A Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profile of Heat Shock Transcription Factor (Hsf) Gene Family in Rhododendron simsii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Gene Identification and Physicochemical Properties of Putative Proteins
2.2. Location of Genes on Chromosomes
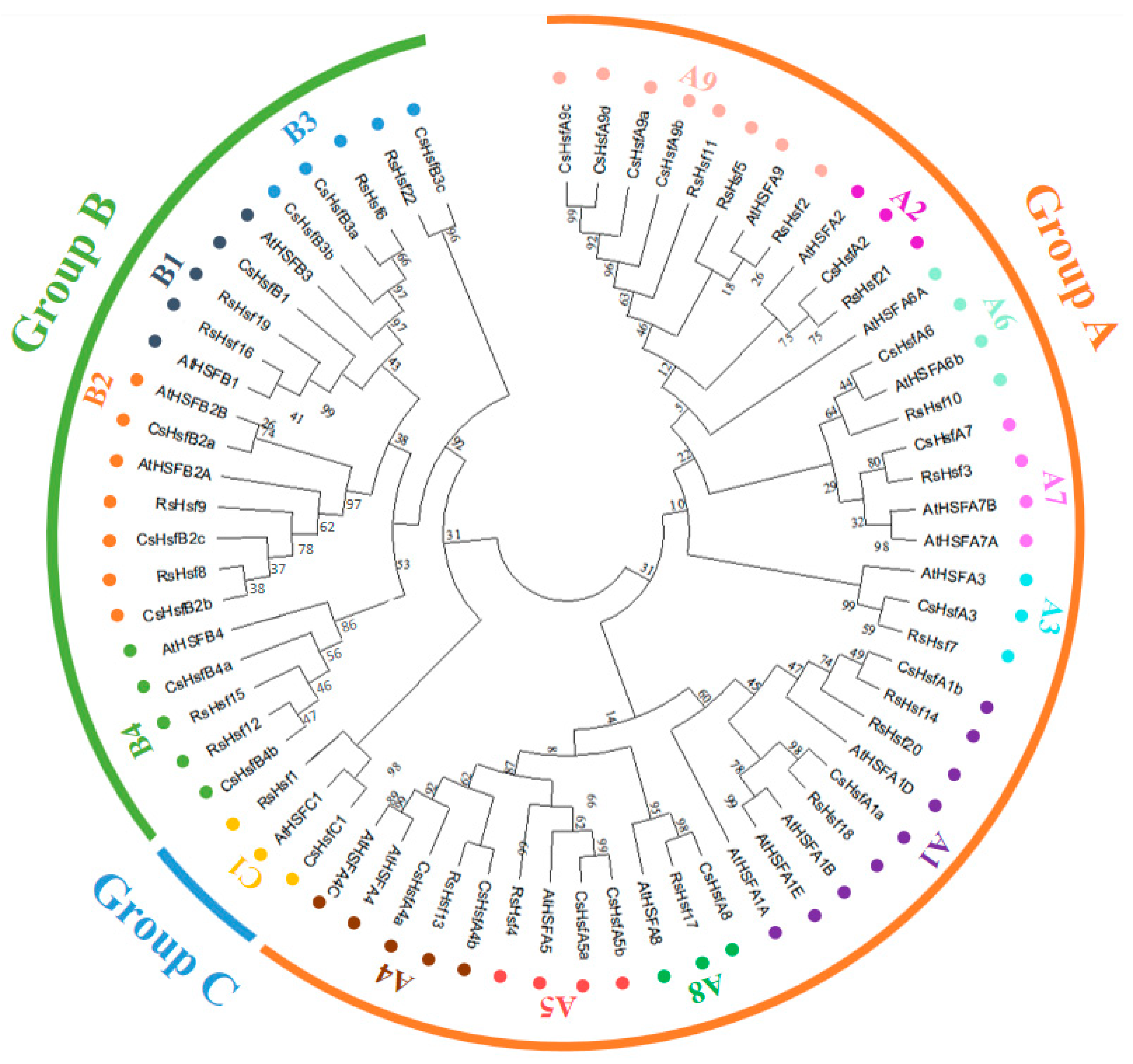
2.3. Phylogenetic Classification
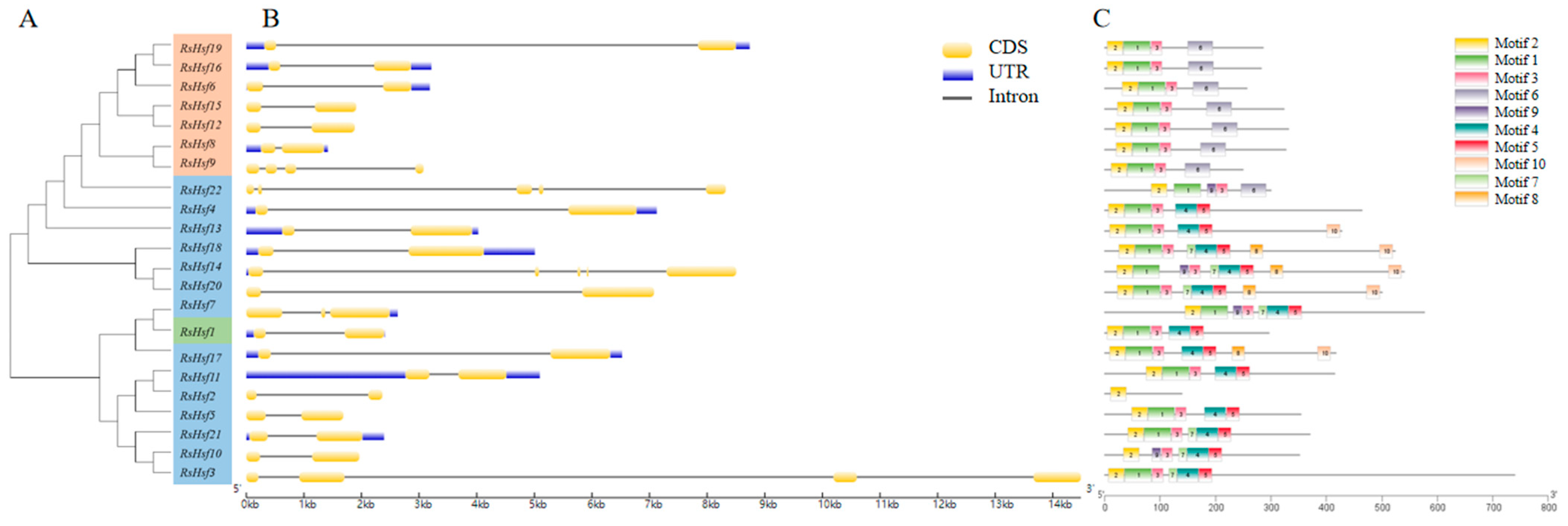
2.4. Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs
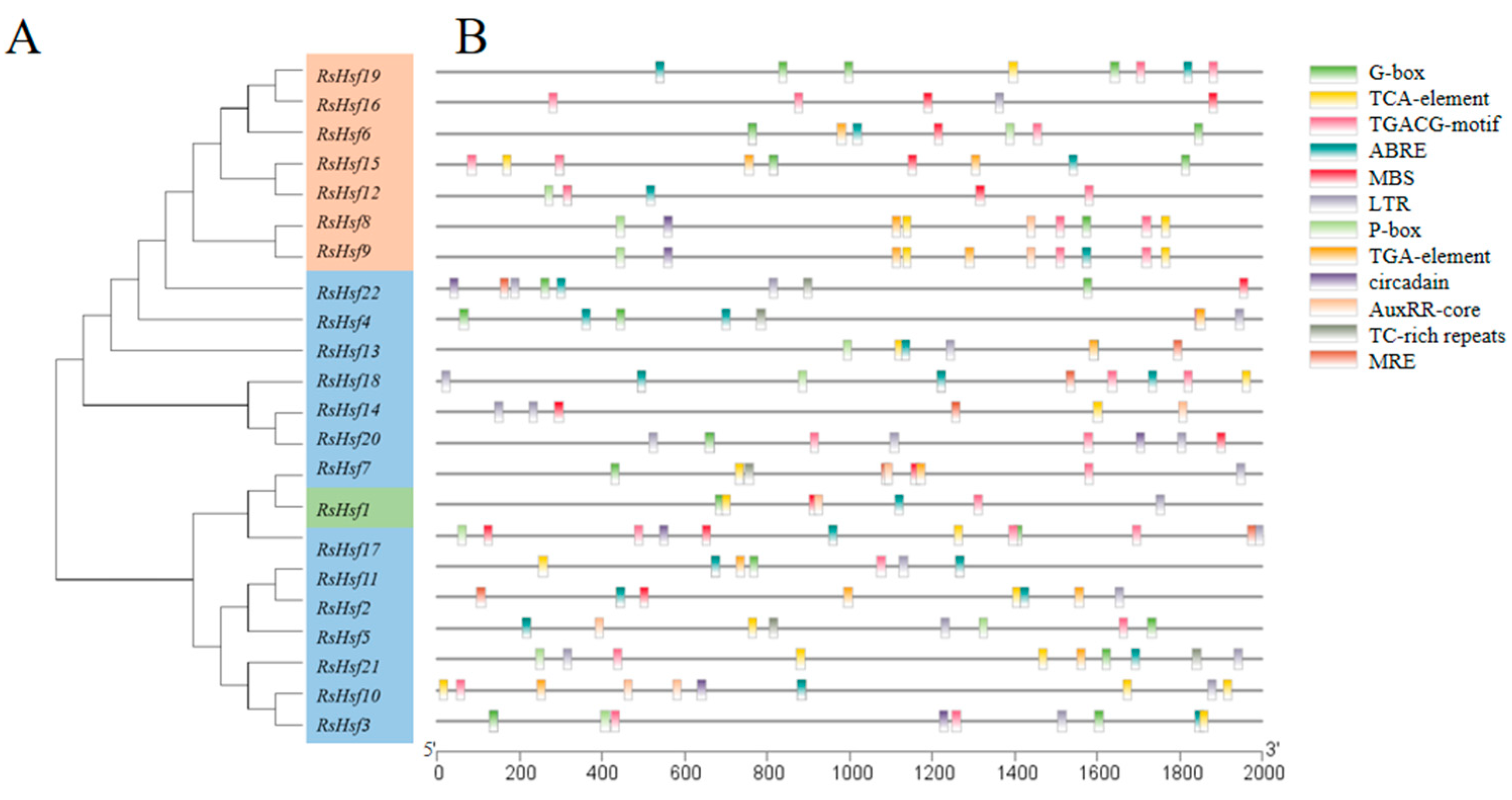
2.5. Promoter Analysis
2.6. Tissue-Specific Transcriptional Profiles of RsHsfs
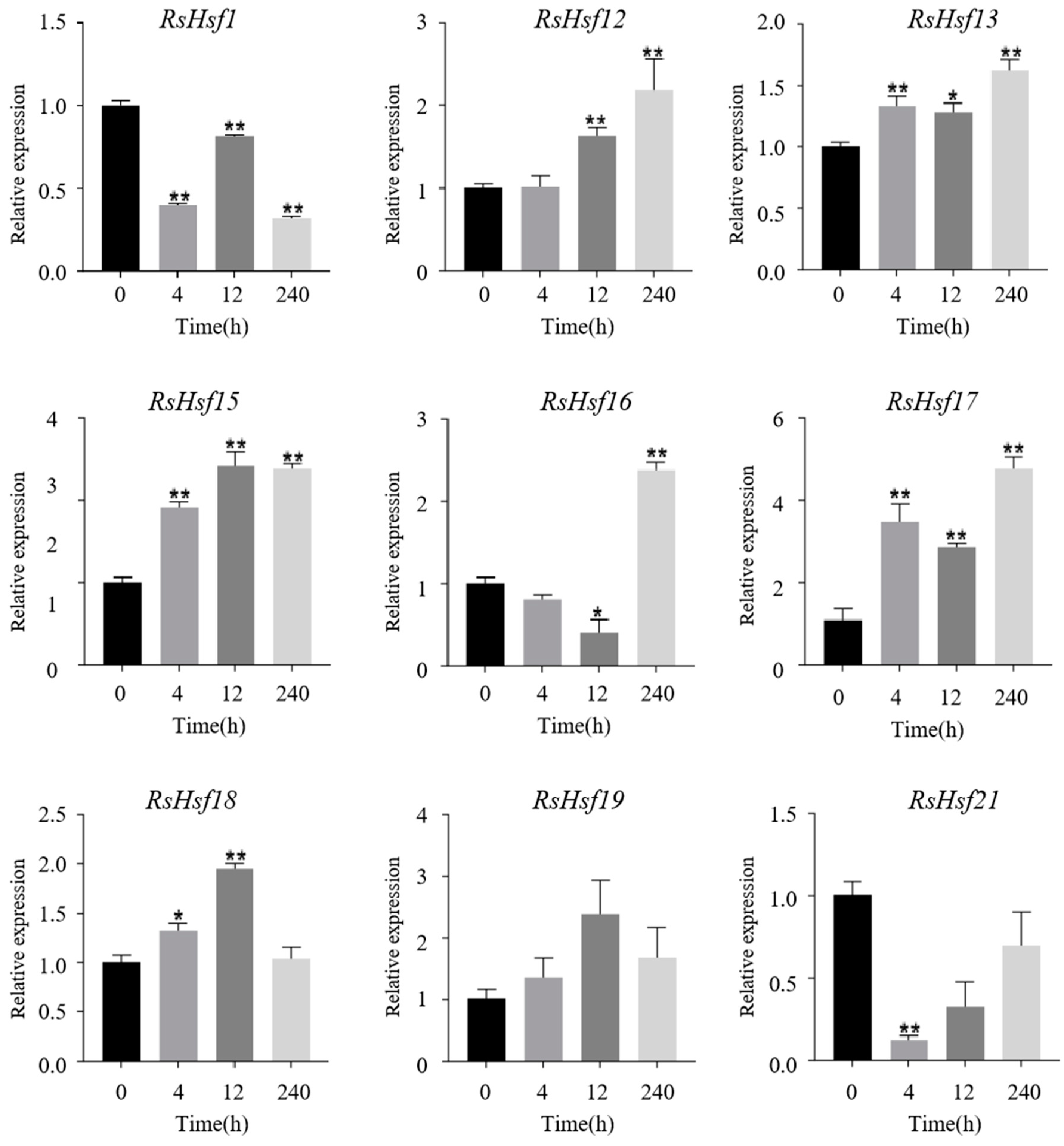
2.7. Transcriptional Profiles of RsHsfs under Abiotic Stresses
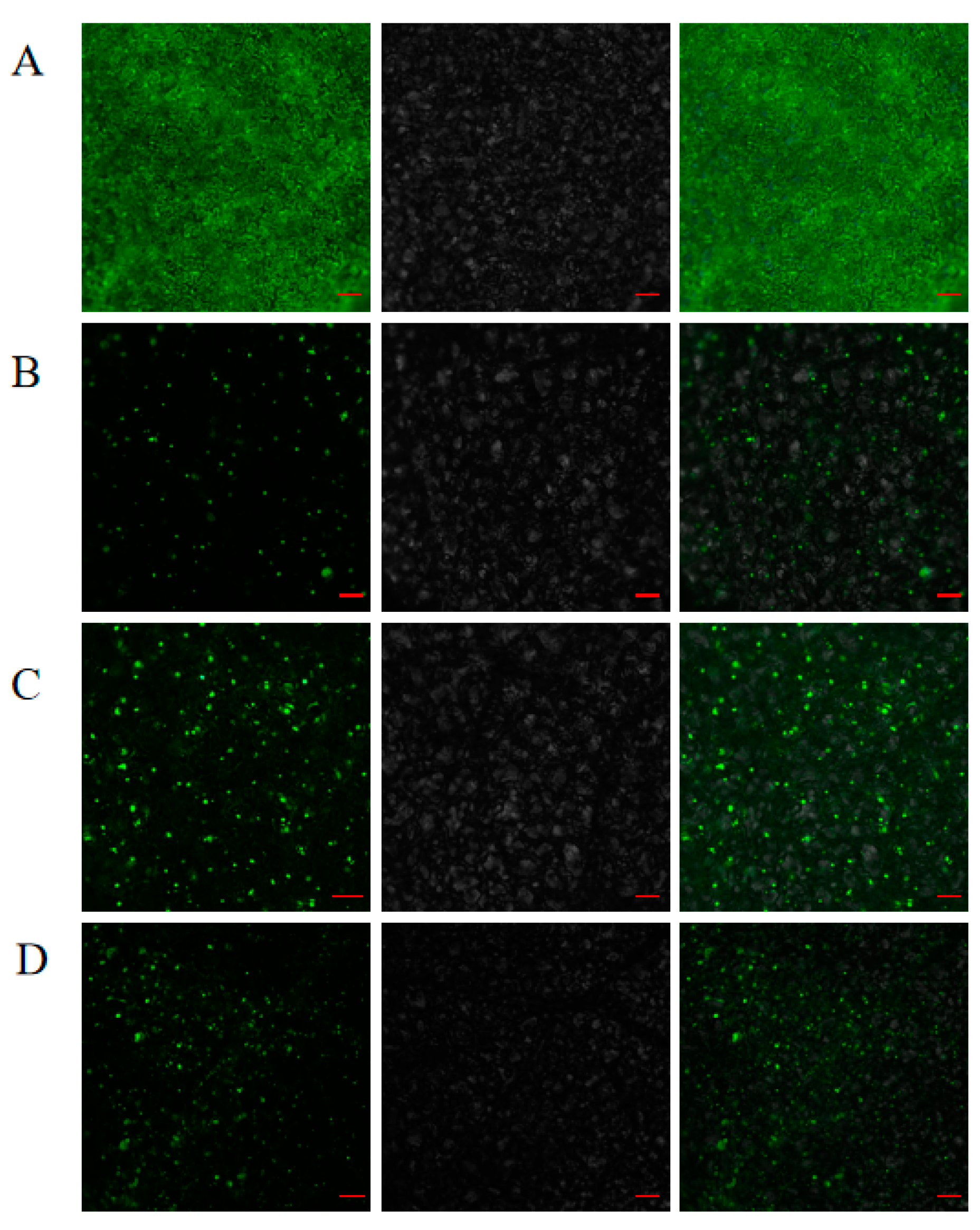
2.8. Subcellular Localization Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
4.2. Gene Identification and Physicochemical Properties of Putative Proteins
4.3. Chromosome Location
4.4. Construction of Phylogenetic Tree
4.5. Gene Structures and Motifs, and Analysis of Gene Promoter Regions
4.6. Detection of RsHsf Transcript Levels by qRT-PCR
4.7. Subcellular Localization Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyer, J.S. Plant Productivity and Environment. Science 1982, 218, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorothea, B.; Ramanjulu, S. Drought and Salt Tolerance in Plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2005, 24, 23–58. [Google Scholar]
- Klaus, D.S.; Thomas, B.; Ingo, E.; Lutz, N. The plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family: Structure, function and evolution. BBA-Gene Regul. Mech. 2012, 1819, 104–119. [Google Scholar]
- Sorger, P.K.; Pelham, H.R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3035–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clos, J.; Westwood, J.T.; Becker, P.B.; Wilson, S.; Lambert, K.; Wu, C. Molecular cloning and expression of a hexameric Drosophila heat shock factor subject to negative regulation. Cell 1990, 63, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabindran, S.K.; Giorgi, G.; Clos, J.; Wu, C. Molecular cloning and expression of a human heat shock factor; HSF1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6906–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarge, K.D.; Zimarino, V.; Holm, K.; Wu, C.I.; Morimoto, R. Cloning