Characterization of Carotenoid Cleavage Oxygenase Genes in Cerasus humilis and Functional Analysis of ChCCD1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization of ChCCOs
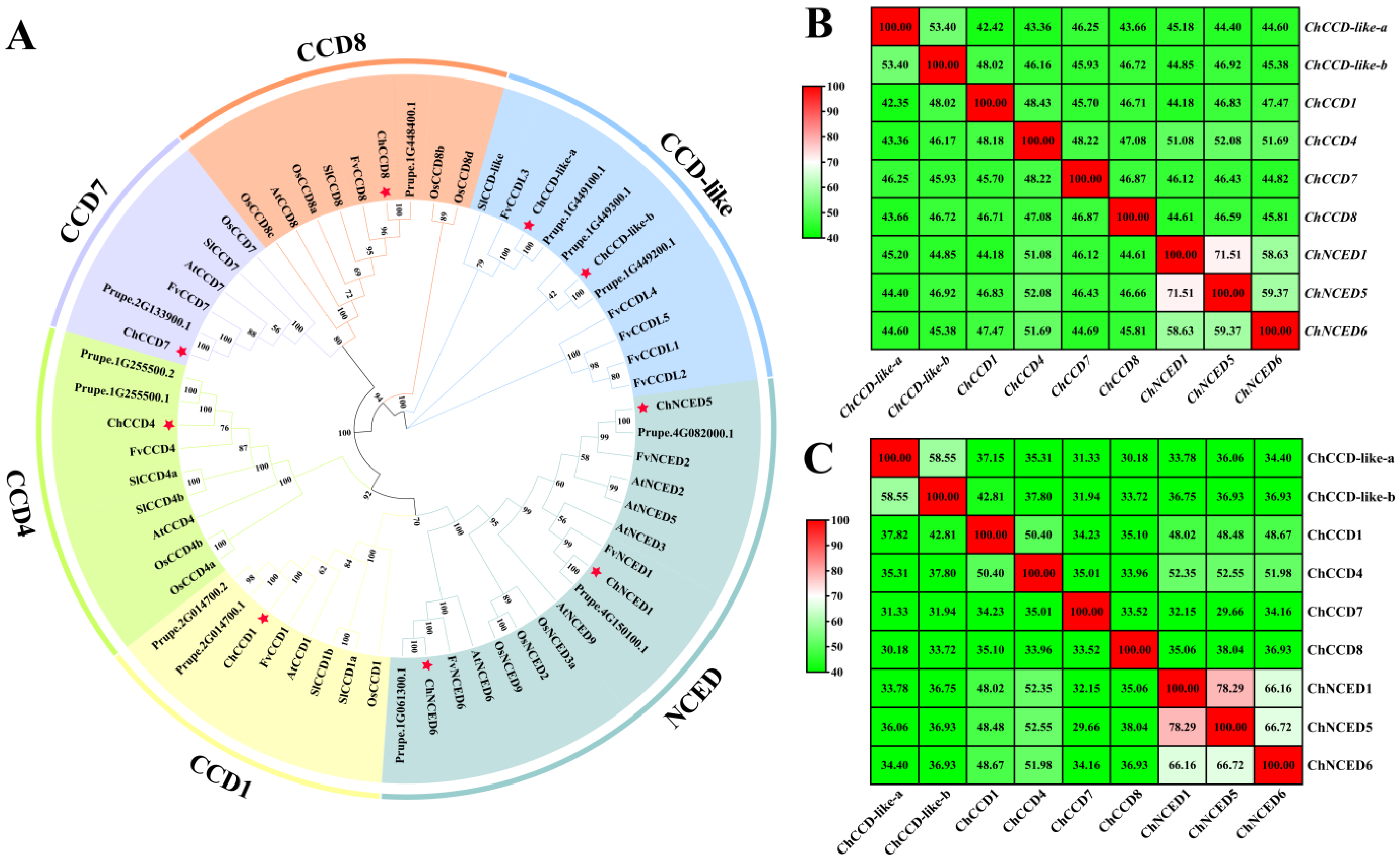
2.2. Chromosome Location and Synteny Analysis of ChCCOs
2.3. Conserved Motifs in ChCCOs and Gene Structures of Their Corresponding Genes
2.4. Promoter Analysis of ChCCOs
2.5. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis of ChCCOs
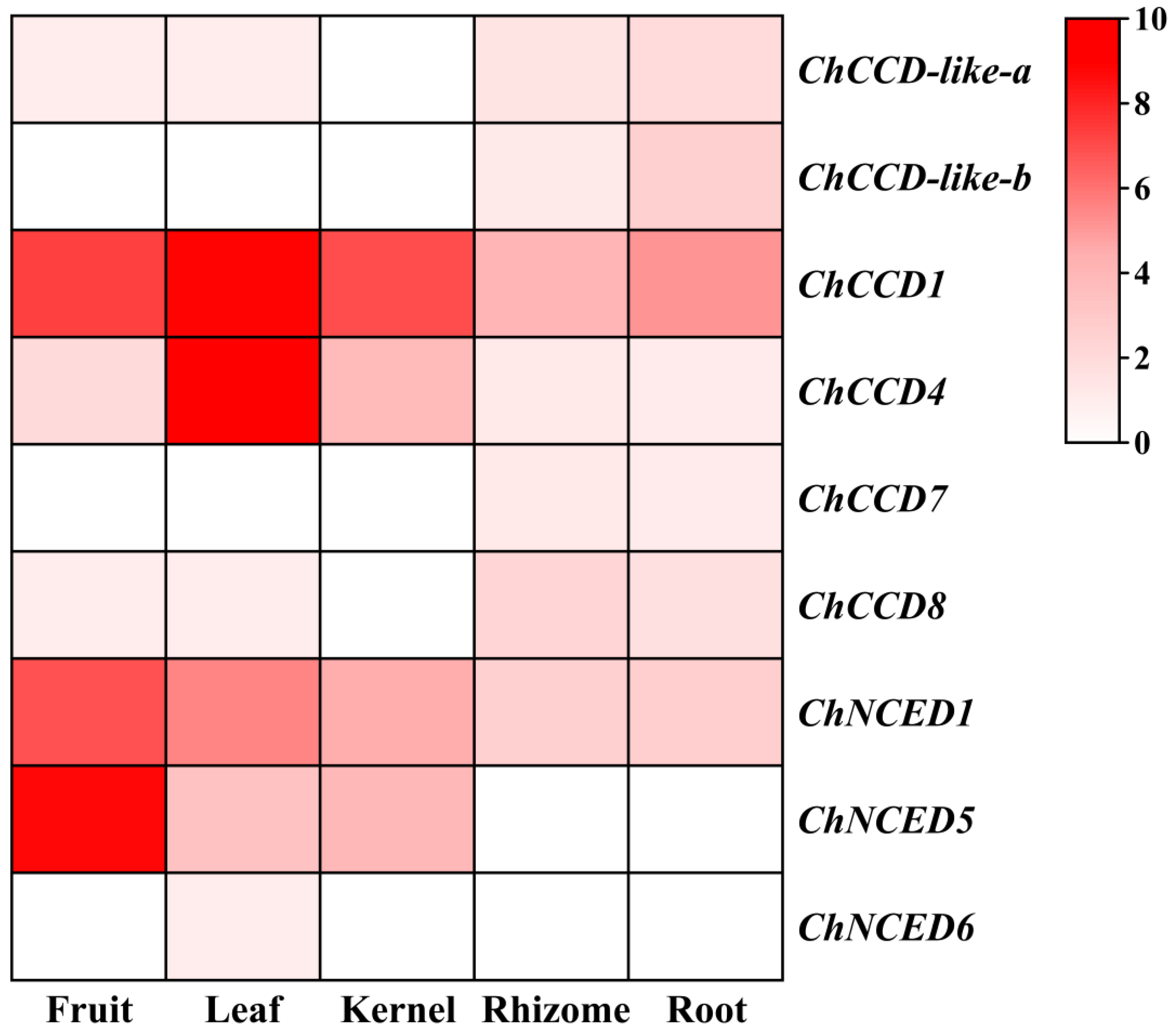
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis of ChCCOs
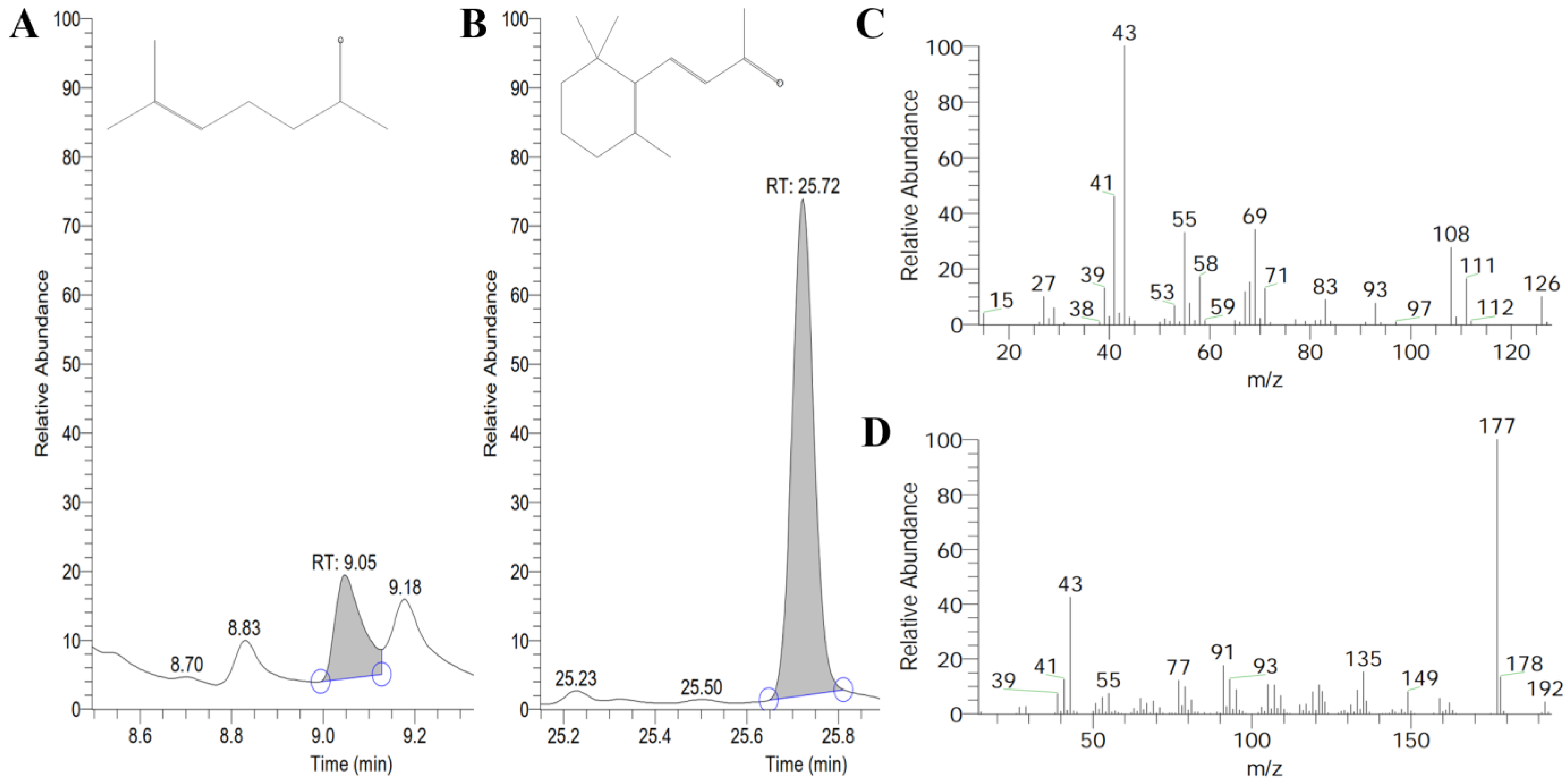
2.7. Prokaryotic Expression and Enzyme Assay Analysis of ChCCD1 and ChCCD4 Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Identification of Cerasus humilis CCO Genes
4.3. Bioinformatic Analysis of ChCCOs and Their Encoded Proteins
4.4. Gene Expression Analysis
4.5. Expression of ChCCD1 and ChCCD4 in Escherichia coli
4.6. Enzyme Assays In Vitro and Volatile Compounds Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, J.; Nageswaran, D.; Li, L. Carotenoid metabolism and regulation in horticultural crops. Hortic. Res. 2015, 2, 15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.H.; He, Y.J.; Liu, D.M.; Jiang, J.G. Regulation of carotenoid degradation and production of apocarotenoids in natural and engineered organisms. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 513–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, A. Identification of the carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase genes and functional analysis reveal DoCCD1 is potentially involved in beta-ionone formation in Dendrobium officinale. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 967819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.-C.; Joseph, L.M.; Deng, W.-T.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.-B.; Cline, K.; McCarty, D.R. Molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis 9-cis epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene family. Plant J. 2003, 35, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.H.; Tan, B.C.; Gage, D.A.; Zeevaart, J.A.; McCarty, D.R. Specific oxidative cleavage of carotenoids by VP14 of maize. Science 1997, 276, 1872–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, M.K.; Mishra, S.; Bhat, A.; Chib, S.; Kaul, S. Plant carotenoid cleavage oxygenases: Structure-function relationships and role in development and metabolism. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2020, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wan, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, R.; Ruan, M.; Ye, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, G.; Yao, Z.; Yang, Y. A Comprehensive analysis of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases genes in Solanum Lycopersicum. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 34, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Meng, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, S.; Bao, T.; Kimani, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, L. Cloning and functional characterization of a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 2 gene in safranal and crocin biosynthesis from Freesia hybrida. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 154, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Haider, I.; Jamil, M.; Fiorilli, V.; Saito, Y.; Mi, J.; Baz, L.; Kountche, B.A.; Jia, K.P.; Guo, X.; et al. The apocarotenoid metabolite zaxinone regulates growth and strigolactone biosynthesis in rice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frusciante, S.; Diretto, G.; Bruno, M.; Ferrante, P.; Pietrella, M.; Prado-Cabrero, A.; Rubio-Moraga, A.; Beyer, P.; Gomez-Gomez, L.; Al-Babili, S.; et al. Novel carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase catalyzes the first dedicated step in saffron crocin biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12246–12251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Upadhyay, S.; Shukla, R.K. The role of strigolactones and their potential cross-talk under hostile ecological conditions in plants. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrazem, O.; Rubio-Moraga, A.; Berman, J.; Capell, T.; Christou, P.; Zhu, C.; Gomez-Gomez, L. The carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase CCD2 catalysing the synthesis of crocetin in spring crocuses and saffron is a plastidial enzyme. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Jia, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ruan, M.; Ye, Q.; Wang, R.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; et al. Evolutionary origin of the carotenoid cleavage oxygenase family in plants and expression of pepper genes in response to abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 792832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.C.; Molnar, P.; Schwab, W. Cloning and functional characterization of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 4 genes. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 3011–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.C.; Horvath, G.; Molnar, P.; Turcsi, E.; Deli, J.; Schrader, J.; Sandmann, G.; Schmidt, H.; Schwab, W. Substrate promiscuity of RdCCD1, a carotenoid cleavage oxygenase from Rosa damascena. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, F.; Suire, C.; Mutterer, J.; Camara, B. Oxidative remodeling of chromoplast carotenoids: Identification of the carotenoid dioxygenase CsCCD and CsZCD genes involved in Crocus secondary metabolite biogenesis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auldridge, M.E.; Block, A.; Vogel, J.T.; Dabney-Smith, C.; Mila, I.; Bouzayen, M.; Magallanes-Lundback, M.; DellaPenna, D.; McCarty, D.R.; Klee, H.J. Characterization of three members of the Arabidopsis carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase family demonstrates the divergent roles of this multifunctional enzyme family. Plant J. 2006, 45, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Hannoufa, A.; Soroka, J.; Xu, N.; Li, X.; Zebarjadi, A.; Gruber, M. Enhanced β-ionone emission in Arabidopsis over-expressing AtCCD1 reduces feeding damage in vivo by the crucifer flea beetle. Env. Entomol. 2011, 40, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, A.J.; Schwartz, S.H.; Auldridge, M.; Taylor, M.G.; Klee, H.J. The tomato carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 1 genes contribute to the formation of the flavor volatiles β-ionone, pseudoionone, and geranylacetone. Plant J. 2004, 40, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, A.J.; Underwood, B.A.; Auldridge, M.; Loucas, H.M.; Shibuya, K.; Schmelz, E.; Clark, D.G.; Klee, H.J. Circadian regulation of the PhCCD1 carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase controls emission of β-ionone, a fragrance volatile of petunia flowers. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3504–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, M.; Jing, T.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, F.; Wan, X.; Schwab, W.; et al. Dehydration-induced carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 1 reveals a novel route for β-ionone formation during tea (Camellia sinensis) withering. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2020, 68, 10815–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Us-Camas, R.; Aguilar-Espinosa, M.; Rodriguez-Campos, J.; Vallejo-Cardona, A.A.; Carballo-Uicab, V.M.; Serrano-Posada, H.; Rivera-Madrid, R. Identifying Bixa orellana L. New carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases 1 and 4 potentially involved in bixin biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 829089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latari, K.; Wust, F.; Hubner, M.; Schaub, P.; Beisel, K.G.; Matsubara, S.; Beyer, P.; Welsch, R. Tissue-specific