Micromorphology of Pine Needle Primordia and Young Needles after Bud Dormancy Breaking
Abstract
1. Introduction
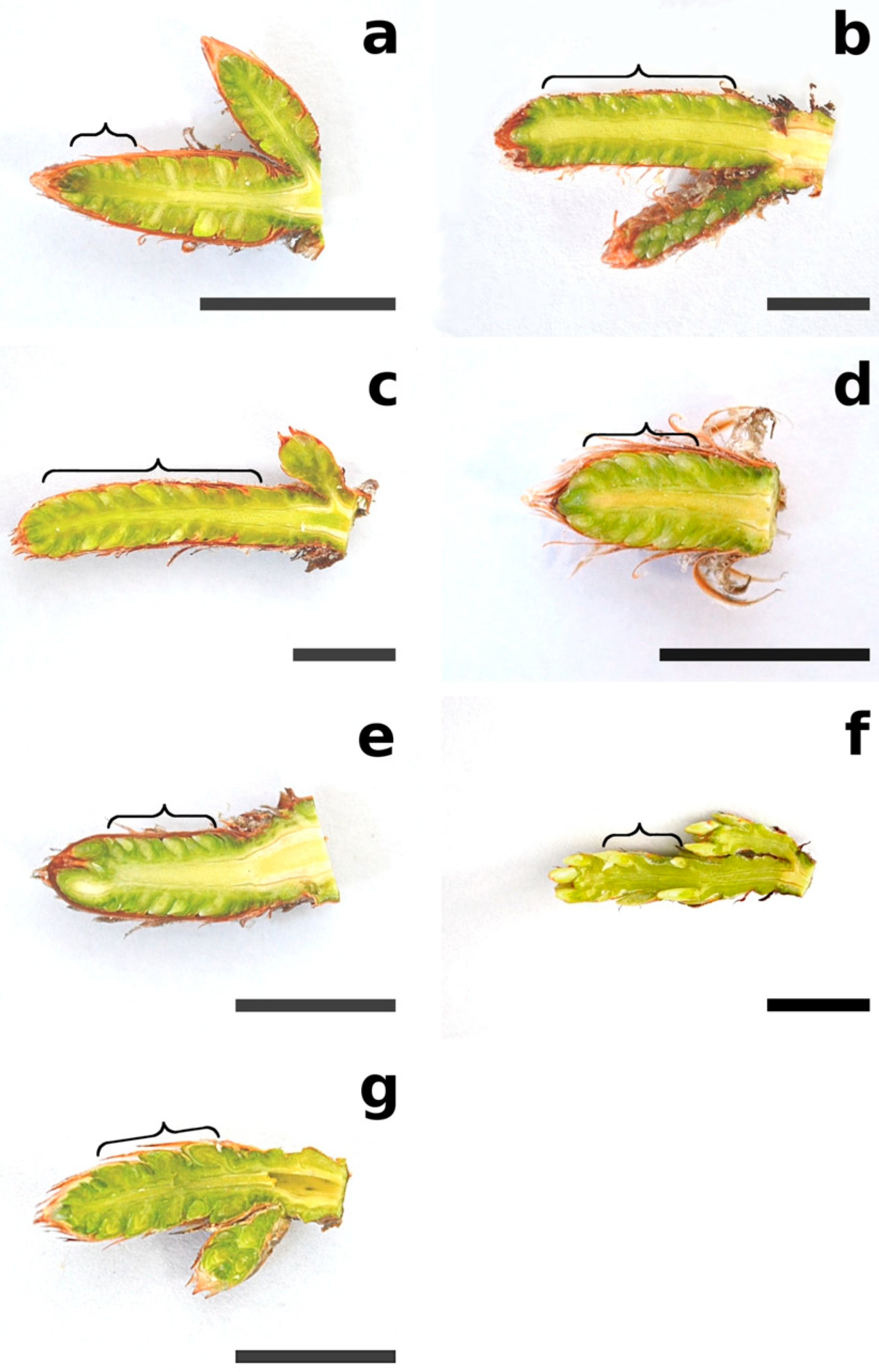
2. Results
2.1. B2 Phase
2.2. B3 Phase
| Diploxylon | Haploxylon | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Needle Trait | Phase | P. sylvestris | P. mugo | P. rigida | P. nigra | P. uncinata | P. cembra | P. strobus |
| needle tip | B2 | rounded | rounded | pointed | pointed | pointed | rounded, with very few teeth | pointed, with teeth |
| B3 | pointed | pointed | pointed | long and pointed | more or less pointed | pointed | slightly rounded, with teeth | |
| teeth on needle margin | B2 | not visible | small, pointed, near needle tip | not visible | not visible | not visible | few, rounded on the tip, pointed on base | numerous, rounded in upper part, pointed on tip |
| B3 | small, pointed, near needle apex | numerous, pointed | small and pointed, some near needle apex | numerous, small, pointed | few, small, pointed | few, small, pointed | numerous, big, pointed teeth covering needle tip | |
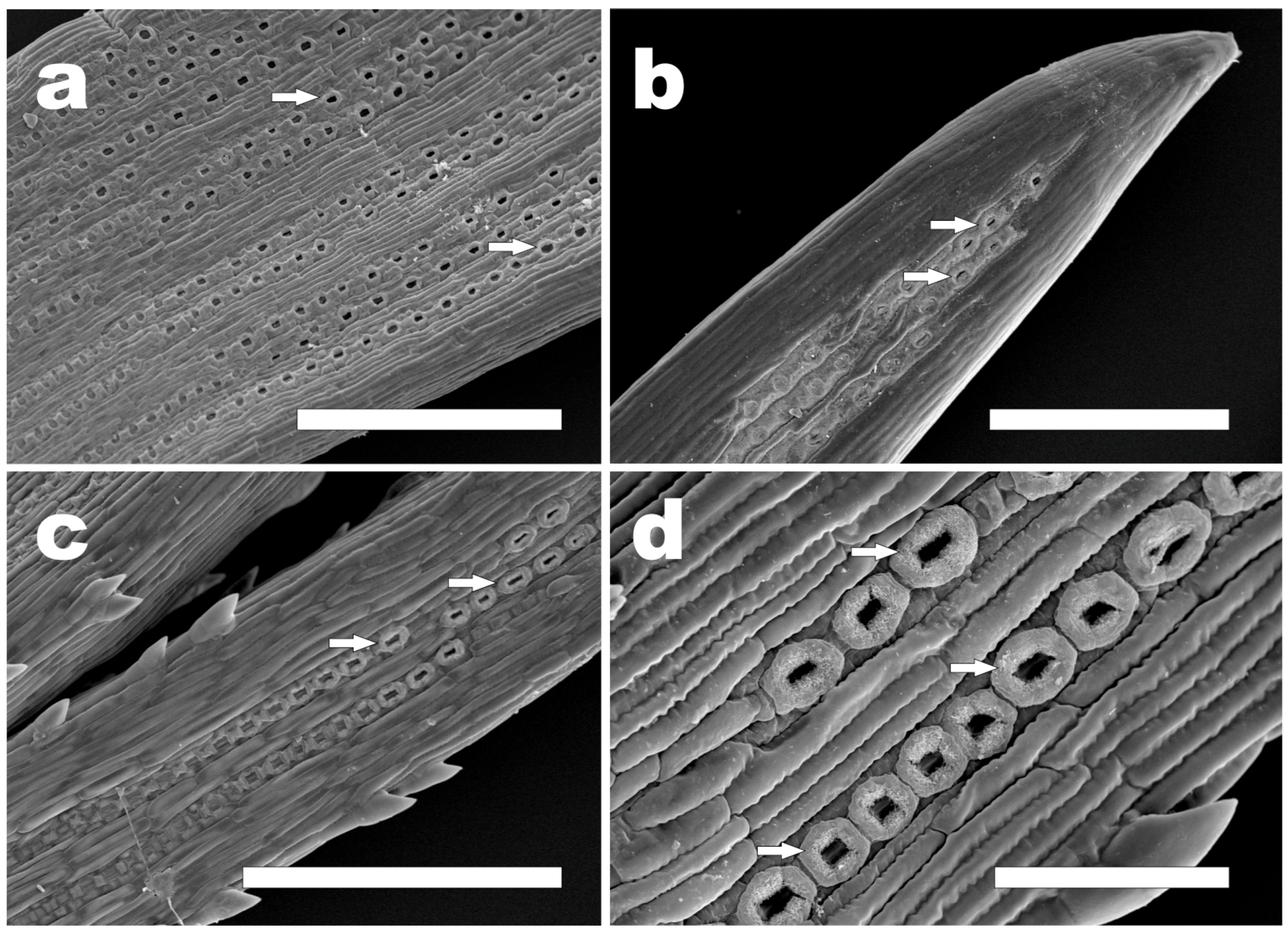
| stomata | B2 | few stomata near needle tip | few stomata near needle tip | not visible | few stomata near needle tip | not visible | not visible | not visible |
| B3 | numerous, arranged in rows, clearly visible Florin rings | numerous, arranged in rows | numerous, arranged in rows | numerous, arranged in rows | numerous, arranged in rows | numerous, arranged in rows, visible Florin rings | numerous, arranged in rows, visible Florin rings | |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doak, C.C. Evolution of Foliar Types, Dwarf Shoots, and Cone Scales of Pinus; Illinois Botanical Monographs; University of Illinois: Urbana, IL, USA, 1935; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Sacher, J.A. Dwarf shoot ontogeny in Pinus lambertiana. Am. J. Bot. 1955, 42, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.D.; Popham, R.A. The developmental anatomy of long-branch terminal buds of Pinus banksiana. Am. J. Bot. 1972, 59, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejnowicz, A. Budowa i Rozwój Wegetatywnych Pąków Sosny Zwyczajnej (Pinus sylvestris L.) [Structure and Development of Vegetative Buds of Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris L.)]; Instytut Dendrologii: Kórnik, Poland, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, J.N. The Reproductive Biology of Lodgepole Pine; Forest Renewal BC: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2006.
- Hejnowicz, A. Anatomia i Embriologia [Anatomy and Embryology]. In Biologia Sosny Zwyczajnej [Biology of Scots Pine]; Białobok, S., Boratyński, A., Bugała, W., Eds.; Polska Akademia Nauk—Instytut Dendrologii w Kórniku: Poznań-Kórnik, Poland, 1993; pp. 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sacher, J.A. Structure and seasonal activity of the shoot apices of Pinus lambertiana and Pinus ponderosa. Am. J. Bot. 1954, 41, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romberger, J.A. Meristems, Growth, and Development in Woody Plants; Technical Bulletin; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1963; Volume 1293.
