Metabolomics as a Potential Chemotaxonomical Tool: Application on the Selected Euphorbia Species Growing Wild in Serbia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of the Extraction for the NMR-Based Metabolomic Analysis of Euphorbia Species
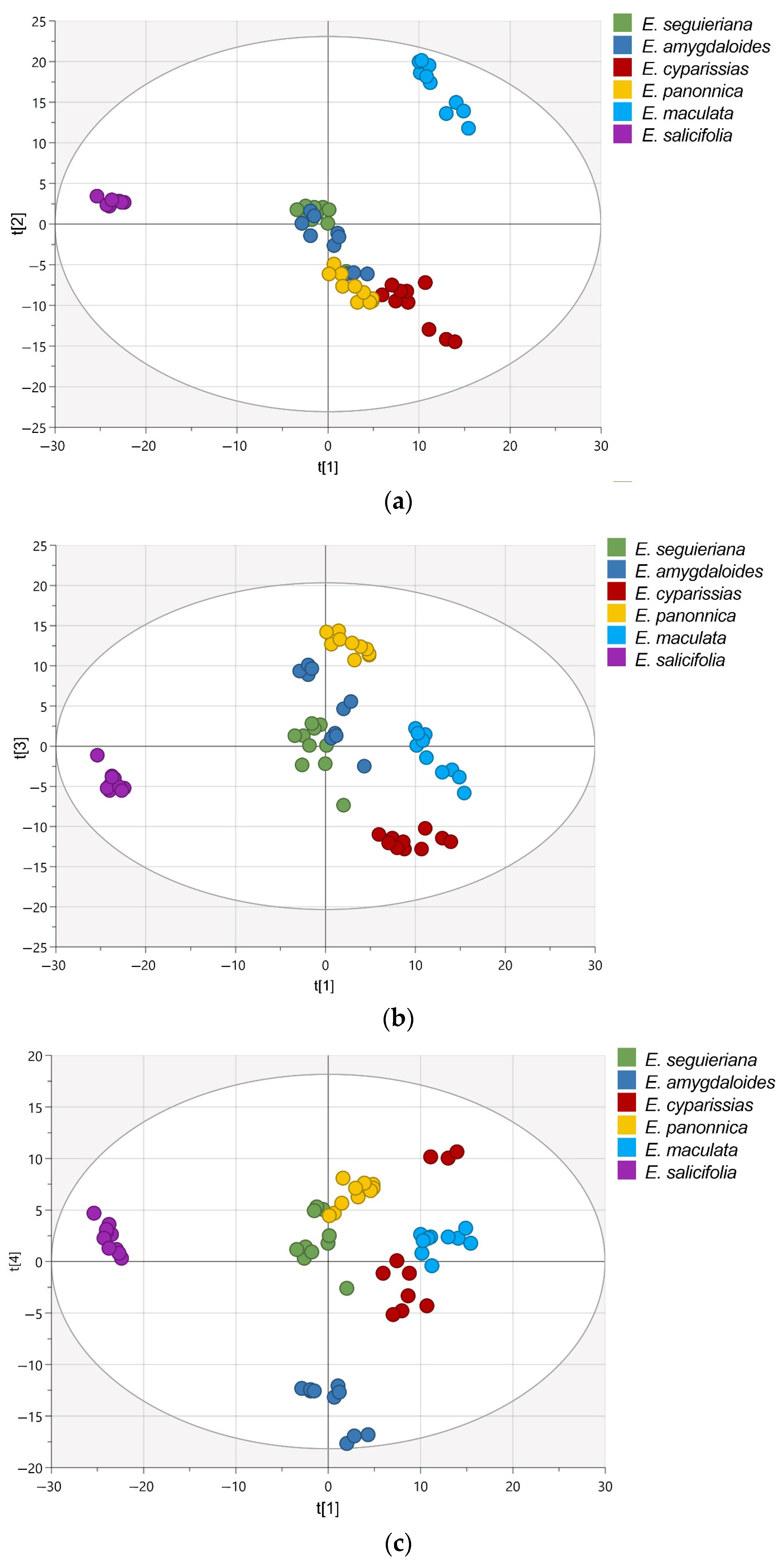
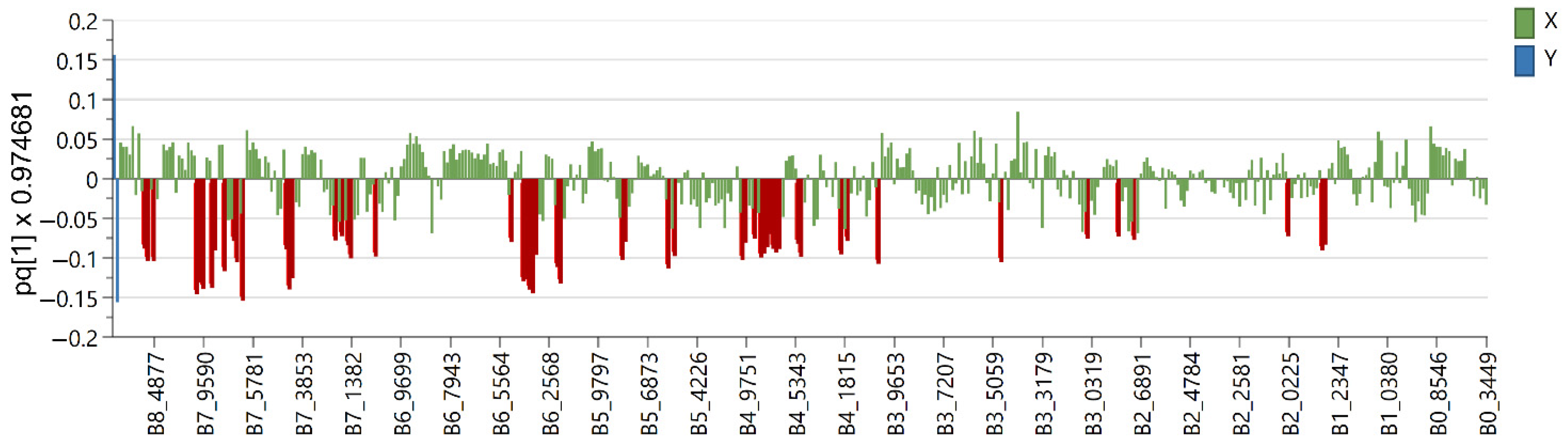
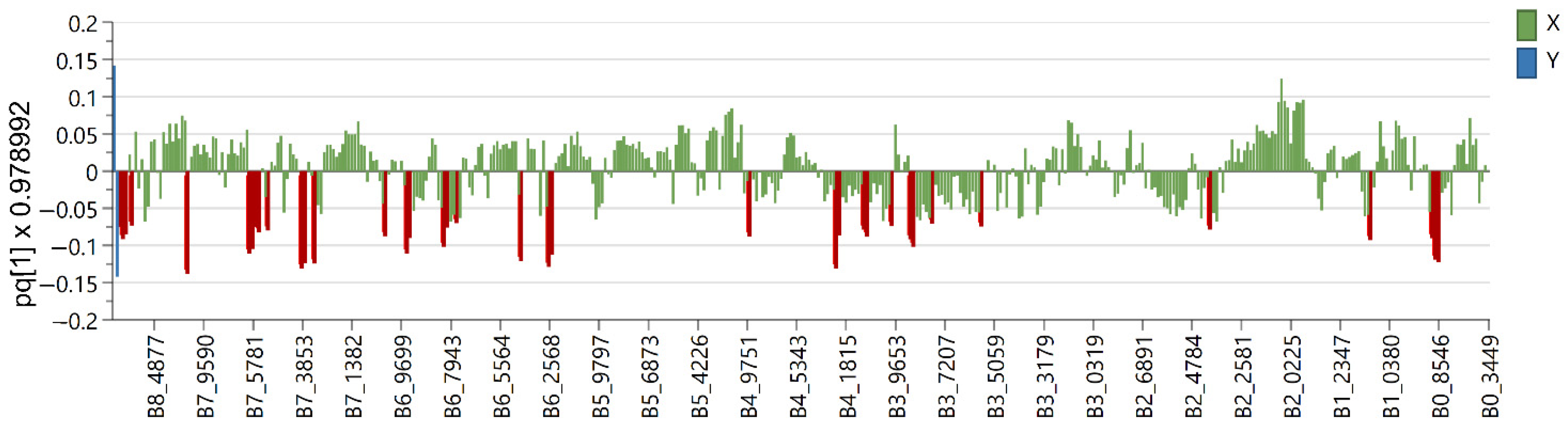
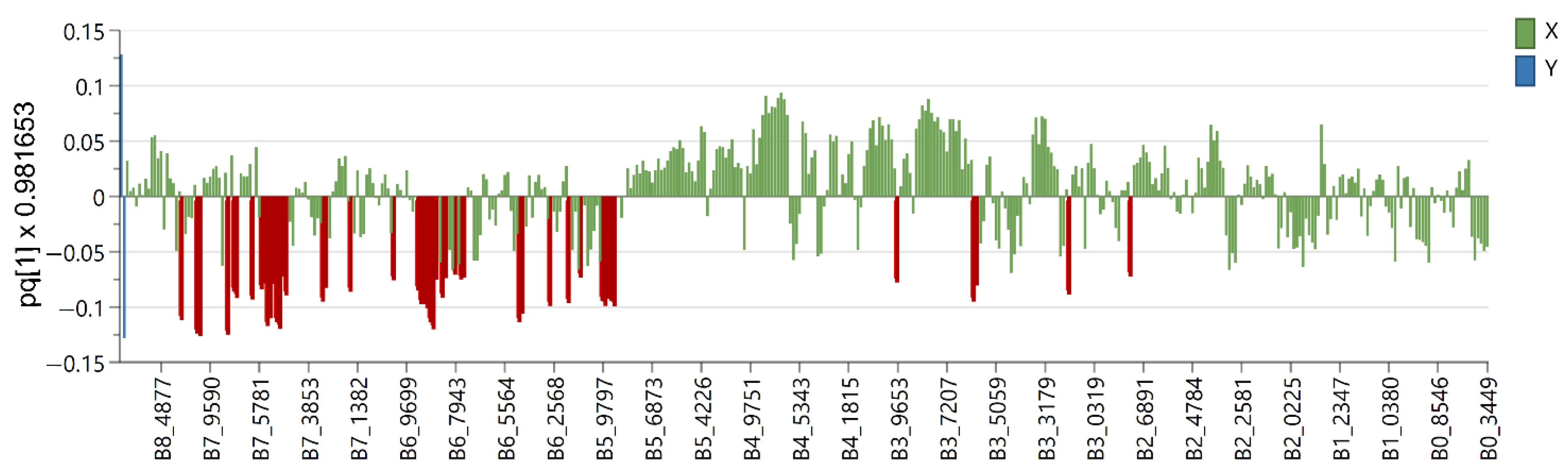
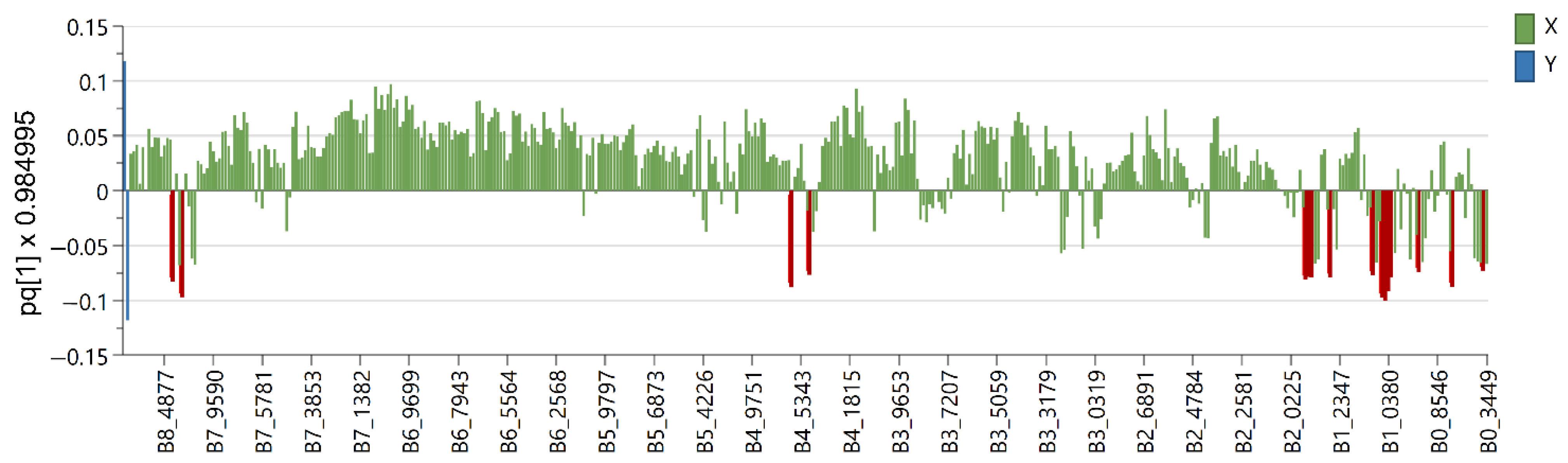
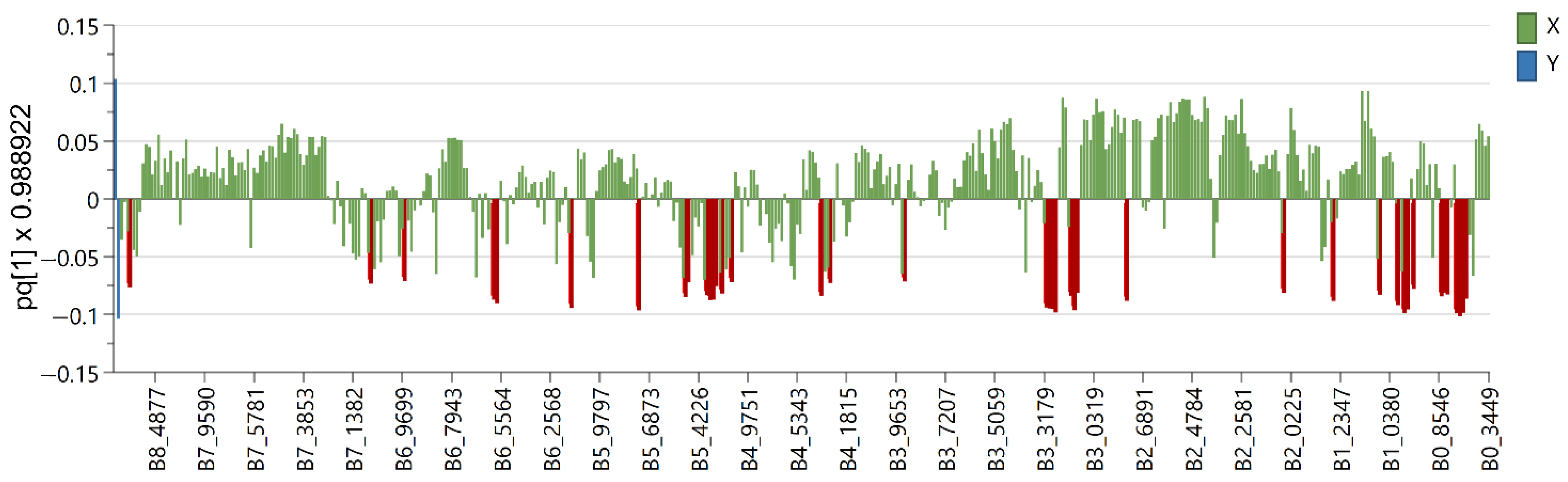
2.2. Multivariate Data Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals, Samples and Extraction Protocol
3.2. NMR Measurements and Multivariate Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfender, J.-L.; Rudaz, S.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, H.K. Plant metabolomics: From holistic data to relevant biomarkers. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 1056–1090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Böttcher, C.; von Roepenack-Lahaye, E.; Schmidt, J.; Schmotz, C.; Neumann, S.; Scheel, D.; Clemens, S. Metabolome analysis of biosynthetic mutants reveals a diversity of metabolic changes and allows identification of a large number of new compounds in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 2107–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macel, M.; Van Dam, N.M.; Keurentjes, J.J.B. Metabolomics: The chemistry between ecology and genetics. