Soybean Hydrophobic Protein Response to External Electric Field: A Molecular Modeling Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
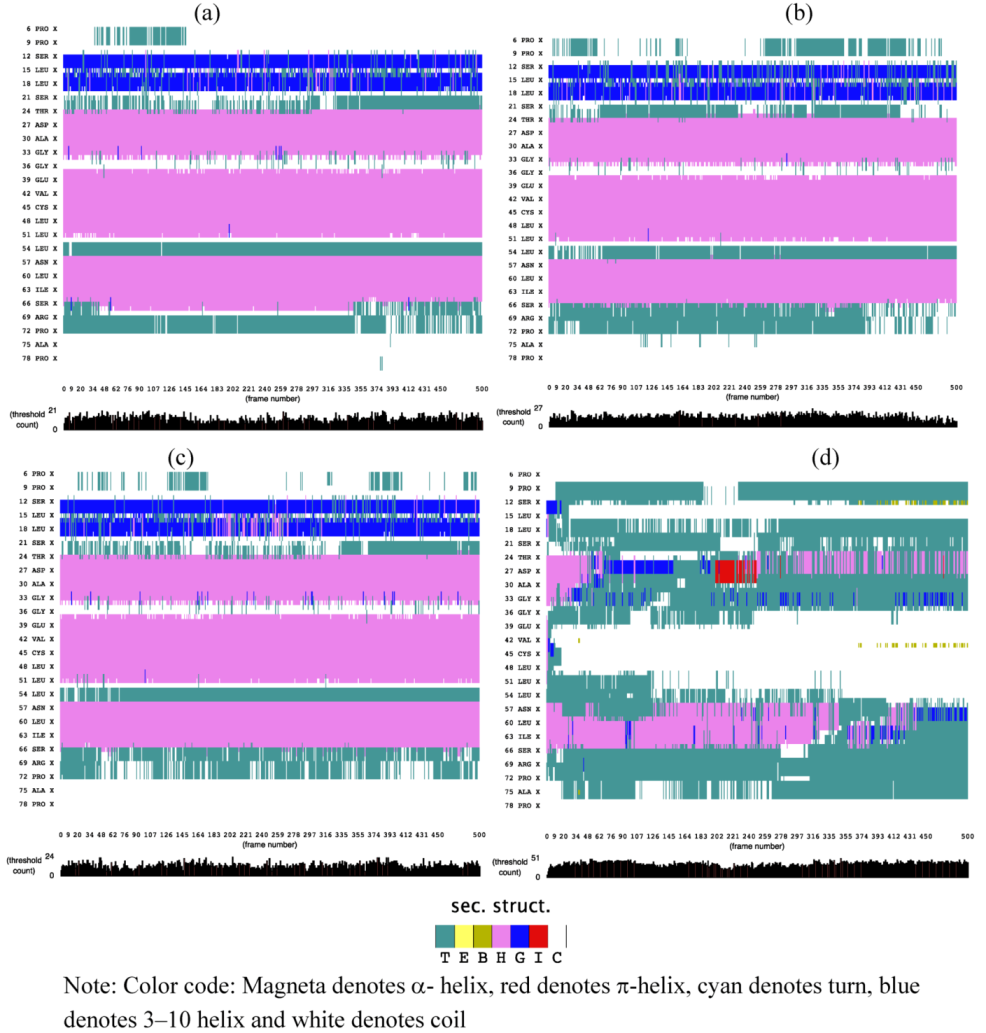
2.1. Secondary Structure Analysis
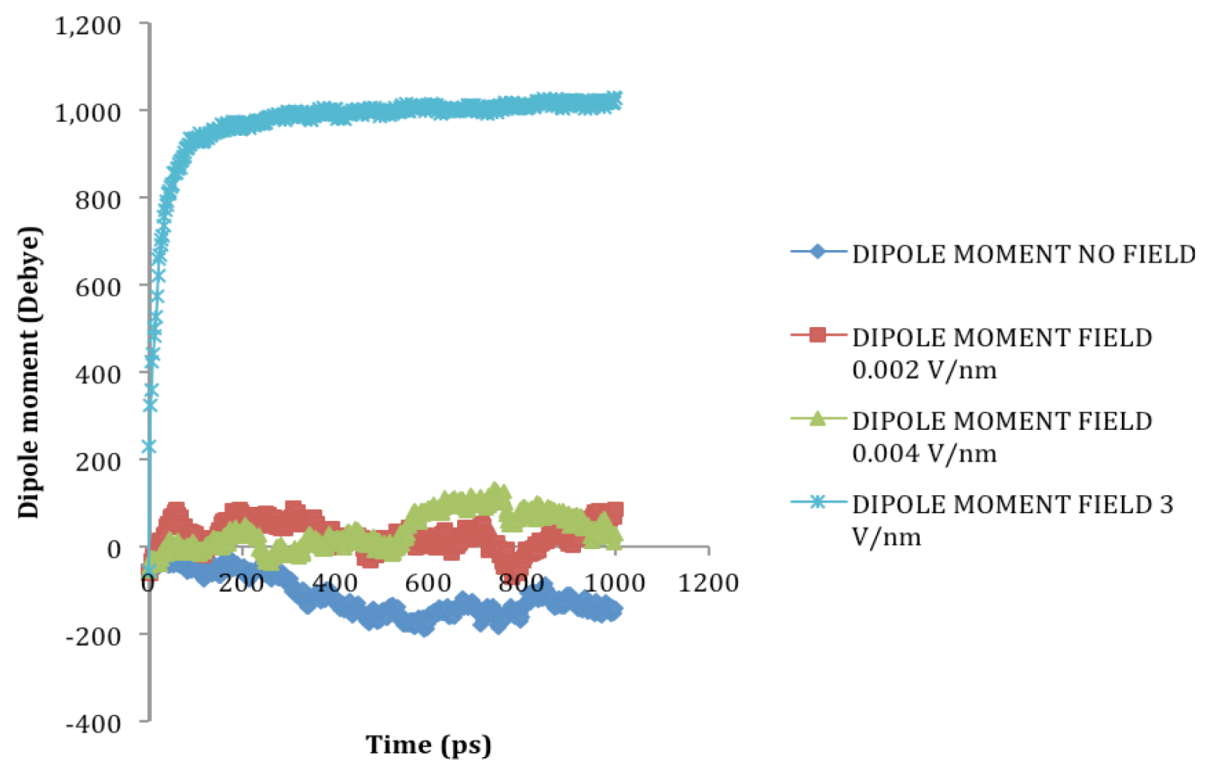
2.2. Dipole Moment Distribution

 is the dipole, qi is the charge of the atom i,
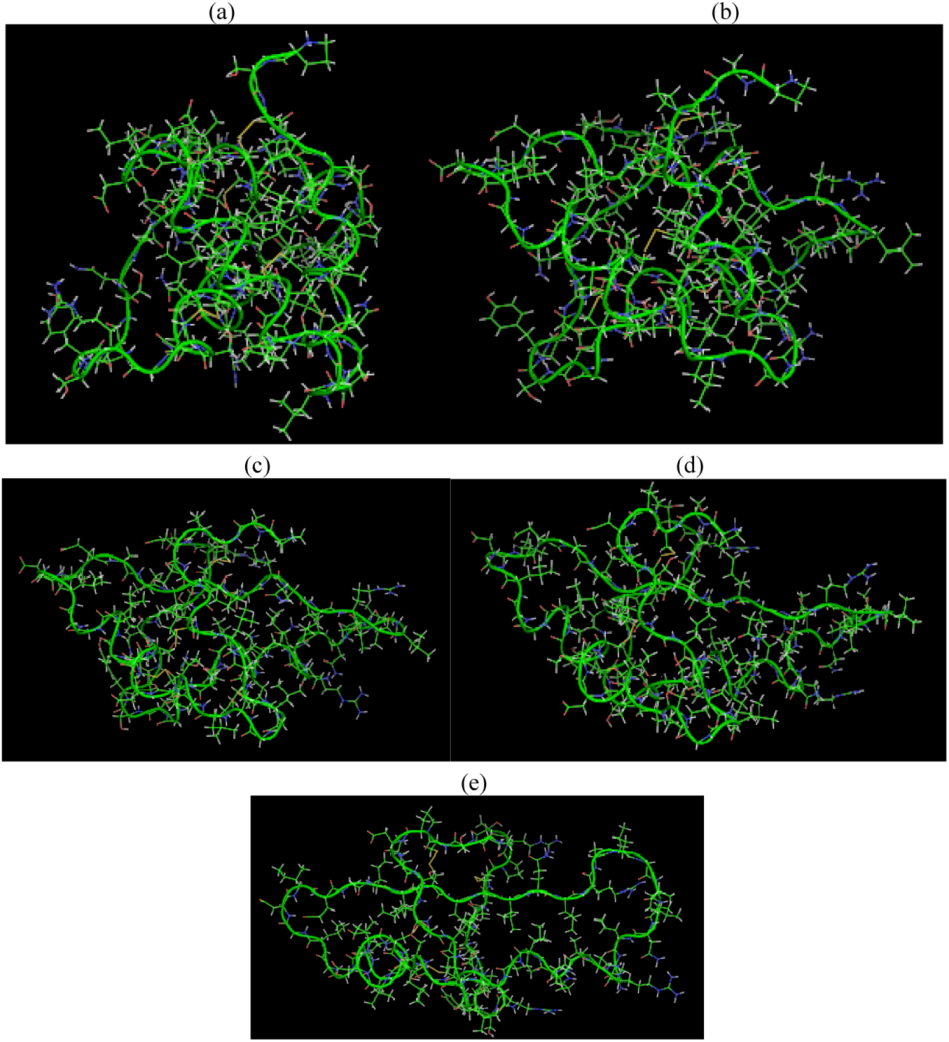
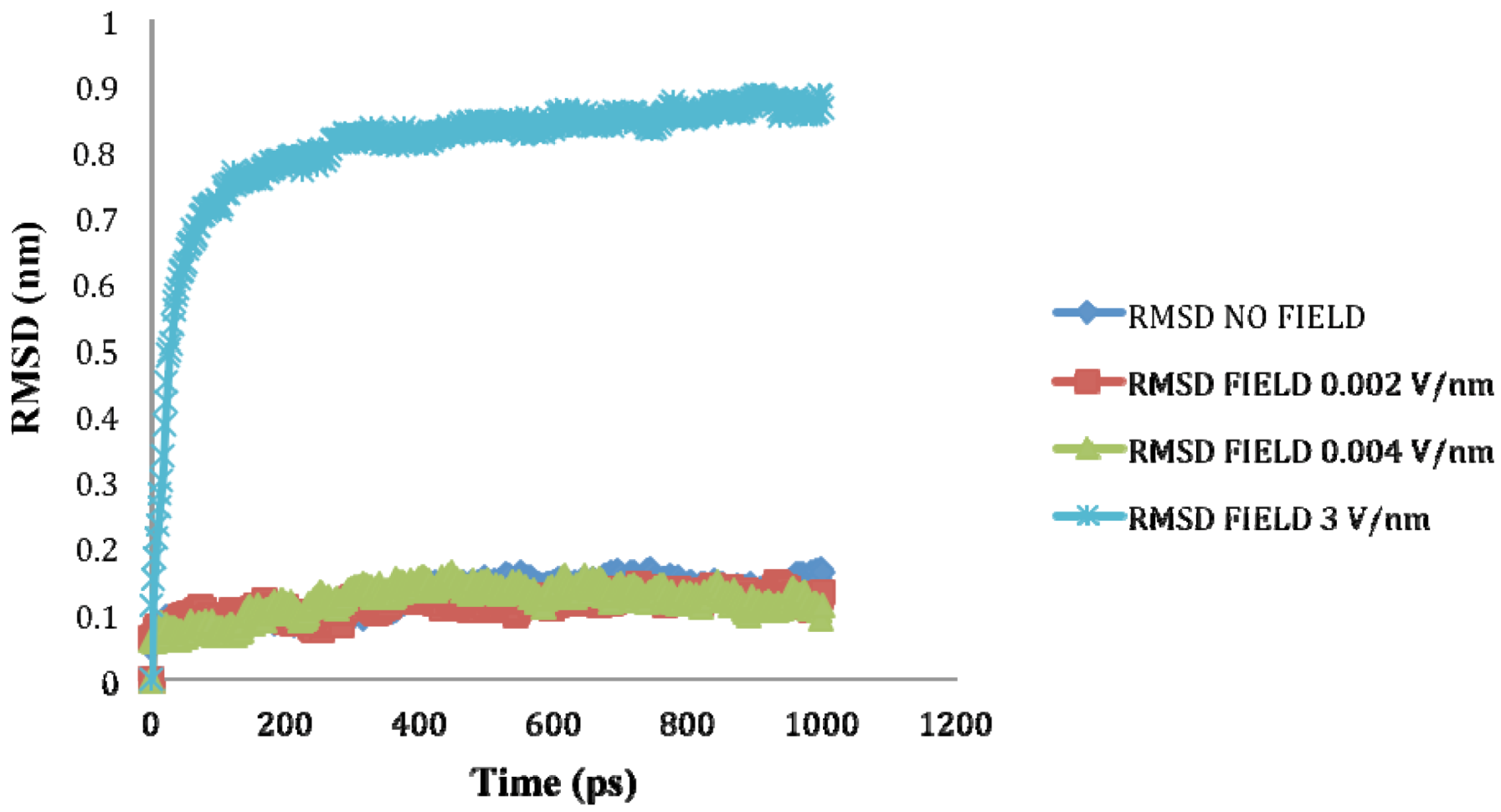
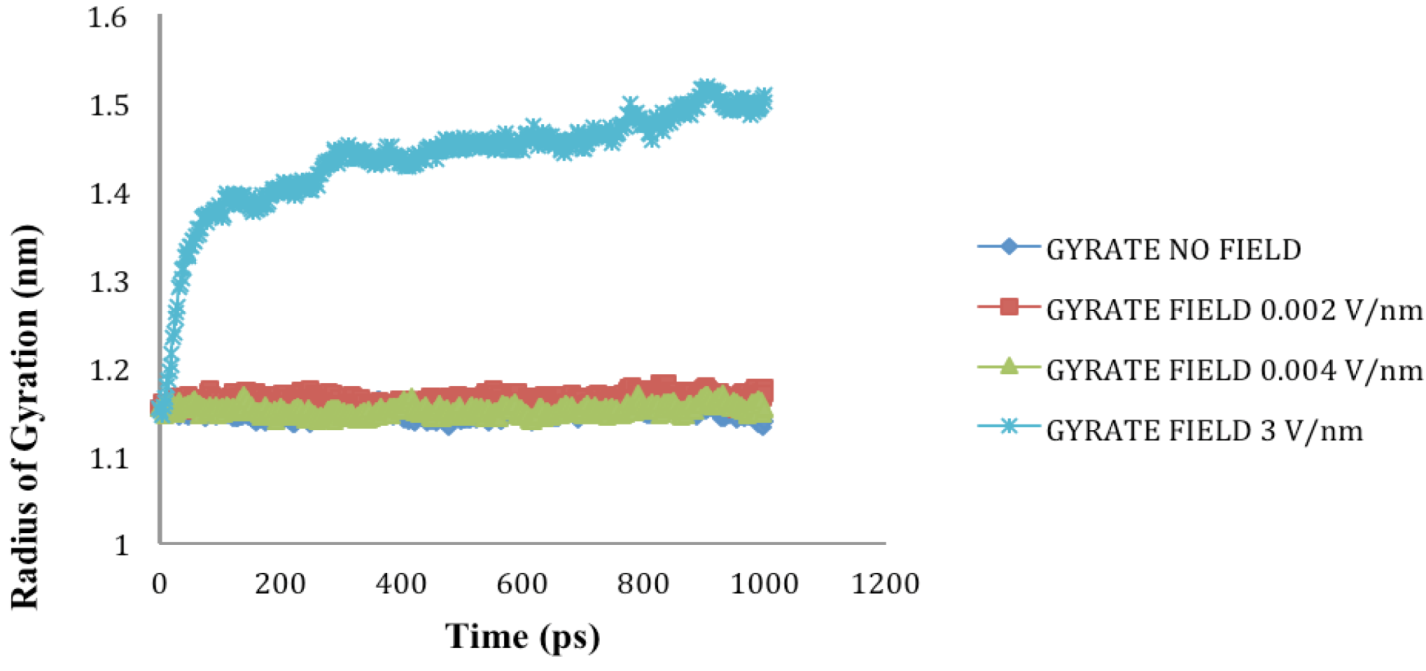
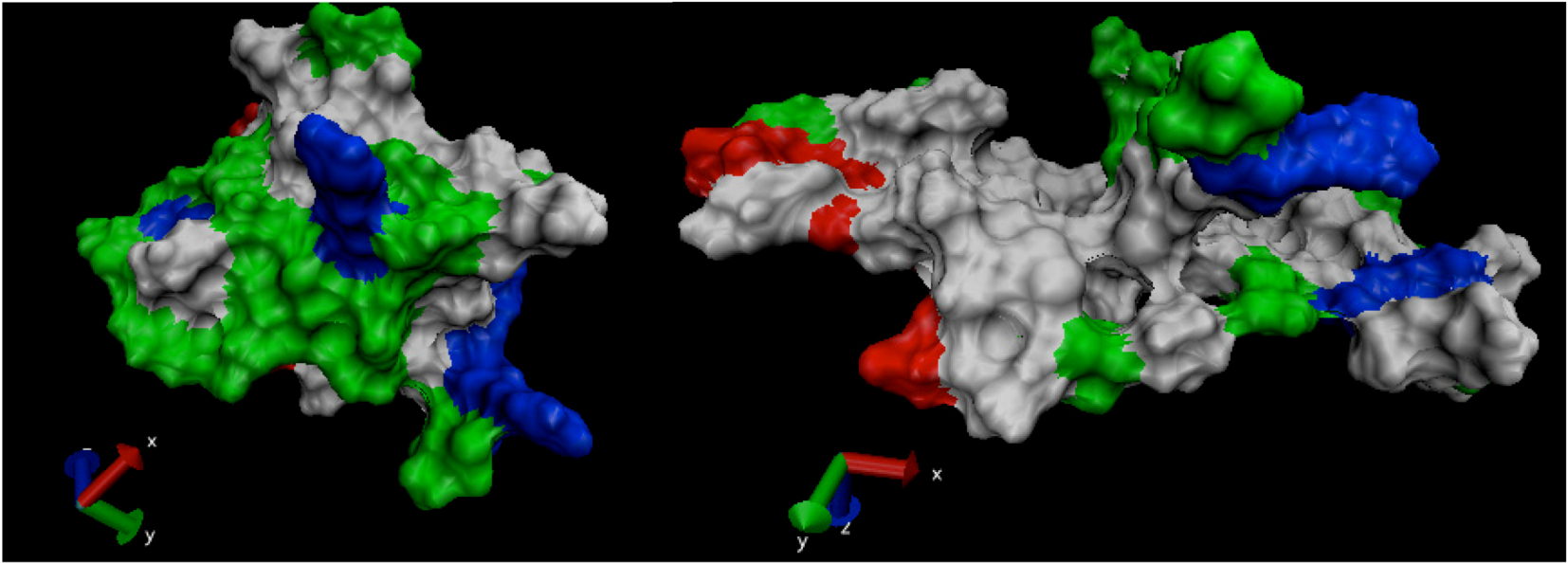
is the dipole, qi is the charge of the atom i,  is the directional vector of each atom and N is the number of atoms. When an external electric field E is applied the protein orients itself in the direction of the field and in our study, the electric field was applied in the x-axis. Depending on the strength of the applied field, unfolding or re-orientation of protein is observed. From Figure 2 and Table 1 it can be noted that application of an external electric field changed the total dipole moment of SHP under MD simulation. The total dipole moment for