Activation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Promotes Differentiation of Cortical Layer 4 Neurons via Regulation of Their Cell Positioning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. In Utero Electroporation
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of the Cell Positioning
2.5. Statistical Analysis
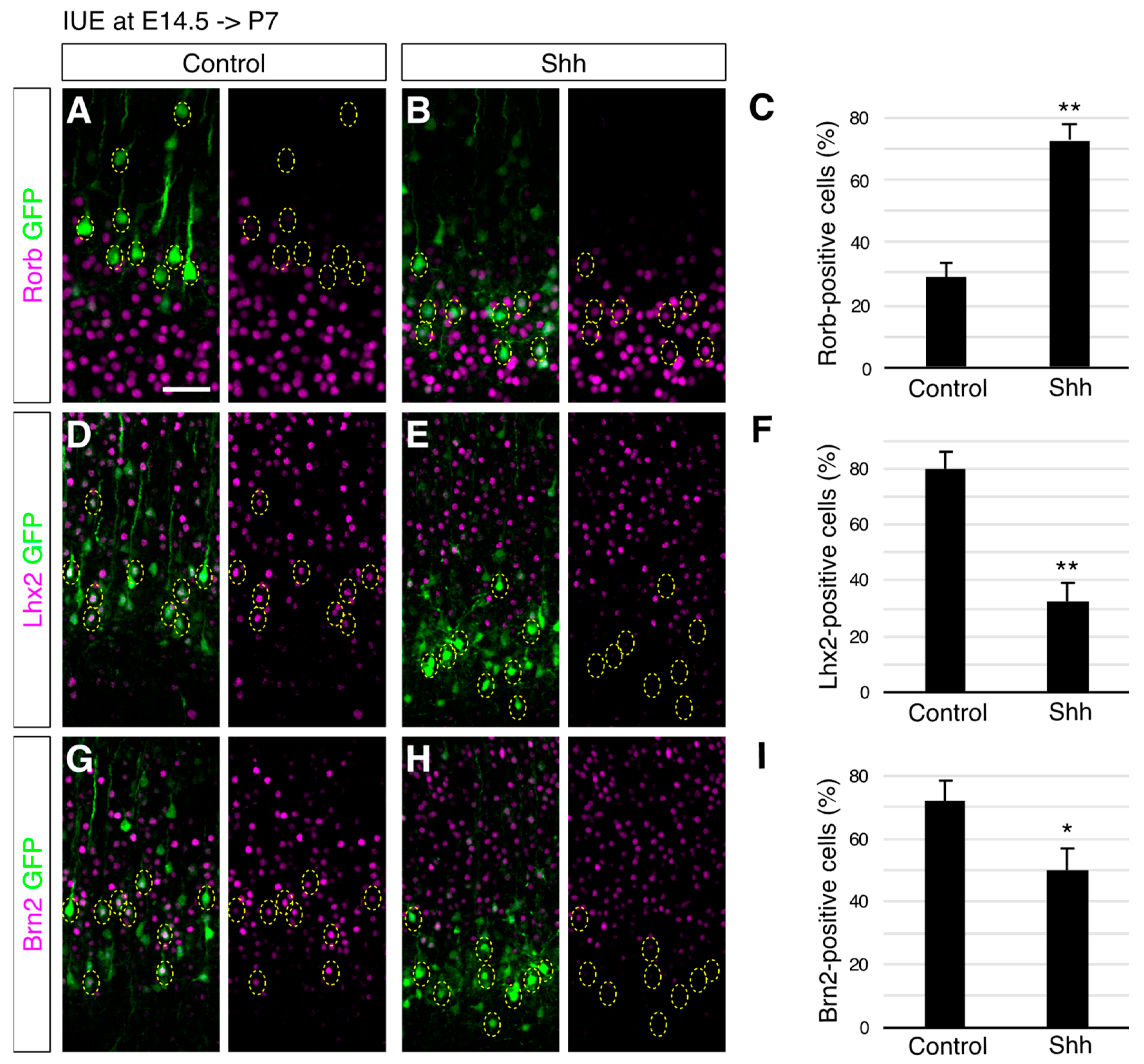
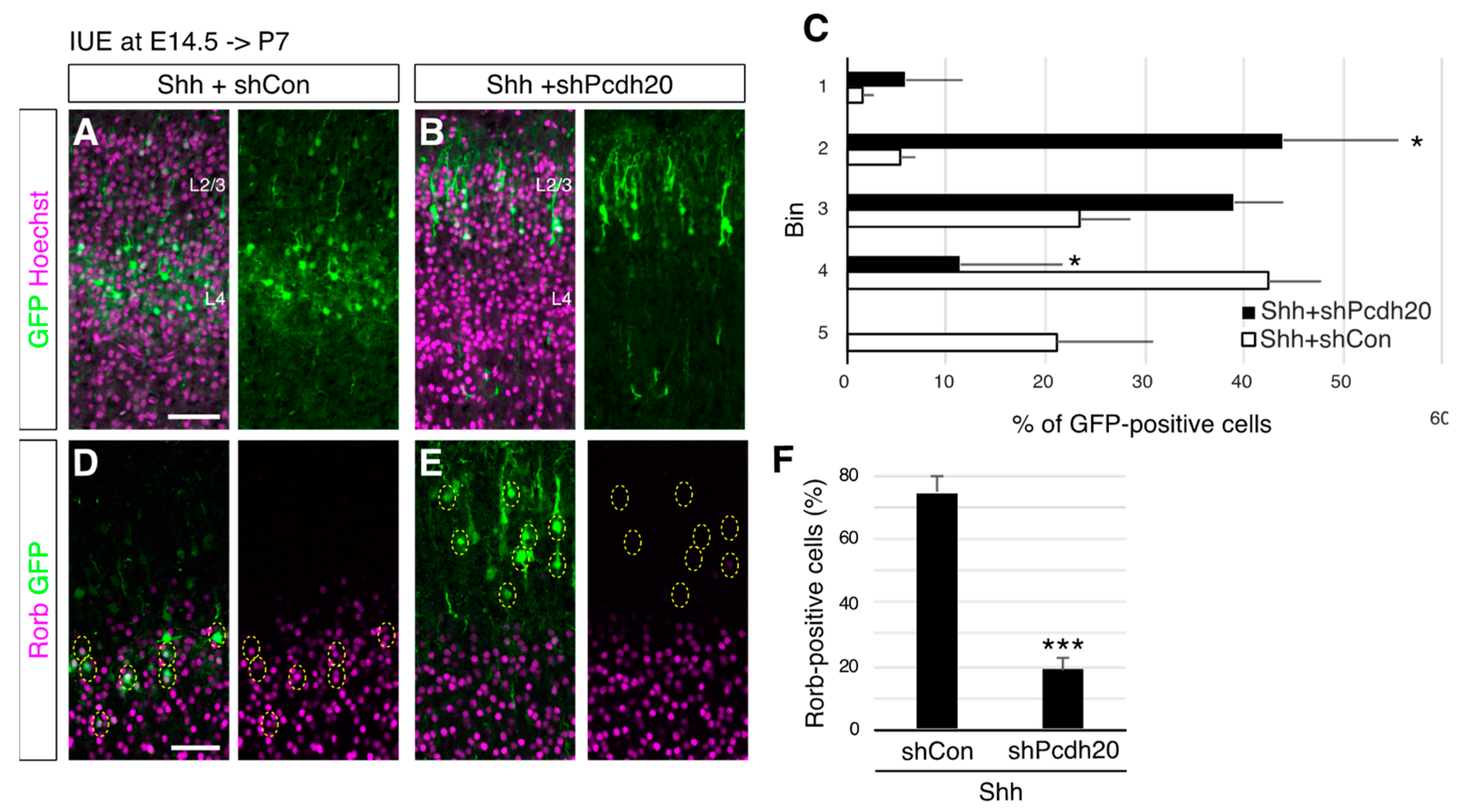
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lodato, S.; Arlotta, P. Generating neuronal diversity in the mammalian cerebral cortex. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 31, 699–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, L.C.; Woodworth, M.; Galazo, M.; Padmanabhan, H.; Macklis, J.D. Molecular logic of neocortical projection neuron specification, development and diversity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, K. Control of tangential/non-radial migration of neurons in the developing cerebral cortex. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 51, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, O.; Rubenstein, J.L.R. A long, remarkable journey: Tangential migration in the telencephalon. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, K.; Nakajima, K. Subtype Specification of Cerebral Cortical Neurons in Their Immature Stages. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, G. Elucidating the developmental trajectories of GABAergic cortical interneuron subtypes. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 138, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, H. Diverse subtypes of astrocytes and their development during corticogenesis. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, K.Y.; Sestan, N.; Anton, E.S. Transcriptional co-regulation of neuronal migration and laminar identity in the neocortex. Development 2012, 139, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Goto, T.; Miyama, S.; Nowakowski, R.; Caviness, V.S., Jr. Sequence of neuron origin and neocortical laminar fate: Relation to cell cycle of origin in the developing murine cerebral wall. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10357–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network (BICCN). A multimodal cell census and atlas of the mammalian primary motor cortex. Nature 2021, 598, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Schaevitz, L.R.; McConnell, S.K. Fezl regulates the differentiation and axon targeting of layer 5 subcortical projection neurons in cerebral cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17184–17189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneaux, B.J.; Arlotta, P.; Hirata, T.; Hibi, M.; Macklis, J.D. Fezl is required for the birth and specification of corticospinal motor neurons. Neuron 2005, 47, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.G.; Rašin, M.