Phenolic Acid Derivatives, Flavonoids and Other Bioactive Compounds from the Leaves of Cardiocrinum cordatum (Thunb.) Makino (Liliaceae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
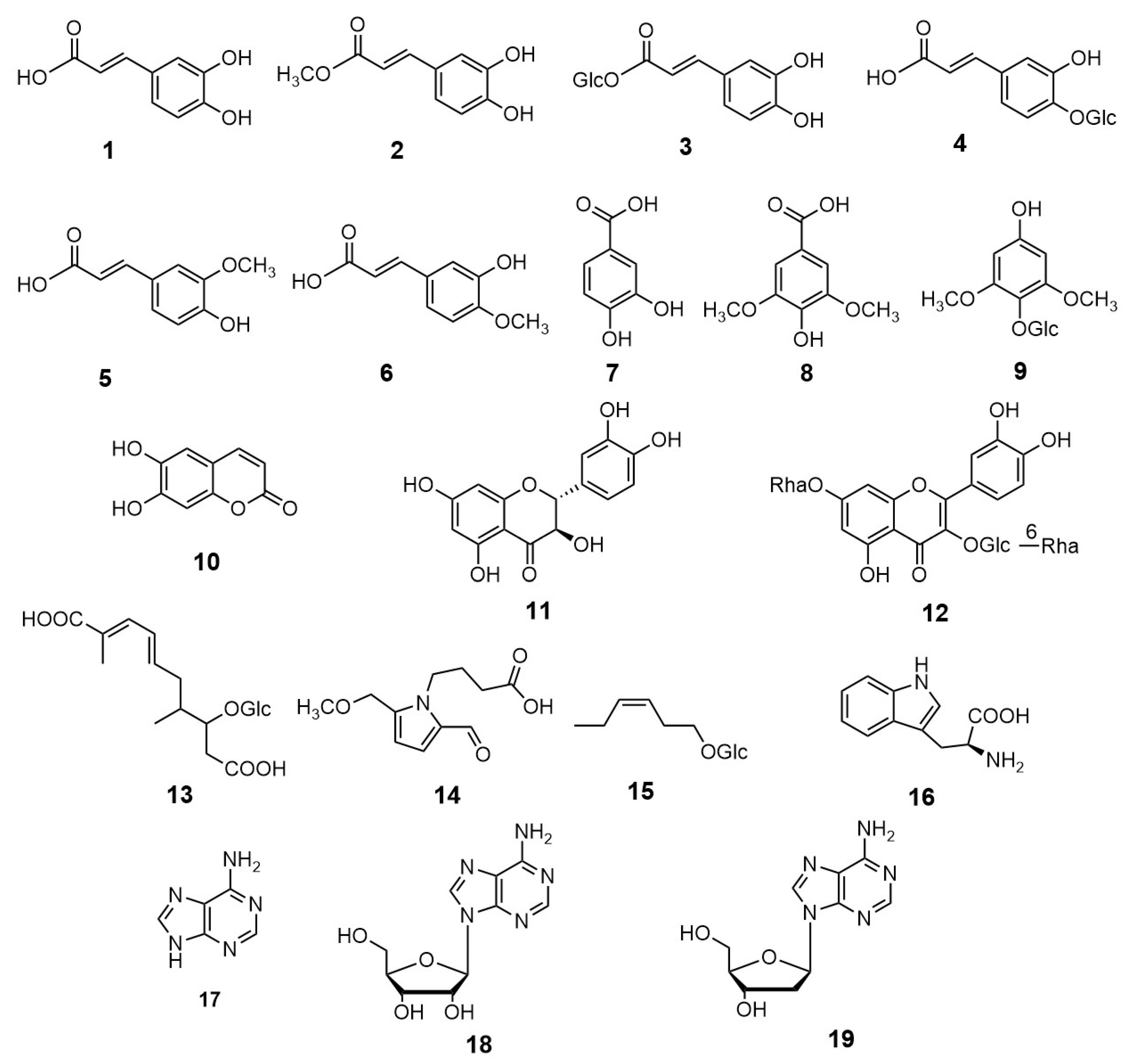
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Esculetin (10)
3.5. 2,7-Dimethyl-2,4-diene-deca-α,ω-diacid β-glucopyranoside (13)
3.6. 4-[Formyl-5-(methoxymethyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-ly]butanoic acid (14)
3.7. (3-Z)-3-Hexenyl β-glucopyranoside (15)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, R.S.; Li, P.; Qiu, Y.X. The complete chloroplast genomes of three Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) species: Comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Dao, Z. Isolation and characterization of 21 microsatellite loci in Cardiocrinum giganteum var. yunnanense (Liliaceae), an important economic plant in China. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Songyun, L.; Tamura, M.N. 19. Cardiocrinum (Endlicher) Lindley, Veg. Kingd. 205. 1846. In Flora of China. (Flagellariaceae through Marantaceae); Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2000; Volume 24, pp. 134–135. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Rajbhandari, K.R.; Malla, K.J.; Devkota, H.P.; Yahara, S. A Handbook of Medicinal Plants of Nepal Supplement I; Ayurseed L.E.I.: Kanagawa, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, K.; Shimatani, K.; Nishizawa, M.; Yoshizane, T.; Ohara, M. Growth and survival patterns of Cardiocrinum cordatum var. glehnii (Liliaceae) based on a 13-year monitoring study: Life history characteristics of a monocarpic perennial herb. Botany 2010, 88, 745–752. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M.; Devkota, H.P.; Sugimura, K.; Watanabe, T. A Guidebook of Medicinal Plant Park; School of Pharmacy, Kumamoto University: Kumamoto, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, H.; Hashino, A.; Takagi, H. Edible wild plants. XVII. Starches from wild plants. Eiyo Shokuryo Gakkaishi 1955, 7, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shiozaki, M.; Ishii, S. Composition of Cardiocrinum cordatum var. glehnii and Traditional Derived Dried Foods of the Ainu. Jpn. J. Nutr. Diet. 2004, 62, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.R.; Lin, Z.X.; Lu, X.Y.; Xia, X.; Jiang, R.W.; Chen, Q.B. CGY-1, a biflavonoid isolated from Cardiocrinum giganteum seeds, improves memory deficits by modulating the cholinergic system in scopolamine-treated mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, J.W.; Zhang, R.R.; Wu, H.Y.; Xia, X.; Nie, H.; Jiang, R.W.; Shaw, P.C. Isolation of novel biflavonoids from Cardiocrinum giganteum seeds and characterization of their antitussive activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 222, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Wang, G.N.; Wu, H.Y.; Tian, H.Y.; Shaw, P.C.; Jiang, R. Isolation and identification of antioxidant flavonoids from the seeds Cardicrinum giganteum var. yunnanense. J. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 6, 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.W.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, I.K.; Choi, S.U.; Ryu, S.Y.; Lee, K.R. Phytochemical constituents of Bistorta manshuriensis. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2009, 15, 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.-B.; Tezuka, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Nakano, H.; Tamaoki, T.; Park, J.-H. Constituents of a Fern, Davallia mariesii Moore. I. Isolation and Structures of Davallialactone and a New Flavanone Glucuronide. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 3218–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, F.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. A new ferulic acid ester from Rhodiola wallichiana var. cholaensis (Crassulaceae). Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.R.; Kuo, Y.H.; Ho, Y.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, C.S.; Lin, C.W.; Chang, Y.S. Studies on cytotoxic constituents from the leaves of Elaeagnus oldhamii Maxim. In non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 9515–9534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Inoshiri, S.; Sato, T.; Yamasaki, K. Phenolic compounds from Coix lachryma-jobi var. Ma-yuen. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.R.; Devkota, H.P.; Yahara, S. Chemical analysis of flowers of Bombax ceiba from Nepal. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimitsu, H.; Nishida, M.; Hashimoto, F.; Tanaka, M.; Sakata, Y.; Okawa, M.; Nohara, T. Chromone and flavonol glycosides from Delphinium hybridum cv. “Belladonna Casablanca”. J. Nat. Med. 2007, 61, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.R.; Pu, H.; Patel, M.; Jachens, A.; Gullo, V.P.; Chan, T.M. A new antitumor compound from the plant Oryctanthus sp. as a VEGF receptor binding inhibitor. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4907–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Pan, L.; Naman, C.B.; Deng, Y.; Chai, H.; Keller, W.J.; Kinghorn, A.D. Pyrrole alkaloids with potential cancer chemopreventive activity isolated from a goji berry-contaminated commercial sample of African mango. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5054–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, K.; Yuda, M.; Tanaka, O.; Saruwatari, Y.I.; Fuwa, T.; Jia, M.R.; Ling, Y.K.; Pu, X.F. Chemical Studies on Chinese Traditional Medicine, Dangshen. I. Isolation of (Z)-3- and (E)-2-Hexenyl β-D-Glucosides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 2689–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffreda, P.; Casati, S.; Manzocohi, A. Spectral assignments and reference data complete 1H and 13C NMR spectral assignment of α- And β-adenosine, 2′-deoxyadenosine and their acetate derivatives. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2007, 45, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadernowski, R.; Naczk, M.; Nesterowicz, J. Phenolic acid profiles in some small berries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, P.; Hellström, J.; Törrönen, R. Phenolic acids in berries, fruits, and beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7193–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agati, G.; Azzarello, E.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: Location and functional significance. Plant Sci. 2012, 196, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, J.B.; Williams, C.A. Advances in flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Bilal, M.; Huang, D.F. Role of flavonoids in plant interactions with the environment and against human pathogens—A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, R.; Saito, K. Integrated metabolomics for abiotic stress responses in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 24, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.M.; Chakraborty, D.; Dey, S. Phenolic acids act as signaling molecules in plant-microbe symbioses. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, H.B. Phenolic-storing cells: Keys to programmed cell death and periderm formation in wilt disease resistance and in general defence responses in plants? Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2000, 57, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, H. Bioactive compounds in fruit and juice. Fruit Process. 2004, 1, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, L.; Dueñas, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Baptista, P.; Santos-Buelga, C. Phenolic acids determination by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS in sixteen different Portuguese wild mushrooms species. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nile, S.H.; Park, S.W. Edible berries: Bioactive components and their effect on human health. Nutrition 2014, 30, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, D.; Maggio, B.; Raimondi, M.V.; Plescia, F.; Daidone, G. Recent discoveries of anticancer flavonoids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic acids: Natural versatile molecules with promising therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, B.; Pagano, E.; Montanaro, V.; Fortunato, A.L.; Milic, N.; Borrelli, F. Novel insights into the pharmacology of flavonoids. Phyther. Res. 2013, 27, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Li, G.; Huang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, C.; Ren, B.; Lu, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Chemical constituents from Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 45, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; He, J. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicological aspects of the genus Hosta (Liliaceae): A comprehensive review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 265, 113323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, J.; Attia, F.A.K.; Kang, W.; Wei, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, C. A critical review on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Lilium. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; D’Abrosca, B.; Pacifico, S.; Mastellone, C.; Piscopo, V.; Monaco, P. Spectroscopic identification and antioxidant activity of glucosylated carotenoid metabolites from Cydonia vulgaris fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, J.; Suter, P.J. The structure of a C12-acid from the seed of Phaseolus multiflorus. Tetrahedron 1967, 23, 2417–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.W.; Lim, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, D.Y.; Suh, Y.G.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, J. Hepatoprotective pyrrole derivatives of Lycium chinense fruits. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagumo, S.; Kawai, K.; Nagase, H. Sesquiterpenoids and (Z)-3-hexenyl glucoside from Pertya glabrescens and a glucosidic sesquiterpene from P. scandens. Yakugaku Zasshi 1984, 104, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawabe, A.; Obata, T.; Nochika, Y.; Morita, M.; Yamashita, N.; Matsubara, Y.; Okamoto, T. Investigation of functional molecules in African Celosia argentea L. Stud. Plant Sci. 1999, 6, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, S.; Devkota, H.P.; Joshi, K.R.; Malla, K.J.; Watanabe, T.; Yahara, S. Chemical constituents from the aerial parts and rhizomes of Roscoea purpurea. Jpn. J. Pharmacogn. 2014, 68, 99–100. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hori, K.; Watanabe, T.; Devkota, H.P. Phenolic Acid Derivatives, Flavonoids and Other Bioactive Compounds from the Leaves of Cardiocrinum cordatum (Thunb.) Makino (Liliaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020320
Hori K, Watanabe T, Devkota HP. Phenolic Acid Derivatives, Flavonoids and Other Bioactive Compounds from the Leaves of Cardiocrinum cordatum (Thunb.) Makino (Liliaceae). Plants. 2021; 10(2):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020320
Chicago/Turabian StyleHori, Kengo, Takashi Watanabe, and Hari Prasad Devkota. 2021. "Phenolic Acid Derivatives, Flavonoids and Other Bioactive Compounds from the Leaves of Cardiocrinum cordatum (Thunb.) Makino (Liliaceae)" Plants 10, no. 2: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020320
APA StyleHori, K., Watanabe, T., & Devkota, H. P. (2021). Phenolic Acid Derivatives, Flavonoids and Other Bioactive Compounds from the Leaves of Cardiocrinum cordatum (Thunb.) Makino (Liliaceae). Plants, 10(2), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020320