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, T. The evolution of chemosystematics. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2887–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.-X.; Chen, T.-L.; Li, M.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.-Q.; Cui, G.-H.; Zhao, A.-H.; Jia, W.; Huang, L.-Q.; Qi, X. Use of the Metabolomics Approach to Characterize Chinese Medicinal Material Huangqi. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, M.; Anđelković, B.; Stevanović, V.; Jadranin, M.; Đorđević, I.; Tešević, V.; Milosavljević, S.; Gođevac, D. NMR-based metabolomics study of Amphoricarpos species from Montenegro. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, P.S.F.; Meyer, J.J.M. Integrating chemotaxonomic-based metabolomics data with DNA barcoding for plant identification: A case study on south-east African Erythroxylaceae species. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 146, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirahata, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Kudo, T.; Takada, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Taga, Y.; Minakuchi, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Horiguchi, R.; Hirayama, T.; et al. Metabolic fingerprinting for discrimination of DNA-authenticated Atractylodes plants using 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.M.; Leyva, V.; Maruenda, H. Pure Shift Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: A New Tool for Plant Metabolomics. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 173, e62719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, M.I.; Ali, K.; Alipieva, K.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Metabolic differentiations and classification of Verbascum species by NMR-based metabolomics. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Saifullah; Khan, S.; Wilson, E.G.; Kricun, S.D.P.; Meissner, A.; Goraler, S.; Deelder, A.M.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic classification of South American Ilex species by NMR-based metabolomics. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Yang, H.; Qi, L.-W.; Liu, E.-H.; Ren, M.-T.; Yan, Y.-T.; Chen, J.; Li, P. Unbiased metabolite profiling by liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multivariate data analysis for herbal authentication: Classification of seven Lonicera species flower buds. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1245, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwine, J.T.; Damme, P. Van Why do Euphorbiaceae tick as medicinal plants?: A review of Euphorbiaceae family and its medicinal features. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 652–662. [Google Scholar]
