Reproductive-Toxicity-Related Endpoints in C. elegans Are Consistent with Reduced Concern for Dimethylarsinic Acid Exposure Relative to Inorganic Arsenic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Dosing
2.2. Worm Maintenance
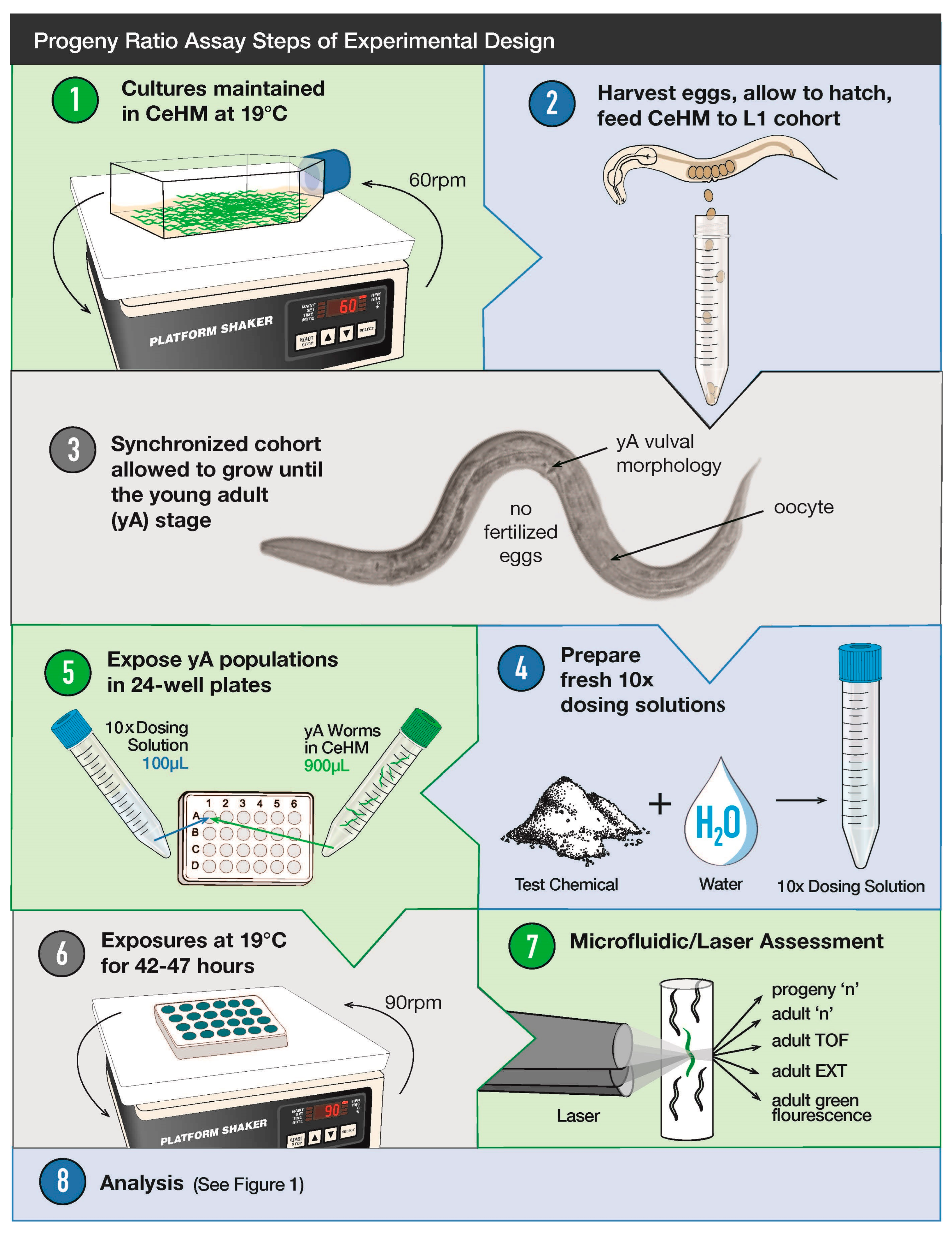
2.3. Progeny Ratio
2.4. Germline Health—Apoptosis
2.5. Epigenetic Germline De-Silencing—Histone Regulation Assay
3. Results
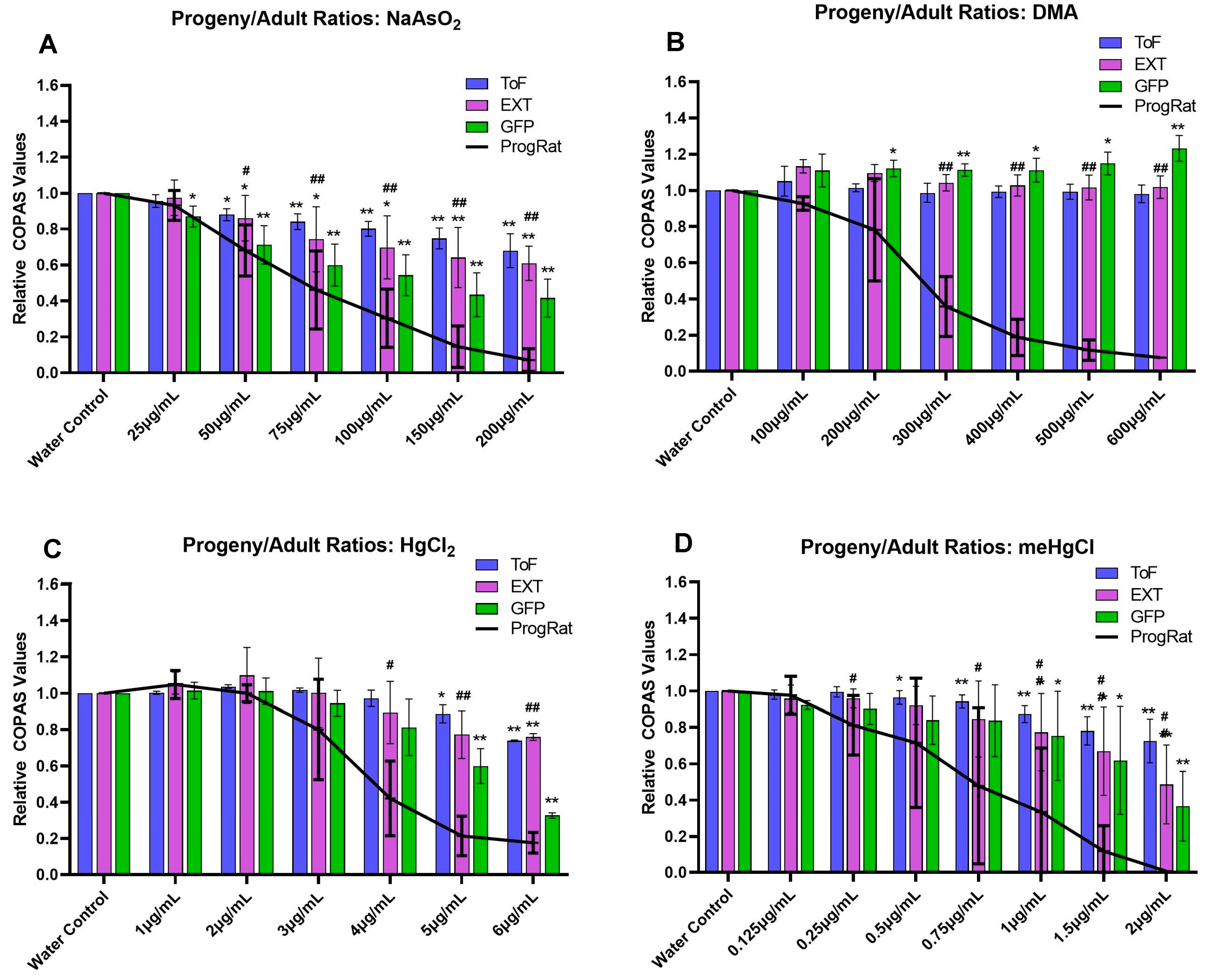
3.1. Progeny/Adult Ratio
3.2. Germline Health—Apoptosis
3.3. Epigenetic Germline de-Silencing—Histone Regulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Environmental Contaminants in Food. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/chemical-contaminants-pesticides/environmental-contaminants-food (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Closer to Zero: Reducing Childhood Exposure to Contaminants from Foods. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/environmental-contaminants-food/closer-zero-reducing-childhood-exposure-contaminants-foods#Introduction (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/tsca-inventory/about-tsca-chemical-substance-inventory (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Racz, P.I.; Wildwater, M.; Rooseboom, M.; Kerkhof, E.; Pieters, R.; Yebra-Pimentel, E.S.; Dirks, R.P.; Spaink, H.P.; Smulders, C.; Whale, G.F. Application of Caenorhabditis elegans (nematode) and Danio rerio embryo (zebrafish) as model systems to screen for developmental and reproductive toxicity of Piperazine compounds. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 44, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Voet, M.; Teunis, M.; Louter-van de Haar, J.; Stigter, N.; Bhalla, D.; Rooseboom, M.; Wever, K.E.; Krul, C.; Pieters, R.; Wildwater, M.; et al. Towards a reporting guideline for developmental and reproductive toxicology testing in C. elegans and other nematodes. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH S5 (R3) Guideline on Reproductive Toxicology: Detection of Toxicity to Reproduction for Human Pharmaceuticals; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Nonclinical Considerations for Mitigating Nonhuman Primate Supply Constraints Arising from the COVID-19 Pandemic; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022.