applied field strength of 3V/nm increased until 1000 Debye in approximately 200 ps and remained constant thereafter because the protein completely unfolded and all the major secondary structures were lost (Figure 5). From Figure 3 and Figure 4 it can also be observed that at the end of the simulation, the helices of SPI were realigned in the direction of the applied electric field, but no preferential alignment of helices were observed in the reference (no field), confirming that under an external electric field, proteins orient themselves in the direction of the field [9,15,17].
is the directional vector of each atom and N is the number of atoms. When an external electric field E is applied the protein orients itself in the direction of the field and in our study, the electric field was applied in the x-axis. Depending on the strength of the applied field, unfolding or re-orientation of protein is observed. From Figure 2 and Table 1 it can be noted that application of an external electric field changed the total dipole moment of SHP under MD simulation. The total dipole moment for applied field strength of 3V/nm increased until 1000 Debye in approximately 200 ps and remained constant thereafter because the protein completely unfolded and all the major secondary structures were lost (Figure 5). From Figure 3 and Figure 4 it can also be observed that at the end of the simulation, the helices of SPI were realigned in the direction of the applied electric field, but no preferential alignment of helices were observed in the reference (no field), confirming that under an external electric field, proteins orient themselves in the direction of the field [9,15,17]. | Molecule | Electric field strength (V/nm) | RMSD average (nm) | Rg average (nm) | Total Dipole moment (Debye) |
| SHP (1HYP) | 0 | 0.122 ± 0.022 | 1.150 ± 0.024 | −121 ± 45.311 |
| SHP (1HYP) | 0.002 | 0.114 ± 0.016 | 1.163 ± 0.037 | 27 ± 31.444 |
| SHP (1HYP) | 0.004 | 0.119 ± 0.021 | 1.150 ± 0.021 | 38 ± 42.460 |
| SHP (1HYP) | 3 | 0.803 ± 0.060 | 1.435 ± 0.043 | 971 ± 102.666 |
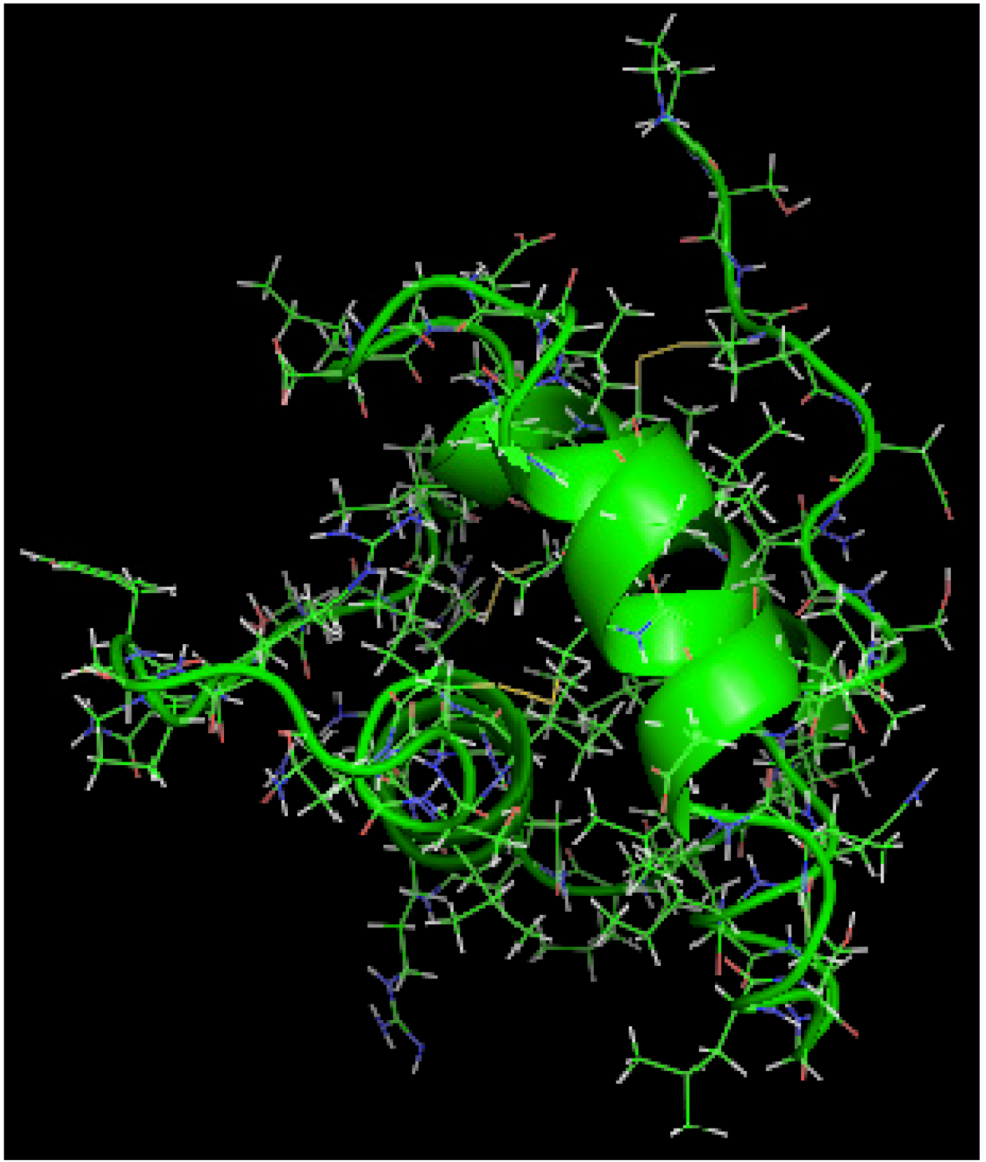
