Abstract
This paper deals with the design of an optimal cable-driven parallel robot (CDPR) for upper limb rehabilitation. The robot’s prescribed workspace is identified with the help of an occupational therapist based on three selected daily life activities, which are tracked using a Qualisys motion capture system. A preliminary architecture of the robot is proposed based on the analysis of the tracked trajectories of all the activities. A multi-objective optimization process using the genetic algorithm method is then performed, where the cable tensions and the robot size are selected as the objective functions to be minimized. The cables tensions are bounded between two limits, where the lower limit ensures a positive tension in the cables at all times and the upper limit represents the maximum torque of the motor. A sensitivity analysis is then performed using the Monte Carlo method to yield the optimal design selected out of the non-dominated solutions, forming the obtained Pareto front. The robot with the highest robustness toward the disturbances is identified, and its dexterity and elastic stiffness are calculated to investigate its performance.
1. Introduction
Typical rehabilitation is based on the manual assistance performed by a physiotherapist. Its goal is to help patients with motor impairments totally or partially regain their functional abilities. To ensure the effectiveness of this therapy and improve its quality, the physiotherapist needs to perform repetitive motions [1]. However, the availability of specialists and the duration of the sessions are limited. In addition, the physiotherapist’s performance decreases with time, and the consistency of reproducing the movements is not guaranteed [1]. Rehabilitation robots are known to have good repeatability and do not suffer from fatigue, which makes them a good alternative to manual rehabilitation [2,3,4]. Indeed, robots can assist and move the impaired member accurately and in a controlled manner. Moreover, robot sensors could be helpful in monitoring the patient’s movement and responsiveness to the treatment [5].
This paper proposes an optimized structure of a cable-driven parallel robot (CDPR) able to move the patient’s impaired member along some paths, prescribed by an occupational therapist [6]. This kind of robot was chosen due to its interesting characteristics, such as its low inertia and the large workspace [7].
This paper is structured as follows. Section 2 details the rehabilitation movements, identified by the occupational therapist, and the used experimental protocol. Section 3 proposes the design of the robot. Section 4 formulates the multi-objective optimization problem, as well as the criteria and the constraints selected to obtain the optimal solution. A sensitivity analysis based on the Monte Carlo method is performed in Section 5 with the aim of selecting the optimal design vector. The last section concludes the paper.
2. Rehabilitation Task Analysis
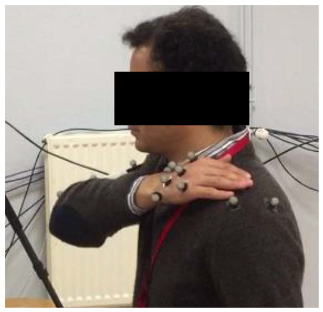
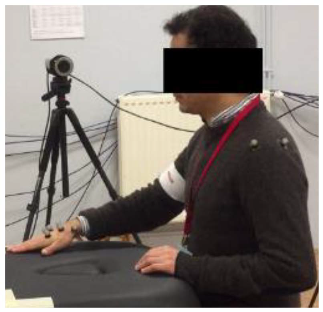
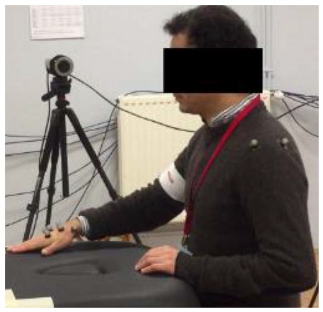
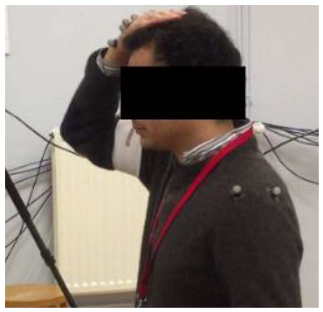
Rehabilitation where the physiotherapist assists the patients to perform daily living activities gives better outcomes compared with treating each joint separately [8]. With the help of an occupational therapist from Poitiers University Hospital, three daily life activities, illustrated in Table 1, were identified. They consisted of moving the patient’s hand from an initial position to a final position, where the patient touched with his hand either his mouth, his head or his shoulder, then returned to the starting position. These movements are involved in basic daily tasks such as eating, hair combing or wearing clothes. During the motion capture procedure, no prior information about a specific daily life activity was given to the volunteers in order to avoid their movement being biased. Thus, a larger number of functional tasks could be targeted by the robot rehabilitation.