-R.; Kwan, K.Y.; Šestan, N. Zfp312 is required for subcortical axonal projections and dendritic morphology of deep-layer pyramidal neurons of the cerebral cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17792–17797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlotta, P.; Molyneaux, B.J.; Chen, J.; Inoue, J.; Kominami, R.; Macklis, J.D. Neuronal subtype-specific genes that control corticospinal motor neuron development in vivo. Neuron 2005, 45, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabaudon, D.; Shnider, S.J.; Tischfield, D.; Galazo, M.; Macklis, J.D. RORβ induces barrel-like neuronal clusters in the developing neocortex. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, K.; Aramaki, M.; Nakajima, K. Mutually repressive interaction between Brn1/2 and Rorb contributes to the establishment of neocortical layer 2/3 and layer 4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3371–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hevner, R.F.; Shi, L.; Justice, N.; Hsueh, Y.-P.; Sheng, M.; Smiga, S.; Bulfone, A.; Goffinet, A.M.; Campagnoni, A.T.; Rubenstein, J.L. Tbr1 regulates differentiation of the preplate and layer 6. Neuron 2001, 29, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, E.A.; Chirivella, L.; Dautzenberg, M.; Dobreva, G.; Fariñas, I.; Grosschedl, R.; McConnell, S.K. Satb2 regulates callosal projection neuron identity in the developing cerebral cortex. Neuron 2008, 57, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britanova, O.; de Juan Romero, C.; Cheung, A.; Kwan, K.Y.; Schwark, M.; Gyorgy, A.; Vogel, T.; Akopov, S.; Mitkovski, M.; Agoston, D.; et al. Satb2 is a postmitotic determinant for upper-layer neuron specification in the neocortex. Neuron 2008, 57, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohwi, M.; Doe, C.Q. Temporal fate specification and neural progenitor competence during development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehay, C.; Kennedy, H. Cell-cycle control and cortical development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, T.; Suda, Y.; Nakao, K.; Narimatsu, M.; Hirano, T.; Hibi, M. Zinc finger gene fez-like functions in the formation of subplate neurons and thalamocortical axons. Dev. Dyn. 2004, 230, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, M.H.; Ayoub, A.E.; Rakic, P. POU-III transcription factors (Brn1, Brn2, and Oct6) influence neurogenesis, molecular identity, and migratory destination of upper-layer cells of the cerebral cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 2632–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, K.; Nakagawa, N.; Tachikawa, K.; Sasaki, S.; Aramaki, M.; Hirano, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Yoshimura, Y.; Nakajima, K. Identity of neocortical layer 4 neurons is specified through correct positioning into the cortex. eLife 2016, 