- Frodin, D.G. History and concepts of big plant genera. Taxon 2004, 53, 753–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaerts, R.; Frodin, D.G.; Radcliffe-Smith, A.; Carter, S. World Checklist and Bibliography of Euphorbiaceae (with Pandaceae), 2nd ed.; Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: Richmond, UK, 2000; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.J. Investigating the Diversity of Latex Metabolites in Species of the Euphorbia. Genus. Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hawary, S.S.; Mohammed, R.; Tawfike, A.F.; Lithy, N.M.; AbouZid, S.F.; Amin, M.N.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Amin, E. Cytotoxic Activity and Metabolic Profiling of Fifteen Euphorbia Species. Metabolites 2021, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomé-Abarca, L.F.; Gođevac, D.; Kim, M.S.; Hwang, G.-S.; Park, S.C.; Jang, Y.P.; Van Den Hondel, C.A.M.J.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Klinkhamer, P.G.L.; Choi, Y.H. Latex Metabolome of Euphorbia Species: Geographical and Inter-Species Variation and its Proposed Role in Plant Defense against Herbivores and Pathogens. J. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 47, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, G.; Anđelković, B.; Choi, Y.H.; Vajs, V.; Stević, T.; Tešević, V.; Gođevac, D. Metabolic changes in Euphorbia palusrtis