Genetic Behavior of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Germplasm Governing Heavy Metal Tolerance and Yield Traits under Wastewater Irrigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
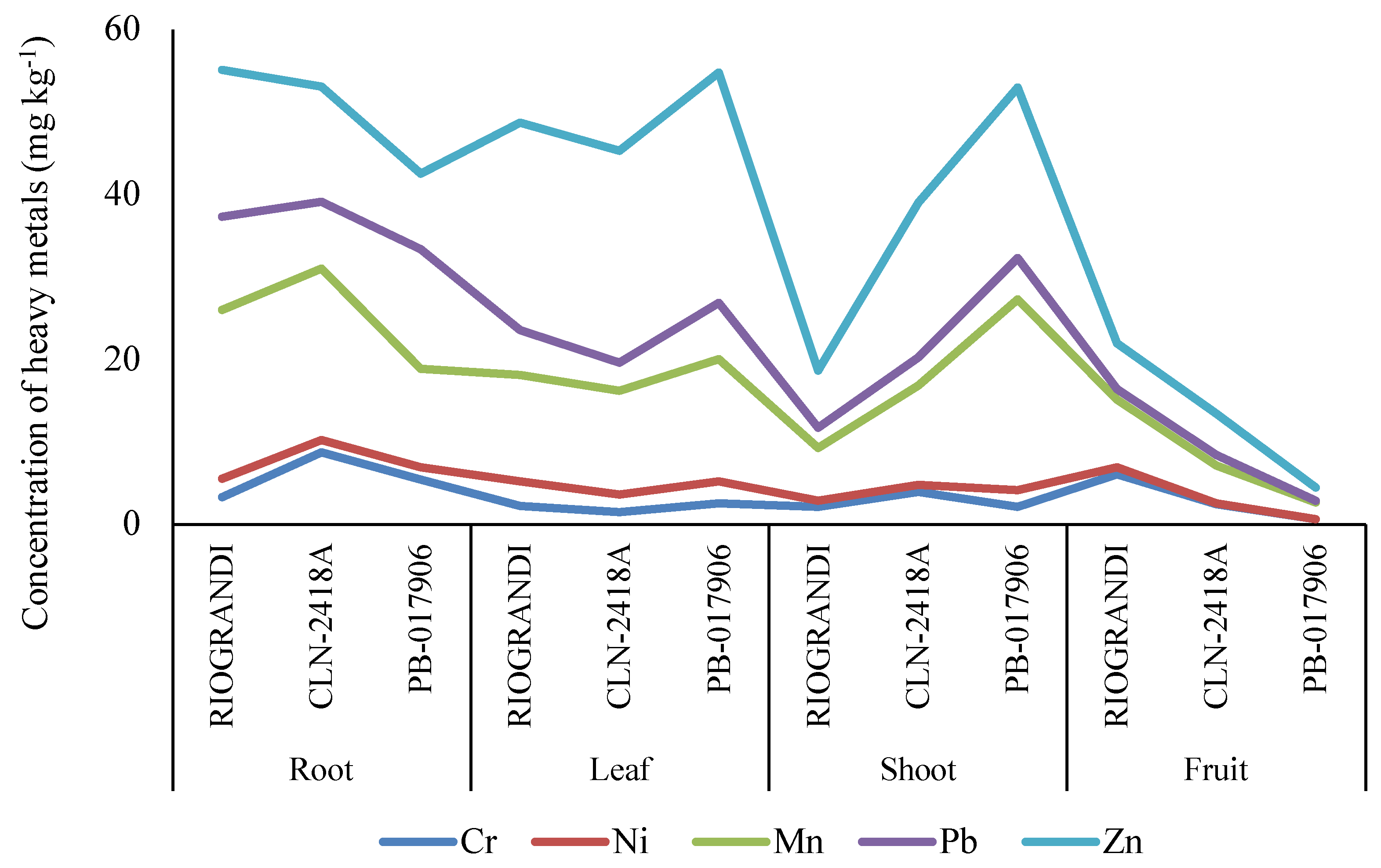
2.1. Heavy Metals Accumulation under Hydroponic Conditions
2.2. Variations in Yield and Heavy Metals Accumulation
2.3. Tomato Yield-Related Traits
2.4. Heavy Metals Tolerance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experiment
4.1.1. Re-Assessment of Initial Screening Experiment
4.1.2. Breeding Experiment
4.2. Emasculation
4.3. Pollen Collection
4.4. Pollination
4.5. Seed Extraction
4.6. Assessment of Plant Material for Genetic Studies
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Caparros, P.; Lao, M.T. The Effects of Salt Stress on Ornamental Plants and Integrative Cultivation Practices. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Wastewater Irrigation: Past, Present, and Future. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 6, e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keisham, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhatla, S.C. Mechanisms of Sodium Transport in Plants—Progresses and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, X. Occurrence and Fate of Heavy Metals in Municipal Wastewater in Heilongjiang Province, China: A Monthly Reconnaissance from 2015 to 2017. Water 2020, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.-E.; Sweetman, A.J.; Zhang, H.; Jones, K.C. DGT Passive Sampling for Quantitative in Situ Measurements of Compounds from Household and Personal Care Products in Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13274–13281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantinho, P.; Matos, M.; Trancoso, M.A.; dos Santos, M.M. Behaviour and Fate of Metals in Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, V.; Rodríguez, Y.; Albaigés, J. A Comparative Assessment of Intensive and Extensive Wastewater Treatment Technologies for Removing Emerging Contaminants in Small Communities. Water Res. 2016, 88, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoh, A.I.; Odjadjare, E.E.; Igbinosa, E.O.; Osode, A.N. Wastewater Treatment Plants as a Source of Microbial Pathogens in Receiving Watersheds. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 2932–2944. [Google Scholar]
- Malash, N.M.; Flowers, T.J.; Ragab, R. Effect of Irrigation Methods, Management and Salinity of Irrigation Water on Tomato Yield, Soil Moisture and Salinity Distribution. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Shakir, M.; Ali, Q.; Rani, N.; Fatima, N.; Farooq, S.; Shafiq, S.; Kanwal, N.; Ali, F.; Nasir, I.A. Rhizobacteria and Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2016, 5, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldetsadik, D.; Drechsel, P.; Keraita, B.; Itanna, F.; Gebrekidan, H. Heavy Metal Accumulation and Health Risk Assessment in Wastewater-Irrigated Urban Vegetable Farming Sites of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Contam. 2017, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensink, J.H.J.; Mahmood, T.; Van der Hoek, W.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Amerasinghe, F.P. A Nationwide Assessment of Wastewater Use in Pakistan: An Obscure Activity or a Vitally Important One? Water Policy 2004, 6, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Ali, B.; Mohammad, A.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, I.; Napar, A.A.; Kazi, A.G.; Ali, A.; Shah, S.S.