Table 1.
Movements prescribed by occupational therapists. Movement 1 (M1) = hand–mouth, Movement 2 (M2) = hand–shoulder, and Movement 3 (M3) = hand–head.
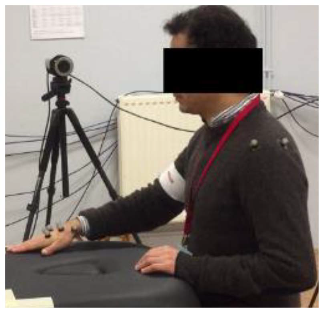
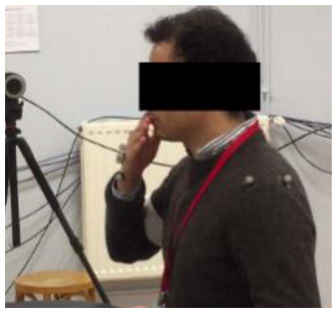
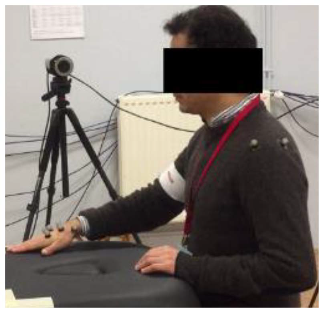
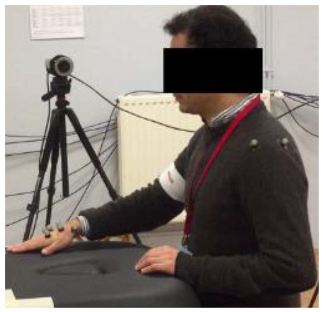
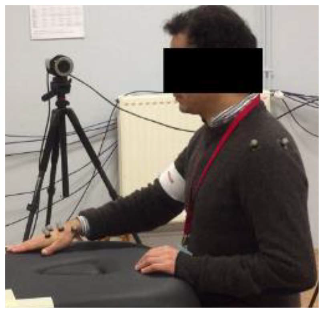
In order to study the gestures of these three movements and characterize each elementary activity, an experimental measurement campaign was carried out using a motion capture system. All prescribed movements were recorded using a Qualisys motion capture system, composed of 8 high-resolution infrared cameras and 19 reflective markers fixed in anatomical locations, with most of them attached to each volunteer’s dominant upper limb as follows:
- Five markers were fixed on the opisthenar area of the hand (one in the middle and the others around it);
- Two markers were attached to the wrist (one on each side);
- Two markers were fixed on the elbow (one on the olecranon and the other on the lateral epicondyle);
- Four markers were scattered on the arm (the markers at location A i were fixed on a support, and thus the distances between them were the same for all the volunteers);
- Two markers were attached to the dorsal of the left and right shoulders and two were on the ventral shoulders;
- Two last markers were attached to the back of the subjects on the iliocostalis lumborum muscles.
These positions, shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, were replicated for all the participants in order to avoid unwanted variations in the measured data.
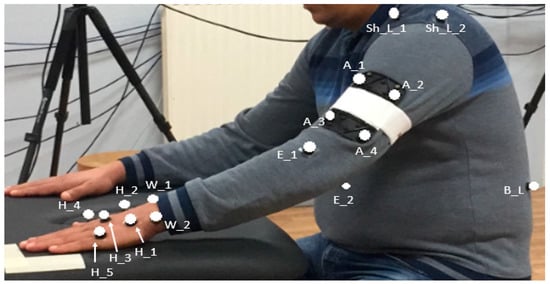
Figure 1.
