Identification and Expression of the MADS-box Gene Family in Different Versions of the Ginkgo biloba Genome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of GbMADS Proteins
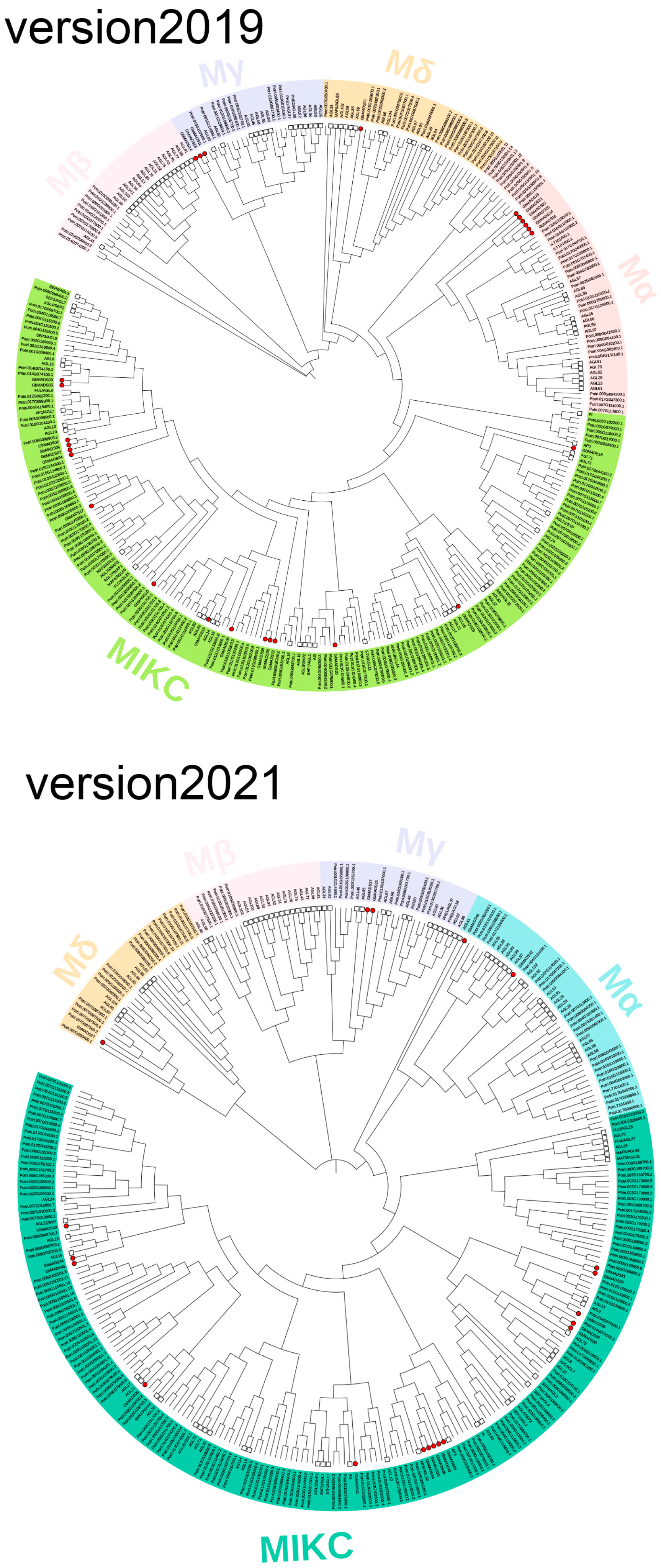
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Gene Structure of GbMADS
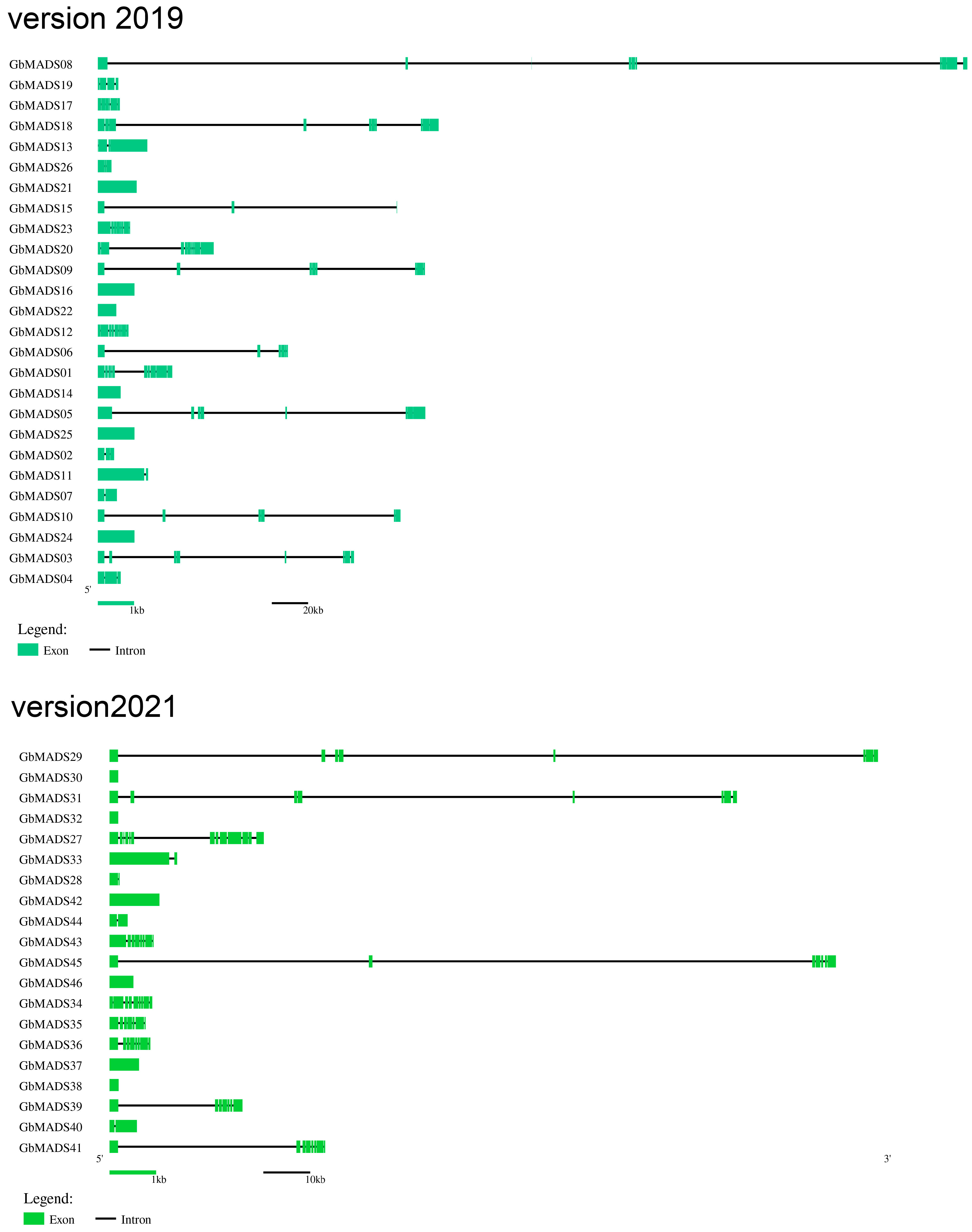
2.3. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis
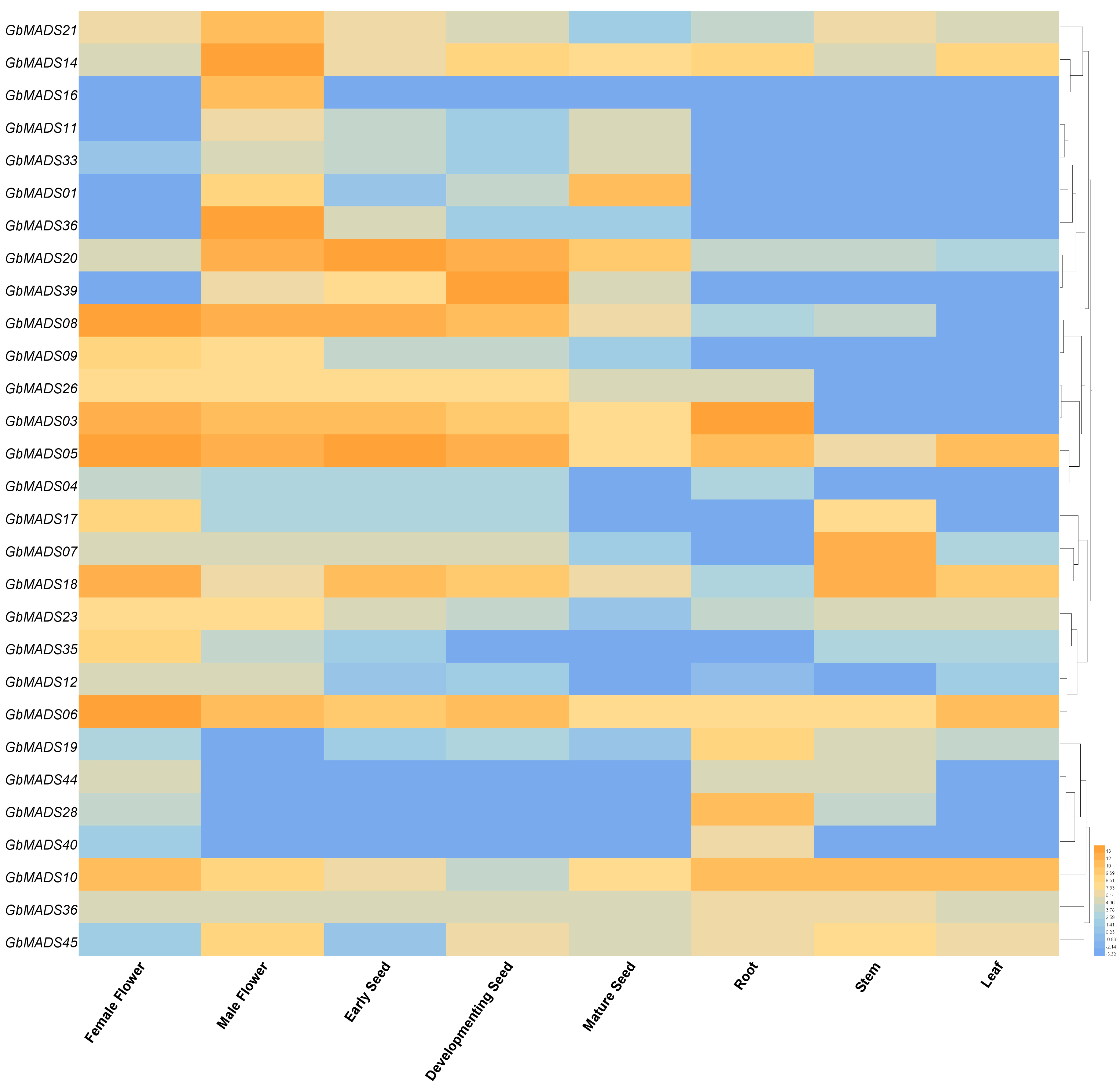
2.4. Interaction Network and Expression Analysis of GbMADS
3. Discussion
3.1. Number and Type of GbMADS Proteins
3.2. Gene Structure of GbMADS genes
3.3. Gene Expression and Potential Function
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of GbMADS Proteins
4.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Gene Structure and Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
4.4. Plant Tissues and Quantitative Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Messenguy, F.; Dubois, E. Role of MADS-box proteins and their cofactors in combinatorial control of gene expression and cell development. Gene 2003, 316, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizek, B.A.; Fletcher, J.C. Molecular mechanisms of flower development: An armchair guide. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenicova, L.; de Folter, S.; Kieffer, M.; Horner, D.S.; Favalli, C.; Busscher, J.; Cook, H.E.; Ingram, R.M.; Kater, M.M.; Davies, B.; et al. Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the complete MADS-box transcription factor family in Arabidopsis: New openings to the MADS world. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1538–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leseberg, C.H.; Li, A.; Kang, H.; Duvall, M.; Mao, L. Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Gene 2006, 378, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Agarwal, P.; Ray, S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V.P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Kapoor, S. MADS-box gene family in rice: Genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaczniak, C.; Immink, R.G.; Angenent, G.C.; Kaufmann, K. Developmental and evolutionary diversity of plant MADS-domain factors: Insights from recent studies. Development 2012, 139, 3081–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.H.; Nadeau, E.T.; Grayhack, E.J. Multiple phosphorylated forms of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mcm1 protein include an isoform induced in response to high salt concentrations. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Cai, T.; Zhang, R.; Li, A.; Huo, N.; Li, S.; Gu, Y.Q.; Vogel, J.; Jia, J.; Qi, Y.; et al. Novel microRNAs uncovered by deep sequencing of small RNA transcriptomes in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Brachypodium distachyon (L.) Beauv. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2009, 9, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, R.-Z.; Guo, J.-J.; Liu, D.-M.; Li, A.-L.; Fan, R.-C.; Mao, L.; Zhang, X.-Q. Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-J.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.-T.; Zhang, G.-F.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Que, S.-P.; Mao, F.; Pervaiz, T.; Lin, J.-X.; Li, Y.; et al. MADS-box transcription factors MADS11 and DAL1 interact to mediate the vegetative-to-reproductive transition in pine. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Yang, T.; Dong, S.; Wei, T.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Feng, X.; et al. The Cycas genome and the early evolution of seed plants. Nat. Plants 2022, 8, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramzow, L.; Theissen, G. A hitchhiker’s guide to the MADS world of plants. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bodt, S.; Raes, J.; Florquin, K.; Rombauts, S.; Rouze, P.; Theißen, G.; Van de Peer, Y. Genome-wide structural annotation and evolutionary analysis of the type I MADS-box genes in plants. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 56, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, K.; Melzer, R.; Theißen, G. MIKC-type MADS-domain proteins: Structural modularity, protein interactions and network evolution in land plants. Gene 2005, 347, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Chen, C.; Dobes, C.; Fu, C.X.; Koch, M.A. Phylogeography of a living fossil: Pleistocene glaciations forced Ginkgo biloba L. (Ginkgoaceae) into two refuge areas in China with limited subsequent postglacial expansion. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 48, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q. The main active constituents and detoxification process of Ginkgo biloba seeds and their potential use in functional health foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 83, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Ye, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the MADS-Box Family in Ginkgo biloba. Forests 2022, 13, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, G.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Liang, X.; et al. Draft genome of the living fossil Ginkgo biloba. Gigascience 2016, 5, s13742-016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cui, P.; Wu, S.; Ai, C.; Hu, N.; Li, A.; He, B.; Shao, X.; et al. The nearly complete genome of Ginkgo biloba illuminates gymnosperm evolution. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, M.; Hassanin, A.; Manuel, M.; Guyader, H.L.; Deutsch, J. MADS-box genes in Ginkgo biloba and the evolution of the AGAMOUS family. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Cheng, J.; Feng, X.; Xing, L.; Zhang, W.; Yong, L.; Cheng, S.; Li, X. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a MADS-Box gene (GbMADS2) from Ginkgo biloba. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2015, 43, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Meng, X. Characterization and functional analysis of a MADS-box transcription factor gene (GbMADS9) from Ginkgo biloba. Sci. Hortic 2016, 212, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Li, J.; Bo, W.; Yang, W.; Zuccolo, A.; Giacomello, S.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.; et al. The Chinese pine genome and methylome unveil key features of conifer evolution. Cell 2021, 185, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, C.; Sun, H.; Rosli, H.G.; Pombo, M.A.; Zhang, P.; Banf, M.; Dai, X.; Martin, G.B.; Giovannoni, J.J.; et al. iTAK: A program for genome-wide prediction and classification of plant transcription factors, transcriptional regulators, and protein kinases. Mol. Plant Breed. 2016, 9, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Bi, C.; He, B.; Ye, N.; Yin, T.; Xu, L.-A. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the MADS-box gene family in Salix suchowensis. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hao, Z.; Long, X.