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A. Combating Water Scarcity for Global Food Security. In Agricultural Systems in the 21st Century; Nova Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, S.; Ali, Z.; Hussain, S.; Mohammad, A.; Riaz, Y.; Shakeel, A.; Ahmad, I.; Mussarat, M.; Malik, R.N.; Khan, K.Y.; et al. Metal Accumulation Potential, Human Health Risks, and Yield Attributes of Hundred Bread Wheat Genotypes on Irrigation with Municipal and Remediated Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 35023–35037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.I.; Rathore, H.A.; Sattar, M.Z.A.; Chatha, S.A.S.; ud din Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, A.; Johns, E.J. Phenolic Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Various Extracts from Citrullus Colocynthis (L.) from the Pakistani Flora. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- Alghobar, M.A.; Suresha, S. Evaluation of Metal Accumulation in Soil and Tomatoes Irrigated with Sewage Water from Mysore City, Karnataka, India. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2017, 16, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharose, R.; Lal, S.B.; Singh, S.K.; Srivastava, P.K. Heavy Metals Pollution in Soil-Water-Vegetation Continuum Irrigated with Ground Water and Untreated Sewage. Bull. Environ. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, M.M.; Nardella, E.; Gagliardi, A.; Gatta, G. Deficit Irrigation and Partial Root-Zone Drying Techniques in Processing Tomato Cultivated under Mediterranean Climate Conditions. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.; Khan, A.I.; Awan, F.S.; Sadaqat, H.A.; Bahadur, S.; Baloch, F.S. Genetic Diversity of Some Tomato Cultivars and Breeding Lines Commonly Used in Pakistani Breeding Program. Turk. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soomro, A.F.; Ali, M.; Yasin, A. Tomato Cluster Feasibility and Transformation Study. Clust. Dev. Based Agric. Transform. Plan Vision-2025 2020, 131, 434. [Google Scholar]
- Hameeda; Gul, S.; Bano, G.; Manzoor, M.; Chandio, T.A.; Awan, A.A. Biochar and Manure Influences Tomato Fruit Yield, Heavy Metal Accumulation and Concentration of Soil Nutrients under Wastewater Irrigation in Arid Climatic Conditions. Cogent Food Agric. 2019, 5, 1576406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Yan, G. Wheat Genotypes Tolerant to Heat at Seedling Stage Tend to Be Also Tolerant at Adult Stage: The Possibility of Early Selection for Heat Tolerance Breeding. Crop. J. 2022, 10, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, K.; Louws, F.J.; Williamson, J.D.; Panthee, D.R. Diversity Analysis of Tomato Genotypes Based on Morphological Traits with Commercial Breeding Significance for Fresh Market Production in Eastern USA. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2016, 10, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagómez-Aranda, A.L.; Feregrino-Pérez, A.A.; García-Ortega, L.F.; González-Chavira, M.M.; Torres-Pacheco, I.; Guevara-González, R.G. Activating Stress Memory: Eustressors as Potential Tools for Plant Breeding. Plant Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 1481–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, S.; Hannan, A.; Tahjib-Ul-Arif, M.; Sagor, G.H.M. Genetic Association and Path Coefficient Analysis among Yield and Nutritional Traits of Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum L.). J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2019, 17, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.M.S.N.