Involvement of Target of Rapamycin (TOR) Signaling in the Regulation of Crosstalk between Ribosomal Protein Small Subunit 6 Kinase-1 (RPS6K-1) and Ribosomal Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
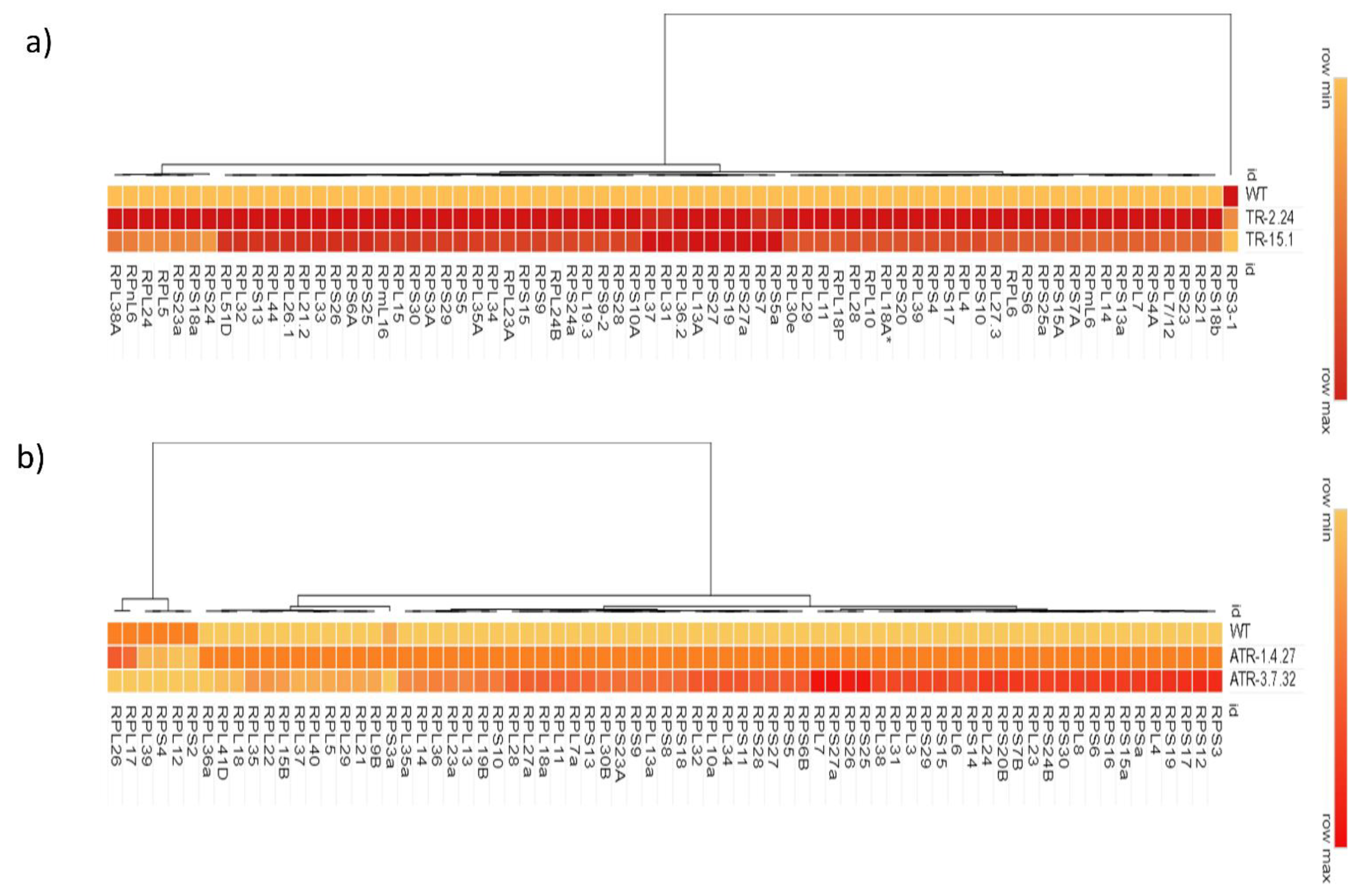
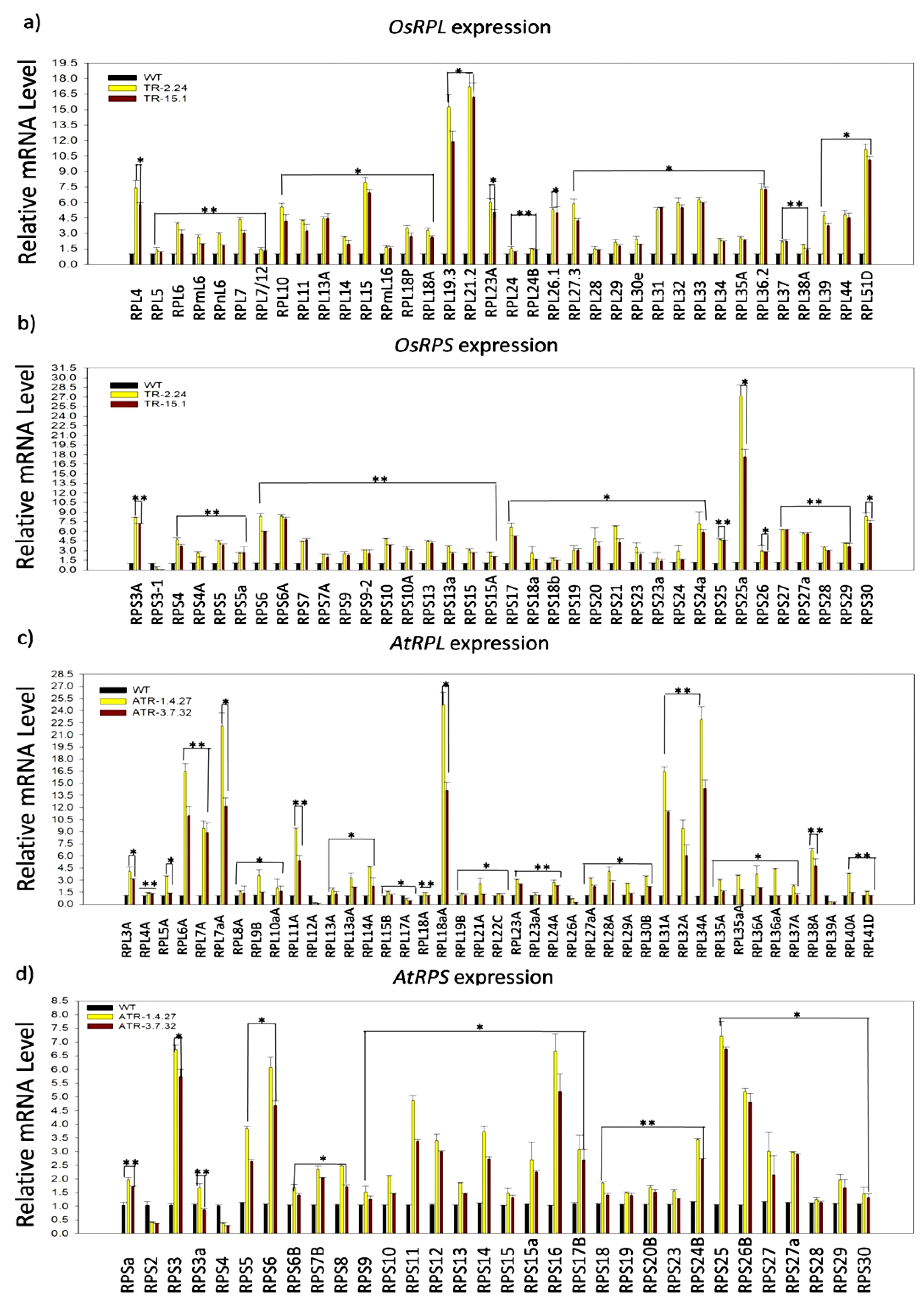
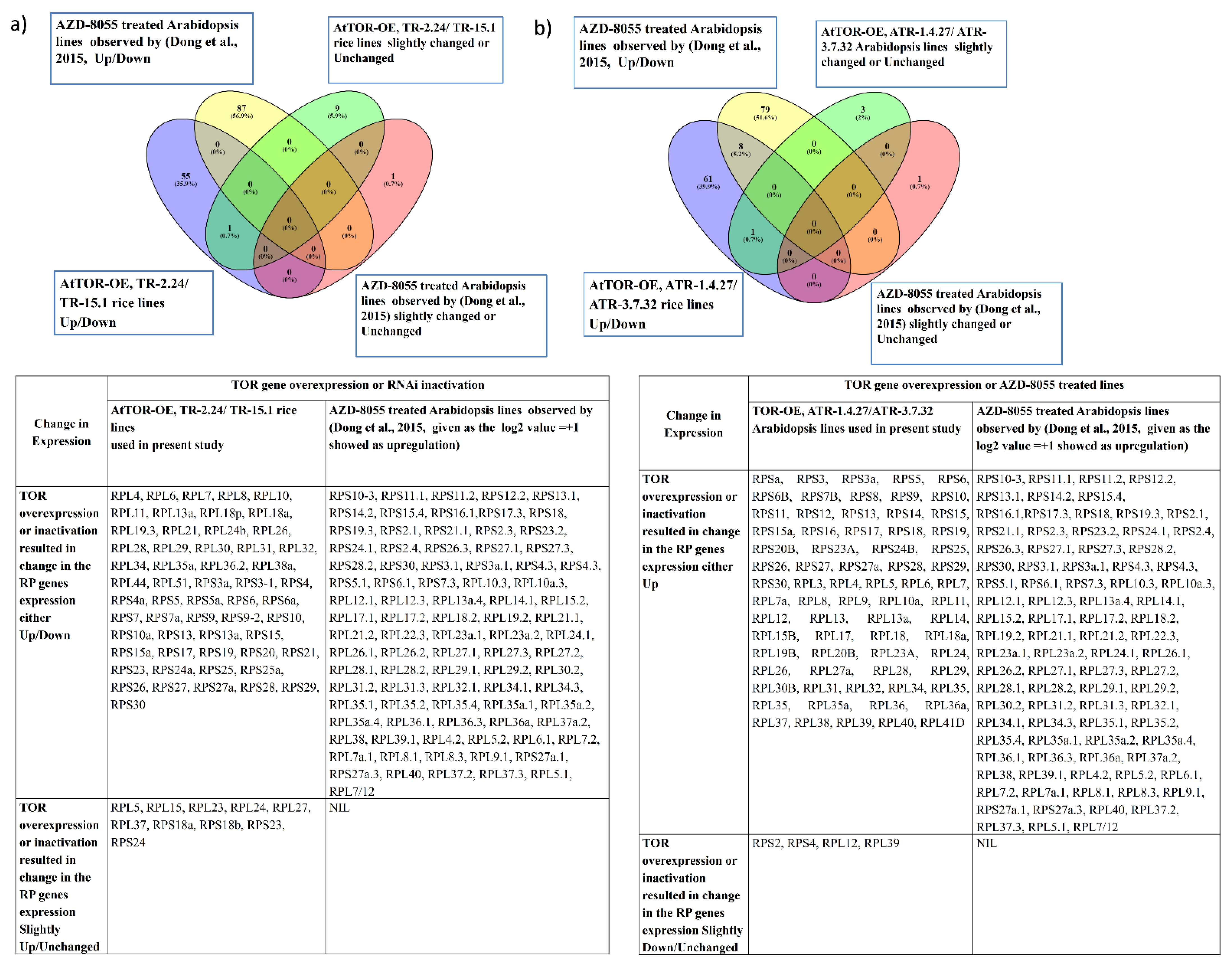
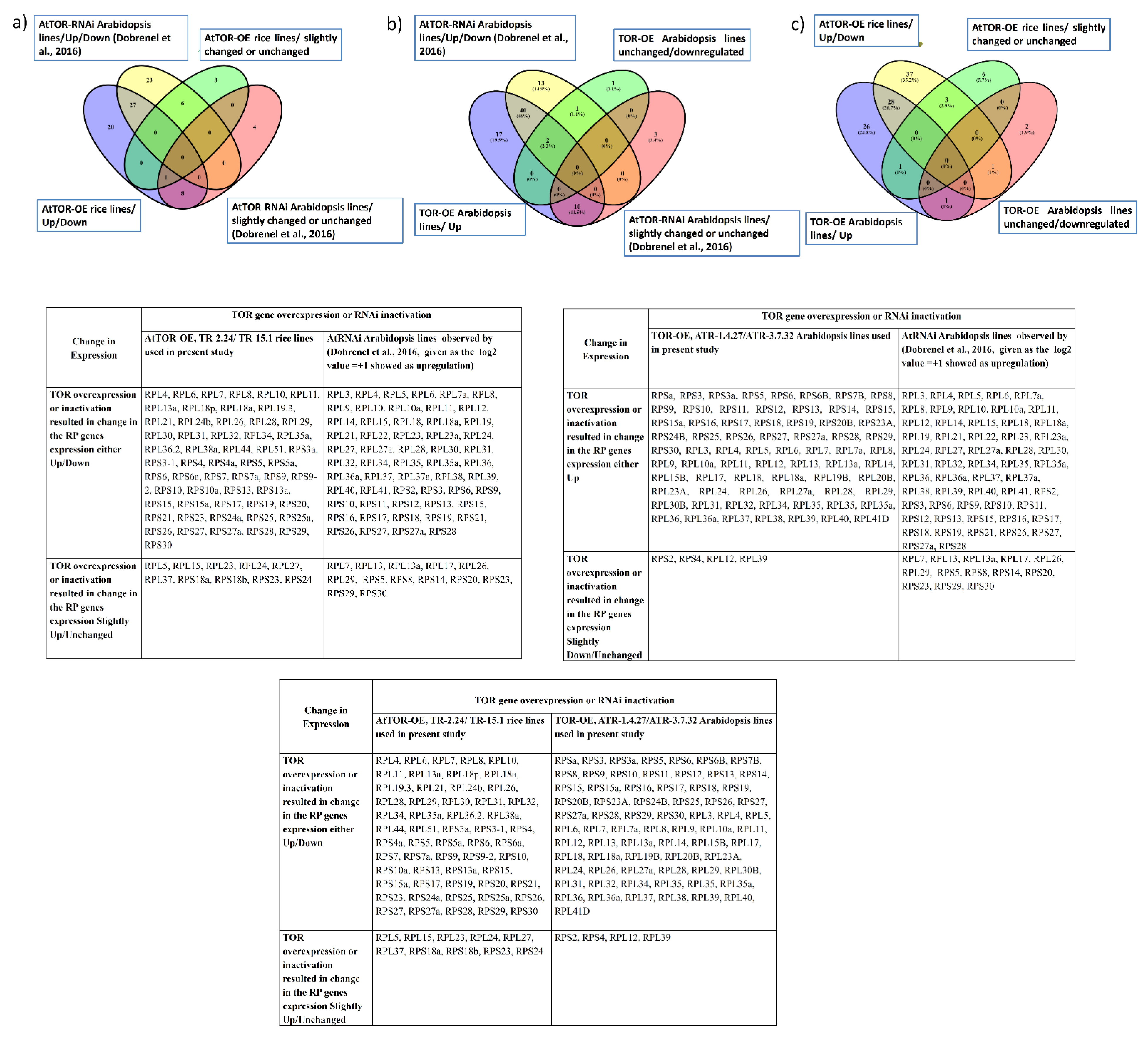
2.1. Expression Analysis of RP Genes in the TOR-OE Lines of Rice and Arabidopsis
2.2. Identification of Putative Phosphorylation Sites and Protein Kinase Binding Motifs in RPL and RPS Proteins
2.3. Genotyping of Arabidopsis Mutant Lines
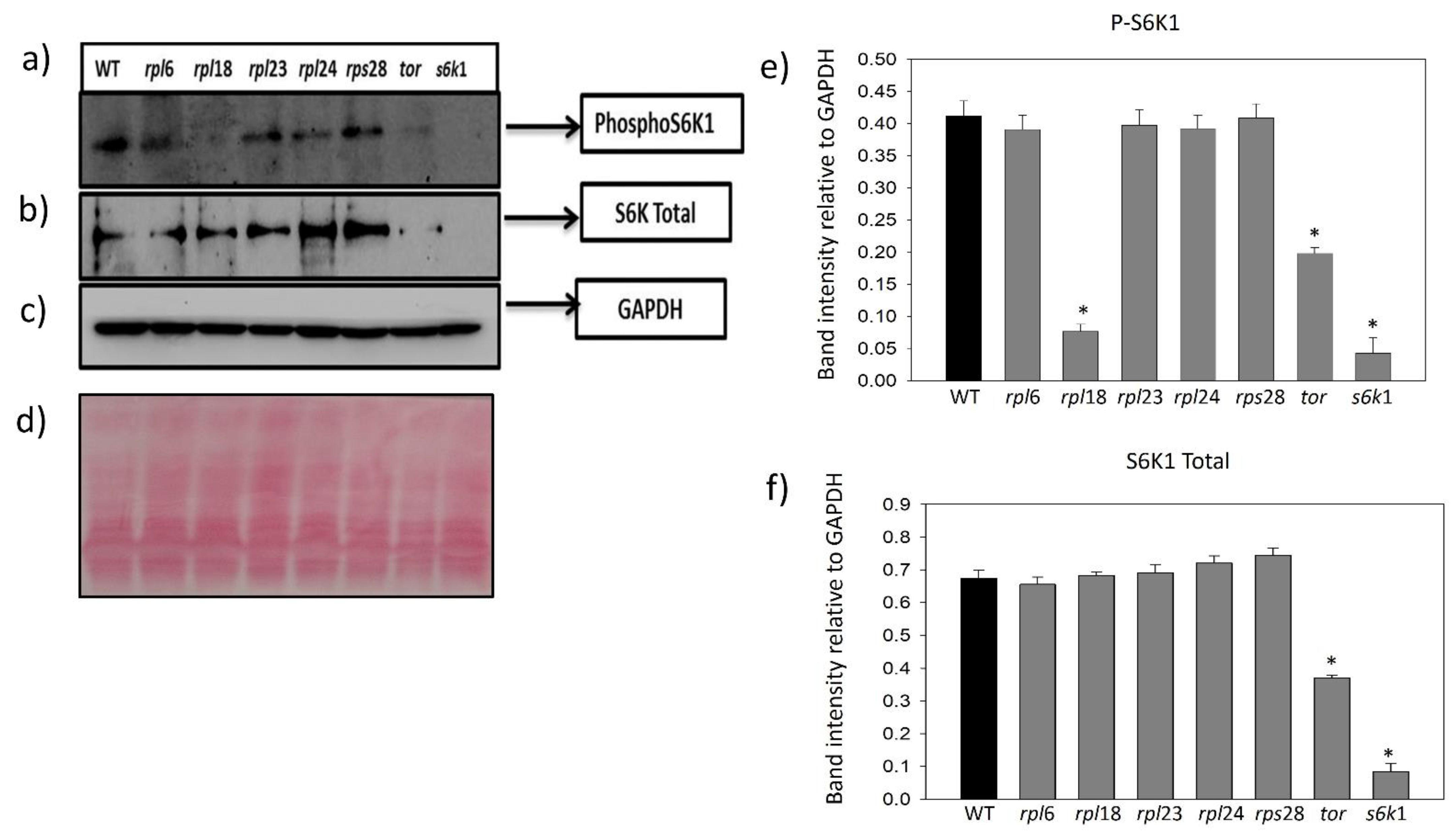
2.4. Ribosomal Protein Inhibition Modulates Feedback Regulation of S6K1 Phosphorylation
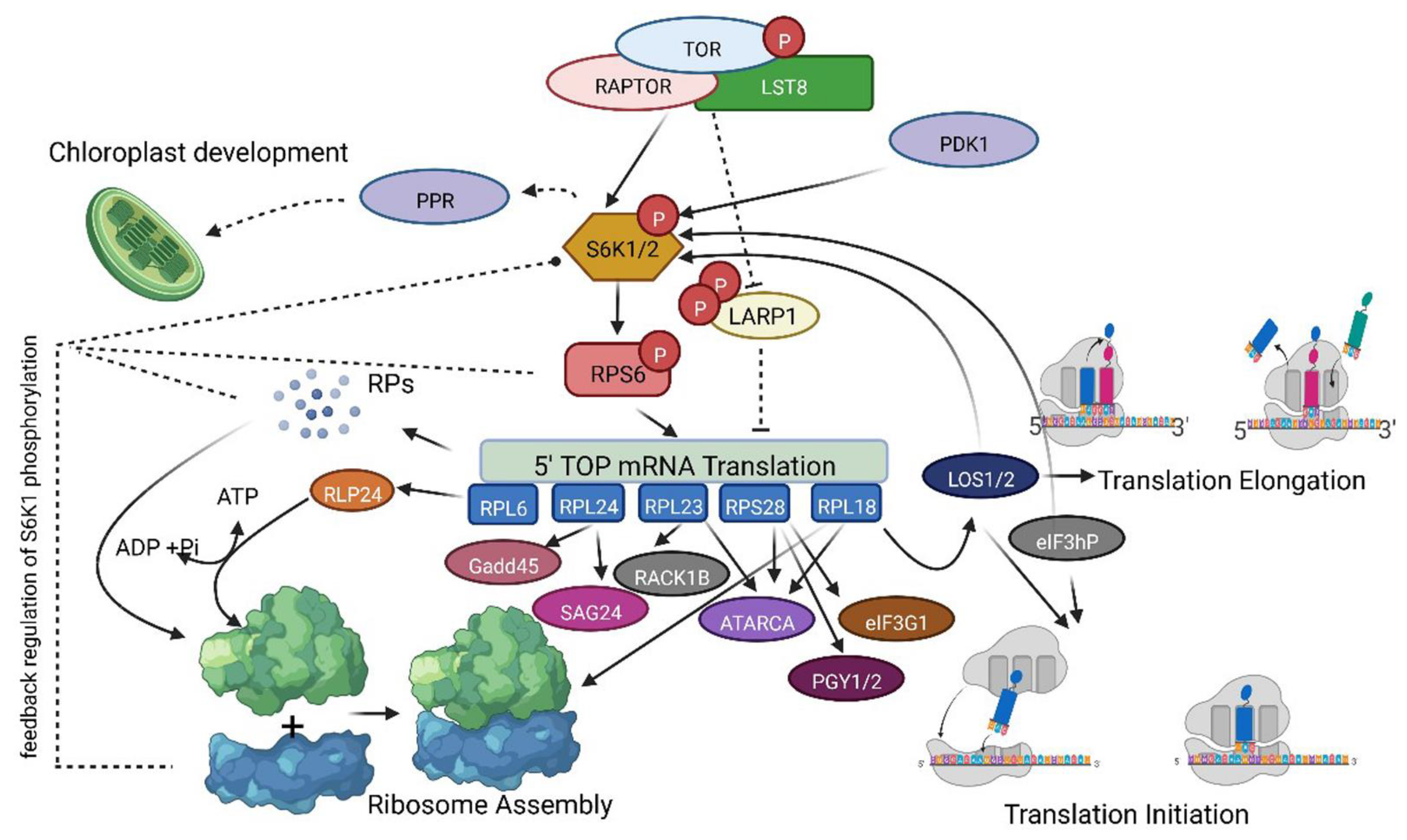
2.5. Identification of Putative Networking Partners of TOR-S6K1-RP Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of TOR-OE Lines of Rice and Arabidopsis
4.2. Growth Conditions of Rice and Arabidopsis Lines
4.3. Nucleotide Sequence Retrieval of RPS and RPL Genes of Rice and Arabidopsis
4.4. Realtime-qPCR (RT-qPCR) Analyses
4.5. In Silico Prediction of Putative Ser/Thr Phosphorylation Sites in the ribosomal protein Genes of Rice and Arabidopsis
4.6. Genotyping of Arabidopsis Mutants
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Identification of Interaction between TOR and Ribosomal Proteins
4.9. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Urban, J.; Soulard, A.; Huber, A.; Lippman, S.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Deloche, O.; Wanke, V.; Anrather, D.; Ammerer, G.; Riezman, H.; et al. Sch9 is a major target of TORC1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Qiu, S.; Venglat, P.; Xiang, D.; Li, F.; Datla, R. Target of Rapamycin Regulates Development and Ribosomal RNA Expression through Kinase Domain in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 1367–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoreen, C.C.; Chantranupong, L.; Keys, H.R.; Wang, T.; Gray, N.S.; Sabatini, D.M. A unifying model for mTORC1-mediated regulation of mRNA translation. Nature 2012, 485, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyuhas, O.; Kahan, T. The race to decipher the top secrets of TOP mRNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, A.J.; Thoreen, C.C.; Dedeic, Z.; Chettle, J.; Roux, P.P.; Sarah, B.P. Controversies around the function of LARP1. RNA Biol. 2020, 11, 1733787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, L.; van den Elzen, A.M.G.; Watson, M.J.; Thoreen, C.C. Global analysis of LARP1 translation targets reveals tunable and dynamic features of 5′ TOP motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5319–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpin, M.R.; Leiboff, S.; Brunkard, J.O. Parallel global profiling of plant TOR dynamics reveals a conserved role for LARP1 in translation. eLife 2020, 9, e58795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, R.; Magyar, Z.; Monardes, A.; Khan, S.; Zalejski, C.; Orellana, J.; Szabados, L.; de la Torre, C.; Koncz, C.; Bogre, L. Arabidopsis S6 kinase mutants display chromosome instability and altered RBR1-E2F pathway activity. Embo J. 2010, 29, 2979–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, B.; Ekim, B.; Fingar, D.C. Regulation and function of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K) within mTOR signalling networks. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, M.; Ikeya, S.; Kozaki, A. The activation mechanism of plant S6 kinase (S6K), a substrate of TOR kinase, is different from that of mammalian S6K. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Sheen, J. Rapamycin and glucose-target of rapamycin (TOR) protein signaling in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2836–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfouz, M.M.; Kim, S.; Delauney, A.J.; Verma, D.P. Arabidopsis TARGET OF RAPAMYCIN interacts with RAPTOR, which regulates the activity of S6 kinase in response to osmotic stress signals. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepetilnikov, M.; Dimitrova, M.; Mancera-Martínez, E.; Geldreich, A.; Keller, M.; Ryabova, L.A. TOR and S6K1 promote translation reinitiation of uORF-containing mRNAs via phosphorylation of eIF3h. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, B.D.; Smith, E.M.; Yelle, N.; Alain, T.; Bushell, M.; Pause, A. The ever-evolving role of mTOR in translation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, C.S.; Ahn, H.K.; Pai, H.S. Overexpression of the PP2A regulatory subunit Tap46 leads to enhanced plant growth through stimulation of the TOR signalling pathway. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Zhang, R.; Meng, Z.; Deng, K.; Que, Y.; Zhuo, F.; Feng, L.; Guo, S.; Datla, R.; Ren, M. Brassinosteriod insensitive 2 (BIN2) acts as a downstream effector of the target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling pathway to regulate photoautotrophic growth in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlen, J.; Roiuk, M.; Teleman, A.A. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 differentially affects mRNA translation based on ORF length. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 13062–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, I.G. The structure and function of eukaryotic ribosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1979, 48, 719–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrenel, T.; Mancera-Martínez, E.; Forzani, C.; Azzopardi, M.; Davanture, M.; Moreau, M.; Schepetilnikov, M.; Chicher, J.; Langella, O.; Zivy, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis TOR Kinase Specifically Regulates the Expression of Nuclear Genes Coding for Plastidic Ribosomal Proteins and the Phosphorylation of the Cytosolic Ribosomal Protein S6. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.E.; Soulard, A.; Hall, M.N. TOR regulates ribosomal protein gene expression via PKA and the Forkhead transcription factor FHL1. Cell 2004, 119, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, J.T.; Hall, D.B.; Struhl, K. The transcription factor Ifh1 is a key regulator of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Nature 2004, 432, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deprost, D.; Yao, L.; Sormani, R.; Moreau, M.; Leterreux, G.; Nicolaı, M.; Bedu, M.; Robaglia, C.; Meyer, C. The Arabidopsis TOR kinase links plant growth, yield, stress resistance and mRNA translation. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, A.; Moin, M.; Kumar, M.U.; Reddy, A.B.; Ren, M.; Datla, R.; Siddiq, E.A.; Kirti, P.B. Ectopic expression of Arabidopsis Target of Rapamycin (AtTOR) improves water-use efficiency and yield potential in rice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 23, 42835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, A.; Moin, M.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Target of Rapamycin (TOR), a master regulator of multiple signaling pathways and a potential candidate gene for crop improvement. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, A.; Moin, M.; Madhav, M.S.; Datla, R.; Kirti, P.B. Target of rapamycin (tor) negatively regulates chlorophyll degradation and lipid peroxidation and controls responses under abiotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Stress 2021, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Suzuki, T.; Kato, T.; Enomoto, K.-I.; Sato, S.; Kato, T.; Tabata, S.; Sa’ez-Vasquez, J.; Echeverría, M.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. Sugar-inducible expression of the nucleolin-1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana and its role in ribosome synthesis, growth and development. Plant J. 2007, 49, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, F.; Que, Y.; Wang, K.; Yu, L.; Li, Z.; Ren, M. Expression profiling and functional analysis reveals that TOR is a key player in regulating photosynthesis and phytohormone signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; McCormack, M.; Li, L.; Hall, Q.; Xiang, C.; Sheen, J. Glucose-TOR signalling reprograms the transcriptome and activates meristems. Nature 2013, 496, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.J.; Werner-Fraczek, J.; Chang, I.F.; and Bailey-Serres, J. Regulated phosphorylation of 40S ribosomal protein S6 in root tips of maize. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 2086–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.F.; Szick-Miranda, K.; Pan, S.; Bailey-Serres, J. Proteomic characterization of evolutionarily conserved and variable proteins of Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosomes. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.J.; Heazlewood, J.L.; Ito, J.; Millar, A.H. Analysis of the Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosome proteome provides detailed insights into its components and their post-translational modification. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2008, 7, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenhardt, R.F.; Bonham-Smith, P.C. Transcript profiling demonstrates absence of dosage compensation in Arabidopsis following loss of a single RPL23a paralog. Planta 2008, 228, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryamanesh, N.; Ruwe, H.; Sanglard, L.V.; Eshraghi, L.; Bussell, J.D.; Howell, K.A.; Small, I.; des Francs-Small, C.C. The Pentatricopeptide Repeat Protein EMB2654 Is Essential for Trans-Splicing of a Chloroplast Small Ribosomal Subunit Transcript. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.; Szick-Miranda, K.; Chang, I.F.; Guyot, R.; Blanc, G.; Cooke, R.; Delseny, M.; Bailey-Serres, J. The organization of cytoplasmic ribosomal protein genes in the Arabidopsis genome. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moin, M.; Bakshi, A.; Saha, A.; Dutta, M.; Kirti, P.B. Rice Ribosomal Protein Large Subunit Genes & their Spatio-temporal & stress regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moin, M.; Bakshi, A.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Expression Profiling of Ribosomal Protein Gene Family in Dehydration Stress Responses and Characterization of Transgenic Rice Plants Overexpressing RPL23A for Water-Use Efficiency and Tolerance to Drought and Salt Stresses. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Das, S.; Moin, M.; Dutta, M.; Bakshi, A.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Genome-wide identification and comprehensive expression profiling of Ribosomal protein small subunit (RPS) genes and their comparative analysis with the large subunit (RPL) genes in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, M.; Jain, N.; Davis, J.H.; Williamson, J.R.; Britton, R.A. Functional Interaction between Ribosomal Protein L6 and RbgA during Ribosome Assembly. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hagner, P.R.; Mazan-Mamczarz, K.; Dai, B.; Balzer, E.M.; Corl, S.; Martin, S.S.; Zhao, X.F.; Gartenhaus, R.B. Ribosomal protein S6 is highly expressed in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and associates with mRNA containing a 5 terminal oligopyrimidine tract. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leh, V.; Yot, P.; Keller, M. The cauliflower mosaic virus translational transactivator interacts with the 60S ribosomal subunit protein L18 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Virology 2000, 266, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, P.; Han, H. Cloning of mouse genomic ribosomal protein L6 gene and analysis of its promoter. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1576, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, F.; Daròs, J.A. Tobacco etch virus protein P1 traffics to the nucleolus and associates with the host 60S ribosomal subunits during infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10725–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Ribosomal protein L18 is an essential factor that promote rice stripe virus accumulation in small brown planthopper. Virus Res. 2018, 247, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, I.C.B.; Yokoo, S.; Granato, D.C.; Meneguello, L.; Carnielli, C.M.; Tavares, M.R.; do Amara, C.L.; de Freitas, L.B.; PaesLeme, A.F.; Luchessi, A.D.; et al. Different interactomes for p70-S6K1 and p54-S6K2 revealed by proteomic analysis. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2650–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijnen, H.F.; van Wijk, R.; Pereboom, T.C.; Goos, Y.J.; Seinen, C.W.; van Oirschot, B.A.; van Dooren, R.; Gastou, M.; Giles, R.H.; van Solinge, W.; et al. Ribosomal Protein Mutations Induce Autophagy through S6 Kinase Inhibition of the Insulin Pathway. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; He, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y. Ribosomal protein S27-like regulates autophagy via the β-TrCP-DEPTORmTORC1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, J.A.; Berg, C.; Hendrick, J.P.; La Branche-Chabot, H.; Metspalu, A.; Rinke, J.; Yario, T. A 5S rRNA/L5 complex is a precursor to ribosome assembly in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, M.; Stark, J.; Yeh, L.C.C.; Lee, J.C.; Woolford, J.L. Multiple regions of yeast ribosomal protein L1 are important for its interaction with 5 S rRNA and assembly into ribosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 30148–30156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, Z.M. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of ribosomal L18/L5e gene in Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R. Br. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, A.; Jia, J.; Willard, B.; Li, X.; Fox, L.P. Multisite Phosphorylation of S6K1 Directs a Kinase Phospho-code that Determines Substrate Selection. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta DeltaC(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oñate-Sánchez, L.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J. DNA-free RNA isolation protocols for Arabidopsis thaliana, including seeds and siliques. BMC Res. Notes 2008, 1, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| S. No. | Locus Name | Protein Accession | Protein Name | Species Name | Position and Peptide Sequence of Threonine (Thr)-Specific Phosphorylation Sites for AGC Kinases (PKC, PKG, RSK, PKA, PKB) | Position and Peptide Sequence of Serine (Ser)-Specific Phosphorylation Sites for AGC Kinases (PKC, PKG, RSK, PKA, PKB) | Total No. of Ser/Thr Phosphorylation Sites for AGC Kinases (PKC, PKG, RSK, PKA, PKB) | Amino Acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AT4G31700 | O48549 | AtRPS6A | Arabidopsis thaliana | 9/VANPTTGCQ 10/ANPTTGCQK 69/QGVLTPGRV 81/LHRGTPCFR 91/HGRRTGERR 127/LPGLTDTEK 129/GLTDTEKPR 157/DDVRTYVNT 161/TYVNTYRRK 167/RRKFTNKKG 185/QRLVTPLTL 188/VTPLTLQRK 249/KPSVTA--- | 33/DKRISQEVS 37/SQEVSGDAL 98/RRRKSVRGC 105/GCIVSPDLS 109/SPDLSVLNL 141/PKRASKIRK 175/GKEVSKAPK 208/AKANSDAAD 219/KLLASRLKE 229/RDRRSESLA 231/RRSESLAKK 237/AKKRSRLSS 240/RSRLSSAAA 241/SRLSSAAAK 247/AAKPSVTA- | 28 | 250 |