- Kozlowski, T.T. Growth And Development of Trees. Volume I: Seed Germination, Ontogeny and Shoot Growth; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Wareing, P.F. Growth studies in woody species I. Photoperiodism in first-year seedlings of Pinus silvestris. Physiol. Plant. 1950, 3, 258–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanner, R.M. Origin of the summer shoot of pinyon pines. Can. J. Bot. 1970, 48, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debazac, E.F. Les modalités de la croissance en longueur chez les Pins. Bull. Soc. Bot. Fr. 1966, 113, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R. Electron microscopy of the development of needles of Pinus nigra var. maritima. Ann. Bot. 1972, 36, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.N.; Molder, M. Development of long-shoot terminal buds of western white pine (Pinus monticola). Can. J. Bot. 1977, 55, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollman, M.P. Morphology of long-shoot development in Pinus radiata. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 1983, 13, 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- Jordy, M.-N. Seasonal variation of organogenetic activity and reserves allocation in the shoot apex of Pinus pinaster Ait. Ann. Bot. 2004, 93, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaudinova, E.V.; Mironov, P.V. Lipids of the meristems of the main coniferous edificators from Central Siberia under low-temperature adaptation: 1. The characteristics of the fatty acid composition of phospholipids from winter meristems of Larix sibirica Ledeb., Picea obovata L., and Pinus sylvestris L. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2010, 36, 867–871. [Google Scholar]
- Szubert, M. Monografia sosny pospolitey [Monograph of Scots pine]. Sylwan 1820, 1, 55–122. [Google Scholar]
- Beerling, D.J.; Kelly, C.K. Stomatal density responses of temperate woodland plants over the past seven decades of CO2 increase: A comparison of Salisbury (1927) with contemporary data. Am. J. Bot. 1997, 84, 1572–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S.; Kozlowski, T.T. The role of cotyledons in early development of pine seedlings. Can. J. Bot. 1968, 46, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Kozlowski, T.T. Effects of cotyledon and hypocotyl photosynthesis on growth of young pine seedlings. New Phytol. 1970, 69, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, J.; Štokrová, J. Structure of the needles in the early phases of development in Pinus ponderosa P. et C. Lawson with special reference to plastids. Ann. Bot. 1993, 72, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, A.M.; Woodward, F.I. The Role of stomata in sensing and driving environmental change. Nature 2003, 424, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krassilov, V.; Berner, A.; Barinova, S. Morphology as clue to developmental