Flora of Northeast Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Floristic Composition of Floras in Northeast Asia
2.1.1. Basic Composition of the Flora
2.1.2. Analysis of the Components of the Families
2.1.3. Analysis of the Components of the Genera
2.1.4. Analysis of the Components of the Species and Infraspecific Taxa
2.2. Statistics and Analysis of the Geographical Components of the Genera
2.2.1. Statistics and Analysis of the Geographical Components of the Seed Plant Genera in Northeast Asia
2.2.2. Statistics and Analysis of the Geographical Components of the Genera in Five Regions
2.3. Distribution of Species and Infraspecific Taxa of the Northeast Asia Flora
2.3.1. Distribution of Species and Infraspecific Taxa of the Northeast Asia Flora
2.3.2. Distribution of Locally Endemic Species and Infraspecific Taxa across the Five Regions
2.4. The Relationship between Species Distribution Patterns and Climate in Northeast Asia
2.4.1. The Dominant Factor in Classifying the Climate Types of Northeast Asia: Continentality
2.4.2. The Relationship between Species Distribution Patterns and Continental and Altitude Factors in Northeast Asia
2.5. Threatened Species Situation in Northeast Asia
The Threatened Species List of Five Regions in Northeast Asia
3. Discussion
3.1. The Tropical Composition of Northeast Asia
3.2. The Large-Scale Spatial Patterns of Plant Diversity in Northeast Asia
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIO1 | 0.2429 | −0.3024 | 0.0071 | 0.0418 | 0.0484 |
| BIO2 | −0.2506 | −0.1029 | −0.0839 | 0.2398 | −0.5201 |
| BIO3 | −0.0071 | −0.0858 | −0.5265 | 0.4997 | −0.3949 |
| BIO4 | −0.2505 | −0.0185 | 0.3558 | −0.1360 | −0.2059 |
| BIO5 | 0.0996 | −0.4549 | 0.1793 | −0.0598 | −0.2647 |
| BIO6 | 0.2761 | −0.1548 | −0.1609 | 0.0230 | 0.1440 |
| BIO7 | −0.2640 | −0.0577 | 0.2762 | −0.0571 | −0.3009 |
| BIO8 | 0.1153 | −0.4252 | 0.2569 | 0.0237 | 0.0042 |
| BIO9 | 0.2662 | −0.1873 | −0.1632 | −0.0064 | 0.0383 |
| BIO10 | 0.1573 | −0.4088 | 0.2197 | −0.0377 | −0.0766 |
| BIO11 | 0.2685 | −0.1936 | −0.1544 | 0.0797 | 0.1060 |
| BIO12 | 0.2674 | 0.1868 | 0.1548 | 0.1058 | −0.1290 |
| BIO13 | 0.2165 | 0.1816 | 0.3010 | 0.3710 | 0.0069 |
| BIO14 | 0.2612 | 0.1546 | −0.0310 | −0.2403 | −0.3169 |
| BIO15 | −0.2352 | −0.1290 | 0.1136 | 0.3439 | 0.1224 |
| BIO16 | 0.2277 | 0.1957 | 0.2759 | 0.3224 | −0.0276 |
| BIO17 | 0.2653 | 0.1562 | −0.0256 | −0.2210 | −0.2962 |
| BIO18 | 0.2208 | 0.1984 | 0.2892 | 0.3350 | −0.0127 |
| BIO19 | 0.2561 | 0.1585 | −0.0343 | −0.2587 | −0.3287 |
Appendix C
| PC | Eigen Value | Proportion of Variance (%) | Cumulative Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.0439 | 58.1257 | 58.12567 |
| 2 | 3.7064 | 19.5074 | 77.63305 |
| 3 | 1.9811 | 10.4269 | 88.05994 |
| 4 | 1.2678 | 6.6726 | 94.73251 |
| 5 | 0.6494 | 3.4178 | 98.15035 |
| 6 | 0.1902 | 1.0010 | 99.15132 |
| 7 | 0.0782 | 0.4118 | 99.56316 |
| 8 | 0.0317 | 0.1667 | 99.72984 |
| 9 | 0.0148 | 0.0781 | 99.80793 |
| 10 | 0.0097 | 0.0512 | 99.85909 |
| 11 | 0.0081 | 0.0427 | 99.90175 |
| 12 | 0.0068 | 0.0359 | 99.93762 |
| 13 | 0.0064 | 0.0337 | 99.97132 |
| 14 | 0.0020 | 0.0107 | 99.98203 |
| 15 | 0.0015 | 0.0081 | 99.99013 |
| 16 | 0.0011 | 0.0057 | 99.9958 |
| 17 | 0.0007 | 0.0034 | 99.99923 |
| 18 | 0.0001 | 0.0008 | 100 |
| 19 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 100 |
References