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Ye, D.; Peng, Y.; Wu, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, G.; et al. The Transcriptome of Cunninghamia lanceolata male/female cone reveal the association between MIKC MADS-box genes and reproductive organs development. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the MADS-box gene family in sesame. Gene 2015, 569, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, M.; Ke, Y.; Johnson, L.F. Stimulation of gene expression by introns: Conversion of an inhibitory intron to a stimulatory intron by alteration of the splice donor sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 5901–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vain, P.; Finer, K.R.; Engler, D.E.; Pratt, R.C.; Finer, J.J. Intron-mediated enhancement of gene expression in maize (Zea mays L.) and bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.). Plant Cell Rep. 1996, 15, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Du, R.; Gou, J.; Guo, L.; Shen, H.; Liu, H.; Nguyen, J.K.; Ming, R.; Yin, T.; Huang, S.; et al. The genomic architecture of the sex-determining region and sex-related metabolic variation in Ginkgo biloba. Plant J. 2020, 104, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portereiko, M.F.; Lloyd, A.; Steffen, J.G.; Punwani, J.A.; Otsuga, D.; Drews, G.N. AGL80 is required for central cell and endosperm development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, J.G.; Kang, I.H.; Portereiko, M.F.; Lloyd, A.; Drews, G.N. AGL61 interacts with AGL80 and is required for central cell development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, C.A.; Ma, H. Spatially and temporally regulated expression of the MADS-box gene AGL2 in wild-type and mutant Arabidopsis flowers. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 26, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, R.; Pinyopich, A.; Battaglia, R.; Kooiker, M.; Borghi, L.; Ditta, G.; Yanofsky, M.F.; Kater, M.M.; Colombo, L. MADS-box protein complexes control carpel and ovule development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, S.C.; Bracko, O.; Park, M.S.; Schwab, R.; Chun, H.J.; Park, K.M.; Seo, J.S.; Grbic, V.; Balasubramanian, S.; Schmid, M.; et al. Control of lateral organ development and flowering time by the Arabidopsis thaliana MADS-box Gene AGAMOUS-LIKE6. Plant J. 2010, 62, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.; He, F.; Dong, X.; Liu, L.Y.; Coupland, G.; Turck, F.; de Meaux, J. miR824-regulated AGAMOUS-LIKE16 contributes to flowering time repression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2024–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Suh, S.