Diversity Temporal–Spatial Dynamics of Potato Rhizosphere Ciliates and Contribution to Nitrogen- and Carbon-Derived Nutrition in North-East China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
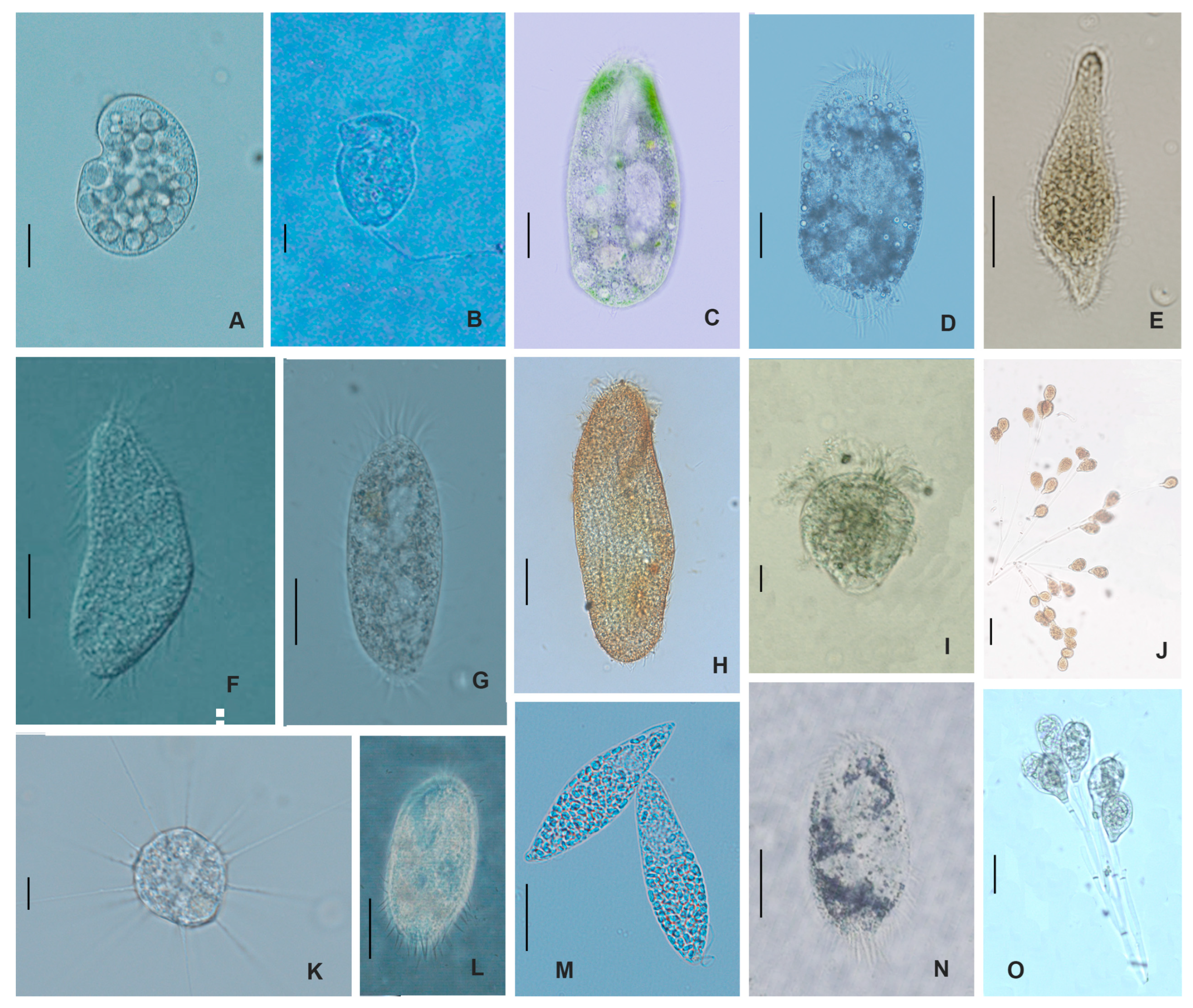
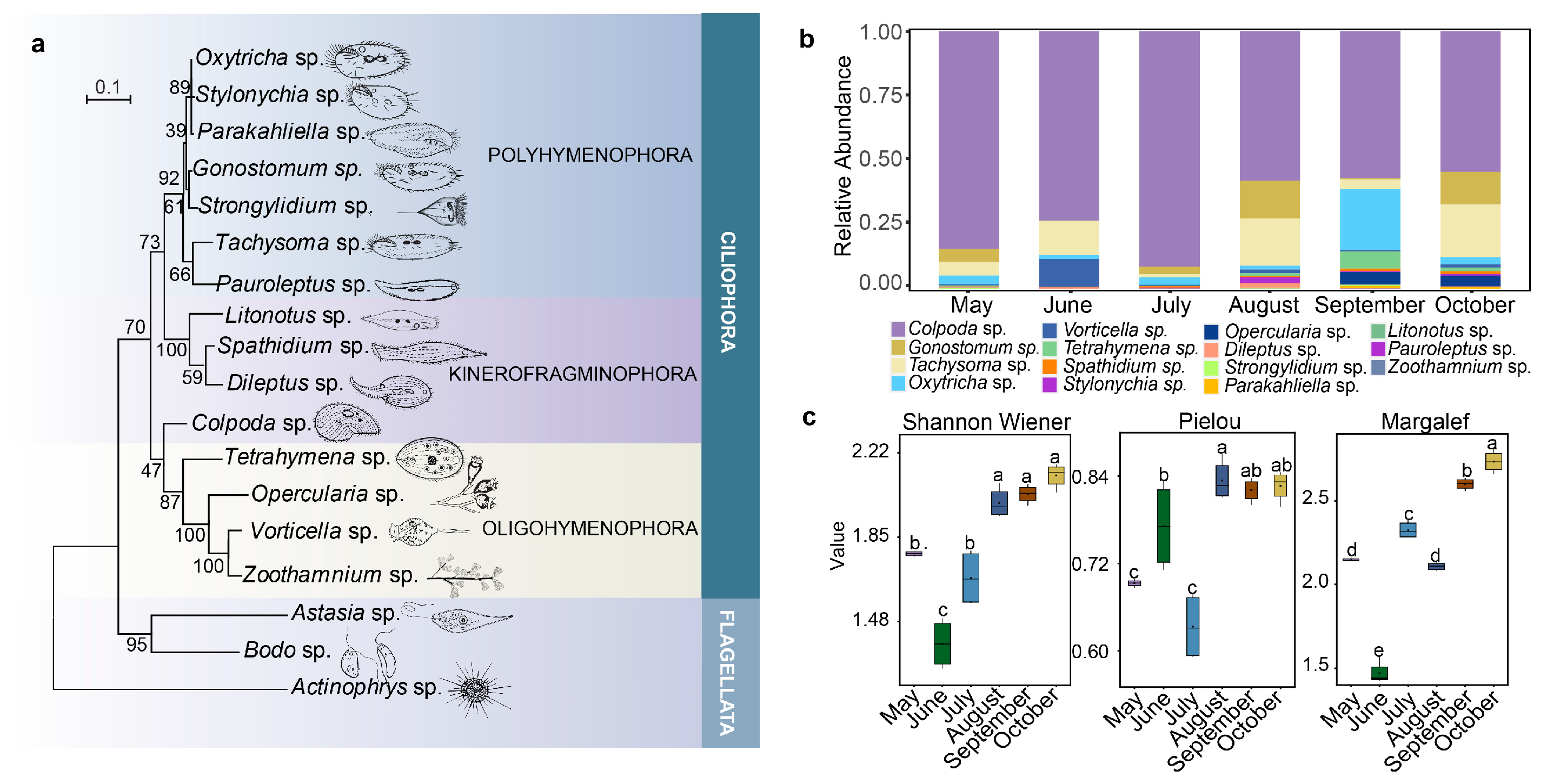
2.1. Composition and Diversity of Ciliates Community
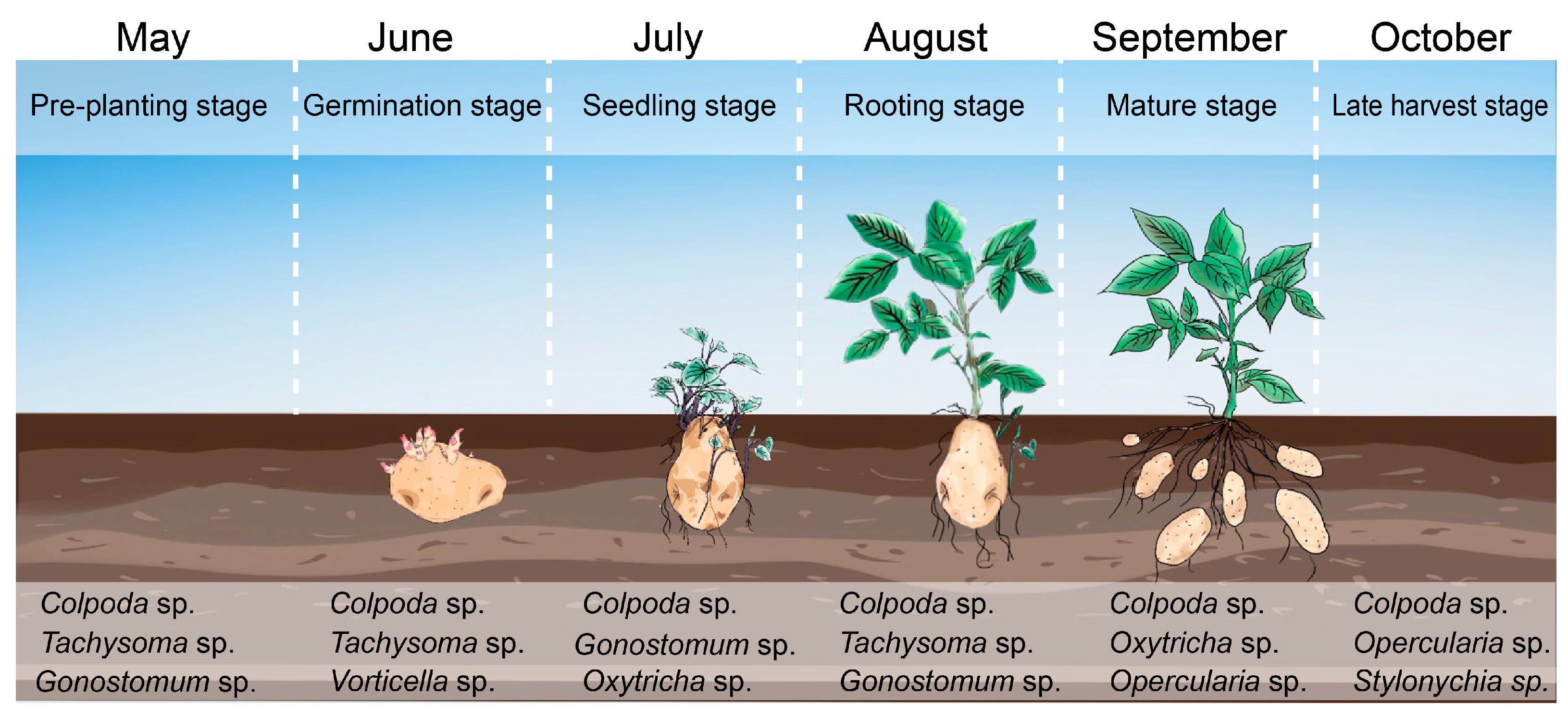
2.2. Spatial–Temporal Dynamics of Ciliates
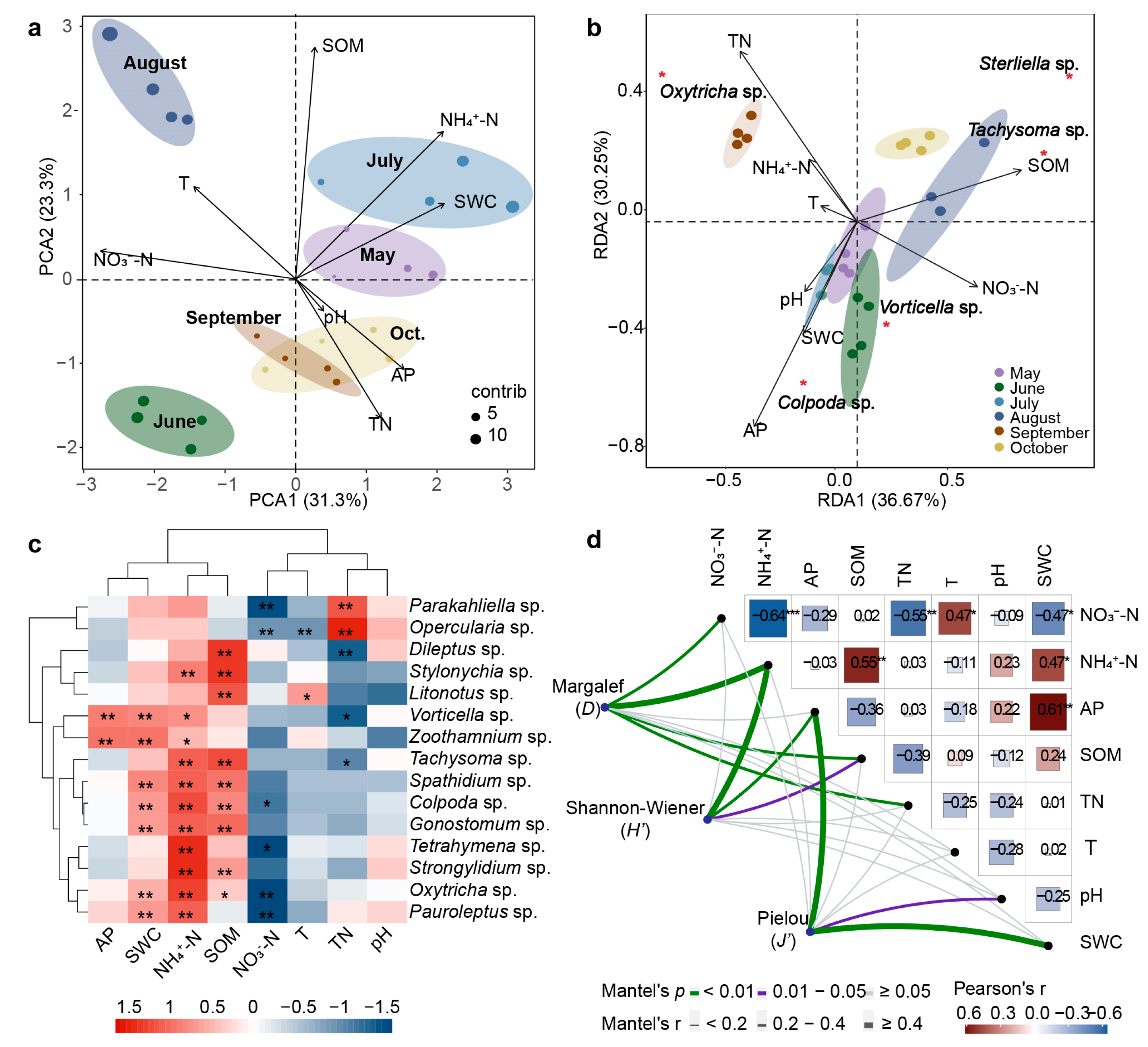
2.3. Correlation Analysis of Physicochemical Factors and Ciliate Community
3. Discussion
3.1. Contribution of Rhizosphere Ciliates on Potato Growth
3.2. Driving Factors of Potato Rhizosphere Ciliate Community
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Species Identification
4.2. Physicochemical Soil Analyses
4.3. Estimation of Carbon and Nitrogen Contribution Rates
4.4. Statistics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Species | Ciliate Abundance (ind./g) | Body Length (μm) | Body Width (μm) | Volume (×104 μm3) | Biomass (×10−9 g/ind.) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May | June | July | August | September | October | |||||
| Colpoda sp. | 66,000.00 | 891.00 | 90,500.00 | 5600.00 | 1925.00 | 2340.00 | 81.46 | 61.31 | 6.40 | 3.84 |
| Tachysoma sp. | 4200.00 | 160.00 | 1250.00 | 1760.00 | 127.00 | 880.00 | 120.00 | 48.46 | 8.92 | 5.17 |
| Oxytricha sp. | 2600.00 | 17.90 | 2860.00 | 150.00 | 800.00 | 120.00 | 89.08 | 38.85 | 5.14 | 3.17 |
| Gonostomum sp. | 4000.00 | 0.00 | 2940.00 | 1410.00 | 11.90 | 540.00 | 85.15 | 41.54 | 5.04 | 3.12 |
| Vorticella sp. | 422.60 | 131.00 | 272.00 | 127.00 | 18.00 | 50.00 | 72.46 | 26.00 | 3.05 | 2.06 |
| Spathidium sp. | 75.00 | 2.90 | 520.00 | 55.00 | 33.50 | 47.00 | 79.92 | 30.00 | 3.80 | 2.46 |
| Dileptus sp. | 194.00 | 5.90 | 11.90 | 180.00 | 0.00 | 9.20 | 82.15 | 32.15 | 4.10 | 2.62 |
| Stylonychia sp. | 47.00 | 0.00 | 281.00 | 216.90 | 8.30 | 24.00 | 112.77 | 51.15 | 8.44 | 4.92 |
| Pauroleptus sp. | 25.00 | 0.00 | 16.00 | 0.00 | 6.40 | 2.50 | 68.92 | 33.31 | 3.28 | 2.18 |
| Parakahliella sp. | 25.00 | 0.00 | 13.50 | 0.00 | 27.00 | 21.00 | 78.00 | 33.38 | 3.90 | 2.51 |
| Tetrahymena sp. | 370.00 | 0.00 | 242.00 | 98.00 | 224.00 | 64.00 | 46.00 | 17.62 | 1.27 | 1.12 |
| Strongylidium sp. | 157.00 | 0.00 | 32.50 | 20.00 | 18.00 | 4.90 | 142.85 | 59.77 | 12.90 | 7.28 |
| Opercularia sp. | 101.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 170.00 | 182.00 | 51.62 | 23.62 | 1.78 | 1.39 |
| Litonotus sp. | 0.00 | 0.00 | 53.50 | 18.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 80.00 | 33.38 | 4.04 | 2.59 |