- Ackley, D.; Birkebak, J.; Blumel, J.; Bourcier, T.; de Zafra, C.; Goodwin, A.; Halpern, W.; Herzyk, D.; Kronenberg, S.; Mauthe, R.; et al. FDA and industry collaboration: Identifying opportunities to further reduce reliance on nonhuman primates for nonclinical safety evaluations. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 138, 105327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Frank R. Lautenberg Chemical Safety for the 21st Century Act. In Public Law; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Administrator Wheeler Signs Memo to Reduce Animal Testing, Awards $4.25 Million to Advance Research on Alternative Methods to Animal Testing; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA’s Predictive Toxicology Roadmap; US Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017.
- Kavlock, R.J.; Austin, C.P.; Tice, R.R. US vision for toxicity testing in the 21st Century. In The History of Alternative Test Methods in Toxicology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Piersma, A.H.; Baker, N.C.; Daston, G.P.; Flick, B.; Fujiwara, M.; Knudsen, T.B.; Spielmann, H.; Suzuki, N.; Tsaioun, K.; Kojima, H. Pluripotent stem cell assays: Modalities and applications for predictive developmental toxicity. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 3, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, R.A.; Bianchi, E.; LaRocca, J.; Marty, M.S.; Mehta, V. Identifying the landscape of developmental toxicity new approach methodologies. Birth Defects Res. 2022, 114, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.; Cuenca, L.; Karthikraj, R.; Kannan, K.; Colaiacovo, M.P. Assessing effects of germline exposure to environmental toxicants by high-throughput screening in C. elegans. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athar, F.; Templeman, N.M. C. elegans as a model organism to study female reproductive health. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 266, 111152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Arsenic; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1993.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Mercury; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1994.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Metals and Your Food. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/chemicals-metals-pesticides-food/metals-and-your-food (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Arsenic in Rice and Rice Products Risk Assessment Report; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2016.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Action Level for Inorganic Arsenic in Rice Cereals for Infants; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Technical Information on Development of FDA/EPA Advice about Eating Fish for Those Who Might Become or Are Pregnant or Breastfeeding and Children Ages 1–11 Years; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. National Primary Drinking Water Regulations; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 2.
- Twaddle, N.C.; Vanlandingham, M.; Beland, F.A.; Doerge, D.R. Metabolism and disposition of arsenic species after repeated oral dosing with sodium arsenite in drinking water. II. Measurements in pregnant and fetal CD-1 mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 115, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, M.C.; Loureiro, S.; Fardilha, M.; Herdeiro, M.T. Exposure to mercury and human reproductive health: A systematic review. Reprod. Toxicol. 2019, 85, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.T.; Atkinson, A.; Graham, T.C.; Thompson, S.J.; Ali, S.; Shireen, K.F. Effects of inorganic mercury on reproductive performance of mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElwee, M.K.; Ho, L.A.; Chou, J.W.; Smith, M.V.; Freedman, J.H. Comparative toxicogenomic responses of mercuric and methyl-mercury. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, J.; de Conti, A.; Pogribny, I.P.; Sprando, R.L.; Hunt, P.R. Assessment of the effects of organic vs. inorganic arsenic and mercury in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 3, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nass, R.; Hamza, I. The nematode C. elegans as an animal model to explore toxicology in vivo: Solid and axenic growth culture conditions and compound exposure parameters. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2007, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, E.D.; Lapenotiere, H.F.; French, D.Y.; Szilagyi, M. Use of CeHR axenic medium for exposure and gene expression studies. In Proceedings of the 2002 East Coast Worm Meeting, Reproductive Hazards Laboratory, US Army Center for Environmental Health Research, Fort Detrick, MD, USA, 14 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sprando, R.L.; Olejnik, N.; Cinar, H.N.; Ferguson, M. A method to rank order water soluble compounds according to their toxicity using Caenorhabditis elegans, a Complex Object Parametric Analyzer and Sorter, and axenic liquid media. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, P.R.; Olejnik, N.; Bailey, K.D.; Vaught, C.A.; Sprando, R.L. C. elegans Development and Activity Test detects mammalian developmental neurotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, P.; Colaiácovo, M.P. Mechanistic insights into the action of Bisphenol A on the germline using C. elegans. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, A.; Boag, P.R.; Blackwell, T.K. Germline Survival and Apoptosis. In WormBook: The Online Review of C. elegans Biology; WormBook: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, J.; Truong, L.; Kurt, Z.; Chen, Y.-W.; Morselli, M.; Gutierrez, G.; Pellegrini, M.; Yang, X.; Allard, P. The Memory of Environmental Chemical Exposure in C. elegans Is Dependent on the Jumonji Demethylases jmjd-2 and jmjd-3/utx-1. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundby, Z.; Camacho, J.; Allard, P. Fast functional germline and epigenetic assays in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. In High-Throughput Screening Assays in Toxicology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, C.; Lafayette, I.; Antoniou-Kourounioti, M.; Haque, M.; King, J.; Johnsen, B.; Baillie, D.; Gutierrez, C.; Martin, J.A.; de Pomerai, D. Transgenic nematodes as biosensors for metal stress in soil pore water samples. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Dernburg, A.F. A conserved checkpoint monitors meiotic chromosome synapsis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2005, 310, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaner, C.E.; Kelly, W.G. Germline chromatin. In WormBook: The Online Review of C. elegans Biology; WormBook: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitch, H.G.; Tang, W.W.C.; Surani, M.A. Chapter Five—Primordial Germ-Cell Development and Epigenetic Reprogramming in Mammals. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Heard, E., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 104, pp. 149–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, W.G.; Fire, A. Chromatin silencing and the maintenance of a functional germline in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 1998, 125, 2451–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.G.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Fire, A. Distinct requirements for somatic and germline expression of a generally expressed Caernorhabditis elegans gene. Genetics 1997, 146, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antebi, A.; Norris, C.R.; Hedgecock, E.M.; Garriga, G. Cell and Growth Cone Migrations. In C. elegans II; Riddle, D.L., Blumenthal, T., Meyer, B.J., Priess, J.R., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, P.W.; Myers, G.J.; Weiss, B. Mercury exposure and child development outcomes. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francesconi, K.A. Toxic metal species and food regulations--making a healthy choice. Analyst 2007, 132, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion on arsenic in food. Efsa J. 2009, 7, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Safety Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Prepared by the Seventy-Second Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Wang, A.; Holladay, S.D.; Wolf, D.C.; Ahmed, S.A.; Robertson, J.L. Reproductive and developmental toxicity of arsenic in rodents: A review. Int. J. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, A.; Sedha, S. Occupational and environmental mercury exposure and human reproductive health—A review. J. Turk. Ger. Gynecol. Assoc. 2022, 23, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Mercury; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022.
- Buchet, J.P.; Lauwerys, R.R. Influence of 2,3 dimercaptopropane-1-sulfonate and dimercaptosuccinic acid on the mobilization of mercury from tissues of rats pretreated with mercuric chloride, phenylmercury acetate or mercury vapors. Toxicology 1989, 54, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, T.F.; Lam, H.S.; Ng, P.C.; Yip, A.S.; Sin, N.C.; Chan, I.H.; Gu, G.J.; So, H.K.; Wong, E.M.; Lam, C.W. Fetal methylmercury exposure as measured by cord blood mercury concentrations in a mother–infant cohort in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.L.; Flanigan, T.J.; Law, C.D.; Loukotková, L.; Woodling, K.A.; da Costa, G.G.; Fitzpatrick, S.C.; Ferguson, S.A. Developmental neurotoxicity of inorganic arsenic exposure in Sprague-Dawley rats. Neurotoxicology Teratol. 2019, 72, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, M.S.; Macintosh, M.S.; Baumrind, N. Developmental and reproductive toxicity of inorganic arsenic: Animal studies and human concerns. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 1998, 1, 199–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, L.M.; Wang, Y. Arsenic Exposure and Compromised Protein Quality Control. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormo, M.; Cubitt, A.B.; Kallio, K.; Gross, L.A.; Tsien, R.Y.; Remington, S.J. Crystal structure of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein. Science 1996, 273, 1392–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, M.K.; Tony, S.R.; Siddique, A.E.; Karim, M.R.; Haque, N.; Islam, Z.; Islam, M.S.; Khatun, M.; Islam, J.; Hossain, S.; et al. Arsenic Secondary Methylation Capacity Is Inversely Associated with Arsenic Exposure-Related Muscle Mass Reduction. Int J Env. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A.; Thompson, S.; Khan, A.; Graham, T.; Ali, S.; Shannon, C.; Clarke, O.; Upchurch, L. Assessment of a two-generation reproductive and fertility study of mercuric chloride in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-F.; Liu, S.-H.; Hsu, C.-J.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y. Neurotoxicological effects of low-dose methylmercury and mercuric chloride in developing offspring mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 201, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, W. Perinatal exposure to low-dose methylmercury induces dysfunction of motor coordination with decreases in synaptophysin expression in the cerebellar granule cells of rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1464, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.A.A.S.; Liu, L.; Keefe, D.L. In Vivo Effects of Arsenite on Meiosis, Preimplantation Development, and Apoptosis in the Mouse1. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 70, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschaeve, L.; Léonard, A. Dominant lethal test in female mice treated with methyl mercury chloride. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. 1984, 136, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamani, I.J.; Keefe, D.L. Epigenetics and Female Reproductive Aging. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.-B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.-P.; Wu, C.-Y.; Jin, J.; Sang, J.-R.; Lu, H.-Y.; Gong, A.-H.; Du, F.-Y.; Peng, W.-X. Aging alters histone H3 lysine 4 methylation in mouse germinal vesicle stage oocytes. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2015, 27, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manosalva, I.; Gonzalez, A. Aging changes the chromatin configuration and histone methylation of mouse oocytes at germinal vesicle stage. Theriogenology 2010, 74, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessler, J.B.; Andersen, E.C.; Villeneuve, A.M. Differential localization and independent acquisition of the H3K9me2 and H3K9me3 chromatin modifications in the Caenorhabditis elegans adult germ line. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.W.; Jung, Y.L.; Liu, T.; Alver, B.H.; Lee, S.; Ikegami, K.; Sohn, K.-A.; Minoda, A.; Tolstorukov, M.Y.; Appert, A. Comparative analysis of metazoan chromatin organization. Nature 2014, 512, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Rechtsteiner, A.; Egelhofer, T.A.; Vielle, A.; Latorre, I.; Cheung, M.-S.; Ercan, S.; Ikegami, K.; Jensen, M.; Kolasinska-Zwierz, P. Broad chromosomal domains of histone modification patterns in C. elegans. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Brind’Amour, J.; Karimi, M.M.; Shirane, K.; Bogutz, A.; Lefebvre, L.; Sasaki, H.; Shinkai, Y.; Lorincz, M.C. Setdb1 is required for germline development and silencing of H3K9me3-marked endogenous retroviruses in primordial germ cells. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2041–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, C.G.; Gamble, M.V. Influence of Arsenic on Global Levels of Histone Posttranslational Modifications: A Review of the Literature and Challenges in the Field. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.D.; Lam, W.L. Health Effects Associated with Pre- and Perinatal Exposure to Arsenic. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 664717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, N.; Laudati, G.; Anzilotti, S.; Sirabella, R.; Cuomo, O.; Brancaccio, P.; Santopaolo, M.; Galgani, M.; Montuori, P.; Di Renzo, G. Methylmercury upregulates RE-1 silencing transcription factor (REST) in SH-SY5Y cells and mouse cerebellum. Neurotoxicology 2016, 52, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronican, A.A.; Fitz, N.F.; Carter, A.; Saleem, M.; Shiva, S.; Barchowsky, A.; Koldamova, R.; Schug, J.; Lefterov, I. Genome-wide alteration of histone H3K9 acetylation pattern in mouse offspring prenatally exposed to arsenic. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, C.R.; Hafez, A.K.; Solomon, E.R.; Allan, A.M. Developmental exposure to 50 parts-per-billion arsenic influences histone modifications and associated epigenetic machinery in a region-and sex-specific manner in the adult mouse brain. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 288, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudgalvyte, M.; Peltonen, J.; Lakso, M.; Wong, G. Chronic MeHg exposure modifies the histone H3K4me3 epigenetic landscape in Caenorhabditis elegans. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 191, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvan, M.J., 3rd; Kalluvila, T.A.; Klingler, R.H.; Larson, J.K.; Pickens, M.; Mora-Zamorano, F.X.; Connaughton, V.P.; Sadler-Riggleman, I.; Beck, D.; Skinner, M.K. Mercury-induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of abnormal neurobehavior is correlated with sperm epimutations in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, T.; Tinkov, A.A.; Skalny, A.V.; Santamaria, A.; Rocha, J.B.; Bowman, A.B.; Chen, W.; Aschner, M. Epigenetics and Methylmercury-Induced Neurotoxicity, Evidence from Experimental Studies. Toxics 2023, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishchenko, N.; Karpova, N.; Sabri, F.; Castrén, E.; Ceccatelli, S. Long-lasting depression-like behavior and epigenetic changes of BDNF gene expression induced by perinatal exposure to methylmercury. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, T.B.; Cortez, C.C.; Yoo, C.B.; Liang, G.; Abe, M.; Kelly, T.K.; Marquez, V.E.; Jones, P.A. DZNep is a global histone methylation inhibitor that reactivates developmental genes not silenced by DNA methylation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bi, C.; Cheong, L.-L.; Mahara, S.; Liu, S.-C.; Tay, K.-G.; Koh, T.-L.; Yu, Q.; Chng, W.-J. The histone methyltransferase inhibitor, DZNep, up-regulates TXNIP, increases ROS production, and targets leukemia cells in AML. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 118, 2830–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Okabe, H.; Hayashi, H.; Hashimoto, D.; Yokoyama, N.; Tokunaga, R.; Sakamoto, K.; Kuroki, H.; Mima, K. Epigenetic therapy with the histone methyltransferase EZH2 inhibitor 3-deazaneplanocin A inhibits the growth of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Test Chemical | Abbreviation | CAS RN | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium (meta)arsenite | NaAsO2 | 7784–46-5 | 129.91 |
| Dimethylarsinic acid (DMAV) | DMA | 75–60-5 | 138.00 |
| Mercury(ii) chloride | HgCl2 | 7487–94-7 | 271.50 |
| Methylmercury chloride | meHgCl | 115–09-3 | 251.08 |
| Chemical | Assay | C. elegans Strain | Stage (Duration) of Exposure | LOEL µg/mL (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium (meta)arsenite | Progeny ratio | PD4251 | yA (2 days) | 50 (385) |
| Germline apoptosis | N2 wild type | L4 (24 h) | 50 (385) | |
| Germline histone regulation | NL2507 | L4 (24 h) | 20 (155) | |
| Dimethylarsinic acid (DMAV) | Progeny ratio | PD4251 | yA (2 days) | 300 (2200) |
| Germline apoptosis | N2 wild type | L4 (24 h) | 400 (2900) | |
| Germline histone regulation | NL2507 | L4 (24 h) | 100 (750) | |
| Mercury(ii) chloride | Progeny ratio | PD4251 | yA (2 days) | 4 (15) |
| Germline apoptosis | N2 wild type | L4 (24 h) | 3 (11) | |
| Germline histone regulation | NL2507 | L4 (24 h) | 2.5 (9) | |
| Methylmercury chloride | Progeny ratio | PD4251 | yA (2 days) | 0.25 (1) |
| Germline apoptosis | N2 wild type | L4 (24 h) | 2 (8) | |
| Germline histone regulation | NL2507 | L4 (24 h) | 0.5 (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camacho, J.A.; Welch, B.; Sprando, R.L.; Hunt, P.R. Reproductive-Toxicity-Related Endpoints in C. elegans Are Consistent with Reduced Concern for Dimethylarsinic Acid Exposure Relative to Inorganic Arsenic. J. Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb11020018
Camacho JA, Welch B, Sprando RL, Hunt PR. Reproductive-Toxicity-Related Endpoints in C. elegans Are Consistent with Reduced Concern for Dimethylarsinic Acid Exposure Relative to Inorganic Arsenic. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2023; 11(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb11020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamacho, Jessica A., Bonnie Welch, Robert L. Sprando, and Piper R. Hunt. 2023. "Reproductive-Toxicity-Related Endpoints in C. elegans Are Consistent with Reduced Concern for Dimethylarsinic Acid Exposure Relative to Inorganic Arsenic" Journal of Developmental Biology 11, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb11020018
APA StyleCamacho, J. A., Welch, B., Sprando, R. L., & Hunt, P. R. (2023). Reproductive-Toxicity-Related Endpoints in C. elegans Are Consistent with Reduced Concern for Dimethylarsinic Acid Exposure Relative to Inorganic Arsenic. Journal of Developmental Biology, 11(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb11020018






