Establishment of a Sensitive and Reliable Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Primers and Probe Design
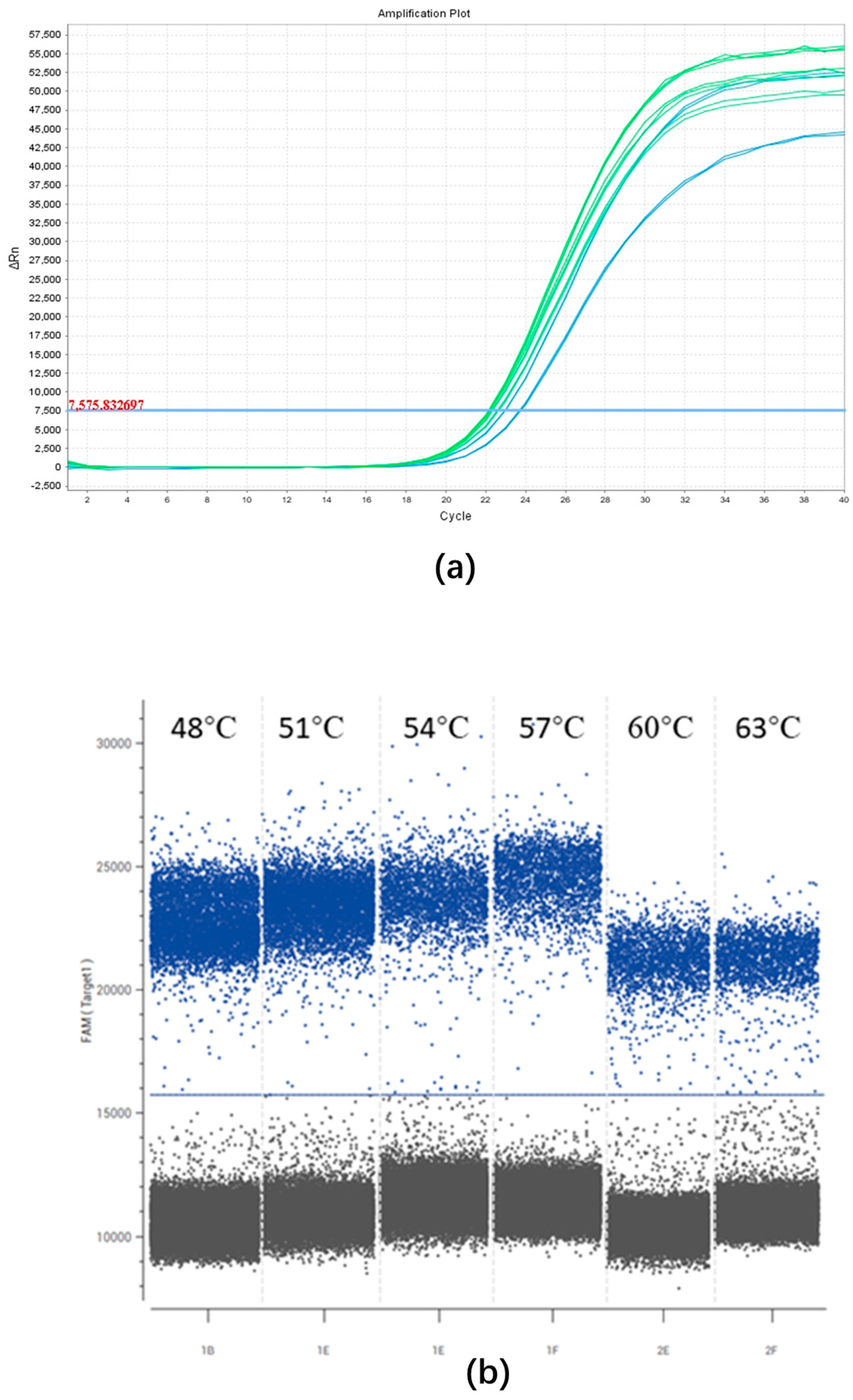
2.2. Optimization of the ddPCR Assay
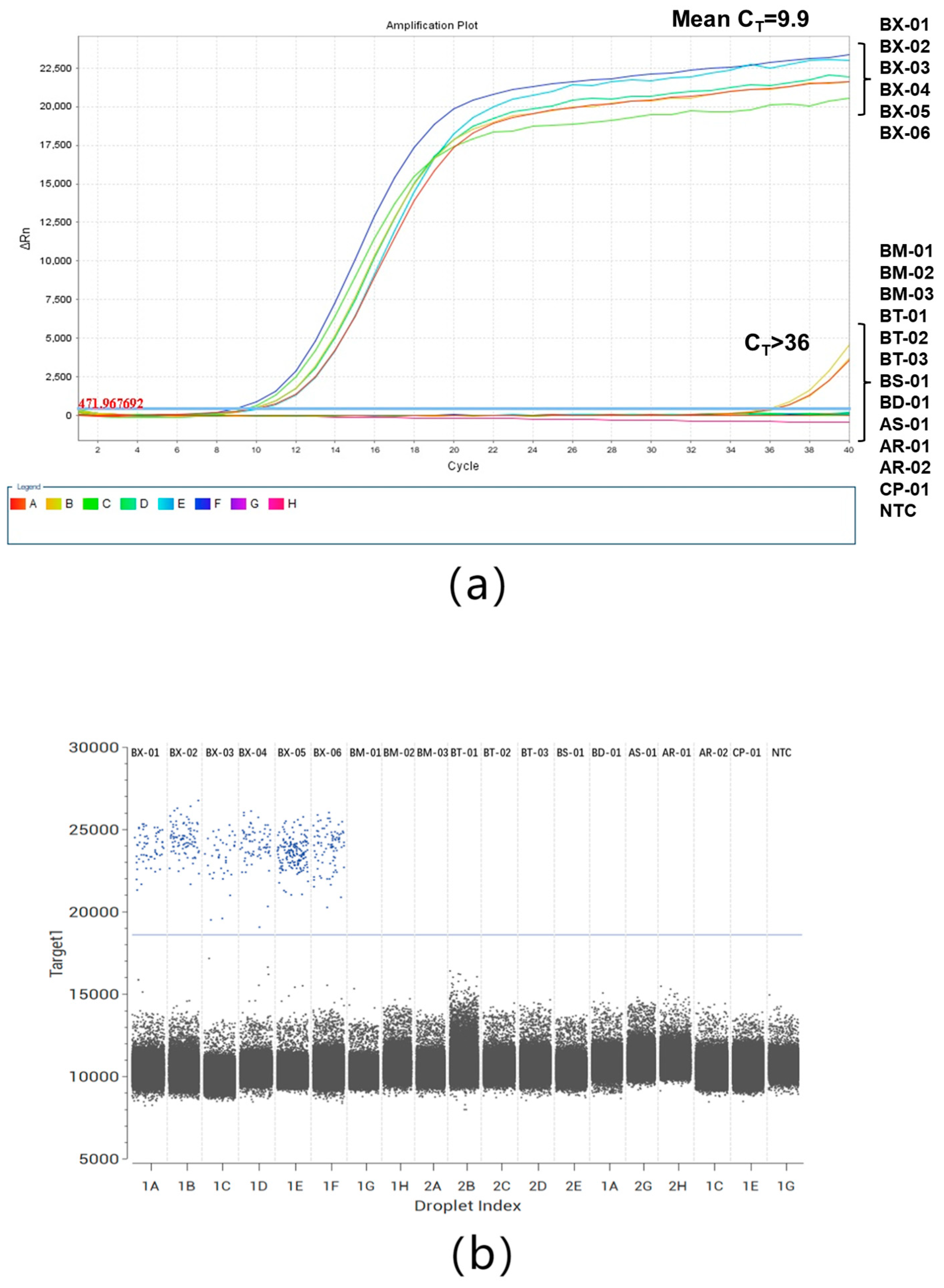
2.3. Specificity of ddPCR and qPCR
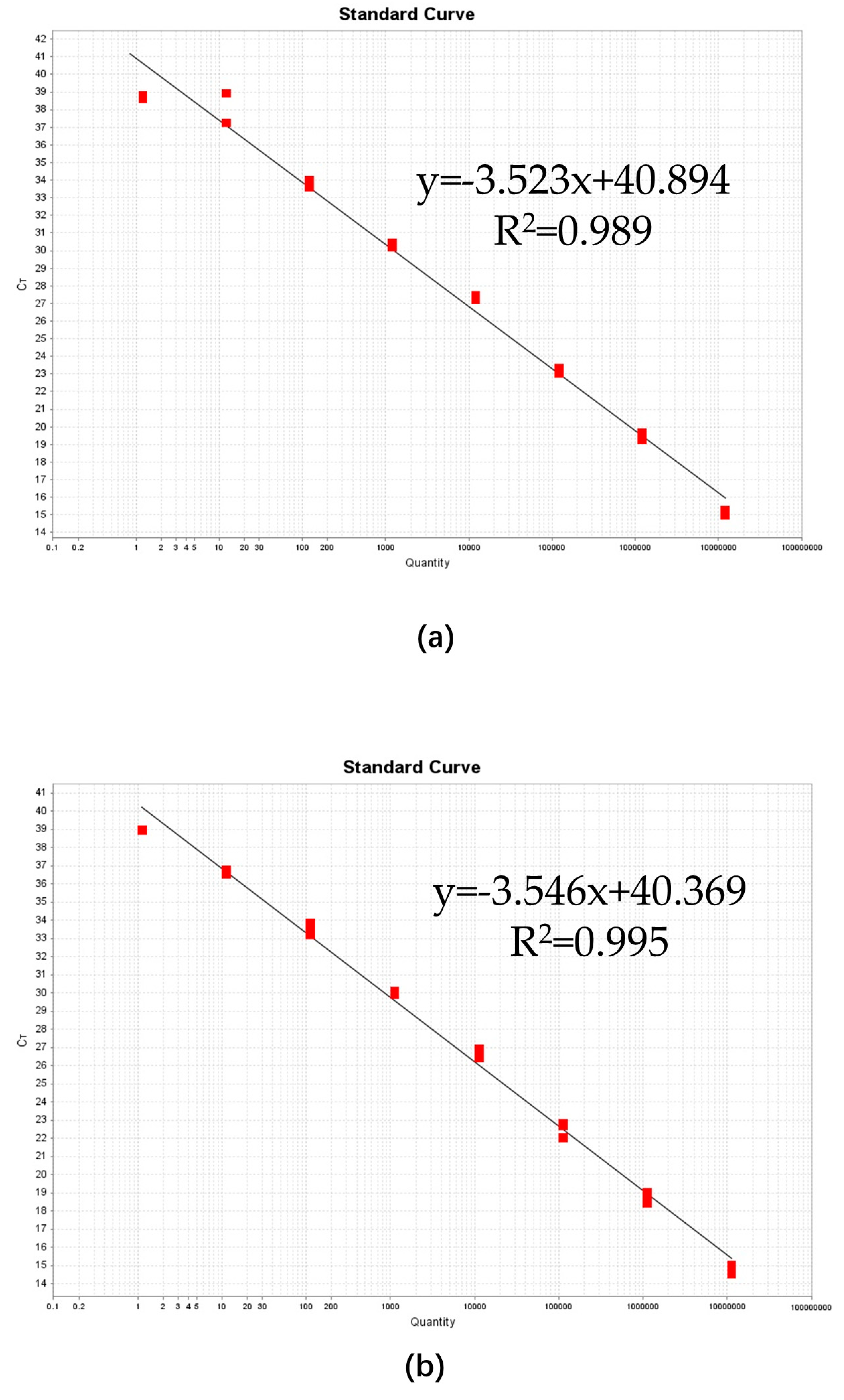
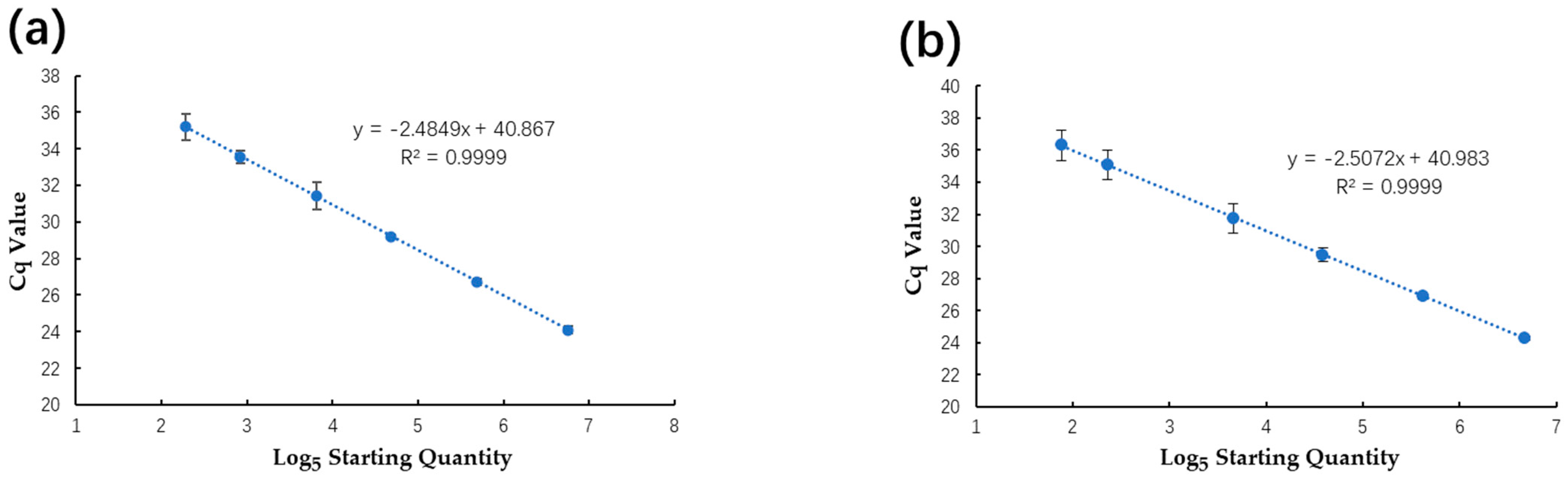
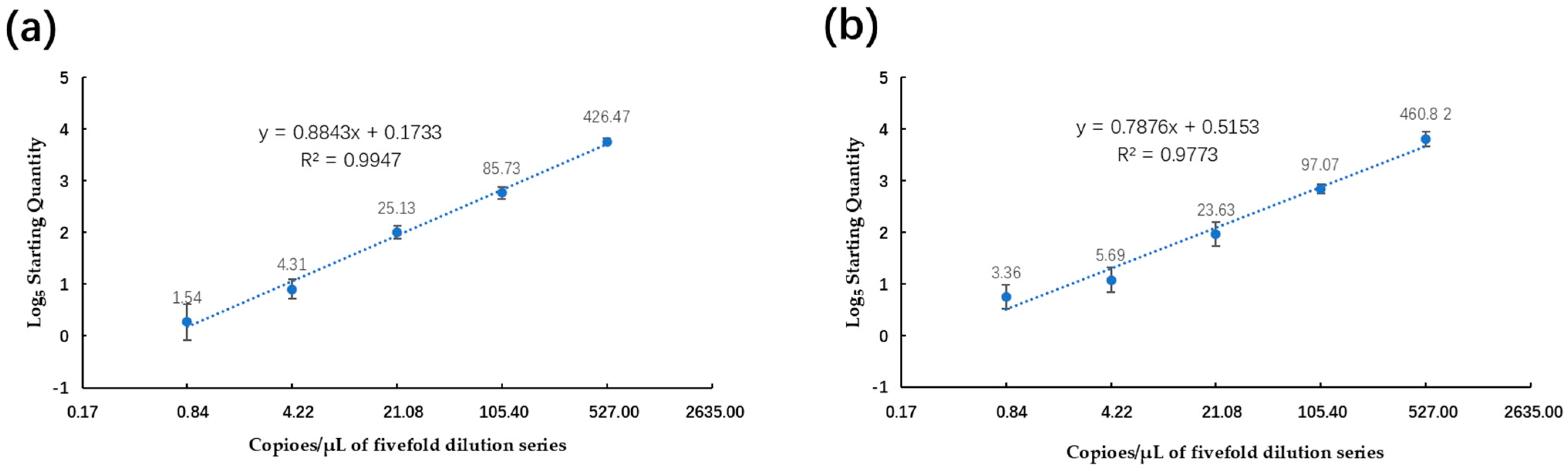
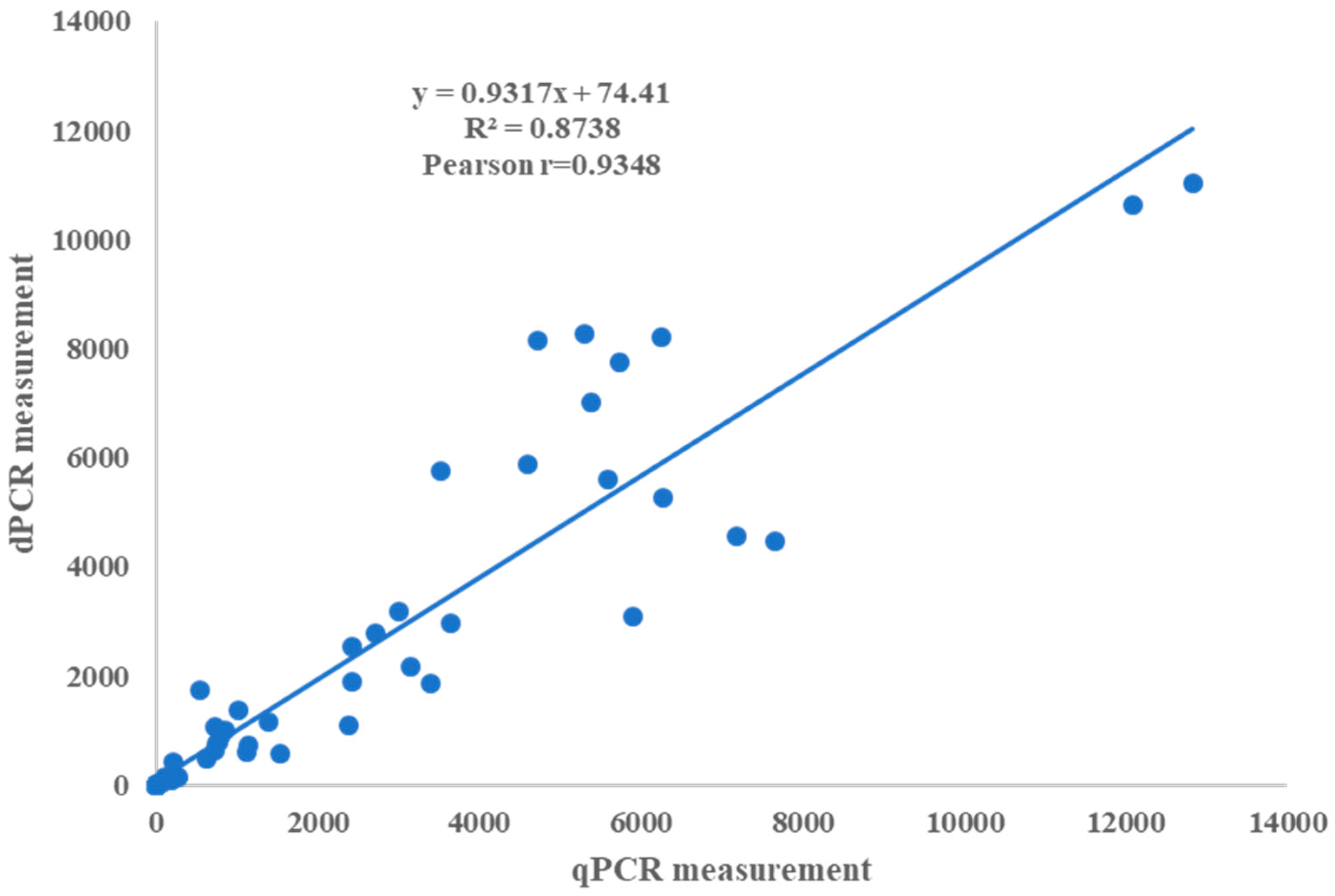
2.4. Comparison of Analytical Sensitivity, Linearity, and Dynamic Range between ddPCR and qPCR Assays
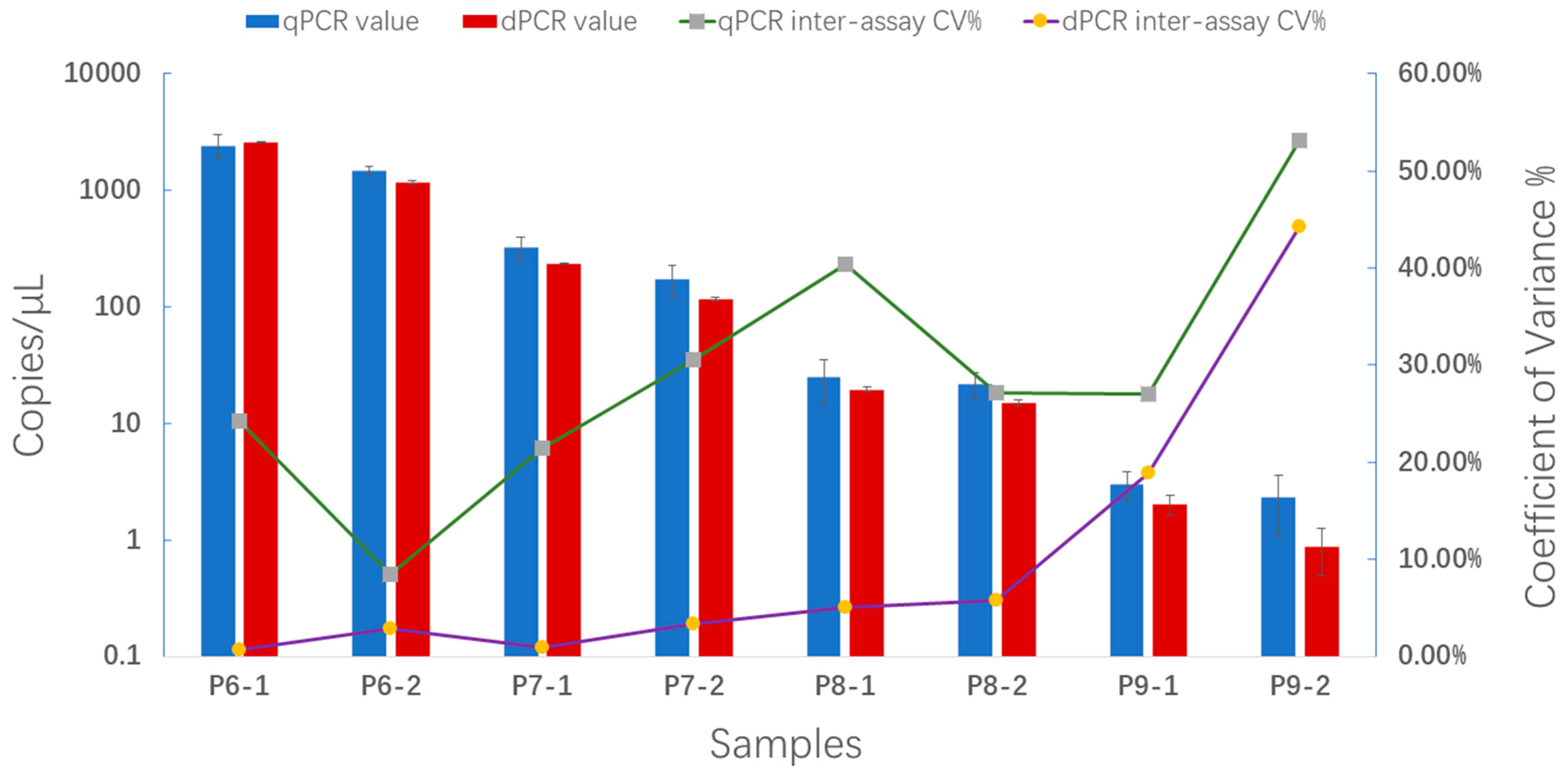
2.5. Comparison of Reproducibility between qPCR and ddPCR Assays
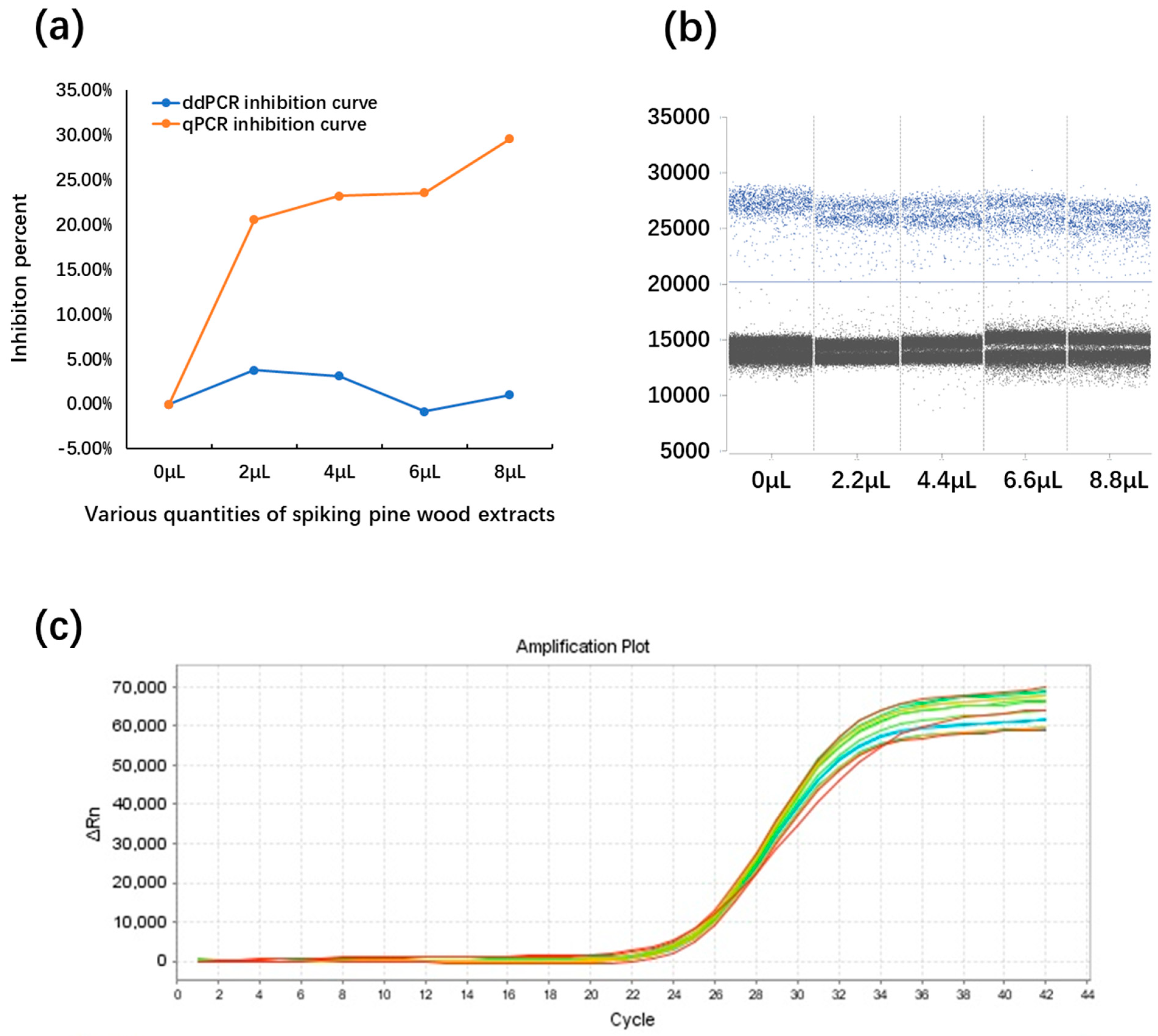
2.6. The Influence of PCR Inhibitors on the qPCR and ddPCR Assays
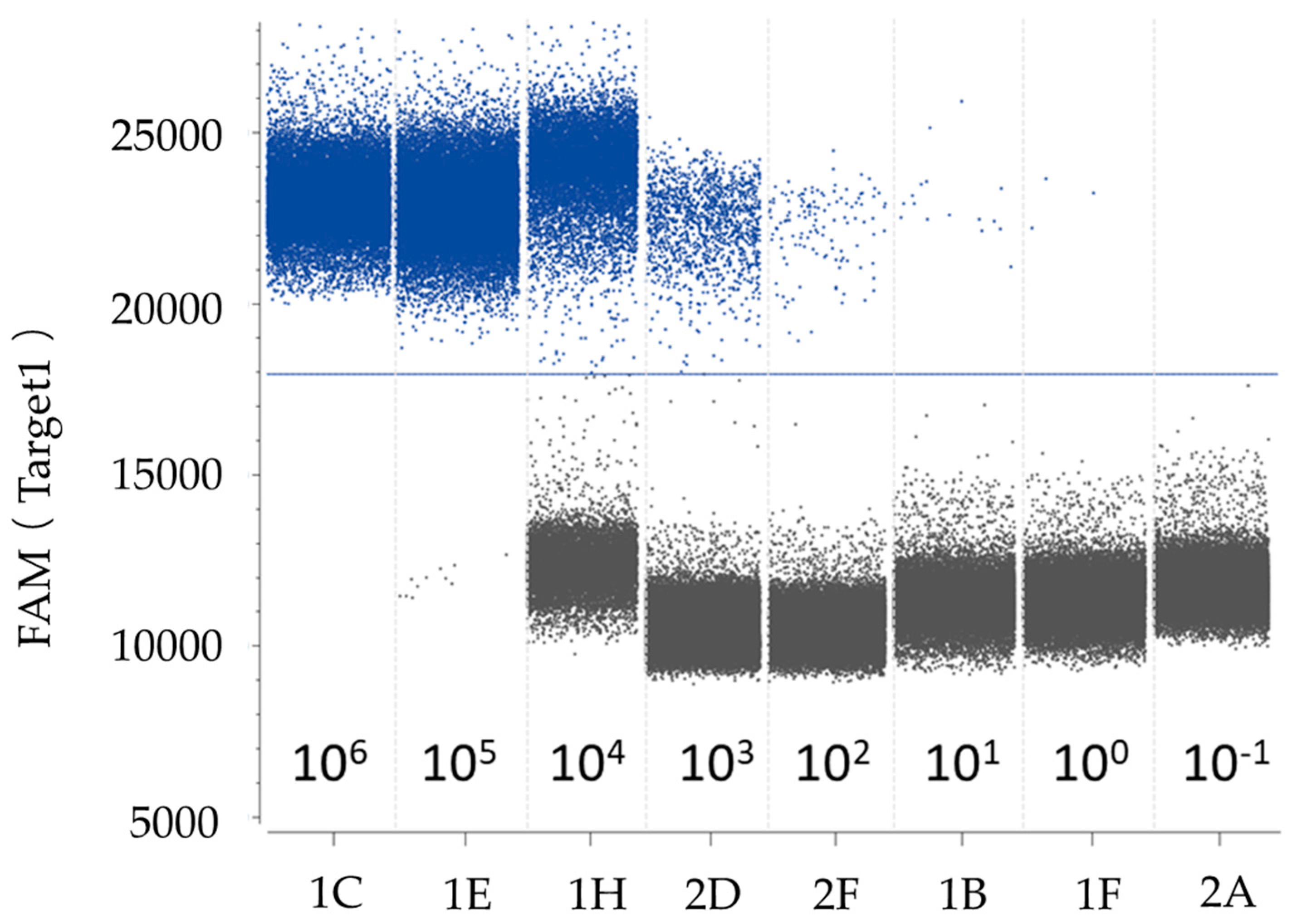
2.7. Comparison of Detection Sensitivity between ddPCR and qPCR Assays
2.8. Evaluation of the Method for Extracting DNA from Wood Samples
2.9. Comparison of Diagnostic Performance between ddPCR and qPCR Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Nematodes, PWN-Infected Pinewood Samples, and Spiked Samples
4.2. DNA Extraction
4.3. Primers and Taqman Probe Design
4.4. Preparation of Cloned Plasmid Standard
4.5. Quantitative PCR
4.6. Droplet Digital PCR
4.7. Assessing Inter-Assay Variability between ddPCR and qPCR Assays for Independent Experiments
4.8. Estimation of Tolerance to Inhibitors
4.9. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mamiya, Y. Pathology of the Pine Wilt Disease Caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1983, 21, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, F.; Hasegawa, K.; Mota, M.; Vicente, C. Bacterial Role in Pine Wilt Disease Development—Review and Future Perspectives: Bacteria in Pine Wilt Disease. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 7, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-L.; Fan, C.-J.; Jiang, X.-H.; Tian, X.-Y.; Han, Z.-M. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: An Important Pathogenic Factor of Pine Wilt Disease and Its Relationship with Bursaphelenchus mucronatus. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.F. Pathogenesis in Pine Wilt Caused by Pinewood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Nematol. 1988, 20, 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Bolla, R.I.; Weaver, C.; Winter, R.E.K. Genomic Differences among Pathotypes of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Nematol. 1988, 20, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Dwinell, L.D. First Report of Pine Wood Nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus) in Mexico. Plant Dis. 1993, 77, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, L.; Wick, R. First Report of Bursaphelenchus antoniae from Pinus strobus in the U.S. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiya, Y. History of Pine Wilt Disease in Japan. J. Nematol. 1988, 20, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.R.; Lin, M.S.; Li, W.Q. The Occurrence of a Pine Wilting Disease Caused by a Nematode Found in Nanjing. For. Pest. Dis. 1983, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Fei, K.; Zhang, C.; Xu, M.; Sun, J.; Ma, X.; Lai, R.; et al. Molecular Phylogeny of Geographical Isolates of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: Implications on the Origin and Spread of This Species in China and Worldwide. J. Nematol. 2008, 40, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Ren, J.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Pine Wilt Disease in Northeast and Northwest China: A Comprehensive Risk Review. Forests 2023, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.M. Pests and Disease Problems in European Forests. FAO Plant Prot. Bull. 1985, 33, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, M.M.; Braasch, H.; Bravo, M.A.; Penas, A.C.; Burgermeister, W.; Metge, K.; Sousa, E. First Report of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Portugal and in Europe. Nematology 1999, 1, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, H. Morphology of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Compared with Other Bursaphelenchus Species. In The Pinewood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 127–143. ISBN 978-90-474-1309-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bogale, M.; Baniya, A.; DiGennaro, P. Nematode Identification Techniques and Recent Advances. Plants 2020, 9, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Ding, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. The Detection of Pine Wilt Disease: A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, H.; Burgermeister, W.; Gu, J. Revised Intra-Generic Grouping of Bursaphelenchus fuchs, 1937 (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae). J. Nematode Morphol. Syst. 2009, 12, 65–88. [Google Scholar]
- Akbulut, S.; Vieira, P.; Ryss, A.; Valadas, V.; Keten, A.; Mota, M. Bursaphelenchus fuchs, 1937 (Nematoda: Parasitaphelenchidae) Species Associated with Pinus Species in Northern Turkey. Helminthologia 2008, 45, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Moreira, C.; Fonseca, L.; van Asch, B.; Mota, M.; Abrantes, I.; Amorim, A. New Insights into the Phylogeny and Worldwide Dispersion of Two Closely Related Nematode Species, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Bursaphelenchus mucronatus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Fengmao, C.; Xie, L.; Pan, H.; Ye, J. Genetic Diversity of Pine-Parasitic Nematodes Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Bursaphelenchus mucronatus in China. For. Pathol. 