| Zoothamnium sp. | 0.00 | 0.00 | 21.70 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 110.54 | 39.69 | 7.09 | 4.20 |
| Total biomass (×10−4 g/plant) | 9.07 | 0.47 | 3.53 | 0.61 | 0.12 | 0.16 | ||||
| Species | May | June | July | August | September | October | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | Rank | N | % | Rank | N | % | Rank | N | % | Rank | N | % | Rank | N | % | Rank | |
| Colpoda sp.* | 128.38 | 50.2 | 1 | 14.68 | 48.68 | 1 | 148.3 | 52.84 | 1 | 36.88 | 30.82 | 1 | 21.86 | 33.41 | 1 | 23.98 | 29.85 | 1 |
| Tachysoma sp.* | 32.38 | 12.69 | 2 | 6.26 | 21.69 | 2 | 17.61 | 6.69 | 4 | 20.92 | 18.85 | 2 | 5.59 | 8.37 | 6 | 14.76 | 18.93 | 6 |
| Gonostomum sp.* | 30.46 | 9.92 | 3 | 0 | 0 | - | 27.1 | 10.83 | 2 | 18.74 | 17.06 | 3 | 1.7 | 2.44 | 9 | 11.5 | 14.19 | 9 |
| Oxytricha sp.* | 25.24 | 9.06 | 4 | 2.02 | 6.26 | 4 | 26.7 | 10.45 | 3 | 6.09 | 5.33 | 6 | 14.1 | 21.66 | 2 | 5.26 | 5.68 | 8 |
| Tetrahymena sp. | 9.59 | 3.62 | 5 | 0 | 0 | - | 7.74 | 2.94 | 8 | 4.86 | 4 | 8 | 6.93 | 7.85 | 8 | 3.97 | 5.01 | 14 |
| Vorticella sp.* | 9.68 | 2.91 | 6 | 5.51 | 16.7 | 3 | 8.24 | 3.24 | 7 | 5.57 | 4.7 | 7 | 2.07 | 2.84 | 14 | 3.49 | 4.31 | 10 |
| Dileptus sp. | 6.95 | 2.65 | 7 | 1.21 | 4.44 | 5 | 1.65 | 0.53 | 14 | 6.68 | 6.01 | 5 | 0 | 0 | - | 1.51 | 1.98 | 4 |
| Strongylidium sp. | 6.24 | 2.32 | 8 | 0 | 0 | -- | 2.81 | 1 | 10 | 2.22 | 1.94 | 10 | 2.08 | 2.86 | 10 | 1.09 | 1.33 | 12 |
| Opercularia sp.* | 5.02 | 1.95 | 9 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | 6.32 | 8.43 | 3 | 6.6 | 7.79 | 2 |
| Spathidium sp. | 4.31 | 1.61 | 10 | 0.8 | 2.24 | 6 | 11.37 | 4.37 | 5 | 3.69 | 3.21 | 9 | 2.89 | 4.61 | 7 | 3.43 | 4.69 | 13 |
| Stylonychia sp.* | 3.42 | 1.31 | 11 | 0 | 0 | - | 8.38 | 3.35 | 6 | 7.32 | 6.42 | 4 | 1.43 | 2.11 | 4 | 2.39 | 2.78 | 3 |
| Pauroleptus sp. | 2.48 | 0.91 | 12 | 0 | 0 | - | 1.99 | 0.76 | 12 | 0 | 0 | - | 1.26 | 1.89 | 12 | 0.78 | 0.95 | 5 |
| Parakahliella sp. | 2.46 | 0.85 | 13 | 0 | 0 | - | 1.83 | 0.69 | 13 | 0 | 0 | - | 2.54 | 3.51 | 5 | 2.22 | 2.51 | 7 |
| Litonotus sp. | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | 3.66 | 1.45 | 9 | 2.07 | 1.65 | 11 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - |
| Zoothamnium sp. | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | 2.31 | 0.86 | 11 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - |
| H’ | J’ | D | |
|---|---|---|---|
| May 1 | 1.78 | 0.70 | 2.14 |
| May 2 | 1.76 | 0.69 | 2.16 |
| May 3 | 1.77 | 0.69 | 2.15 |
| May 4 | 1.79 | 0.70 | 2.15 |
| June 1 | 1.45 | 0.81 | 1.44 |
