The Dual Role of Macrophage Extracellular Traps in Host Defense and Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Formation Mechanisms of METs
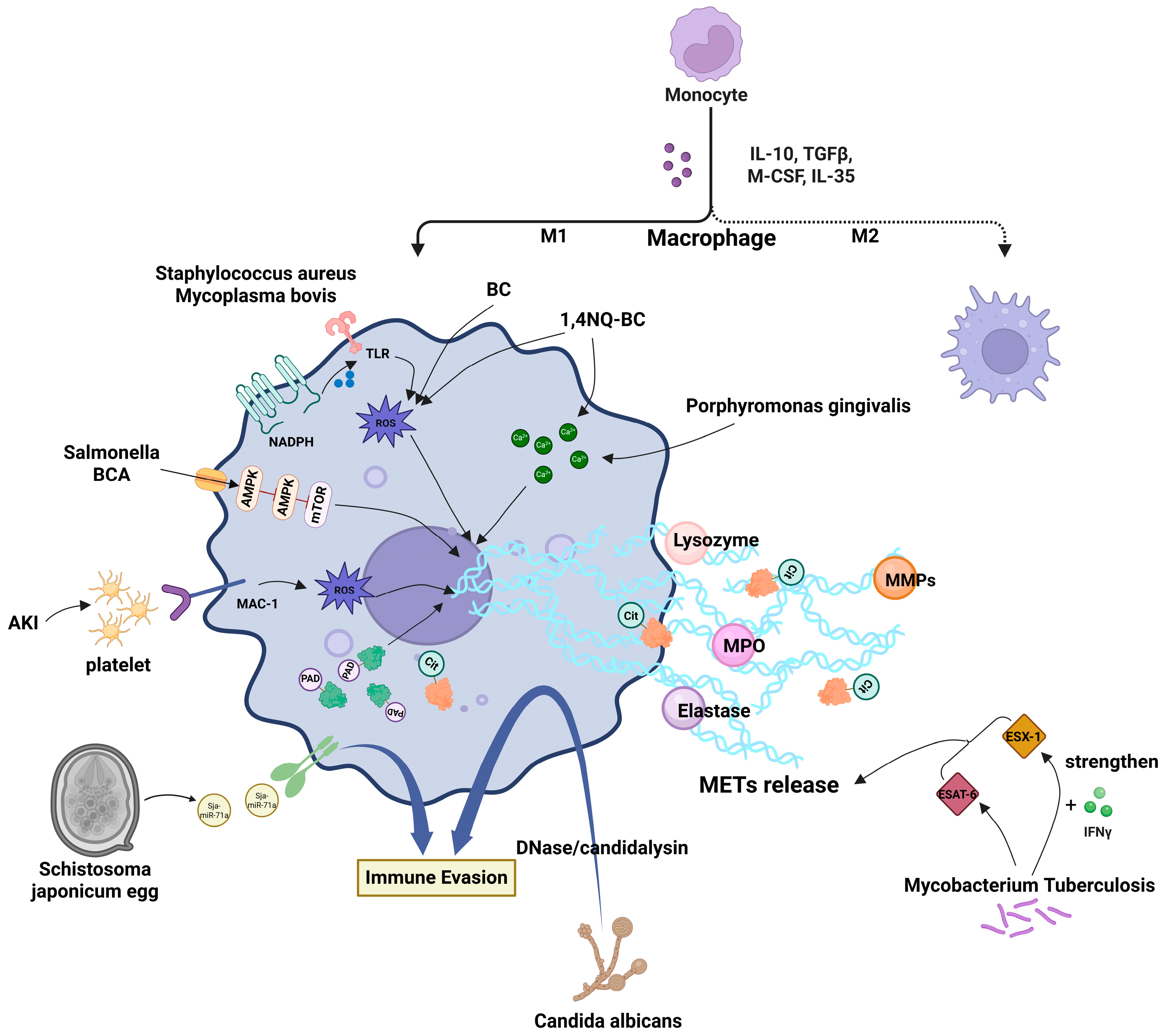
3. Mechanistic Studies on MET Formation Induced by Various Stimuli
3.1. Mechanisms Underlying MET Formation Induced by Pathogenic Microorganisms
3.2. Mechanisms of Environmental Pollutant-Induced MET Formation
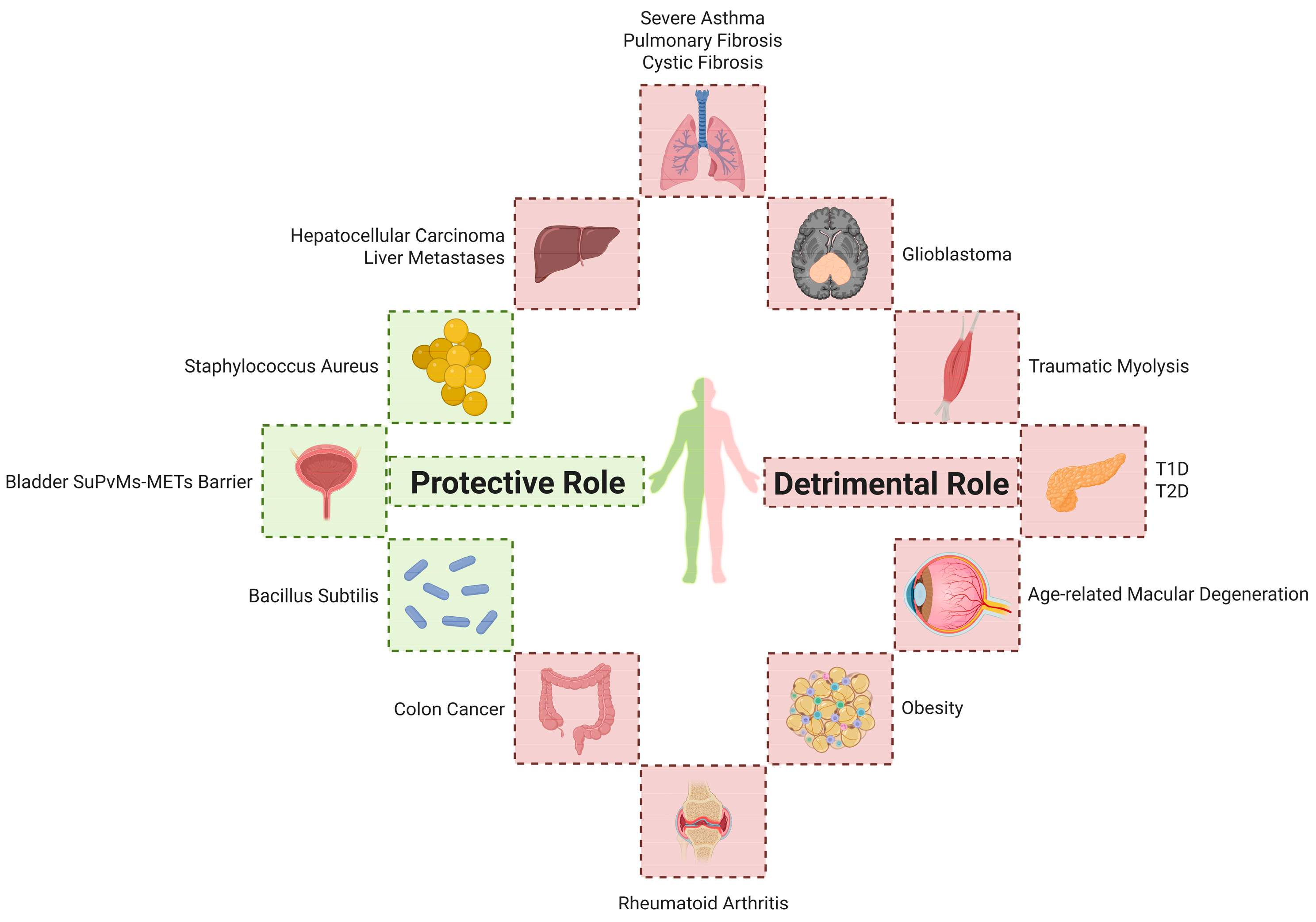
4. METs in the Pathogenesis of Various Diseases
4.1. Infectious Diseases
4.2. Respiratory Diseases
4.3. Autoimmune Diseases
4.4. Metabolic Diseases
4.5. Tumors
4.6. Transplantation and Tissue Injury
4.7. Others
5. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Macrophage Extracellular Trap Mechanisms
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Abbreviation | Full Name |
| ACPAs | Anti-Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies | ESX-1 | ESAT-6 Secretion System 1 |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury | ETs | Extracellular Traps |
| ALI | Acute Lung Injury | HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| ARHGDIG | Rho GDP Dissociation Inhibitor Gamma | IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| BC | Black Carbon | IL-4/6/10/33 | Interleukin-4/6/10/33 |
| BCA | Biochanin A | ILK | Integrin-Linked Kinase |
| BMDMs | Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages | IP-10 | Interferon γ-induced Protein 10 |
| CCDC25 | Coiled-Coil Domain Containing Protein 25 | IRI | Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury |
| CF | Cystic Fibrosis | IRS-1 | Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 |
| citH3 | Citrullinated Histone H3 | LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| CLS | Crown-Like Structures | METs | Macrophage Extracellular Traps |
| CXCL10 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 | METosis | Macrophage Extracellular Traps-associated Cell Death |
| CXCR3 | C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 3 | MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| ddcfDNA | Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA | mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| E-EVs | Egg-derived Extracellular Vesicles | NADPH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate |
| ELs | Ectopic Lymphoid Structures | NE | Neutrophil Elastase |
| ESAT-6 | 6kDa Early Secretory Antigen Target | NETs | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps |
| PADs | Peptidyl Arginine Deiminases | NOD | Non-Obese Diabetic |
| PFOS | Perfluorooctane Sulfonate | NTHi | Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae |
| PMA | Phorbol Myristate Acetate | SA | Severe Asthma |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma | SPI1 | Spleen Focus Forming Virus Proviral Integration Oncogene 1 |
| PR | Photoreceptor | sST2 | Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity 2 |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species | suPVMs | Sub-urothelial Perivascular Macrophages |
| HPS-PF | Hermansky–Pudlak Syndrome-associated Pulmonary Fibrosis | T1/2D | Type 1/2 Diabetes |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
References
