Distribution Patterns and Determinants of Invasive Alien Plants in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Composition of IAPs in China
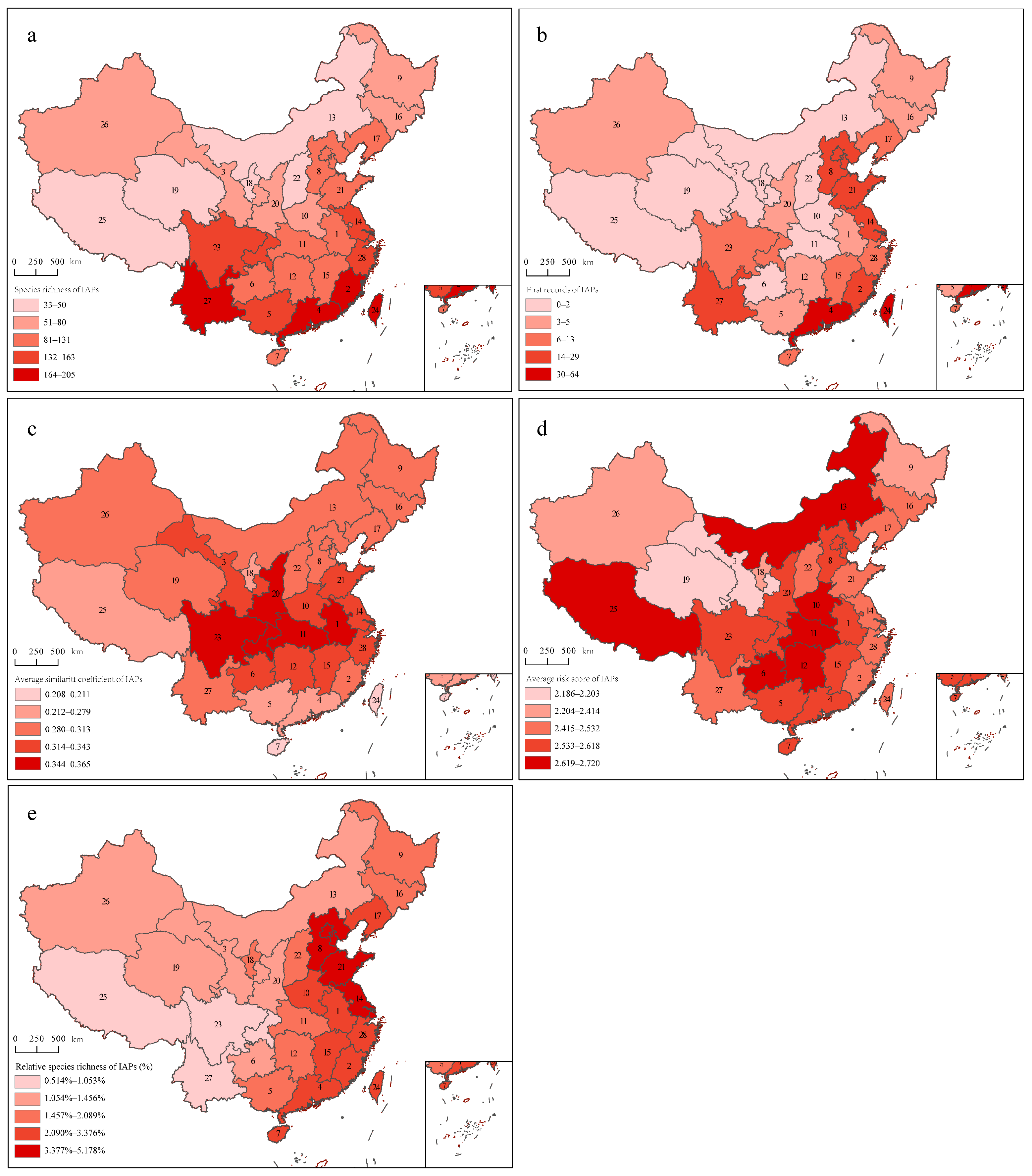
2.2. IAP Distribution Patterns in China
2.2.1. IAP Species Richness
2.2.2. First Records of IAPs
2.2.3. Average Similarity Coefficient of IAPs
2.2.4. Average Risk Score of IAPs
2.2.5. Relative Species Richness of IAPs
2.2.6. Synthetic Score of IAP Invasion Risk
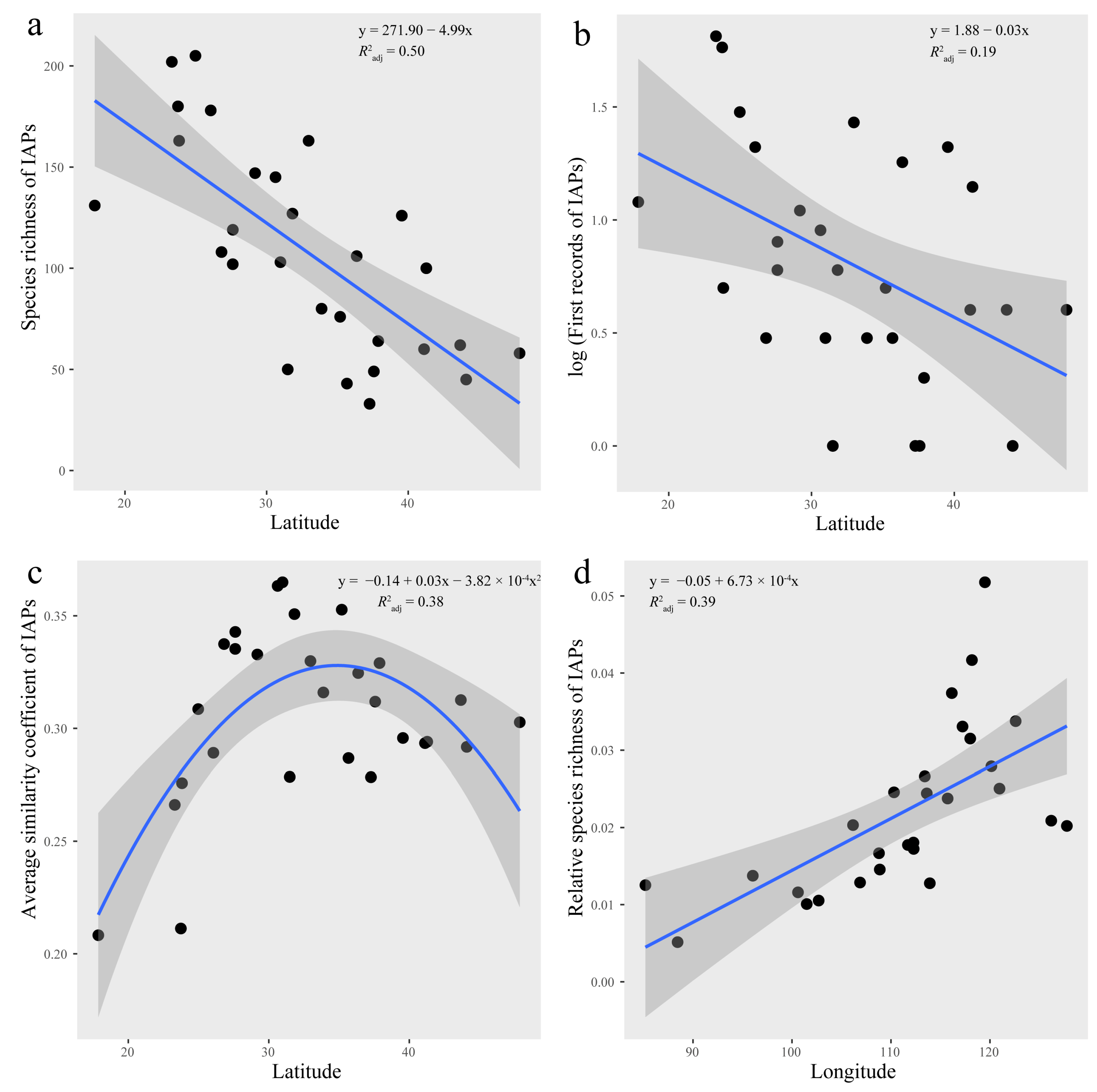
2.3. Impacts of Multiple Factors on the Spatial Distribution of IAPs
2.4. Impacts of Multiple Factors on the Spatial Distribution of Different Families of IAPs
3. Discussion
3.1. Species Composition of IAPs in China
3.2. IAP Distribution Patterns
3.3. Influences of Multiple Factors on the Spatial Distribution of IAPs of Different Families
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Invasion Indices
4.3. Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pyšek, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Simberloff, D.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Carlton, J.T.; Dawson, W.; Essl, F.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Genovesi, P.; et al. Scientists’ warning on invasive alien species. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Rai, P.; Singh, J.S. Invasive alien plant species: Their impact on environment, ecosystem services and human health. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulme, P.E. Incursion Response in New Zealand; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Ding, H.; Li, M.; Qiang, S.; Guo, J.; Han, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, H.; He, S.; Wu, H.; et al. The distribution and economic losses of alien species invasion to China. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellard, C.; Thuiller, W.; Leroy, B.; Genovesi, P.; Bakkenes, M.; Courchamp, F. Will climate change promote future invasions? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebens, H.; Essl, F.; Dawson, W.; Fuentes, N.; Moser, D.; Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P.; van Kleunen, M.; Weber, E.; Winter, M.; et al. Global trade will accelerate plant invasions in emerging economies under climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 4128–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seebens, H.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dyer, E.E.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Pagad, S.; Pyšek, P.; Winter, M.; Arianoutsou, M.; et al. No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dyer, E.E.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Pagad, S.; Pyšek, P.; van Kleunen, M.; Winter, M.; et al. Global rise in emerging alien species results from increased accessibility of new source pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2264–E2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tittensor, D.P.; Walpole, M.; Hill, S.L.L.; Boyce, D.G.; Britten, G.L.; Burgess, N.D.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Leadley, P.W.; Regan, E.C.; Alkemade, R.; et al. A mid-term analysis of progress toward international biodiversity targets. Science 2014, 346, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Q.-H.; Wu, J.-Y.; Huang, D.; Zhang, W.-H.; Zhao, N.; Li, X.-F.; Wang, L.