5, e10907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberst, P.; Fièvre, S.; Baumann, N.; Concetti, C.; Bartolini, G.; Jabaudon, D. Temporal plasticity of apical progenitors in the developing mouse neocortex. Nature 2019, 573, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Hatakeyama, J.; Iwasato, T.; Araki, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Shimamura, K. Thalamocortical axons control the cytoarchitecture of neocortical layers by area-specific supply of VGF. Elife 2022, 11, e67549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouchelon, G.; Gambino, F.; Bellone, C.; Telley, L.; Vitali, I.; Lüscher, C.; Holtmaat, A.; Jabaudon, D. Modality-specific thalamocortical inputs instruct the identity of postsynaptic L4 neurons. Nature 2014, 511, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.R.; McConnell, S.K. Progressive restriction in fate potential by neural progenitors during cerebral cortical development. Development 2000, 127, 2863–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabut, O.R.; Pleasure, S.J. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Rises to the Surface: Emerging Roles in Neocortical Development. Brain Plast. 2018, 3, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikata, Y.; Okada, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Ellis, T.; Matsumaru, D.; Shiroishi, T.; Ogawa, M.; Wainwright, B.; Motoyama, J. Ptch1-mediated dosage-dependent action of Shh signaling regulates neural progenitor development at late gestational stages. Dev. Biol. 2011, 349, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hou, S.; Han, Y.-G. Hedgehog signaling promotes basal progenitor expansion and the growth and folding of the neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, G.L.; Araújo, J.A.; Schroeder, T.; Tort, A.B.; Costa, M.R. Sonic hedgehog signaling regulates mode of cell division of early cerebral cortex progenitors and increases astrogliogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozniak, C.D.; Langseth, A.J.; Dijkgraaf, G.J.P.; Choe, Y.; Werb, Z.; Pleasure, S.J. Sox10 directs neural stem cells toward the oligodendrocyte lineage by decreasing Suppressor of Fused expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21795–21800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.A.; Fu, M.; Garcia, A.D.R. Sonic hedgehog signaling in astrocytes. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, N.; Dahmane, N. Sonic hedgehog signaling in forebrain development and its interactions with pathways that modify its effects. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, H.; Nakajima, K. Efficient in utero gene transfer system to the developing mouse brain using electroporation: Visualization of neuronal migration in the developing cortex. Neuroscience 2001, 103, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staiger, J.F.; Flagmeyer, I.; Schubert, D.; Zilles, K.; Kötter, R.; Luhmann, H.J. Functional diversity of layer IV spiny neurons in rat somatosensory cortex: Quantitative morphology of electrophysiologically characterized and biocytin labeled cells. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; O’Leary, D.D. Dynamic patterned expression of orphan nuclear receptor genes RORalpha and RORbeta in developing mouse forebrain. Dev. Neurosci. 2003, 25, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeren-Wiemers, N.; André, E.; Kapfhammer, J.P.; Becker-André, M. The expression pattern of the orphan nuclear receptor RORbeta in the developing and adult rat nervous system suggests a role in the processing of sensory information and in circadian rhythm. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 2687–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Johnson, J.E.; O’Leary, D.D.M. Graded and areal expression patterns of regulatory genes and cadherins in embryonic neocortex independent of thalamocortical input. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10877–10885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvilly, R.J.; de Diaz, M.O.; Schonemann, M.D.; Hooshmand, F.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Transcriptional regulation of cortical neuron migration by POU domain factors. Science 2002, 295, 1528–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugitani, Y.; Nakai, S.; Minowa, O.; Nishi, M.; Jishage, K.-I.; Kawano, H.; Mori, K.; Ogawa, M.; Noda, T. Brn-1 and Brn-2 share crucial roles in the production and positioning of mouse neocortical neurons. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Qiao, L.; Guo, Z.; Lin, J. Sonic Hedgehog Regulation of the Neural Precursor Cell Fate During Chicken Optic Tectum Development. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huangfu, D.; Anderson, K.V. Signaling from Smo to Ci/Gli: Conservation and divergence of Hedgehog pathways from Drosophila to vertebrates. Development 2006, 133, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, S.V.; Wichterle, H.; Fishell, G. Sonic hedgehog contributes to oligodendrocyte specification in the mammalian forebrain. Development 2001, 128, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolay, D.J.; Doucette, J.R.; Nazarali, A.J. Transcriptional control of oligodendrogenesis. Glia 2007, 55, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.D.R.; Petrova, R.; Eng, L.; Joyner, A.L. Sonic hedgehog regulates discrete populations of astrocytes in the adult mouse forebrain. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 13597–13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwell, C.C.; Parker, P.R.; Gee, S.M.; Okada, A.; McConnell, S.K.; Kreitzer, A.C.; Kriegstein, A.R. Sonic hedgehog expression in corticofugal projection neurons directs cortical microcircuit formation. Neuron 2012, 73, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andhika Rhaditya, P.A.; Oishi, K.; Nishimura, Y.V.; Motoyama, J. [Ca2+]i fluctuation mediated by T-type Ca2+ channel is required for the differentiation of cortical neural progenitor cells. Dev. Biol. 2022, 489, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, S.; Ishii, Y.; Horigane, S.