Identification of F3H, Major Secondary Metabolite-Related Gene That Confers Resistance against Whitebacked Planthopper through QTL Mapping in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
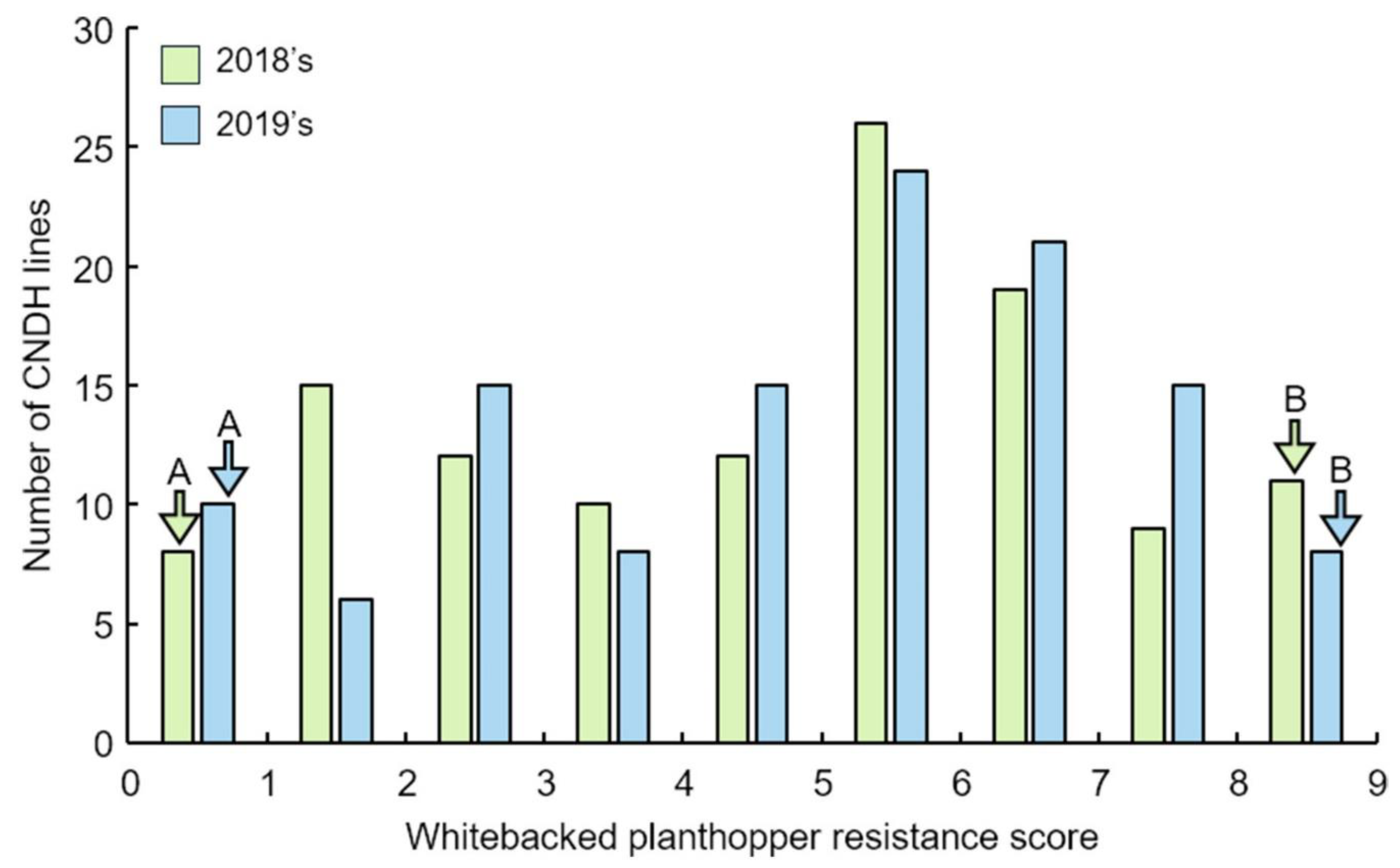
2.1. Analysis of QTLs Associated with WBPH Resistance
2.2. Candidate Gene Search Associated with WBPH Resistance Based on QTL Mapping
2.3. Comparative Analysis of the Selection of Candidate Genes for WBPH Resistance
2.4. Phylogenetic Tree and Homology Sequence Analysis of Candidate Genes
2.5. Relative Expression Levels with Plant Defense Genes
3. Discussions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
4.2. WBPH Rearing
4.3. Evaluation of WBPH Resistance in the CNDH Line
4.4. QTLs Analysis of WBPH Resistance
4.5. Identification of Candidate Genes through QTL Mapping
4.6. Analysis of Expression Levels of Candidate Genes Resistant to WBPH
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, D.K.; Mueller, N.D.; West, P.C.; Foley, J.A. Yield trends are insufficient to double global crop production by 2050. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.T. Occurrence and Population Dynamics of Spiders in Transplanting Rice Fields under Different Levels of Pest Management. Korean J. Ecol. 2005, 28, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.H.; Wen, J.J.; Cai, D.J.; Li, P.; Xu, D.L.; Zhang, S.G. Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus: A new proposed Fiji virus species in the family Reoviridae. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, K.; Suresh, S.; Soundararajan, R.P.; Boopathi, T. Evaluation of resistance in some rice genotypes against Whitebacked Planthopper (WBPH) Sogatella furcifera (Horvath). J. Entomol. Zool. 2017, 5, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, L.; Xie, G.; Ji, C.; Ling, B.; Zhang, M.; Xu, D.; Zhou, G. Transmission characteristics of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus by rice planthoppers. Crop Prot. 2012, 41, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.S.; Ko, J.K.; Ko, J.C.; Kim, B.K.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, Y.D.; Nam, J.K.; Ha, K.Y.; Kim, K.Y.; Baek, M.G.; et al. A Brown Planthopper Resistance and High Quality Rice Variety ‘Chinnong’. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2012, 44, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, J.P.; Jeung, J.U.; Kim, Y.G.; Jena, K.K.; Cho, Y.C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.K.; Hong, H.C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.J.; et al. A Brown Planthopper Resistant and High Grain Quality Rice Variety ‘Anmi’ Developed by Molecular Breeding Method. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2014, 46, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Lee, J.O.; Park, J.S. Studies on the Varietal Resistance of Rice to the White-backed Planthopper, Sogatella furcifera Horvath (III). Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 1973, 12, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.T.; Heu, M.H. Linkage analysis of the resistance genes to whitebacked planthopper (Sogatella furcifera Horvath) in rice. Korean J. Crop Sci. 1984, 29, 136–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.M.; Park, Y.H. Studies of the Life Cycle and Rearing Methods of Whitebacked Planthopper (Sogatella furcifera Horváth). J. Life Sci. 2018, 28, 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Yeo, U.S.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Song, C.S.; Shin, M.S.; Kang, H.W.; Sohn, J.K. Marker Assisted Selection of Brown Planthopper Resistance and Development of Multi-Resistance to Insect and Diseases in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2011, 43, 413–421. [Google Scholar]
- Khush, G.S.; Brar, D.S. Genetics of resistance to insects in crop plants. Adv. Agron. 1991, 45, 223–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.F.; Goto, S.; Tamai, K.; Ichii, M. Role of root hairs and lateral roots in silicon uptake by rice. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Wong, C.C.; Cheng, K.W.; Chen, F. Antioxidant properties in vitro and total phenolic contents in methanol extracts from medicinal plants. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Zhong, W.; Song, D.; Thornton, S.; Jiang, X. E. coli-expressed recombinant norovirus capsid proteins maintain authentic antigenicity and receptor binding capability. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.G.; Hong, S.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, K.Y.; Lim, J.W.; Lee, J.H. Occurrence of stink bugs and pecky rice damage by stink bugs in paddy fields in Gyeonggi-do, Korea. Korean J. Appl. 2009, 48, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, H.; Ikeda, R.; Kaneda, C. New genes for resistance to brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stal, in rice. Jpn. J. Breed. 