An Artificial Neural Network Based Robot Controller that Uses Rat’s Brain Signals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Rat Training
- (1)
- Press any lever to get food supplied manually by a human.
- (2)
- Press levers as above, except with their head restricted.
- (1)
- The robot is placed in front of the rat and it moves straight forward when any lever is pressed.
- (2)
- The robot is placed on the right (left) side of the rat and it follows half of a U-shape trajectory when only the right (left) lever is pressed.
- (3)
- The robot is placed initially on the right or left side of the rat and it moves to the right or left of a U-shape when the respective lever is pressed.
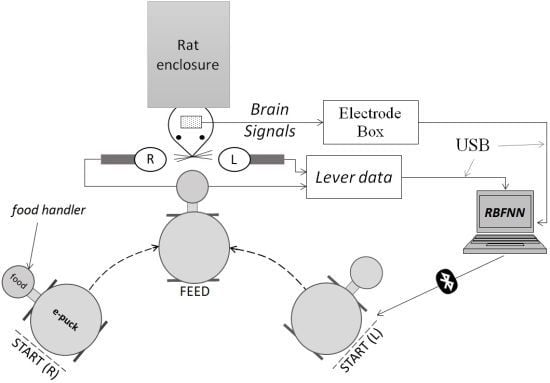
3. Method
3.1. Signal and Event Acquisition
- (1)
- Electrodes, L1 and R1, were implanted in the motor cortex area, respectively in the left and right hemisphere.
- (2)
- Electrodes, L2 and R2, were implanted in the somatosensory cortex area, respectively in the left and right hemisphere.

3.2. Feature Extraction and Neural Network
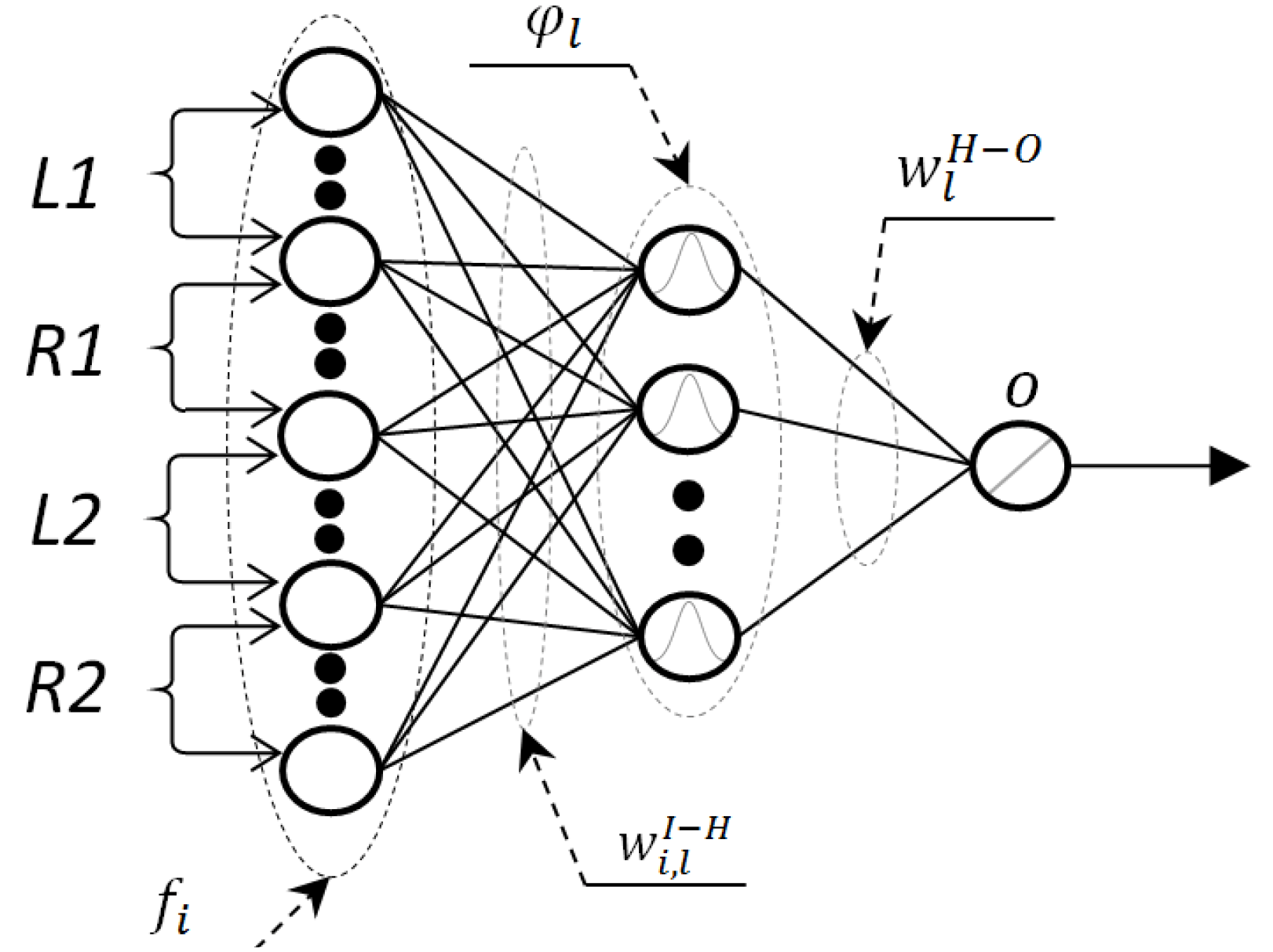
 in the vicinity of the lever press events, as shown in Figure 3.
in the vicinity of the lever press events, as shown in Figure 3.
