Bio-Fabrication of Euryale ferox (Makhana) Leaf Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Material Required
2.1. Material Required
2.2. Green Synthesis of ELAgNPs
2.3. Characterization of ELAgNPs
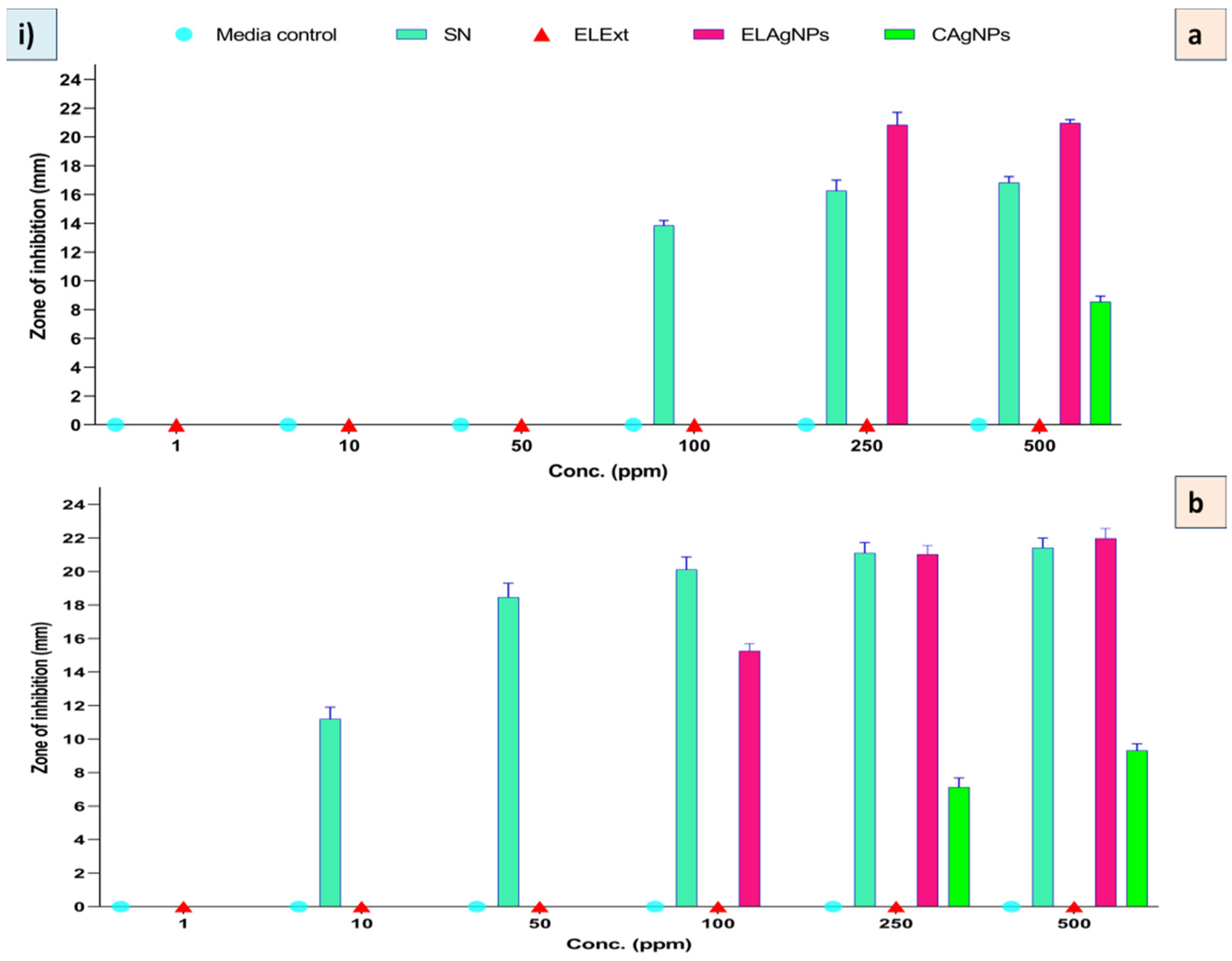
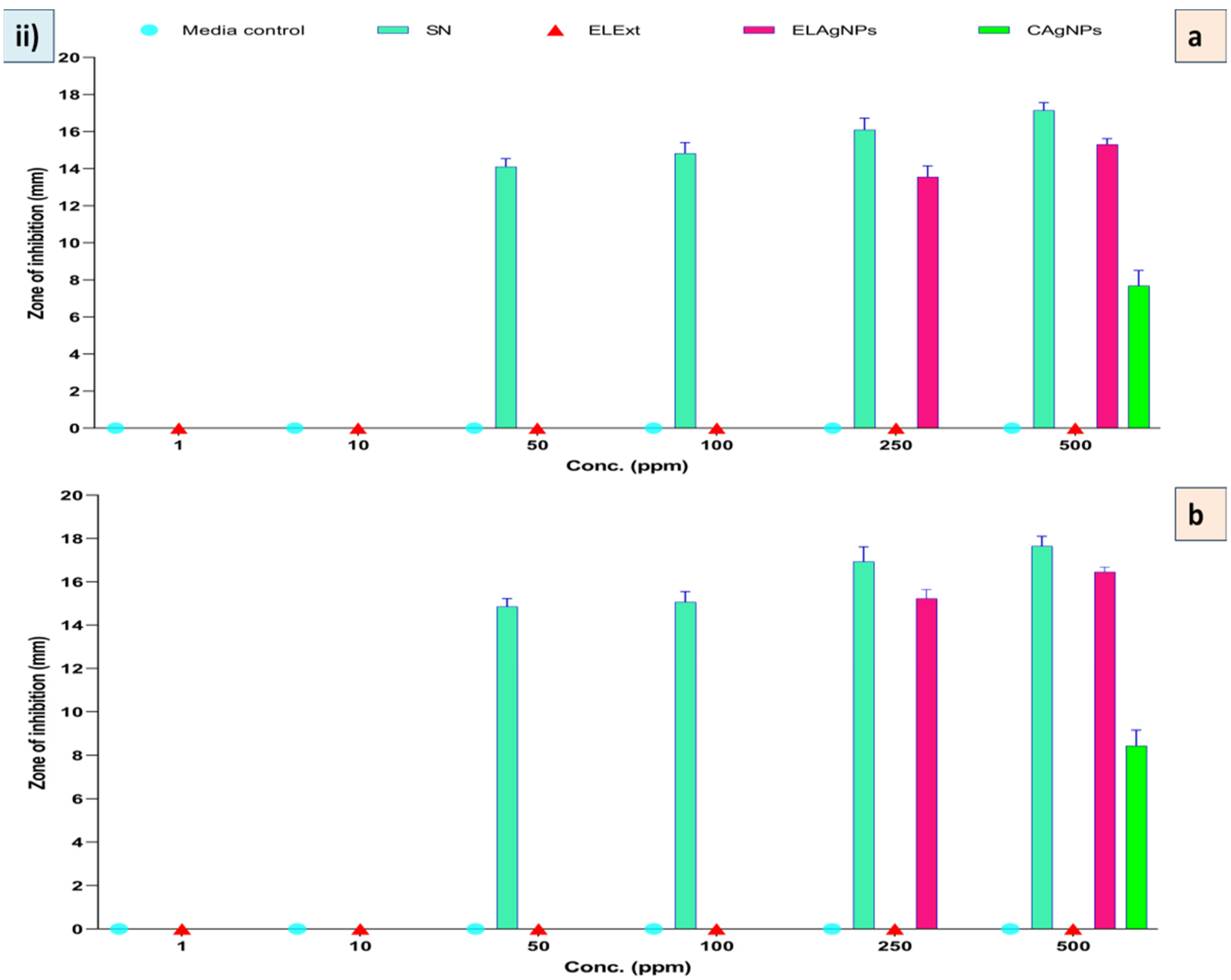
2.4. Antibacterial Activity of ELAgNPs
2.5. Antioxidant Potential of ELAgNPs
2.5.1. DPPH-Based Antioxidant Activity
2.5.2. Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging Activity
2.5.3. OH− Radical Scavenging Activity
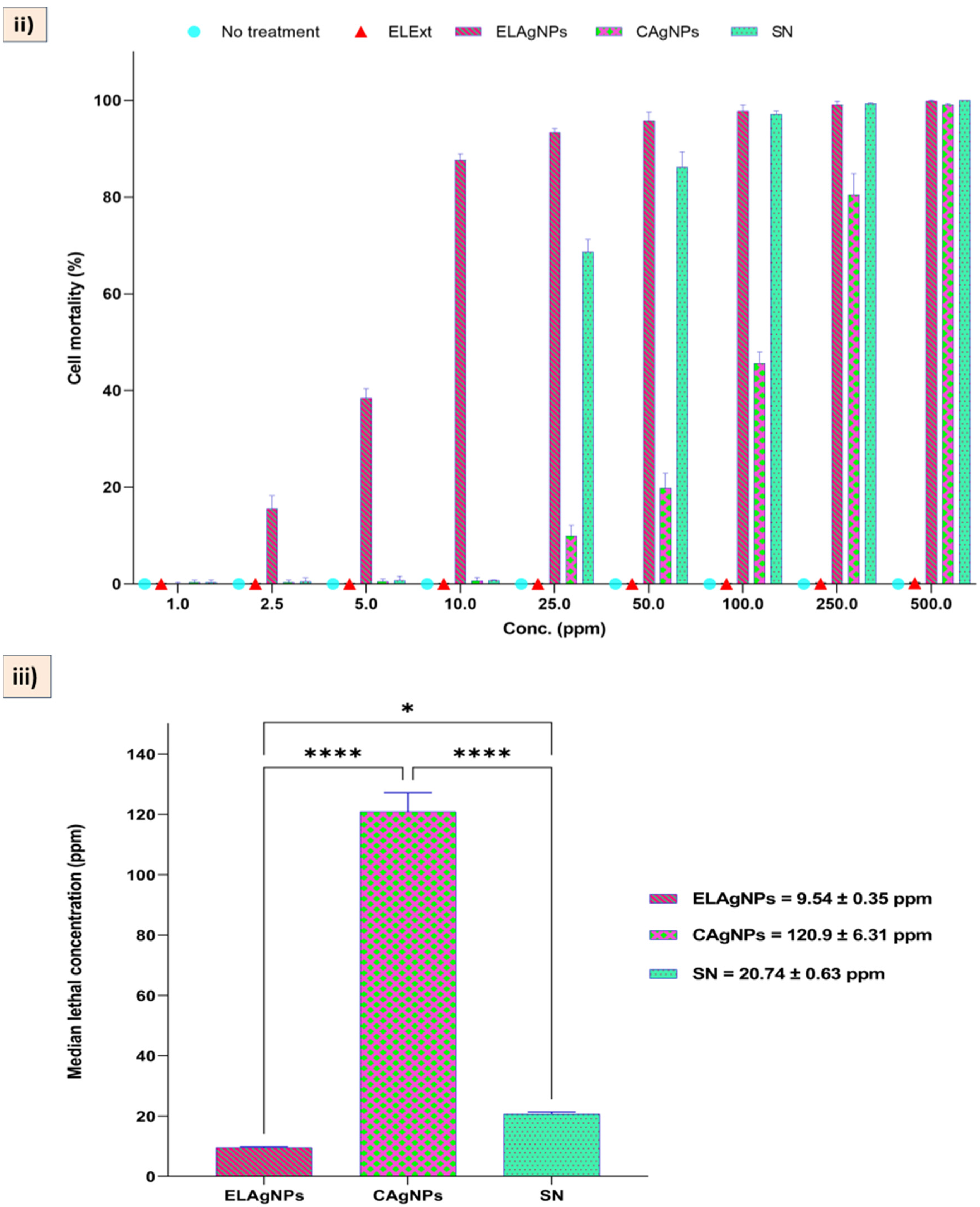
2.6. Toxicity Analysis of ELAgNPs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
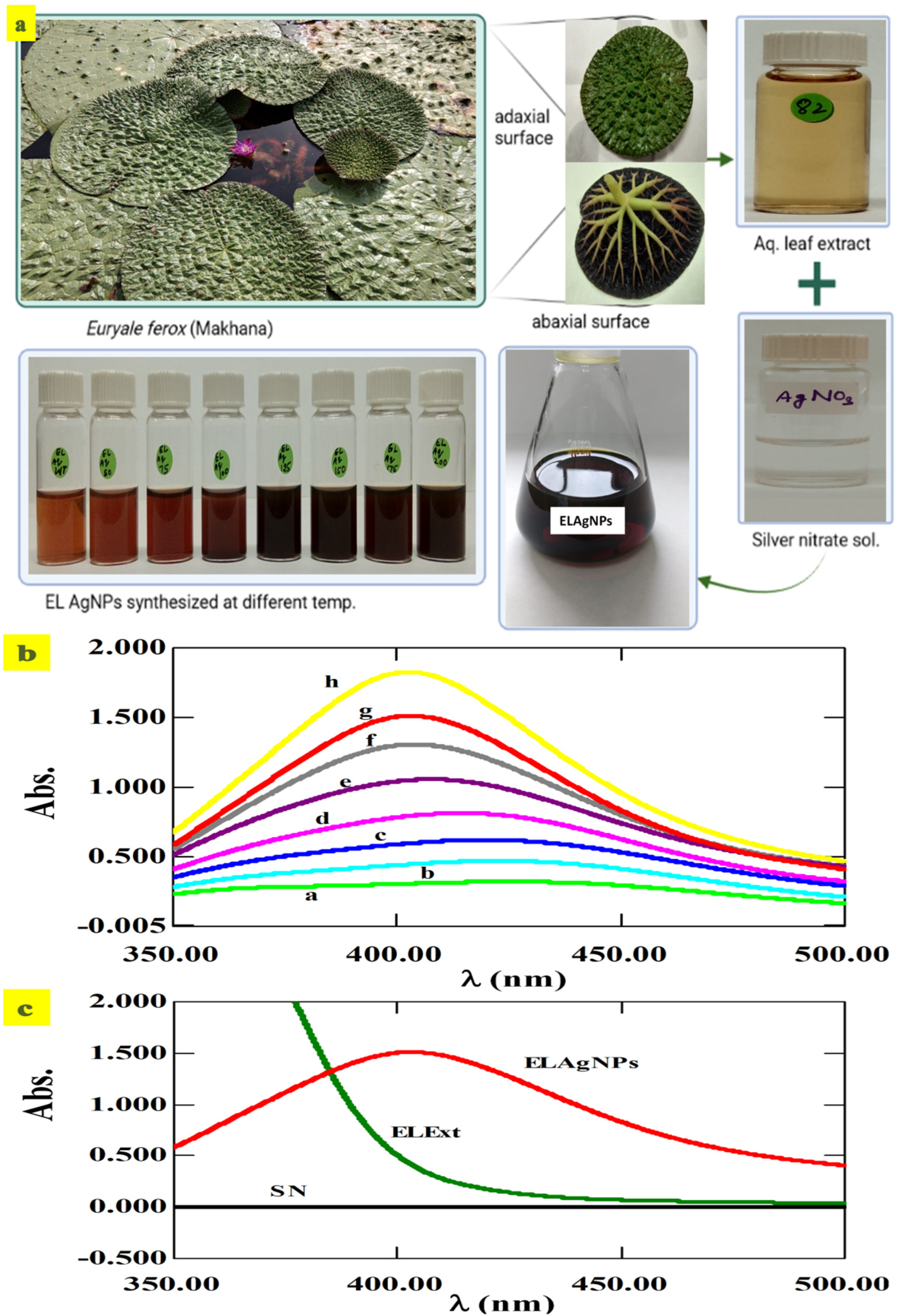
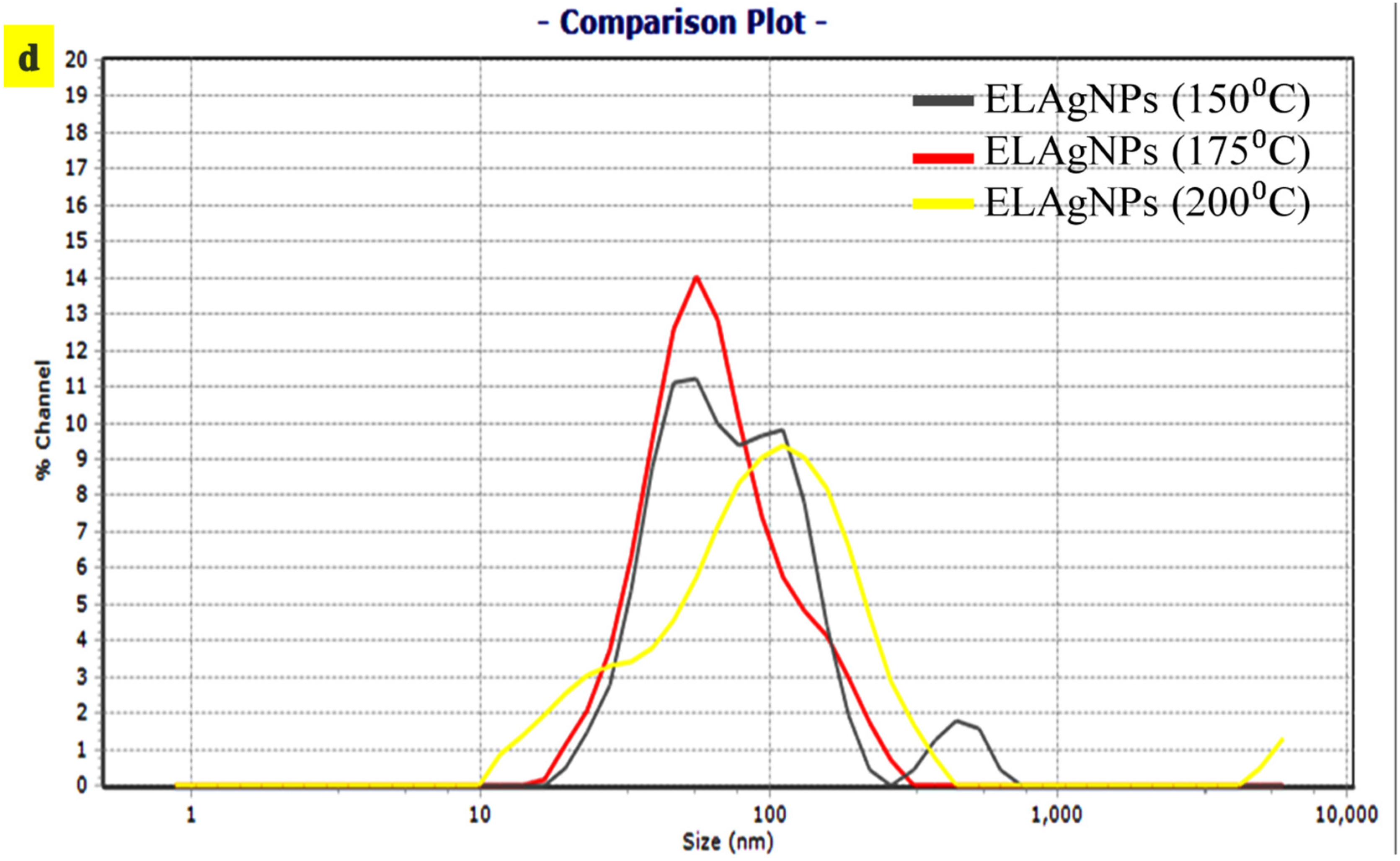
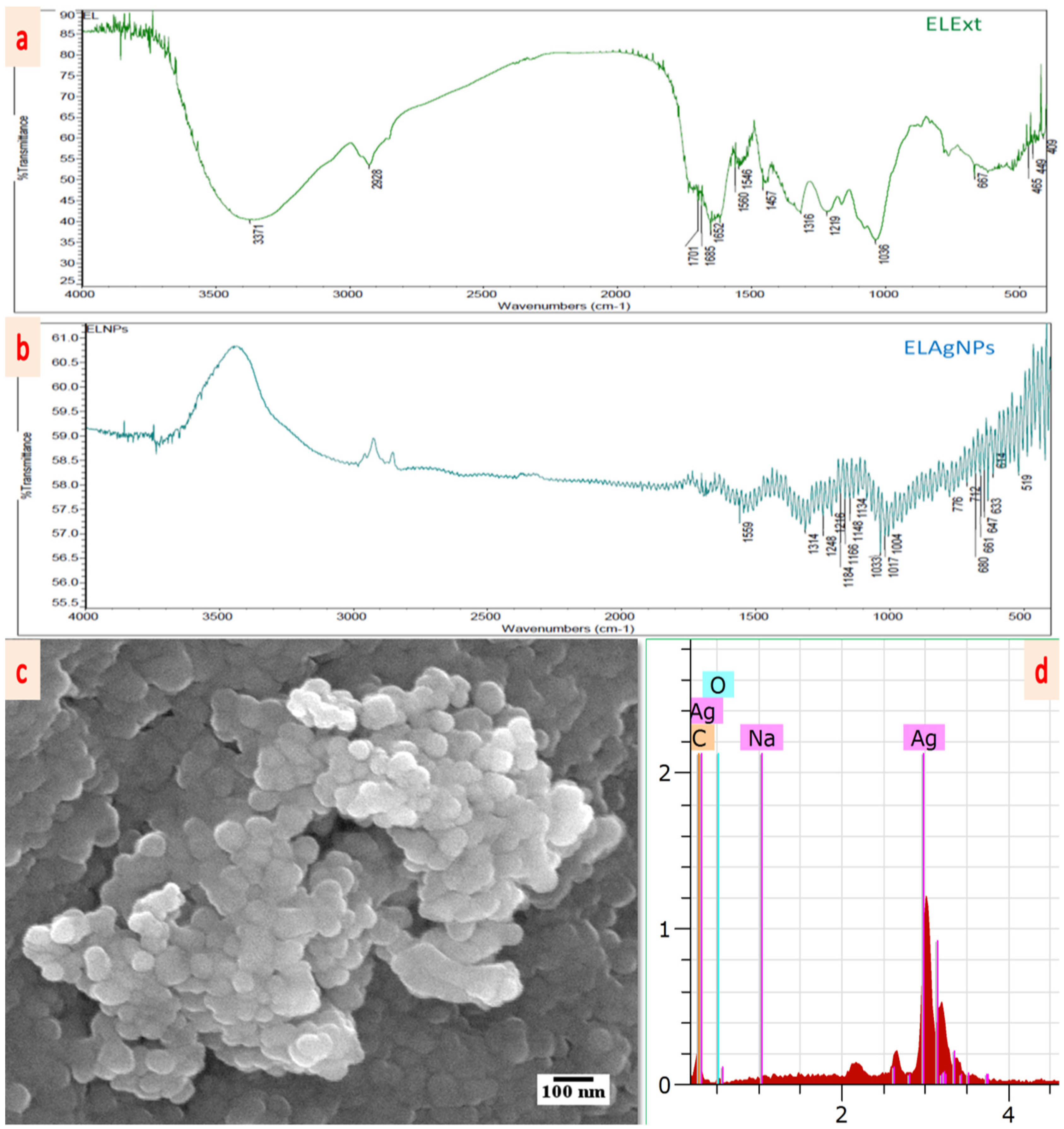
3.1. Green Synthesis and Characterization of ELAgNPs
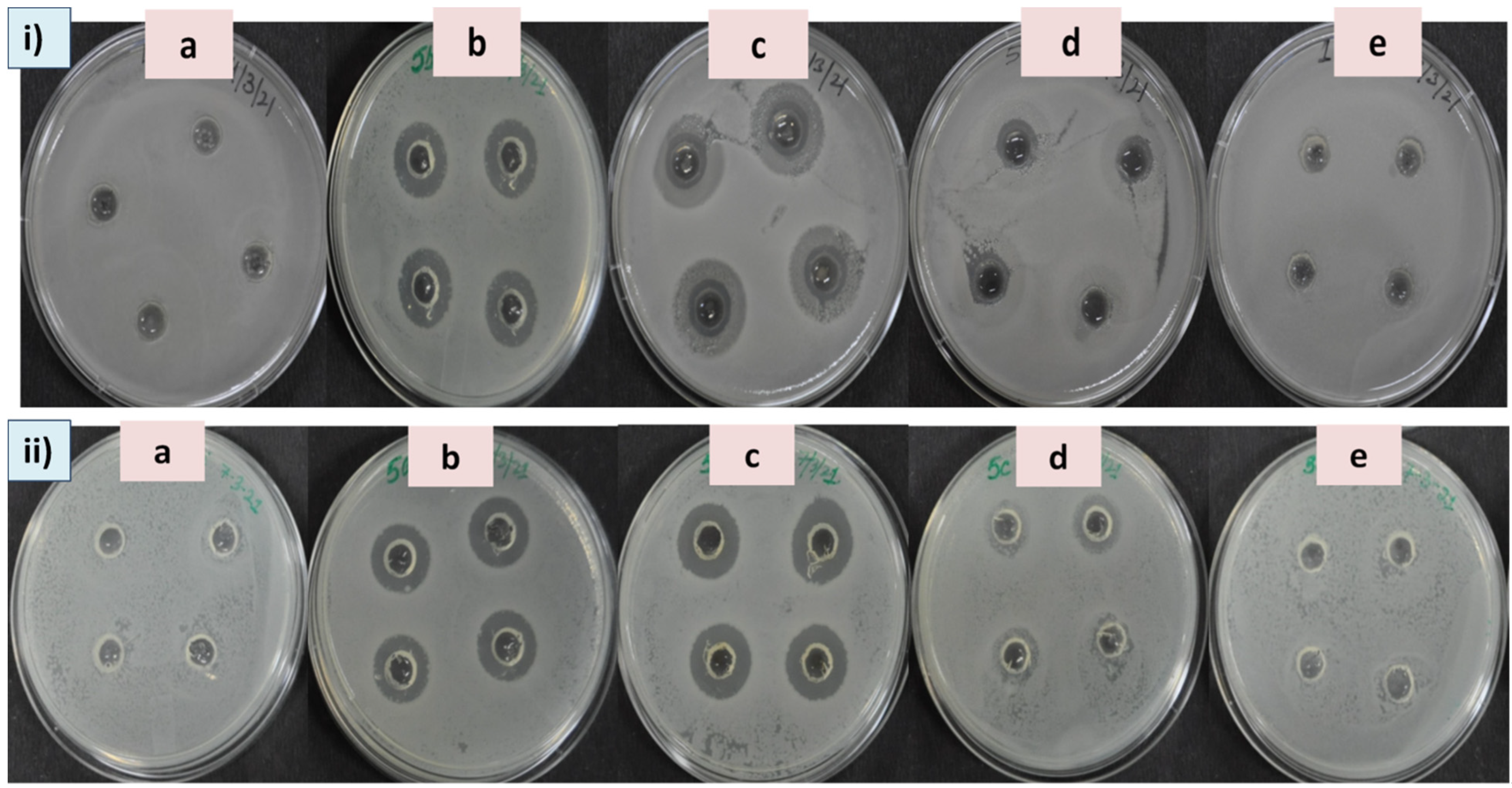
3.2. Assessment of Antibacterial Efficacy of ELAgNPs
3.3. Antioxidant Activity of ELAgNPs
3.4. Toxicity of ELAgNPs against VERO Cell Line
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejías, J.H.; Salazar, F.J.; Pérez, L.; Hube, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Alfaro, M.A. Nanofertilizers: A cutting-edge approach to increase nitrogen use efficiency in grasslands. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, N. Methods of preparation of nanoparticles-a review. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2015, 7, 1806. [Google Scholar]
- Fabiano, B.; Reverberi, A.P.; Varbanov, P.S. Safety opportunities for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles and short-cut approach to workplace risk evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gautam, P.K.; Verma, A.; Singh, V.; Shivapriya, P.M.; Shivalkar, S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles as effective alternatives to treat antibiotics resistant bacterial infections: A review. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 25, e00427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Raja, N.I.; Iqbal, M.; Ejaz, M.; Aslam, S. Green synthesis and evaluation of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial and biochemical profiling in Kinnow (Citrus reticulata L.) to enhance fruit quality and productivity under biotic stress. IET Nanobiotechnology 2019, 13, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the flower extract of Abelmoschus esculentus for cytotoxicity and antimicrobial studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaabipour, S.; Hemmati, S. A review on the green and sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles and one-dimensional silver nanostructures. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 102–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.; Rani, K.; Kharb, P.; Prasad, M. Herbal Medicine for Urinary Tract Infections with the Blazing Nanotechnology. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 3495–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, K.; Devi, N.; Saharan, V.; Kharb, P. Glycyrrhiza glabra: An insight to nanomedicine. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Wu, Y.; Cao, B. Research progress of E. ferox seeds. China Veget. 2007, 2, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, S.N.; Prasad, S. Post–harvest technology of gorgon nut. In Makhana; Mishra, R.K., Vidyanath, J., Dharai, P.V., Eds.; ICAR: New Delhi, India, 2003; pp. 194–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.N.; Su, R.N.; Gong, L.L.; Yang, W.W.; Chen, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Pan, W.J.; Lu, Y.M.; Chen, Y. Structural characterization and in vitro hypoglycemic activity of a glucan from Euryale ferox Salisb. seeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, D.; Khan, M.I.; Sharma, M.; Khan, M.F. Novel pentacyclic triterpene isolated from seeds of Euryale ferox Salisb. ameliorates diabetes in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2018, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Nam, I.J.; Kwak, H.S.; Kim, K.C.; Lee, S.H. Cellular anti-melanogenic effects of a Euryale ferox seed extract ethyl acetate fraction via the lysosomal degradation machinery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9217–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.H.; Jo, K.J.; Park, Y.S.; Kawk, H.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.M. In vitro and in vivo induction of p53-dependent apoptosis by extract of Euryale ferox salisb in A549 human caucasian lung carcinoma cancer cells is mediated through Akt signaling pathway. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, B.R.; Md, I. Anti-aging amino acids in Euryale ferox (Salisb.). Adv. Plants Agric. Res. 2018, 8, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liaquat, M.; Pasha, I.; Ahsin, M.; Salik, A. Roasted fox nuts (Euryale Ferox L.) contain higher concentration of phenolics, flavonoids, minerals and antioxidants, and exhibit lower Glycemic Index (GI) in human subjects. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2022, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, R.; Sun, G.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Q. Extract of Euryale ferox Salisb exerts antidepressant effects and regulates autophagy through the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase—UNC-51-like kinase 1 pathway. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, J.A.; Ayensu, E.S. Medicinal Plants of China; Reference Publication, Inc.: Algonac, MI, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T. Euryale ferox Rice Dumplings and Preparation Method Thereof. Chinese Patent CN106261716, 22 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W. Euryale ferox Tea. Chinese Patent CN109645177, 12 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, X.H.; Yue, W.; Wu, Q.N. Waste Euryale ferox salisb. leaves as a potential source of anthocyanins: Extraction optimization, identification and antioxidant activities evaluation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 4327–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.H.; Yin, M.J.; Wang, Q.; Bao, K.; Zhou, P.N.; Liu, C.C.; Wu, Q.N. Expression profiling and functional verification of flavonoid 3’-hydroxylase gene from leaves of Euryale ferox. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2021, 46, 4712–4720. [Google Scholar]
- Magaldi, S.; Mata-Essayag, S.; De Capriles, C.H.; Pérez, C.; Colella, M.T.; Olaizola, C.; Ontiveros, Y. Well diffusion for antifungal susceptibility testing. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 8, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhakya, S.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Sukumaran, M.; Muthukumar, M. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshari, A.K.; Srivastava, R.; Singh, P.; Yadav, V.B.; Nath, G. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Cestrum nocturnum. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2020, 11, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, P. Activity of Turbinaria ornata (Turner) J. Agade against Blue Tongue Virus (Btv). IOSR J. Pharm. 2016, 6, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhiraj, V.; Kumar, K.S.; Madhusudhanan, J.; Sandhya, J. Antitumor activity of biosynthesized silver nano particles from leaves of Momordica charantia against MCF-7 cell line. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2015, 8, 351–362. [Google Scholar]
- Shehzad, A.; Qureshi, M.; Jabeen, S.; Ahmad, R.; Alabdalall, A.H.; Aljafary, M.A.; Al-Suhaimi, E. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using Rhazya stricta. PeerJ 2018, 6, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Jung, H.C.; Baek, Y.J.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, S.W. Antibacterial activity of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles using Areca catechu extract against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Singh, H.; Trivedi, R.; Soni, V. Biogenic synthesis of AgNPs employing Terminalia arjuna leaf extract and its efficacy towards catalytic degradation of organic dyes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, L.; Bandara, S.; Joseph, M.; Green, T.; Grady, T.; Osuji, G.; Weerasooriya, A.; Ampim, P.; Woldesenbet, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties using Phyla dulcis plant extract. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Arul Prasad, A.; Mary Vithiya, S. Evaluation of antioxidant, antibacterial and photo catalytic effect of silver nanoparticles from methanolic extract of Coleus vettiveroids–an endemic species. J. Nanostruct. 