2017, 47, e12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahori, H.; Kanzaki, N.; Futai, K. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and B. mucronatus in Japan: Where Are They From? In Proceedings of the Fourth International Congress of Nematology, Tenerife, Spain, 8–13 June 2022; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, L.; Vieira dos Santos, C.; Santos, M.N.; Curtis, R.; Abrantes, I. Morpho-Biometrical Characterisation of Portuguese Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Isolates with Mucronate, Digitate or Round Tailed Females. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2008, 47, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Iwahori, H.; Tsuda, K.; Kanzaki, N.; Izui, K.; Futai, K. PCR-RFLP and Sequencing Analysis of Ribosomal DNA of Bursaphelenchus nematodes Related to Pine Wilt Disease. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1998, 21, 655–666. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Ye, J.; Tang, J.; Wu, X. Discrimination of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Bursaphelencus mucronatus by PCR-RFLP Technique. Front. For. China 2007, 2, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, T.; Kanzaki, N.; Maehara, N. ITS-RFLP Pattern of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) Does Not Reflect Nematode Virulence. J. For. Res. 2013, 18, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.A. DNA Amplification by the Polymerase Chain Reaction. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, K.; Togashi, K. A Simple Method for Discriminating Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and B. mucronatus by Species-Specific Polymerase Chain Reaction Primer Pairs. Nematology 2004, 6, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-P.; Sekhon, S.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, B.K.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. The Pine Wood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Molecular Diagnostic Methods. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2020, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Kanzaki, N.; Futai, K. A Nested PCR-Based Method for Detecting the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, from Pine Wood. Nematology 2005, 7, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Sambrook, J. Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2019, 2019, pdb.prot095182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xu, X.