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ismail, S.I.; JJ., N.; Ramlee, S.I. Improvement of Important Economic Traits in Chilli through Heterosis Breeding: A Review. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybysz, A.; Wrochna, M.; Gawrońska, H.; Małecka-Przybysz, M.; Pietrzyk, S.; Gawroński, S.W. Effect of Manganese on Yield and Quality of Hydroponically Grown Lettuce. J. Elem. 2017, 22, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, R.A.; Fry, S.C. The Oxidation of Dehydroascorbic Acid and 2, 3-Diketogulonate by Distinct Reactive Oxygen Species. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 3451–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S. Toxic Metal Accumulation, Responses to Exposure and Mechanisms of Tolerance in Plants. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, M.A.; Ahmad, G.; Anjum, F.M.; Asghar, A.; Sajid, M.W. Heavy Metal Contents and Their Daily Intake in Vegetables under Peri-Urban Farming System of Multan, Pakistan. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 51, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq, S.; Zeb, Q.; Ali, A.; Sajjad, Y.; Nazir, R.; Widemann, E.; Liu, L. Lead, Cadmium and Zinc Phytotoxicity Alter DNA Methylation Levels to Confer Heavy Metal Tolerance in Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhe, M.Y.; Mulpuri, S.; Meena, H.P.; Ajjanavara, R.R.G.; Kodeboyina, V.S.; Adala, V.R. Genetic Variability, Diversity and Identification of Trait-Specific Accessions from the Conserved Sunflower Germplasm for Exploitation in the Breeding Programme. Agric. Res. 2020, 9, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Meuwissen, T.H.E.; Woolliams, J.A.; Gjøen, H.M. Genomic Dissection of Maternal, Additive and Non-Additive Genetic Effects for Growth and Carcass Traits in Nile Tilapia. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2020, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamir, D.; Eshed, Y. Case History in Germplasm Introgression: Tomato Genetics and Breeding Using Nearly Isogenic Introgression Lines Derived from Wild Species. In Molecular Dissection of Complex Traits; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 207–218. ISBN 0429117779. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, M.P.; Gangaprasad, S. Studies on Mode of Gene Action for Fruit Quality Characteristics Governing Shelf Life in Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.). Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.M.; Ali, E.E.; Mohamed, T.Y. Study of Heritability and Genetic Variability among Different Plant and Fruit Characters of Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.). J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2018, 1, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ignatius, A.; Arunbabu, V.; Neethu, J.; Ramasamy, E. V Rhizofiltration of Lead Using an Aromatic Medicinal Plant Plectranthus Amboinicus Cultured in a Hydroponic Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) System. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13007–13016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- January, M.C.; Cutright, T.J.; Van Keulen, H.; Wei, R. Hydroponic Phytoremediation of Cd, Cr, Ni, As, and Fe: Can Helianthus Annuus Hyperaccumulate Multiple Heavy Metals? Chemosphere 2008, 70, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, P.H.; Kumar, S.A.; Rajasheker, G.; Madhavi, D.; Jalaja, N.; Shridhar, K.K.; Scinthia, K.P.; Divya, D.; Sri, M.S.; Akhila, C. Transgenic Tomatoes for Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Fruit Traits: A Review of Progress and a Preview of Potential. Genet. Modif. Crop. 2020, 2, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyanarayana, S.R.; Warke, V.G.; Mahajan, G.B.; Annapure, U.S. Comparative Studies of Microbial and Heavy Metal Safety Assessment of the Herbs Cultivated in Hydroponically and Regular Soil System. J. Food Saf. 2021, 41, e12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, E.; Matsunaga, H.; Onogi, A.; Kajiya-Kanegae, H.; Minamikawa, M.; Suzuki, A.; Shirasawa, K.; Hirakawa, H.; Nunome, T.; Yamaguchi, H. A Simulation-Based Breeding Design That Uses Whole-Genome Prediction in Tomato. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sappah, A.H.; Elrys, A.S.; Desoky, E.-S.M.; Zhao, X.; Bingwen, W.; El-Sappah, H.H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, J. Comprehensive Genome Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of MTP Gene Family in Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum) under Multiple Heavy Metal Stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6946–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosakivska, I.V.; Babenko, L.M.; Romanenko, K.O.; Korotka, I.Y.; Potters, G. Molecular Mechanisms of Plant Adaptive Responses to Heavy Metals Stress. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, H.M.; Gasti, V.D.; Bhavidoddi, A.; Yashavantakumar, H.K.; Prashantha, A.; Srikantaprasad, D. Genetic Variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance in Determinate Types of Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.). Pharma Innov. J. 2022, 11, 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.M.; Saeed, A.; Khan, A.A.; Javid, S.; Fatima, B. Differential Responses of One Hundred Tomato Genotypes Grown under Cadmium Stress. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 13162–13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.I.M.; El-Mansy, A.B. Performance, Manifestation of Heterosis and Combining Ability for Growth, Productivity and Fruit Quality of Indeterminate Tomato. J. Plant Prod. 2020, 11, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisya, S.I.; Wahyuni, S.; Syukur, M.; Witono, J.R. The Estimation of Combining Ability and Heterosis Effect for Yield and Yield Components in Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum Mill.) at Lowland. Ekin J. Crop. Breed. Genet. 2016, 2, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, A.S.T.; Resende, J.T.V.; Faria, M.V.; Paula, J.T.; Rizzardi, D.A.; Meert, L. Agronomic Evaluation and Combining Ability of Tomato Inbred Lines Selected for the Industrial Segment. Hortic. Bras. 2016, 34, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daej, M.I. Line× Tester Analysis of Heterosis and Combining Ability in Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum Mill.) Fruit Quality Traits. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 21, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, K.Y. Genetic Study of Heterosis for Yield and Quality Components in Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 5585–5591. [Google Scholar]