| June 2 | 1.49 | 0.83 | 1.57 |
| June 3 | 1.31 | 0.73 | 1.43 |
| June 4 | 1.28 | 0.71 | 1.43 |
| July 1 | 1.79 | 0.68 | 2.38 |
| July 2 | 1.76 | 0.67 | 2.35 |
| July 3 | 1.57 | 0.59 | 2.28 |
| July 4 | 1.56 | 0.59 | 2.29 |
| August 1 | 2.09 | 0.87 | 2.13 |
| August 2 | 2.01 | 0.84 | 2.12 |
| August 3 | 1.95 | 0.81 | 2.10 |
| August 4 | 1.96 | 0.82 | 2.08 |
| September 1 | 2.08 | 0.84 | 2.64 |
| September 2 | 2.03 | 0.82 | 2.56 |
| September 3 | 2.06 | 0.83 | 2.59 |
| September 4 | 1.99 | 0.80 | 2.62 |
| October 1 | 2.15 | 0.84 | 2.76 |
| October 2 | 2.17 | 0.85 | 2.81 |
| October 3 | 2.12 | 0.83 | 2.71 |
| October 4 | 2.05 | 0.80 | 2.66 |
| Rank | R | Environmental Variables | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.677 | NH4+-N, SOM, TN, pH | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.677 | NH4+-N, SOM, TN | 0.01 |
| 3 | 0.673 | NH4+-N, AP, SOM, pH | 0.01 |
| 4 | 0.672 | NO3−-N, NH4+-N, SOM, TN | 0.01 |
| 5 | 0.672 | NO3−, NH4+-N, SOM, TN, pH | 0.01 |
| 6 | 0.671 | NH4+-N, AP, SOM, TN, pH | 0.01 |
| 7 | 0.671 | NO3−-N, NH4+-N, AP, SOM, TN, pH | 0.01 |
| 8 | 0.670 | NH4+-N, AP, SOM, TN | 0.01 |
| 9 | 0.669 | NO3−-N, NH4+-N, AP, SOM, TN | 0.01 |
| 10 | 0.668 | NH4+-N, AP, pH | 0.01 |
References
- Laforest-Lapointe, I.; Arrieta, M.-C. Microbial Eukaryotes: A Missing Link in Gut Microbiome Studies. Msystems 2018, 3, e00201-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kou, X.; Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Ferris, H. Frequency of stover mulching but not amount regulates the decomposition pathways of soil micro-foodwebs in a no-tillage system. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 144, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manirakiza, N.; Şeker, C. Effects of compost and biochar amendments on soil fertility and crop growth in a calcareous soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 3002–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-B.; He, J.-Z.; Geisen, S.; Han, L.-L.; Wang, J.-T.; Shen, J.-P.; Wei, W.-X.; Fang, Y.-T.; Li, P.-P.; Zhang, L.-M. Protist communities are more sensitive to nitrogen fertilization than other microorganisms in diverse agricultural soils. Microbiome 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Karlsson, I.; Geisen, S.; Kowalchuk, G.; Jousset, A. Protists: Puppet Masters of the Rhizosphere Microbiome. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Su, T.; Ma, N.