Marker locations. H_i, W_i, E_i, A_i, Sh_i, and B refer to the markers attached to the patient’s hand, wrist, elbow, arm, shoulder and back, respectively.
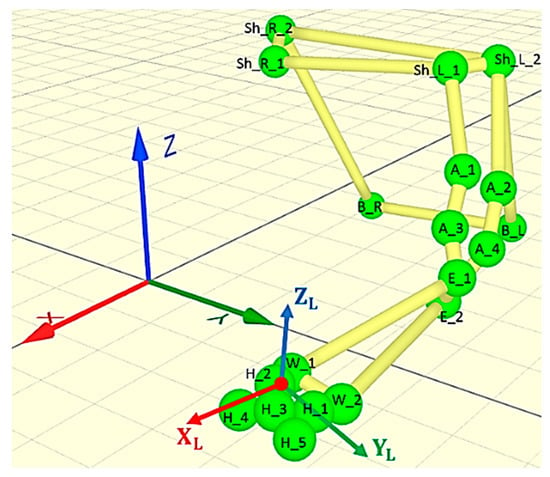
Figure 2.
Representation of the local and global frames and labeling of the markers.
Five volunteers were asked to perform 5 cycles of each movement at a natural speed (see Table 2). Since the patient’s hand would be attached to the robot’s end effector, our interest was given to the hand motion. A local and a global frame were attached to the participant’s hand and to the table, respectively, as illustrated in Figure 2. The prescribed trajectories were obtained by tracking the positions taken by the marker {H_3}, located at the center of the patient’s hand, with respect to the global frame. Figure 3 shows the set of identified trajectories for both a left-handed and a right-handed volunteer.

Table 2.
Volunteer data.
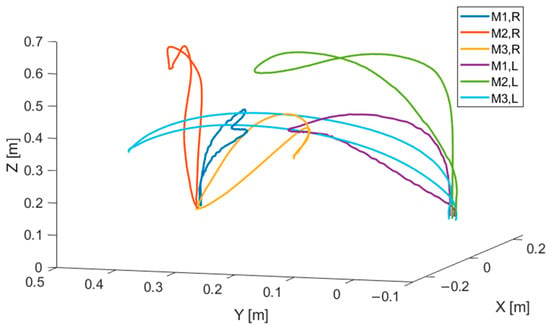
Figure 3.
The hand trajectories, recorded during the three studied movements, of a right-handed and a left-handed subject.
The hand orientation was determined using Cardan angles, where the roll , the pitch and the yaw represent the rotations along the , , and axis. The corresponding rotation matrix is given by Equation (1):
where and refer to and , respectively.
Figure 4 presents the hand orientation computed for a right-handed volunteer performing the three selected tasks. For this subject, the general range of motion varied in the range of [−8.37°, 63.16°] for the roll angle, [−31.05°, 22.38°] for the pitch angle and [−3.82°, 132.42°] for the yaw angle.
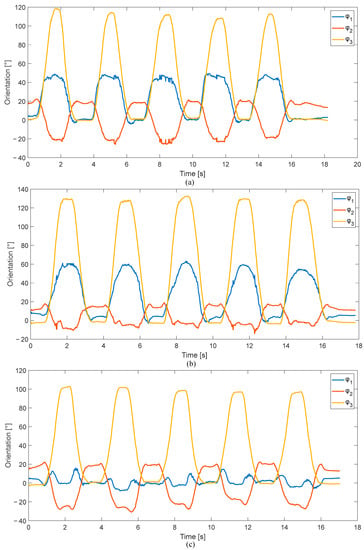
Figure 4.
The hand orientation of a right-handed subject during the movement (a) M1, (b) M2 and (c) M3.
The data given by the other markers, attached to the rest of the upper limb and on the back, were exploited to identify the workspace of the upper member and the trunk of the patient during the movements in order to prevent collisions with the robot structure.