-S.; Park, E.; Cho, E.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, S.-G.; Lee, J.S.; Kwon, Y.M.; Lee, I. The AGAMOUS-LIKE20 MADS domain protein integrates floral inductive pathways in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2366–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, T.; Li, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Identification and cloning of GbMADS6, a SOC1 homolog gene involved in floral development in Ginkgo biloba. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregis, V.; Sessa, A.; Colombo, L.; Kater, M.M. AGL24, SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE, and APETALA1 redundantly control AGAMOUS during early stages of flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovisetto, A.; Baldan, B.; Pavanello, A.; Casadoro, G. Characterization of an AGAMOUS gene expressed throughout development of the fleshy fruit-like structure produced by Ginkgo biloba around its seeds. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erdmann, R.; Gramzow, L.; Melzer, R.; Theißen, G.; Becker, A. GORDITA (AGL63) is a young paralog of the Arabidopsis thaliana Bsister MADS box gene ABS (TT16) that has undergone neofunctionalization. Plant J. 2010, 63, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Mistry, J.; Schuster-Böckler, B.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Hollich, V.; Lassmann, T.; Moxon, S.; Marshall, M.; Khanna, A.; Durbin, R.; et al. Pfam: Clans, web tools and services. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Sequence ID | Length (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | GRAVY | Subcellular Localization | Type | Intron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version 2019 | ||||||||
| GbMADS01 | Gb_31417 | 381 | 43,295.54 | 5.96 | −0.672 | Nucleus | Mδ | 10 |
| GbMADS02 | Gb_38365 | 134 | 15,267.48 | 9.34 | −0.480 | Nucleus | MIKC | 2 |
| GbMADS03 | Gb_41549 | 245 | 28,348.38 | 9.61 | −0.754 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS04 | Gb_41550 | 201 | 22,539.02 | 9.28 | −0.051 | Nucleus | MIKC | 2 |