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Wu, Z.; Liang, W.; Cheng, W. Soil micro-food web interactions and rhizosphere priming effect. Plant Soil 2018, 432, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Parihar, P.; Prasad, S.M. Sulfur and Calcium Simultaneously Regulate Photosynthetic Performance and Nitrogen Metabolism Status in As-Challenged Brassica juncea L. Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asiloglu, R.; Shiroishi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Turgay, O.C.; Murase, J.; Harada, N. Protist-enhanced survival of a plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, Azospirillum sp. B510, and the growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 154, 103599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.A.; Adams, B.J.; Barrett, J.E.; Lyons, W.B.; Virginia, R.A.; Wall, D.H. Stable C and N isotope ratios reveal soil food web structure and identify the nematode Eudorylaimus antarcticus as an omnivore–predator in Taylor Valley, Antarctica. Polar. Biol. 2018, 41, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Shinohara, Y.; Asakawa, S.; Murase, J. Susceptibility and resilience of the soil ciliate community to high temperatures. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 66, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.-B.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Du, M.-L.; Ge, C.; Wang, Q.-H.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Yang, M.-L.; Zheng, X.-D.; Chen, Y.; et al. Dominant protozoan species in rhizosphere soil over growth of Beta vulgaris L. in Northeast China. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Custer, G.F.; van Diepen, L.T.A.; Stump, W. An Examination of Fungal and Bacterial Assemblages in Bulk and Rhizosphere Soils under Solanum tuberosum in Southeastern Wyoming, USA. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 1, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracmarova, M.; Karpiskova, J.; Uhlik, O.; Strejcek, M.; Szakova, J.; Balik, J.; Demnerova, K.; Stiborova, H. Microbial Communities in Soils and Endosphere of Solanum tuberosum L. and their Response to Long-Term Fertilization. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantigoso, H.A.; Manter, D.K.; Vivanco, J.M. Differential Effects of Phosphorus Fertilization on Plant Uptake and Rhizosphere Microbiome of Cultivated and Non-cultivated Potatoes. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, R.U.; Tantray, A.Y.; Kouser, N.; Allie, K.A.; Wani, S.M.; Alamri, S.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Shah, A.A. Influence of ecological and edaphic factors on biodiversity of soil nematodes. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3049–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Xiao, X.; Li, C.; Shi, L.; Cheng, K.; Li, W.; Wen, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, K. Microbial carbon source utilization in rice rhizosphere soil with different tillage practice in a double cropping rice field. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; You, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X. Elevational is the main factor controlling the soil microbial community structure in alpine tundra of the Changbai Mountain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunhikannan, S.; Thomas, C.J.; Franks, A.E.; Mahadevaiah, S.; Kumar, S.; Petrovski, S. Environmental hotspots for antibiotic resistance genes. Microbiologyopen 2021, 10, e1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, G.; Matsumoto, K.; Nemoto, K.; Inokuchi, M.; Hirotsu, N. Transition from Proto-Kranz-Type Photosynthesis to HCO3− Use Photosynthesis in the Amphibious Plant Hygrophila polysperma. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 675507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiong, B.; Wang, S.; Deng, X.; Yin, L.; Li, H. Regulation Effects of Water and Nitrogen on the Source-Sink Relationship in Potato during the Tuber Bulking Stage. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Du, J.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, Z.; Yu, X. The response of potato tuber yield, nitrogen uptake, soil nitrate nitrogen to different nitrogen rates in red soil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, J.M.; Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Rhizosphere microbiome assemblage is affected by plant development. ISME J. 2014, 8, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gao, W.; Ding, G.-C.; et al. A Rhizosphere-Derived Consortium of Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma harzianum Suppresses Common Scab of Potato and Increases Yield. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Protozoan grazing affects estimates if carbon utilization efficiency of the soil microbial community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trap, J.; Bonkowski, M.; Plassard, C.; Villenave, C.; Blanchart, E. Ecological importance of soil bacterivores for ecosystem functions. Plant Soil 2015, 398, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pernthaler, J. Predation on prokaryotes in the water column and its ecological implications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, D.F.; Tuorto, S.; Taghon, G.L. Growth Phase and Elemental Stoichiometry of Bacterial Prey Influences Ciliate Grazing Selectivity. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandarana, K.A.; Amaresan, N. Soil protists: An untapped microbial resource of agriculture and environmental importance. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Ramírez, C.A.; Mayén-Estrada, R. Ecological Study of the Active Ciliate Community from Bromeliads during the Humid Season in Different Types of Forests of the Mexican Neotropics. Diversity 2022, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.S.; Sripoorna, S.; Dagar, J.; Jangra, S.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, K.; Singh, S.; Goyal, A.; Maurya, S.; Gambhir, G.; et al. Soil ciliates of the Indian Delhi Region: Their community characteristics with emphasis on their ecological implications as sensitive bio-indicators for soil quality. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, W.; Noman, A.; Naveed, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.Y.H. Role of environmental factors in shaping the soil microbiome. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 41225–41247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandarana, K.A.; Pramanik, R.S.; Amaresan, N. Interaction between ciliate and plant growth promoting bacteria influences the root structure of rice plants, soil PLFAs and respiration properties. Rhizosphere 2022, 21, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.; Patterson, D.J.; Dunthorn, M.; Clamp, J.C.; Achilles-Day, U.E.; Aescht, E.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Al-Rasheid, K.; Carr, M.; et al. Beyond the “Code”: A Guide to the Description and Documentation of Biodiversity in Ciliated Protists (Alveolata, Ciliophora). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2016, 64, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, K.; Xue, Y.; Rønn, R.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Rensing, C.; Yang, J. Dynamics and determinants of amoeba community, occurrence and abundance in subtropical reservoirs and rivers. Water Res. 2018, 146, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, Y.; Moreno-Mesonero, L.; Amorós, I.; Perez, J.A.M.; Morillo, J.; Alonso, J. Multiple identification of most important waterborne protozoa in surface water used for irrigation purposes by 18S rRNA amplicon-based metagenomics. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X. Effects of foliar application of selenate and selenite at different growth stages on Selenium accumulation and speciation in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Food Chem. 2013, 14, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacEachren, A.M.; Davidson, J.V. Sampling and Isometric Mapping of Continuous Geographic Surfaces. Am. Cartogr. 