 . The data were similarly processed to extract the feature vector, which was classified by the RBFNN. In online sessions, only the RBFNN was used to control the robot motion. In any case, BPNN performance was tested with the online acquired datasets, after the online sessions were finished, and the results are shown in Section 5.
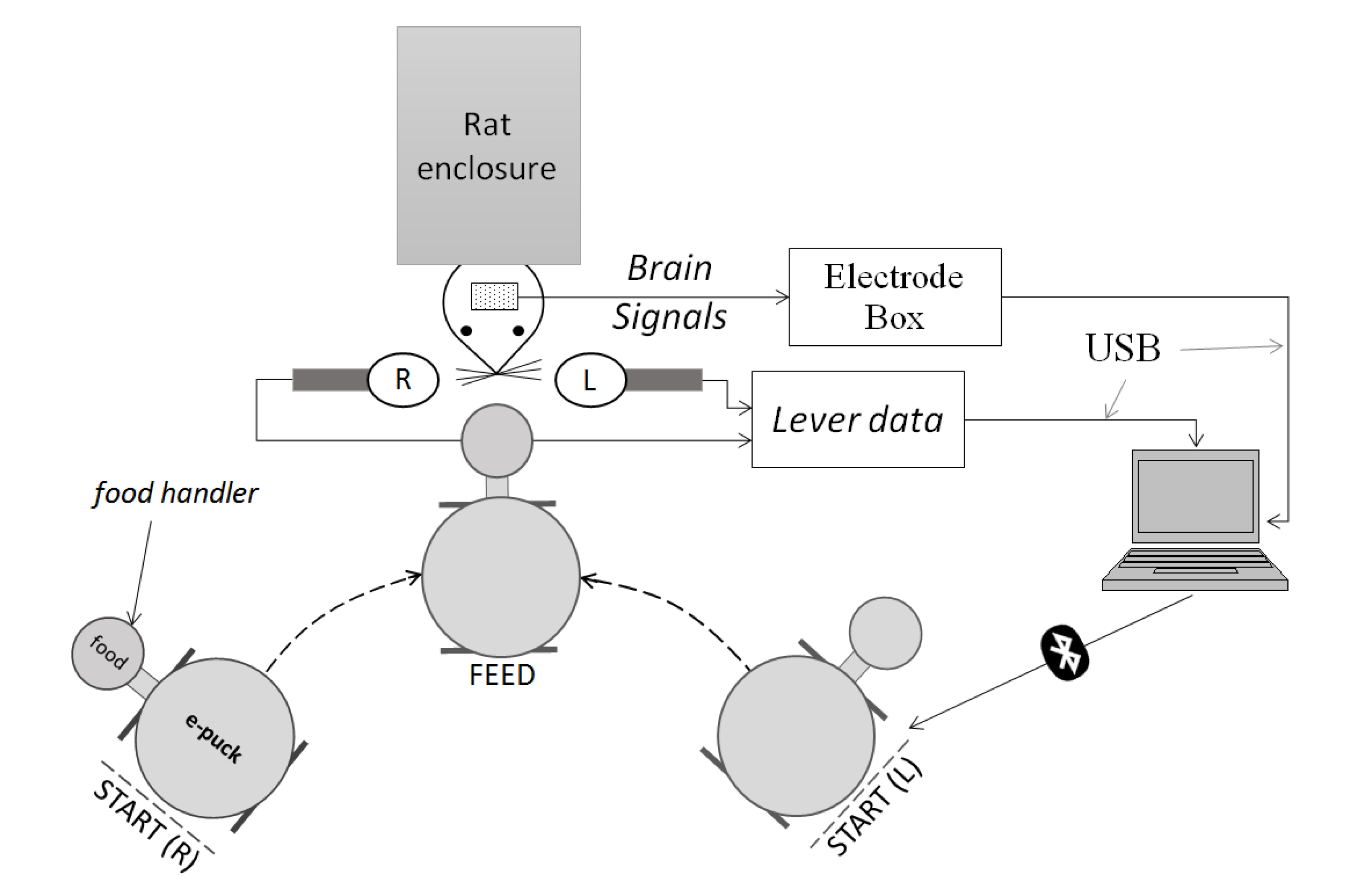
. The data were similarly processed to extract the feature vector, which was classified by the RBFNN. In online sessions, only the RBFNN was used to control the robot motion. In any case, BPNN performance was tested with the online acquired datasets, after the online sessions were finished, and the results are shown in Section 5.3.2.1. RBFNN


 , W1-H and WH-O are the input-to-hidden layer weights and hidden-to-output layer weights, respectively. The activation function of the hidden layer neurons φ1, is a Gaussian function with center ch and spread σh. In our RBFNN, σh is set to 1.
, W1-H and WH-O are the input-to-hidden layer weights and hidden-to-output layer weights, respectively. The activation function of the hidden layer neurons φ1, is a Gaussian function with center ch and spread σh. In our RBFNN, σh is set to 1.3.2.2. BPNN


4. Experimental Setup
5. Results
5.1. Neural Network
| Session | Duration (min) | Purpose | Lever press events | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Total | |||
| 1 | 20 | train | 16 | 26 | 42 |
| 2 | 30 | train | 19 | 12 | 31 |
| 3 | 27 | test | 25 | 13 | 38 |
| TOTAL | 60 | 51 | 111 | ||
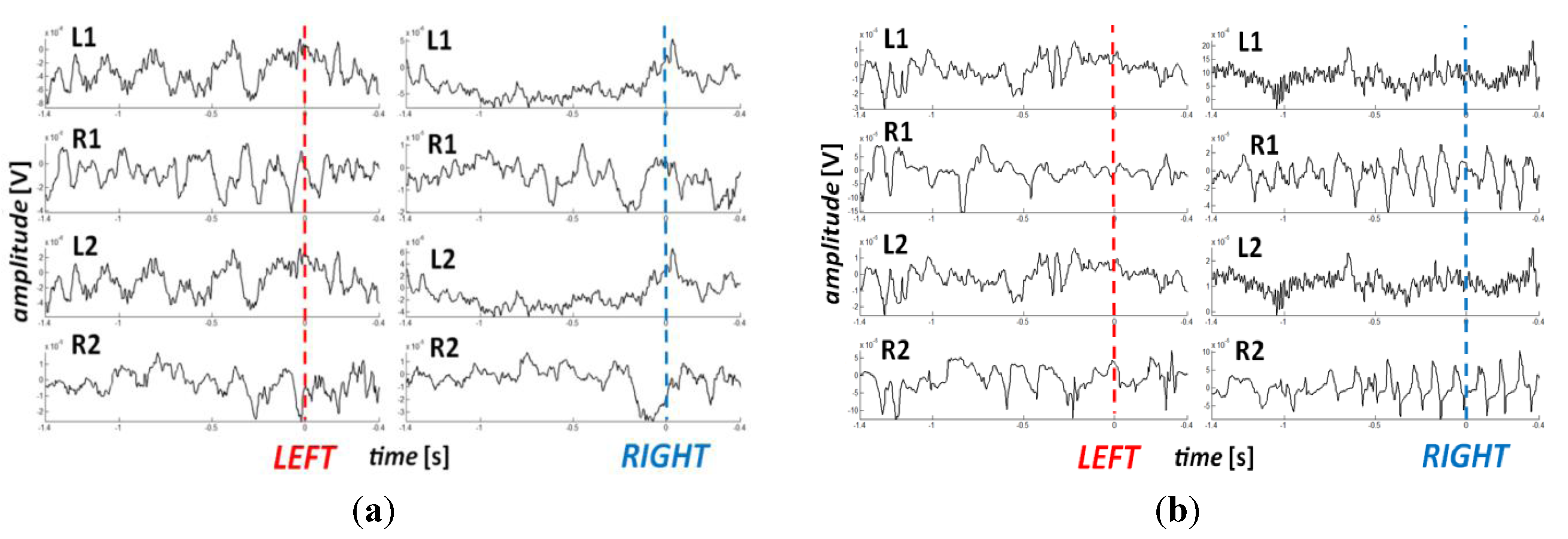