-L.; Wu, X.-Q.; Chen, F.-M.; Li, C.; Ye, J.-R.; Huang, L.; Xu, X.-L.; Wu, X.-Q.; Chen, F.-M.; et al. A Nested PCR Assay Targeting the DNA Topoisomerase I Gene to Detect the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Phytoparasitica 2010, 38, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, S.; Lu, B. Detection of the Pinewood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, Using a Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay. Phytopathology 2005, 95, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, I.; Allen, E.; Humble, L.; Green, M.; Rott, M. Application of Conventional PCR and Real-Time PCR Diagnostic Methods for Detection of the PineWood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, in Wood Samples from Lodgepole Pine. In Pine Wilt Disease: A Worldwide Threat to Forest Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 197–210. ISBN 978-1-4020-8454-6. [Google Scholar]
- Seesao, Y.; Gay, M.; Merlin, S.; Viscogliosi, E.; Aliouat-Denis, C.M.; Audebert, C. A Review of Methods for Nematode Identification. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 138, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Hu, L.; Wu, X. Identification of a Novel Effector BxSapB3 That Enhances the Virulence of Pine Wood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, A.-Y.; Han, H.; Moon, Y.; Koh, Y.H. Development of Two Alternative Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Tools for Detecting Pathogenic Pine Wood Nematodes. For. Pathol. 2014, 45, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Aikawa, T.; Oeda, Y.; Karim, N.; Kanzaki, N. A Rapid and Precise Diagnostic Method for Detecting the Pinewood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Genes Encoding Potential Molecular Mimicry Proteins as the Specific Targets for Detecting Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in PCR and Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 890949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, R.; Fockler, C.; Dollinger, G.; Watson, R. Kinetic PCR Analysis: Real-Time Monitoring of DNA Amplification Reactions. Nat. Biotechnol. 1993, 11, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, R.T.; Gu, Z.; Ingersoll, J.; Abdul-Ali, D.; Shi, L.; Pounds, S.; Caliendo, A.M. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR to Real-Time PCR for Quantitative Detection of Cytomegalovirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, P.; Neoh, S.H.; Brisco, M.; Hughes, E.; Condon, J.; Morley, A. Quantitation of Targets for PCR by Use of Limiting Dilution. BioTechniques 1992, 13, 444–449. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, M.; Komatsu, J.; Matsuura, S.; Takashima, K.; Katsura, S.; Mizuno, A. Single-Molecule PCR Using Water-in-Oil Emulsion. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 102, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, L.; Coleman, V.; Hindson, C.; Herrmann, J.; Hindson, B.; Bhat, S.; Emslie, K. Evaluation of a Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction Format for DNA Copy Number Quantification. Anal. Chem. 2011, 84, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, N.; Kadir, R.; Chan, K.A.; Chi, C.; Mellars, G.; Tuddenham, E.; Leung, T.; Lau, T.; Chiu, R.; Lo, D. Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Hemophilia by Microfluidics Digital PCR Analysis of Maternal Plasma DNA. Blood 2011, 117, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-Z.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Fang, W.-Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, C.-M.; Gao, Z.-H.; Gu, B.; Guo, X.-G.; Duan, C.-H. Establishment of Droplet Digital PCR for the Detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 110, 116351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, Z.; Song, K.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Cui, Y.; Du, Z.; Yang, R.; Song, Y.; Jing, L.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a Multi-Target Droplet Digital PCR Assay for Highly Sensitive and Specific Detection of Yersinia pestis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.; Carbonneau, J.; Shelton, D.; Boivin, G. Optimization of Droplet Digital PCR from RNA and DNA Extracts with Direct Comparison to RT-qPCR: Clinical Implications for Quantification of Oseltamivir-Resistant Subpopulations. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 224, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Raith, M.; Griffith, J. Droplet Digital PCR for Simultaneous Quantification of General and Human-Associated Fecal Indicators for Water Quality Assessment. Water Res. 2015, 70, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, L.; Simmons, M.; Wegleitner, B.; Jerde, C.; Mahon, A. Quantifying Environmental DNA Signals for Aquatic Invasive Species Across Multiple Detection Platforms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12800–12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothrock, M.; Hiett, K.; Kiepper, B.; Ingram, K.; Hinton Jr, A. Quantification of Zoonotic Bacterial Pathogens within Commercial Poultry Processing Water Samples Using Droplet Digital PCR. Adv. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floren, C.; Kilic, I.; Brenig, B.; Schütz, E.; Beck, J. Species Identification and Quantification in Meat and Meat Products Using Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR). Food Chem. 2015, 173, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowski-Mock, U.; Hauber, I.; Fehse, B. Digital PCR to Assess Gene-Editing Frequencies (GEF-dPCR) Mediated by Designer Nucleases. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, Q.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR and Quantitative PCR Assays for Quantitative Detection of Xanthomonas citri subsp. Citri. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Liu, X.; Lou, B.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X. Development of a Sensitive and Reliable Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Detection of ‘Candidatus liberibacter Asiaticus’. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, M.; Bonifacio, L.; Inacio, M.L.; Mota, M.; Boa, E. Review Article: Pine Wilt Disease: A Global Threat to Forestry. Plant Pathol. 2024, 73, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.S. Pine Wilt Disease: What Do We Know from Proteomics? BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 98, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Q. Rapid On-Site Detection of the Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Combined With Lateral Flow Dipstick That Eliminates Interference From Primer-Dependent Artifacts. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 856109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, I.; Allen, E.; Foord, B.; Anema, J.; Reisle, C.; Uzunovic, A.; Varga, A.; James, D. Detection of Living Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Wood, Using Reverse Transcriptase Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP). For. Pathol. 2015, 45, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Giblin-Davis, R.M. Molecular Characterization and Development of Real-Time PCR Assay for Pine-Wood Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Parasitaphelenchidae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Futai, K. Diagnosis and Quantification of the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhner), in Wood of Pinus Thunbergii with Real-Time PCR. Jpn. J. Nematol. 2009, 39, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Filipiak, A.; Hasiów-Jaroszewska, B. The Use of Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction with High Resolution Melting (Real-Time PCR-HRM) Analysis for the Detection and Discrimination of Nematodes Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Bursaphelenchus mucronatus. Mol. Cell. Probes 2016, 30, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Fonseca, L.; Abrantes, I. Direct Molecular Detection of the Pinewood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, from Pine Wood, Bark and Insect Vector. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Cho, K.-S. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR and Quantitative Real-Time PCR in mcrA-Based Methanogen Community Analysis. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharuthram, A.; Paximadis, M.; Picton, A.C.P.; Tiemessen, C.T. Comparison of a Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay and Droplet Digital PCR for Copy Number Analysis of the CCL4L Genes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 25, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, N.; Guarnera, M.; Jiang, F. Quantification of Plasma miRNAs by Digital PCR for Cancer Diagnosis. Biomark. Insights 2013, 8, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, T.C.; Sedlak, R.H.; Cook, L.; Jerome, K.R. Tolerance of Droplet-Digital PCR vs Real-Time Quantitative PCR to Inhibitory Substances. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1670–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, R.; Kuypers, J.; Jerome, K. A Multiplexed Droplet Digital PCR Assay Performs Better than qPCR on Inhibition Prone Samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 80, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, C.; Chevillet, J.; Briggs, H.; Gallichotte, E.; Ruf, I.; Hindson, B.; Vessella, R.; Tewari, M. Absolute Quantification by Droplet Digital PCR versus Analog Real-Time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, R.; Ma, B.; Zhang, M.; Song, H.; Zhang, X. A Multiplex Digital PCR Assay for Detection and Quantitation of Porcine Circovirus Type 2 and Type 3. Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langrell, S.; Barbara, D. Magnetic Capture Hybridisation for Improved PCR Detection of Nectria galligena from Lignified Apple Extracts. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2001, 19, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.B.; Cooper, T.A. Improved Direct PCR Screen for Bacterial Colonies: Wooden Toothpicks Inhibit PCR Amplification. BioTechniques 1995, 18, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fengmao, C.; Ye, J.-R.; Wu, X.-Q.; Tan, J.-J.; Huang, L. Two Kinds of Applied Molecular Skills to Detect Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Beijing Linye Daxue Xuebao J. Beijing For. Univ. 2011, 33, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, M. DNA Has a 521-Year Half-Life. Nature 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer and Probe Name | Primer and Probe Sequence 5′-3′ | TM | %GC | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1663F | GATGTTTCGGCATTGTCTTT | 53.9 | 40 | 20 |
| P2562R | GCTTACTGATATGCTTAAG | 41.4 | 37 | 19 |