and characterization of two mouse heat shock factors with distinct inducible and constitutive DNA-binding ability. Genes Dev. 1991, 5, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, N.; Kapil, B.; Pascal, D.; Shravan, K.M.; Arnab, G.I.; Klaus, D.S. Arabidopsis and the heat stress transcription factor world: How many heat stress transcription factors do we need. Cell Stress. Chaperones 2001, 6, 177–189. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.H.; Chen, S.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Ni, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L. Isolation of heat shock factor HsfA1a-binding sites in vivo revealed variations of heat shock elements in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-X.; Jiang, H.-Y.; Chu, Z.-X.; Tang, X.-L.; Zhu, S.-W.; Cheng, B.-J. Genome-wide identification, classification and analysis of heat shock transcription factor family in maize. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, N.; Deng, T.; Zhang, L.; Zuo, K. Genome-wide cloning, identification, classification and functional analysis of cotton heat shock transcription factors in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, G.P.; Sadat, S.; Drenth, J.; McIntyre, C.L. The heat shock factor family from regulation of heat shock protein genes. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anckar, J.; Sistonen, L. Regulation of HSF1 function in the heat stress response: Implications in aging and disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 1089–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoudi, M.; Chen, J.; Lou, Q. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) gene family in Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) rootstock under drought stress suggested the potential role of these chaperones in stress tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banti, V.; Loreti, E.; Novi, G.; Santaniello, A.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. Heat acclimation and cross-tolerance against anoxia in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2008, 31, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, F.; Ganguli, A.; Kiehlmann, E.; Englich, G.; Walch, D.; von Koskull-Doring, P. The heat stress transcription factor HsfA2 serves as a regulatory amplifier of a subset of genes in the heat stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 60, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banti, V.; Mafessoni, F.; Loreti, E.