Genetic Variability in the Physicochemical Characteristics of Cultivated Coffea canephora Genotypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Field Experiment and Sample Collection
3.2. Physicochemical Analysis
3.3. Statistical Analyzes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Espindula, M.C.; Dalazen, J.R.; Rocha, R.B.; Teixeira, A.T.; Diocleciano, J.M.; Dias, J.R.M.; Schmidt, R.; Lima, P.P.; Lima, G.M.; Gama, W. Robustas Amazônicos os Cafeeiros Cultivados em Rondônia, 1st ed.; Embrapa: Porto Velho, RO, Brazil, 2022; ISBN 9786589957256. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, F.D.F.; Caixeta, E.T.; Ferrão, L.F.V.; Pena, G.F.; Sakiyama, N.S.; Zambolim, E.M.; Zambolim, L.; Cruz, C.D. Molecular Diversity in Coffea Canephora Germplasm Conserved and Cultivated in Brazil. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2013, 13, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.A.; Rocha, R.B.; Alves, E.A.; Teixeira, A.L.; Dalazen, J.R.; da Fonseca, F.A. Characterization of beverage quality in Coffea Canephora Pierre Ex A. Froehner 2018, 13, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.L.; Rocha, R.B.; Espindula, M.C.; Ramalho, A.R.; Vieira Júnior, J.R.; Alves, E.A.; Lunz, A.M.P.; de Souza, F.F.; Costa, J.N.M.; de Fernandes, C.F. Amazonian Robustas-New Coffea Canephora Coffee Cultivars for the Western Brazilian Amazon. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2020, 20, e323420318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viencz, T.; Acre, L.B.; Rocha, R.B.; Alves, E.A.; Ramalho, A.R.; de Toledo Benassi, M. Caffeine, Trigonelline, Chlorogenic Acids, Melanoidins, and Diterpenes Contents of Coffea Canephora Coffees Produced in the Amazon. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 117, 105140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fássio, L.H.; da Silva, A.E.S. Importância Econômica e do Café Conilon; Coocacer Araguari: Araguari, Brazil, 2007; pp. 34–49. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, D.R.; Damaceno, J.B.D.; Andrade, R.A.; Domingues, C.G.; da Silva, C.A.; Martins, J.K.D.; Traspadini, E.I.F.; Dubberstein, D.; Dias, J.R.M. Compatibility Test and Agronomic Performance of Coffee Genotypes (Coffea canephora Pierre Ex Froehner) in the State of Rondônia, Brazil. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqueta, M.R.; Alves, E.A.; Valderrama, P.; Pallone, J.A.L. Brazilian Canephora Coffee Evaluation Using NIR Spectroscopy and Discriminant Chemometric Techniques. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 116, 105065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.; Trugo, L.C. Distribuição de isômeros de ácido clorogênico e teores de cafeína e trigonelina em cafés solúveis brasileiros. Ciênc. Tecnol. Aliment. 2003, 23, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletti, B.Z.; Oliveira, E.C.S.; Pinheiro, P.F.; Saraiva, S.H. Discrimination of Arabica and Conilon Coffee from Physicochemical Properties Allied to Chemometrics. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2019, 11, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, A.R.; Batali, M.E.; Ristenpart, W.D.; Guinard, J.X. Consumer Preferences for Black Coffee Are Spread over a Wide Range of Brew Strengths and Extraction Yields. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; De Moraes Gonçalves, J.L.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s Climate Classification Map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, E.A.V.; Taques, R.C.; Maso, L.J.; Costa, A.F.S.; Ferrão, R.G. Estimativa de perdas na produção agrícola capixaba em 2015. Incaper Em Rev. 2016, 6, 26–41. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L.R.; dos Reis, E.F.; Schwan, M.G.; Ribeiro, W.R.; Dardengo, M.C.J.D.; Da Silva, S.F. Tamanho de Grãos Do Cafeeiro Irrigado e Não Irrigado Durante Quatro Safras. IRRIGA 2021, 1, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kath, J.; Mittahalli Byrareddy, V.; Mushtaq, S.; Craparo, A.; Porcel, M. Temperature and Rainfall Impacts on Robusta Coffee Bean Characteristics. Clim. Risk Manag. 2021, 32, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, M.D.V. de Software Selegen-REML/BLUP: A Useful Tool for Plant Breeding ARTICLE. MDV Resende Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.D.; Carneiro, P.C.S.; Bhering, L.L. Biometry in Plant Breeding ARTICLE. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2021, 21, 380621–380626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar, Á.; Jurado, M.J.; Martín, J.M.; Pablos, F.; González, A.G. Enzymatic-Spectrophotometric Determination of Sucrose in Coffee Beans’Angela. Talanta 2005, 67, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.M.; Pereira, R.G.F.A.; Pinto, N.A.V.D.; Nery, M.C.; Pádua, F.R.M. DE Constituintes químicos e teor de extrato aquoso de cafés arábica (Coffea arabica l.) e conilon (Coffea canephora pierre) torrados. Ciênc. Agrotec. 2003, 25, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celestino, S.M.C.; Veiga, A.D. Caracterização Físico-Química e Produtividade de Grãos de Cafeeiros Do Banco de Germoplasma da Embrapa Cerrados; Embrapa Cerrados: Planaltina, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Espíndula, M.C.; José, F.; Botelho, E.; Da Consolação, A.; Clemente, S.; Teixeira, A.L.; Quele, G.; Alves, F.; Oliveira, M.E. Quality evaluation of Coffea canephora “apoatã” seeds for rootstock production. Coffea Sci. 2017, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- da Eira Aguiar, A.T.; Salva, T.D.; Fazuoli, L.C.; Favarin, J.L. Variação No Teor de Lipídios em Grãos de Variedades de Coffea Canephora Variation of Seed Lipid Content among Coffea Canephora Varieties. Pesq. Agropec. Bras 2005, 40, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; da Silva, C.A.; Silva, L.O.E.; Espindula, M.C.; Rodrigues, W.P.; Vieira, H.D.; Tomaz, M.A.; Partelli, F.L. Accumulation of Nutrients and the Relation between Fruit, Grain, and Husk of Coffee Robusta Cultivated in Brazilian Amazon. Plants 2023, 12, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arruda Rodrigues, H.C.; de Carvalho, S.P.; de Carvalho, A.A.; dos Santos, C.E.; de Carvalho Filho, J.L. Correlações genotípicas, fenotípicas e ambientais entre caracteres de mamoneira Genotypic, Phenotypic and Environmental Correlations among Castor Bean Variables. Ciência Agrotecnologia 2010, 34, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, S.; Alves, M.R.; Mendes, E.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Ferreira, M.A. Discrimination between Arabica and Robusta Coffee Species on the Basis of Their Amino Acid Enantiomers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Ma, G.; Zhang, T.; Lei, W.; Pei, H.; Li, X.; Gao, L. Insights into Flavor and Key Influencing Factors of Maillard Reaction Products: A Recent Update. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 973677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lim, L.T. Investigation of CO2 Precursors in Roasted Coffee. Food Chem. 2017, 219, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.F.; Perez, C.; da Cunha, P.H.P.; Filgueiras, P.R.; Pereira, L.L.; Almeida da Fonseca, A.F.; Ifa, D.R.; Scherer, R. Chemical and Sensory Profile of New Genotypes of Brazilian Coffea Canephora. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinicke, L.C.T.S.; Espindua, M.C.; Rocha, R.B. Divergência genética dos atributos sensoriais de clones de coffea canephora cultivados na amazônia ocidental genetic divergence of the sensory properties of coffea canephora clones grown in the western amazon. Int. Sci. J. 2023, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.D.; Trevisan, F.; de Vos, R.C.H. Coffee Berry and Green Bean Chemistry—Opportunities for Improving Cup Quality and Crop Circularity. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Scholz, M.B.; Kitzberger, C.S.; Prudencio, S.H. The Typicity of Coffees from Different Terroirs Determined by Groups of Physico-Chemical and Sensory Variables and Multiple Factor Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.; Monteiro, M.C.; Calado, V.; Franca, A.S.; Trugo, L.C. Correlation between Cup Quality and Chemical Attributes of Brazilian Coffee. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Lassabliere, B.; Yu, B.; Liu, S.Q. Coffee Flavour Modification through Controlled Fermentations of Green Coffee Beans by Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Pichia Kluyveri: Part I. Effects from Individual Yeasts. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Adolfo Lutz. Métodos Físico-Químicos Para Análise de Alimentos; Instituto Adolfo Lutz: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008.