1984, 39, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yencho, G.C.; Cohen, M.B.; Byrne, P.F. Applications of tagging and mapping insect resistance loci in lants. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethanjali, S.; Kadirvel, P.; Gunathilagaraj, K.; Maheswaran, M. Detection of quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with resistance to whitebacked planthopper (Sogatella furcifera) in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Breed. 2009, 128, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogawa, K.; Liu, G.J.; Shen, J.H. A review on the hyper-susceptibility of Chinese hybrid rice to insect pests. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2003, 17, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Yasui, H. Genetic basis of ovicidal response to whitebacked planthopper (Sogatella furcifera Horvath) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol. Breed. 2003, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Thompson, R. Efficiency of marker-assisted selection in the improvement of quantitative traits. Genetics 1990, 124, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forster, B.P.; Thomas, W.T. Doubled haploids in genetics and plant breeding. Plant Breed. Rev. 2005, 25, 57–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.S.; Wu, Y.R.; Hu, B.; Wu, P.; Cui, H.R.; Shu, Q.Y. QTL for rice grain quality based on a DH population derived from parents with similar apparent amylose content. Euphytica 2002, 128, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Parco, A.; Mew, T.; Magpantay, G.; McCouch, S.; Guiderdoni, E.; Khush, G.S. RFLP mapping of isozymes, RAPD and QTLs for grain shape, brown planthopper resistance in a doubled haploid rice population. Mol. Breed. 1997, 3, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, R.; Khan, M.A.; Asaf, S.; Lee, I.J.; Kim, K.M. Overexpression of OsF3H modulates WBPH stress by alteration of phenylpropanoid pathway at a transcriptomic and metabolomic level in Oryza sativa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucini, L.; Baccolo, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G.; Bavaresco, L.; Trevisan, M. Chitosan treatment elicited defence mechanisms, pentacyclic triterpenoids and stilbene accumulation in grape (Vitis vinifera L.) bunches. Phytochemistry 2018, 156, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Nie, P.; Ding, S.; Zheng, L.; Chen, C.; Feng, R.; Zhou, S. Quantitative proteomic analysis provides insights into rice defense mechanisms against Magnaporthe oryzae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, M.S.; Fitzgerald, H.A.; Yadav, R.C.; Canlas, P.E.; Dong, X.; Ronald, P.C. Evidence for a disease-resistance pathway in rice similar to the NPR1-mediated signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2001, 27, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Yu, J.; Bai, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X. Induced defense responses in rice plants against small brown planthopper infestation. Crop. J. 2014, 2, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Gomi, K.; Matsumura, M.; Takabayashi, J.; Sasaki, K.; Ohashi, Y.; Kanno, H. Whitebacked planthopper–induced disease resistance in rice. In Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia; IRRI, International Rice research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2009; pp. 327–340. ISBN 978-971-22-0251-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Xin, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, L.; Lou, Y.; Lu, J. (E)-β-caryophyllene functions as a host location signal for the rice white-backed planthopper Sogatella furcifera. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 91, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuji, H. Development of disease-resistant rice using regulatory components of induced disease resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazan, K.; Manners, J.M. The interplay between light and jasmonate signalling during defence and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4087–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, G.; Xin, Z.; Ji, R.; Lou, Y. (Z)-3-Hexenal, one of the green leaf volatiles, increases susceptibility of Rice to the white-backed Planthopper Sogatella furcifera. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 33, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treutter, D. Significance of flavonoids in plant resistance: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2006, 4, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, N.T. The molecular biology of disease resistance. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 19, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croteau, R.; Kutchan, T.M.; Lewis, N.G. Natural products (secondary metabolites). Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 24, 1250–1319. [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyne, T.; Pieters, L.; Deelstra, H.; Vlietinck, A. Condensed vegetable tannins: Biodiversity in structure and biological activities. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1999, 27, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.M.; Chia, L.S.; Goh, N.K.; Chia, T.F.; Brouillard, R. Analysis and biological activities of anthocyanins. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marles, M.S.; Ray, H.; Gruber, M.Y. New perspectives on proanthocyanidin biochemistry and molecular regulation. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Toledo, R.T. Health aspects of functional grape seed constituents. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, C.; Di Ferdinando, M.; Fini, A.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as antioxidants and developmental regulators: Relative significance in plants and humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3540–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetinkaya, H.; Kulak, M.; Karaman, M.; Karaman, H.S.; Kocer, F. Flavonoid accumulation behavior in response to the abiotic stress: Can a uniform mechanism be illustrated for all plants? In Flavonoids—From Biosynthesis to Human Health; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Lister, C.E.; Lancaster, J.E.; Walker, J.R. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) activity and its relationship to anthocyanin and flavonoid levels in New Zealand-grown apple cultivars. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1996, 121, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samyor, D.; Das, A.B.; Deka, S.C. Pigmented rice a potential source of bioactive compounds: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, M.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Ha, S.H.; Lim, S.H. Molecular and biochemical analysis of two rice flavonoid 3’-hydroxylase to evaluate their roles in flavonoid biosynthesis in rice grain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmouth, R.C.; Turnbull, J.J.; Welford, R.W.; Clifton, I.J.; Prescott, A.G.; Schofield, C.J. Structure and mechanism of anthocyanidin synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Structure 2002, 10, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev-Yadun, S.; Gould, K.S. Role of anthocyanins in plant defence. In Anthocyanins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, B.; Singh, K. Functional characterization of flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene from Phyllanthus emblica (L.). J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asem, I.D.; Imotomba, R.K.; Mazumder, P.B.; Laishram, J.M. Anthocyanin content in the black scented rice (Chakhao): Its impact on human health and plant defense. Symbiosis 2015, 66, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBPGR-IRRI Rice Advisory Committee. International Board for Plant Genetic Resources. In Descriptors for Rice (Oryza Sativa L.); International Rice Research Institute: Manilla, Philippines, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- De Datta, S.K.; Malabuyoc, J.A.; Aragon, E.L. A field screening technique for evaluating rice germplasm for drought tolerance during the vegetative stage. Field Crops Res. 1988, 19, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Basten, C.J.; Zeng, Z.B. Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5; Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.-G.; Yun, S.; Park, J.-R.; Kim, K.-M. Identification of F3H, Major Secondary Metabolite-Related Gene That Confers Resistance against Whitebacked Planthopper through QTL Mapping in Rice. Plants 2021, 10, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010081
Kim E-G, Yun S, Park J-R, Kim K-M. Identification of F3H, Major Secondary Metabolite-Related Gene That Confers Resistance against Whitebacked Planthopper through QTL Mapping in Rice. Plants. 2021; 10(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eun-Gyeong, Sopheap Yun, Jae-Ryoung Park, and Kyung-Min Kim. 2021. "Identification of F3H, Major Secondary Metabolite-Related Gene That Confers Resistance against Whitebacked Planthopper through QTL Mapping in Rice" Plants 10, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010081
APA StyleKim, E.-G., Yun, S., Park, J.-R., & Kim, K.-M. (2021). Identification of F3H, Major Secondary Metabolite-Related Gene That Confers Resistance against Whitebacked Planthopper through QTL Mapping in Rice. Plants, 10(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010081