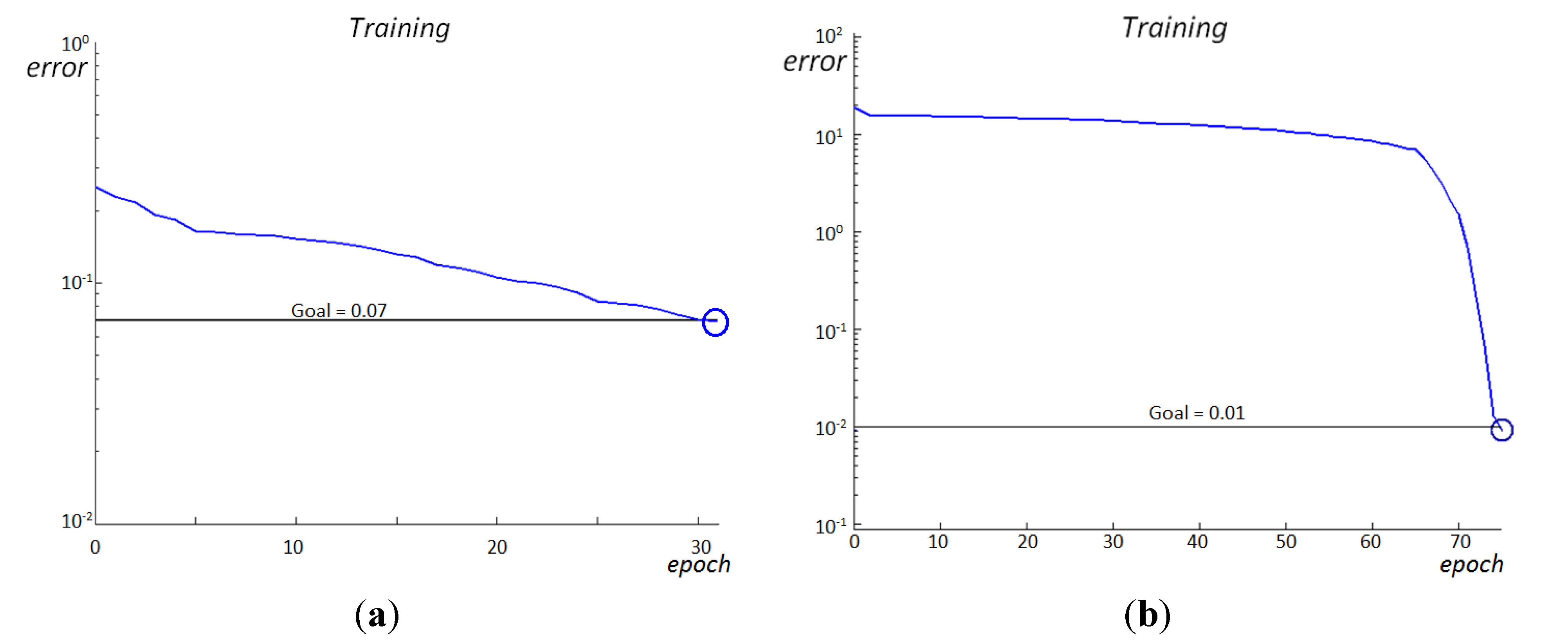
| Offline Session | RBFNN | BPNN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Total | Left | Right | Total | |
| 1 (train) | 100.0 | 96.2 | 97.6 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 2 (train) | 94.7 | 100.0 | 96.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 3 (test) | 92.0 | 61.5 | 81.6 | 60.0 | 69.2 | 63.2 |
5.2. Online Robot Control
| OnlineSession | Duration | All Events | Misclassified events | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Total | Left | Right | Total | ||
| 1 | 36.8 | 18 | 16 | 34 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| 2 | 32.7 | 20 | 15 | 35 | 4 | 2 | 6 |
| TOTAL | 38 | 29 | 69 | 7 | 5 | 12 | |

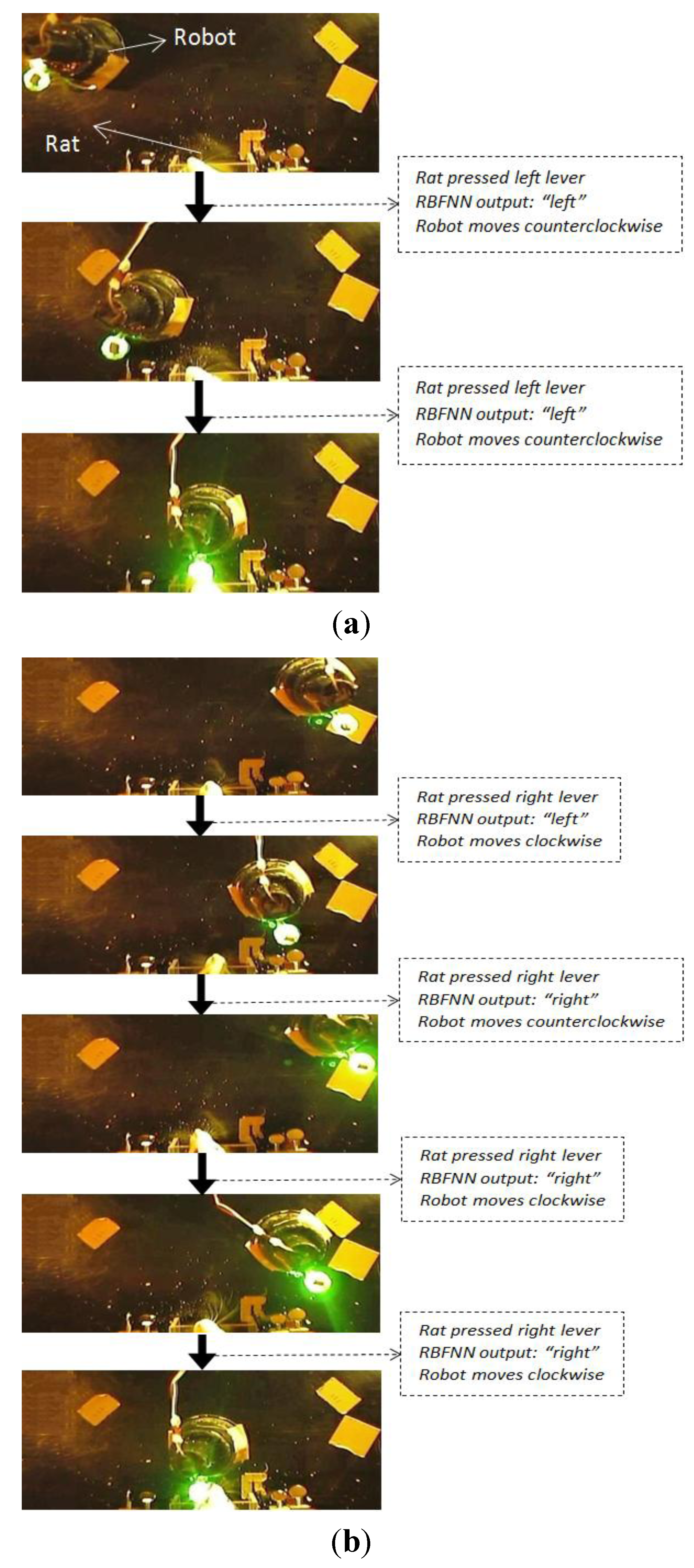
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; Heetderks, W.J.; McFarland, D.J.; Peckham, P.H.; Schalk, G.; Donchin, E.; Quatrano, L.A.; Robinson, C.J.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain-computer interface technology: A review of the first international meeting. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.D.R.; Rupp, R.; Müller-Putz, G.R.; Murray-Smith, R.; Giugliemma, C.; Tangermann, M.; Vidaurre, C.; Cincotti, F.; Kübler, A; Leeb, R.; et al. Combining brain-computer interfaces and assistive technologies: State-of-the-art and challenges. Front. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, D.M.; Tillery, S.I.H.; Schwartz, A.B. Direct cortical control of 3D neuroprosthetic devices. Science 2002, 296, 1829–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmena, J.M.; Lebedev, M.A.; Crist, R.E.; O’Doherty, J.E.; Santucci, D.M.; Dimitrov, D.F.; Patil, P.G.; Henriquez, C.S.; Nicolelis, M.A.L. Learning to control a brain-machine interface for reaching and grasping by primates. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velliste, M.; Perel, S.; Spalding, M.C.; Whitford, A.S.; Schwartz, A.B. Cortical control of a prosthetic arm for self-feeding. Nature 2008, 453, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, J.K.; Moxon, K.A.; Markowitz, R.S.; Nicolelis, M.A. Real-time control of a robot arm using simultaneously recorded neurons in the motor cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessberg, J.; Stambaugh, C.R.; Kralik, J.D.; Beck, P.D.; Laubach, M.; Chapin, J.K.; Kim, J.; Biggs, S.J.; Srinivasan, M.A.; Nicolelis, M.A. Real-time prediction of hand trajectory by ensembles of cortical neurons in primates. Nature 2000, 408, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa, T.; Hirata, M.; Saitoh, Y.; Kishima, H.; Matsushita, K.; Goto, T.; Fukuma, R.; Yokoi, H.; Kamitani, Y.; Yoshimine, T. Electrocorticographic control of a prosthetic arm in paralyzed patients. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 71, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger, T.; Veit, R.; Wilhelm, B.; Weiskopf, N.; Vatine, J.