regulation: Stomata. Plant 2013, 1, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouwenberg, L.L.R.; McElwain, J.C.; Kürschner, W.M.; Wagner, F.; Beerling, D.J.; Mayle, F.E.; Visscher, H. Stomatal frequency adjustment of four conifer species to historical changes in atmospheric CO2. Am. J. Bot. 2003, 90, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boratyńska, K.; Bobowicz, M.A. Pinus uncinata Ramond taxonomy based on needle characters. Plant Syst. Evol. 2001, 227, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boratyńska, K.; Jasińska, A.K.; Boratyński, A. Taxonomic and geographic differentiation of Pinus mugo complex on the needle characteristics. Syst. Biodivers. 2015, 13, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romberger, J.A.; Hejnowicz, Z.; Hill, J.F. Plant Structure: Function and Development a Treatise on Anatomy and Vegetative Development, with Special Reference to Woody Plants; Softcover Reprint of the Original 1st ed. 1993; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kouwenberg, L.L.R.; Kürschner, W.M.; Visscher, H. Changes in stomatal frequency and size during elongation of Tsuga heterophylla needles. Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.N. Initiation and development of leaves in Douglas fir. Can. J. Bot. 1968, 46, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.N.; Tranquillini, W. Studies on upper timberline: Morphology and anatomy of Norway spruce (Picea abies) and stone pine (Pinus cembra) needles from various habitat conditions. Can. J. Bot. 1976, 54, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, F.I.; Lake, J.A.; Quick, W.P. Stomatal development and CO2: Ecological consequences. New Phytol. 2002, 153, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carins Murphy, M.R.; Jordan, G.J.; Brodribb, T.J. Acclimation to humidity modifies the link between leaf size and the density of veins and stomata: VPD alters the link between leaf size and anatomy. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T. The variability of stomatal sensitivity to leaf water potential across tree species indicates a continuum between isohydric and anisohydric behaviours. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yu, G.; He, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, N.; Xu, Z.; Ge, J. Latitudinal variation of leaf stomatal traits from species to community level in forests: Linkage with ecosystem productivity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esau, K. Anatomy of Seed Plants, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Pallardy, S.G. Physiology of Woody Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wyman, D. Simple key to the pines. Arnoldia 1951, 11, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- An, P.-C.; Tang, D.-L.; Chen, H.; Yang, Q.; Ding, S.-T.; Wu, J.-Y. Pliocene white pine (Pinus subgenus Strobus) needles from Western Yunnan, Southwestern China. Hist. Biol. 2019, 31, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Whang, S.S.; Pak, J.