latex after fungal infection. Phytochemistry 2016, 131, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, G.; Kostić, A.; Jadranin, M.; Pešić, M.; Novaković, M.; Aljančić, I.; Vajs, V. Two new jatrophane diterpenes from the roots of Euphorbia nicaeensis: Scientific paper. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2021, 86, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassbi, A.R. Chemistry and biological activity of secondary metabolites in Euphorbia from Iran. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemboi, D.; Peter, X.; Langat, M.; Tembu, J. A Review of the Ethnomedicinal Uses, Biological Activities, and Triterpenoids of Euphorbia Species. Molecules 2020, 25, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, G.; Jadranin, M.; Todorović, N.M.; Pešić, M.; Stanković, T.; Aljančić, I.S.; Tešević, V.V. Jatrophane diterpenoids with multidrug-resistance modulating activity from the latex of Euphorbia nicaeensis. Phytochemistry 2018, 148, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, W.F.; Enríquez, R.G. Choosing the Best Pulse Sequences, Acquisition Parameters, Postacquisition Processing Strategies, and Probes for Natural Product Structure Elucidation by NMR Spectroscopy. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of plants. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklund, S.; Johansson, E.; Sjöström, L.; Mellerowicz, E.J.; Edlund, U.; Shockcor, J.P.; Gottfries, J.; Moritz, T.; Trygg, J. Visualization of GC/TOF-MS-based metabolomics data for identification of biochemically interesting compounds using OPLS class models. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeske, F.; Jakupovic, J.; Berendsohn, W. Diterpenes from Euphorbia seguieriana. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshamy, A.I.; Mohamed, T.A.; Al-Rowaily, S.L.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M.; Dar, B.A.; Shahat, A.A.; Hegazy, M.-E.F. Euphosantianane E-G: Three New Premyrsinane Type Diterpenoids from Euphorbia sanctae-catharinae with Contribution to Chemotaxonomy. Molecules 2019, 24, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohmann, J.; Evanics, F.; Dombi, G.; Szabó, P. Salicifoline and salicinolide, new diterpene polyesters from Euphorbia salicifolia. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 6581–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassana, G.F.; Omera, M.A.; Babadoustb, S.; Naja, D.D. Flavonoids from Euphorbia condylocarpa roots. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2014, 6, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Barile, E.; Corea, G.; Lanzotti, V. Diterpenes from Euphorbia as Potential Leads for Drug Design. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1934578X0800300629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corea, G.; Fattorusso, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Lanzotti, V. Amygdaloidins A–L, twelve new 13 α-OH jatrophane diterpenes from Euphorbia amygdaloides L. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 4485–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, L.; Tang, M.; Feng, B.; Pei, Y.; Yasukawa, K. Triterpenoids from Euphorbia maculata and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Molecules 2018, 23, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agata, I.; Hatano, T.; Nakaya, Y.; Sugaya, T.; Nishibe, S.; Yoshida, T.; Okuda, T. Tannins and Related Polyphenols of Euphorbiaceous Plants. VIII. Eumaculin A and Eusupinin A, and Accompanying Polyphenols from Euphorbia maculata L. and E. supina RAFIN. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1991, 39, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
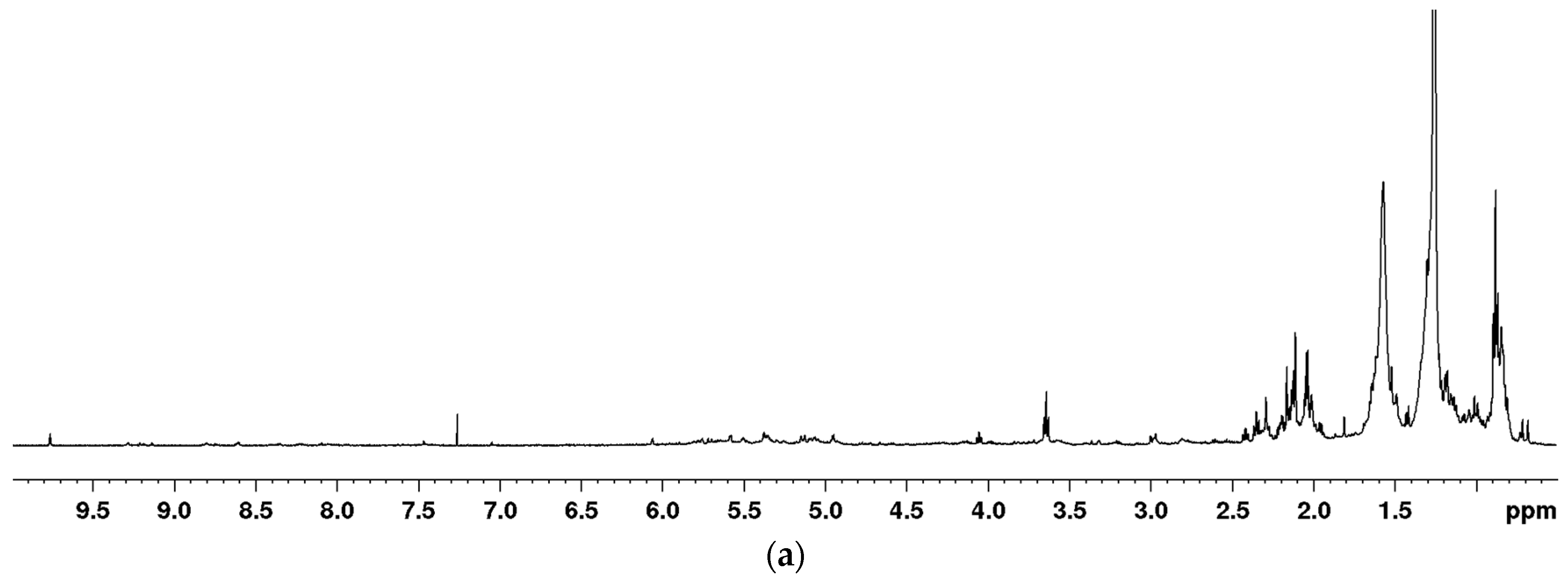
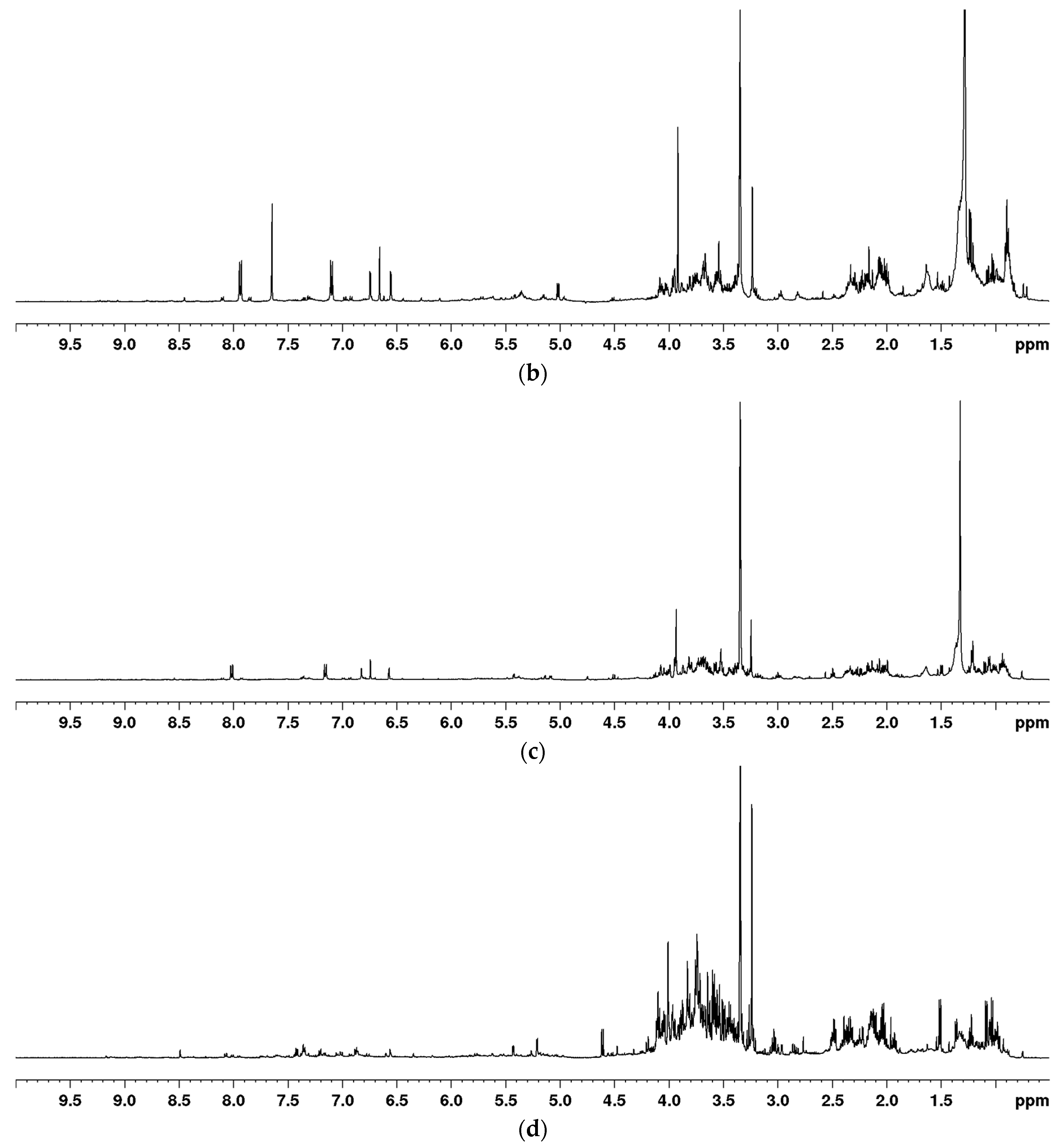


| Structure | C/H | δC | δH (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 2 | 165.1 | |
| 3 | 104.3 | 6.6 s | |
| 4 | 182.8 | ||
| 4a | 106.1 | ||
| 5 | 161.8 | ||
| 6 | 100.6 | 6.55 d(2.1) | |
| 7 | 163.1 | ||
| 8 | 96.0 | 6.74 d(2.1) | |
| 8a | 157.6 | ||
| 1′ | 123.0 | ||
| 2′/6′ | 115.2 | 7.00 d(9.1) | |
| 3′/5′ | 128.9 | 7.93 d(9.1) | |
| 1″ | 55.6 | 3.91 | |