apocarotenoid glycosylation contributes to carotenoid homeostasis in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol. 2015, 168, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashbrooke, J.G.; Young, P.R.; Dockrall, S.J.; Vasanth, K.; Vivier, M.A. Functional characterisation of three members of the Vitis vinifera L. carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase gene family. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmiya, A.; Kishimoto, S.; Aida, R.; Yoshioka, S.; Sumitomo, K. Carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase (CmCCD4a) contributes to white color formation in chrysanthemum petals. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yi, S.; Mu, X.; Zhang, J.; Du, J. Chromosome-level genome assembly of Cerasus humilis using PacBio and Hi-C technologies. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Hao, Y.; Yang, S.; Zheng, B.; Niu, Z.; Du, J. Overexpression of ChPSY gene from Cerasus humilis improved carotenoids synthesis in transgenic tomato. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2014, 41, 1563–1572. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, P.J.; Bugg, T.D. Enzymology of the carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases: Reaction mechanisms, inhibition and biochemical roles. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 544, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliakov, E.; Gentleman, S.; Cunningham, F.X., Jr.; Miller-Ihli, N.J.; Redmond, T.M. Key role of conserved histidines in recombinant mouse β-carotene 15,15’-monooxygenase-1 activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29217–29223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, K.; Fu, W.; Jia, Z.; Li, W.; Tran, L.P.; Jia, K.P.; et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression profiles of the CCD gene family in Gossypium species. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Yang, Y.L.; Xia, H.X.; Li, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases gene family in Forsythia suspensa: Expression profile and cold and drought stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 998911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Qiu, C.; Lu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Zhu, G.; He, J.; Lin, Q. Cloning and prokaryotic expression of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases from mulberry (Morus notabilis). Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 4811144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Feng, J.; Feng, A.; You, C.; Ren, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, T.; Su, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of the carotenoid cleavage oxygenase (CCO) gene family in Saccharum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, G.; Gu, T.; Ding, J.; Li, Y. Bioinformatic and expression analyses on carotenoid dioxygenase genes in fruit development and abiotic stress responses in Fragaria vesca. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2017, 292, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zuo, X.; Shao, H.; Fan, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, C.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Han, M. Genome-wide analysis of carotenoid cleavage oxygenase genes and their responses to various phytohormones and abiotic stresses in apple (Malus domestica). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Qin, G. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the carotenoid cleavage oxygenase gene family in five Rosaceae species. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 39, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Y. Genome-wide identification of CCD gene family in six Cucurbitaceae species and its expression profiles in melon. Genes 2022, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.K.; Li, J.G.; Rui, X.; Ding, F.; Hu, F.C.; Wang, X.H.; Ma, W.Q.; Zhou, K.B. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of carotenoid cleavage oxygenase genes in Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, L.; Dong, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Tang, R.; Wang, W.; Ji, Z.; Cao, Q.; Xie, H.; et al. Integrated metabolic and transcriptional analysis reveals the role of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 4 (IbCCD4) in carotenoid accumulation in sweetpotato tuberous roots. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Luo, D.; Lin, A.; Zhang, C.; Shan, L.; He, P.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, B.; Yuan, Z.; et al. A tomato B-box protein SlBBX20 modulates carotenoid biosynthesis by directly activating PHYTOENE SYNTHASE 1, and is targeted for 26S proteasome-mediated degradation. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Guzman, M.; Apostolova, N.; Belles, J.M.; Barrero, J.M.; Piqueras, P.; Ponce, M.R.; Micol, J.L.; Serrano, R.; Rodriguez, P.L. The short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase ABA2 catalyzes the conversion of xanthoxin to abscisic aldehyde. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1833–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, B.; Liu, H.; Ji, W.; Wen, J.; Chu, C.; Tadege, M.; et al. The MYB activator WHITE PETAL1 associates with MtTT8 and MtWD40-1 to regulate carotenoid-derived flower pigmentation in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 2751–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J. Branching in rice. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Jimenez, A.J.; Morote, L.; Niza, E.; Mondejar, M.; Rubio-Moraga, A.; Diretto, G.; Ahrazem, O.; Gomez-Gomez, L. Subfunctionalization of D27 isomerase genes in Saffron. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, G.; Giliberto, L.; Rosati, C. Carotenoid isomerase: A tale of light and isomers. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Ishak, A.; Yu, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, L. Identification and functional analysis of three MAX2 orthologs in chrysanthemum. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, H.; Ren, F.; Wang, L.; Gu, C.; Liao, L.; Han, Y. Inactivation of a gene encoding carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase (CCD4) leads to carotenoid-based yellow coloration of fruit flesh and leaf midvein in peach. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 32, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibdah, M.; Azulay, Y.; Portnoy, V.; Wasserman, B.; Bar, E.; Meir, A.; Burger, Y.; Hirschberg, J.; Schaffer, A.A.; Katzir, N.; et al. Functional characterization of CmCCD1, a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase from melon. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilg, A.; Beyer, P.; Al-Babili, S. Characterization of the rice carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 1 reveals a novel route for geranial biosynthesis. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, N.; Satomi, Y.; Kondo, K.; Yokoyama, A.; Kajiwara, S.; Saito, T.; Ohtani, T.; Miki, W. Structure and functional analysis of a marine bacterial carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster and astaxanthin biosynthetic pathway proposed at the gene level. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6575–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | Chr | CDS/bp | Number of AA | Molecular Weight/Da | pI | Instability Index | GRAVY | Subcellular Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChCCD-like-a | Chr1 | 2109 | 702 | 78,364.26 | 5.44 | 36.82 | −0.196 | Chloroplast, Cytoplasm |
| ChCCD-like-b | Chr1 | 1677 | 558 | 62,470.54 | 5.49 | 28.40 | −0.292 | Cytoplasm |
| ChCCD1 | Chr5 | 1644 | 547 | 61,777.14 | 6.05 | 34.76 | −0.258 | Cytoplasm |
| ChCCD4 | Chr1 | 1794 | 597 | 65,717.9 | 6.10 | 38.51 | −0.229 | Chloroplast, Cytoplasm |