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; AOAC: Arlington, TX, USA, 1990; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, A.S.G.; Alves, R.C.; Vinha, A.F.; Barreira, S.V.P.; Nunes, M.A.; Cunha, L.M.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Optimization of Antioxidants Extraction from Coffee Silverskin, a Roasting by-Product, Having in View a Sustainable Process. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 53, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonade, I.R.; Carvalho, P.G.B.; Ferreira, N.A.; Moulin, B.S.F. Protocolo Para Determinação de Açúcares Redutores Pelo Método de Somogyi-Nelson. Comun. Técnico 2013, 86, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, C.D. GENES—Software Para Análise de Dados Em Estatística Experimental e Em Genética Quantitativa. Acta Sci. Agron. 2013, 35, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceasar, S.A.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Vinod, K.K.; Roch, G.V.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Baker, A.; Ignacimuthu, S. Phenotypic Responses of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) Genotypes to Phosphate Supply under Greenhouse and Natural Field Conditions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulamba, N.N.; Mock, J.J. Improvement of Yield Potential of the Eto Blanco Maize (Zea mays L.) Population by Breeding for Plant Traits. Egypt. J. Genet. Cytol. 1978, 7, 40–57. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, H.F. A discriminant function for plant selection. Ann. Eugen. 1936, 7, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SV | DF | AE | TA | TTA | pH | TCP | EE |
| Genotypes (G) | 67 | 3.38 ** | 3.23 ** | 2.80 ** | 1.53 * | 3.90 ** | 3.62 ** |
| Years (Y) | 1 | 5.15 * | 18.75 ** | 54.48 ** | 14.96 ** | 546.85 ** | 12.73 ** |
| GxE | 67 | 36.45 ** | 36.79 ** | 11.83 ** | 36.12 ** | 18.96 ** | 11.92 ** |
| Residue | 272 | ||||||
| Sum | 407 | ||||||
| Mean 1° year | 29.81 a | 4.70 a | 158.77 b | 5.19 a | 15.20 a | 5.18 a | |
| Mean 2° year | 29.75 a | 4.73 a | 161.91 a | 5.19 a | 14.43 b | 5.08 a | |
| Mean | 29.78 | 4.72 | 160.34 | 5.19 | 14.81 | 5.13 | |