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. The heat-inducible transcription factor HsfA2 enhances anoxia tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-L.; Zhang, H.-N.; Shao, H.; Wang, G.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhao, L.-N.; Guo, X.-L.; Sheteiwy, M.S. ZmHsf05, a new heat shock transcription factor from Zea mays L. improves thermotolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana and rescues thermotolerance defects of the athsfa2 mutant. Plant Sci. 2019, 283, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokotani, N.; Ichikawa, T.; Kondou, Y.; Matsui, M.; Hirochika, H.; Iwabuchi, M.; Oda, K. Expression of rice heat stress transcription factor OsHsfA2e enhances tolerance to environmental stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 2008, 227, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.-P.; Drenth, J.; McIntyre, C.L. TaHsfA6f is a transcriptional activator that regulates a suite of heat stress protection genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) including previously unknown Hsf targets. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liao, H.; Charng, Y. The role of class A1 heat shock factors (HSFA1s) in response to heat and other stresses in Arabidopsis. Plant, Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, B.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Mijiti, A.; Ren, C.; Qu, G.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L. CarHSFB2, a Class B Heat Shock Transcription Factor Is Involved in Different Developmental Processes and Various Stress Responses in Chickpea (Cicer Arietinum L.). Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2016, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, A.; Xu, X.; Li, J. Ectopic overexpression of SlHsfA3, a heat stress transcription factor from tomato, confers increased thermotolerance and salt hypersensitivity in germination in transgenic Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, K.; Shi, J.; Yang, Y.; He, M.; Wang, Y. A Novel Heat Shock Transcription Factor, VpHsf1, from Chinese Wild Vitis pseudoreticulata is Involved in Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 31, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lei, Y.S.