A Comparison between Inbred and Hybrid Maize Haploid Inducers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Variance
2.2. Heterosis and Hybrid Performance
2.3. Inbred-Hybrid Relationship
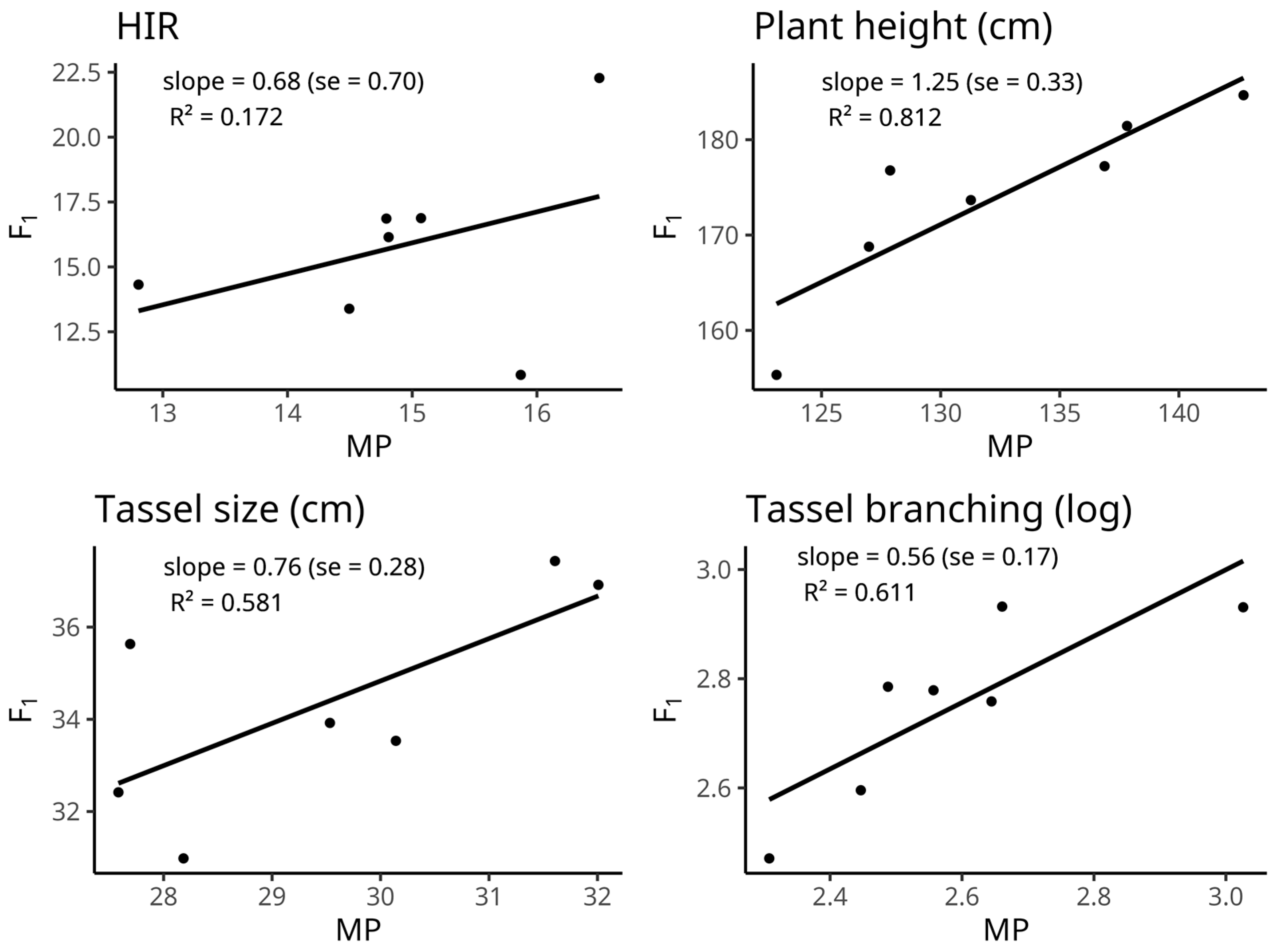
2.4. Trait Correlations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Data Collection
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaikam, V.; Molenaar, W.; Melchinger, A.E.; Prasanna, M.B. Doubled haploid technology for line development in maize: Technical advances and prospects. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 3227–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, S.P.; Russell, W.A.; Lamkey, K.R. Performance and genetic variance among S1 lines and testcrosses of iowa stiff stalk synthetic maize. Crop Sci. 1991, 31, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R.L.; Hallauer, A.R. Inbreeding depression in maize by selfing and full-sibbing. Crop Sci. 1977, 17, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.M. Doubled haploid (DH) technology in maize breeding: An overview. In Doubled Haploid Technology in Maize Breeding: Theory and Practice; Prasanna, B.M., Chaikam, V., Mahuku, G., Eds.; CIMMYT: Mexico City, Mexico, 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kelliher, T.; Starr, D.; Richbourg, L.; Chintamanani, S.; Delzer, B.; Nuccio, M.L.; Green, J.; Chen, Z.; McCuiston, J.; Wang, W.; et al. MATRILINEAL, a sperm-specific phospholipase, triggers maize haploid induction. Nature 2017, 542, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, C.; Qi, X.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, B.; Tian, X.; et al. Mutation of ZmDMP enhances haploid induction in maize. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yue, Y.; Zhao, H.; Fei, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Lai, J.; Song, W. Loss-of-function alleles of ZmPLD3 cause haploid induction in maize. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint-Garcia, S.A.; McMullen, M.D.; Darrah, L.L. Genetic relationship of stalk strength and ear height in maize. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Mei, M.; Frei, U.K.; Trampe, B.; Lübberstedt, T. Maize doubled haploids. Plant Breed. Rev. 2016, 40, 123–166. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, H.H. Doubled haploids in hybrid maize breeding. Maydica 2009, 54, 485–499. [Google Scholar]
- Prigge, V.; Schipprack, W.; Mahuku, G.; Atlin, G.N.; Melchinger, A.E. Development of in vivo haploid inducers for tropical maize breeding programs. Euphytica 2012, 185, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikam, V.; Nair, S.K.; Martinez, L.; Lopez, L.A.; Utz, H.F.; Melchinger, A.E.; Boddupalli, P.M. Marker-assisted breeding of improved maternal haploid inducers in maize for the tropical/subtropical regions. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uliana Trentin, H.; Frei, U.K.; Lübberstedt, T. Breeding maize maternal haploid inducers. Plants 2020, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revilla, P.; Tracy, W.F. Heterotic patterns among open-pollinated sweet corn cultivars. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1997, 122, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, T.E.; Tracy, W.F. Heterosis for flowering time and agronomic traits among early open-pollinated sweet corn cultivars. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2002, 127, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.F.; Zeppa, A.; Mulugeta, S.D. Combining ability, genetic diversity and heterosis in relation to F1 performance of tropically adapted shrunken (sh2) sweet corn lines. Plant Breed. 2012, 131, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Yang, J.H.; Lim, S.B.; Lee, H.B. Genetic distance and heterosis degree among the developed waxy corn lines. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2015, 60, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermail, A.; Suriharn, B.; Chankaew, S.; Sanitchon, J.; Lertrat, K. Hybrid prediction based on SSR-genetic distance, heterosis and combining ability on agronomic traits and yields in sweet and waxy corn. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 259, 108817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estakhr, A.; Heidari, B. Combining ability and gene action for maturity and agronomic traits in different heterotic groups of maize inbred lines and their diallel crosses. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 15, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, G.A.; Nyadanu, D.; Obeng-Antwi, K.; Amoah, A.; Danso, F.C.; Amissah, S. Estimating gene action, combining ability and heterosis for grain yield and agronomic traits in extra-early maturing yellow maize single-crosses under three agro-ecologies of Ghana. Euphytica 2017, 213, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, K.T.; Reddy, D.M.; Saida, N.V.; Nagaraju, C. Heterosis for leaf, tassel characters and yield in single cross hybrids of maize (Zea mays L.). Progress. Agric. 2012, 3, 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Brewbaker, J.L. Diversity and genetics of tassel branch numbers in maize. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East, E.M. Heterosis. Genetics 1936, 21, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, B. Heterosis Breeding; Agro-Biological Publications: Delhi, India, 1979; pp. 50–83. [Google Scholar]
- Vollbrecht, E.; Springer, P.S.; Goh, L.; Buckler, E.S.; Martienssen, R. Architecture of floral branch systems in maize and related grasses. Nature 2005, 436, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer, J.A.; Romay, M.C.; Gore, M.A.; Flint-Garcia, S.A.; Zhang, Z.; Millard, M.J.; Gardner, C.A.C.; McMullen, M.D.; Holland, J.B.; Bradbury, P.J.; et al. The genetic architecture of maize height. Genetics 2014, 196, 1337–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigge, V.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Babu, R.; Chen, S.; Atlin, G.N.; Melchinger, A.E. New insights into the genetics of in vivo induction of maternal haploids, the backbone of doubled haploid technology in maize. Genetics 2012, 190, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.W.; Li, L.; Dong, X.; Jin, W.E.; Melchinger, A.E.; Chen, S.J. Gametophytic and zygotic selection leads to segregation distortion through in vivo induction of a maternal haploid in maize. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araus, J.L.; Cairns, J.E. Field high-throughput phenotyping: The new crop breeding frontier. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 19, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsy, H.S.; Sharma, D. Study of cytoplasmic effects in reciprocal crosses of divergent varieties of maize (Zea mays L.). Euphytica 1972, 21, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khehra, A.S.; Bhalla, S.K. Cytoplasmic effects on quantitative characters in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 1976, 47, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, L.; Derera, J.; Tongoona, P.; MacRobert, J. Combining ability and reciprocal cross effects of elite quality protein maize inbred lines in subtropical environments. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermail, A.; Suriharn, B.; Lertrat, K.; Chankaew, S.; Sanitchon, J. Reciprocal cross effects on agronomic traits and heterosis in sweet and waxy corn. Sabrao J. Breed. Genet. 2018, 50, 444–460. [Google Scholar]
- Nanda, D.K.; Chase, S.S. An embryo marker for detecting monoploids of maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci. 1966, 6, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A.A. Statistical Procedure for Agricultural Research; John Wiley and Sons: Singapore, 1984; pp. 359–442. [Google Scholar]
| Source | HIR | Seed Sets | Plant Height | Ear Height | Tassel Size | (Log) Tassel Branch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 39.7 (3, 8.1) | 135.0 (3, 8.1) | 111.9 (2, 6) | 141.89 (2, 6) | 14.48 (1, 4) | 0.03 (1, 4) |
| Inducer | 22.4 *** (15,117) | 16.13 *** (15, 117) | 338.0 *** (15, 90) | 38.84 *** (15, 90) | 38.97 *** (15, 59) | 15.47 *** (15, 59) |
| Year × Inducer | 11.0 *** (44, 117) | 6.58 *** (44, 117) | 14.6 *** (30, 90) | 4.25 *** (30, 90) | 1.94 * (15, 59) | 1.19 ns (15, 59) |
| Variance components estimates: | ||||||
| Rep (Year) | 0.0466 | 0 | 2.43 | 0 | 0.39 | 0 |
| Error | 4.832 | 668 | 19.70 | 34.7 | 3.42 | 0.0222 |
| Year | Hybrid Inducers | Haploid Induction Rate (%) | Seed Set (Seeds Per Donor Ear) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | F1 | MPH (%) | MP | F1 | MPH (%) | ||
| 16 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 12.1 | 14.9 | 23.1 | 179.8 | 236.0 | 31.2 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 15.9 | 16.3 | 2.7 | 190.3 | 211.7 | 11.2 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 13.9 | 16.4 | 18.2 | 176.2 | 169.3 | −3.9 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 15.3 | 14.5 | −4.9 | 255.3 | 226.7 | −11.2 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 13.8 | 17.1 | 24.2 | 208.7 | 185.7 | −11 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 11.8 | 13.6 | 15.1 | 151.0 | 167.3 | 10.8 | |
| 17 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 16.9 | 22.7 | 34.4 | 225.3 | 211.7 | −6.1 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 15.0 | 24.8 | 65.7 | 227.2 | 119.7 | −47.3 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 15.7 | 12.8 | −18.3 | 227.2 | 215.7 | −5.1 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 17.8 | 16.0 | −10.5 | 205.2 | 235.3 | 14.7 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 19.7 | 20.8 | 5.4 | 205.0 | 206.7 | 0.8 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 18.1 | 21.1 | 16.9 | 216.3 | 201.3 | −6.9 | |
| PHI-3/RWS | 14.1 | 14.3 | 1.5 | 169.2 | 244.7 | 44.6 | |