- Chow, O.A.; Von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Bright, A.T.; Hensler, M.E.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Cogen, A.L.; Gallo, R.L.; Monestier, M.; Wang, Y.; Glass, C.K.; et al. Statins Enhance Formation of Phagocyte Extracellular Traps. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Kill Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Z.; Chen, W.; Zhou, C.-K.; Ma, K.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.-J. Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) Promotes Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Extracellular Traps Formation via the ROS-ERK Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 836880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, S.; Quan, H.; Yoon, Y.; Na, Y.; Kim, B.-J.; Seok, S.H. Mycobacterium Massiliense Induces Macrophage Extracellular Traps with Facilitating Bacterial Growth. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, G.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, J.; Yuan, D.; Li, H.; Hei, Z.; Yao, W. Macrophage Extracellular Traps Aggravate Iron Overload-Related Liver Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3783–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wu, X.; Liao, C.; Liu, X.; Du, J.; Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Peng, P.; Yu, L.; et al. Escherichia coli and Candida albicans Induced Macrophage Extracellular Trap-Like Structures with Limited Microbicidal Activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiana, M.; Aranda, F.; De Larrañaga, G. A Focus on the Roles of Histones in Health and Diseases. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 94, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; O’Sullivan, K.M.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Bardin, P.G.; King, P.T. Visualizing Macrophage Extracellular Traps Using Confocal Microscopy. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 128, 56459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiao, Q.; Yang, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Tian, Z.; Zeng, Z. A Bladder-Blood Immune Barrier Constituted by Suburothelial Perivascular Macrophages Restrains Uropathogen Dissemination. Immunity 2025, 58, 568–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsum, S.; Braian, C.; Koeken, V.A.C.M.; Raffetseder, J.; Lindroth, M.; Van Crevel, R.; Lerm, M. The Cording Phenotype of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Induces the Formation of Extracellular Traps in Human Macrophages. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Sun, Y. Enhanced Responsive Formation of Extracellular Traps in Macrophages Previously Exposed to Porphyromonas Gingivalis. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doster, R.S.; Sutton, J.A.; Rogers, L.M.; Aronoff, D.M.; Gaddy, J.A. Streptococcus Agalactiae Induces Placental Macrophages to Release Extracellular Traps Loaded with Tissue Remodeling Enzymes via an Oxidative Burst-Dependent Mechanism. mBio 2018, 9, e02084-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tang, X.; Guo, N.; An, Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; et al. Biochanin a Enhances the Defense Against Salmonella Enterica Infection Through AMPK/ULK1/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy and Extracellular Traps and Reversing SPI-1-Dependent Macrophage (MΦ) M2 Polarization. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shikh, M.E.M.; El Sayed, R.; Nerviani, A.; Goldmann, K.; John, C.R.; Hands, R.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Lewis, M.J.; Pitzalis, C. Extracellular Traps and PAD4 Released by Macrophages Induce Citrullination and Auto-Antibody Production in Autoimmune Arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 105, 102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-J.; Wang, P.-W.; Weng, S.-W. The Role of Mitochondria in Immune-Cell-Mediated Tissue Regeneration and Ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.; Thorsen, N.W.; Hallberg, L.A.E.; Hägglund, P.; Hawkins, C.L. New Insight into the Composition of Extracellular Traps Released by Macrophages Exposed to Different Types of Inducers. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 202, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, B.S.; Zhang, Y.; Brown, B.E.; Reyes, L.; Cogger, V.C.; Hawkins, C.L. Role of Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) and Other Inflammatory Mediators in the Induction of Macrophage Extracellular Trap Formation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulik, N.A.; Hellenbrand, K.M.; Czuprynski, C.J. Mannheimia Haemolytica and Its Leukotoxin Cause Macrophage Extracellular Trap Formation by Bovine Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, H.; Okubo, K.; Iida, K.; Kawakami, H.; Takayama, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Haruta, J.; Sasaki, J.; Hayashi, K.; Hirahashi, J. Multiple Site Inflammation and Acute Kidney Injury in Crush Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1458997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, K.; Kurosawa, M.; Kamiya, M.; Urano, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Hase, K.; Homma, K.; Sasaki, J.; Miyauchi, H.; et al. Macrophage Extracellular Trap Formation Promoted by Platelet Activation Is a Key Mediator of Rhabdomyolysis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummarapurugu, A.B.; Zheng, S.; Ma, J.; Ghosh, S.; Hawkridge, A.; Voynow, J.A. Neutrophil Elastase Triggers the Release of Macrophage Extracellular Traps: Relevance to Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 66, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mónaco, A.; Canales-Huerta, N.; Jara-Wilde, J.; Härtel, S.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Moreno, M.; Scavone, P. Salmonella Typhimurium Triggers Extracellular Traps Release in Murine Macrophages. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 639768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Xu, K.; Zhang, M.; Niu, J.; Zhao, T.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; He, L.; et al. 5′-Nucleotidase Is Dispensable for the Growth of Salmonella typhimurium but Inhibits the Bactericidal Activity of Macrophage Extracellular Traps. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, A.A.; Chen, S.; Hao, H.; Jin, X.; Lan, S.; Li, Z.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, Y. Macrophage Extracellular Traps Are Induced by Mycoplasma bovis in Bovine Macrophages through NADPH Oxidase/ROS-dependent Manner and Their Antibacterial Efficacy. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e70238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, F.A.B.; Hilsenstein, V.; Weerasinghe, H.; Weir, A.; Hughes, S.; Crawford, S.; Vince, J.E.; Hickey, M.J.; Traven, A. The Escape of Candida albicans from Macrophages Is Enabled by the Fungal Toxin Candidalysin and Two Host Cell Death Pathways. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, A.; Pais, C.; Sampaio, P. Relevance of Macrophage Extracellular Traps in C. Albicans Killing. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-W.; Jacobs, W.R. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Exploits Human Interferon γ to Stimulate Macrophage Extracellular Trap Formation and Necrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-W. The Role of ESX-1 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Pathogenesis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.M.; Gey Van Pittius, N.C.; DiGiuseppe Champion, P.A.; Cox, J.; Luirink, J.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; Appelmelk, B.J.; Bitter, W. Type VII Secretion—Mycobacteria Show the Way. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousha, L.; Sharma, R.; Lim, S.; Ngui, J.; Buckle, A.M.; King, P.T. Assessing Respiratory Immune Responses to Haemophilus Influenzae. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 172, 62572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.T.; Sharma, R.; O’Sullivan, K.; Selemidis, S.; Lim, S.; Radhakrishna, N.; Lo, C.; Prasad, J.; Callaghan, J.; McLaughlin, P.; et al. Nontypeable Haemophilus Influenzae Induces Sustained Lung Oxidative Stress and Protease Expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, L. Schistosome Egg-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Deliver Sja-miR-71a Inhibits Host Macrophage and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps via Targeting Sema4D. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaire, S.; Elhabazi, A.; Bensussan, A.; Boumsell, L. CD100 Is a Leukocyte Semaphorin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1998, 54, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. CD100/Sema4D, a Lymphocyte Semaphorin Involved in the Regulation of Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo-Barrera, C.M.; Castrillón-Rivera, L.E.; Palma-Ramos, A.; Castañeda-Sánchez, J.I.; Luna-Herrera, J. Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis, Probiotics That Induce the Formation of Macrophage Extracellular Traps. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonello, S.; Carniato, F.; Rizzi, M.; Migliario, M.; Rocchetti, V.; Marchese, L.; Renò, F. Charged Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes Trigger In Vitro METosis via Both Oxidative Stress and Autophagy. Life Sci. 2017, 190, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Hao, W.; Jiang, J.; Meng, Q.; Wei, X. 1,4-Naphthoquinone-Coated Black Carbon, a Kind of Atmospheric Fine Particulate Matter, Affects Macrophage Fate: New Insights into Crosstalk between Necroptosis and Macrophage Extracellular Traps. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 6095–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hao, W.; Jiang, J.; Meng, Q.; Wei, X. Black Carbon Nanoparticles Activate the Crosstalk Mechanism between Necroptosis and Macrophage Extracellular Traps to Change Macrophages Fate. Environ. Res. 2023, 232, 116321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Hao, W.; Jiang, J.; Meng, Q.; Wei, X. Ozone-Oxidized Black Carbon Particles Change Macrophage Fate: Crosstalk between Necroptosis and Macrophage Extracellular Traps. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, H.L.; Green, D.M.; Trifillis, A.L.; Johnson, D.E.; Chippendale, G.R.; Lockatell, C.V.; Jones, B.D.; Warren, J.W. Pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli and Killing of Cultured Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells: Role of Hemolysin in Some Strains. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quoc, Q.L.; Cao, T.B.T.; Moon, J.-Y.; Jang, J.-H.; Shin, Y.S.; Choi, Y.; Ryu, M.S.; Park, H.-S. Contribution of Monocyte and Macrophage Extracellular Traps to Neutrophilic Airway Inflammation in Severe Asthma. Allergol. Int. 2024, 73, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Huang, C.; Chen, G.; Kong, W.; Zhao, L.; Jie, H.; Zhen, G. The Role of Extracellular Traps Released by Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Macrophages in Asthma. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, S.M.; Ashrani, A.; Park, M.S.; Chen, D. Histological Findings of ETosis in Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome with Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Follow-Up Case Report. J. Chest Surg. 2024, 58, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashar, S.J.; Holmes, C.L.; Shelef, M.A. Macrophage Extracellular Traps Require Peptidylarginine Deiminase 2 and 4 and Are a Source of Citrullinated Antigens Bound by Rheumatoid Arthritis Autoantibodies. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1167362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shi, R.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, C.; You, Q.; Fan, H.; Wu, J. Role of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 4–Dependent Macrophage Extracellular Trap Formation in Type 1 Diabetes Pathogenesis. Diabetes 2024, 73, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, L.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Leung, W.Y.; Fu, K.; Wu, J.; Liu, K.; Man, K.; Yang, X.; et al. Macrophage P38α Promotes Nutritional Steatohepatitis through M1 Polarization. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, N. CXCR3 Ligands in Cancer and Autoimmunity, Chemoattraction of Effector T Cells, and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, Q.; Yan, S.; Zhang, W.; Han, L.; Zhong, M. Hepcidin Gene Silencing Ameliorated Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Adipose Tissue of Db/Db Mice via Inhibiting METs Formation. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 133, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertiwi, K.R.; De Boer, O.J.; Mackaaij, C.; Pabittei, D.R.; De Winter, R.J.; Li, X.; Van Der Wal, A.C. Extracellular Traps Derived from Macrophages, Mast Cells, Eosinophils and Neutrophils Are Generated in a Time-Dependent Manner during Atherothrombosis. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yi, N.; Zhu, P.; Gao, J.; Lv, J. Sorafenib-Induced Macrophage Extracellular Traps via ARHGDIG/IL4/PADI4 Axis Confer Drug Resistance through Inhibiting Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biol. Direct 2024, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-Y.; Li, G.; Kang, F.