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Z.Y.; Ji, X.; Yang, S.H.; Xu, Y.X. Cloning and expression analysis of Rhododendron bHLH transcription factor RsMYC2 under abiotic stress. Mol. Plant Breed. 2023, 21, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.-S.; Nie, S.; Liu, H.; Shi, T.-L.; Tian, X.-C.; Zhou, S.-S.; Bao, Y.-T.; Jia, K.-H.; Guo, J.-F.; Zhao, W.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of a parent species of widely cultivated azaleas. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wan, X.-L.; Yu, J.-Y.; Wang, K.-L.; Zhang, J. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, and Expression Analysis of the Hsf Gene Family in Carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Tan, D.; Reiter, R.J.; Ye, T.; Yang, F.; Chan, Z. Melatonin induces class A1 heat-shock factors (HSFA1s) and their possible involvement of thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-X.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Z.-Y.; Huang, S.-X.; Di, H.-C.; He, Y.; Jin, S.-H. Physiological and transcriptome analyses provide new insights into the mechanism mediating the enhanced tolerance of melatonin-treated rhododendron plants to heat stress. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2397–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Guo, X. Genome-wide identification and abiotic stress-responsive pattern of heat shock transcription factor family in Triticum aestivum L. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Lu, J.-P.; Zhai, Y.-F.; Chai, W.-G.; Gong, Z.-H.; Lu, M.-H. Genome-wide analysis, expression profile of heat shock factor gene family (CaHsfs) and characterisation of CaHsfA2 in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhu, W.; Song, X.; Lin, X.; Cai, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q. Genome-wide identification and function analyses of heat Shock transcription factors in potato. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Guo, Q.; Pang, X.; Zhang, P.; Kong, D.; Liu, J. New Insights into Evolution of Plant Heat Shock Factors (Hsfs) and Expression Analysis of Tea Genes in Response to Abiotic Stresses. Plants 2020, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Meng, X.Z.; Yuan, S.N.; Li, G.L.; Yang, Y.; Duan, S.N.; Zhang, H.N.; Guo, X.L. Biological Characteristics and Thermotolerance Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factor TaHsfA1 Subfamily Genes in Wheat (Triticum aestivum). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.Y.; Huang, Q.; Sun, W.J.; Ma, Z.T.; Huang, L.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Z.Z.; Bu, T.L.; Li, C.L.; Chen, H. Genome-wide investigation of the heat shock transcription factor (Hsf) gene family in Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.H. Mechanism Analysis of Response to Heat Stress of LIHSFA1 and Its Downstream LIHSP70 from Lily (Lilium longiflorum). Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.S. Cloning, Function, and Thermotolerant Mechanism of Heat Stress Transcription Factor (HSF) in Soybean, Wheat, and Arabidopsis. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Yangling, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, Z.B.; Wen, L.C.; Deng, Z.C.; Chu, Y.M.; Liu, T.; Cui, M.M.; Guo, Y.F. Genome-wide Identification and Systemic Analysis of the Hsf Gene Family in Nicotiana tabacum L. China Tob. Sci. 2022, 43, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.S.; Zheng, W.J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M.; Cai, S.C.; Ma, L.J.; Xu, Z.S. Genome-wide identification, classification, and high temperature of Hsf family in Brachypodium diatachyon. J. China Agric. Univ. 2015, 20, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Baniwal, S.K.; Bharti, K.; Chan, K.Y.; Fauth, M.; Ganguli, A.; Kotak, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Nover, L.; Port, M.; Scharf, K.-D.; et al. Heat stress response in plants: A complex game with chaperones and more than twenty heat stress transcription factors. J. Biosci. 2004, 29, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-C.; Charng, Y.-Y. Common and distinct functions of Arabidopsis class A1 and A2 heat shock factors in diverse abiotic stress responses and development. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davletova, S.; Rizhsky, L.; Liang, H.; Zhong, S.Q.; Oliver, D.J.; Coutu, J.; Shulaev, V.; Schlauch, K.; Mittler, R. Cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 1 is a central component of the reactive oxygen gene network of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, A.; Yabuta, Y.; Yoshida, E.; Maruta, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Shigeoka, S. Arabidopsis heat shock transcription factor A2 as a key regulator in response to several types of environmental stress. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 48, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswari, U.; Jabbari, K.; Petit, J.-L.; Porcel, B.M.; Allen, A.E.; Cadoret, J.-P.; De Martino, A.; Heijde, M.; Kaas, R.; La Roche, J.; et al. Digital expression profiling of novel diatom transcripts provides insight into their biological functions. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Ye, Y.; Shang, L.; Hong, S.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, C. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of HSF transcription factors in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under Abiotic Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Ni, D.; Wang, M.; Guo, G. Genome-wide characterization of tea plant (Camellia sinensis) Hsf transcription factor family and role of CsHsfA2 in heat tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wu, C.L.; Hu, W. Clone and Expression Analysis of MeHSF18 in Cassava. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Personat, J.M.; Tejedor-Cano, J.; Prieto-Dapena, P.; Almoguera, C.; Jordano, J. Co-overexpression of two Heat Shock Factors results in enhanced seed longevity and in synergistic effects on seedling tolerance to severe dehydration and oxidative stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, U.; Albihlal, W.S.; Lawson, T.; Fryer, M.J.; Sparrow, P.A.; Richard, F.; Persad, R.; Bowden, L.; Hickman, R.; Martin, C.; et al. Arabidopsis HEAT SHOCK TRANSCRIPTION FACTORA1b overexpression enhances water productivity, resistance to drought, and infection. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3467–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, P.; Treuter, E.; Kistner, C.; Lyck, R.; Chen, A.; Nover, L. The Role of AHA motifs in the activator function of tomato heat stress transcription factors HsfA1 and HsfA2. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charng, Y.-Y.; Liu, H.-C.; Liu, N.-Y.; Chi, W.-T.; Wang, C.