1987, 14, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissner, W.; Khaled, A.R. Notes on Soil Ciliates (Protozoa, Ciliophora) from TheNetherlands, with Description of Keronopsis schminkei nov. spec. and Apobryophyllum schmidingeri nov. spec. Acta Protozool. 2007, 46, 201. [Google Scholar]
- Foissner, W. An updated compilation of world soil ciliates (Protozoa, Ciliophora), with ecological notes, new records, and descriptions of new species. Eur. J. Protistol. 1998, 34, 195–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissner, W. An update of ‘basic light and scanning electron microscopic methods for taxonomic studies of ciliated protozoa’. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Choi, J.K.; Song, W. An Improved Silver Carbonate Impregnation for Marine Ciliated Protozoa. Acta Protozool. 2003, 42, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wilbert, N.; Song, W. A further study on littoral ciliates (Protozoa, Ciliophora) near King George Island, Antarctica, with description of a new genus and seven new species. J. Nat. Hist. 2008, 42, 979–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, Y.; Wang, F. Chiral compounds from bacterial polyesters: Sugars to plastics to fine chemicals. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 65, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.; Srivastava, R.; Gupta, M.N. Immobilization of acid phosphatase from arachis hypogaea on CM-cellulose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1987, 29, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimek, K.; Grujčić, V.; Nedoma, J.; Jezberová, J.; Šorf, M.; Matoušů, A.; Pechar, L.; Posch, T.; Bruni, E.P.; Vrba, J. Microbial food webs in hypertrophic fishponds: Omnivorous ciliate taxa are major protistan bacterivores. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 2295–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, T. An analysis of metabolic characteristics of planktonic heterotrophic protozoans. J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šolić, M.; Šantić, D.; Šestanović, S.; Bojanić, N.; Jozić, S.; Ordulj, M.; Tomaš, A.V.; Kušpilić, G. Changes in the Trophic Pathways within the Microbial Food Web in the Global Warming Scenario: An Experimental Study in the Adriatic Sea. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erős, T.; Kuehne, L.; Dolezsai, A.; Sommerwerk, N.; Wolter, C. A systematic review of assessment and conservation management in large floodplain rivers—Actions postponed. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Nutrient Element | Parameters (g/Plant) | May | June | July | August | September | October | Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Ingestion | 144.73 | 2.24 | 183.22 | 17.83 | 6.23 | 7.93 | 60.36 |