-X. Historical introduction, geographical distribution, and biological characteristics of alien plants in China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, R.; Kim, K.C.; Suarez, A.V. Spatial Pattern and Determinants of the First Detection Locations of Invasive Alien Species in Mainland China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Zhou, G.; Cheng, X.; Xu, R. Fast economic development accelerates biological invasions in China. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Qiang, S.; Genovesi, P.; Ding, H.; Wu, J.; Meng, L.; Han, Z.; Miao, J.; Hu, B.; Guo, J. An inventory of invasive alien species in China. NeoBiota 2012, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Feng, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Corlett, R.T.; Hughes, A.C.; Pimm, S.; Schmid, B.; Shi, S.; et al. The global significance of biodiversity science in China: An overview. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwab032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Z. Roles of Dispersal Limit and Environmental Filtering in Shaping the Spatiotemporal Patterns of Invasive Alien Plant Diversity in China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 544670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.M.; Pyšek, P. Plant invasions: Merging the concepts of species invasiveness and community invasibility. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2006, 30, 409–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyšek, P.; Jarošík, V.; Hulme, P.E.; Kühn, I.; Wild, J.; Arianoutsou, M.; Bacher, S.; Chiron, F.; Didžiulis, V.; Essl, F.; et al. Disentangling the role of environmental and human pressures on biological invasions across Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12157–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, F.-H.; Yang, N.-W. Invasion and Management of Agricultural Alien Insects in China. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wilgen, B.W.; Richardson, D.M. Challenges and trade-offs in the management of invasive alien trees. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.; Feng, X.; Maitner, B.S.; Ernst, K.C.; Enquist, B.J. Darwin’s naturalization conundrum can be explained by spatial scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10904–10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.R.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Geerts, S.; Hoffman, M.T.; MacFadyen, S.; Measey, J.; Mills, A.; Richardson, D.M.; Robertson, M.P.; van Wilgen, B.W. The role of environmental factors in promoting and limiting biological invasions in South Africa. In Biological Invasions in South Africa; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 355–385. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, J.V.; Stokes, K.E.; van Klinken, R.D. Predicting the potential distribution of a riparian invasive plant: The effects of changing climate, flood regimes and land-use patterns. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 1738–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulos, P.G.; Koukoulas, S.; Galanidis, A.; Delipetrou, P.; Gounaridis, D.; Touloumi, K.; Arianoutsou, M. Factors shaping alien plant species richness spatial patterns across Natura 2000 Special Areas of Conservation of Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymura, T.H.; Szymura, M.; Zając, M.; Zając, A. Effect of anthropogenic factors, landscape structure, land relief, soil and climate on risk of alien plant invasion at regional scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, D.