-N.; Chang, S.-H.; Wang, T.-T. A heat-inducible transcription factor, HsfA2, is required for extension of acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Melatonin in flowering, fruit set and fruit ripening. Plant Reprod. 2020, 33, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.D. Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Physiological Responses of Cucumber Seedlings under High Temperature Stress. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Yangling, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Melatonin synthesis in rice seedlings in vivo is enhanced at high temperatures and under dark conditions due to increased serotonin N-acetyltransferase and N-acetylserotonin methyltransferase activities. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Tan, D.X.; Allan, A.C.; Zuo, B.; Zhao, Y.; Reiter, R.J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Chloroplastic biosynthesis of melatonin and its involvement in protection of plants from salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Du, G.; Wang, J. Selection and Evaluation of Candidate Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-Time PCR in Aboveground Tissues and Drought Conditions in Rhododendron Delavayi. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 876482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆Ct method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Lei, Y.S.; Huang, S.X.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Z.Y.; Zhu, X.T.; Jin, S.H. Combined de novo transcriptomic and physiological analyses reveal RyALS3-mediated aluminum tolerance in Rhododendron yunnanense Franch. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 951003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene Name | Gene ID | Amino Acid | Molecular Weight (KDa) | Theoretical Isoelectric Point | Instability Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RsHsf1 | Rhsim01G0094400 | 296 | 33.01 | 5.42 | 57.20 | −0.47 |
| RsHsf2 | Rhsim01G0168300 | 140 | 16.63 | 4.50 | 55.62 | −0.37 |
| RsHsf3 | Rhsim01G0272100 | 740 | 83.56 | 6.84 | 53.50 | −0.74 |
| RsHsf4 | Rhsim02G0062200 | 464 | 52.26 | 5.35 | 60.59 | −0.82 |
| RsHsf5 | Rhsim02G0071200 | 354 | 39.70 | 6.29 | 44.08 | −0.70 |
| RsHsf6 | Rhsim03G0027200 | 257 | 29.01 | 5.56 | 70.97 | −0.84 |
