Drosophila COMPASS Complex Subunits Set1 and Ash2 Are Required for Oocyte Determination and Maintenance of the Synaptonemal Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drosophila Husbandry
2.2. Germline-Specific RNAi
2.3. Ovaries Immunostaining
2.4. Signal Analysis and Quantification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Set1 and Ash2 Are Required for Primary Oocyte Determination
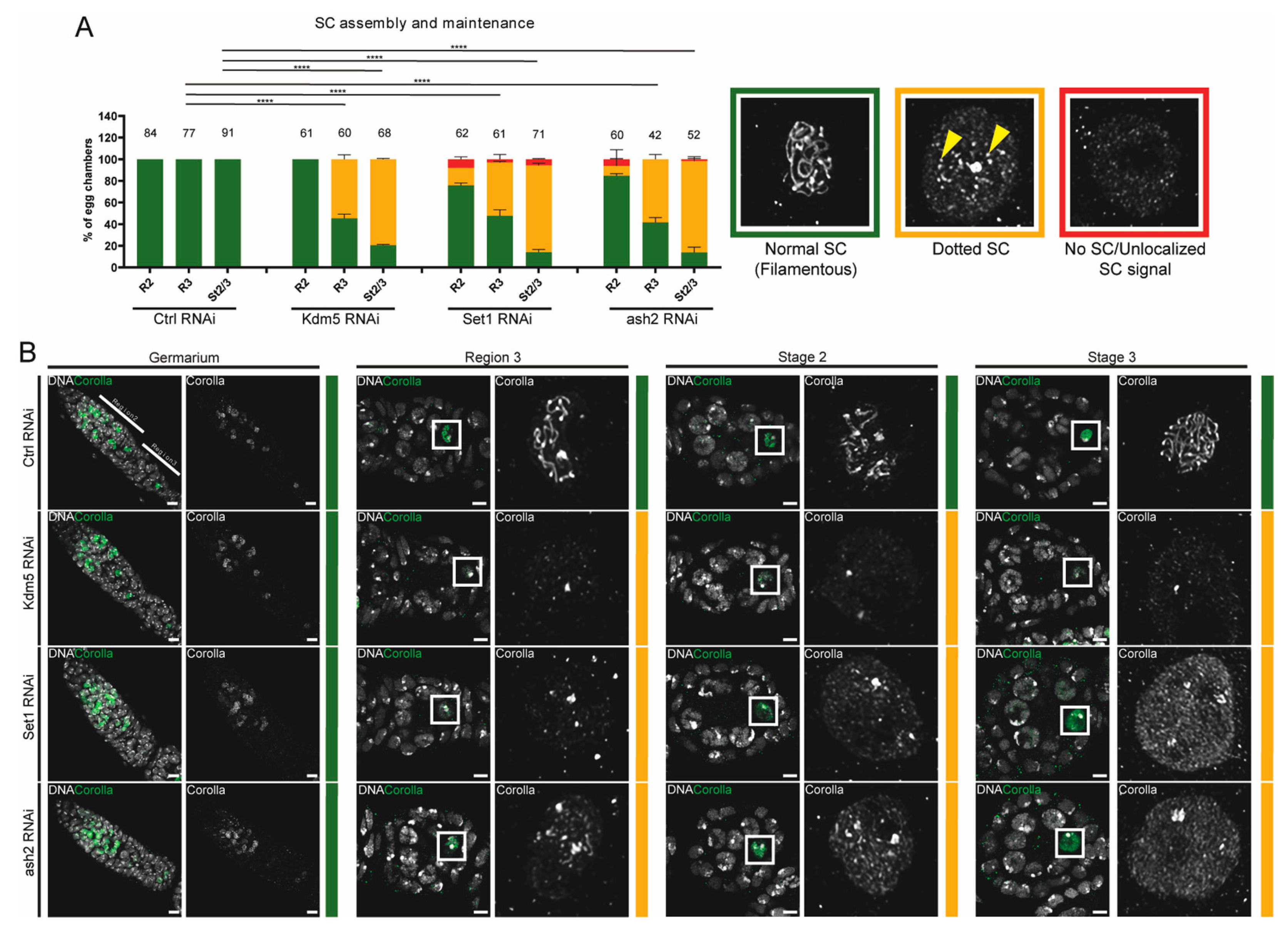
3.2. Set1 and Ash2 Are Required for Maintenance of SC Assembly
3.3. Delayed Oocyte Determination Fails to Rescue SC Assembly
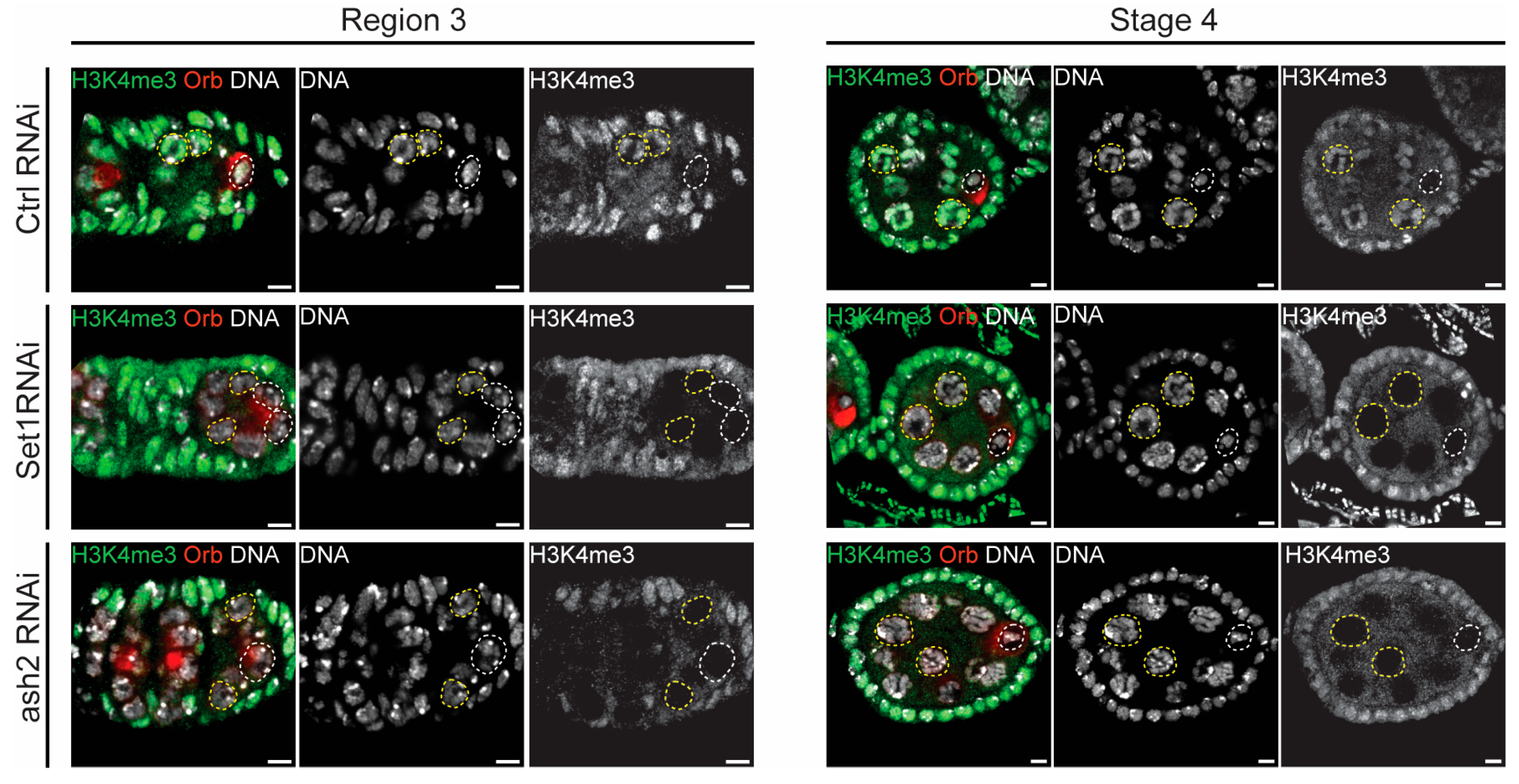
3.4. Set1 and Ash2 Are Required for Germline H3K4 Trimethylation
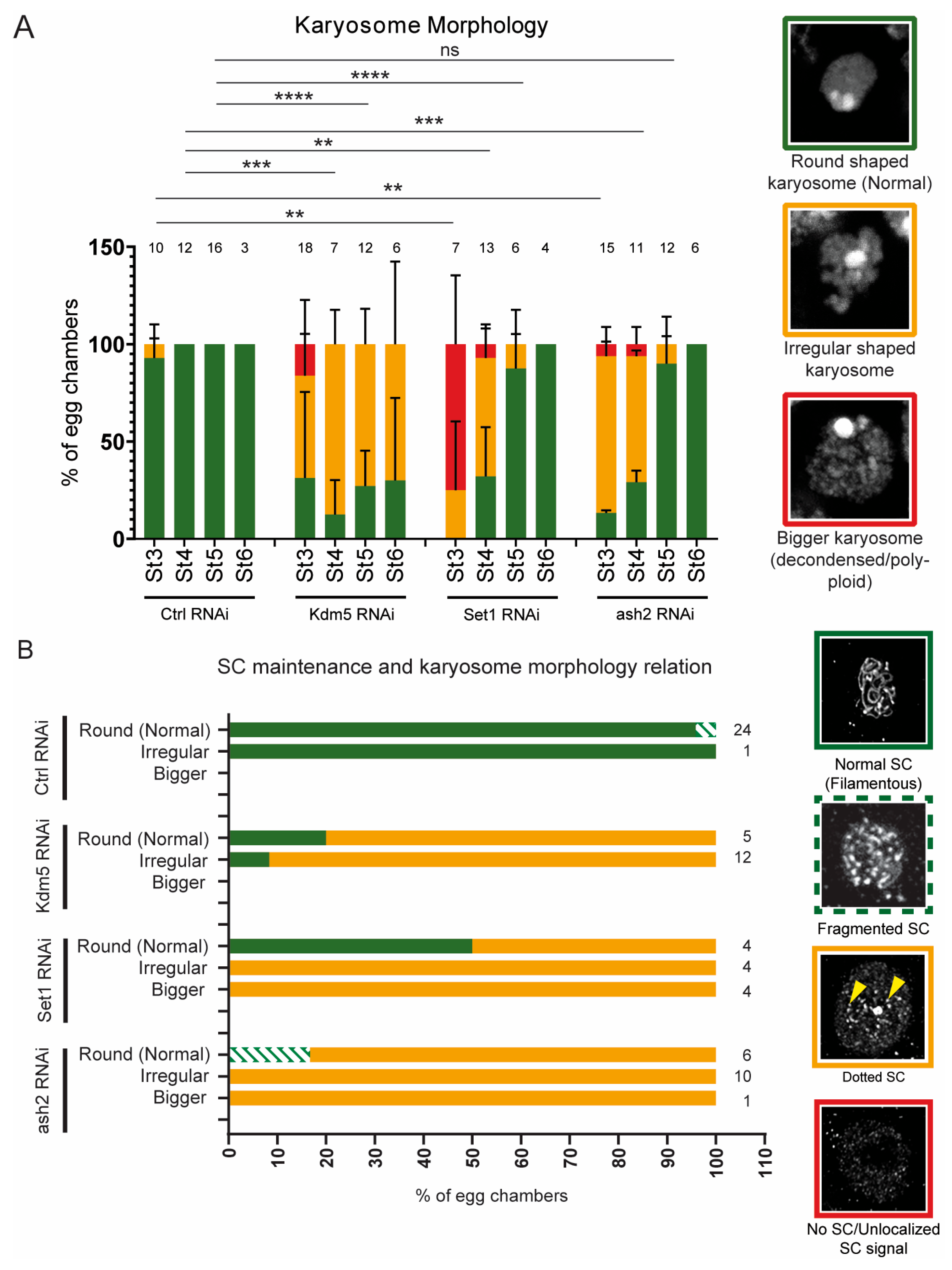
3.5. Delayed Karyosome Formation Does Not Correlate with Recovery of SC Assembly
4. Discussion
5. Final Remarks and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niu, W.; Spradling, A.C. Mouse oocytes develop in cysts with the help of nurse cells. Cell 2022, 185, 2576–2590.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan-Miklos, S.; Cooley, L. Intercellular cytoplasm transport during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 1994, 165, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.R.; St Johnston, D. The origin of asymmetry: Early polarisation of the Drosophila germline cyst and oocyte. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, R438–R449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matova, N.; Cooley, L. Comparative aspects of animal oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2001, 231, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spradling, A.C.; Niu, W.; Yin, Q.; Pathak, M.; Maurya, B. Conservation of oocyte development in germline cysts from Drosophila to mouse. Elife 2022, 11, e83230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Costa, P.; McCarthy, A.; Prudencio, P.; Greer, C.; Guilgur, L.G.; Becker, J.D.; Secombe, J.; Rangan, P.; Martinho, R.G. Early programming of the oocyte epigenome temporally controls late prophase I transcription and chromatin remodelling. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, S.; Liu, H.; Kaneko, N.; Ooga, M.; Nagata, M.; Aoki, F. Alterations in epigenetic modifications during oocyte growth in mice. Reproduction 2007, 133, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, R. Chromatin modifications in the germinal vesicle (GV) of mammalian oocytes. Dev. Biol. 2006, 292, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Khawar, M.B.; Liu, C.; Li, W. The histone codes for meiosis. Reproduction 2017, 154, R65–R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, S.Z.; Ghildiyal, M.; Pang, L.Y.; Spradling, A.C. Differentiating Drosophila female germ cells initiate Polycomb silencing by regulating PRC2-interacting proteins. Elife 2020, 9, e56922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yeh, Y.H.; Munakata, Y.; Abe, H.; Sakashita, A.; Maezawa, S.; Vidal, M.; Koseki, H.; Hunter, N.; Schultz, R.M.; et al. PRC1-mediated epigenetic programming is required to generate the ovarian reserve. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovino, N.; Ciabrelli, F.; Cavalli, G. PRC2 controls Drosophila oocyte cell fate by repressing cell cycle genes. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feijao, T.; Marques, B.; Silva, R.D.; Carvalho, C.; Sobral, D.; Matos, R.; Tan, T.; Pereira, A.; Morais-de-Sa, E.; Maiato, H.; et al. Polycomb group (PcG) proteins prevent the assembly of abnormal synaptonemal complex structures during meiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2204701119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Zhao, H.; Dan, J.; Kim, S.; Hardikar, S.; Hollowell, D.; Lin, K.; Lu, Y.; Takata, Y.; Shen, J.; et al. Maternal Setdb1 Is Required for Meiotic Progression and Preimplantation Development in Mouse. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eymery, A.; Liu, Z.; Ozonov, E.A.; Stadler, M.B.; Peters, A.H. The methyltransferase Setdb1 is essential for meiosis and mitosis in mouse oocytes and early embryos. Development 2016, 143, 2767–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Lee, K.S.; Park, J.S.; Yu, K.; Paik, S.G.; Kang, Y.K. dSETDB1 and SU(VAR)3-9 sequentially function during germline-stem cell differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, E.; Moon, W.; Wang, S.; Smith, K.; Hazelrigg, T. Histone methylation is required for oogenesis in Drosophila. Development 2007, 134, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangan, P.; Malone, C.D.; Navarro, C.; Newbold, S.P.; Hayes, P.S.; Sachidanandam, R.; Hannon, G.J.; Lehmann, R. piRNA production requires heterochromatin formation in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, K.; Kotb, N.M.; Lemus, A.; Martin, E.T.; McCarthy, A.; Camacho, J.; Iqbal, A.; Valm, A.M.; Sammons, M.A.; Rangan, P. A feedback loop between heterochromatin and the nucleopore complex controls germ-cell-to-oocyte transition during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev. Cell 2023, 58, 2580–2596.