-J.; Birbaumer, N. Neuronal mechanisms underlying control of a brain-computer interface. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 3169–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, K.K.; Guan, C.; Chua, K.S.G.; Ang, B.T.; Kuah, C.; Wang, C.; Phua, K.S.; Chin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H. A Clinical Study of Motor Imagery-Based Brain-Computer Interface for Upper Limb Robotic Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC 2009), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 5981–5984.
- Majima, K.; Kamitani, Y. An outlook on the present and future of brain-machine interface research. Brain Nerve. 2011, 63, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Blankertz, B.; Tomioka, R.; Lemm, S.; Kawanabe, M.; Muller, K. Optimizing spatial filters for robust EEG single-trial analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Brown, E.N. A hierarchical Bayesian approach for learning sparse spatio-temporal decompositions of multichannel EEG. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 1929–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capi, G. Real robots controlled by brain signals—A BMI approach. Int. J. Adv. Intell. 2010, 2, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.; Yu, H.; Wilamowski, B. Comparison between Traditional Neural Networks and Radial Basis Function Networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Gdansk, Poland, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 1194–1199.
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation; Griffin, J., Ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, US, 1999; Volume 13, pp. 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, D.J.C. Bayesian interpolation. Neural Comput. 1992, 4, 415–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mano, M.; Capi, G.; Tanaka, N.; Kawahara, S. An Artificial Neural Network Based Robot Controller that Uses Rat’s Brain Signals. Robotics 2013, 2, 54-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics2020054
Mano M, Capi G, Tanaka N, Kawahara S. An Artificial Neural Network Based Robot Controller that Uses Rat’s Brain Signals. Robotics. 2013; 2(2):54-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics2020054
Chicago/Turabian StyleMano, Marsel, Genci Capi, Norifumi Tanaka, and Shigenori Kawahara. 2013. "An Artificial Neural Network Based Robot Controller that Uses Rat’s Brain Signals" Robotics 2, no. 2: 54-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics2020054
APA StyleMano, M., Capi, G., Tanaka, N., & Kawahara, S. (2013). An Artificial Neural Network Based Robot Controller that Uses Rat’s Brain Signals. Robotics, 2(2), 54-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics2020054