| ChCCD7 | Chr5 | 1848 | 615 | 68,499.76 | 5.67 | 46.35 | −0.219 | Cytoplasm |
| ChCCD8 | Chr1 | 1698 | 565 | 62,461.97 | 6.20 | 34.98 | −0.270 | Cytoplasm |
| ChNCED1 | Chr3 | 1899 | 632 | 70,288.74 | 6.73 | 45.34 | −0.435 | Chloroplast, Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| ChNCED5 | Chr3 | 1854 | 617 | 68,027.19 | 6.45 | 46.67 | −0.335 | Cytoplasm |
| ChNCED6 | Chr1 | 1818 | 605 | 66,921.84 | 6.97 | 38.59 | −0.287 | Chloroplast |
| Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChActin | TTCAAAGACCAGCTCATCTGTGG | CAATGCCAGGGAACATAGTGGA | qRT-PCR |
| ChCCD-like-a | AAGTCAAGACCACCCTCTCCTCC | AACTCGTCTACGGGGCCAAAG | qRT-PCR |
| ChCCD1 | ATGGCGGAGGTTGAAGATGAGG | TTGGTGGGAGGAGTTTCATCAAG | qRT-PCR |
| ChCCD1 | CGGGATCCATGGCGGAGGTTGAAGATG | CCCTCGAGTTAGAGCTTTGCTTGTTCTTGC | Vector construction |
| ChCCD4 | GGATGCCTTCTCTTCCTCTTTCC | CGCGAGCTTTTGTTGTTAGTGG | qRT-PCR |
| ChCCD4 | CGGGATCCATGGATGCCTTCTCTTCCTC | CCCTCGAGCTACAACTTGTTGAGATCAC | Vector construction |
| ChCCD8 | ATGGCTTCCATAGCATTTTCCG | AGCCACTATTGCCGCTCTCTCT | qRT-PCR |
| ChNCED1 | CCTCTTCCTCTTCCAGCCCAA | GGCACTGGCTTTGAGGATTTAGA | qRT-PCR |
| ChNCED5 | GCTCTTCCAAAAGCACCCAATT | GGAAGTGAAGAACCGAGGGAGAT | qRT-PCR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.; Yang, R.; Yin, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, L.; Lu, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Mu, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Characterization of Carotenoid Cleavage Oxygenase Genes in Cerasus humilis and Functional Analysis of ChCCD1. Plants 2023, 12, 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112114
Cheng C, Yang R, Yin L, Zhang J, Gao L, Lu R, Yang Y, Wang P, Mu X, Zhang S, et al. Characterization of Carotenoid Cleavage Oxygenase Genes in Cerasus humilis and Functional Analysis of ChCCD1. Plants. 2023; 12(11):2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112114
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chunzhen, Rui Yang, Lu Yin, Jianying Zhang, Limin Gao, Rong Lu, Yan Yang, Pengfei Wang, Xiaopeng Mu, Shuai Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Characterization of Carotenoid Cleavage Oxygenase Genes in Cerasus humilis and Functional Analysis of ChCCD1" Plants 12, no. 11: 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112114
APA StyleCheng, C., Yang, R., Yin, L., Zhang, J., Gao, L., Lu, R., Yang, Y., Wang, P., Mu, X., Zhang, S., Zhang, B., & Zhang, J. (2023). Characterization of Carotenoid Cleavage Oxygenase Genes in Cerasus humilis and Functional Analysis of ChCCD1. Plants, 12(11), 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112114







