Abstract
The proliferation of trophoblast stem (TS) cells and their differentiation into multiple lineages are pivotal for placental development and functions. Various transcription factors (TFs), such as CDX2, EOMES, GATA3, TFAP2C, and TEAD4, along with their binding sites and cis-regulatory elements, have been studied for their roles in trophoblast cells. While previous studies have primarily focused on individual enhancer regions in trophoblast development and differentiation, recent attention has shifted towards investigating the role of super-enhancers (SEs) in different trophoblast cell lineages. SEs are clusters of regulatory elements enriched with transcriptional regulators, forming complex gene regulatory networks via differential binding patterns and the synchronized stimulation of multiple target genes. Although the exact role of SEs remains unclear, they are commonly found near master regulator genes for specific cell types and are implicated in the transcriptional regulation of tissue-specific stem cells and lineage determination. Additionally, super-enhancers play a crucial role in regulating cellular growth and differentiation in both normal development and disease pathologies. This review summarizes recent advances on SEs’ role in placental development and the pathophysiology of placental diseases, emphasizing the potential for identifying SE-driven networks in the placenta to provide valuable insights for developing therapeutic strategies to address placental dysfunctions.
1. Introduction
The placenta is a highly specialized organ crucial for fetal development, formed through the proliferation and differentiation of trophoblast stem (TS) cells [1]. The proliferation of TS cells and their differentiation into multiple lineages are pivotal for placental development and function [2,3]. The placenta’s development is governed by intricate gene regulatory mechanisms, ensuring the proper formation of structures essential for maternal–fetal interaction. As TS cells differentiate into cytotrophoblasts, these cells give rise to extravillous trophoblasts that invade the maternal decidua and remodel the spiral arteries, establishing vital maternal–fetal blood flow [4,5,6,7]. The syncytiotrophoblast, which is formed via the fusion of cytotrophoblasts, is responsible for exchanging gases and nutrients between the mother and fetus. Aberrant trophoblast differentiation, defective invasion, and syncytiotrophoblast dysfunction are associated with a variety of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia (PE), fetal growth restriction, and gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD), highlighting the critical role of precise regulatory pathways in placental health and function [8,9,10,11,12]. While various gene regulation mechanisms have been studied for their roles in trophoblast cells, much about their precise regulatory functions remains poorly understood.
Cell proliferation and differentiation are dependent on lineage-specific gene expression. Moreover, a well-regulated gene expression pattern is the cornerstone for maintaining unique cell identity. Such genetic homeostasis at the cellular level is accomplished through coordination at multiple levels, including the epigenetic regulation of chromatin architecture, binding of transcriptional regulators to cis-regulatory DNA elements, and interaction of the RNA polymerase components [9]. Transcription factors (TFs), including caudal type homeobox 2 (CDX2), eomesodermin (EOMES), transcription factor AP-2 gamma (TCFAP2C), GATA binding protein 3 GATA3, ETS proto-oncogene 2 transcription factor (ETS2), E74-like ETS transcription factor 5 (ELF5), estrogen-related receptor beta (ESRRB), SRY-box transcription factor 2 (SOX2), inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1), ID2, TEA domain transcription factor 4 (TEAD4), SATB homeobox 1 (SATB1), and SATB2, have been identified as key regulators of trophoblast lineage determination [13,14,15]. However, although some controversies remain, the emerging literature suggests that distinct species-specific transcription factors (TFs) regulate TS cell differentiation and function in humans and mice [16,17]. While TFs such as CDX2 and EOMES may play critical roles in human iTP cell generation, a comparative study of mouse and human placentae across gestation identified species-specific regulators of placental development [16]. Notably, VGLL1, which is co-expressed with TEAD4, was identified as a human-specific marker of proliferative cytotrophoblasts, whereas CDX2 and ELF5 were expressed in early trophoblast subpopulations in both species, but EOMES was not [17]. The regulatory DNA elements to which the TFs bind, are also decisive for regulating trophoblast functions [13,14,18,19]. Studies have shown that sequence variation within enhancer regions can impact trophoblast development [13,14,18,19].
While most previous studies have emphasized the roles of individual transcriptional regulators in trophoblast development or differentiation, recent studies have highlighted the cluster of enhancers enriched in TF-binding, vital for trophoblast lineage determination and placental development. Such clusters of enhancers are known as super-enhancers (SEs). This review article has summarized the role of SEs in TS cell proliferation, lineage-specific trophoblast differentiation, placental development, and placental diseases.
2. Super-Enhancers
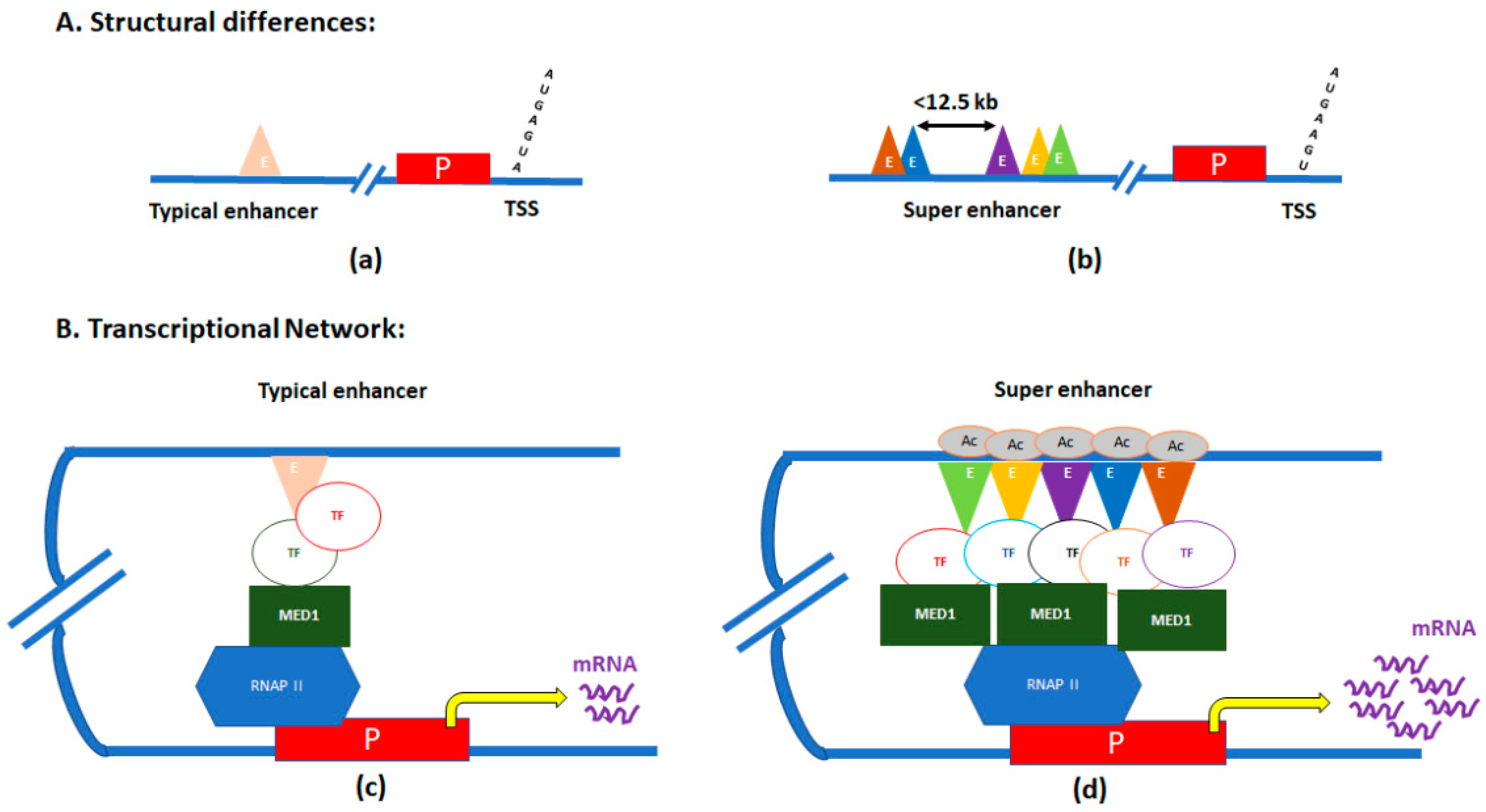
SEs are clusters of enhancers located in close proximity, and with significantly elevated binding of the transcription coactivator Mediator complex [20,21]. SEs were first identified in ChIP-Seq experiments of three master regulators of pluripotency—POU class 5 homeobox 1 (OCT4), SOX2, and nanog homeobox (NANOG) in mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells [20,22]. Those genes were also associated with other pluripotency factors like SOX2, Pim-1 proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (PIM1), and fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), which are evolutionarily conserved in mammals to maintain pluripotency in stem cells [23]. In a single SE, numerous enhancers in proximity (<12.5 kb) are stitched together (Figure 1) [24].
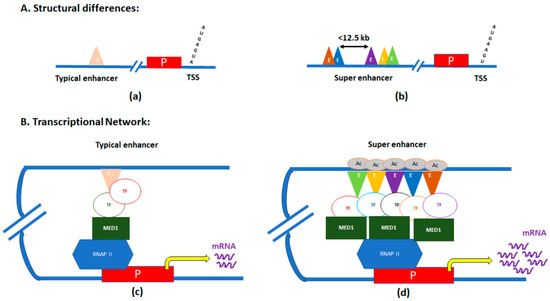
Figure 1.
