Recombinant Fusion Protein Joining E Protein Domain III of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and HSP70 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis as an Antigen for the TI-Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
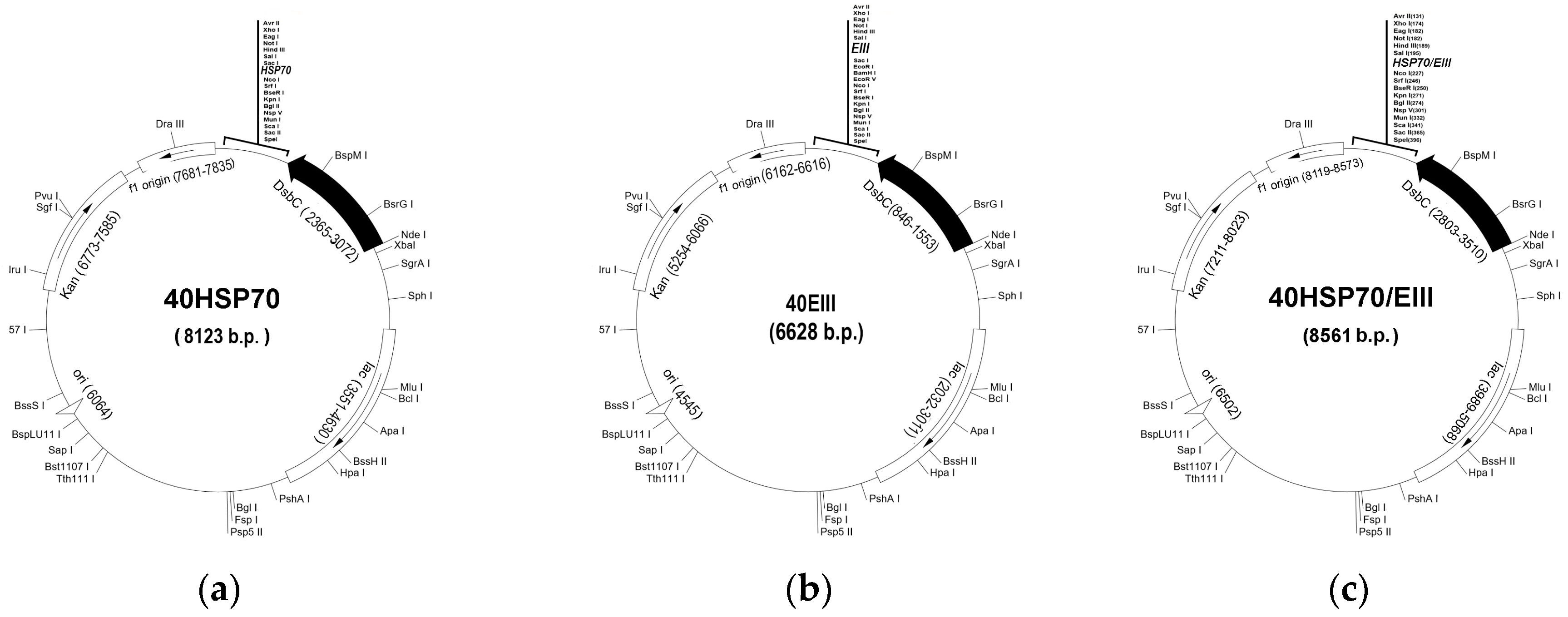
2.1. Construction of Chimeric Plasmids
2.2. Expression of the Recombinant Plasmids
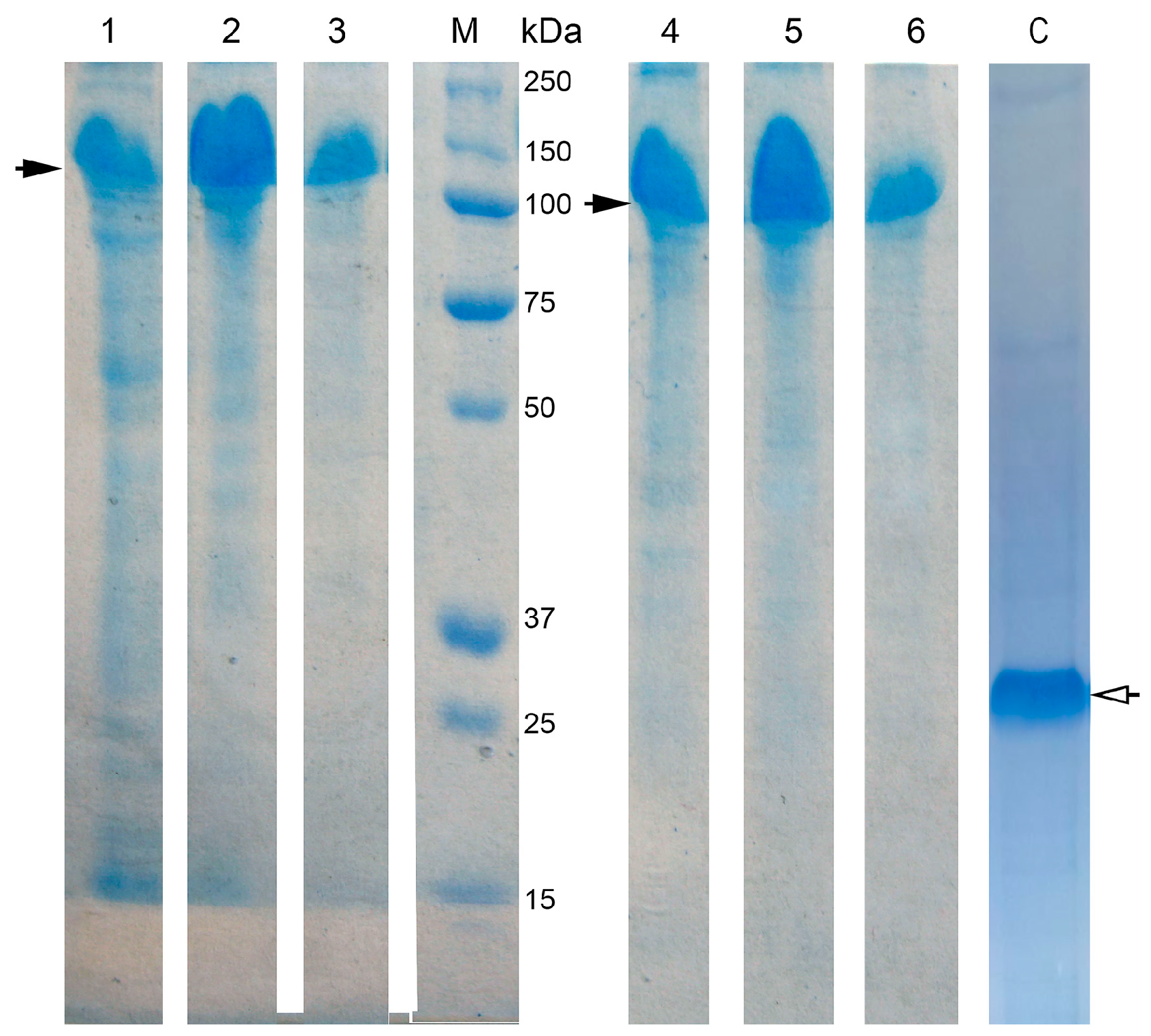
2.3. Recombinant Protein Purification
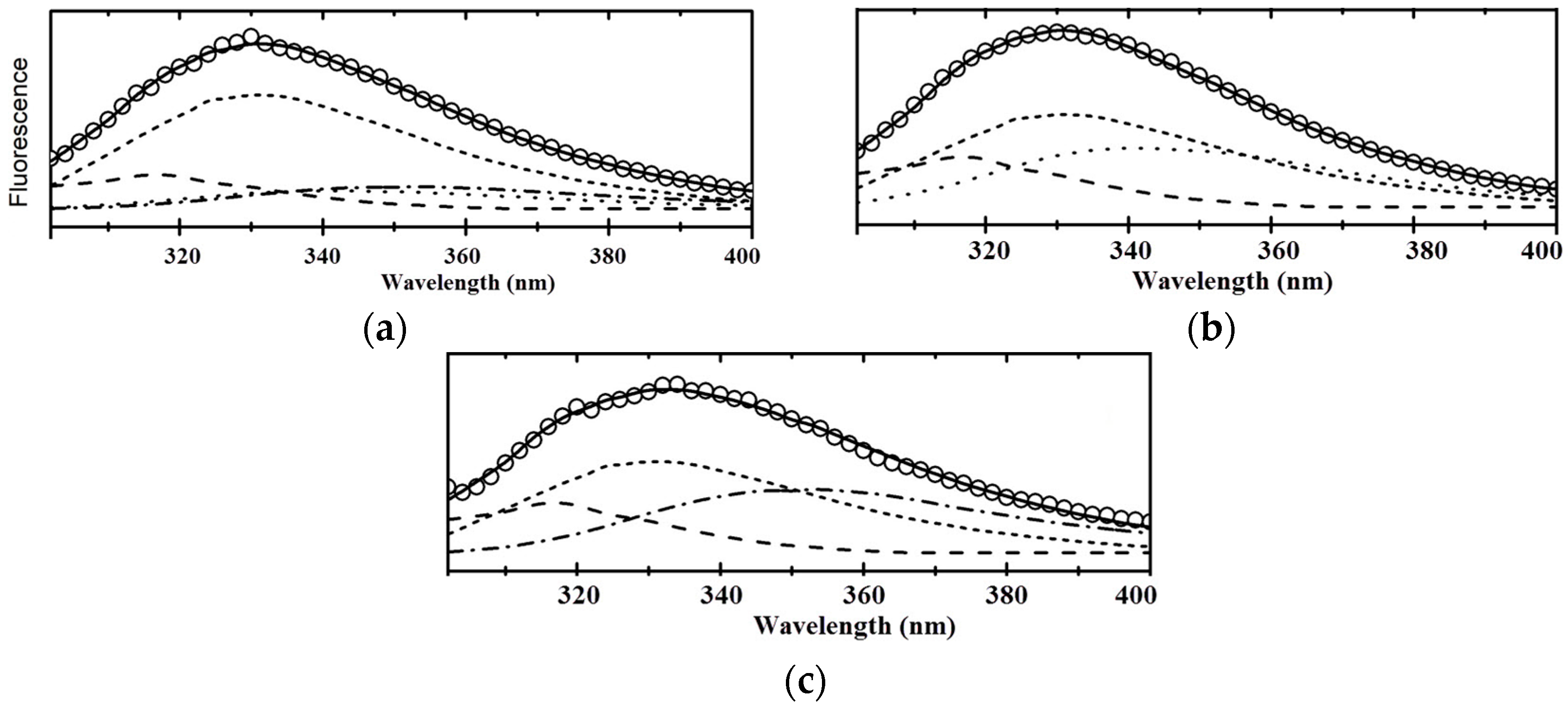
2.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.5. Calorimetry
2.6. Preparation of TI-Complexes
2.7. Animals and Immunization
2.8. ELISA and Statistical Analyses
2.9. Computational Analysis of the Intrinsic Disorder Predisposition of the Chimeric HSP70/EIII Protein
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haditsch, M.; Kunze, U. Tick-borne encephalitis: A disease neglected by travel medicine. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2013, 11, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollaritsch, H.; Paulke-Korinek, M.; Holzmann, H.; Hombach, J.; Bjorvatn, B.; Barrett, A. Vaccines and vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ershova, A.S.; Gra, O.A.; Lyaschuk, A.M.; Grunina, T.M.; Tkachuk, A.P.; Bartov, M.S.; Savina, D.M.; Sergienko, O.V.; Galushkina, Z.M.; Gudov, V.P.; et al. Recombinant domains III of tick-borne encephalitis virus envelope protein in combination with dextran and CpGs induce immune response and partial protectiveness against TBE virus infection in mice. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.S. Application of radiation technology in vaccines development. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2015, 4, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Füzik, T.; Formanová, P.; Růžek, D.; Yoshii, K.; Niedrig, M.; Plevka, P. Structure of tick-borne encephalitis virus and its neutralization by a monoclonal antibody. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressanelli, S.; Stiasny, K.; Allison, S.L.; Stura, E.A.; Duquerroy, S.; Lescar, J.; Heinz, F.X.; Rey, F.A. Structure of a flavivirus envelope glycoprotein in its low-pH-induced membrane fusion conformation. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenkova, A.M.; Chopenko, N.S.; Davydova, L.A.; Mazeika, A.N.; Bystritskaya, E.P.; Portnyagina, O.Y.