-H.; Hill, R.S.; Kim, K. Cuticle micromorphology of leaves of Pinus (Pinaceae) from Mexico and Central America. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2001, 135, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Álvarez, S.; Morla Juaristi, C.; Paull, R.; García-Amorena, I. A Taxonomic tool for identifying needle remains of South-Western European Pinus species of the Late Quaternary. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 175, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, S.S.; Kim, K.; Hill, R.S. Cuticle micromorphology of leaves of Pinus (Pinaceae) from North America. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 144, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovides, A.P.; Galicia, S. G-fibers and Florin ring-like structures in Dioon (Zamiaceae). Bot. Sci. 2016, 94, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, R.J.; Melville, L.H.; Peterson, R.L. Epistomatal chambers in the needles of Pinus strobus L. (eastern white pine) function as microhabitat for specialized fungi. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2001, 162, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilf, P.; Little, S.A.; Iglesias, A.; del Carmen Zamaloa, M.; Gandolfo, M.A.; Cúneo, N.R.; Johnson, K.R. Papuacedrus (Cupressaceae) in Eocene Patagonia: A new fossil link to Australasian rainforests. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 2031–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockey, R.A.; Ko, H.; Woltz, P. Cuticle micromorphology of Falcatifolium de Laubenfels (Podocarpaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 1992, 153, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florin, R. Untersuchungen zur Stammesgeschichte der Coniferales und Cordiatales: T. 1, Morphologie und Epidermisstruktur der Assimilationsorgane bei den rezenten Koniferen; Almqvist & Wiksell: Stockholm, Sweden, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Boulter, M.C. Fine Details of Some Fossil and Recent Conifer Leaf Cuticles. In Scanning Electron Microscopy. Systematic and Evolutionary Applications, Proceedings of an International Symposium, Department of Botany, University of Reading; Heywood, V.H., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 211–235. [Google Scholar]
- Oladele, F.A. Scanning electron microscope study of stomatal-complex configuration in Cupressaceae. Can. J. Bot. 1983, 61, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshie, F.; Sara, A. Types of Florin rings, distributional patterns of epicuticular wax, and their relationships in the genus Pinus. Can. J. Bot. 1985, 63, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjon, A.; Styles, B.T. Pinus (Pinaceae); Flora Neotropica; New York Botanical Garden: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 75. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Whang, S.S.; Hill, R.S. Cuticle micromorphology of leaves of Pinus (Pinaceae) in East and South-East Asia. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1999, 129, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florin, R. Evolution in cordaites and conifers. Acta Horti Berg. 1951, 15, 285–388. [Google Scholar]