| 2 | AT5G10360 | P51430 | AtRPS6B | Arabidopsis thaliana | 9/VANPTTGCQ 10/ANPTTGCQK 69/QGVLTPGRV 81/LHRGTPCFR 91/HGRRTGERR 127/LPGLTDTEK 129/GLTDTEKPR 161/KYVNTYRRT 165/TYRRTFTNK 167/RRTFTNKKG 185 /QRLVTPLTL 188/VTPLTLQRK | 33/DKRLSQEVS 37/SQEVSGDAL 98/RRRKSVRGC 105/GCIVSPDLS 109/SPDLSVLNL 121/KKGVSDLPG 141/PKRASKIRK 175/GKKVSKAPK 208/AKANSDAAD 219/KLLASRLKE 229/RDRRSESLA 231/RRSESLAKK 237/AKKRSRLSS 240/RSRLSSAPA 241/SRLSSAPAK | 27 | 249 |
| 3 | LOC_Os07g0622100 | Q8LH97 | OsRPS6 | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 9/IANPTTGCQ 10/ANPTTGCQK 69/QGVLTAGRV 81/LHRGTPCFR 127/LPGLTDTEK 129/GLTDTEKPR 161/KYVNTYRRT 165/TYRRTFTTK 167/RRTFTTKNG 168/RTFTTKNGK 185/QRLVTPLTL 188/VTPLTLQRK 248/KAAATTA-- 249/AAATTA--- | 33/DKRISQEVS 37/SQEVSGDAL 98/RRRKSVRGC 105/GCIVSQDLS 109/SQDLSVINL 141/PKRASKIRK 150/LFNLSKDDD 175/GKKVSKAPK 208/AKKKSEAAE 229/RERRSESLA 231/RRSESLAKR 237/AKRRSKLSS 240/RSKLSSAAK 241/SKLSSAAKA | 28 | 250 |
| 4 | LOC_Os03g27260 | Q75LR5 | OsRPS6 | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 9/IANPTTGCQ 10/ANPTTGCQK 69/QGVLTSGRV 81/LHRGTPCFR 127/LPGLTDTEK 129/GLTDTEKPR 161/KYVNTYRRT 165/TYRRTFTTK 167/RRTFTTKNG 168/RTFTTKNGK 185/QRLVTPLTL 188/VTPLTLQRK 243/LSAATTA-- 244/SAATTA--- | 33/DKRISQEVS 37/SQEVSGDAL 70/GVLTSGRVR 98/RRRKSVRGC 105/GCIVSQDLS 109/SQDLSVINL 141/PKRASKIRK 175/GKKVSKAPK 208/AKKKSEAAE 229/RERRSESLA 231/RRSESLAKR 237/AKRRSKLSA 240/RSKLSAATT | 27 | 245 |
| 5 | AT1G18540 | Q9FZ76 | AtRPL6A | Arabidopsis thaliana | 7/AAKRTPKVN 83/KPKPTKLKA 90/KASITPGTV 93/ITPGTVLII 121/LLLVTGPFK 142/YVIGTSTKI 144/IGTSTKIDI 153/SGVNTEKFD 172/KKKKTEGEF 197/EDQKTVDAA | 24/VGKYSRSQM 26/KYSRSQMYH 88/KLKASITPG 114/LKQLSSGLL 115/KQLSSGLLL 143/VIGTSTKID 149/KIDISGVNT 205/ALIKSIEAV 221/GARFSLSQG 223/RFSLSQGMK | 20 | 233 |
| 6 | AT1G74060 | Q9C9C6 | AtRPL6B | Arabidopsis thaliana | 12/AKQRTAKVN 84/PNRRTAKPA 95/RASITPGTV 98/ITPGTVLII 126/LLLVTGPF 147/YVIGTSTKV 149/IGTSTKVDI 157/ISGVTLDKF 177/KKKKTEGEF 219/PELKTYLGA | 1/----SPQCC 29/VGKYSRSQM 31/KYSRSQMYH 57/HDAKSKVDA 93/KLRASITPG 120/KQLASGLLL 148/VIGTSTKVD 154/KVDISGVTL 226/GARFSLKQG | 19 | 233 |
| 7 | LOC_Os04g0473400 | Q7XR19 | OsRPL6 | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 4/-MAPTSKLS 19/SRSHTYHRR 66/RQPSTRKPN 72/KPNPTKLRS 79/RSSITPGTV 82/ITPGTVLIL 110/LLLVTGPFK 131/YVIATSTKV 133/IATSTKVDI 161/KAKKTEGEL 168/ELFETEKEA 173/EKEATKNLP 203/PDLKTYLGA | 5/MAPTSKLSQ 8/TSKLSQGIK 15/IKKASRSHT 17/KASRSHTYH 65/PRQPSTRKP 76/TKLRSSITP 77/KLRSSITPG 104/KQLKSGLLL 132/VIATSTKVD 138/KVDISGVNV 151/DKYFSRDKK 210/GARFSLRDG | 25 | 222 |
| 8 | At5g27840 | A0A178UKW4 | AtRPL18e/L15P | Arabidopsis thaliana | 14/KSKKTKRTA 17/KTKRTAPKS 72/VEFMTGKDD 84/VLVGTITDD 86/VGTITDDLR 100/AMKVTALRF 105/ALRFTERAR 121/GECLTFDQL 135/LGQNTVLLR 162/PHSNTKPYV | 11/AGGKSKKTK 21/TAPKSDDVY 40/LVRRSNSNF 42/RRSNSNFNA 55/RLFMSKVNK 63/PLSLSRL 65/PLSLSRLVE 144/GPKNSREAV 160/GVPHSNTKP 182/GKRKSRGFK | 20 | 127 |
| 9 | At5g27850 | A0A1P8BGQ0 | AtRPL18e/L15 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 19/VEFMTGKDD 31/VLVGTITDD 33/VGTITDDLR 47/AMKVTALRF 52/ALRFTERAR 68/GECLTFDQL 82/LGQNTVLLR 109/PHSNTKPYV | 2/---MSKVNK 10/ KAPLSLSRL 12/PLSLSRLVE 91/GPKNSREAV 107/GVPHSNTKP 129/GKRKSRGFK | 15 | 134 |