| CVe | 0.93 | 1.22 | 2.68 | 0.37 | 2.25 | 5.15 | |
| r | 70.48 | 69.1 | 64.34 | 34.91 | 74.4 | 72.41 | |
| CVg | 3.57 | 4.53 | 5.06 | 0.67 | 6.86 | 11.78 | |
| CVg/Cve | 3.84 | 3.71 | 1.89 | 1.81 | 3.05 | 2.29 | |
| SV | DF | TSS | Ratio | TPC | SS | TRS | NRS |
| Genotypes (G) | 67 | 2.34 ** | 2.26 ** | 3.18 ** | 2.84 ** | 2.58 ** | 2.78 ** |
| Years (Y) | 1 | 183.36 ** | 186.31 ** | 104.44 ** | 120.06 ** | 1097.38 ** | 38.53 ** |
| GxE | 67 | 3.75 ** | 6.02 ** | 63.29 ** | 19.35 ** | 24.45 ** | 18.18 ** |
| Residue | 272 | ||||||
| Sum | 407 | ||||||
| Mean 1° year | 33.53 a | 0.21 a | 5.07 a | 7.75 a | 1.47 a | 6.29 a | |
| Mean 2° year | 31.97 b | 0.20 b | 4.99 a | 7.31 b | 1.26 b | 6.04 a | |
| Mean | 32.75 | 0.20 | 5.03 | 7.53 | 1.36 | 6.16 | |
| CVe | 3.57 | 4.69 | 1.45 | 5.47 | 4.71 | 6.71 | |
| r | 57.33 | 55.93 | 68.63 | 64.79 | 61.34 | 64.03 | |
| CVg | 3.27 | 5.3 | 6.98 | 13.34 | 11.99 | 15.6 | |
| CVg/Cve | 0.92 | 1.13 | 4.81 | 2.44 | 2.55 | 2.32 |
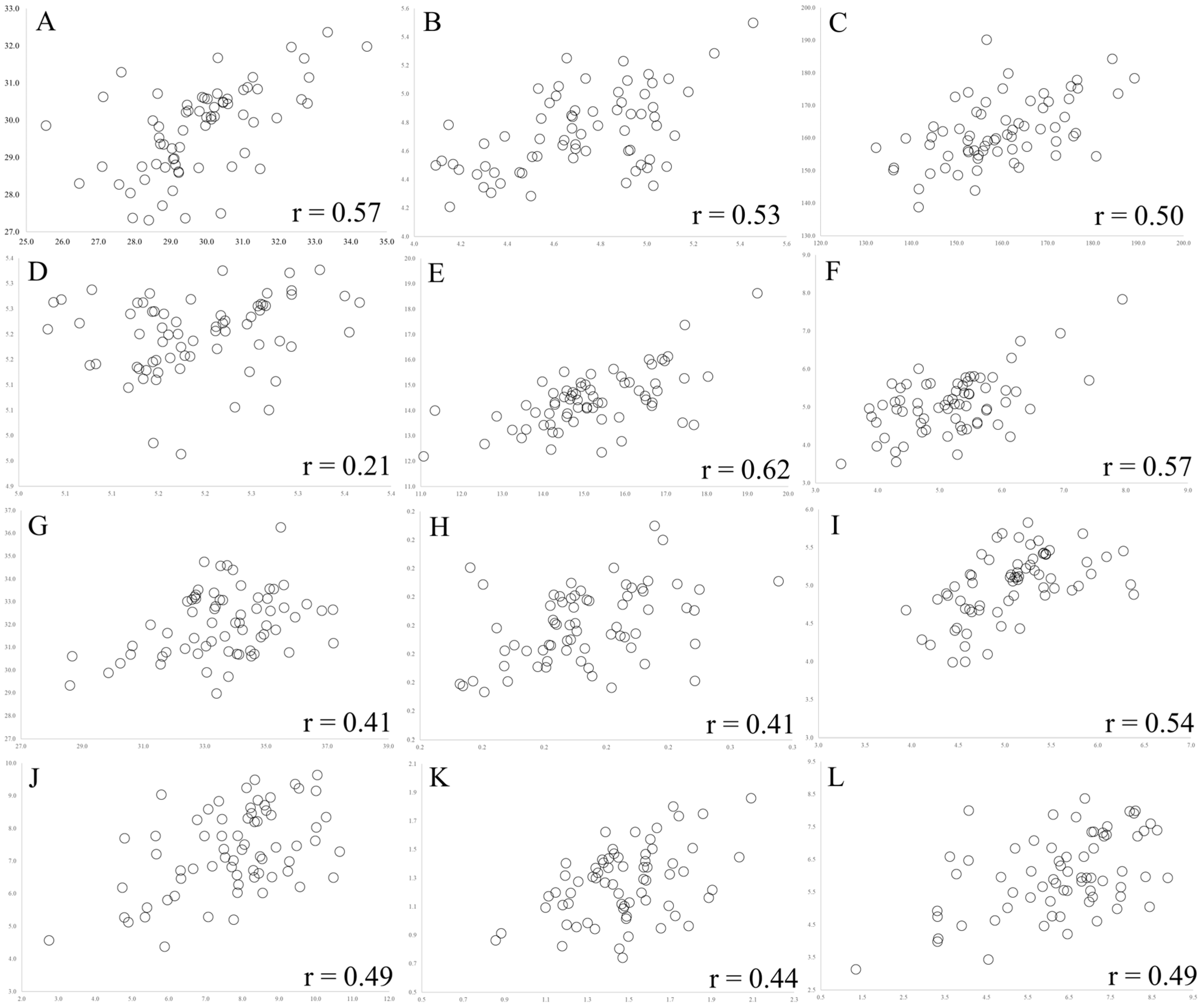
| n | Variable | rpe | rge | n | Variable | rpe | rge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AE × TA | 0.36 ** | 0.37 ++ | 24 | TTA × TRS | 0.36 ** | 0.40 ++ |
| 2 | AE × TTA | 0.33 ** | 0.34 ++ | 25 | pH × TCP | −0.25 * | −0.30 NS |
| 3 | AE × pH | −0.16 NS | −0.17 NS | 26 | pH × EE | 0.10 NS | 0.10 NS |
| 4 | AE × TCP | 0.14 NS | 0.13 NS | 27 | pH × TSS | −0.25 NS | −0.30 NS |
| 5 | AE × EE | −0.18 NS | −0.18 NS | 28 | pH × TPC | −0.25 NS | −0.31 NS |
| 6 | AE × TSS | 0.24 * | 0.36 NS | 29 | pH × SS | −0.08 NS | −0.06 NS |
| 7 | AE × TPC | 0.42 ** | 0.44 ++ | 30 | pH × TRS | −0.19 NS | −0.22 NS |
| 8 | AE × SS | 0.15 NS | 0.14 NS | 31 | TCP × EE | −0.09 NS | −0.09 NS |
| 9 | AE × TRS | 0.17 NS | 0.16 NS | 32 | TCP × TSS | 0.50 NS | 0.52 NS |
| 10 | TA × TTA | 0.42 ** | 0.44 ++ | 33 | TCP × TPC | 0.42 NS | 0.44 ++ |
| 11 | TA × pH | −0.04 NS | −0.05 NS | 34 | TCP × SS | −0.11 NS | −0.13 NS |
| 12 | TA × TCP | 0.22 NS | 0.22 NS | 35 | TCP × TRS | 0.49 NS | 0.52 NS |
| 13 | TA × EE | −0.09 NS | −0.11 NS | 36 | EE × SST | −0.04 NS | −0.03 NS |
| 14 | TA × TSS | 0.20 NS | 0.21 NS | 37 | EE × TPC | −0.04 NS | −0.04 NS |