| 18-1 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 17.5 | 7.1 | −59.5 | 61.2 | 118.0 | 92.9 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 18.3 | 30.5 | 66.8 | 85.8 | 165.3 | 92.6 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 15.4 | 12.4 | −19.2 | 66.8 | 131.3 | 96.5 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 16.1 | 5.1 | −68.5 | 84.3 | 150.3 | 78.3 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 13.8 | 15.2 | 10.5 | 91.0 | 130.7 | 43.6 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 15.4 | 20.9 | 35.9 | 75.0 | 155.7 | 107.6 | |
| PHI-3/RWS | 14.5 | 13.1 | −9.7 | 119.3 | 293.0 | 145.5 | |
| 18-2 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 13.7 | 22.8 | 65.8 | 97.5 | 134.0 | 37.4 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 16.9 | 17.5 | 3.7 | 103.0 | 153.7 | 49.2 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 13.1 | 12.0 | −8.7 | 83.8 | 111.0 | 32.4 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 14.3 | 7.8 | −45.4 | 133.5 | 109.7 | −17.9 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 12.0 | 11.5 | −4.3 | 112.8 | 162.7 | 44.2 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 13.9 | 11.8 | −14.9 | 97.5 | 132.3 | 35.7 | |
| PHI-3/RWS | 9.8 | 15.5 | 58.8 | 119.8 | 149.3 | 24.6 | |
| Year | Hybrid Inducers | Plant Height (cm) | Ear Height (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | F1 | MPH (%) | MP | F1 | MPH (%) | ||
| 17 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 119.1 | 139.7 | 17.2 | 44.2 | 46.3 | 4.8 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 115.8 | 157.0 | 35.6 | 48.2 | 59.3 | 23 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 115.0 | 147.0 | 27.9 | 44.4 | 57.7 | 29.9 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 127.1 | 166.0 | 30.6 | 46.1 | 59.7 | 29.6 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 130.8 | 159.3 | 21.8 | 49.1 | 50.3 | 2.6 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 127.1 | 165.7 | 30.3 | 49.9 | 68.3 | 37.0 | |
| PHI-3/RWS | 118.2 | 156.7 | 32.6 | 36.7 | 57.3 | 56.4 | |
| 18-1 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 127.3 | 185.7 | 45.8 | 42.8 | 52.3 | 22.2 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 130.8 | 185.7 | 41.9 | 42.0 | 53.7 | 27.8 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 141.0 | 189.3 | 34.3 | 44.0 | 56.3 | 28.0 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 141.7 | 186.0 | 31.3 | 42.7 | 58.7 | 37.5 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 151.8 | 199.3 | 31.3 | 51.3 | 61.0 | 18.8 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 151.2 | 193.7 | 28.1 | 56.2 | 60.0 | 6.8 | |
| PHI-3/RWS | 120.0 | 150.3 | 25.3 | 34.7 | 39.3 | 13.5 | |
| 18-2 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 134.5 | 181.0 | 34.6 | 57.8 | 81.7 | 41.2 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 137.0 | 187.7 | 3.0 | 60.7 | 84.0 | 38.5 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 137.8 | 184.7 | 34.0 | 55.8 | 82.7 | 48.1 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 141.8 | 179.7 | 26.7 | 60.8 | 80.3 | 32.1 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 145.5 | 195.3 | 34.2 | 59.0 | 77.0 | 30.5 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 135.2 | 185.0 | 36.9 | 58.5 | 93.3 | 59.5 | |
| PHI-3/RWS | 131.2 | 159.0 | 21.2 | 53.7 | 60.0 | 11.8 | |