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassis, J.A.; Kennison, J.A.; Tamkun, J.W. Polycomb and Trithorax Group Genes in Drosophila. Genetics 2017, 206, 1699–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, S.J.; Paro, R. Trithorax and Polycomb group-dependent regulation: A tale of opposing activities. Development 2015, 142, 2876–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuettengruber, B.; Martinez, A.M.; Iovino, N.; Cavalli, G. Trithorax group proteins: Switching genes on and keeping them active. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, P.; Vakoc, C.R. WRAD: Enabler of the SET1-family of H3K4 methyltransferases. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2012, 11, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallson, G.; Hollebakken, R.E.; Li, T.; Syrzycka, M.; Kim, I.; Cotsworth, S.; Fitzpatrick, K.A.; Sinclair, D.A.; Honda, B.M. dSet1 is the main H3K4 di- and tri-methyltransferase throughout Drosophila development. Genetics 2012, 190, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, M.; Herz, H.M.; Smith, E.R.; Zhang, Y.; Jackson, J.; Washburn, M.P.; Florens, L.; Eissenberg, J.C.; Shilatifard, A. The COMPASS family of H3K4 methylases in Drosophila. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 4310–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.; Krogan, N.J.; Dover, J.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Johnston, M.; Greenblatt, J.F.; Shilatifard, A. COMPASS: A complex of proteins associated with a trithorax-related SET domain protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12902–12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, C.W.; Huang, J.; Belton, C.; Reinhardt, S.; Dahl, A.; Andrews, S.; Stewart, A.F.; Kranz, A.; Kelsey, G. Loss of histone methyltransferase SETD1B in oogenesis results in the redistribution of genomic histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brici, D.; Zhang, Q.; Reinhardt, S.; Dahl, A.; Hartmann, H.; Schmidt, K.; Goveas, N.; Huang, J.; Gahurova, L.; Kelsey, G.; et al. Setd1b, encoding