A comparative study was carried out in a previous work [9]. Its main objective was to analyze each movement kinematics and select, if it existed, a common workspace allowing it to cope with the maximum number of patients. Based on the results given by [9], even for subjects having close heights, a proper trajectory was followed by each one, and a common concentrated workspace was almost impossible to be determined. Thus, when comparing each volunteer’s trajectories, the one that occupied the largest workspace was selected as the robot task workspace.
The constraint of the CDPR is the risk of collisions between the cables themselves and between the cables and the end effector [10]. Despite their large workspace over the other types of robots, they need a large number of cables to ensure both translation and orientation. The latter have reduced allowed ranges. In our case, this would complicate the structure and reduce the patient’s ability to move freely inside the robot workspace. To solve this issue, the CDPR would deal only with the translational degrees of freedom (DOF). An orthosis would be attached to the robot’s end effector and actuated in a way that the patient’s hand rotations could be ensured independently. In the following parts of this paper, only the three DOF related to the hand position are considered in the robot’s design.
3. Robot Structure Selection
The design of a robot for rehabilitation has to take into account several requirements, such as the ergonomics, the stiffness of the structure, the low cost and the ability to reach the task workspace [11]. In this paper, a CDPR with three translational DOF is considered. To fully constrain this robot, four cables were needed. Several structure designs could be proposed as candidates for the CDPR. A comparison among these structures was performed in a previous work [12], and a quantitative rating was given, as illustrated in Table 3.

Table 3.
Rating of different candidate structures.
The comparison showed that the triangular structure was the most suitable candidate for the rehabilitation task. Actually, circular profile manufacturing is costly and complicated. Regarding the rectangular structure, it could be a suitable choice if more than four cables were used. In fact, to fully constrain a spatial robot with four cables, no more than three vertices of one face were needed for the cable exit points. Thus, the size, the cost and the weight of the rectangular structure would be overestimated, since it provided one extra vertex in each face. Regarding the workspace, a structure with several vertical bars prevented the patient’s upper limb from moving freely.
Cafolla et al. proposed a cable-driven parallel robot for upper and lower limbs using the triangular structure [13]. The upper and lower bases of their robot were equal, and each formed an isosceles triangle with one imposed angle. In our case, a structure with two scalene triangle bases was sought.
The design of the non-optimal adopted triangular structure is given in Figure 5. In this paper, the end effector is assumed to be a point mass.
Figure 5.
CAD of the proposed structure with the static equilibrium workspace in red, the attainable workspace in black and the trajectories of a right-handed and left-handed subject in green. (a) left view, (b) front view, (c) top view, and (d) 3D view.
The workspace of the proposed structure was the intersection of the attainable workspace and the static equilibrium workspace [14]. The first was the volume built by the intersection between four spheres, each expressed mathematically by Equation (2). The center of each sphere was located at each cable’s exit point on the structure, and its radius was the maximum length, which was identical for all the cables. The latter was the set of postures that the end effector could attain statically, taking only gravity into account, as well as having the shape of a triangular prism and satisfying Equation (3):
where , and are the coordinates of the center of the mass of the platform, , and are cable exit points’ coordinates, is the identical maximum length for all the cables and are the external forces acting on the end effector, including the weight force and the cable tensions.
4. Formulation and Optimization
4.1. Problem Formulation
The CDPR structure could be described using nine design parameters—, , , , , , , and —as shown in Figure 6. The robot homing position was selected at the starting point of the trajectories. The two variables and , related to the position of the point M4, were then predefined as the projection of the starting position onto the table plane. The other parameters represent the design vector of the robot. The location of the robot in the reference frame was defined using the coordinates of the point M1. The coordinates of the points M2 and M3 were computed according to the point M1 as follows:
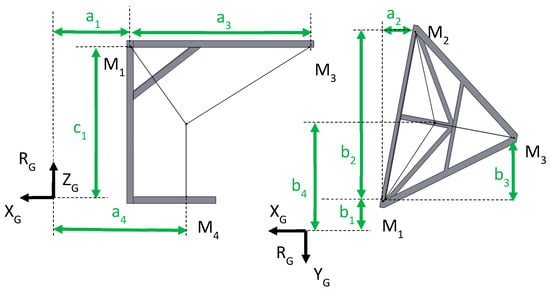
Figure 6.
