Spartina alterniflora Leaf and Soil Eco-Stoichiometry in the Yancheng Coastal Wetland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
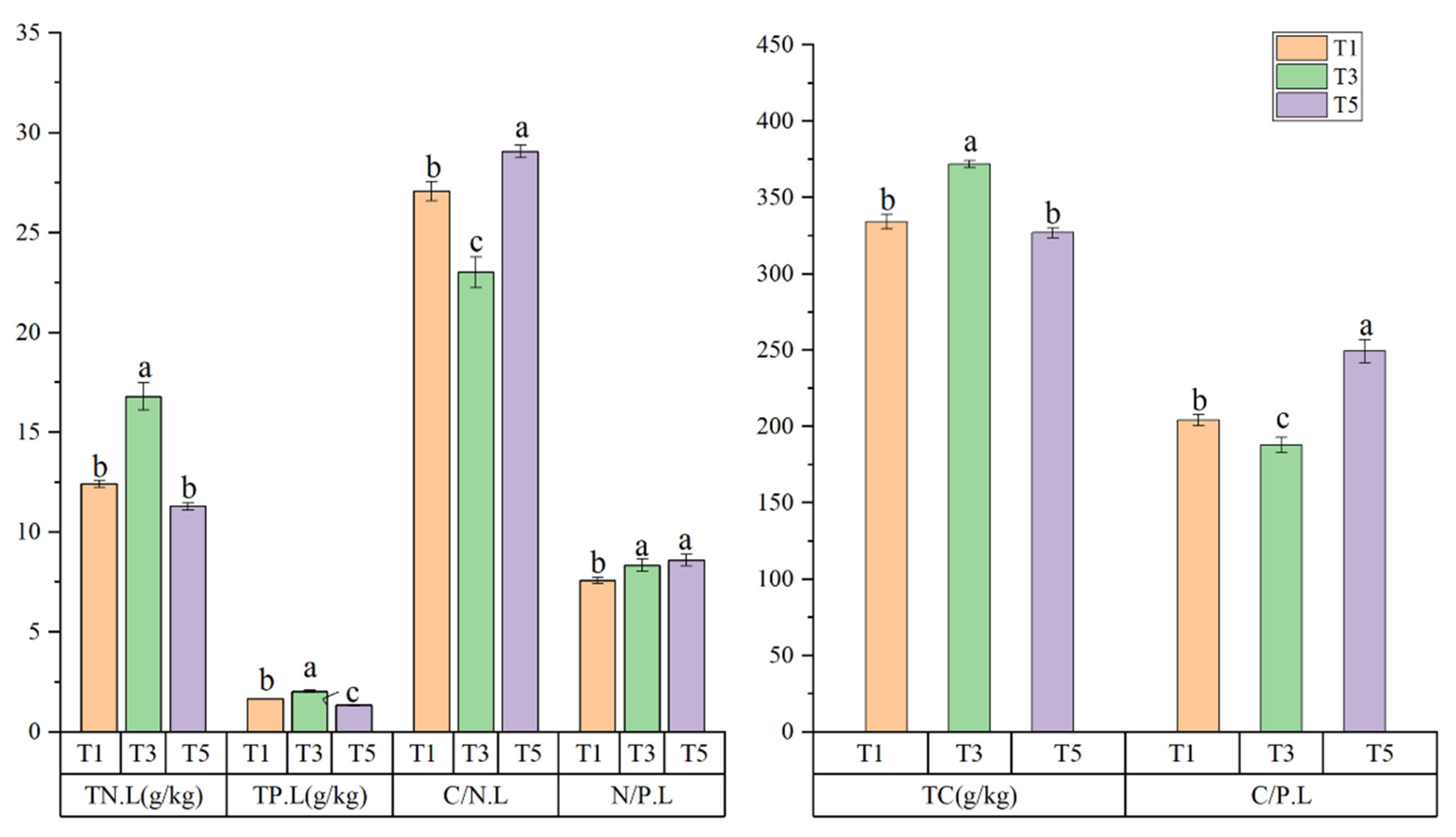
3.1. Stoichiometric Characteristics of C, N, and P in Leaves of S. alterniflora Leaves
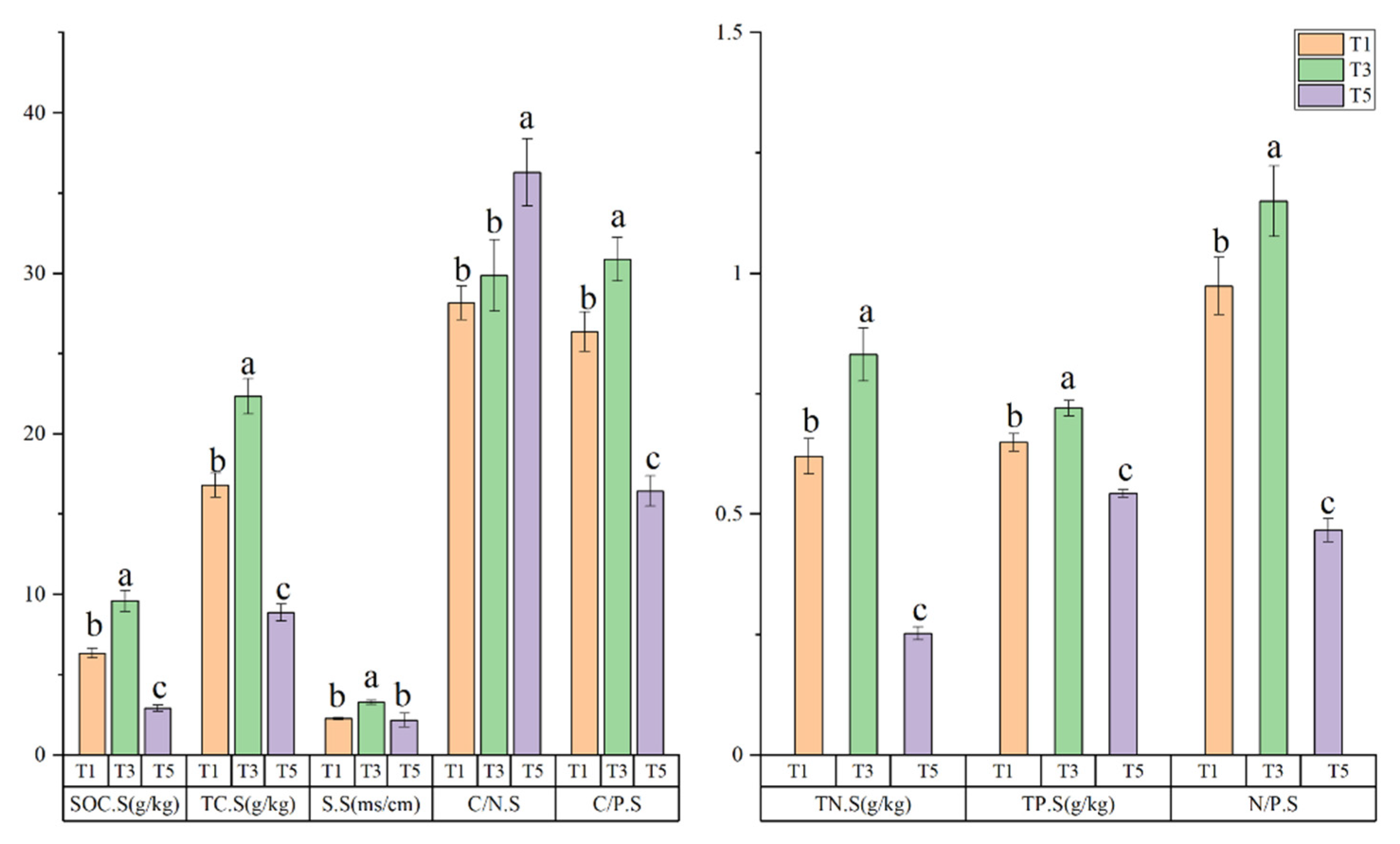
3.2. Stoichiometric and Other Characteristics of Soil C, N, and P
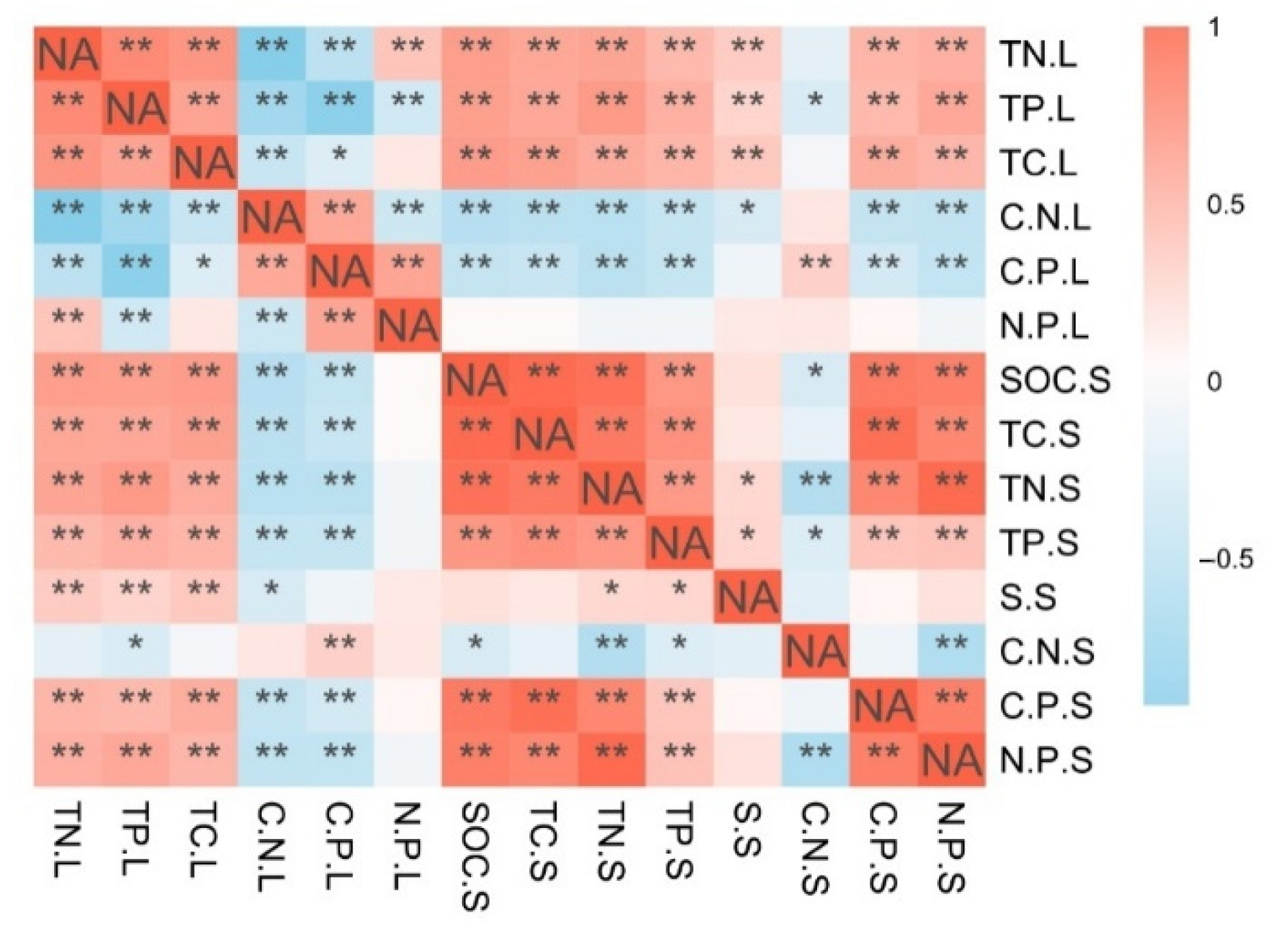
3.3. Relationship between the Leaf and Soil C, N, P Stoichiometric Characteristics and Other Physical and Chemical Properties
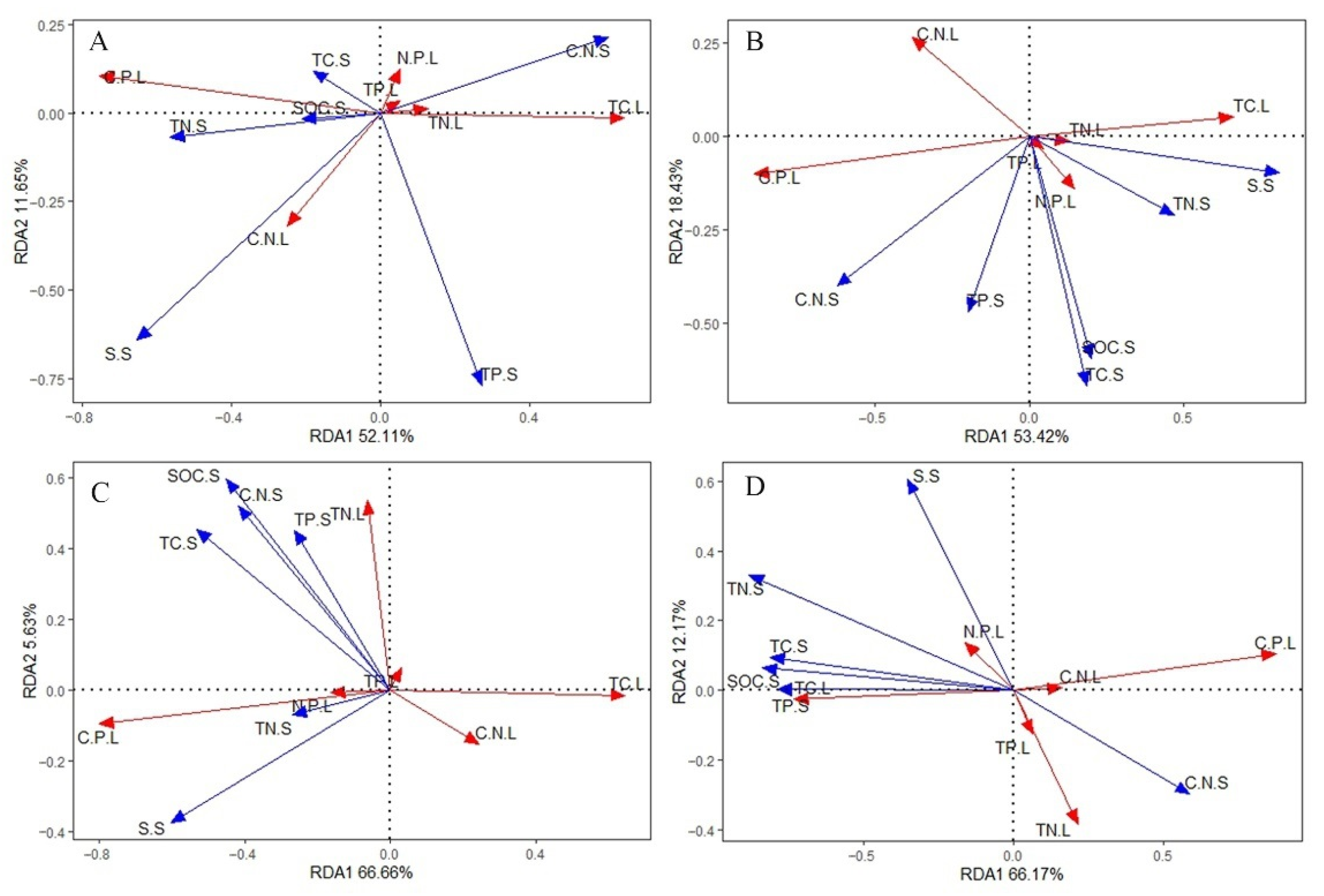
3.4. Effects of Soil Eco-Stoichiometry on Leaf Eco-Stoichiometry
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationships between the Eco-Stoichiometry of S. alterniflora Leaves and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
4.2. Key Soil Factors That Affect Leaf Eco-Stoichiometry
4.3. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Wei, Y. Revised normalized difference nitrogen index (NDNI) for estimating canopy nitrogen concentration in wetlands. Optik 2016, 127, 7676–7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheaves, M.; Brookes, J.; Coles, R.; Freckelton, M.; Groves, P.; Johnston, R.; Wingberg, P. Repair and revitalisation of Australia’s tropical estuaries and coastal wetlands: Opportunities and constraints for the reinstatement of lost function and productivity. Mar. Policy 2014, 47, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Su, X.Z.; Liu, J.H.; Li, B.; Lei, G. Coastal erosion in China under the condition of global climate change and measures for its prevention. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Feagin, R.A.; Innocenti, R.A.; Hu, B.; He, M.; Li, H. Invasion and ecological effects of exotic smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora in China. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 143, 105670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M.; Chang, Y.; Yan, X.; Bu, R.; Zhao, D.; Li, Z. Introduction and Spread of an Exotic Plant, Spartina alterniflora, Along Coastal Marshes of China. Wetlands 2017, 37, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.Q.; Gu, B.H.; Zhou, C.F.; Wang, Z.S.; Deng, Z.F.; Zhi, Y.B.; Li, H.L.; Chen, L.; Yu, D.H.; Liu, Y.H. Spartina invasion in China: Implications for invasive