a histone 3 lysine 4 methyltransferase, is a maternal effect gene required for the oogenic gene expression program. Development 2017, 144, 2606–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, T.; Xin, T.; He, J.; Tan, J.; Gao, Y.; Feng, S.; He, L.; Zhao, G.; Li, M. dBre1/dSet1-dependent pathway for histone H3K4 trimethylation has essential roles in controlling germline stem cell maintenance and germ cell differentiation in the Drosophila ovary. Dev. Biol. 2013, 379, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Neumuller, R.A.; Buckner, M.; Ayers, K.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Yang-Zhou, D.; Pan, L.; Wang, X.; Kelley, C.; et al. A regulatory network of Drosophila germline stem cell self-renewal. Dev. Cell 2014, 28, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doren, M.; Williamson, A.L.; Lehmann, R. Regulation of zygotic gene expression in Drosophila primordial germ cells. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaunova, L.; Ohkura, H.; Breuer, M. Kdm5/Lid Regulates Chromosome Architecture in Meiotic Prophase I Independently of Its Histone Demethylase Activity. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.Q.; Zhou, R.; Czech, B.; Liu, L.P.; Holderbaum, L.; Yang-Zhou, D.; Shim, H.S.; Tao, R.; Handler, D.; Karpowicz, P.; et al. A genome-scale shRNA resource for transgenic RNAi in Drosophila. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lantz, V.; Chang, J.S.; Horabin, J.I.; Bopp, D.; Schedl, P. The Drosophila orb RNA-binding protein is required for the formation of the egg chamber and establishment of polarity. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, J.R.; St Johnston, D. The role of BicD, Egl, Orb and the microtubules in the restriction of meiosis to the Drosophila oocyte. Development 2000, 127, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, O.M.; Cullen, C.F.; Ohkura, H. NHK-1 phosphorylates BAF to allow karyosome formation in the Drosophila oocyte nucleus. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, O.M.; Breuer, M.; Cullen, C.F.; Ito, T.; Ohkura, H. The meiotic recombination checkpoint suppresses NHK-1 kinase to prevent reorganisation of the oocyte nucleus in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.E.; Miller, D.E.; Miller, A.L.; Hawley, R.S. Female Meiosis: Synapsis, Recombination, and