| GbMADS05 | Gb_36364 | 404 | 46,738.33 | 9.32 | −0.733 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS06 | Gb_30604 | 166 | 19,373.46 | 10.20 | −0.710 | Nucleus | MIKC | 5 |
| GbMADS07 | Gb_38922 | 165 | 18,369.30 | 9.37 | 0.131 | Nucleus | MIKC | 1 |
| GbMADS08 | Gb_01884 | 372 | 42,803.94 | 9.66 | −0.272 | Nucleus | MIKC | 9 |
| GbMADS09 | Gb_19178 | 246 | 28,197.98 | 6.26 | −0.594 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS10 | Gb_39109 | 199 | 22,576.68 | 6.22 | −0.513 | Nucleus | MIKC | 5 |
| GbMADS11 | Gb_38883 | 445 | 50,951.76 | 5.93 | −0.667 | Nucleus | Mγ | 1 |
| GbMADS12 | Gb_28587 | 257 | 29,385.11 | 9.90 | −0.416 | Nucleus | MIKC | 8 |
| GbMADS13 | Gb_05359 | 439 | 49,658.40 | 4.70 | −0.653 | Nucleus | Mγ | 3 |
| GbMADS14 | Gb_33168 | 209 | 24,345.65 | 5.53 | −0.708 | Nucleus | Mγ | 0 |
| GbMADS15 | Gb_12778 | 91 | 10,584.23 | 9.76 | −0.693 | Nucleus | MIKC | 2 |
| GbMADS16 | Gb_19258 | 336 | 37,202.07 | 8.33 | −0.704 | Nucleus | Mα | 0 |
| GbMADS17 | Gb_03807 | 190 | 20,981.41 | 10.05 | −0.104 | Nucleus | MIKC | 5 |
| GbMADS18 | Gb_05128 | 412 | 47,476.12 | 6.33 | −0.385 | Nucleus | MIKC | 9 |
| GbMADS19 | Gb_03068 | 162 | 18,422.89 | 9.96 | −0.608 | Nucleus | MIKC | 3 |
| GbMADS20 | Gb_16301 | 380 | 43,797.09 | 8.93 | −0.226 | Nucleus | MIKC | 8 |
| GbMADS21 | Gb_12586 | 356 | 40,514.41 | 6.32 | −0.650 | Nucleus | Mα | 0 |
| GbMADS22 | Gb_21526 | 169 | 19,411.53 | 10.17 | −0.499 | Nucleus | Mα | 0 |
| GbMADS23 | Gb_15398 | 277 | 31,889.43 | 8.886 | −0.405 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS24 | Gb_40092 | 336 | 37,284.17 | 8.33 | −0.680 | Nucleus | Mα | 0 |
| GbMADS25 | Gb_37613 | 336 | 37,284.17 | 8.33 | −0.680 | Nucleus | Mα | 0 |
| GbMADS26 | Gb_12581 | 122 | 13,740.90 | 10.02 | −0.397 | Nucleus | MIKC | 2 |
| Version 2021 | ||||||||
| GbMADS27 | GWHPBAVD000173 | 451 | 51,348.86 | 5.61 | −0.562 | Nucleus | Mδ | 12 |
| GbMADS28 | GWHPBAVD000308 | 67 | 7532.78 | 10.58 | −0.194 | Nucleus | MIKC | 1 |
| GbMADS29 | GWHPBAVD001358 | 252 | 29,170.87 | 8.88 | −0.917 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS30 | GWHPBAVD001363 | 61 | 6849.08 | 10.21 | −0.292 | Nucleus | MIKC | 0 |
| GbMADS31 | GWHPBAVD001364 | 245 | 28,348.38 | 9.61 | −0.754 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS32 | GWHPBAVD001372 | 61 | 6881.08 | 10.29 | −0.461 | Nucleus | MIKC | 0 |