- Florin, R. Studien über die Cycadales des Mesozoikums nebst Erörterungen über die Spaltöffnungsapparate der Bennettitales. Kongliga Sven. Vetensk.-Akad. Handl. 1933, 12, 1–134. [Google Scholar]
- Froyd, C.A. Fossil stomata reveal early pine presence in Scotland: Implications for postglacial colonization analyses. Ecology 2005, 86, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Zain Ul Abidin, S.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Liu, J.; Lubna; Jamshed, S.; Kiliç, Ö. Taxonomic importance of sem and lm foliar epidermal micro-morphology: A tool for robust identification of gymnosperms. Flora 2019, 255, 42–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudall, P.J.; Hilton, J.; Bateman, R.M. Several developmental and morphogenetic factors govern the evolution of stomatal patterning in land plants. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-Q.; Mingram, J.; Stebich, M.; Li, J.-F. A key for the identification of conifer stomata from N.E. China based on fluorescence microscopy. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2016, 233, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsinger, W.; Tinner, W. New insights on stomata analysis of European conifers 65 years after the pioneering study of Werner Trautmann (1953). Veget. Hist. Archaeobot. 2020, 29, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElwain, J.C.; Steinthorsdottir, M. Paleoecology, ploidy, paleoatmospheric composition, and developmental biology: A review of the multiple uses of fossil stomata. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, E.-M.; Schmidt, A.; Seyfullah, L.; Kunzmann, L. Conifers of the “Baltic Amber Forest” and their palaeoecological significance. Stapfia 2017, 106, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzin, S.E. Plant Microtechnique and Microscopy; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA; Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guzicka, M.; Marek, S.; Gawlak, M.; Tomaszewski, D. Micromorphology of Pine Needle Primordia and Young Needles after Bud Dormancy Breaking. Plants 2023, 12, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040913
Guzicka M, Marek S, Gawlak M, Tomaszewski D. Micromorphology of Pine Needle Primordia and Young Needles after Bud Dormancy Breaking. Plants. 2023; 12(4):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040913
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuzicka, Marzenna, Sławomir Marek, Magdalena Gawlak, and Dominik Tomaszewski. 2023. "Micromorphology of Pine Needle Primordia and Young Needles after Bud Dormancy Breaking" Plants 12, no. 4: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040913
APA StyleGuzicka, M., Marek, S., Gawlak, M., & Tomaszewski, D. (2023). Micromorphology of Pine Needle Primordia and Young Needles after Bud Dormancy Breaking. Plants, 12(4), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040913