species management and future research. Weed Res. 2007, 47, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Lin, G. Interactions between mangroves and exotic Spartina in an anthropogenically disturbed estuary in southern China. Ecology 2012, 93, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, J. Local competitive effects of introduced Spartina alterniflora on Scirpus mariqueter at Dongtan of Chongming Island, the Yangtze River estuary and their potential ecological consequences. Hydrobiologia 2004, 528, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.M.; Zheng, R.S.; Li, X.; Elmer, W.H.; Wolfe, L.M.; Li, B. Indirect effects of non-native and its fungal pathogen (fusarium palustre) on native saltmarsh plants in China. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A.; Neira, C.; Grosholz, E.D. Invasive Cordgrass Modifies Wetland Trophic Function. Ecology 2006, 87, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.Z.; Luo, Y.Q.; Fang, C.M.; Chen, J.K.; Li, B. Litter pool sizes, decomposition, and nitrogen dynamics in Spartina alterniflora-invaded and native coastal marshlands of the Yangtze Estuary. Oecologia 2008, 156, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, C.; Zhang, L.H.; Wang, W.Q.; Gauci, V.; Marrs, R.; Liu, B.G.; Jia, R.X.; Zeng, C.S. Contrasting nutrient stocks and litter decomposition in stands of native and invasive species in a sub-tropical estuarine marsh. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wilgen, B.W.; Raghu, S.; Sheppard, A.W.; Schaffner, U. Quantifying the social and economic benefits of the biological control of invasive alien plants in natural ecosystems. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 38, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.C.; Lei, Y.B.; Tan, Y.H.; Sun, X.C.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.Q.; Liu, X.Y. Plant nitrogen and phosphorus utilization under invasive pressure in a montane ecosystem of tropical China. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyšek, P.; Richardson, D.M. Traits Associated with Invasiveness in Alien Plants: Where Do we Stand? In Biological Invasions; Nentwig, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 97–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, D.; Both, S.; Bruelheide, H.; Ding, B.