-P.; Lin, C.-F.; Xie, C.-K.; Wu, Y.-D.; Hu, J.-F.; Lin, H.-Y.; Zhu, S.-C.; Huang, X.-X.; et al. Necroptosis Enhances ‘Don’t Eat Me’ Signal and Induces Macrophage Extracellular Traps to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Liver Metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Nan, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, A.; Zhang, T.; Qu, X.; Li, C. Interaction Between Macrophage Extracellular Traps and Colon Cancer Cells Promotes Colon Cancer Invasion and Correlates with Unfavorable Prognosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 779325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiba, A.; Shiogama, K.; Tsukamoto, T.; Hirayama, M.; Yamada, S.; Abe, M. Morphologic Analysis of M2 Macrophage in Glioblastoma: Involvement of Macrophage Extracellular Traps (METs). Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 55, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Shen, J.; Lei, W.; Yan, P.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, R. Plasma Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA Levels Are Associated With the Inflammatory Burden and Macrophage Extracellular Trap Activity in Renal Allografts. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 796326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conedera, F.M.; Kokona, D.; Zinkernagel, M.S.; Stein, J.V.; Lin, C.P.; Alt, C.; Enzmann, V. Macrophages Coordinate Immune Response to Laser-Induced Injury via Extracellular Traps. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, S.; Horibata, S.; McElwee, J.L.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Coonrod, S.A. Identification of Macrophage Extracellular Trap-Like Structures in Mammary Gland Adipose Tissue: A Preliminary Study. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, F.; Schulz, M.; Pilatz, A.; Wagenlehner, F.; Schuppe, H.-C.; Conejeros, I.; Uribe, P.; Taubert, A.; Sánchez, R.; Hermosilla, C. Increase of Leucocyte-Derived Extracellular Traps (ETs) in Semen Samples from Human Acute Epididymitis Patients—A Pilot Study. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020, 37, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, L.; Hao, F.; Ji, X.; Hu, X.; Luo, M.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, B.; Wu, Y.; et al. Macrophage Membrane-Coated Polydopamine Nanomedicine for Treating Acute Lung Injury through Modulation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and M2 Macrophage Polarization. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 32, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Tang, X.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, X.; An, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, B.; et al. Fosfomycin Enhances Phagocyte-Mediated Killing of Staphylococcus aureus by Extracellular Traps and Reactive Oxygen Species. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; Li, S.; Xu, S.; Li, S. Cannabidiol Alleviates Perfluorooctane Sulfonate-Induced Macrophage Extracellular Trap Mediate Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice Liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, P.; Shen, W.