| RsHsf7 | Rhsim03G0081300 | 577 | 63.55 | 4.70 | 60.67 | −0.52 |
| RsHsf8 | Rhsim03G0178900 | 327 | 36.11 | 5.45 | 54.93 | −0.64 |
| RsHsf9 | Rhsim03G0236900 | 250 | 28.23 | 9.45 | 46.61 | −0.70 |
| RsHsf10 | Rhsim04G0197300 | 352 | 39.11 | 4.83 | 56.31 | −0.61 |
| RsHsf11 | Rhsim05G0018200 | 415 | 46.58 | 4.83 | 51.85 | −0.72 |
| RsHsf12 | Rhsim06G0051500 | 332 | 37.54 | 6.73 | 61.12 | −0.61 |
| RsHsf13 | Rhsim06G0124200 | 428 | 48.77 | 5.26 | 56.09 | −0.77 |
| RsHsf14 | Rhsim07G0130600 | 540 | 59.94 | 5.16 | 59.15 | −0.60 |
| RsHsf15 | Rhsim07G0227900 | 324 | 36.93 | 5.94 | 58.81 | −0.68 |
| RsHsf16 | Rhsim08G0100600 | 282 | 31.20 | 6.38 | 33.73 | −0.77 |
| RsHsf17 | Rhsim09G0088300 | 417 | 47.75 | 4.64 | 50.57 | −0.51 |
| RsHsf18 | Rhsim09G0213400 | 524 | 57.63 | 5.50 | 52.32 | −0.43 |
| RsHsf19 | Rhsim10G0118300 | 286 | 31.88 | 8.76 | 31.74 | −0.74 |
| RsHsf20 | Rhsim11G0019200 | 501 | 55.43 | 4.86 | 65.34 | −0.63 |
| RsHsf21 | Rhsim11G0043100 | 370 | 42.03 | 4.79 | 67.84 | −0.54 |
| RsHsf22 | Rhsim13G0177200 | 300 | 35.04 | 9.13 | 46.37 | −0.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; He, D.; Di, H.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Y. A Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profile of Heat Shock Transcription Factor (Hsf) Gene Family in Rhododendron simsii. Plants 2023, 12, 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223917
Xu Y, Jin Y, He D, Di H, Liang Y, Xu Y. A Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profile of Heat Shock Transcription Factor (Hsf) Gene Family in Rhododendron simsii. Plants. 2023; 12(22):3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223917
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yanan, Ying Jin, Dan He, Haochen Di, Ying Liang, and Yanxia Xu. 2023. "A Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profile of Heat Shock Transcription Factor (Hsf) Gene Family in Rhododendron simsii" Plants 12, no. 22: 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223917
APA StyleXu, Y., Jin, Y., He, D., Di, H., Liang, Y., & Xu, Y. (2023). A Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profile of Heat Shock Transcription Factor (Hsf) Gene Family in Rhododendron simsii. Plants, 12(22), 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223917