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Dolgikh, D.A.; et al. Engineering of chimeric protein based on E protein domain III of tick- borne encephalitis virus and OmpF porin of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Protein Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciocca, D.R.; Cayado-Gutierrez, N.; Maccioni, M.; Cuello-Carrion, F.D. Heat shock proteins (HSPs) based anti-cancer vaccines. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanina, N.M.; Kostetsky, E.Y.; Shnyrov, V.L.; Tsybulsky, A.V.; Novikova, O.D.; Portniagina, O.Y.; Vorobieva, N.S.; Mazeika, A.N.; Bogdanov, M.V. The influence of monogalactosyldiacylglycerols from different marine macrophytes on immunogenicity and conformation of protein antigen of tubular immunostimulating complex. Biochimie 2012, 94, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanina, N.; Davydova, L.; Chopenko, N.; Kostetsky, E.; Shnyrov, V. Modulation of immunogenicity and conformation of HA1 subunit of influenza A virus H1/N1 hemagglutinin in tubular immunostimulating complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobieva, N.; Sanina, N.; Vorontsov, V.; Kostetsky, E.; Mazeika, A.; Tsybulsky, A.; Kim, N.; Shnyrov, V. On the possibility of lipid-induced regulation of conformation and immunogenicity of influenza a virus H1/N1 hemagglutinin as antigen of TI-complexes. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belikov, S.I.; Kondratov, I.G.; Potapova, U.V.; Leonova, G.N. The relationship between the structure of the tick-borne encephalitis virus strains and their pathogenic properties. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golotin, V.A.; Balabanova, L.A.; Noskova, Y.A.; Slepchenko, L.V.; Bakunina, I.Y.; Vorobieva, N.S.; Terenteva, N.A.; Rasskazov, V.A. Optimization of cold-adapted alpha-galactosidase expression in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 123, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostetsky, E.Y.; Sanina, N.M.; Mazeika, A.N.; Tsybulsky, A.V.; Vorobyeva, N.S.; Shnyrov, V.L. Tubular immunostimulating complex based on cucumarioside A2-2 and monogalactosyldiacylglycerol from marine macrophytes. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanina, N.M.; Goncharova, S.N.; Kostetsky, E.Y. Seasonal change of fatty acid composition and thermotropic behavior of polar lipids from marine macrophytes. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portnyagina, O.Y.; Novikova, O.D.; Vostrikova, O.P.; Solov’eva, T.F. Dynamics of immune response to porine from Yersinia pseudotuberculosis outer membrane. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1999, 128, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Williams, R.W.; Dunker, A.K.; Uversky, V.N. PONDR-FIT: A meta-predictor of intrinsically disordered amino acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, P.; Obradovic, Z.; Li, X.; Garner, E.C.; Brown, C.J.; Dunker, A.K. Sequence complexity of disordered protein. Proteins 2001, 42, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, Z.; Peng, K.; Vucetic, S.; Radivojac, P.; Dunker, A.K. Exploiting heterogeneous sequence properties improves prediction of protein disorder. Proteins 2005, 61, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, Z.; Peng, K.; Vucetic, S.; Radivojac, P.; Brown, C.J.; Dunker, A.K. Predicting intrinsic disorder from amino acid sequence. Proteins 2003, 53, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosztanyi, Z.; Csizmok, V.; Tompa, P.; Simon, I. IUPred: Web server for the prediction of intrinsically unstructured regions of proteins based on estimated energy content. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3433–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Vucetic, S.; Radivojac, P.; Brown, C.J.; Dunker, A.K.; Obradovic, Z. Optimizing long intrinsic disorder predictors with protein evolutionary information. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2005, 3, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.L.; Kurgan, L. Comprehensive comparative assessment of in-silico predictors of disordered regions. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2012, 13, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Kurgan, L. Accurate prediction of disorder in protein chains with a comprehensive and empirically designed consensus. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 32, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunker, A.K.; Lawson, J.D.; Brown, C.J.; Williams, R.M.; Romero, P.; Oh, J.S.; Oldfield, C.J.; Campen, A.M.; Ratliff, C.M.; Hipps, K.W.; et al. Intrinsically disordered protein. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2001, 19, 26–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prilusky, J.; Felder, C.E.; Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T.; Rydberg, E.H.; Man, O.; Beckmann, J.S.