GLP-1-Mediated Pregnancy and Neonatal Complications in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. mRNA Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Real-Time PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
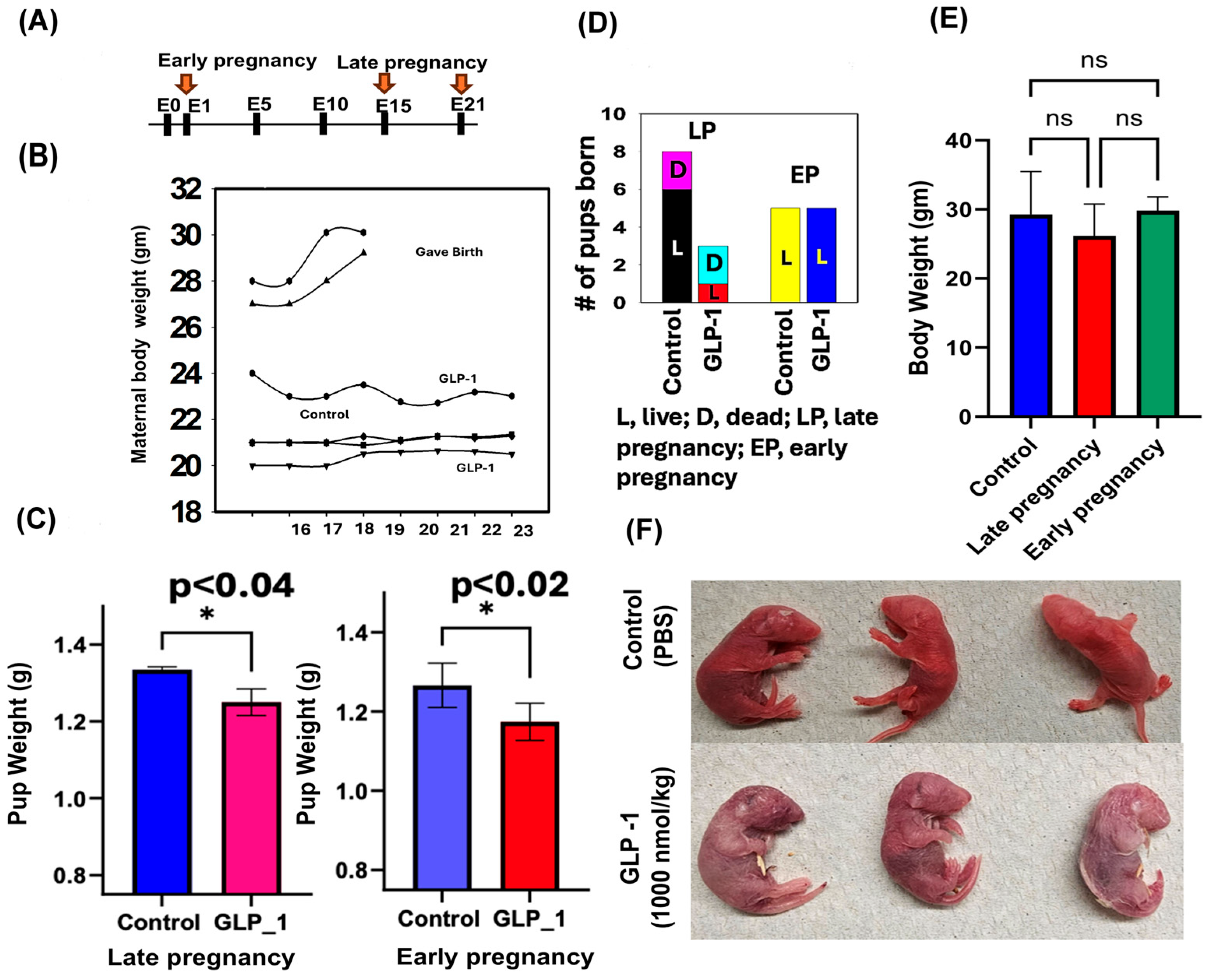
3.1. Morphological Changes
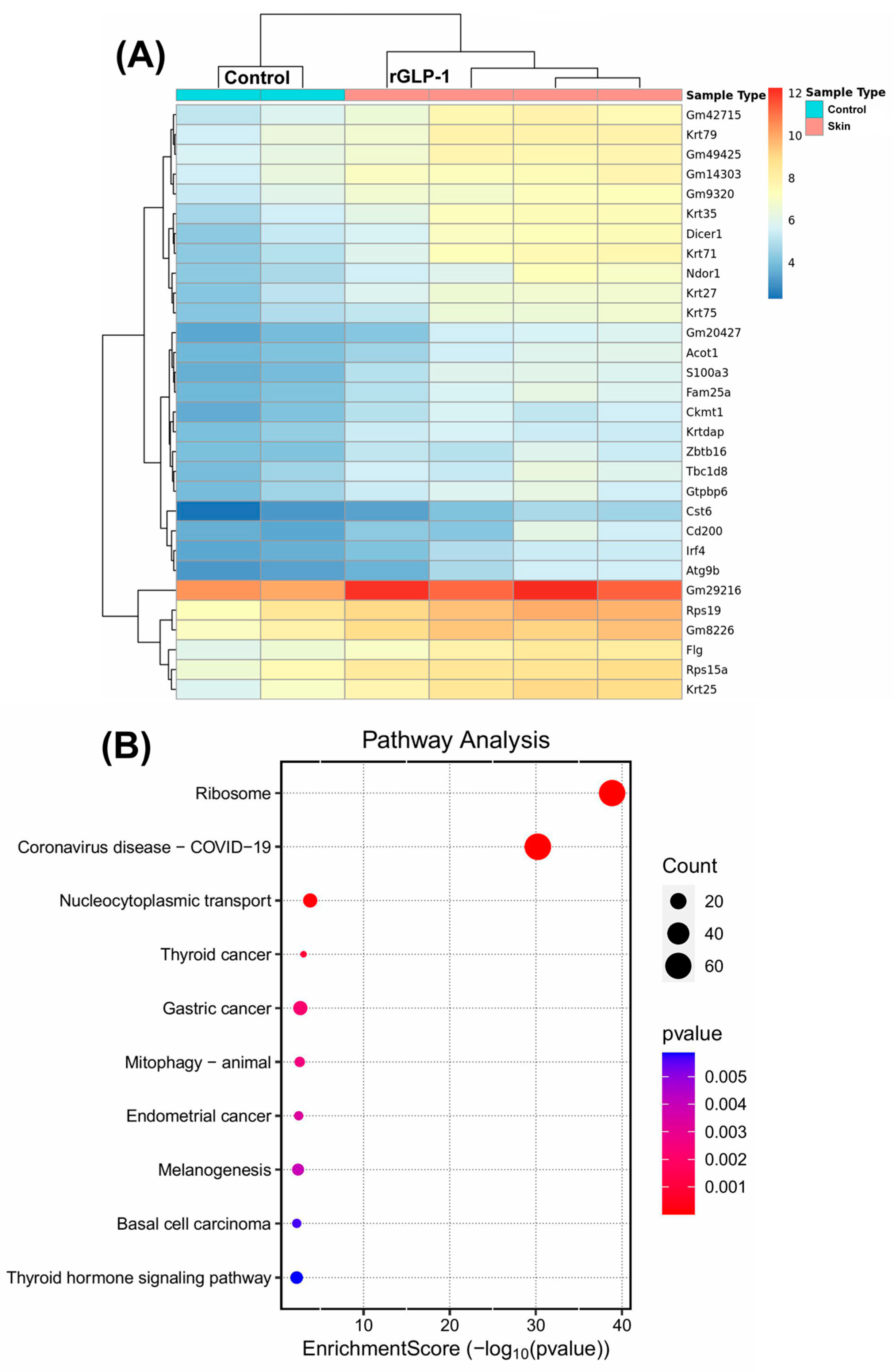
3.1.1. Molecular Changes in the Skin
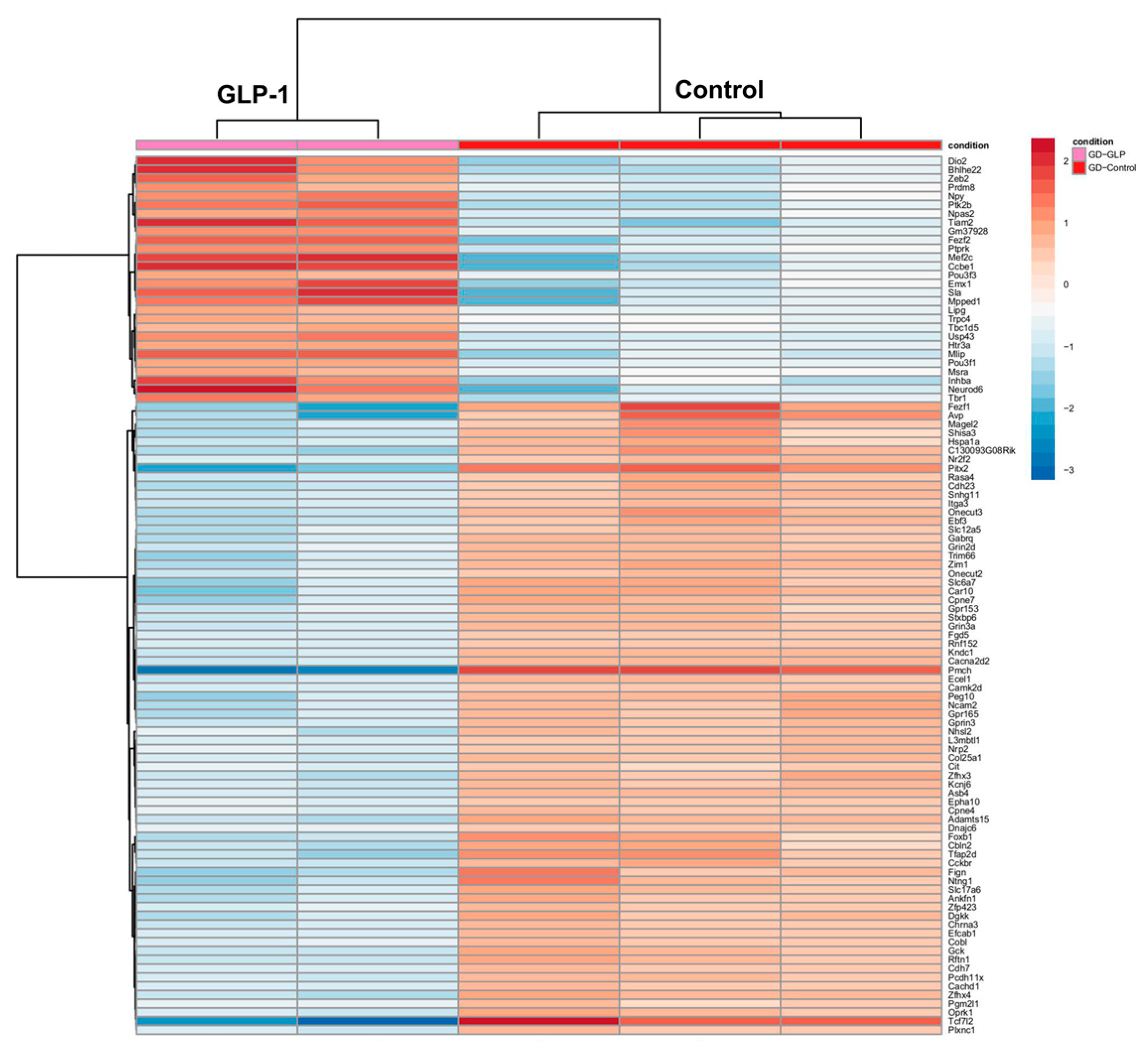
3.1.2. Molecular Changes in the Brain
3.1.3. Molecular Changes in the Lung
3.1.4. Molecular Changes in the Liver
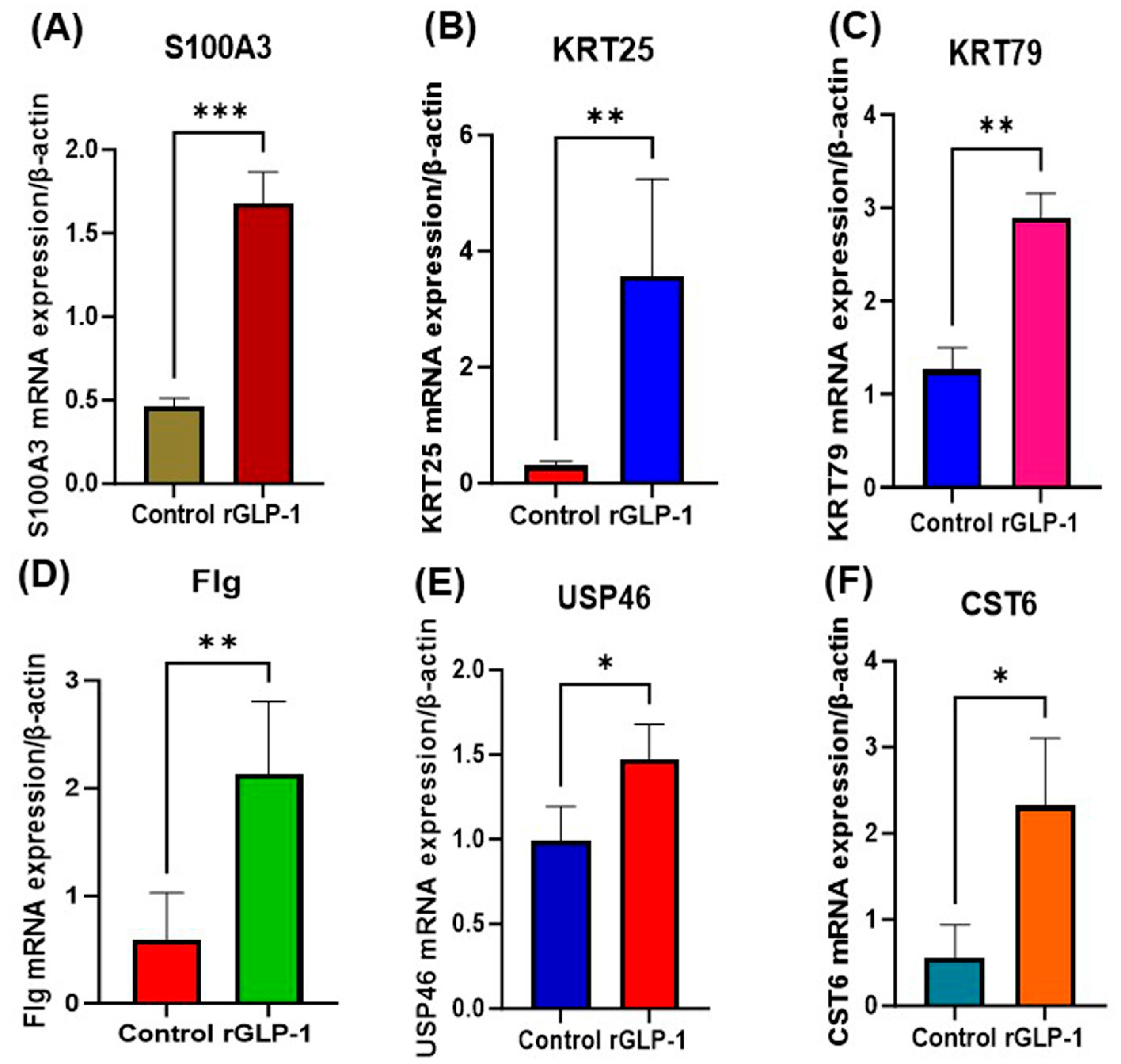
3.2. Real-Time PCR Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Skin
4.2. Brain
4.3. Liver
4.4. Lungs
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EP | Early Pregnancy |
| LP | Late Pregnancy |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| GO | Gene Ontologies |
| GLP-1Ras | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists |
| PCOS | Polycystic ovary syndrome |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| rGLP-1 | recombinant GLP-1 |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
References
- Collins, L.; Costello, R.A. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551568/ (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Cesta, C.E.; Rotem, R.; Bateman, B.T.; Chodick, G.; Cohen, J.M.; Furu, K.; Gissler, M.; Huybrechts, K.F.; Kjerpeseth, L.J.; Leinonen, M.K.; et al. Safety of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Other Second-Line Antidiabetics in Early Pregnancy. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, K.; Shechtman, S.; Weber-Schoendorfer, C.; Diav-Citrin, O.; Murad, R.H.; Berlin, M.; Hazan, A.; Richardson, J.L.; Eleftheriou, G.; Rousson, V.; et al. Use of GLP-1 receptor agonists in early pregnancy and reproductive safety: A multicentre, observational, prospective cohort study based on the databases of six Teratology Information Services. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e083550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumolt, J.H.; Rosario, F.J.; Kramer, A.C.; Horwitz, S.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Maternal glucagon-like peptide-1 is positively associated with fetal growth in pregnancies complicated with obesity. Clin. Sci. 2023, 137, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Lu, C.; Zang, T.; Dzyuba, B.; Shao, J. Maternal GLP-1 receptor activation inhibits fetal growth. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 326, E268–E276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, M.P.; Kampmeijer, A.; Jimenez, J.; Zia, S.; Vanbree, R.; Verbist, G.; Toelen, J.; Deprest, J.A. The Effect of Transplacental Administration of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 on Fetal Lung Development in the Rabbit Model of Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2016, 39, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, D.R.P.; Stenvers, D.J.; Malekzadeh, A.; Holleman, F.; Painter, R.C.; Siegelaar, S.E. Effects of GLP-1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors during pregnancy and lactation on offspring outcomes: A systematic review of the evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1215356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, C.A.; Capozzi, M.E.; Varanko, A.K.; Tong, J.