- Bineau, E.; Rambla, J.L.; Duboscq, R.; Corre, M.-N.; Bitton, F.; Lugan, R.; Granell, A.; Plissonneau, C.; Causse, M. Inheritance of Secondary Metabolites and Gene Expression Related to Tomato Fruit Quality. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Ren, A.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H. Heterosis and Combining Ability Analysis of Fruit Yield, Early Maturity, and Quality in Tomato. Agronomy 2021, 11, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdr, M.F.; Anshori, M.F.; Emanuella, G.; Pratiwi, N.; Ermiyanti, I.; Yovita, V.; Musdalifa, M.; Nasaruddin, N. High Lycopene Tomato Breeding through Diallel Crossing. Agrotech J. 2020, 5, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zook, E.G.; Greene, F.E.; Morris, E.R. Nutrient Composition of Selected Wheats and Wheat Products. 6. Distribution of Manganese, Copper, Nickel, Zinc, Magnesium, Lead, Tin, Cadmium, Chromium, and Selenium as Determined by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Colorimetry. Cereal Chem. 1970, 47, 720–731. [Google Scholar]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. In Principles and Procedures of Statistics, A Biometrical Approach; McGraw-Hill Kogakusha, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey, M.J. Biometrical Analysis of a Random Mating Population: A Comparison of Five Experimental Designs. Heredity 1965, 20, 205–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkoong, G. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics in Forestry; Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, G.W.; de Devane, E.H. Estimating Heritability in Tall Fescue (Festuca Arundinacea) from Replicated Clonal Material 1. Agron. J. 1953, 45, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.W.; Robinson, H.F.; Comstock, R.E. Estimates of Genetic and Environmental Variability in Soybeans 1. Agron. J. 1955, 47, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comstock, R.E.; Robinson, H.F. Genetic Parameters, Their Estimation and Significance. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Grassland Congress, University Park, State College, PA, USA, 17–23 August 1952; Volume 1, pp. 248–291. [Google Scholar]
| Source | NOFL | NOF | Cr | Pb | Zn | Ni | Mn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater | Replication | 71 ns | 8 ns | 0.235 ns | 0.004 ns | 0.69 ns | 0.2448 ns | 0.363 ns |
| Males | 9478 ** | 13438 ** | 5.13 ** | 4.68 ** | 160.37 ** | 1.36 ** | 17.36 ** | |
| Females | 206,852 ** | 225,698 ** | 73.51 ** | 8.86 ** | 549.45 ** | 11.50 ** | 118.97 ** | |
| M × F | 2293 ** | 811 ** | 14.06 ** | 4.78 ** | 205.25 ** | 4.19 ** | 64.26 ** | |
| Error | 56 | 5 | 1.98 | 1.26 | 18.22 | 0.57 | 6.54 | |
| MSf/MSm | 21.8 | 16.8 | 14.3 | 1.9 | 3.4 | 8.4 | 6.9 | |
| Canal water | Replication | 2 ns | 27 ns | 0.0871 ns | 0.0695 ns | 0.130 ns | 0.2419 ns | 0.259 ns |
| Males | 9601 ** | 10,383 ** | 2.6534 ** | 1.2923 ** | 29.208 ** | 1.0211 ** | 11.652 ** | |
| Females | 198,808 ** | 180,755 ** | 18.3007 ** | 6.6098 ** | 283.268 ** | 3.6906 ** | 19.598 ** | |
| M × F | 1683 ** | 1476 ** | 4.7114 ** | 1.5910 ** | 81.290 ** | 1.3026 ** | 14.064 ** | |
| Error | 29 | 53 | 0.3506 | 0.3447 | 5.743 | 0.2240 | 2.215 | |
| MSf/MSm | 20.70 | 17.41 | 6.90 | 5.123 | 9.69 | 3.6 | 1.68 |
| Genetic Component | NOF | NOFL | Zn | Cr | Mn | Ni | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater | σ2m | 601.3 | 342.2 | −2.14 | −0.42 | −2.23 | −0.13 | −0.01 |
| σ2f | 8329.1 | 7576.3 | 12.75 | 2.20 | 2.03 | 0.27 | 0.15 | |
| σ2m×f | 268.9 | 745.5 | 62.34 | 4.03 | 19.24 | 1.21 | 1.17 | |
| σ2H | 1075.4 | 2981.9 | 249.372 | 16.1 | 76.9 | 4.83 | 4.69 | |
| σ2D | 11,907.2 | 10,557.9 | 14.15 | 2.37 | −0.28 | 0.18 | 0.20 | |
| [σ2H/σ2D]1/2 | 0.30 | 0.53 | 4.19 | 2.54 | −16.69 | 5.13 | 4.89 | |