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. FoldIndex: A simple tool to predict whether a given protein sequence is intrinsically unfolded. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3435–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campen, A.; Williams, R.M.; Brown, C.J.; Meng, J.; Uversky, V.N.; Dunker, A.K. TOP-IDP-scale: A new amino acid scale measuring propensity for intrinsic disorder. Protein Pept. Lett. 2008, 15, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosztanyi, Z.; Csizmok, V.; Tompa, P.; Simon, I. The pairwise energy content estimated from amino acid composition discriminates between folded and intrinsically unstructured proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 347, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, I.; Giollo, M.; Di Domenico, T.; Ferrari, C.; Zimmermann, O.; Tosatto, S.C. Comprehensive large-scale assessment of intrinsic protein disorder. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Kurgan, L. On the complementarity of the consensus-based disorder prediction. In Proceedings of the Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, Fairmont Orchid, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2012; pp. 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Golotin, V.; Balabanova, L.; Likhatskaya, G.; Rasskazov, V. Recombinant production and characterization of a highly active alkaline phosphatase from marine bacterium Cobetia marina. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, M.; Takemoto, S.; Takakura, Y. Heat shock protein derivatives for delivery of antigens to antigen presenting cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzue, K.; Young, R.A. Heat shock proteins as immunological carriers and vaccines. EXS 1996, 77, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Xie, D.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, G.; Wen, J. Fusion of Hsp70 to Mage-a1 enhances the potency of vaccine-specific immune responses. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 111, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalka, A.K.; Kirkegaard, T.; Jukola, L.T.; Jaatela, M.; Kinnunen, P.K.J. Human heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) as a peripheral membrane protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 1344–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armijo, G.; Okerblom, J.; Cauvi, D.M.; Lopez, V.; Schlamadinger, D.E.; Kim, J.; Arispe, N.; De Maio, A. Interaction of heat shock protein 70 with membranes depends on the lipid environment. Cell Stress Chaperones 2014, 19, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.Q.; Sturtevant, J.M. Thermodynamic study of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Arribas, A.; Santamaría, R.I.; Zhadan, G.G.; Villar, E.; Shnyrov, V.L. Differential scanning calorimetric study of the thermal stability of xylanase from Streptomyces halstedii JM8. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 13787–13791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, C.; Protasevich, I.; Gilli, R.; Tsvetkov, P.; Lobachov, V.; Peyrot, V.; Briand, C.; Makarov, A. The two-stage process of the heat shock protein 90 thermal denaturation: Effect of calcium and magnesium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 249, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanina, N.; Chopenko, N.; Mazeika, A.; Kostetsky, E. Nanoparticulate tubular immunostimulating complexes: Novel formulation of effective adjuvants and antigen delivery systems. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permyakov, E.A. The Method of Intrinsic Protein Luminescence; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2003; pp. 73–88. ISBN 5-02-006453-X. [Google Scholar]
- Reshetnyak, Y.; Burstein, E. Decomposition of protein tryptophan fluorescence spectra into log-normal components. II. The statistical proof of discreteness of tryptophan classes in proteins. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 1710–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| dnaK-X-Nco-dir | 5′-ATATCCATGGCGATGGGTAAAATTATTGGTATCGAC-3′ |
| dnaK-X-Sac-rev | 5′-TATAGAGCTCGCTTTTTTGTCTTTTACTTCTTCGAATTC-3′ |
| E3-X-Sac-L-dir | 5′-TATAGAGCTCGGGTGGTGGTGGTTCTGGTGGTGGTGGTTCTGGTGGTGGTGGTTCTGGTCTTACATACACAATGTGCGACAAGACGAAATTCAC-3′ |
| E3-X-Sal-stop-rev | 5′-TATA GTCGAC TTA GTTAAAGGCACCGCCAAGAACTGT-3′ |
| Hsp70 | HSP70/EIII | HSP70/EIII + MGDG U. lactuca | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tm1, °C | 54.6 ± 0.1 | 54.2 ± 0.1 | 55.4 ± 0.1 |
| ΔH1, kcal/mol | 92.1 ± 0.7 | 99.5 ± 1.7 | 96.9 ± 1.4 |
| Tm2, °C | - | 58.4 ± 0.3 | 63.2 ± 0.1 |