Graphic illustration of differences between typical enhancers and super-enhancers (SEs). (A) Structural differences between typical enhancers (a) and SEs (b). (B) Transcriptional loops/networks of typical enhancers (c) and SEs (d). E, enhancer regions; P, promoter of the gene; TSS, transcription start site; TF, transcription factor; MED, mediator subunit 1; RNAP II, RNA polymerase II; and Ac, acetylation.
The mediator subunit MED1’s binding levels are significantly elevated within these ‘stitched’ genomic regions. The mediator binds with the chromatin-associated protein cohesin, forming the mediator–cohesin complex, thereby facilitating formation of DNA loops to physically connect enhancers with core promoters to activate transcription [25]. As the mediator–cohesin complex occupies different promoters in different cell types, specific cell-type DNA loops are formed. Given this fact, along with the characteristic enrichment of Mediator and cohesin at SEs, SEs may act as directors of cellular identity through cell-type-specific reorganization of 3D chromatin architecture [3,25]. Thus, SEs can act as ‘switches’ that control the expression of specific regulatory genes determining cell fate.
In addition to MED1, multiple pro-transcriptional regulators, which are hallmarks of active transcription, are enriched at SEs. For example, the enriched binding of RNA polymerase II and the histone acetyltransferases p300 and creb-binding protein (CBP), cohesion structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) complexes, and chromatin remodeling factors, have all been found within SE regions [20,26]. Furthermore, high levels of enhancer-specific H3 lysine 27 acetylation marks have also been associated with SEs [3,27].
3. Placental Development
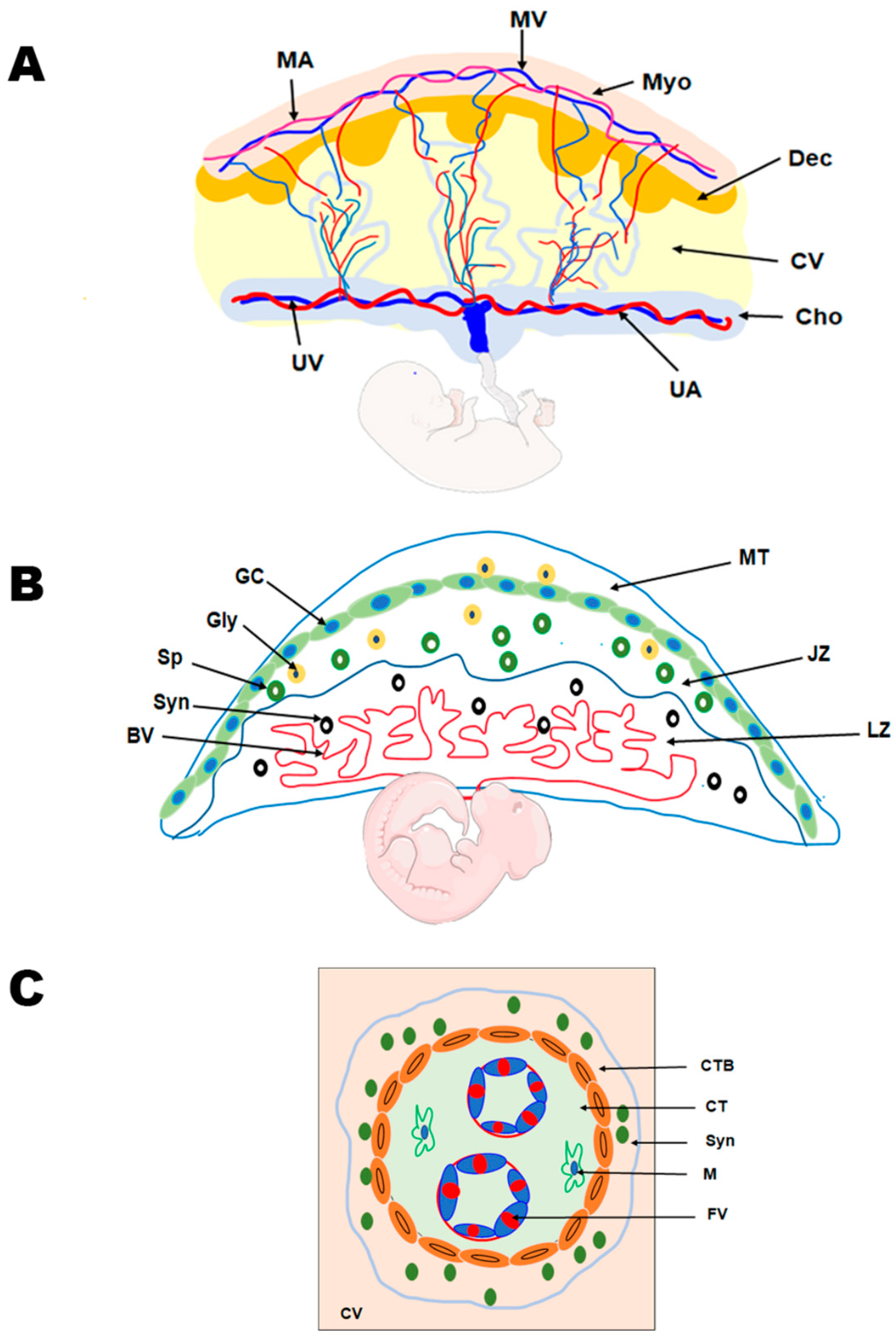
Trophoblasts, specialized epithelial cells in the placenta, are the primary cell type responsible for its development. They play a crucial role in embryo implantation and establishing the essential connection between the embryo and the maternal decidua, facilitating the formation of the maternal–fetal interface. As the precursor for all trophoblast cell types in the placenta, the blastocyst’s multipotent trophectoderm ensures proper trophoblast lineage determination. In humans, the trophectoderm is formed approximately 4–5 days post fertilization and consists of TS cells. The TS cells will differentiate into cytotrophoblasts, which undergo several rounds of proliferation, breaking through the primary syncytium to form the primary villi. These villous cytotrophoblasts will continue to proliferate and undergo fusion to generate the secondary villi [18,19]. The multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast forms when villous cytotrophoblasts proliferate asymmetrically. This asymmetric proliferation is followed by differentiation and fusion with the syncytium, forming tertiary villi comprising fetal blood vessels, thereby establishing the maternal–fetal blood and nutrient exchange (Figure 2) [28]. The cytotrophoblasts at the anchoring villi that attach the placenta to the uterine wall form the cell column trophoblasts. These cell column trophoblasts will differentiate into the extravillous trophoblast cells that are involved in vascular remodeling. The extravillous trophoblasts further differentiate into two types of cells—endovascular extravillous trophoblasts that remodel the maternal spiral arteries and the interstitial extravillous trophoblasts that remodel the maternal decidual stroma [28,29,30].
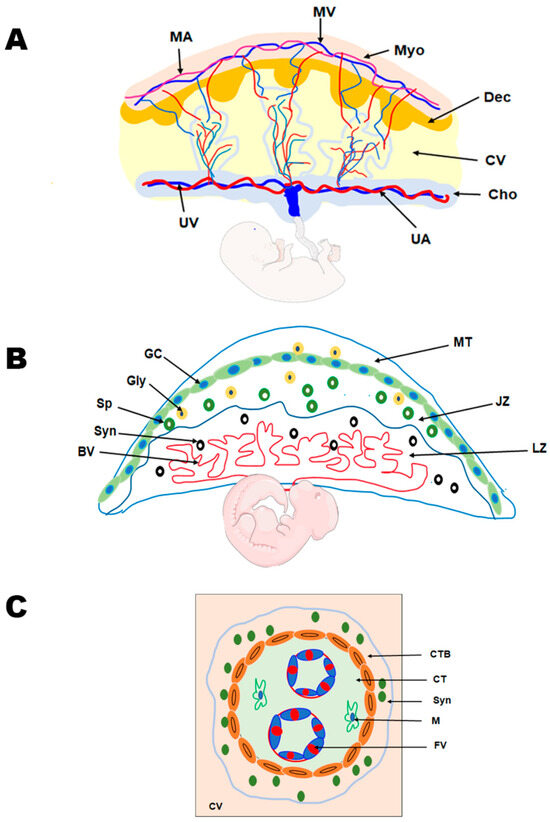
Figure 2.
Comparative anatomy of human and mouse placenta. (A) Schematic representation of the human placenta illustrating the maternal and fetal surfaces, which are attached by the maternal decidua and the associated vasculature. MA, maternal artery; MV, maternal vein; Myo, myometrium; Dec, decidua; CV, chorionic villus; Cho, Chorion; UA, umbilical artery; and UV, umbilical vein. (B) Schematic representation of the rodent placenta showing the labyrinth (LZ) and junctional zones (JZ) that are overlaid by the mesometrial triangle (MT). The labyrinth zone is rich in maternal and fetal blood vessels (BV) and syncytiotrophoblast (Syn) cells. The junctional zone, overlying the labyrinth zone, mainly contains the spongiotrophoblast (Sp), glycogen cells (GC), and the giant cells (GC). (C) Schematic representation of the chorionic villus in the human placenta demonstrating the cytotrophoblast (CTB), syncytiotrophoblast (Syn) cells, and the connective tissue constituting of macrophages (M) and the fetal vessels (FVs).