| 10 | At5g27850 | Q940B0 | AtRPL18C | Arabidopsis thaliana | 14/KSKKTKRTA 17/KTKRTAPKS 72/VEFMTGKDD 84/VLVGTITDD 86/VGTITDDLR 100/AMKVTALRF 105/ALRFTERAR 121/GECLTFDQL 135/LGQNTVLLR 162/PHSNTKPYV | 11/AGGKSKKTK 21/TAPKSDDVY 40/LVRRSNSNF 42/RRSNSNFNA 55/RLFMSKVNK 63/KAPLSLSRL 65/PLSLSRLVE 144/GPKNSREAV 160/GVPHSNTKP 182/GKRKSRGFK | 20 | 187 |
| 11 | LOC_Os01g54870 | Q943F3 | OsRPL18A | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 18/RGLPTPTDE 20/LPTPTDEHP 34/KLWATNEVR 72/EKNPTTIKN 73/KNPTTIKNY 87/YQSRTGYHN 99/EYRDTTLNG 100/YRDTTLNGA 110/EQMYTEMAS 128/QIIKTATVH 130/IKTATVHFK 141/KRDNTKQFH 162/VRPPTRKLK 167/RKLKTTFKA 168/KLKTTFKAS | 41/VRAKSKFWY 56/KVKKSNGQI 85/LRYQSRTGY 114/TEMASRHRV 147/QFHKSDIKF 172/TFKASRPNL | 21 | 178 |
| 12 | At2g39460 | Q8LD46 | AtRPL23aA | Arabidopsis thaliana | 8/AKVDTTKKA 9/KVDTTKKAD 40/KKIRTKVTF 43/RTKVTFHRP 49/HRPKTLTKP 51/PKTLTKPRT 55/TKPRTGKYP 64/KISATPRNK 80/KYPLTTESA 81/YPLTTESAM 93/EDNNTLVFI 119/YDIQTKKVN 124/KKVNTLIRP 131/RPDGTKKAY 139/YVRLTPDYD | 2/---MSPAKV 27/KAVKSGQAF 62/YPKISATPR 83/LTTESAMKK | 19 | 154 |
| 13 | At3g55280 | Q9M3C3 | AtRPL23aB | Arabidopsis thaliana | 8/AKVDTTKKA 9/KVDTTKKAD 40/KKIRTKVTF 43/RTKVTFHRP 49/HRPKTLTKP 51/PKTLTKPRT 55/TKPRTGKYP 64/KISATPRNK 80/KYPLTTESA 81/YPLTTESAM 93/EDNNTLVFI 119/YDIQTKKVN 124/KKVNTLIRP 131/RPDGTKKAY 139/YVRLTPDYD | 2/---MSPAKV 27/KAVKSGQAF 62/YPKISATPR 83/LTTESAMKK | 19 | 154 |
| 14 | LOC_Os03g04590 | Q10S10 | OsRPL23A | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 25/PVAATVNCA 32/CADNTGAKN 64/MVMATVKKG 118/GSAITGPIG | 2/---MSKRGR 9/GRGGSAGNK 17/KFRMSLGLP 41/LYIISVKGI 54/NRLPSACVG 115/EMKGSAITG 134/PRIASAANA | 11 | 140 |
| 15 | LOC_Os10g32920 | Q9AV77 | OsRPL23B | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 25/PVAATVNCA 32/CADNTGAKN 64/MVMATVKKG 118/GSAITGPIG | 2/---MSKRGR 9/GRGGSAGNK 17/KFRMSLGLP 41/LYIISVKGI 54/NRLPSACVG 115/EMKGSAITG 134/PRIASAANA | 11 | 140 |
| 16 | At2g36620 | Q42347 | AtRPL24A | Arabidopsis thaliana | 5/MVLKTELCR 54/KLCWTAMYR 77/RRRATKKPY 89/IVGATLEVI 122/RIKKTKDEK | 11/LCRFSGQKI 26/RFIRSDSQV 28/IRSDSQVFL 36/LFLNSKCKR 49/KLKPSKLCW 82/KKPYSRSIV 84/PYSRSIVGA 135/VEYASKQQK 140/KQQKSQVKG 149/NIPKSAAPK | 15 | 164 |
| 17 | At3g53020 | P38666 | AtRPL24B | Arabidopsis thaliana | 5/MVLKTELCR 54/KLAWTAMYR 77/RRRATKKPY 89/IVGATLEVI 122/RIKKTKDEK | 11/LCRFSGQKI 26/RFIRSDSQV 28/IRSDSQVFL 36/LFLNSKCKR 49/KLKPSKLAW 82/KKPYSRSIV 84/PYSRSIVGA 135/EFASKQQK 151/AAAASKGPK | 14 | 163 |
| 18 | LOC_Os05g40820/ Os01g0815800 | Q5N754-1 | OsRPL24A | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 5/MVLKTELCR 52/PAKLTWTAM 54/KLTWTAMYR 76/KRRRTTKKP 77/RRRTTKKPY 122/RIKKTKDEK 134/KAEVTKSQK | 11/LCRFSGQKI 28/IRADSQVFL 36/LFANSKCKR 82/KKPYSRSIV 84/PYSRSIVGA 89/IVGASLEVI 136/EVTKSQKSQ 139/KSQKSQSKG 141/QKSQSKGAA 149/APRGSKGPK | 17 | 161 |