| ΔH2, kcal/mol mol−1 | - | 79.9 ± 1.5 | 103.0 ± 1.9 |
| Tm3, °C | 66.4 ± 0.2 | 67.1 ± 0.1 | 67.7 ± 0.1 |
| ΔH3, kcal/mol | 81.5 ± 1.5 | 116.0 ± 1.5 | 170.0 ± 1.9 |
| Tm4, °C | 68.5 ± 0.4 | 70.1 ± 0.6 | 71.3 ± 0.5 |
| ΔH4, kcal/mol | 129.0 ± 1.3 | 124.0 ± 1.9 | 126.0 ± 2.6 |
| Protein | Spectral Forms (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | I | II | III | |
| HSP70 | 13.6 ± 0.3 | 58.5 ± 0.5 | 12.2 ± 0.3 | 15.7 ± 0.2 |
| HSP70/EIII | 19.5 ± 0.5 | 45.7 ± 0.4 | 34.8 ± 0.5 | 0 |
| HSP70/EIII + MGDG U. lactuca | 19.3 ± 0.5 | 42.8 ± 0.5 | 0 | 37.9 ± 0.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golotin, V.; Sanina, N.; Davydova, L.; Chopenko, N.; Mazeika, A.; Roig, M.; Shnyrov, V.; Uversky, V.N.; Kostetsky, E. Recombinant Fusion Protein Joining E Protein Domain III of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and HSP70 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis as an Antigen for the TI-Complexes. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8030082
Golotin V, Sanina N, Davydova L, Chopenko N, Mazeika A, Roig M, Shnyrov V, Uversky VN, Kostetsky E. Recombinant Fusion Protein Joining E Protein Domain III of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and HSP70 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis as an Antigen for the TI-Complexes. Biomolecules. 2018; 8(3):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8030082
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolotin, Vasily, Nina Sanina, Ludmila Davydova, Natalia Chopenko, Andrey Mazeika, Manuel Roig, Valery Shnyrov, Vladimir N. Uversky, and Eduard Kostetsky. 2018. "Recombinant Fusion Protein Joining E Protein Domain III of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and HSP70 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis as an Antigen for the TI-Complexes" Biomolecules 8, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8030082
APA StyleGolotin, V., Sanina, N., Davydova, L., Chopenko, N., Mazeika, A., Roig, M., Shnyrov, V., Uversky, V. N., & Kostetsky, E. (2018). Recombinant Fusion Protein Joining E Protein Domain III of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus and HSP70 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis as an Antigen for the TI-Complexes. Biomolecules, 8(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8030082