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Campbell, J.E.; Chilkoti, A. Sustained release of a GLP-1 and FGF21 dual agonist from an injectable depot protects mice from obesity and hyperglycemia. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz9890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borner, T.; Geisler, C.E.; Fortin, S.M.; Cosgrove, R.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Dogra, M.; Doebley, S.; Sanchez-Navarro, M.J.; Leon, R.M.; Gaisinsky, J.; et al. GIP Receptor Agonism Attenuates GLP-1 Receptor Agonist-Induced Nausea and Emesis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, R.F.; Seif, K.E.; Reece, E.A. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use in pregnancy: A review. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2025, 232, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xu, D.; Xiao, H.; Dai, Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. Developmental toxicity and programming alterations of multiple organs in offspring induced by medication during pregnancy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 460–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.; Sousa, N. Maternal hormonal milieu influence on fetal brain development. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e00920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- List, J.F.; He, H.; Habener, J.F. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and proglucagon expression in mouse skin. Regul. Pept. 2006, 134, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Thompson, B.; Fisk, J.N.; Nebert, D.W.; Bruford, E.A.; Vasiliou, V.; Bunick, C.G. Update of the keratin gene family: Evolution, tissue-specific expression patterns, and relevance to clinical disorders. Hum. Genom. 2022, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, E.; Nillni, E.A.; Sanchez, V.C.; Stuart, R.C.; Good, D.J. Deletion of the Nhlh2 transcription factor decreases the levels of the anorexigenic peptides alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and thyrotropin-releasing hormone and implicates prohormone convertases I and II in obesity. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Han, Y.; Gao, S.; Dong, W.; Yu, Y. The Physiological Functions and Polymorphisms of Type II Deiodinase. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 38, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yu, K.; Lu, F.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.N.; Zhao, C.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Mu, D.; et al. Transcriptional Regulator ZEB2 Is Essential for Bergmann Glia Development. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahara, R.; Matono, T.; Sugihara, T.; Matsuki, Y.; Yamane, M.; Okamoto, T.; Miyoshi, K.; Nagahara, T.; Okano, J.I.; Koda, M.; et al. Gene Expression Analysis of the Activating Factor 3/Nuclear Protein 1 Axis in a Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Mouse Model. Yonago Acta Med. 2019, 62, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Seo, J.; Lim, C.; Yang, L.; Shiratsuchi, T.; Lee, M.