| Egestion | 3.01 | 0.16 | 1.17 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.77 | |
| Respiration | 2.26 | 0.12 | 0.88 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.58 | |
| Carbon flow | 139.46 | 1.96 | 181.17 | 17.47 | 6.16 | 7.83 | 59.01 | |
| Carbon contribution rate (%) | - | 12.26 | 94.36 | 7.94 | 7.71 | - | 30.57 | |
| Nitrogen | Ingestion | 27.83 | 0.43 | 35.23 | 3.43 | 1.2 | 1.52 | 11.61 |
| Egestion | 0.78 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.20 | |
| Respiration | 0.59 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.15 | |
| Nitrogen flow | 26.46 | 0.36 | 34.7 | 3.34 | 1.18 | 1.50 | 11.26 | |
| Nitrogen contribution rate (%) | - | 8.96 | 72.29 | 6.07 | 5.90 | - | 23.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, W.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, S.; Ge, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Cui, J.; Ren, N.; Chen, Y. Diversity Temporal–Spatial Dynamics of Potato Rhizosphere Ciliates and Contribution to Nitrogen- and Carbon-Derived Nutrition in North-East China. Plants 2023, 12, 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122260
Zheng W, Zheng X, Wu Y, Lv S, Ge C, Wang X, Wang Q, Cui J, Ren N, Chen Y. Diversity Temporal–Spatial Dynamics of Potato Rhizosphere Ciliates and Contribution to Nitrogen- and Carbon-Derived Nutrition in North-East China. Plants. 2023; 12(12):2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122260
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Weibin, Xiaodan Zheng, Yuqing Wu, Shaoyang Lv, Chang Ge, Xiang Wang, Qiuhong Wang, Jingjing Cui, Nanqi Ren, and Ying Chen. 2023. "Diversity Temporal–Spatial Dynamics of Potato Rhizosphere Ciliates and Contribution to Nitrogen- and Carbon-Derived Nutrition in North-East China" Plants 12, no. 12: 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122260
APA StyleZheng, W., Zheng, X., Wu, Y., Lv, S., Ge, C., Wang, X., Wang, Q., Cui, J., Ren, N., & Chen, Y. (2023). Diversity Temporal–Spatial Dynamics of Potato Rhizosphere Ciliates and Contribution to Nitrogen- and Carbon-Derived Nutrition in North-East China. Plants, 12(12), 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122260