Information on human placental development in vivo is limited, as studies have primarily been conducted on term placenta, primary placental cultures, choriocarcinoma, and immortalized cell lines due to ethical constraints. Hence, placental development has been increasingly studied using rodent models. Both humans and rodents display hemochorial placentation, in which the trophoblasts directly interact with maternal blood; however, the placental structure and types of trophoblast cells vary between the two species. The ease of genetic manipulation, shorter pregnancy, genetic uniformity, easy availability, and presence of human orthologous genes in mice make mouse models attractive for studying placental pathophysiology. The trophectoderm (TE) of the mouse blastocyst is classified as mural TE or polar TE. The polar TE, which lies in contact with the inner cell mass (ICM), undergoes rapid proliferation to generate the extraembryonic ectoderm and ectoplacental cone. Conversely, the mural TE, lying away from the ICM, differentiates into multinucleated trophoblast giant cells (TGCs) [10,30,31,32]. As pregnancy proceeds, the ectoplacental cone gives rise to trophoblast cells of the labyrinth and junctional zones. The labyrinth zone has three types of trophoblast cells—multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast I and II and mononucleated sinusoidal giant cells. The junctional zone, which lies above the labyrinth zone, consists of spongiotrophoblast cells, glycogen cells, and TGCs [28,33,34] (Figure 2). The glycogen cells that invade the stroma are the interstitial invasive trophoblasts, and those that invade the blood vessels are known as endovascular trophoblasts [32,35]. It is also reported that glycogen cells can invade the maternal decidua and the overlying maternal metrial gland to a lower extent [36].
4. Role of Super-Enhancers in Placental Development
4.1. Super-Enhancers in Trophectoderm Development and Trophoblast Differentiation
The known association of SEs with master pluripotent factors has prompted recent investigations on studying SEs in trophectoderm differentiation. Still, the idea that SEs may act as the drivers of trophectoderm differentiation is a relatively new concept. Although several TF regulators of trophoblast lineage specification have been identified historically, the role of SEs in driving large-scale identity-dependent gene expression has become more evident following advances in genome mapping.
Currently, it is hypothesized that the epigenetic regulation of the trophectoderm genome may be a foundation for proper fetal development and healthy pregnancy. In mice, one identified SE-associated transcription factor is the caudal homeobox transcription factor, CDX2. RNA-Seq and ChIP-In mice seq analyses revealed that CDX2 is associated with SEs in embryonic tissues and acts as a regulator of trophoblast self-renewal and early lineage specification [1]. In addition, a time-dependent expression pattern of CDX2 within the trophectoderm was observed, where high levels of the TF were gradually downregulated as TS cells underwent differentiation [1,37]. CDX2 expression is weak within the mouse placenta, restricted to trophectoderm precursor cells, leading to the postulation that the SE-associated TF is primarily involved in trophoblast self-renewal and early lineage specification [1,37]. Concurrent with the tight spatial and temporal expression patterns of CDX2, Strumpf et al. reported that proper expression of SE-associated CDX2 is required for the segregation of the ICM from the remainder of the blastocysts and subsequent functional trophectoderm development [37]. In humans, CDX2 is expressed by 5-day post-fertilization blastocysts, although its trophectoderm expression lags by 2 days compared to the mouse [38]. CDX2 is weakly expressed by cytotrophoblast cells and human-induced trophoblast progenitor cells [16,17,39,40]. However, its role seems to be less critical in humans than in mice, as human trophoblast development and differentiation depend more on other factors.
The determination of trophoblast lineage is a highly complex process, dependent on a complex network of TFs. Specifically, mapping such SE-associated TFs revealed “highly intertwined transcriptional regulatory circuitry”, but distinct classes of expression patterns [1]. Within this complex intra-regulatory network, the evidence suggests that SE-associated-TFs regulate each other collaboratively, without any clear hierarchal structure between TFs. For example, in addition to CDX2’s role in driving trophectoderm differentiation, CDX2 is also known to regulate the activity of another SE-associated TF, OCT4, to ensure proper blastocyst differentiation in rodents. While CDX2 and OCT4 have been deemed ‘prime movers’ of the first cell-specific lineages, these TFs have separate and occasionally mutually exclusive effects [41]. Specifically, CDX2 plays a role in ICM segregation and trophectoderm differentiation, while OCT4 is an ICM-specific TF required to maintain ICM fate and embryonic stem cell pluripotency [37]. The roles of CDX2 and OCT4 in a complex and collaborative intra-regulatory network may instead imply a separate hierarchical structure. While current data suggest a lack of stable hierarchy among those TFs that bind and activate SEs, transitory hierarchal structures may exist secondarily to competing TF expression levels. It has been hypothesized that proper blastomere differentiation into trophectoderms or ICM may be predicated upon an epigenetic tug-of-war relationship between CDX2 and OCT4 levels and the SE-associated genes they each activate. Current evidence suggests that the ratio of CDX2 to OCT4 expression determines trophectoderm fate. Specifically, Niwa et al.’s combined qPCR and stem cell luciferase reporter experiments demonstrated that OCT4 expression is conserved and consistent across all blastomeres of early morulae [42]. As the outer layer of cells differentiates into trophectoderms during blastocyst formation, the expression of OCT4 is suppressed while CDX2 increases [37]. Before blastocyst formation, a high OCT4–CDX2 ratio (OCT4 > CDX2) was shown to promote the maintenance of the ICM, whereas a low OCT4–CDX2 ratio (CDX2 > OCT4) stimulated differentiation into trophectoderms [37,42]. However, these intricate interactions between CDX2 and OCT4 have not been fully explored in human trophoblast cells and should be extrapolated to human studies with caution, as the suppression of OCT4 by CDX2, observed in mouse embryos and embryonic stem cells, was not observed in a study using human trophoblast cells derived from ES and iPS cells [43].
Recent evidence suggests that the expression levels of master TFs, CDX2, and OCT4 are determined by two factors: an interconnected autoregulatory feedback loop and SEs [22]. More specifically, it has previously been shown that master TFs (including OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG) form an interconnected autoregulatory loop in murine embryonic stem cells, whereby all three TFs bind as a group to the promoters of each of their genes to regulate transcription [22]. Furthermore, using a combination of ChIP-Seq and OCT4 luciferase reporters, Whyte et al. reported that many of the enhancers occupied by OCT4 were associated with the genes OCT4 and CDX2 themselves [22]. Given SEs’ role in driving higher-level transcription and associating with these master TFs, SEs may function as types of master regulators responsible for activating specific TF expression profiles and maintaining appropriate stoichiometric ratios of CDX2 and OCT4.
Recently, SEs have been increasingly implicated in cell differentiation events linked to generating various trophoblast lineages from TS cells. The SE-bound TFs that are associated with mouse trophoblast lineages have been categorized into classes 1–4 based on hierarchical clustering analysis [1]. Within these classes, the class 2 TFs are associated with the maintenance of TSC self-renewal and trigger early trophectoderm lineage specification, while class 3 TFs are highly expressed in the placenta and involved in trophoblast differentiation pathways [1]. The interactions between these different classes of SE-associated TFs, based on their stoichiometric ratios in the cell determine whether the TSC maintains its identity or differentiates into other cell lineages. For example, ELF5, a class 2 TF, aids in TSC self-renewal and triggers trophoblast differentiation networks via interactions with EOMES and TFAP2C [44,45,46,47]. The presence of equal stoichiometric quantities of EOMES, ELF5, and TFAP2C proteins in TS cells results in the binding of ELF5 to EOMES. The ELF5–EOMES interaction triggers the recruitment of TFAP2C protein to triple occupancy sites located in genes for TSC identity. Conversely, when levels of ELF5 and TFAP2C exceed those of EOMES, ELF5 directly interacts with TFAP2C. The ELF5–TFAP2C interaction triggers the recruitment of TFAP2C to double- and single-occupancy TFAP2C motifs in differentiation-specific genes for the TS cells to undergo differentiation [44].
Accurate trophectoderm development and trophoblast lineage differentiation may be directed by higher-level SEs that maintain a balance of isolated temporospatial TF expression within a complex regulatory network. The efficient CDX2–OCT4 balance, regulated by SEs, may control mouse ICM maintenance and/or trophectoderm cell fate determination. Conversely, trophoblast cell differentiation may be determined by specific SE-mediated transcription loops, wherein the TFs bind in a coordinated manner to initiate downstream effects. Further studies on how such transcription loops are intricately triggered by SE during placentation could provide valuable clues on the mechanisms involved in trophectoderm/trophoblast differentiation.
4.2. Super-Enhancers in Trophoblast Invasion
The invasion of trophoblasts into the maternal tissue during pregnancy promotes blood flow to the placenta via spiral artery remodeling. Several gene networks involved in trophoblast invasion for spiral artery remodeling have been identified by studies on rodents [48,49]. These gene expression networks coordinate the expression of cell adhesion molecules, growth factors, extracellular matrix proteins, and TFs. Recent studies have mapped epigenetic modifiers (such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation) and generated subsequent knockout models to assess changes in the invasion phenotype to better understand the underlying epigenetic landscape required for placental development and trophoblast invasion [26,50]. Thus, epigenetic regulation may act as a foundation for proper trophoblast invasion [51].