| GbMADS33 | GWHPBAVD001859 | 445 | 50,951.76 | 5.93 | −0.667 | Nucleus | Mγ | 1 |
| GbMADS34 | GWHPBAVD009827 | 257 | 29,385.11 | 9.9 | −0.416 | Nucleus | MIKC | 8 |
| GbMADS35 | GWHPBAVD009828 | 221 | 25,387.11 | 9.73 | −0.666 | Nucleus | MIKC | 6 |
| GbMADS36 | GWHPBAVD009829 | 234 | 26,706.47 | 9.26 | −0.601 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS37 | GWHPBAVD012282 | 209 | 24,345.65 | 5.53 | −0.708 | Nucleus | Mγ | 0 |
| GbMADS38 | GWHPBAVD018550 | 64 | 7293.57 | 10.09 | −0.169 | Nucleus | MIKC | 0 |
| GbMADS39 | GWHPBAVD019150 | 231 | 26,662.61 | 9.11 | −0.554 | Nucleus | MIKC | 6 |
| GbMADS40 | GWHPBAVD021889 | 186 | 21,179.73 | 9.68 | −0.159 | Nucleus | MIKC | 1 |
| GbMADS41 | GWHPBAVD021902 | 229 | 26,337 | 8.96 | −0.624 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS42 | GWHPBAVD004734 | 356 | 40,514.41 | 6.32 | −0.65 | Nucleus | Mα | 0 |
| GbMADS43 | GWHPBAVD006355 | 277 | 31,917.44 | 8.87 | −0.407 | Nucleus | MIKC | 7 |
| GbMADS44 | GWHPBAVD006759 | 120 | 13,179.19 | 9.36 | −0.26 | Nucleus | MIKC | 1 |
| GbMADS45 | GWHPBAVD008845 | 227 | 26,228.68 | 6.02 | −0.718 | Nucleus | MIKC | 6 |
| GbMADS46 | GWHPBAVD009168 | 169 | 19,411.53 | 10.17 | −0.499 | Nucleus | Mα | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q. Identification and Expression of the MADS-box Gene Family in Different Versions of the Ginkgo biloba Genome. Plants 2023, 12, 3334. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12183334
Zhou P, Wang Z, Li Y, Zhou Q. Identification and Expression of the MADS-box Gene Family in Different Versions of the Ginkgo biloba Genome. Plants. 2023; 12(18):3334. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12183334
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Pengyan, Zesen Wang, Yingang Li, and Qi Zhou. 2023. "Identification and Expression of the MADS-box Gene Family in Different Versions of the Ginkgo biloba Genome" Plants 12, no. 18: 3334. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12183334
APA StyleZhou, P., Wang, Z., Li, Y., & Zhou, Q. (2023). Identification and Expression of the MADS-box Gene Family in Different Versions of the Ginkgo biloba Genome. Plants, 12(18), 3334. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12183334