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Bezuidenhout, H.; McGeoch, M.A. Human population density explains alien species richness in protected areas. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 159, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kleunen, M.; Essl, F.; Pergl, J.; Brundu, G.; Carboni, M.; Dullinger, S.; Early, R.; González-Moreno, P.; Groom, Q.J.; Hulme, P.E.; et al. The changing role of ornamental horticulture in alien plant invasions. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 1421–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essl, F.; Dawson, W.; Kreft, H.; Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P.; Van Kleunen, M.; Weigelt, P.; Mang, T.; Dullinger, S.; Lenzner, B.; et al. Drivers of the relative richness of naturalized and invasive plant species on Earth. AoB PLANTS 2019, 11, plz051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malavasi, M.; Carboni, M.; Cutini, M.; Carranza, M.L.; Acosta, A.T.R. Landscape fragmentation, land-use legacy and propagule pressure promote plant invasion on coastal dunes: A patch-based approach. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirbu, C.; Miu, I.V.; Gavrilidis, A.A.; Gradinaru, S.R.; Niculae, I.M.; Preda, C.; Oprea, A.; Urziceanu, M.; Camen-Comanescu, P.; Nagoda, E. Distribution and pathways of introduction of invasive alien plant species in Romania. NeoBiota 2022, 75, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morente-López, J.; Arjona, Y.; Salas-Pascual, M.; Reyes-Betancort, J.A.; del Arco-Aguilar, M.J.; Emerson, B.C.; García-Gallo, A.; Jay-García, L.S.; Naranjo-Cigala, A.; Patiño, J. Biogeographic origins and drivers of alien plant invasions in the Canary Islands. J. Biogeogr. 2023, 50, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, H. Spatial distribution patterns of invasive alien species in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 26, e01432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Chisholm, R.; Sang, W.; Dong, M. Spatial Risk Assessment of Alien Invasive Plants in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7624–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Musa, A.; Ma, Q.; Yu, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, L. Geographical distribution and determining factors of different invasive ranks of alien species across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhu, Y. Alien invasive plants in China: Risk assessment and spatial patterns. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 3489–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Xiao, L.; Chen, X.; Lin, K.; Liu, B.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; Zheng, S. Invasive Alien Plants and Invasion Risk Assessment on Pingtan Island. Sustainability 2022, 14, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, H. The Checklist of the Alien Invasive Plants in China; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Wu, J.; Cui, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Musa, A.; Ma, Q.; Yu, H.; Liang, W.; Jiang, S.; et al. Geographical distribution of the dispersal ability of alien plant species in China and its socio-climatic control factors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Bian, Z.; Ren, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Shrestha, N. Spatial patterns and hotspots of plant invasion in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 43, e02424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, F.; Xie, B.; Yang, G.; Wang, N.