| 15 | TA × TPC | 0.29 * | 0.37 NS | 38 | EE × SS | 0.01 NS | 0.01 NS |
| 16 | TA × SS | 0.06 NS | 0.06 NS | 39 | EE × TRS | −0.02 NS | −0.03 NS |
| 17 | TA × TRS | 0.43 ** | 0.46 ++ | 40 | TSS × TPC | 0.25 NS | 0.35 NS |
| 18 | TTA × pH | −0.39 ** | −0.41 ++ | 41 | TSS × SS | 0.03 NS | 0.03 NS |
| 19 | TTA × TCP | 0.35 ** | 0.38 ++ | 42 | TSS × TRS | 0.37 NS | 0.46 NS |
| 20 | TTA × EE | 0.05 NS | 0.07 NS | 43 | TPC × SS | 0.09 NS | 0.09 NS |
| 21 | TTA × TSS | 0.23 NS | 0.27 + | 44 | TPC × TRS | 0.46 NS | 0.48 ++ |
| 22 | TTA × TPC | 0.60 ** | 0.68 NS | 45 | SS × TRS | 0.21 NS | 0.22 NS |
| 23 | TTA × SS | 0.16 NS | 0.14 NS |
| Estimates of Progress with Selection | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | AE | TA | TTA | pH | TCP | EE | TSS | TPC | SS | TRS | SG | |
| Direct selection #1 | 0.89 | 0.52 | 1.3 | −0.1 | −1.54 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 1.13 | 24.66 | 4.88 | 32.2 | |
| Genotype Ideotype #2 | −1.43 | 2.44 | 7.01 | −0.19 | 7.11 | 14.06 | 2.5 | 5.85 | 6.58 | 14.93 | 58.86 | |
| Smith & Razel #3 | 2.29 | 1.63 | 9.23 | −0.38 | 4.94 | 6.51 | 2.43 | 8.86 | 10.84 | 10.84 | 57.19 | |
| Mulamba & Mock #4 | 3.14 | 3.02 | 7.21 | −0.94 | 7.92 | 1.78 | 3.89 | 8.63 | 9.47 | 8.84 | 52.96 | |
| Ordering of genotypes selected by each index | ||||||||||||
| Genotypes | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | ||||||||
| BRS3193 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
| AS3 | 2 | NS | 4 | 3 | ||||||||
| GJ25 | 3 | NS | NS | NS | ||||||||
| LB30 | 4 | NS | NS | NS | ||||||||
| BAG19 | 5 | NS | NS | NS | ||||||||
| AS7 | 6 | 7 | 3 | NS | ||||||||
| AS2 | 7 | NS | NS | NS | ||||||||
| AR106 | 8 | NS | NS | 6 | ||||||||
| LB88 | 9 | 5 | NS | NS | ||||||||
| CA1 | NS | 2 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||
| GJ30 | NS | 3 | 5 | NS | ||||||||
| BRS2299 | NS | 4 | 6 | 5 | ||||||||
| GJ8 | NS | 6 | NS | NS | ||||||||
| BRS3213 | NS | 8 | NS | NS | ||||||||
| BAG38 | NS | 9 | NS | 9 | ||||||||
| AS6 | NS | NS | 7 | NS | ||||||||
| BAG22 | NS | NS | 8 | 4 | ||||||||
| AS1 | NS | NS | 9 | 2 | ||||||||