-Y.; Gao, M.; Härdtle, W.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Erfmeier, A. Functional trait similarity of native and invasive herb species in subtropical China—Environment-specific differences are the key. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 83, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, J.L.; Glenwinkel, L.A.; Sack, L. Differential Allocation to Photosynthetic and Non-Photosynthetic Nitrogen Fractions among Native and Invasive Species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Llusià, J.; Owen, S.M.; Carnicer, J.; Giambelluca, T.W.; Rezende, E.L.; Waite, W.; Niinemets, Ü. Faster returns on ‘leaf economics’ and different biogeochemical niche in invasive compared with native plant species. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 16, 2171–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.P.; Simões, M.P.; Ferreira, L.F.; Madeira, M.; Gazarini, L.C. Comparison of Biomass and Nutrient Dynamics Between an Invasive and a Native Species in a Mediterranean Saltmarsh. Wetlands 2010, 30, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.L.; Kominoski, J.S.; Danger, M.; Ishida, S.; Iwai, N.; Rubach, A. Can ecological stoichiometry help explain patterns of biological invasions? Oikos 2010, 119, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Porder, S.; Houlton, B.Z.; Chadwick, O.A. Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: Mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen–phosphorus interactions. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 25, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, J.G.; Ravit, B.; Elgersma, K. Feedback in the Plant-Soil System. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 30, 75–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.H.; Chen, G.S. Ecological stoichiometry: A science to explore the complexity of living systems. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 2005, 29, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, Q. Changes in sediment nutrients following Spartina alterniflora invasion in a subtropical estuarine wetland, China. Catena 2019, 180, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Fang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Invasion of Spartina alterniflora Enhanced Ecosystem Carbon and Nitrogen Stocks in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Z. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on biogenic elements in a subtropical coastal mangrove wetland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Zeng, C.; Tong, C.; Chen, G.; Huang, J.; Pan, H.; Peguero, G.; Vallicrosa, H.; et al. The response of stocks of C, N, and P to plant invasion in the coastal wetlands of China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostálek, T.; Münzbergová, Z.; Kladivová, A.; Macel, M. Plant–soil feedback in native vs. invasive populations of a range expanding plant. Plant Soil 2015, 399, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Lu, T.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, W. Effects of Nitrogen Addition on the Characteristics of Foliar and Soil Ecological Stoichiometry in Xishuangbanna Tropical Rainforest, Southwest China. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2020, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Zhu, H. Ecological stoichiometry and invasive strategies of two alien species (Bidens pilosa and Mikania micrantha) in subtropical China. Ecol. Res. 2019, 34, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Wen, R.; Tsou, J.Y.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring Suaeda salsa Spectral Response to Salt Conditions in Coastal Wetlands: A Case Study in Dafeng Elk National Nature Reserve, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; Qin, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Comparisons of ecosystem services among three conversion systems in Yancheng National Nature Reserve. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 609–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Zhu, X.D.; Zou, X.Q.; Gao, J.H. Study on landscape ecosystem of coastal wetlands in Yancheng, Jiangsu Province. Bull. Mar. Sci. Miami 2005, 24, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.A.; Tabatabai, M.A. Automated instruments for the determination of total Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Sulfur, and Oxygen. Soil Environ. Anal. Mod. Instrum. Tech. 2003, 6, 202–246. [Google Scholar]