2018, 8, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to read and interpret FTIR spectroscope of organic material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, C.; Selvam, K.; Govarthanan, M.; Senthilkumar, B.; Sengottaiyan, A.; Stalin, M.; Selvankumar, T. Acorus calamus rhizome extract mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their bactericidal activity against human pathogens. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 13, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allafchian, A.R.; Mirahmadi-Zare, S.Z.; Jalali, S.A.H.; Hashemi, S.S.; Vahabi, M.R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phlomis leaf extract and investigation of their antibacterial activity. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2016, 6, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gootz, T.D. The global problem of antibiotic resistance. In Critical Reviews™ in Immunology; Begell House: Danbury, CT, USA, 2010; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.E. Green synthesis, antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles mediated by Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaf extract. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirtarighat, S.; Ghannadnia, M.; Baghshahi, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the plant extract of Salvia spinosa grown in vitro and their antibacterial activity assessment. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.L.; Bhumi, G.; Savithramma, N. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Allamanda cathartica L. leaf extract and evaluation for antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 6, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibo, D.; Borbón-Nuñez, H.A.; de León, J.N.D.; García Mendoza, E.; Estrada, I.; Toledano-Magaña, Y.; Tiznado, H.; Ovalle-Marroquin, M.; Soto-Ramos, A.G.; Blanco, A.; et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lysiloma acapulcensis exhibit high-antimicrobial activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, J. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: Structural effects. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 701503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sène, M.A.; Kiesslich, S.; Djambazian, H.; Ragoussis, J.; Xia, Y.; Kamen, A.A. Haplotype-resolved de novo assembly of the Vero cell line genome. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsalam, S.; Agastian, P.; Esmail, G.A.; Ghilan, A.K.M.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Musa acuminata colla flower and its pharmaceutical activity against bacteria and anticancer efficacy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 201, 111670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moadab, S.; Ahari, H.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Motalebi, A.A.; Anvar, A.A.; Rahmania, J.; Shokrgozar, M.R. Toxicity Study of Nanosilver (Nanocid®) on Osteoblast Cancer Cell Line; International Nano Letters (INL): Kermanshah, Iran, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, K.; Devi, N.; Banakar, P.; Kharb, P.; Kaushik, P. Nematicidal potential of green silver nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous root extract of Glycyrrhiza glabra. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


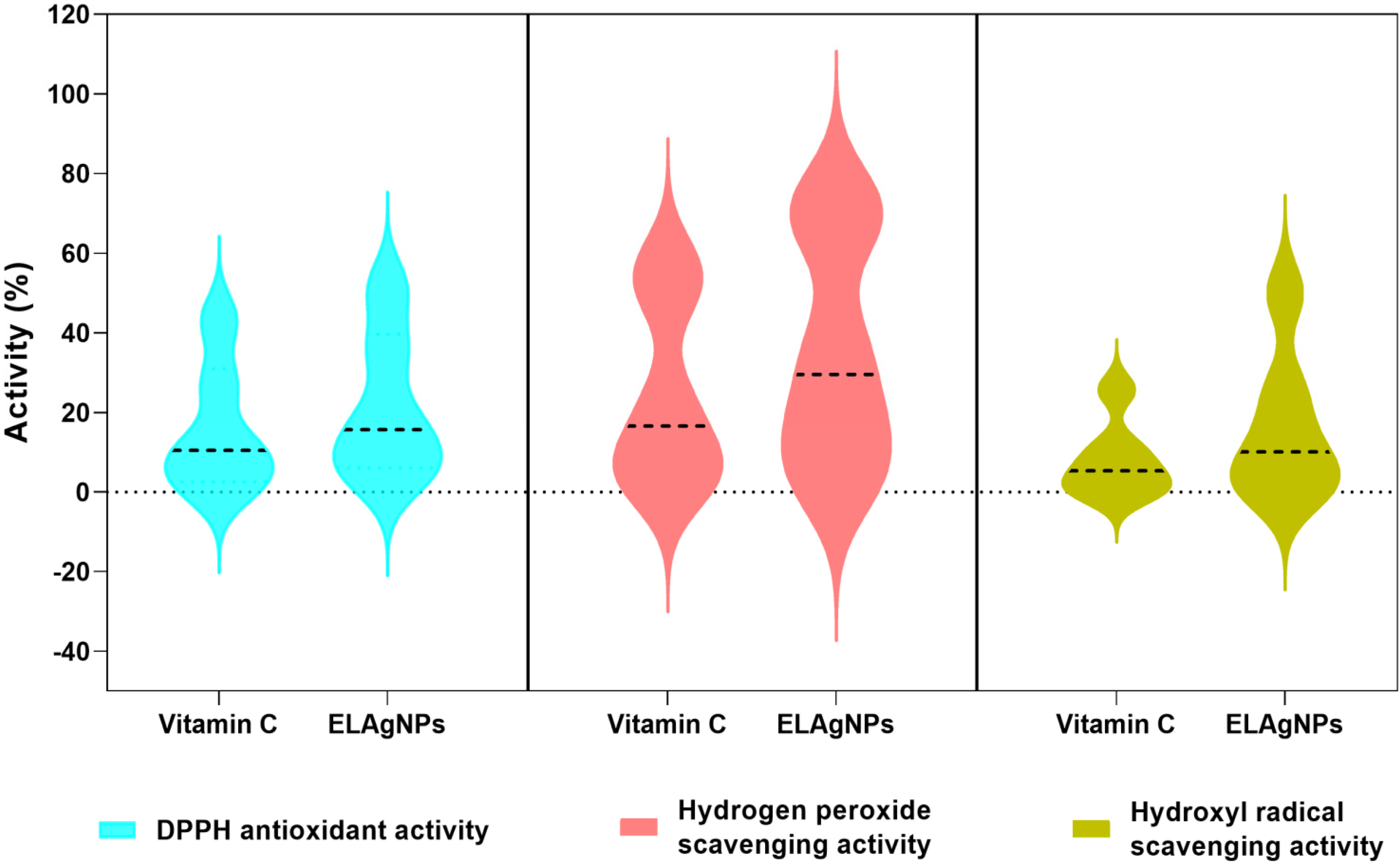

| Concentration (ppm) | DPPH Antioxidant Activity (%) | Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging Activity (%) | Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | ELAgNPs | Vitamin C | ELAgNPs | Vitamin C | ELAgNPs | |