Segregation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2018, 208, 875–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzova, M.N.; Parfenov, V.N. Karyosphere in oogenesis and intranuclear morphogenesis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1993, 144, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, J.; Gilmutdinov, R.; Wang, L.; Shidlovskii, Y.; Schedl, P. The Drosophila CPEB Protein Orb Specifies Oocyte Fate by a 3′UTR-Dependent Autoregulatory Loop. Genetics 2019, 213, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, M.; Hira, S.; Nakamura, K.; Nakamura, S.; Kimura, H.; Sato, M.; Kobayashi, S. H3K36 Trimethylation-Mediated epigenetic regulation is activated by bam and promotes germ cell differentiation during early oogenesis in drosophila. Biol. Open 2015, 4, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorth, P. Gal4 in the Drosophila female germline. Mech. Dev. 1998, 78, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.Y.; DeLuca, S.; Zhu, H.; Urban, J.M.; Spradling, A.C. Chromatin and gene expression changes during female Drosophila germline stem cell development illuminate the biology of highly potent stem cells. Elife 2023, 12, e90509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabrita, B.; Enyioko, M.; Martinho, R.G. Drosophila COMPASS Complex Subunits Set1 and Ash2 Are Required for Oocyte Determination and Maintenance of the Synaptonemal Complex. J. Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13030030
Cabrita B, Enyioko M, Martinho RG. Drosophila COMPASS Complex Subunits Set1 and Ash2 Are Required for Oocyte Determination and Maintenance of the Synaptonemal Complex. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2025; 13(3):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabrita, Brigite, Mary Enyioko, and Rui Gonçalo Martinho. 2025. "Drosophila COMPASS Complex Subunits Set1 and Ash2 Are Required for Oocyte Determination and Maintenance of the Synaptonemal Complex" Journal of Developmental Biology 13, no. 3: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13030030
APA StyleCabrita, B., Enyioko, M., & Martinho, R. G. (2025). Drosophila COMPASS Complex Subunits Set1 and Ash2 Are Required for Oocyte Determination and Maintenance of the Synaptonemal Complex. Journal of Developmental Biology, 13(3), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb13030030