-I.; Suzuki, K.; Ohkura, M.; Nakai, J.; Fujii, H.; Takemoto-Kimura, S.; Bito, H. A Critical Neurodevelopmental Role for L-Type Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels in Neurite Extension and Radial Migration. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 5551–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rash, B.G.; Ackman, J.B.; Rakic, P. Bidirectional radial Ca(2+) activity regulates neurogenesis and migration during early cortical column formation. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teperino, R.; Amann, S.; Bayer, M.; McGee, S.; Loipetzberger, A.; Connor, T.; Jaeger, C.; Kammerer, B.; Winter, L.; Wiche, G.; et al. Hedgehog partial agonism drives Warburg-like metabolism in muscle and brown fat. Cell 2012, 151, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komada, M.; Saitsu, H.; Kinboshi, M.; Miura, T.; Shiota, K.; Ishibashi, M. Hedgehog signaling is involved in development of the neocortex. Development 2008, 135, 2717–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Mikoshiba, K.; Nakajima, K. Regulation of cortical neuron migration by the Reelin signaling pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramanappa, S.; Saaber, F.; Abe, P.; Schütz, D.; Kumar, P.A.; Stumm, R. Cxcr4 and Ackr3 regulate allocation of caudal ganglionic eminence-derived interneurons to superficial cortical layers. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oishi, K.; Nakajima, K.; Motoyama, J. Activation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Promotes Differentiation of Cortical Layer 4 Neurons via Regulation of Their Cell Positioning. J. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10040050
Oishi K, Nakajima K, Motoyama J. Activation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Promotes Differentiation of Cortical Layer 4 Neurons via Regulation of Their Cell Positioning. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2022; 10(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleOishi, Koji, Kazunori Nakajima, and Jun Motoyama. 2022. "Activation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Promotes Differentiation of Cortical Layer 4 Neurons via Regulation of Their Cell Positioning" Journal of Developmental Biology 10, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10040050
APA StyleOishi, K., Nakajima, K., & Motoyama, J. (2022). Activation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Promotes Differentiation of Cortical Layer 4 Neurons via Regulation of Their Cell Positioning. Journal of Developmental Biology, 10(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb10040050