SEs have been increasingly implicated as drivers of the expression levels necessary for trophoblast invasion (Table 1). As human TS cells gain an invasive phenotype, increased enhancer-driven gene regulatory networks are detected in these extravillous trophoblast cells [52]. ATAC-Seq identified 1283 SEs in regulatory regions specific to extravillous trophoblast cells [52]. In Tuteja et al.’s ChIP-Seq of trophoblast invasion gene enhancers and accompanying trans-binding TFs, three TFs were identified as most likely to bind migration enhancers: fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit 1 (FOSL1), ETS2, and TFAP2C [13,53,54,55]. Identifying FOSL1 was especially notable, as Lee et al. found the TF to be SE-associated, undergoing gradual upregulation throughout trophoblast differentiation [1,13,56,57]. Furthermore, the TF is known to dimerize with jun proto-oncogene (JUN) proteins to form the AP-1 complex, a transcriptional regulator of cell survival, proliferation, and migration [56,57]. A downstream target of AP-1 is matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) of the matrix metallopeptidase family of proteases. Involved in cell invasion and extracellular matrix remodeling, MMP9is preferentially expressed in endometrial stromal cells and natural killer cells (NK) cells [13,58,59,60]. MMP9 is also known to be constitutively expressed in placental bed trophoblasts, where it is upregulated throughout pregnancy. There is no concrete evidence of SE regulation of MMP9 in trophoblasts, although more recent findings suggest MMP9 to be associated with some SEs. For example, Chandra et al.’s recent transcriptomic analysis revealed SEs’ regulation of MMP9 within neutrophils [58]. Furthermore, Tuteja et al.’s analysis of enhancers associated with trophoblast invasion revealed the presence of an E7.5, a timepoint-specific, potent enhancer of MMP9 [13,14]. MMP9 has been implicated in several disease states, as weak or absent expression has been found in PE, while the knockdown of the gene is lethal and associated with abnormal implantation [1,13,59,61].Another relevant TF that may be relevant to placentation is the TF TFAP2C. Initially, Lee et al. identified the association of TFAP2C with SEs. It was further confirmed by Tuteja et al. that TFAP2C acts on a SE during trophoblast migration [1,13]. This TF has been previously implicated in trophectoderm lineage determination and placental development, while RNA-Seq revealed changes in TFAP2C expression during trophoblast invasion [15]. Using ChIP-Seq analyses, Tuteja et al. reported TFAP2C as one of a few genes whose enhancer enrichment changed during the height of trophoblast invasion at E7.5 [13]. Furthermore, TFAP2C expression was observed in invasive extravillous trophoblasts, while TFAP2C knockdown resulted in embryo lethality secondary to a placental defect [62]. TFAP2C aids in the differentiation of extravillous trophoblast cells and the conversion of fibroblast cells into trophoblast cells [52]. As such, TFAP2C exemplifies the evolving notion of SE involvement in regulating trophoblast invasion.
In summary, SE-targeted TFs have been identified as drivers of trophoblast invasion, although underlying regulatory mechanisms of invasion appear highly complex and are presently poorly understood. Continued inquiry into the identities and impact of both trans-acting TFs and cis-acting SEs on gene expression will be needed to improve our understanding of the specific roles of SEs in directing trophoblast invasion.
4.3. Super-Enhancers in Placental Vascular Remodeling
Vascular remodeling events during trophoblast invasion are tightly coordinated cellular processes, converting maternal spiral arteries into “low resistance, high capacitance vessels”, for increased blood flow to the fetus [63,64,65,66]. The disruption of these vascular remodeling events leads to pregnancy-related complications such as PE [67]. With the advent of genome sequencing and mapping, the role of SEs has become increasingly apparent in vessel formation and endothelial homeostasis (Table 1). One such regulator of vascular remodeling is the SE-associated TF, ERG. ERG is a member of the ETS family, downstream targets of the RAS/ERK pathway [21]. ERG is primarily known to maintain vascular homeostasis and promote vascular development and angiogenesis through the regulation of several genes, including cadherin 5 (CDH5), angiopoietin (ANGP2), delta-like canonical notch ligand 4 (DLL4), claudin 5 (CLDN5), and Von Willebrand factor (VWF) [56,66,68]. In 2018, Kalna et al. revealed the role of ERG in key endothelial gene SEs by binding enriched DNA-enhancer regions and binding and recruiting histone acetyltransferases in HUVECs [56]. Furthermore, Lee et al.’s mapping of trophoblast regulatory networks revealed the increased expression of ERG in the placenta, with gradual upregulation throughout trophoblast differentiation [1]. Consistent with these findings, several studies have shown that ERG knockout leads to severe vascular dysfunction and subsequent embryo death [69,70]. Furthermore, environmental factors, such as hypoxia and reactive oxygen species, can upregulate ERG expression, as can endogenous growth factors [66]. Notably, the proangiogenic factor VEGF has been shown to upregulate ERG expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), inducing increased ETS promotor binding, expression of ANGP2, and subsequent vessel destabilization necessary for angiogenesis [66,71].
The GATA family of TFs has also been implicated in the SE-mediated regulation of vascular development. The GATA family comprises six isoforms and functions as zinc-coordinated regulatory proteins that bind to consensus DNA regions to regulate gene transcription [51,72]. Although GATA family members are perhaps best known as key regulators of trophectoderm lineage determination, GATA-2 and GATA-3 have been shown to help epigenetically coordinate vascular development [73,74,75,76]. Known to be associated with SEs and having multiple histone acetyltransferase target sites, GATA-3 regulates the expression of the peptide hormone PLF, along with GATA-2 [51,77]. A key positive and negative angiogenic regulator, PLF expression peaks at mid-gestation and stimulates endothelial cell migration, neovascularization, and angiogenesis within murine TGCs [1,51]. Furthermore, SEs may also play a significant role in maintaining the overarching epigenetic coordination for proper placental vascular development. Such studies are valuable for understanding placental diseases hampering fetal development due to aberrant nutrient and gas exchanges caused by defective placental vascular remodeling.

Table 1.
Super-enhancer genes involved in placental development. (A) trophectoderm development and trophoblast differentiation; (B) trophoblast invasion; and (C) vascular remodeling.
Table 1.
Super-enhancer genes involved in placental development. (A) trophectoderm development and trophoblast differentiation; (B) trophoblast invasion; and (C) vascular remodeling.
| Trophoblast-Specific TFs | SE Association | Trophoblast Placental Sub-Cell Types | Species | Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDX2 | Intra-regulatory network with OCT4 TF. | Trophoblast progenitor cells | Mouse | Trophoblast self-renewal and early lineage specification. Inner cell mass (ICM) segregation and trophectoderm differentiation. | [1,17,37,39,40,41,43] |
| ELF5 | Recruitment of TFAP2C protein to double/single- (Interaction with TFAP2C) or triple-occupancy sites (Interaction with EOMES) in genes for TS cell identity or differentiation. | TS cells, Villous cytotrophoblast cells | Human and mouse | TSC self-renewal and trophoblast differentiation. | [44] |
| EOMES | Interacts with ELF5 to recruit TFAP2C to triple-occupancy sites in TS cell identity genes. | TS cells | Mouse and human | TS cell identity. | [44,45,46,47] |
| TFAP2C (human) or TCFAP2c (mouse) | Interacts with TFAP2C to recruit TFAP2C to double- or single-occupancy sites in differentiation genes in TS cells. | TS cells, Invasive trophoblast cells | Mouse and human | Involved in trophectoderm lineage determination, placental development, and trophoblast differentiation. | [13,44,45,46,47] |
| Trophoblast-Specific TFs | SE Association | Trophoblast/Placental Sub-Cell Types | Species | Functions | References |
| FOSLI | Binds to migration enhancers during trophoblast invasion. Dimerizes with JUN to form AP-1 complex. | Extravillous trophoblast cells | Mouse and human | Involved in trophoblast differentiation and migration. | [1,13,56,57] |
| TFAP2C (human) or Tcfap2c (mouse) | Interacts with TFAP2C to recruit TFAP2C to double- or single-occupancy sites in differentiation genes in TS cells. | TS cells, Invasive trophoblast cells | Mouse and human | Involved in trophectoderm lineage determination, placental development, and trophoblast differentiation. | [13,15,44,45,46,47] |
| Trophoblast-Specific TFs | SE Association | Trophoblast/Placental Sub-Cell Types | Species | Functions | References |
| ERG | Regulates CDH5, ANGP2, DLL4, CLDN5, and VW for vascular development and angiogenesis. | Endothelial cells | Mouse and human | Involved in vascular development and angiogenesis. | [1,21,56,66,69,70,71] |
| GATA-2 and GATA-3 | Regulates the expression of hormone PLF along with GATA 3. | Murine trophoblast giant cells, Cytotrophoblast progenitors | Mouse and human | Involved in endothelial cell migration, neovascularization, and angiogenesis. | [51,73,74,75,76,77] |
| ETS2 | Regulates TS cell renewal by regulating CDX2 and trophoblast invasion via MMP-3, MMP-9, and MMP-13. | TS cells | Mouse and human | Regulates trophoblast differentiation and invasion. | [13,53] |
5. Role of Super-Enhancers in Placental Diseases
5.1. Super-Enhancers in Disease Pathogenesis
SEs have been implicated in the pathogenesis of various diseases, as they can have altered functions due to epigenetic alterations, changes in enhancer sequences, or chromosomal rearrangements [78]. Enhancer-mediated mechanisms have now been increasingly linked to cancer and other rare diseases, including congenital disorders and neurodegenerative diseases [78]. If an association of an SE cluster with a specific disease is identified, then the target genes they regulate can be used as disease biomarkers and to develop drug targets. It is known that disease-associated polymorphisms are within non-coding DNA regions and that the most quantitative trait loci (QTL) are expression QTLs (eQTLs). Thus, it is unsurprising that SEs are associated with disease development [20,50,56], and that disease-associated variations are enriched in SEs [26]. In their ChIP-Seq analysis of various human tissues, Hnisz et al. found SNP-enriched SEs in human brain tissues at loci associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Furthermore, genetic variants associated with rheumatoid arthritis were found within lymphoid cell SEs [26].