-H.; Chowdhury, R.R.; Kasahara, H.; Kim, J.-S.; Oh, S.P.; et al. Mitochondrial ATP transporter Ant2 depletion impairs erythropoiesis and B lymphopoiesis. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldbrügge, L.; Splith, K.; Kämmerer, I.; Richter, S.; Riddermann, A.; Ortiz Galindo, S.A.; Krenzien, F.; Müller, T.; Csizmadia, E.; Pratschke, J.; et al. Ecto-Nucleotide Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase-2 (NTPDase2) Deletion Increases Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Okazaki, Y.; Iwane, A.; Hara, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Awazawa, M.; Soeda, K.; Matsushita, M.; Sasako, T.; Yoshimura, K.; et al. Activin B improves glucose metabolism via induction of Fgf21 and hepatic glucagon resistance. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Gene Description | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| CST6 | Cystatin 6 | GAACTTGTCACCCACCGACC TTTGGTGTCTCGGAAGTAGTAGA |
| KRT25 | Keratin 25 | CAACGCCAACGCTGTACTG ACGTCAGCCTCTACGCTCT |
| Flg | Flaggrin | ATGTCCGCTCTCCTGGAAAG TGGATTCTTCAAGACTGCCTGTA |
| RPs19 | Ribosomal Protein S19 | CAGCAGGAGTTCGTCAGAGC CACCCATTCGGGGACTTTCA |
| Krt 79 | Keratin 79 | GTCCAGGCAGACTTTCTCCAC ACATAGTCACTGAGCTGTAGCTG |
| Krt 35 | Keratin 35 | ATGACTGTCCGAAACATCGCC TTGACCAATCCGAAGTAGTGTTC |
| USP46 | Ubiquitin specific peptidase 46 | ATGACTGTCCGAAACATCGCC TTGACCAATCCGAAGTAGTGTTC |