- Wardle, D.A.; Walker, L.R.; Bardgett, R.D. Ecosystem Properties and Forest Decline in Contrasting Long-Term Chronosequences. Science 2004, 305, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, J.T.; Raynal, D.J. Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Yu, G.R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 40, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.F.; Interlandi, S.J.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Tree growth changes with climate and forest type are associated with relative allocation of nutrients, especially phosphorus, to leaves and wood. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 22, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S.; Koerselman, W. Variation in nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations of wetland plants. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2002, 5, 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Q.; Wang, C.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, C.-S.; Tong, C.; Peñuelas, J. Plant invasive success associated with higher N-use efficiency and stoichiometric shifts in the soil–plant system in the Minjiang River tidal estuarine wetlands of China. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, S.E.; Vitousek, P.M. Nutrient limitation of decomposition in hawaiian forests. Ecology 2000, 81, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessen, D.O.; Ågren, G.I.; Anderson, T.R.; Elser, J.J.; De Ruiter, P.C. Carbon Sequestration in Ecosystems: The Role of Stoichiometry. Ecology 2004, 85, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGroddy, M.E.; Daufresne, T.; Hedin, L.O. Scaling of C:N:P Stoichiometry in Forests worldwide: Implications of Terrestrial Redfield-Type ratios. Ecology 2004, 85, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wang, B.; Xin, M.; Wang, M.; He, X.; Wei, Q.; Shi, X.; Sun, X. Characteristics of Vegetation Carbon, Nitrogen, and C/N Ratio in a Tamarix chinensis Coastal Wetland of China. Clean Soil Air Water 2019, 47, 1800452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, L.; Tang, Z.; Fang, J. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations of woody plants differ in responses to climate, soil and plant growth form. Ecography 2013, 36, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zerbe, S.; Han, W.; Thevs, N.; Li, W.; He, P.; Schmitt, A.O.; Liu, Y.; Ji, C. Nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of common reed (Phragmites australis) and its relationship to nutrient availability in northern China. Aquat. Bot. 2014, 112, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springob, G.; Kirchmann, H. Bulk soil C to N ratio as a simple measure of net N mineralization from stabilized soil organic matter in sandy arable soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Rousk, J. Salt effects on the soil microbial decomposer community and their role in organic carbon cycling: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Bai, J.; Zhang, G.; Jia, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Effects of water and salinity regulation measures on soil carbon sequestration in coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta. Geoderma 2018, 319, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Zeng, C.S.; Shao, J.J.; Zhou, X.H. Plant nutrient dynamics and stoichiometric homeostasis of invasive species Spartina alterniflora and native Cyperus malaccensis var. brevifolius in the Minjiang River estuarine wetlands. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wilcox, K.R.; Pierre, K.L.; Knapp, A.K.; Han, X.; Smith, M.D. Stoichiometric homeostasis predicts plant species dominance, temporal stability, and responses to global change. Ecology 2015, 96, 2328–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, X.; Cui, L.; Li, W.; Lei, Y.; Dou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhai, X. Spartina alterniflora Leaf and Soil Eco-Stoichiometry in the Yancheng Coastal Wetland. Plants 2021, 10, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010013
Zuo X, Cui L, Li W, Lei Y, Dou Z, Liu Z, Cai Y, Zhai X. Spartina alterniflora Leaf and Soil Eco-Stoichiometry in the Yancheng Coastal Wetland. Plants. 2021; 10(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Xueyan, Lijuan Cui, Wei Li, Yinru Lei, Zhiguo Dou, Zhijun Liu, Yang Cai, and Xiajie Zhai. 2021. "Spartina alterniflora Leaf and Soil Eco-Stoichiometry in the Yancheng Coastal Wetland" Plants 10, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010013
APA StyleZuo, X., Cui, L., Li, W., Lei, Y., Dou, Z., Liu, Z., Cai, Y., & Zhai, X. (2021). Spartina alterniflora Leaf and Soil Eco-Stoichiometry in the Yancheng Coastal Wetland. Plants, 10(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010013