SEs have also been implicated in states of pathological proliferation, such as cancer. ChIP-Seq data revealed that cancer cells could accumulate SEs as proto-oncogenes mutate into oncogenes, resulting in the unregulated expression of SE-associated genes and subsequent tumorigenesis [26]. One example is the oncogene MYC proto-oncogene, BHLH transcription factor (MYC), a cell growth and apoptosis regulator. ChIP-Seq enriched MYC in nearby SEs in cancer cells, but not in their healthy counterparts [20,26,79]. A separate study of multiple myeloma found that MYC-associated SEs were occupied by remarkably high amounts of the coactivator bromodomain containing 4 (BRD4), a protein involved in the recruitment of elongation factors and binding of Mediator, as well as acetylated histones [80,81]. Furthermore, the inhibition of BRD4 was associated with selective disruption of SEs, thereby implicating the coactivator as a SE-associated driver of tumorigenesis [20]. BRD4 binding to SEs has been conserved across placental mammals, and its inhibition causes reduced pluripotency and activation of SOX2 SEs in porcine stem cells [23]
5.2. Super-Enhancers in Placental Diseases
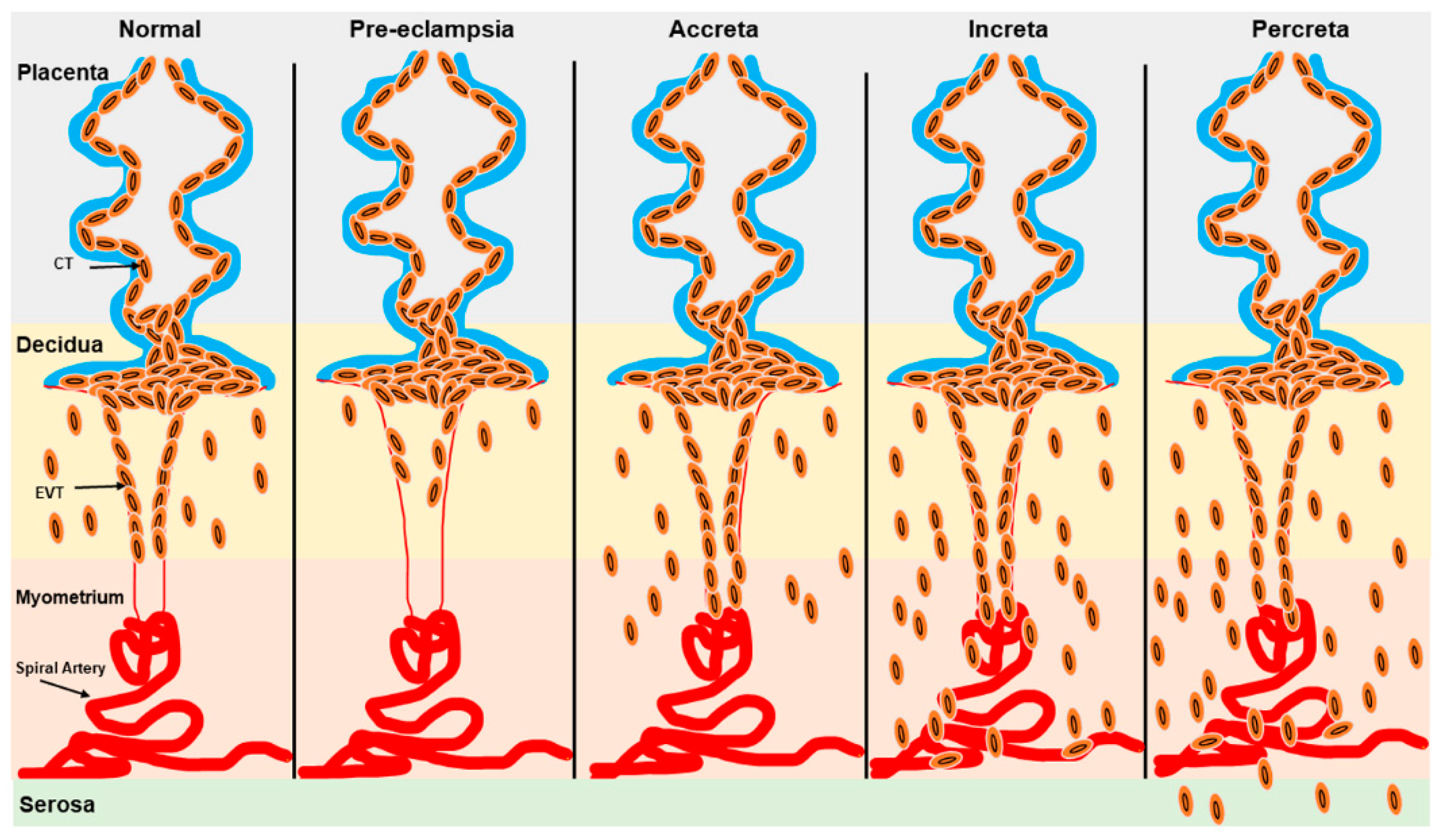
Defective trophoblast differentiation and invasion of the decidual spiral arteries during pregnancy are central to many pregnancy complications, including PE, which is associated with significant maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality worldwide [82,83]. While the exact etiology and pathophysiology of PE remain incompletely understood, a key factor is the failure of extravillous trophoblast cells to properly remodel the spiral arteries [84]. This failure reduces blood flow to the intervillous space, contributing to fetal growth restriction (FGR) and maternal symptoms of PE [85,86]. (Figure 3). Conversely, excessive trophoblast invasion during pregnancy involves placental diseases such as placenta accreta spectrum (PAS), which includes placenta accreta, placenta increta, placenta percreta, and placenta previa (Figure 3). In PAS, trophoblast invasion can extend into various layers of the myometrium and even the uterine serosa, resulting in life-threatening hemorrhage that often necessitates interventions like cesarean sections or hysterectomy [85,86,87,88] (Figure 3). Placenta previa (PP) specifically involves the abnormal implantation of the placenta near the cervix, obstructing the internal os and leading to inflammation, which in turn causes maternal–fetal morbidity and mortality [85,86,89,90]. Preterm births with various etiologies are associated with different neonatal complications. For instance, infants born after spontaneous labor are at a higher risk of intraventricular hemorrhage. In contrast, those delivered preterm due to iatrogenic factors face an increased risk of necrotizing enterocolitis, coagulopathy, and pathologic hypoglycemia [91].
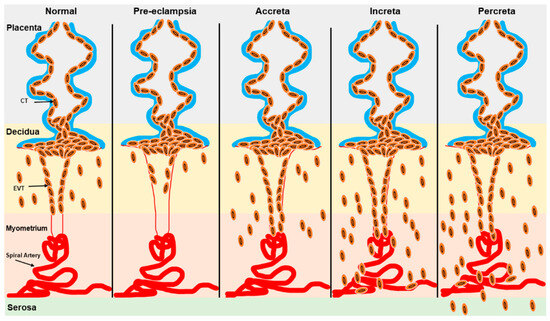
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of trophoblast invasion in normal and pathogenic states. Trophoblast invasion for spiral artery remodeling is severely restricted in the decidua in PE while excessive trophoblast invasion in the myometrium and serosa is observed in placenta accreta, placenta increta, and placenta percreta. EVT: Extravillous trophoblast; CT: cytotrophoblast.
Studies on the pathogenesis of PE involving human term placentas, in vitro cultures, and placental perfusion studies by Doppler, fail to provide mechanistic clues on the onset of this disease [92]. To overcome these difficulties, mouse and rat models of PE have been created by either inducing inflammation, immune system imbalance, angiogenic imbalances via sflt1, genetic manipulation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), or placental ischemia [93,94]. However, none of these models have been able to completely recapitulate the physiological effects observed in humans, and thus provide limited information on the pathogenesis of this disease. Most of these animal models do not replicate the initial events involved in PE, especially where SEs will be increasingly implicated [94].
The lack of studies on the functional significance of SE networks in human placentation has hampered the understanding of the disease pathologies of PE, PAS, and placenta previa. Nonetheless, only a few TFs have been implicated in the pathogenesis of PE [1]. For example, the SE-upregulated gene HTRA1 stabilizes misfolded proteins while GATA3 is involved in placental imprinting in PE [95,96]. Another SE-regulated gene, syndecan 4 (SDC4), is also up-regulated in PE, possibly due to the presence of an inflammatory environment [97].
Enhanceosome formation due to combinatorial binding and collaborative actions of multiple TFs on SEs activates several target genes due to a transcriptional synergy in human TS cells. On the other hand, repression of target genes may result when these TFs function singly or are associated with fewer TFs [98]. In regions where the five SE-enriched TFs, FOS, TEAD4, TFAP2C, GATA2, and MAF BZIP transcription factor K (MAFK), co-bind in TS cells, the expression of target genes is significantly higher than in regions where there is only the binding of single TF or few TFs. The genes associated with the pathogenesis of PE mainly belong to the group of target genes activated by the combined binding of all five TFs [98]. Thus, deregulations in co-binding and actions of multiple TFs to SE regions appear essential in developing PE and other diseases.