| BRS2357 | NS | NS | NS | 8 | ||||||||
| Genotypes | AE | TA | TTA | pH | TCP | EE | TSS | Ratio | TPC | SS | TRS | NRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRS3193 | 30.24 c | 4.78 c | 179.60 a | 5.11 d | 17.42 b | 5.40 e | 33.96 a | 0.19 b | 5.86 a | 9.84 a | 1.47 b | 8.03 a |
| AS3 | 31.21 b | 4.74 c | 175.57 a | 5.17 c | 15.55 c | 5.23 e | 33.87 a | 0.19 b | 5.33 a | 9.57 a | 1.39 b | 7.84 a |
| GJ25 | 30.61 c | 4.54 d | 170.59 b | 5.06 d | 13.89 d | 4.72 f | 33.94 a | 0.20 a | 5.10 b | 9.39 a | 1.42 b | 7.97 a |
| LB30 | 30.47 c | 4.82 c | 154.16 d | 5.14 c | 14.93 c | 5.04 e | 32.72 b | 0.21 a | 5.41 a | 9.38 a | 1.31 b | 7.99 a |
| BAG19 | 31.00 b | 4.67 c | 148.94 d | 5.31 a | 13.74 d | 4.62 f | 30.91 c | 0.20 a | 4.45 c | 9.31 a | 1.30 b | 8.01 a |
| AS7 | 28.96 d | 4.87 b | 183.80 a | 5.16 c | 15.56 c | 4.87 f | 33.00 b | 0.19 a | 5.25 a | 9.02 a | 1.80 a | 7.68 a |
| AS2 | 33.21 a | 4.95 b | 161.34 c | 5.23 b | 14.14 d | 4.63 f | 32.92 b | 0.20 a | 5.11 b | 8.96 a | 1.55 b | 7.41 a |
| AR106 | 31.12 b | 4.65 c | 163.74 c | 5.06 d | 14.87 c | 6.51 c | 34.34 a | 0.21 a | 5.10 b | 8.91 a | 1.29 b | 7.62 a |
| LB88 | 30.11 c | 4.99 b | 161.24 c | 5.26 b | 15.68 c | 6.22 c | 33.34 b | 0.20 a | 4.64 c | 8.85 a | 1.73 a | 7.27 a |
| CA1 | 30.07 c | 5.28 a | 184.33 a | 5.17 c | 15.02 c | 6.94 b | 33.28 b | 0.17 b | 5.47 a | 7.43 b | 1.45 b | 6.01 b |
| GJ30 | 29.01 d | 4.45 d | 176.01 a | 5.32 a | 14.88 c | 7.89 a | 32.57 b | 0.18 b | 5.27 a | 8.31 a | 1.38 b | 6.96 a |
| BRS2299 | 30.03 c | 4.76 c | 173.40 b | 5.13 c | 16.30 b | 5.08 e | 35.87 a | 0.20 a | 5.53 a | 7.78 b | 1.48 b | 6.29 b |
| GJ8 | 27.70 e | 4.91 b | 168.83 b | 5.19 c | 16.36 b | 5.75 d | 33.33 b | 0.19 a | 5.63 a | 5.49 c | 1.97 a | 4.03 c |
| BRS3213 | 28.91 d | 4.45 d | 154.32 d | 5.12 c | 16.68 b | 5.70 d | 34.15 a | 0.22 a | 5.08 b | 8.13 b | 1.57 b | 6.55 b |
| BAG38 | 28.87 d | 5.06 b | 173.41 b | 5.16 c | 15.53 c | 5.35 e | 34.16 a | 0.20 a | 5.39 a | 7.82 b | 1.46 b | 6.36 b |
| AS6 | 30.58 c | 4.76 c | 177.20 a | 5.18 c | 14.66 c | 4.92 f | 32.65 b | 0.18 b | 5.47 a | 7.51 b | 1.49 b | 6.01 b |