| 1 | 0.82 ± 0.43 | 3.09 ± 0.38 | 0.92 ± 0.88 | 1.23 ± 0.11 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| 10 | 3.11 ± 0.78 | 7.13 ± 0.92 | 5.77 ± 0.56 | 10.09 ± 0.83 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 2.12 ± 1.02 |
| 50 | 9.23 ± 1.02 | 11.89 ± 1.32 | 10.37 ± 0.78 | 21.67 ± 0.34 | 3.78 ± 0.45 | 6.17 ± 1.15 |
| 100 | 11.76 ± 0.67 | 19.45 ± 0.13 | 22.81 ± 0.92 | 37.34 ± 0.23 | 6.89 ± 0.48 | 14.02 ± 1.03 |
| 250 | 26.89 ± 0.89 | 35.72 ± 0.22 | 49.93 ± 0.67 | 68.13 ± 0.78 | 11.42 ± 0.86 | 25.38 ± 0.23 |
| 500 | 43.21 ± 1.21 | 51.23 ± 0.34 | 57.75 ± 1.23 | 72.17 ± 0.56 | 25.67 ± 0.34 | 49.98 ± 0.56 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devi, N.; Rani, K.; Kharb, P.; Kaushik, P. Bio-Fabrication of Euryale ferox (Makhana) Leaf Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential. Plants 2022, 11, 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202766
Devi N, Rani K, Kharb P, Kaushik P. Bio-Fabrication of Euryale ferox (Makhana) Leaf Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential. Plants. 2022; 11(20):2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202766
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevi, Nisha, Kanika Rani, Pushpa Kharb, and Prashant Kaushik. 2022. "Bio-Fabrication of Euryale ferox (Makhana) Leaf Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential" Plants 11, no. 20: 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202766
APA StyleDevi, N., Rani, K., Kharb, P., & Kaushik, P. (2022). Bio-Fabrication of Euryale ferox (Makhana) Leaf Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential. Plants, 11(20), 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202766