The combinatorial interplay of multiple TFs and their binding to SEs may be required to stimulate cell type-specific gene expression during placental development [98] (Figure 4). TS cells and cytotrophoblast cells exhibited a higher expression of target genes when all five TFs were bound to the SE regions compared to syncytiotrophoblast and extravillous trophoblast cells [98]. It is worthwhile to assess the mechanism by which these TFs bind to SE regions and create functional networks by activating genes during trophoblast development and invasion. Derangements in such mechanisms may be significant in understanding the pathology of placental diseases and aiding in developing treatment strategies. Placental dysfunctions contributing to pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia and preterm birth, can lead to adverse neonatal outcomes. Investigating the role of SEs in regulating the signaling pathways associated with preterm birth may provide insights for reducing its incidence and the related neonatal complications [99].
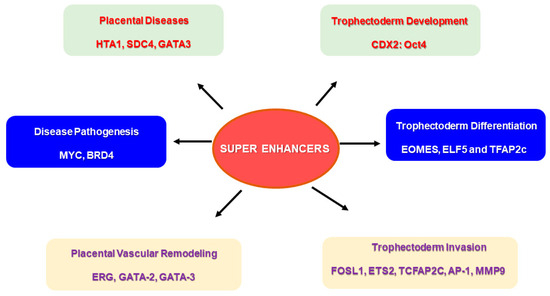
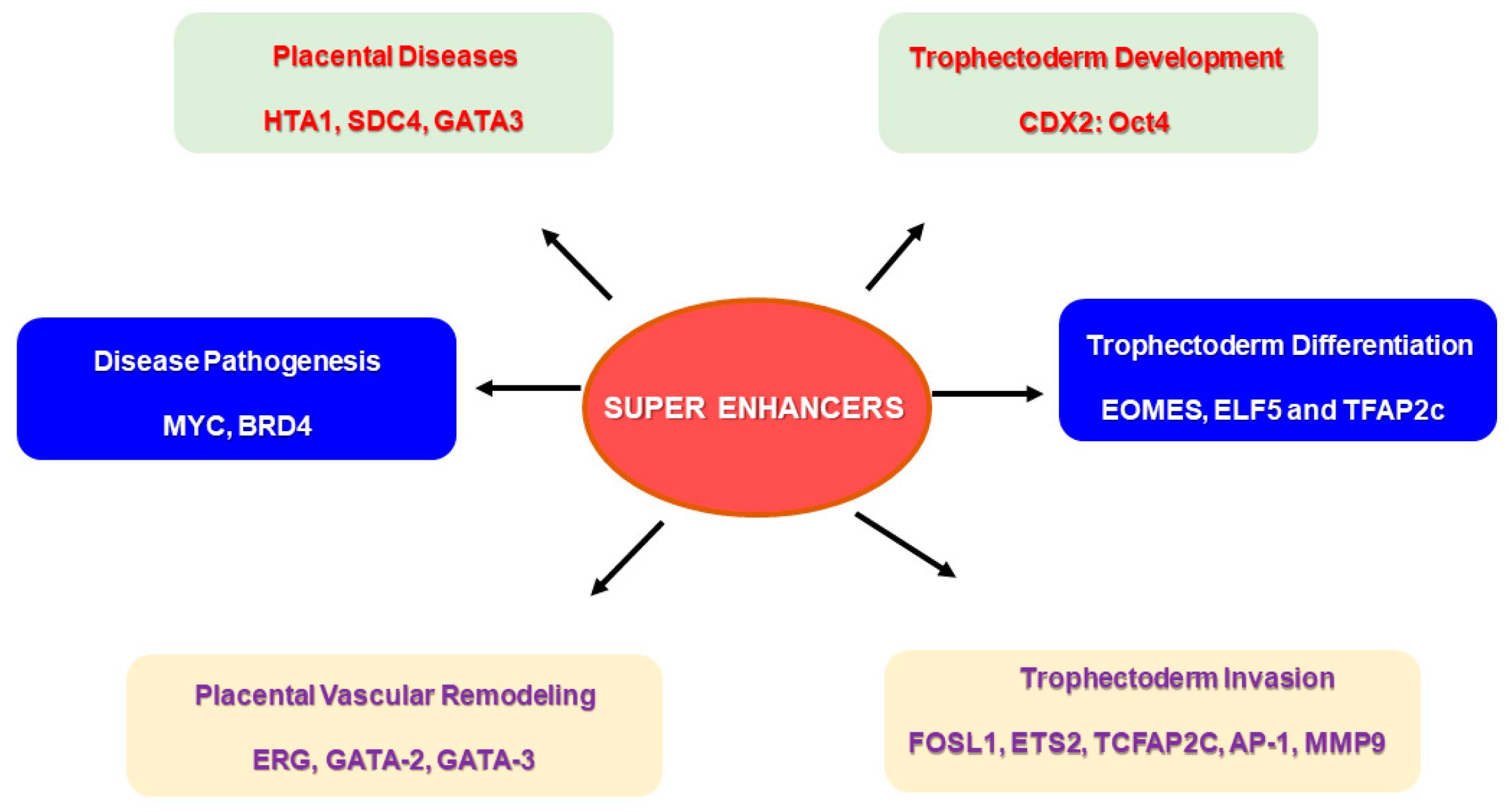
Figure 4.
Super enhancers (SEs) and their putative role in placental physiology. Specific super enhancer-driven networks may have a significant role to play in events required for successful placentation. SE-driven networks can be associated with trophoblast development and differentiation, and trophoblast invasion of spiral arteries, which are important for vascular remodeling during pregnancy. Several SE-driven events may also be responsible for disease pathogenesis, specifically in placental diseases.
6. Conclusions
Although the precise roles of SEs in placental development and pregnancy complications related to defects in placental development are not yet fully understood, emerging evidence suggests that SEs play a significant role in driving the expression of several genes crucial for placental development (Table 1). We recognize that there is still much to be discovered, as SEs represent a relatively new and rapidly evolving area within the fields of epigenetics and transcriptional regulation. The identification of SE-associated TFs is an essential first step toward unraveling the full spectrum of SEs’ functions. Given that SEs rarely act in isolation and commonly share TFs and cofactors, there is much more to explore. Looking ahead, we call for further research into the role of SEs within enhancer landscapes and regulatory networks. The continued characterization of SEs and their associated interactions will deepen our understanding of abnormal placentation and may ultimately uncover novel therapeutic targets for placental diseases. Additionally, investigating SE-associated alterations in chromatin dynamics and the long-range chromatin interactions that drive trophoblast differentiation could be mapped using 5C- and Hi-C-based approaches. With the rapid development of bioinformatics tools like HOMER (http://homer.ucsd.edu/) and ROSE (Rank Order of Super Enhancers), mapping these elusive DNA elements that direct the placental developmental program is feasible.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.X.R., S.B., and N.R.N.; methodology: G.X.R., S.B., M.A.K.R., and N.R.N., data curation, G.X.R., S.B., and M.A.K.R.; writing—original draft preparation, G.X.R., S.B., and N.R.N.; writing—review and editing, G.X.R., S.B., M.A.K.R., S.K., and N.R.N.; supervision, N.R.N.; funding acquisition, N.R.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded and supported by the NIH grant #R01HD088549 (NRN). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the US National Institutes of Health.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Figure 2 has been partly generated using Smart Servier Medical Art, which is licensed under CC BY 4.0. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0) (accessed on 29 January 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SE | Super-enhancers |
| TS cells/TSC | Trophoblast stem cells |
| ICM | Inner cell mass |
| TFs | Transcription factors |
| TGCs | Trophoblast giant cells |
| CDX2 | Caudal-type homeobox 2 |
| EOMES | Eomesodermin |
| TCFAP2C | Transcription factor AP-2 gamma |
| GATA3 | GATA-binding protein 3 |
| ETS2 | ETS proto-oncogene 2, transcription factor |
| ELF5 | E74-like ETS transcription factor 5 |
| ESSRB | Estrogen-related receptor beta |
| SOX2 | SRY-box transcription factor 2 |
| ID1 | Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 |
| TEAD4 | TEA domain transcription factor 4 |
| SATB1 | SATB homeobox 1 |
| TP63 | Tumor protein P63 |
| OCT4 | POU class 5 homeobox 1 |
| NANOG | SOX2, and Nanog homeobox |
| PIM1 | Pim-1 proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase |
| FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 |
| CBP | Creb-binding protein |
| SMC | Cohesion structural maintenance of chromosomes |
| HUVECs | human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| CDH5 | Cadherin 5 |
| ANGP2 | Angiopoietin |
| DLL4 | Delta like canonical notch ligand 4 |
| CLDN5 | Claudin 5 |
| VWR | Von Willebrand factor (VWF) |
| FOSLI | Fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit 1 |
| JUM | Jun proto-oncogene |
| MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| MYC | MYC proto-oncogene, BHLH transcription factor |
| BRD4 | Bromodomain containing 4 |
| MAFK | MAF BZIP transcription factor K |
References
- Lee, B.K.; Jang, Y.J.; Kim, M.; LeBlanc, L.; Rhee, C.; Lee, J.; Beck, S.; Shen, W.; Kim, J. Super-enhancer-guided mapping of regulatory networks controlling mouse trophoblast stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncin, F.; Natale, D.; Parast, M.M. Signaling pathways in mouse and human trophoblast differentiation: A comparative review. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cairns, M.J.; Yan, J. Super-enhancers in transcriptional regulation and genome organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 11481–11496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scifres, C.M.; Nelson, D.M. Intrauterine growth restriction, human placental development and trophoblast cell death. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 3453–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, M.K.; Sharma, N.R.; Petitt, M.; Maulik, D.; Nayak, N.R. Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia and Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Placenta. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, D.K.; Wong, R.J.; Nayak, N.R. Molecular Mechanisms of Pregnancy-Related Vascular Remodeling and Pregnancy Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, L.; Qin, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhang, K. Trophoblast Differentiation: Mechanisms and Implications for Pregnancy Complications. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayder, H.; Shan, Y.; Chen, Y.; O’Brien, J.A.; Peng, C. Role of microRNAs in trophoblast invasion and spiral artery remodeling: Implications for preeclampsia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 995462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, N.R.; Srivastava, A.; Jena, M.K.; Odibo, A.; Sutkin, G. Genetic and Epigenetic Insights into Pregnancy-Related Complications. Genes 2024, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Rai, A.; Kambham, N.; Sung, J.F.; Singh, N.; Petitt, M.; Dhal, S.; Agrawal, R.; Sutton, R.E.; Druzin, M.L.; et al. Endometrial VEGF induces placental sFLT1 and leads to pregnancy complications. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4941–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzioni, D.; Quaranta, A.; Lorenzi, T.; Morroni, M.; Crescimanno, C.; De Nictolis, M.; Toti, P.; Muzzonigro, G.; Baldi, A.; De Luca, A.; et al. Expression pattern alterations of the serine protease HtrA1 in normal human placental tissues and in gestational trophoblastic diseases. Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 24, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardaropoli, S.; Paulesu, L.; Romagnoli, R.; Ietta, F.; Marzioni, D.; Castellucci, M.; Rolfo, A.; Vasario, E.; Piccoli, E.; Todros, T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in fetoplacental tissues from preeclamptic pregnancies with or without fetal growth restriction. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 639342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuteja, G.; Chung, T.; Bejerano, G. Changes in the enhancer landscape during early placental development uncover a trophoblast invasion gene-enhancer network. Placenta 2016, 37, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tuteja, G.; Cheng, E.; Papadakis, H.; Bejerano, G. PESNPdb: A comprehensive database of SNPs studied in association with pre-eclampsia. Placenta 2012, 33, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asanoma, K.; Kubota, K.; Chakraborty, D.; Renaud, S.J.; Wake, N.; Fukushima, K.; Soares, M.J.; Rumi, M.A. SATB homeobox proteins regulate trophoblast stem cell renewal and differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Gong, Y.G.; Khoo, S.K.; Leach, R. Roles of CDX2 and EOMES in human induced trophoblast progenitor cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncin, F.; Khater, M.; To, C.; Pizzo, D.; Farah, O.; Wakeland, A.; Arul Nambi Rajan, K.; Nelson, K.K.; Chang, C.W.; Moretto-Zita, M.; et al. Comparative analysis of mouse and human placentae across gestation reveals species-specific regulators of placental development. Development 2018, 145, dev156273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, N.J.; Savic, D.; Nobrega, M.A. Transcriptional enhancers in development and disease. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, F.; Furlong, E.E. Transcription factors: From enhancer binding to developmental control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, S.; Lieb, J.D. What are super-enhancers? Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Meissner, T.B.; Wang, F.; Du, Z.; Ma, S.; Kshirsagar, S.; Tilburgs, T.; Buenrostro, J.D.; Uesugi, M.; Strominger, J.L. ELF3 activated by a superenhancer and an autoregulatory feedback loop is required for high-level HLA-C expression on extravillous trophoblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025512118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, W.A.; Orlando, D.A.; Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Kagey, M.H.; Rahl, P.B.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell 2013, 153, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, X.; Yu, S.; Shen, Q.; Pan, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, R.; et al. Super-enhancers conserved within placental mammals maintain stem cell pluripotency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2204716119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Chen, S.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, F. Oncogenic super-enhancer formation in tumorigenesis and its molecular mechanisms. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagey, M.H.; Newman, J.J.; Bilodeau, S.; Zhan, Y.; Orlando, D.A.; van Berkum, N.L.; Ebmeier, C.C.; Goossens, J.; Rahl, P.B.; Levine, S.S.; et al. Mediator and cohesin connect gene expression and chromatin architecture. Nature 2010, 467, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lee, T.I.; Lau, A.; Saint-André, V.; Sigova, A.A.; Hoke, H.A.; Young, R.A. Super-enhancers in the control of cell identity and disease. Cell 2013, 155, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yue, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, M.; Chen, X.; Hua, J. Super enhancers-Functional cores under the 3D genome. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, L.; Perez-Garcia, V.; Hemberger, M. Regulation of Placental Development and Its Impact on Fetal Growth-New Insights From Mouse Models. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin Knöfler, S.H.; Saleh, L.; Pollheimer, J.; Gamage, T.K.J.B.; James, J. Human placenta and trophoblast development: Key molecular mechanisms and model systems. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3479–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Muruganandan, S.; Shallie, P.D.; Dhal, S.; Petitt, M.; Nayak, N.R. VEGF Maintains Maternal Vascular Space Homeostasis in the Mouse Placenta through Modulation of Trophoblast Giant Cell Functions. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossant, J.; Cross, J.C. Placental development: Lessons from mouse mutants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panja, S.; Paria, B.C. Development of the Mouse Placenta. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 2021, 234, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Cross, J.C. Development and function of trophoblast giant cells in the rodent placenta. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2010, 54, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokati, A.; Naser Moghadasi, A.; Ghashghaei, A.; Sahraian, M.A.; Chahardouli, B.; Mousavi, S.A.; Ai, J.; Nikbakht, M. Good manufacturing practices production of human placental derived mesenchymal stem cells for therapeutic applications: Focus on multiple sclerosis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Yan, L.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhao, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, H. A differentiation roadmap of murine placentation at single-cell resolution. Cell Discov. 2023, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Hayashi, S.; Usuda, K.; Abe, M.; Hagio, S.; Ogawa, I. Toxicological pathology in the rat placenta. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 24, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strumpf, D.; Mao, C.A.; Yamanaka, Y.; Ralston, A.; Chawengsaksophak, K.; Beck, F.; Rossant, J. Cdx2 is required for correct cell fate specification and differentiation of trophectoderm in the mouse blastocyst. Development 2005, 132, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niakan, K.K.; Eggan, K. Analysis of human embryos from zygote to blastocyst reveals distinct gene expression patterns relative to the mouse. Dev. Biol. 2013, 375, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Okamura, E.; Muto, M.; Ema, M. Similarities and differences in placental development between humans and cynomolgus monkeys. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2023, 22, e12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genbacev, O.; Lamb, J.D.; Prakobphol, A.; Donne, M.; McMaster, M.T.; Fisher, S.J. Human trophoblast progenitors: Where do they reside? Semin. Reprod. Med. 2013, 31, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, R.; Kohn, M.J.; Karavanova, I.; Kaneko, K.J.; Vullhorst, D.; DePamphilis, M.L.; Buonanno, A. Transcription factor TEAD4 specifies the trophectoderm lineage at the beginning of mammalian development. Development 2007, 134, 3827–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, H.; Toyooka, Y.; Shimosato, D.; Strumpf, D.; Takahashi, K.; Yagi, R.; Rossant, J. Interaction between Oct3/4 and Cdx2 determines trophectoderm differentiation. Cell 2005, 123, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seita, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, B.; Treff, N.; Lu, C.-W. CDX2 Expression Marks Trophoblast Progenitors from Differentiating Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 87, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latos, P.A.; Sienerth, A.R.; Murray, A.; Senner, C.E.; Muto, M.; Ikawa, M.; Oxley, D.; Burge, S.; Cox, B.J.; Hemberger, M. Elf5-centered transcription factor hub controls trophoblast stem cell self-renewal and differentiation through stoichiometry-sensitive shifts in target gene networks. Genes. Dev. 2015, 29, 2435–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemberger, M.; Udayashankar, R.; Tesar, P.; Moore, H.; Burton, G.J. ELF5-enforced transcriptional networks define an epigenetically regulated trophoblast stem cell compartment in the human placenta. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 2456–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemberger, M. Epigenetic landscape required for placental development. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2422–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Liang, G.; Tu, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Lu, J. Generation of Elf5-Cre knockin mouse strain for trophoblast-specific gene manipulation. Genesis 2018, 56, e23101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, G.X.; Konno, T.; Soares, M.J. Maternal hypoxia activates endovascular trophoblast cell invasion. Dev. Biol. 2008, 314, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Cui, W.; Rosario, G.X.; Scott, R.L.; Dhakal, P.; Renaud, S.J.; Tachibana, M.; Rumi, M.A.; Mason, C.W.; Krieg, A.J.; et al. HIF-KDM3A-MMP12 regulatory circuit ensures trophoblast plasticity and placental adaptations to hypoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7212–E7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Guerrini, M.M.; Yamamoto, K. Functional genomics of autoimmune diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.T.; Roth, M.E.; Groskopf, J.C.; Tsai, F.Y.; Orkin, S.H.; Grosveld, F.; Engel, J.D.; Linzer, D.I. GATA-2 and GATA-3 regulate trophoblast-specific gene expression in vivo. Development 1997, 124, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varberg, K.M.; Dominguez, E.M.; Koseva, B.; Varberg, J.M.; McNally, R.P.; Moreno-Irusta, A.; Wesley, E.R.; Iqbal, K.; Cheung, W.A.; Schwendinger-Schreck, C.; et al. Extravillous trophoblast cell lineage development is associated with active remodeling of the chromatin landscape. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Tynan, J.A.; Cecena, G.; Williams, R.; Múnera, J.; Mavrothalassitis, G.; Oshima, R.G. Ets2 is required for trophoblast stem cell self-renewal. Dev. Biol. 2007, 312, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamamoto, H.; Flannery, M.L.; Kupriyanov, S.; Pearce, J.; McKercher, S.R.; Henkel, G.W.; Maki, R.A.; Werb, Z.; Oshima, R.G. Defective trophoblast function in mice with a targeted mutation of Ets2. Genes. Dev. 1998, 12, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, A.; Ahuna, K.; Hwang, Y.M.; Pearl, J.; Liao, H.; Shannon, P.; Kadam, L.; Lapehn, S.; Bucher, M.; Roper, R.; et al. A genome scale transcriptional regulatory model of the human placenta. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadf3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalna, V.; Yang, Y.; Peghaire, C.R.; Frudd, K.; Hannah, R.; Shah, A.V.; Osuna Almagro, L.; Boyle, J.J.; Göttgens, B.; Ferrer, J.; et al. The Transcription Factor ERG Regulates Super-Enhancers Associated With an Endothelial-Specific Gene Expression Program. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, L.N.; Rumi, M.A.; Kubota, K.; Lee, D.S.; Soares, M.J. FOSL1 is integral to establishing the maternal-fetal interface. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 4801–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Ehrlich, K.C.; Lacey, M.; Baribault, C.; Ehrlich, M. Epigenetics and expression of key genes associated with cardiac fibrosis: NLRP3, MMP2, MMP9, CCN2/CTGF and AGT. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Pang, Z.J.; Yu, Y.H. Regulation of trophoblast invasion: The role of matrix metalloproteinases. Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 5, e137–e143. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.M.; Hansell, E.J.; Behrendtsen, O.; Flannery, M.L.; Kishnani, N.S.; Hawkes, S.P.; Werb, Z. Expression and function of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors at the maternal-embryonic boundary during mouse embryo implantation. Development 1996, 122, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokry, M.; Omran, O.M.; Hassan, H.I.; Elsedfy, G.O.; Hussein, M.R. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in human trophoblasts of normal and preeclamptic placentas: Preliminary findings. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 87, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, S.; Koch, Y.; Kühnel, E.; Sharma, N.; Gellhaus, A.; Kuckenberg, P.; Schorle, H.; Winterhager, E. Reduced Gene Dosage of Tfap2c Impairs Trophoblast Lineage Differentiation and Alters Maternal Blood Spaces in the Mouse Placenta. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 93, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, R.; Seval, Y.; Huppertz, B. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in the early human placenta. Acta Histochem. 2007, 109, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygmunt, M.; Herr, F.; Münstedt, K.; Lang, U.; Liang, O.D. Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in pregnancy. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2003, 110 (Suppl. 1), S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.K.; Keogh, R.J.; Wareing, M.; Baker, P.N.; Cartwright, J.E.; Aplin, J.D.; Whitley, G.S. Invasive trophoblasts stimulate vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis by a fas ligand-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1863–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.D.; De Long, N.E.; Wang, R.C.; Yazdi, F.T.; Holloway, A.C.; Raha, S. Angiogenesis in the placenta: The role of reactive oxygen species signaling. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 814543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantone, S.; Tossetta, G.; Di Simone, N.; Tersigni, C.; Scambia, G.; Marcheggiani, F.; Giannubilo, S.R.; Marzioni, D. CD93 a potential player in cytotrophoblast and endothelial cell migration. Cell Tissue Res. 2022, 387, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.V.; Birdsey, G.M.; Randi, A.M. Regulation of endothelial homeostasis, vascular development and angiogenesis by the transcription factor ERG. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016, 86, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdsey, G.M.; Shah, A.V.; Dufton, N.; Reynolds, L.E.; Osuna Almagro, L.; Yang, Y.; Aspalter, I.M.; Khan, S.T.; Mason, J.C.; Dejana, E.; et al. The endothelial transcription factor ERG promotes vascular stability and growth through Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraj, P.; Le Bras, A.; Mitchell, N.; Kondo, M.; Juliao, S.; Wasserman, M.; Beeler, D.; Spokes, K.; Aird, W.C.; Baldwin, H.S.; et al. Erg is a crucial regulator of endocardial-mesenchymal transformation during cardiac valve morphogenesis. Development 2012, 139, 3973–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Abe, M.; Yamazaki, T.; Niizeki, O.; Shiiba, K.; Sasaki, I.; Sato, Y. Transcriptional regulation of human angiopoietin-2 by transcription factor Ets-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Leach, R. GATA Transcription Factors in Pregnancy. Med. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 1, 1013. [Google Scholar]
- Kanki, Y.; Nakaki, R.; Shimamura, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamamizu, K.; Katayama, S.; Suehiro, J.I.; Osawa, T.; Aburatani, H.; Kodama, T.; et al. Dynamically and epigenetically coordinated GATA/ETS/SOX transcription factor expression is indispensable for endothelial cell differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 4344–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraineau, S.; Palii, C.G.; Allan, D.S.; Brand, M. Epigenetic regulation of endothelial-cell-mediated vascular repair. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 1605–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Home, P.; Bhattacharya, B.; Ray, S. GATA factors: Master regulators of gene expression in trophoblast progenitors. Placenta 2017, 60 (Suppl. 1), S61–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, R.P.; Ray, S.; Saha, A.; Roy, N.; Dasgupta, P.; Marsh, C.; Paul, S. The GATA transcriptional program dictates cell fate equilibrium to establish the maternal-fetal exchange interface and fetal development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2310502121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, T. Development and Carcinogenesis: Roles of GATA Factors in the Sympathoadrenal and Urogenital Systems. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claringbould, A.; Zaugg, J.B. Enhancers in disease: Molecular basis and emerging treatment strategies. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 1060–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovén, J.; Hoke, H.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Lau, A.; Orlando, D.A.; Vakoc, C.R.; Bradner, J.E.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Selective inhibition of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell 2013, 153, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, Y. The Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Family: Functional Anatomy of BET Paralogous Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, B.; Lorenzini, E.; Ciarrocchi, A. BRD4 and Cancer: Going beyond transcriptional regulation. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, B. Placental origins of preeclampsia: Challenging the current hypothesis. Hypertension 2008, 51, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallie, P.D.; Naicker, T.; Nayak, N.R. Stress-Sensitive Regulators of Fetal Neurodevelopment in HIV and Preeclampsia: An Immunocytochemical Appraisal of Placental OGT and T4 Levels. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2023, 71, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.F.; Fan, X.; Dhal, S.; Dwyer, B.K.; Jafari, A.; El-Sayed, Y.Y.; Druzin, M.L.; Nayak, N.R. Decreased circulating soluble Tie2 levels in preeclampsia may result from inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1148–E1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiworapongsa, T.; Chaemsaithong, P.; Yeo, L.; Romero, R. Pre-eclampsia part 1: Current understanding of its pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronikidi, P.E.; Orovou, E.; Mavrigiannaki, E.; Athanasiadou, V.; Tzitiridou-Chatzopoulou, M.; Iatrakis, G.; Grapsa, E. Placental and Renal Pathways Underlying Pre-Eclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yara, N.; Kinjyo, Y.; Chinen, Y.; Kinjo, T.; Mekaru, K. Placenta Accreta Spectrum with Ureteral Invasion due to Progression of Cesarean Scar Pregnancy. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 2023, 9065978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlando, M.; Collins, S. Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorders: Challenges, Risks, and Management Strategies. Int. J. Womens Health 2020, 12, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheibak, N.; Mahmoudzadeh-Sagheb, H.; Moudi, B.; Heidari, Z. Elevated immunoexpression of interferon-gamma in placenta tissue samples from pregnancies complicated with preeclampsia compared to the placenta previa. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020, 22, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, A.; Deneux-Tharaux, C.; Seco, A.; Sentilhes, L.; Kayem, G. Incidence and risk factors for severe postpartum haemorrhage in women with anterior low-lying or praevia placenta and prior caesarean: Prospective population-based study. BJOG 2023, 130, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, C. Iatrogenic vs. Spontaneous Preterm Birth: A Retrospective Study of Neonatal Outcome Among Very Preterm Infants. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 649749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, K.A.; Schlitt, J.M.; Jackson, D.L.; Schulz, L.C.; Schust, D.J. Preeclampsia: Multiple approaches for a multifactorial disease. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 5, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatford, K.L.; Andraweera, P.H.; Roberts, C.T.; Care, A.S. Animal Models of Preeclampsia: Causes, Consequences, and Interventions. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.; Welsh, M.; Makris, A.; Hennessy, A. Progress in preeclampsia: The contribution of animal models. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2022, 36, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadora, J.; Singh, M.; Herse, F.; Przybyl, L.; Haase, N.; Golic, M.; Yung, H.W.; Huppertz, B.; Cartwright, J.E.; Whitley, G.; et al. Disturbed Placental Imprinting in Preeclampsia Leads to Altered Expression of DLX5, a Human-Specific Early Trophoblast Marker. Circulation 2017, 136, 1824–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xing, F.; He, Y.; Zong, S.; Luo, C.; Li, C.; Duan, T.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Q. Elevated HTRA1 and HTRA4 in severe preeclampsia and their roles in trophoblast functions. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyarajah, M.J.; Jaju Bhattad, G.; Kops, B.F.; Renaud, S.J. Syndecan-4 regulates extravillous trophoblast migration by coordinating protein kinase C activation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Adu-Gyamfi, E.A.; Kim, J.; Lee, B.K. Super-enhancer-associated transcription factors collaboratively regulate trophoblast-active gene expression programs in human trophoblast stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 3806–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, E.L.; Bell, J.S.; Bhattacharya, S. Preeclampsia and preterm delivery: A population-based case-control study. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2016, 35, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).