| anomeric from sugars moiety | 101.0 | 5.01 d(7.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sofrenić, I.; Anđelković, B.; Gođevac, D.; Ivanović, S.; Simić, K.; Ljujić, J.; Tešević, V.; Milosavljević, S. Metabolomics as a Potential Chemotaxonomical Tool: Application on the Selected Euphorbia Species Growing Wild in Serbia. Plants 2023, 12, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020262
Sofrenić I, Anđelković B, Gođevac D, Ivanović S, Simić K, Ljujić J, Tešević V, Milosavljević S. Metabolomics as a Potential Chemotaxonomical Tool: Application on the Selected Euphorbia Species Growing Wild in Serbia. Plants. 2023; 12(2):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020262
Chicago/Turabian StyleSofrenić, Ivana, Boban Anđelković, Dejan Gođevac, Stefan Ivanović, Katarina Simić, Jovana Ljujić, Vele Tešević, and Slobodan Milosavljević. 2023. "Metabolomics as a Potential Chemotaxonomical Tool: Application on the Selected Euphorbia Species Growing Wild in Serbia" Plants 12, no. 2: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020262
APA StyleSofrenić, I., Anđelković, B., Gođevac, D., Ivanović, S., Simić, K., Ljujić, J., Tešević, V., & Milosavljević, S. (2023). Metabolomics as a Potential Chemotaxonomical Tool: Application on the Selected Euphorbia Species Growing Wild in Serbia. Plants, 12(2), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020262