| BAG22 | 31.59 b | 4.76 c | 171.49 b | 5.15 c | 15.53 c | 4.77 f | 34.09 a | 0.20 a | 5.68 a | 7.88 b | 1.56 b | 6.32 b |
| AS1 | 32.86 a | 4.79 c | 168.90 b | 5.13 c | 15.42 c | 4.32 f | 34.13 a | 0.20 a | 5.73 a | 8.48 a | 1.74 a | 6.74 b |
| BRS2357 | 31.01 b | 5.00 b | 167.67 b | 5.14 c | 18.93 a | 3.45 g | 34.91 a | 0.21 a | 5.39 a | 7.08 b | 1.66 a | 5.42 b |
| Concentration (%d.b.) | Genotypes |
|---|---|
| >31.4 | BRS3193; BRS2357 |
| >29.6 | AS3; BRS3213; P50; AS7; LB30; AS1; BRS2299 |
| >27.4 | 31–131; LB88; BAG22; AR106; BAG38; BAG26; LB101; N13; GJ30; BAG41; GJ25; AS2; LB15; AS5; LB68; GJ5; N8(G8); CA1; GJ21; N16; L1; BAG29; AS6; BAG30; BAG19; GJ8; BAG27 |
| >25.6 | BRS3210; GB1; AS12; LB80; R152; SK80; BAG28; P42; VP156; BRS2314; BRS1216; BAG32; LB10; BAG33; BAG21; GB7; BRS3220; GB4; GJ3; LB33; N1; R22 |
| >23.4 | BG180; SK41; WP6; AS10; BAG24; BRS3137; BRS2336; BAG23; N2; GJ20 |
| No. | Genotype | Origin | No. | Genotype | Origin | No. | Genotype | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BAG19 | Embrapa 1 | 24 | BRS3220 | Embrapa 1 | 47 | GB7 | Gilberto Boon 2 |
| 2 | BAG21 | Embrapa 1 | 25 | AS1 | Ademar Schmidt 2 | 48 | LB10 | Laerte Braun 5 |
| 3 | BAG22 | Embrapa 1 | 26 | AS2 | Ademar Schmidt 2 | 49 | LB15 | Laerte Braun 5 |
| 4 | BAG23 | Embrapa 1 | 27 | AS3 | Ademar Schmidt 2 | 50 | LB30 | Laerte Braun 5 |
| 5 | BAG24 | Embrapa 1 | 28 | AS5 | Ademar Schmidt 2 | 51 | LB33 | Laerte Braun 5 |
| 6 | BAG26 | Embrapa 1 | 29 | AS6 | Ademar Schmidt 2 | 52 | LB68 | Laerte Braun 5 |
| 7 | BAG27 | Embrapa 1 | 30 | AS7 | Ademar Schmidt 2 | 53 | LB80 | Laerte Braun 5 |
| 8 | BAG28 | Embrapa 1 | 31 | AS10 | Ademar Schmidt 2 | 54 | LB88 | Laerte Braun 5 |
| 9 | BAG29 | Embrapa 1 | 32 | AS12 | Ademar Schmidt 2 | 55 | LB110 | Laerte Braun 5 |
| 10 | BAG30 | Embrapa 1 | 33 | L1 | Alcides Rosa 3 | 56 | N1 | Nivaldo Ferreira 6 |
| 11 | BAG32 | Embrapa 1 | 34 | BG180 | Adilson Berger 3 | 57 | N2 | Nivaldo Ferreira 6 |
| 12 | BAG33 | Embrapa 1 | 35 | AR106 | Aldinei Raasch 8 | 58 | N8(G8) | Nivaldo Ferreira 6 |
| 13 | BAG38 | Embrapa 1 | 36 | CA1 | Carlos Alves Silva 4 | 59 | N13 | Nivaldo Ferreira 6 |