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Sun, T.; Jiang, C. DNase I-Mediated Chemotactic Nanoparticles for NETs Targeting and Microenvironment Remodeling Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Adv. Sci. 2025, e03689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ling, T.; Ding, Q.; Zhu, F.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Ma, T.; Meng, Q. GlycoRNA-Rich, Neutrophil Membrane-Coated, siMT1-Loaded Nanoparticles Mitigate Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Progression by Inhibiting the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Action Direction | Agents/Strategies | Key Mechanism | Target/Indication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibit METs Formation/Release | PAD inhibitors (CI-amidine, YW3-56, PAD2-IN-1) | Block histone citrullination | RA, SA, T1D [14,42,44,45] |
| Neutralizing antibodies (anti-IL-4/anti-IL-33/anti-ST2) | Inhibit IL-33/ST2 signaling | Asthma [42] | |
| Mac-1 inhibitors | Block platelet-macrophage interaction | Rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI [14] | |
| Iron chelators | Reduce iron overload | Hepatic IRI [5] | |
| Cannabidiol (CBD) | Modulate PAD4/CCDC25/ILK/NF-κB pathway | Reduce PFOS-induced hepatic METs [60] | |
| Enhance Defensive METs | Biochanin A (BCA) | Activate AMPK/ULK1/mTOR autophagy; reverse SPI1-dependent M2 polarization | Anti-Salmonella defense [13] |
| Statins | Suppress phagocytosis; promote MET release | Clearance of S. aureus [1] | |
| Enhance ETs Bactericidal Activity | Fosfomycin (FOM) | Promote ETs formation; increase ROS accumulation | Anti-S. aureus activity [59] |
| Indirect Modulation | CXCR3 antagonist (AMG487) | Block CXCL10/CXCR3 axis | Delay T1D onset (transient effect) [45] |
| Hepcidin gene silencing | Reduce macrophage infiltration | Improve insulin resistance in T2DM [48] | |
| NETs-Targeted Nanotherapies | DNase I-functionalized NPs | Degrade NETs-DNA; scavenge ROS | Cerebrovascular protection [50] |
| Macrophage membrane-coated polydopamine NPs (MM@mPDA-PM NPs) | Downregulate MPO/NE/PAD4; promote M2 polarization | ALI [58] | |
| GlycoRNA-enriched neutrophil membrane vesicles | Deliver siMT1 to disrupt NETs-mediated inflammation | Abdominal aortic aneurysm [62] | |
| Research Gap | MET-targeted nanotherapies | No existing strategies | Future development frontier |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Gao, F. The Dual Role of Macrophage Extracellular Traps in Host Defense and Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091220
Chen Z, Gao F. The Dual Role of Macrophage Extracellular Traps in Host Defense and Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(9):1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091220
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhiyu, and Fei Gao. 2025. "The Dual Role of Macrophage Extracellular Traps in Host Defense and Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications" Biomolecules 15, no. 9: 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091220
APA StyleChen, Z., & Gao, F. (2025). The Dual Role of Macrophage Extracellular Traps in Host Defense and Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Biomolecules, 15(9), 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091220