| P1904-F | CTACGTGCTGTTGTTGAG | 46.4 | 50 | 18 |
| P2052-R | TCCACCGGAGTAACTTAA | 47.4 | 44 | 18 |
| Probe-1938 | 5′-FAM-CCGACAGATGAGACCAGCCA-TAMRA-3′ | 60.8 | 60 | 20 |
| Serial Number | Latin Name | Sample Name | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BX-01 | Liaoning |
| 2 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BX-02 | Chongqing |
| 3 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BX-03 | Shandong |
| 4 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BX-04 | Zhejiang |
| 5 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BX-05 | Guangdong |
| 6 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BX-06 | Fujian |
| 7 | Bursaphelenchus mucronatus | BM-01 | Jilin |
| 8 | Bursaphelenchus mucronatus | BM-02 | Neimenggu |
| 9 | Bursaphelenchus mucronatus | BM-03 | Heilongjiang |
| 10 | Bursaphelenchus thailandae | BT-01 | Shandong |
| 11 | Bursaphelenchus thailandae | BT-02 | Liaoning |
| 12 | Bursaphelenchus thailandae | BT-03 | Jilin |
| 13 | Bursaphelenchus sexdentati | BS-01 | Jilin |
| 14 | Bursaphelenchus dalianensis | BD-01 | Liaoning |
| 15 | Aphelenchoides parasaprophilus | AS-01 | Guangdong |
| 16 | Aphelenchoides resinosi | AR-01 | Liaoning |
| 17 | Aphelenchoides resinosi | AR-02 | Jilin |
| 18 | Cylindrotylenchus pini | CP-01 | Hunan |
| Pine Wood Sample | ddPCR | qPCR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Dead pine trees | 36 | 1 | 36 | 1 |
| Symptom pine trees | 15 | 0 | 13 | 2 |
| Asymptomatic pine trees | 11 | 24 | 1 | 34 |
| Pine Wood Sample by qPCR | Pine Wood Sample by ddPCR | |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |
| Positive | 50 | 0 |
| Negative | 12 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Zhu, X.; Jing, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, H. Establishment of a Sensitive and Reliable Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Plants 2024, 13, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192701
Su Y, Zhu X, Jing H, Yu H, Liu H. Establishment of a Sensitive and Reliable Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Plants. 2024; 13(19):2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192701
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yu, Xuedong Zhu, Haozheng Jing, Haiying Yu, and Huai Liu. 2024. "Establishment of a Sensitive and Reliable Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus" Plants 13, no. 19: 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192701
APA StyleSu, Y., Zhu, X., Jing, H., Yu, H., & Liu, H. (2024). Establishment of a Sensitive and Reliable Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Plants, 13(19), 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192701