| 14 | BAG41 | Embrapa 1 | 37 | GJ3 | Geraldo Jacomini 5 | 60 | N16 | Nivaldo Ferreira 6 |
| 15 | BRS1216 | Embrapa 1 | 38 | GJ5 | Geraldo Jacomini 5 | 61 | R22 | Ronaldo Vitoriano 2 |
| 16 | BRS2299 | Embrapa 1 | 39 | GJ8 | Geraldo Jacomini 5 | 62 | R152 | Ronaldo G Oliveira 2 |
| 17 | BRS2314 | Embrapa 1 | 40 | GJ20 | Geraldo Jacomini 5 | 63 | SK41 | Sergio Kalk 6 |
| 18 | BRS2336 | Embrapa 1 | 41 | GJ21 | Geraldo Jacomini 5 | 64 | SK80 | Sergio Kalk 6 |
| 19 | BRS2357 | Embrapa 1 | 42 | GJ25 | Geraldo Jacomini 5 | 65 | VP156 | Valdecir Piske 2 |
| 20 | BRS3137 | Embrapa 1 | 43 | GJ30 | Geraldo Jacomini 5 | 66 | P50 | Valdecir Piske 2 |
| 21 | BRS3193 | Embrapa 1 | 44 | 31–131 | Geraldo Jacomini 5 | 67 | WP6 | Wanderley Peter 6 |
| 22 | BRS3210 | Embrapa 1 | 45 | GB1 | Gilberto Boon 2 | 68 | P42 | Wanderly Bernabé 7 |
| 23 | BRS3213 | Embrapa 1 | 46 | GB4 | Gilberto Boon 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Junior, H.L.; Rocha, R.B.; Kolln, A.M.; Silva, R.N.d.P.; Alves, E.A.; Teixeira, A.L.; Espíndula, M.C. Genetic Variability in the Physicochemical Characteristics of Cultivated Coffea canephora Genotypes. Plants 2024, 13, 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192780
Junior HL, Rocha RB, Kolln AM, Silva RNdP, Alves EA, Teixeira AL, Espíndula MC. Genetic Variability in the Physicochemical Characteristics of Cultivated Coffea canephora Genotypes. Plants. 2024; 13(19):2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192780
Chicago/Turabian StyleJunior, Hilton Lopes, Rodrigo Barros Rocha, Alana Mara Kolln, Ramiciely Nunes de Paula Silva, Enrique Anastácio Alves, Alexsandro Lara Teixeira, and Marcelo Curitiba Espíndula. 2024. "Genetic Variability in the Physicochemical Characteristics of Cultivated Coffea canephora Genotypes" Plants 13, no. 19: 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192780
APA StyleJunior, H. L., Rocha, R. B., Kolln, A. M., Silva, R. N. d. P., Alves, E. A., Teixeira, A. L., & Espíndula, M. C. (2024). Genetic Variability in the Physicochemical Characteristics of Cultivated Coffea canephora Genotypes. Plants, 13(19), 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192780