| Canal water | σ2m | 424.2 | 2ns | −2.48 | −0.098 | −0.115 | −0.013 | −0.014 |
| σ2f | 6639.95 | 9601 | 7.48 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 0.089 | 0.186 | |
| σ2m×f | 474.31 | 198,808 | 25.18 | 1.45 | 3.9 | 0.36 | 0.42 | |
| σ2H | 9418.8 | 1683 | 6.67 | 0.54 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.23 | |
| σ2D | 1897.22 | 29 | 100.73 | 5.81 | 15.8 | 1.44 | 1.66 | |
| [σ2H/σ2D]1/2 | 0.45 | 20.70 | 3.88 | 3.28 | 11.46 | 3.79 | 2.69 |
| Traits | PV | PCV % | GV | GCV % | h2bs | GA% | EV | ECV % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater | NOFL | 77 | 60 | 77 | 60 | 0.9 | 106 | 46 | 4.71 |
| NOF | 88 | 63 | 88 | 63 | 0.9 | 111 | 4 | 1.45 | |
| Cr | 15 | 75 | 13 | 70 | 0.8 | 113 | 2 | 29 | |
| Ni | 1.6 | 73 | 1.1 | 61 | 0.7 | 91 | 0.5 | 39 | |
| Zn | 105 | 24 | 90 | 22 | 0.8 | 36 | 15 | 9 | |
| Mn | 23 | 50 | 17 | 43 | 0.7 | 65 | 6 | 26 | |
| Pb | 2.7 | 67 | 1.7 | 53 | 0.6 | 73 | 1.03 | 41 | |
| Canal water | NOFL | 7465 | 60 | 7434 | 60 | 0.99 | 106 | 31 | 3.9 |
| NOF | 7375 | 66 | 6740 | 63 | 0.91 | 107 | 634 | 19 | |
| Cr | 4 | 77 | 3 | 65 | 0.7 | 98 | 1.3 | 40 | |
| Ni | 0.6 | 85 | 0.33 | 61 | 0.5 | 77 | 0.31 | 59 | |
| Zn | 45 | 28 | 37 | 26 | 0.8 | 41 | 8.1 | 12 | |
| Mn | 9 | 67 | 6 | 56 | 0.6 | 81 | 2.9 | 37 | |
| Pb | 1.01 | 74 | 0.61 | 58 | 0.6 | 79 | 0.39 | 46 |
| Water Samples | Cr (mg L−1) | Ni (mg L−1) | Mn (mg L−1) | Pb (mg L−1) | Zn (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sewage Water | 10 ± 0.14 | 2.5 ± 0.05 | 1 ± 0.02 | 1.5 ± 0.01 | 6.5 ± 0.05 |
| Canal Water | 8.5 ± 0.06 | 2 ± 0.06 | 6.5 ± 0.05 | 0 ± 0.00 | 4.5 ± 0.06 |
| Soil (0–20 cm) | 0.41 ± 0.09 | 0.43 ± 0.02 | 11.57 ± 0.12 | 1.16 ± 0.02 | 1.41 ± 0.02 |
| Soil (20–40 cm) | 0.4 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 5.69 ± 0.04 | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 0.43 ± 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raja, S.; Farhat, F.; Tariq, A.; Malik, Z.; Aziz, R.B.; Kamran, M.; Elsharkawy, M.M.; Ali, A.; Al-Hashimi, A.; Elshikh, M.S. Genetic Behavior of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Germplasm Governing Heavy Metal Tolerance and Yield Traits under Wastewater Irrigation. Plants 2022, 11, 2973. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212973
Raja S, Farhat F, Tariq A, Malik Z, Aziz RB, Kamran M, Elsharkawy MM, Ali A, Al-Hashimi A, Elshikh MS. Genetic Behavior of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Germplasm Governing Heavy Metal Tolerance and Yield Traits under Wastewater Irrigation. Plants. 2022; 11(21):2973. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212973
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaja, Shameem, Fozia Farhat, Arneeb Tariq, Zaffar Malik, Rana Badar Aziz, Muhamamd Kamran, Mohsen Mohamed Elsharkawy, Asif Ali, Abdulrahman Al-Hashimi, and Mohamed S. Elshikh. 2022. "Genetic Behavior of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Germplasm Governing Heavy Metal Tolerance and Yield Traits under Wastewater Irrigation" Plants 11, no. 21: 2973. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212973
APA StyleRaja, S., Farhat, F., Tariq, A., Malik, Z., Aziz, R. B., Kamran, M., Elsharkawy, M. M., Ali, A., Al-Hashimi, A., & Elshikh, M. S. (2022). Genetic Behavior of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Germplasm Governing Heavy Metal Tolerance and Yield Traits under Wastewater Irrigation. Plants, 11(21), 2973. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212973