| S100a3 | S100 calcium binding domain a3 | CAGTAGCTGCCATCGTGTG TACTCCCCAAAGTCCACTTCG |
| B-Actin | HouseKeeping gene | ATGACCCAAGCCGAGAAGG CGGCCAAGTCTTAGAGTTGTTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramamoorthy, R.; Carden, A.K.; Hussain, H.; Druyan, B.Z.; Chen, P.P.; Hajjar, R.; Fernandez, C.; Elumalai, N.; Rashed, A.B.; Young, K.; et al. GLP-1-Mediated Pregnancy and Neonatal Complications in Mice. J. Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13030029
Ramamoorthy R, Carden AK, Hussain H, Druyan BZ, Chen PP, Hajjar R, Fernandez C, Elumalai N, Rashed AB, Young K, et al. GLP-1-Mediated Pregnancy and Neonatal Complications in Mice. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2025; 13(3):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamamoorthy, Rajalakshmi, Arianna K. Carden, Hussain Hussain, Brian Z. Druyan, Ping Ping Chen, Rima Hajjar, Carmen Fernandez, Nila Elumalai, Amirah B. Rashed, Karen Young, and et al. 2025. "GLP-1-Mediated Pregnancy and Neonatal Complications in Mice" Journal of Developmental Biology 13, no. 3: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13030029
APA StyleRamamoorthy, R., Carden, A. K., Hussain, H., Druyan, B. Z., Chen, P. P., Hajjar, R., Fernandez, C., Elumalai, N., Rashed, A. B., Young, K., Speciale, A. R., West, E. M., Marbin, S., Safro, B., Bishop, I. J., Jayakumar, A. R., Sanchez-Ramos, L., & Paidas, M. J. (2025). GLP-1-Mediated Pregnancy and Neonatal Complications in Mice. Journal of Developmental Biology, 13(3), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13030029







