42.1 | 1926 | 518 (26.9) | 403 (20.9) | 14.7 ± 5.7 |
| B. rapa ssp. pekinensis (♀) X GM B. napus (TG#53) (♂) | F1 hybrid | 252 | 115 | 45.6 | 531 | 350 (65.9) | 146 (27.5) | 10.6 ± 5.7 |
| B. rapa ssp. pekinensis (♀) X GM B. napus (TG#74) (♂) | F1 hybrid | 337 | 206 | 61.1 | 433 | 240 (55.4) | 131 (30.3) | 14.4 ± 2.6 |
| B. rapa ssp. pekinensis (♀) X F1 hybrid | BC1 hybrid | 1640 | 355 | 21.6 | 781 | 218 (27.9) | 210 (26.9) | 2.2 ± 1.4 |
| B. rapa ssp. pekinensis (♀) X BC1 hybrid (♂) | BC2 hybrid | 2992 | 351 | 11.7 | 946 | 100 (10.6) | 426 (45.0) | 2.7 ± 1.9 |
| B. rapa ssp. pekinensis (♀) X BC2 hybrid (♂) | BC3 hybrid | 595 | 46 | 7.7 | 74 | 5 (6.8) | 32 (43.2) | 1.6 ± 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandian, S.; Ban, Y.-S.; Shin, E.-K.; Thamilarasan, S.K.; Muthusamy, M.; Oh, Y.-J.; An, H.-K.; Sohn, S.-I. Introgression of Herbicide-Resistant Gene from Genetically Modified Brassica napus L. to Brassica rapa through Backcrossing. Plants 2024, 13, 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13202863
Pandian S, Ban Y-S, Shin E-K, Thamilarasan SK, Muthusamy M, Oh Y-J, An H-K, Sohn S-I. Introgression of Herbicide-Resistant Gene from Genetically Modified Brassica napus L. to Brassica rapa through Backcrossing. Plants. 2024; 13(20):2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13202863
Chicago/Turabian StylePandian, Subramani, Young-Sun Ban, Eun-Kyoung Shin, Senthil Kumar Thamilarasan, Muthusamy Muthusamy, Young-Ju Oh, Ho-Keun An, and Soo-In Sohn. 2024. "Introgression of Herbicide-Resistant Gene from Genetically Modified Brassica napus L. to Brassica rapa through Backcrossing" Plants 13, no. 20: 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13202863
APA StylePandian, S., Ban, Y.-S., Shin, E.-K., Thamilarasan, S. K., Muthusamy, M., Oh, Y.-J., An, H.-K., & Sohn, S.-I. (2024). Introgression of Herbicide-Resistant Gene from Genetically Modified Brassica napus L. to Brassica rapa through Backcrossing. Plants, 13(20), 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13202863