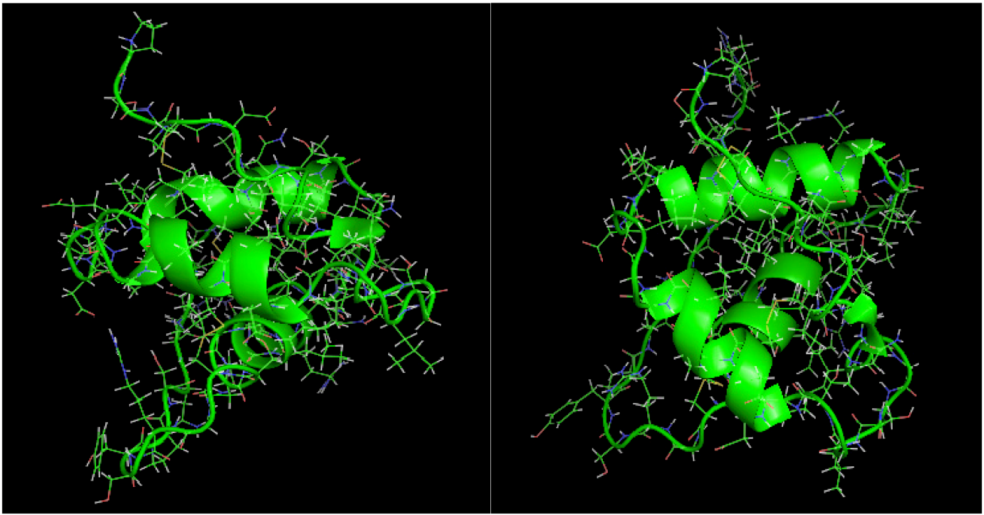
2.3. Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD):

2.4. Radius of Gyration (Rg)

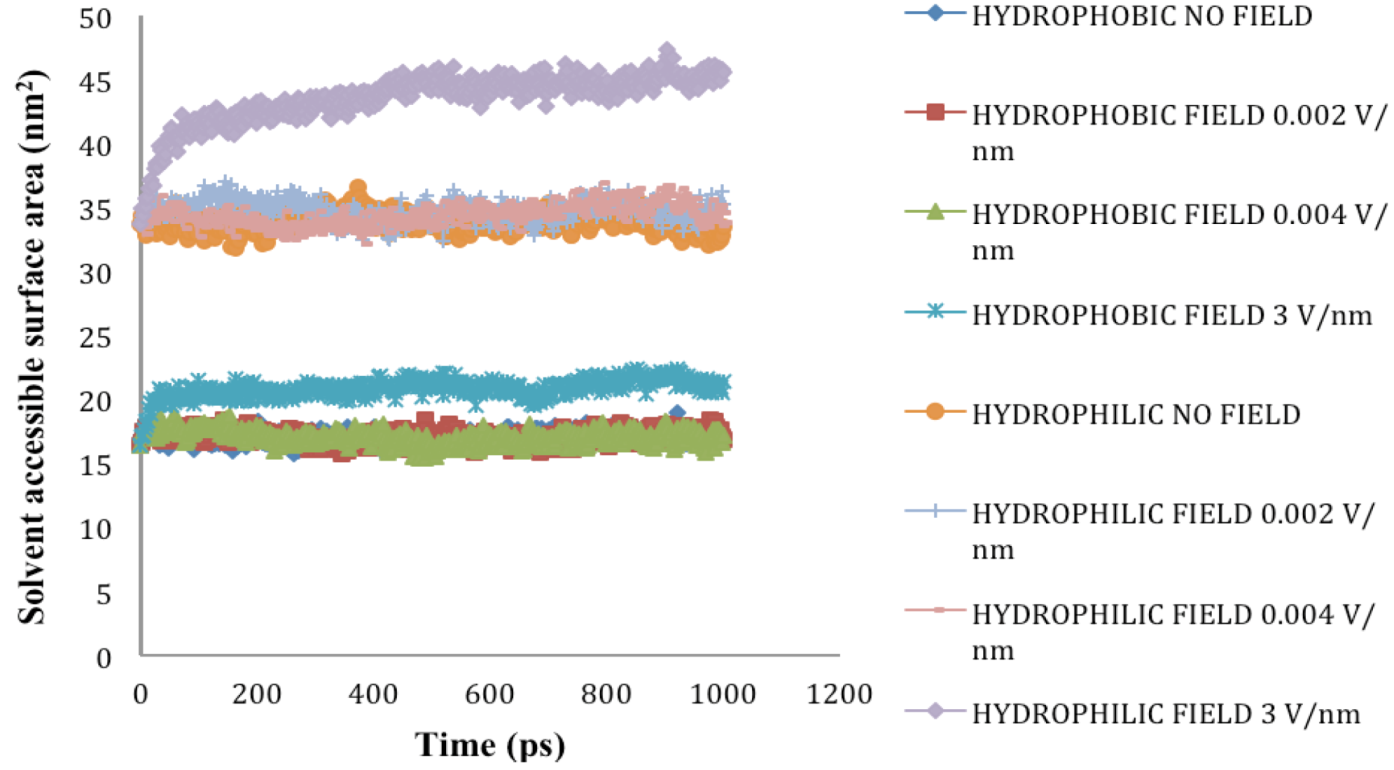
2.5. Solvent Accessible Surface Area
3. Experimental Section
| Protein System | Electric field strength (V/nm) | Temperature (K) and Pressure (bar) | Simulation length (ns) |
| SHP (1HYP) | 0.002 | 300 K, 1 bar | 1 |
| SHP (1HYP) | 0.004 | 300 K, 1 bar | 1 |
| SHP (1HYP) | 3 | 300 K, 1 bar | 1 |

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Alder, B.J.; Wainwright, T.E. Studies in molecular dynamics. I. General method. J. Chem. Phy. 1959, 31, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. A comprehensive review on electrohydrodynamic drying and high voltage electric field in the context of food and bioprocessing. Drying Tech. 2012, 30, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, M.S.; Raghavan, G.S.V. An Overview of Microwave Processing and Dielectric Properties of Agri-food Materials. Biosys. Eng. 2004, 885, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Diaz, M.D.; Barsotti, L.; Dumay, E.; Cheftel, J.C. Effects of pulsed electric fields on ovalbumin solutions and dialyzed egg white. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, J.A.; French, P.W.; Lindner, R.A.; McKenzie, D.R. Biological effects of electromagnetic fields - Mechanisms for the effects of pulsed microwave radiation on protein conformation. J. Theor. Bio. 2000, 206, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pomerai, D.I.; Smith, B.; Dawe, A.; North, K.; Smith, T.; Archer, D.B.; Duce, I.R.; Jones, D.; Candido, E.P.M. Microwave radiation can alter protein conformation without bulk heating. FEBS Lett. 2003, 543, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Mo, H. Effects of pulsed electric fields on physicochemical properties of soybean protein isolates. LWT - Food Sci. Tech. 2007, 40, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, B.Y.; Ngadi, M.O.; Simpson, B.K.; Simpson, M.V. Pulsed electric field induced structural modification of soy protein isolate as studied by fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Food Proc. Preserv. 2011, 35, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrakas, L.; Gousias, C.; Tzaphlidou, M. Electric field effects on chignolin conformation. J. Appli. Phy. 2011, 109, 094702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgentini, D.A.; Wagner, J.R.; Añón, M.C. Effects of thermal treatment of soy protein isolate on the characteristics and structure-function relationship of soluble and insoluble fractions. J. Agri. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppo, C.; Chapleau, N.; Speroni, F.; De Lamballerie-Anton, M.; Michel, F.; Añón, C.; Anton, M. Physicochemical Modifications of High-Pressure-Treated Soybean Protein Isolates. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, J.E. Functional properties of soy proteins. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comp. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, H.G. Accuracy and efficiency of the particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phy. 1995, 103, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrakas, L.G.; Gousias, C.; Tzaphlidou, M. Structural