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Cheng, X.; Ren, M.; Liu, S.; et al. Invasion Biology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pyšek, P.; Pergl, J.; Essl, F.; Lenzner, B.; Dawson, W.; Kreft, H.; Weigelt, P.; Winter, M.; Kartesz, J.; Nishino, M. Naturalized alien flora of the world: Species diversity, taxonomic and phylogenetic patterns, geographic distribution and global hotspots of plant invasion. Preslia 2017, 89, 203–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, S.; Wei, M.; Du, D.; Wang, C. Allelopathy of three Compositae invasive alien species on indigenous Lactuca sativa L. enhanced under Cu and Pb pollution. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 267, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, S. What makes a weed a weed: Life history traits of native and exotic plants in the USA. Oecologia 2004, 141, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Song, H.; Zhu, S. Spatial similarity in the distribution of invasive alien plants and animals in China. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D.; Von Holle, B. Positive interactions of nonindigenous species: Invasional meltdown? Biol. Invasions 1999, 1, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebbing, S.E.; Nuñez, M.A. Negative, neutral, and positive interactions among nonnative plants: Patterns, processes, and management implications. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinca, A.; Chirico, G.B.; Incerti, G.; Bonanomi, G. Regime shift by an exotic nitrogen-fixing shrub mediates plant facilitation in primary succession. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giantomasi, A.; Tecco, P.A.; Funes, G.; Gurvich, D.E.; Cabido, M. Canopy effects of the invasive shrub Pyracantha angustifolia on seed bank composition, richness and density in a montane shrubland (Córdoba, Argentina). Austral Ecol. 2008, 33, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capinha, C.; Essl, F.; Seebens, H.; Moser, D.; Pereira, H.M. The dispersal of alien species redefines biogeography in the Anthropocene. Science 2015, 348, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, P.E. Trade, transport and trouble: Managing invasive species pathways in an era of globalization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, J.; Cui, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Musa, A.; Ma, Q.; Yu, H. Effects of climatic and social factors on dispersal strategies of alien species across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzano, D.; Kotzé, I.; Marais, C.; Cianciullo, S.; Farcomeni, A.; Caroli, P.; Malatesta, L.; Attorre, F. Environmental and anthropogenic determinants of the spread of alien plant species: Insights from South Africa’s quaternary catchments. Plant Ecol. 2018, 219, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qiang, S. China’s Invasive Alien Species, Revised Edition; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Luque, G.M.; Bellard, C.; Bertelsmeier, C.; Bonnaud, E.; Genovesi, P.; Simberloff, D.; Courchamp, F. The 100th of the world’s worst invasive alien species. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Oduor, A.M.; Zhang, Z.; Manea, A.; Tooth, I.M.; Leishman, M.R.; Xu, X.; Van Kleunen, M. Do invasive alien plants benefit more from global environmental change than native plants? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 3363–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, U.B.; Shrestha, B.B. Climate change amplifies plant invasion hotspots in Nepal. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 1599–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whittaker, R.H. Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon 1972, 21, 213–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, H. Environmental determinants of woody plant diversity at a regional scale in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venter, O.; Sanderson, E.W.; Magrach, A.; Allan, J.R.; Beher, J.; Jones, K.R.; Possingham, H.P.; Laurance, W.F.; Wood, P.; Fekete, B.M. Global terrestrial Human Footprint maps for 1993 and 2009. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.M.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, W.; Fan, J.; Gou, J.; Liu, B.; Gide, E.; Soar, J.; Shen, B.; Fazal-e-Hasan, S. A comparative analysis of the principal component analysis and entropy weight methods to establish the indexing measurement. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.R.M.T.; Al Mamun, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Zahid, A. Simultaneous comparison of modified-integrated water quality and entropy weighted indices: Implication for safe drinking water in the coastal region of Bangladesh. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-H.; Su, Z.L.-T.; Lu, E.H.-C. Spatial perspectives toward the recommendation of remote sensing images using the INDEX indicator, based on principal component analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Fei, T.; Wu, G. Monitoring arsenic contamination in agricultural soils with reflectance spectroscopy of rice plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6264–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.E.; Amatangelo, K.L.; Townsend, P.A.; Waller, D.M. Large, connected floodplain forests prone to flooding best sustain plant diversity. Ecology 2016, 97, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ai, L.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, G.; Liao, W. Partial least-squares regression for linking land-cover patterns to soil erosion and sediment yield in watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Ma, F.; Xu, H. Distribution Patterns and Determinants of Invasive Alien Plants in China. Plants 2023, 12, 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122341
Chen J, Zhang Y, Liu W, Wang C, Ma F, Xu H. Distribution Patterns and Determinants of Invasive Alien Plants in China. Plants. 2023; 12(12):2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122341
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jing, Yanjing Zhang, Wei Liu, Chenbin Wang, Fangzhou Ma, and Haigen Xu. 2023. "Distribution Patterns and Determinants of Invasive Alien Plants in China" Plants 12, no. 12: 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122341
APA StyleChen, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Wang, C., Ma, F., & Xu, H. (2023). Distribution Patterns and Determinants of Invasive Alien Plants in China. Plants, 12(12), 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122341