| 19 | LOC_Os07g12250 | LOC_Os07g12250.1 | OsRPL24A | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 5/MVLKTELCR 52/PAKLTWTAM 54/KLTWTAMYR 76/KRRRTTKKP 77/RRRTTKKPY 89/IVGATLEVI 122/RIKKTKDEK | 11/LCRFSGAKI 28/IRADSQVFL 34/VFLFSNSKC 36/LFSNSKCKR 82/KKPYSRSIV 84/PYSRSIVGA 110/AARESALRE 136/EVAKSQKAS 140/SQKASGKGN | 16 | 161 |
| 20 | LOC_Os01g33050/ | LOC_Os01g33050.2/Q84ZF9 | OsRPL24B | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 12/FCSSTIYPG 52/KVKWTKAYR 64/GKDMTQDST 68/TQDSTFEFE 86/DRNVTAQTL 89/VTAQTLKAI 97/IPLITKIRH 109/KKHITERQK 117/KQGKTKQRE 139/PKKDTMLST 143/TMLSTQKTK 146/STQKTKVVV 157/SQQQTEENL | 10/CWFCSSTIY 11/WFCSSTIYP 34/RFCRSKCHK 67/MTQDSTFEF 142/DTMLSTQKT 153/VVKVSQQQT | 19 | 164 |
| 21 | LOC_Os07g19190 | LOC_Os07g19190.1 | RPL24B | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 12/FCSSTVYPG 52/KVKWTKAYR 64/GKDMTQDST 68/TQDSTFEFE 86/DRNVTEQTL 89/VTEQTLKAI 97/ISLITKIRH 109/KKHITERQK 117/KQGKTKQRE 139/PKKVTLSTQ 142/VTLSTQKTK 145/STQKTKVVV 156/SQQQTEENL | 10/CWFCSSTVY 11/WFCSSTVYP 34/RFCRSKCHK 67/MTQDSTFEF 94/LKAISLITK 141/KVTLSTQKT 152/VVKVSQQQT | 20 | 163 |
| 22 | At3g10090/At5g03850 | Q9SR73 | AtRPS28A/B | Arabidopsis thaliana | 17/VMGRTGSRG 24/RGQVTQVRV 31/RVKFTDSDR 52/GDILTLLES | 3/--MDSQIKH 19/GRTGSRGQV 33/KFTDSDRYI 56/TLLESEREA | 8 | 64 |
| 23 | AT5G64140.1 | P34789-1 | AtRPS28C | Arabidopsis thaliana | 17/VMGRTGSRG 24/RGQVTQVRV 31/RVKFTDSDR 52/GDILTLLES | 3/--MDSQIKH 19/GRTGSRGQV 33/KFTDSDRYI 56/TLLESEREA | 8 | 64 |
| 24 | LOC_Os10g0411700 | A0A0P0XU17 | OsRPS28e | Oryza sativa ssp. japonica | 9/RSMDTQVKL 23/VMGRTGSRG 30/RGQVTQVRV 59/GDILTLLES | 6/PEKRSMDTQ 25/GRTGSRGQV 63/TLLESEREA | 7 | 71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakshi, A.; Moin, M.; Gayatri, M.B.; Reddy, A.B.M.; Datla, R.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Involvement of Target of Rapamycin (TOR) Signaling in the Regulation of Crosstalk between Ribosomal Protein Small Subunit 6 Kinase-1 (RPS6K-1) and Ribosomal Proteins. Plants 2023, 12, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010176
Bakshi A, Moin M, Gayatri MB, Reddy ABM, Datla R, Madhav MS, Kirti PB. Involvement of Target of Rapamycin (TOR) Signaling in the Regulation of Crosstalk between Ribosomal Protein Small Subunit 6 Kinase-1 (RPS6K-1) and Ribosomal Proteins. Plants. 2023; 12(1):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010176
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakshi, Achala, Mazahar Moin, Meher B. Gayatri, Aramati B. M. Reddy, Raju Datla, Maganti S. Madhav, and Pulugurtha B. Kirti. 2023. "Involvement of Target of Rapamycin (TOR) Signaling in the Regulation of Crosstalk between Ribosomal Protein Small Subunit 6 Kinase-1 (RPS6K-1) and Ribosomal Proteins" Plants 12, no. 1: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010176
APA StyleBakshi, A., Moin, M., Gayatri, M. B., Reddy, A. B. M., Datla, R., Madhav, M. S., & Kirti, P. B. (2023). Involvement of Target of Rapamycin (TOR) Signaling in the Regulation of Crosstalk between Ribosomal Protein Small Subunit 6 Kinase-1 (RPS6K-1) and Ribosomal Proteins. Plants, 12(1), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010176