| Year | Hybrid Inducers | Tassel Size (cm) | (log) Tassel Branching | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | F1 | MPH (%) | MP | F1 | MPH (%) | ||
| 18-1 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 27.7 | 30.3 | 9.6 | 2.3 | 2.7 | 13.1 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 26.7 | 31.2 | 16.9 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 8.0 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 27.1 | 33.8 | 24.9 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 10.8 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 30.5 | 32.8 | 7.7 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 10.3 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 31.5 | 35.3 | 12.2 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 11.3 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 30.4 | 32.8 | 7.9 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 10.9 | |
| PHI-3/RWS | 29.6 | 35.8 | 21.3 | 3.1 | 3.1 | −1.0 | |
| 18-2 | BHI201/LH82-Ped126 | 28.7 | 31.6 | 10.2 | 2.5 | 2.5 | −0.4 |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped128 | 28.5 | 33.7 | 18.1 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 6.2 | |
| BHI201/LH82-Ped129 | 28.3 | 37.4 | 32.3 | 2.7 | 2.7 | −1.9 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped115 | 29.8 | 34.2 | 14.9 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 7.2 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped117 | 32.5 | 38.5 | 18.4 | 2.7 | 3.0 | 9.1 | |
| BHI201/Mo17-Ped123 | 28.7 | 35.0 | 22.2 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 13.0 | |
| PHI-3/RWS | 33.7 | 39.0 | 15.9 | 3.0 | 2.8 | −5.3 | |
| Traits | Seed Set | HIR | Plant Height | Ear Height | Tassel Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIR | 0.09 | ||||
| Plant height | 0.10 | 0.10 | |||
| Ear height | −0.11 | 0.07 | 0.90 ** | ||
| Tassel size | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.70 ** | 0.70 ** | |
| Tassel branching | 0.40 | −0.32 | 0.02 | −0.10 | 0.33 |
| Seed Set | HIR | Plant Height | Ear Height | Tassel Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIR | −0.17 | ||||
| Plant height | 0.07 | 0.38 | |||
| Ear height | −0.06 | 0.44 | 0.94 ** | ||
| Tassel size | −0.05 | 0.03 | 0.61 ** | 0.43 | |
| Tassel branching | 0.15 | −0.63 | 0.03 | −0.14 | 0.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trentin, H.U.; Yavuz, R.; Dermail, A.; Frei, U.K.; Dutta, S.; Lübberstedt, T. A Comparison between Inbred and Hybrid Maize Haploid Inducers. Plants 2023, 12, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051095
Trentin HU, Yavuz R, Dermail A, Frei UK, Dutta S, Lübberstedt T. A Comparison between Inbred and Hybrid Maize Haploid Inducers. Plants. 2023; 12(5):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051095
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrentin, Henrique Uliana, Recep Yavuz, Abil Dermail, Ursula Karoline Frei, Somak Dutta, and Thomas Lübberstedt. 2023. "A Comparison between Inbred and Hybrid Maize Haploid Inducers" Plants 12, no. 5: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051095
APA StyleTrentin, H. U., Yavuz, R., Dermail, A., Frei, U. K., Dutta, S., & Lübberstedt, T. (2023). A Comparison between Inbred and Hybrid Maize Haploid Inducers. Plants, 12(5), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051095