- Heywood, V.H. Plant Taxonomy; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, S.; Leese, M.; Stahl, D.; Everitt, B.S. Cluster Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ornduff, R. Floristic Regions of the World. Syst. Bot. 1978, 3, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhtadzhian, A.L. Floristic Regions of the World; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Deng, T.; Chen, Y.-S.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, H. Current research and development trends in floristic geography. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H. Tropical flora of southern China. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forest, F.; Grenyer, R.; Rouget, M.; Davies, T.J.; Cowling, R.M.; Faith, D.P.; Balmford, A.; Manning, J.C.; Procheş, Ş.; Van Der Bank, M.; et al. Preserving the evolutionary potential of floras in biodiversity hotspots. Nature 2007, 445, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooyman, R.; Rossetto, M.; Cornwell, W.; Westoby, M. Phylogenetic tests of community assembly across regional to continental scales in tropical and subtropical rain forests. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, N.G.; Umaña, M.N. Phylofloristics: An example from the Lesser Antilles. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 7, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Soejima, A.; Chang, K.S.; Ma, K. Mapping Asia Plants: Current status of floristic information for Northeast Asia. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K. Mapping Asia Plants: A cyberinfrastructure for plant diversity in Asia. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, H.; Krestov, P.; Fu, P.-Y.; Wang, Q.-L.; Song, J.-S.; Chourmouzis, C. Phytogeography of Northeast Asia. In Forest Vegetation of Northeast Asia; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, S. Biogeoclimatic zones of Hokkaido Island, Japan. J. Coll. Lib. Arts Toyama Univ. 1979, 12, 97–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ohwi, J.; Meyer, F.G.; Walker, E.H. Flora of Japan (Revised); Shibundo Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.S.; Li, Z.G.; Jiang, S.F.; Han, J. Natural Geography of Asia; Business Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. Geography of the Vegetation in Northeast China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Krestov, P.; Mikhailo, A. Bioclimate and zonal vegetation in Northeast Asia: First approximation to an integrated study. Phytocoenologia 2007, 37, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Raven, P.H. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Bretschneider, E. History of European Botanical Discoveries in China; Sampson Low, Marston and Company: London, UK, 1898; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Maximowicz, C.J. Primitiae Florae Amurensis. Mem. Acad. Imp. Sci. St. Petersburg 1859, 9, 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Maximowicz, C. Diagnoses Plantarum Novarum Asiaticarum; L’Académie Impériale des Sciences: Petropoli, Brazil, 1893; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Maximowicz, C.J. Diagnoses Breves Plantarum Novarum Japoniae et Mandchuriae; L’Académie Impériale des Sciences: Petropoli, Brazil, 1870; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J. The Outline of Taxonomic Literature of Eastern Asian Higher Plants; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J. A Checklist of Woody Plants from Eastern Asia; Henan Science and Technology Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jaccard, P. Distribution de la flore alpine dans le Bassin des Dranses et dans quelques regions voisines. Bull Soc Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1901, 37, 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng-Yi, W. The Areal-Types of Chinese Genera of Seed Plants. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 1991, 13, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonevicius, E.; Stankunavicius, G.; Rimkus, E. Continentality and Oceanity in the Mid and High Latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere and Their Links to Atmospheric Circulation. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 5746191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Wang, T.; Liu, S. The Response of Vegetation Phenology and Productivity to Drought in Semi-Arid Regions of Northern China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Kim, M.; Kim, R.; Kim, K.; Kim, T.; Rim, C.; Pak, U.; Han, K. Red Data Book of Democratic People’s Republic of Korea; MAB National Committee of Democratic People’s Republic of Korea: Pyongyang, Republic of Korea, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S. Korean Red List of Threatened Species; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Yang, Y.; Dong, S.-Y.; He, Q.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yu, S.; Huiyuan, L.; Liu, B.; Yan, Y.-H.; et al. Threatened Species List of China’s Higher Plants. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 696–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magsar, U. Species Catalogue of Rare and Threatened Vascular Plants of Mongolia; Bembi San: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- MOE. Ministry of the Environment Government of Japan. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Chang, A.; Wu, S.; Raven, P.H.; Iwatsuki, K.; Kubitzki, K. Floristic Characteristics and Diversity of East Asian Plants: Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Floristic Characteristics and Diversity of East Asian Plants; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.-M.; Mao, L.-F.; Yang, T.; Ye, J.-F.; Liu, B.; Li, H.-L.; Sun, M.; Miller, J.T.; Mathews, S.; Hu, H.-H.; et al. Evolutionary history of the angiosperm flora of China. Nature 2018, 554, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ricklefs, R.E.; Cody, M.L. Vascular plant diversity in eastern Asia and North America: Historical and ecological explanations. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 128, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Jin, Y.; Ricklefs, R.E. Phylogenetic diversity anomaly in angiosperms between eastern Asia and eastern North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11452–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, H.; Ricklefs, R.E. Diversity of temperate plants in east Asia. Nature 2001, 413, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Ricklefs, R.E. Large-scale processes and the Asian bias in species diversity of temperate plants. Nature 2000, 407, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, H. An outline of the phytogeography of Japan. Distrib. Maps Flower. Plants Jpn. 1959, 2, 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino, M.M. Natural Regions of Japan. GeoJournal 1980, 4, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, H.P. Plant diversity and endemism in sub-Saharan tropical Africa. J. Biogeogr. 2001, 28, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kier, G.; Mutke, J.; Dinerstein, E.; Ricketts, T.H.; Küper, W.; Kreft, H.; Barthlott, W. Global patterns of plant diversity and floristic knowledge. J. Biogeogr. 2005, 32, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreft, H.; Jetz, W. Global patterns and determinants of vascular plant diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5925–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brummitt, N.; Araújo, A.C.; Harris, T.J. Areas of plant diversity—What do we know? Plants People Planet 2021, 3, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M.; McGill, B.J.; Thompson, P.L.; Antão, L.H.; Bates, A.E.; Blowes, S.A.; Dornelas, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Magurran, A.E.; Supp, S.R.; et al. Species richness change across spatial scales. Oikos 2019, 128, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruelheide, H.; Jiménez-Alfaro, B.; Jandt, U.; Sabatini, F.M. Deriving site-specific species pools from large databases. Ecography 2020, 43, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengler, J.; Matthews, T.J.; Steinbauer, M.J.; Wolfrum, S.; Boch, S.; Chiarucci, A.; Conradi, T.; Dembicz, I.; Marcenò, C.; García-Mijangos, I.; et al. Species–area relationships in continuous vegetation: Evidence from Palaearctic grasslands. J. Biogeogr. 