The robot structure and design vector variables.
The static equilibrium of the end effector is given by Equation (3), where
Using Equations (3) and (7), the cable tension vector can be written as follows:
where is the particular solution of Equation (12), is its homogeneous solution, is the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse of , is the transpose of the Jacobian matrix of the robot, is an arbitrary scalar and Null () is the kernel vector of . The cable tensions were considered to be bounded between the minimum and the maximum acceptable tensions and for each position. Thus, the scalar , given by Equation (9), was chosen such that the minimum cable tension was equal to [15]:
4.2. Optimization Process
The targeted optimal design vector of the CDPR was the one with the smallest size which included the three identified trajectories in its workspace. In order to reduce the energy consumption and actuator cost, each motor must provide a minimum torque; in other words, the cable tensions need to be minimized. To compute the cable tensions vector at the position , , a quasistatic assumption was made. The only considered external force was that of gravity, and thus the possible interactions or resistances of the patient during the movement were assumed to be zero. This robot provided active assistance where the subject was totally passive. Impairments where the patient had the ability to either resist or contribute to the motion could not be rehabilitated using this version of the robot.
The mathematical formulation of the cable tensions minimization criterion is presented by Equations (10) and (11), giving the normalized mean value of the cable tensions when all the positions of the hand are swept:
In this expression, is expressed as
where is the number of points composing the trajectories ().
The workspace size of the robot is presented by , which computes the distance between the end effector position and the bounding surface of each sphere, delimiting the workspace at the point j of the trajectory. The smallest size of the structure is then obtained when takes the minimum possible value for each position. This normalized criterion is formulated as follows:
where
Considering the presented criteria and constraints, the multi-objective optimization problem can be summarized as follows:
where
where denotes the component of the cable tensions vector and and are the minimum and maximum values of , respectively. These values guarantee the avoidance of the risk of overtensioned or slack cables.
and are both normalized in order to have equitable criteria; thus, their values are between 0 and 1.
5. Results and Discussion
The genetic algorithm method [16] implemented under MATLAB was used to solve the optimization problem. The parameters used in the algorithm are listed in Table 4. The upper and lower boundaries of the design variables, used to generate the initial population, are given in Table 5.

Table 4.
Predefined design parameters and constraints.

Table 5.
The lower and upper boundaries of the design parameters.
The results were obtained by minimizing the two objective functions using the genetic algorithm. Figure 7 depicts the set of optimal solutions presented by the Pareto front.
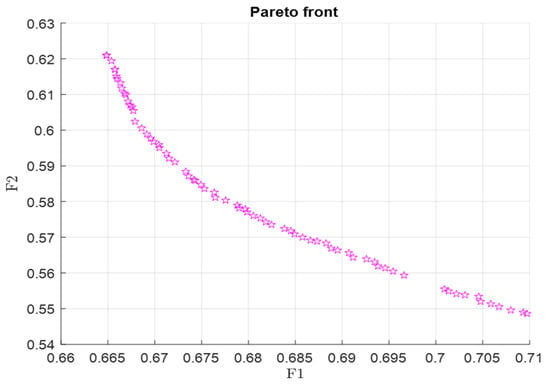
Figure 7.
The multi-objective optimization Pareto front results.
The Pareto front presented multiple solutions, each one giving a potential optimal robot design. The selection of the optimal solution could be made by choosing a weight for each criterion, either by giving the same importance to the two criteria or by privileging one over the other [17].