destabilization of chignolin under the influence of oscillating electric fields. J. Appli. Phy. 2012, 111, 074702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budi, A.; Legge, F.S.; Treutlein, H.; Yarovsky, I. Electric field effects on insulin chain-B conformation. J. Physi. Chem. B 2005, 109, 22641–22648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budi, A.; Legge, F.S.; Treutlein, H.; Yarovsky, I. Effect of frequency on insulin response to electric field stress. J. Physi. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5748–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budi, A.; Legge, S.; Treutlein, H.; Yarovsky, I. Effect of external stresses on protein conformation: A computer modelling study. Eur. Biophy. J. 2004, 33, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budi, A.; Legge, F.S.; Treutlein, H.; Yarovsky, I. Comparative study of insulin chain-B in isolated and monomeric environments under external stress. J. Physi. Chem. B 2008, 112, 7916–7924. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, A.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. Soybean Hydrophobic Protein Response to External Electric Field: A Molecular Modeling Approach. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 168-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom3010168
Singh A, Orsat V, Raghavan V. Soybean Hydrophobic Protein Response to External Electric Field: A Molecular Modeling Approach. Biomolecules. 2013; 3(1):168-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom3010168
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Ashutosh, Valérie Orsat, and Vijaya Raghavan. 2013. "Soybean Hydrophobic Protein Response to External Electric Field: A Molecular Modeling Approach" Biomolecules 3, no. 1: 168-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom3010168
APA StyleSingh, A., Orsat, V., & Raghavan, V. (2013). Soybean Hydrophobic Protein Response to External Electric Field: A Molecular Modeling Approach. Biomolecules, 3(1), 168-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom3010168