2020, 47, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keil, P.; Chase, J.M. Global patterns and drivers of tree diversity integrated across a continuum of spatial grains. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, F.M.; Jiménez-Alfaro, B.; Jandt, U.; Chytrý, M.; Field, R.; Kessler, M.; Lenoir, J.; Schrodt, F.; Wiser, S.K.; Arfin Khan, M.A.S.; et al. Global patterns of vascular plant alpha diversity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 46–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruelheide, H.; Dengler, J.; Jiménez-Alfaro, B.; Purschke, O.; Hennekens, S.M.; Chytrý, M.; Pillar, V.D.; Jansen, F.; Kattge, J.; Sandel, B. sPlot–A new tool for global vegetation analyses. J. Veg. Sci. 2019, 30, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, F.M.; Lenoir, J.; Hattab, T.; Arnst, E.A.; Chytrý, M.; Dengler, J.; De Ruffray, P.; Hennekens, S.M.; Jandt, U.; Jansen, F.; et al. sPlotOpen–An environmentally balanced, open-access, global dataset of vegetation plots. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 1740–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisz, M.S.; Pottier, J.; Kissling, W.D.; Pellissier, L.; Lenoir, J.; Damgaard, C.F.; Dormann, C.F.; Forchhammer, M.C.; Grytnes, J.-A.; Guisan, A.; et al. The role of biotic interactions in shaping distributions and realised assemblages of species: Implications for species distribution modelling. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2013, 88, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, E.; Chen, Y.; Fang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, S. Environmental drivers of plant distributions at global and regional scales. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J. Climatic Tolerance and the Distribution of Plants. New Phytol. 1987, 106, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.-G.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Wang, T.-R.; Su, T.-H.; Huang, P.-H.; Meng, H.-H.; Li, J. Latitudinal Diversity Gradient in the Changing World: Retrospectives and Perspectives. Diversity 2022, 14, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, D.J.; Paquin, V. Large-scale biogeographical patterns of species richness of trees. Nature 1987, 329, 326–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krestov, P.V.; Nakamura, Y. Phytosociological study of the Picea jezoensis forests of the far east. Folia Geobot. 2002, 37, 441–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Krestov, P. Coniferous forests of the temperate zone of Asia. Conifer. For. Ser. Ecosyst. World 2005, 6, 163–220. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, S.P.; Yu, G.; Takahara, H.; Prentice, I.C. Diversity of temperate plants in east Asia. Nature 2001, 413, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Boufford, D.E.; Ohba, H. Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1993; Volume 3a. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Boufford, D.E.; Ohba, H. Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1995; Volume 3b. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Boufford, D.E.; Ohba, H. Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; Volume 2a. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Boufford, D.E.; Ohba, H. Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 2001; Volume 2b. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Boufford, D.E.; Ohba, H. Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; Volume 2c. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Boufford, D.E.; Ohba, H. Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; Volume 4b. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Boufford, D.E.; Ohba, H. Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 2020; Volume 4a. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-S.; Kim, H.; Chang, K.S. Provisional Checklist of Vascular Plants for the Korea Peninsula Flora (KPF); Designpost Seoul: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.-W. The Genera of Vascular Plants of Korea; Academy Publ.: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Urgamal, M.; Oyuntsetseg, B.; Nyambayar, D.; Dulamsuren, C.; Sanchir, C.; Žamsran, C. Conspectus of the Vascular Plants of Mongolia; Admon Printing: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Species 2000. Catalogue of Life China: 2022 Annual Checklist; The Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2022; Available online: http://www.sp2000.org.cn/ (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Liou, T.N. Flora Plantarum Herbacearum Chinae Boreali-Orientalis; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; He, X.; Chen, W.; Xu, S. Atlas of Northeast Plant Distribution; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Li, D. Inventory of species diversityof Liaoning higher plants. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 22038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Cao, R. Flora Intra Mongolica; Inner Mongolia People’s Publishing House: Inner Mongolia, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, B.; Hopkins, N.; Lu, Z.; Garay, J.A.R.; Mozzherin, D.; Rees, T.; Matasci, N.; Narro, M.L.; Piel, W.H.; Mckay, S.J.; et al. The taxonomic name resolution service: An online tool for automated standardization of plant names. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- POWO. Plants of the World Online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on the Internet. Available online: http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- WFO. World Flora Online. Published on the Internet. 2023. Available online: http://www.worldfloraonline.org (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- TPL: The Plant List Version 1. Published on the Internet. Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/ (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden. Available online: https://tropicos.org (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Group, T.A.P.; Chase, M.W.; Christenhusz, M.J.M.; Fay, M.F.; Byng, J.W.; Judd, W.S.; Soltis, D.E.; Mabberley, D.J.; Sennikov, A.N.; Soltis, P.S.; et al. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; Huang, L. EVenn: Easy to create repeatable and editable Venn diagrams and Venn networks online. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 30 April 2023).








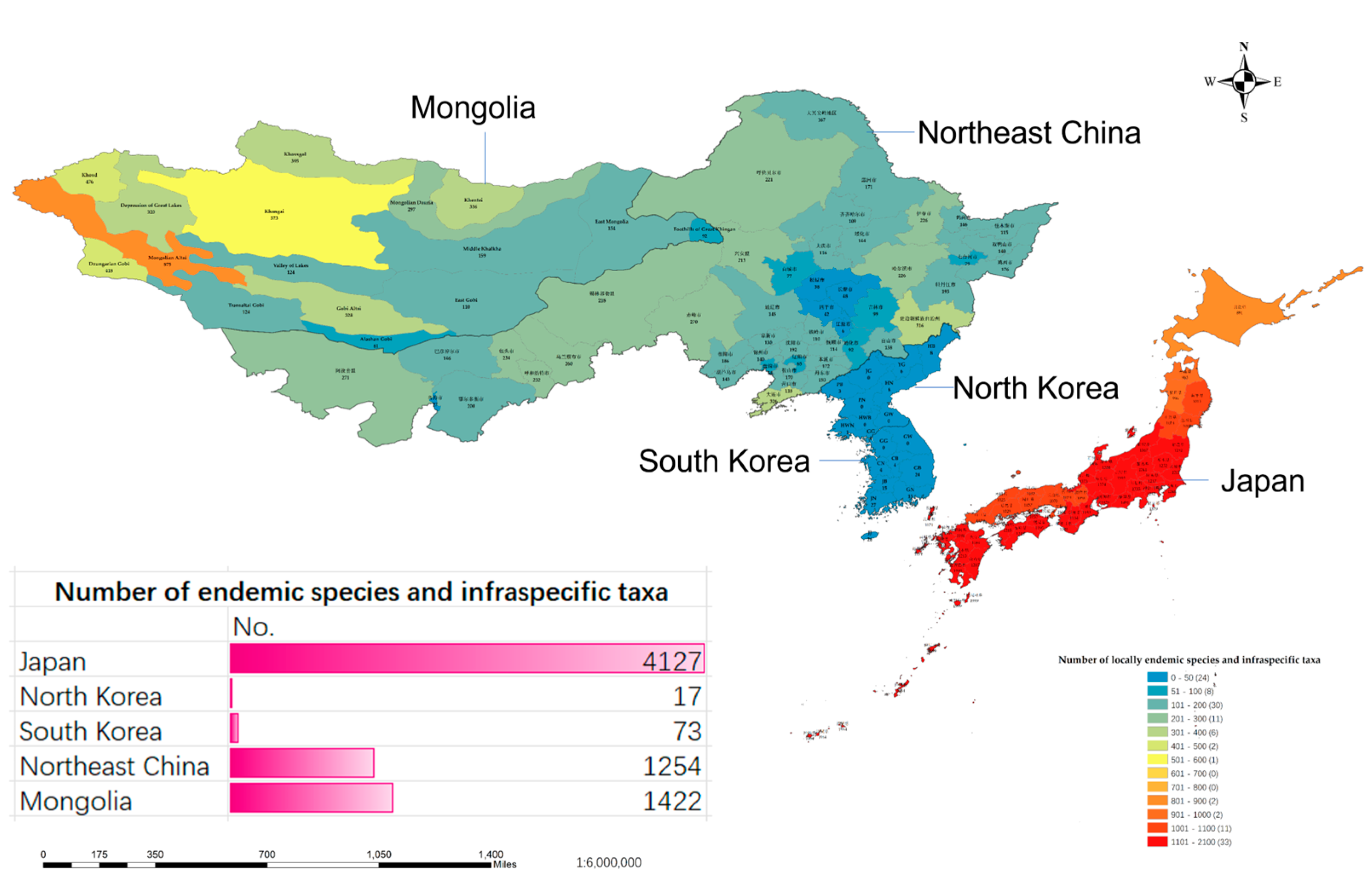






| Taxon Level | Plants | Japan | North Korea | South Korea | Northeast China | Mongolia | Northeast Asia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | Ferns | 17 | 11 | 15 | 10 | 6 | 17 |
| Lycophytes | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| Gymnosperms | 6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 7 | |
| Angiosperms | 190 | 131 | 144 | 134 | 96 | 198 | |
| Sum. | 216 | 147 | 165 | 149 | 107 | 225 | |
| Genus | Ferns | 90 | 37 | 57 | 33 | 17 | 91 |
| Lycophytes | 5 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 5 | |
| Gymnosperms | 16 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 19 | |
| Angiosperms | 1352 | 684 | 774 | 831 | 645 | 1667 | |
| Sum. | 1463 | 731 | 845 | 876 | 670 | 1782 | |
| Species and infraspecific taxa | Ferns | 764 | 114 | 225 | 113 | 40 | 810 |
| Lycophytes | 43 | 17 | 19 | 20 | 6 | 55 | |
| Gymnosperms | 44 | 14 | 19 | 45 | 21 | 91 | |
| Angiosperms | 5544 | 1974 | 2200 | 3632 | 2853 | 9558 | |
| Sum. | 6395 | 2119 | 2463 | 3810 | 2920 | 10,514 |
| Genus-Level | No. | Japan | North Korea | South Korea | Northeast China | Mongolia | Northeast Asia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra-large genera | No. Gen. | 11 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 27 |