In this paper, we proposed to adopt the sensitivity of the solution toward design parameter disturbance as a decision criterion. This disturbance affects the positioning accuracy of the cable exit points and can be caused by faulty assembly or a clearance. For this purpose, the sensitivity of each solution was studied using the Monte Carlo method [18] in order to identify the least sensitive solution among the ones presented in the Pareto front and thus a robust design vector of the robot. This method consisted of varying each design parameter according to a normal distribution and assessing their impacts on the objective functions [19,20]. The flowchart of this method is given in Figure 8.
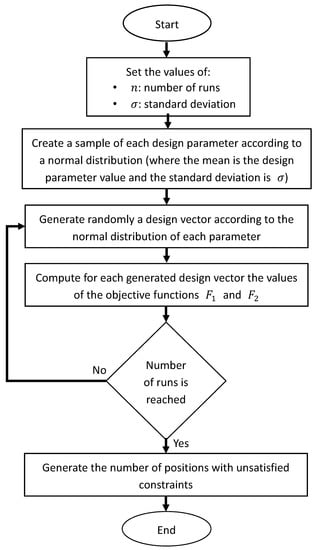
Figure 8.
The Monte Carlo method flowchart.
The method described above was performed for all 70 solutions presented in the Pareto front. For each solution, 10,000 design vectors were randomly generated according to a normal distribution, where the standard deviation was set to 1%. This choice led to a disturbance between +3 and −3 cm around the value of each design vector parameter. The prescribed trajectory was composed of 900 points. Then, for each disturbed design vector, the number of positions reached without respecting the predefined constraints related to cable tension conditions was calculated. Figure 9 presents for each perturbed solution the total number of points where the constraints were not satisfied.
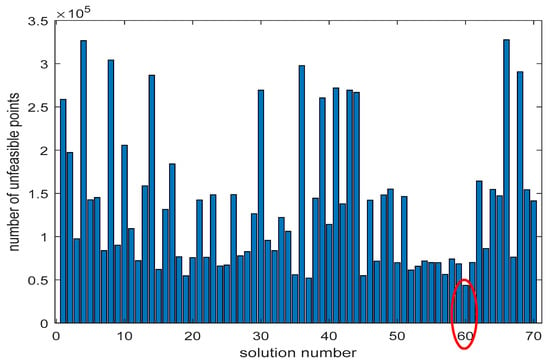
Figure 9.
Comparison of the number of unsatisfied points of each solution.
Solution number 60, shown in Equation (18), presented the least number of unsatisfied points (43,665 over 9 × 106 points). Thus, it would be selected as the optimal design vector:
A spatial representation of the CDPR with its optimal design as well as the prescribed trajectories are given in Figure 10. The proposed structure presented in Section 3 will be adjusted so that the cables exit points positions are those resulting from the optimization process.
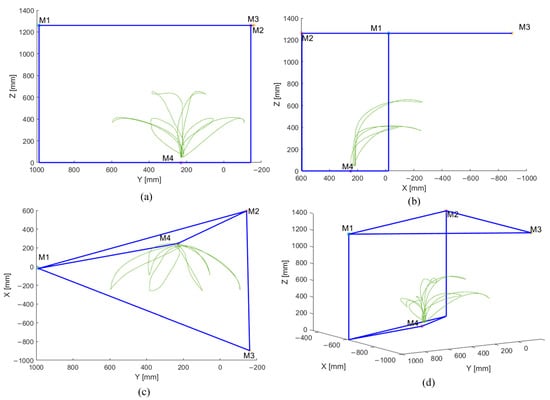
Figure 10.
The optimal positions of the cable exit points and the prescribed trajectories. (a) front view, (b) left view, (c) top view, and (d) 3D view.
The maximal cable tension distribution over the prescribed trajectory, given by Equation (19), is illustrated in Figure 11. To have better judgment about the optimization results, the elastic stiffness and the dexterity of the resulting robot were also investigated. Their distributions are illustrated in Figure 12a,b. For each pose, the dexterity index () [21] and the elastic stiffness index () [22] are defined as given in Equations (20) and (21). These two kinematic properties can be integrated into the optimization process in a future work:
where is the singular value of the Jacobian matrix and is the eigenvalue of the stiffness matrix.