| No. sp. | 1024 | 153 | 160 | 382 | 570 | 2664 | |
| Large genera | No. Gen. | 49 | 6 | 7 | 25 | 14 | 83 |
| No. sp. | 1341 | 152 | 172 | 729 | 374 | 2466 | |
| Medium genera | No. Gen. | 85 | 29 | 38 | 55 | 36 | 132 |
| No. sp. | 1120 | 348 | 472 | 718 | 454 | 1730 | |
| Small genera | No. Gen. | 604 | 312 | 352 | 395 | 319 | 748 |
| No. sp. | 2196 | 1084 | 1213 | 1584 | 1228 | 2862 | |
| Single-species genera | No. Gen. | 714 | 384 | 448 | 401 | 294 | 792 |
| No. sp. | 714 | 384 | 448 | 401 | 294 | 792 |
| The Percentages of the Total Number of Species and Infraspecific Taxa | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Areal Types | South Korea | North Korea | Mongolia | Northeast China | Japan | Northeast Asia |
| 1. Cosmopolitan | 24.64% | 27.37% | 26.68% | 26.51% | 19.50% | 21.14% |
| 2. Pantropic | 9.38% | 7.50% | 1.37% | 4.65% | 12.07% | 8.21% |
| 3. Trop. Asia and Trop. Amer. Disjuncted | 0.97% | 0.61% | 0.14% | 0.42% | 1.41% | 0.95% |
| 4. Old World Tropics | 2.07% | 1.89% | 0.89% | 1.39% | 3.25% | 2.29% |
| 5. Tropical Asia and Trop. Australasia | 1.83% | 1.04% | 0.07% | 0.45% | 3.05% | 1.95% |
| 6. Trop. Asia to Trop. Africa | 0.65% | 0.61% | 0.03% | 0.50% | 1.16% | 0.79% |
| 7. Trop. Asia (Indo-Malesia) | 2.92% | 1.79% | 2.33% | 1.76% | 3.38% | 2.87% |
| 8. North Temperate | 28.46% | 33.41% | 42.77% | 37.85% | 26.96% | 33.24% |
| 9. E. Asia and N. Amer. Disjuncted | 4.91% | 4.91% | 1.68% | 3.75% | 3.94% | 3.28% |
| 10. Old World Temperate | 8.00% | 8.97% | 12.81% | 12.26% | 5.80% | 9.12% |
| 11. Temp. Asia | 0.93% | 1.32% | 2.64% | 1.97% | 0.47% | 1.25% |
| 12. Mediterranea, W. Asia to C. Asia | 0.28% | 0.33% | 4.42% | 1.71% | 0.55% | 1.70% |
| 13. C. Asia | 0.08% | 0.14% | 2.29% | 1.02% | 0.02% | 0.77% |
| 14. E. Asia | 4.95% | 3.92% | 0.31% | 2.28% | 5.83% | 4.21% |
| Total | 90.09% | 93.82% | 98.42% | 96.51% | 87.38% | 91.78% |
| No. of Genera | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Areal Types | South Korea | North Korea | Mongolia | Northeast China | Japan | Northeast Asia |
| 1. Cosmopolitan | 88 | 86 | 85 | 95 | 104 | 114 |
| 2. Pantropic | 110 | 81 | 26 | 82 | 223 | 230 |
| 3. Trop. Asia and Trop. Amer. Disjuncted | 14 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 37 | 39 |
| 4. Old World Tropics | 33 | 26 | 7 | 22 | 97 | 97 |
| 5. Tropical Asia and Trop. Australasia | 32 | 16 | 2 | 11 | 106 | 109 |
| 6. Trop. Asia to Trop. Africa | 8 | 6 | 1 | 10 | 34 | 37 |
| 7. Trop. Asia (Indo-Malesia) | 32 | 13 | 5 | 14 | 81 | 83 |
| 8. North Temperate | 211 | 226 | 242 | 265 | 271 | 327 |
| 9. E. Asia and N. Amer. Disjuncted | 56 | 50 | 20 | 57 | 91 | 104 |
| 10. Old World Temperate | 85 | 83 | 114 | 120 | 112 | 168 |
| 11. Temp. Asia | 19 | 24 | 37 | 39 | 18 | 52 |
| 12. Mediterranea, W. Asia to C. Asia | 4 | 5 | 59 | 33 | 23 | 79 |
| 13. C. Asia | 1 | 1 | 45 | 20 | 1 | 45 |
| 14. E. Asia | 90 | 66 | 7 | 65 | 170 | 202 |
| Total | 783 | 690 | 651 | 840 | 1368 | 1686 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-Q.; Dong, X.-Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, H.-F.; Ma, K.-P. Flora of Northeast Asia. Plants 2023, 12, 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122240
Wang S-Q, Dong X-Y, Ye L, Wang H-F, Ma K-P. Flora of Northeast Asia. Plants. 2023; 12(12):2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122240
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Si-Qi, Xue-Yun Dong, Liang Ye, Hong-Feng Wang, and Ke-Ping Ma. 2023. "Flora of Northeast Asia" Plants 12, no. 12: 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122240
APA StyleWang, S.-Q., Dong, X.-Y., Ye, L., Wang, H.-F., & Ma, K.-P. (2023). Flora of Northeast Asia. Plants, 12(12), 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122240