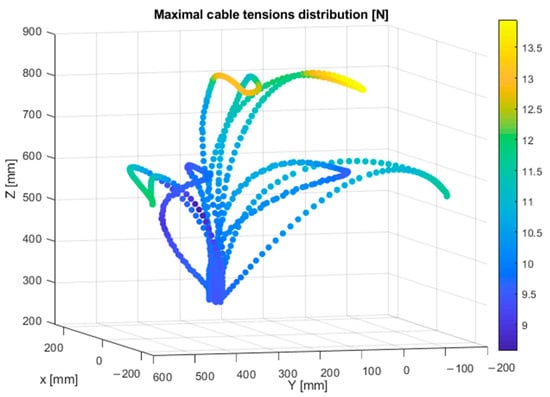
Figure 11.
Cable tension distribution of the optimal robot.
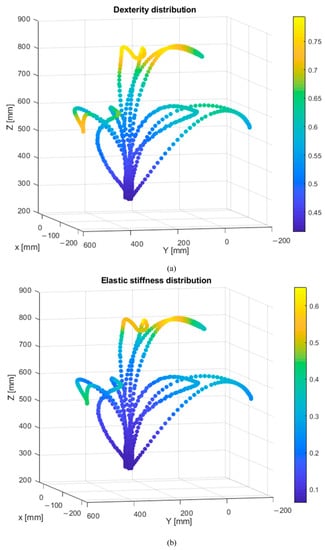
Figure 12.
(a) Dexterity and (b) elastic stiffness performance of the optimal robot.
For this optimal solution, the sensitivity of each design parameter was also investigated using the Monte Carlo method by varying the parameters one by one and fixing the others. This technique is called the one-at-a-time (OAT) method, and it is the most used method in the literature [23] since it allows one to quantify the impact of each design parameter perturbation separately. To determine whether this perturbation leads to unfeasible points where the constraints are not satisfied, the objective functions and are computed as follows:
where is the number of unfeasible points.
The sensitivity measures the uncertainty of the objective functions caused by the perturbation of each design parameter. It is computed as given in Equation (24). The results are summarized in Table 6:

Table 6.
The sensitivity of the design parameters.
From Table 6, we can conclude that the parameters , and are more sensitive compared with the others, since their perturbations led to a large variation of the objective functions. The actuator positioning in these specific coordinates related to the points M1 and M3 should then be done with the appropriate precision to avoid disturbance. The variation of the other parameters did not have a great impact on the objective functions. Thus, the positioning of the actuators related to these parameters was more tolerant.
6. Conclusions
A four-cable and three degrees of freedom parallel robot was designed to help patients with motor impairments to move their upper member and perform some daily activities. First, these daily tasks were performed by five volunteers. The motion was tracked using a motion capture system and then analyzed to determine the task workspace. Then, a multi-objective optimization based on the genetic algorithm method was formulated, considering the cable exit points’ coordinates as the design variables and the cable tensions and robot size as objective functions to be minimized. Among the numerous non-dominated solutions out of the obtained Pareto front, a robust robot design was selected based on a sensitivity analysis performed using the Monte Carlo method. This analysis showed that the obtained design is highly sensitive to only three out of the seven geometric parameters defining the system. The dexterity and the elastic stiffness of the selected robot were also investigated to show the performance of the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing—review and editing, M.A.L., A.C., J.S.S.A., A.M., L.R., S.B. and S.Z.; software and writing—original draft preparation, F.E. and M.A.L.; project administration, M.A.L. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the PHC Utique program of the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Ministry of higher education, research and innovation and the Tunisian Ministry of higher education and scientific research in the CMCU, project number 19G1121.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Prange, G.B.; Jannink, M.J.A.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, C.G.M.; Hermens, H.J.; Jzerman, M.J.I. Systematic review of the effect of robot-aided therapy on recovery of the hemiparetic arm after stroke. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2006, 43, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, P.S.; Burgar, C.G.; der Loos, M.V.; Shor, P.C.; Majmundar, M.; Yap, R. MIME robotic device for upper-limb neurorehabilitation in subacute stroke subjects: A follow-up study. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2006, 43, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nef, T.; Riener, R. ARMin—Design of a Novel Arm Rehabilitation Robot. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005; pp. 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinkensmeyer, D.J.; Schmit, B.D. Understanding treating arm movement impairment after chronic brain injury: Progress with the ARM guide. JRDD 2000, 37, 653–662. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejasz, P.; Eschweiler, J.; Gerlach-Hahn, K.; Jansen-Troy, A.; Leonhardt, S. A survey on robotic devices for upper limb rehabilitation. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennaiem, F.; Chaker, A.; Arévalo, J.S.; Laribi, M.A.; Bennour, S.; Mlika, A.; Romdhane, L.; Zeghloul, S. Optimal Design of a Rehabilitation Four Cable-Driven Parallel Robot for Daily Living Activities. Adv. Serv. Ind. Robot. 2020, 84, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Zi, B.; Shang, W.-W.; Xu, Q.-S. A Review on Cable-driven Parallel Robots. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 31, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, B.; Stanghelle, J.K. Bobath or Motor Relearning Programme? A comparison of two different approaches of physiotherapy in stroke rehabilitation: A randomized controlled study. Clin. Rehabil. 2000, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennaiem, F.; Chaker, A.; Laribi, M.A.; Sandoval, J.; Bennour, S.; Mlika, A.; Romdhane, L.; Zeghloul, S. Daily Life Activities Analysis for Rehabilitation Purposes. In International Workshop on Medical and Service Robots; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabritius, M.; Martin, C.; Pott, A. Calculation of the cable-platform collision-free total orientation workspace of cable-driven parallel robots. In Cable Driven Parallel Robots; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 74, pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Diao, X. A review of cable-driven rehabilitation devices. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2020, 15, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozisek, A. Cable Driven Parallel Robot for Lower Limb Rehabilitation Tasks. Master’s Thesis, Poitiers University, Poitiers, France, Rome Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cafolla, D.; Russo, M.; Carbone, G. CUBE, a cable-driven device for limb rehabilitation. J. Bion. Eng. 2019, 16, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.J.; Duan, X. Workspace classification and quantification calculations of cable-driven parallel robots. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 6, 358727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.L.; Gallina, P.; Vadia, J. Planar Translational Cable-Direct-Driven Robots. J. Robot. Syst. 2003, 20, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorman, S.M.; Pitchay, S.A. Significance of parameters in genetic algorithm, the strengths, its limitations and challenges in image recovery. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Collette, Y.; Siarry, P. Optimisation Multiobjectif: Algorithmes; Editions Eyrolles: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, C.E.; Yeung, H. Uncertainty estimation and Monte Carlo simulation method. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2001, 12, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, A.; Mlika, A.; Laribi, M.A.; Romdhane, L.; Zeghloul, S. Robust Design Synthesis of Spherical Parallel Manipulator for Dexterous Medical Task. In Computational Kinematics; Thomas, F., Gracia, A.P., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.A.; Laribi, M.A.; Zeghloul, S. Multi-robot system optimization based on redundant serial spherical mechanism for robotic minimally invasive surgery. Robotica 2019, 37, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, C. Kinematic Analysis, Optimization and Programming of Parallel Robotic Manipulators. Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Montréal, QC, Canada, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolshah, S.; Zanotto, D.; Rosati, G.; Agrawal, S.K. Optimizing Stiffness and Dexterity of Planar Adaptive Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. J. Mech. Robot. 2017, 9, 031004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, F.; Saltelli, A.; Tarantola, S. Trends in sensitivity analysis practice in the last decade. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).