Improving Cofactor Promiscuity of HMG-CoA Reductase from Ruegeria pomeroyi Through Rational Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmids, and DNA
2.2. Reagents and Kits
2.3. Vector Construction and Mutant Construction
2.4. Construction of Mutant Libraries
2.5. Preparation of Crude Protein Enzyme Extract
2.6. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
2.7. Protein Expression and Purification
2.8. Protein Rational Design
2.9. Activity Assay
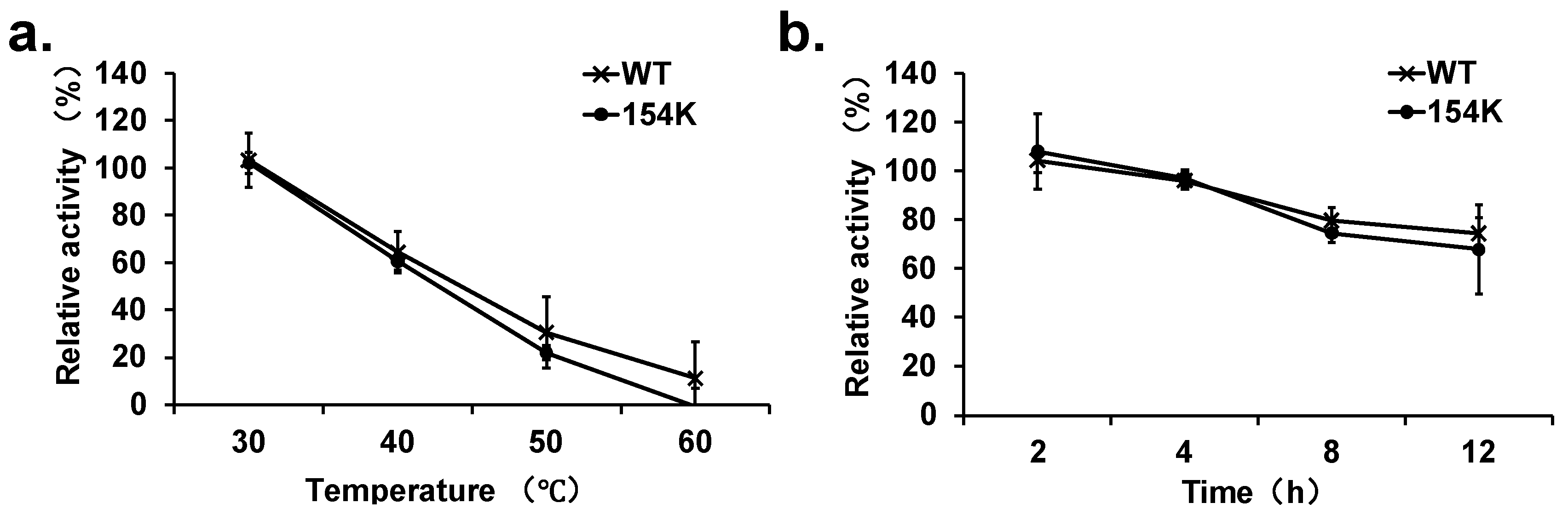
2.10. Thermal Stability Analysis
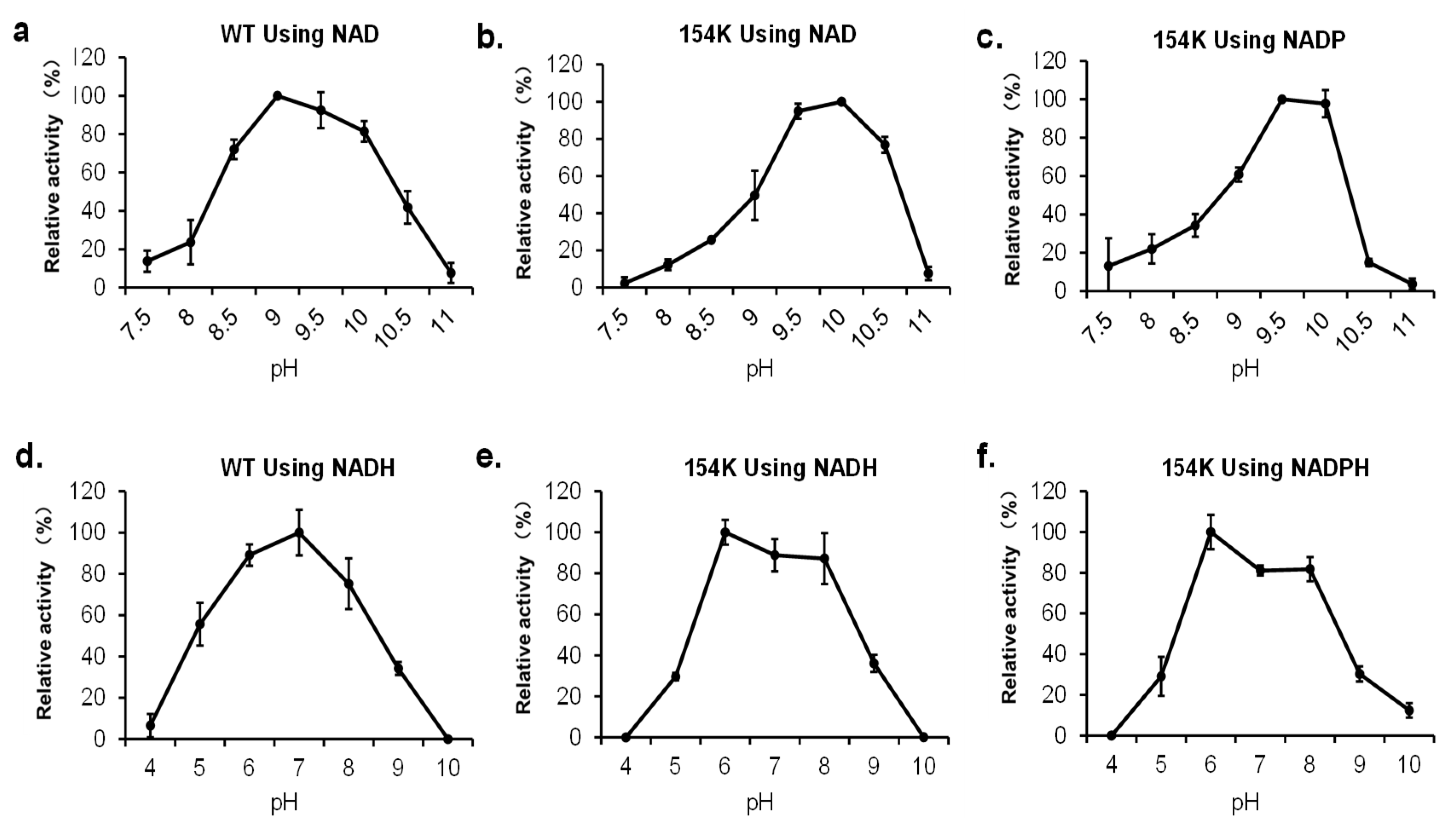
2.11. pH Profile of rpHMGR
3. Results and Discussion
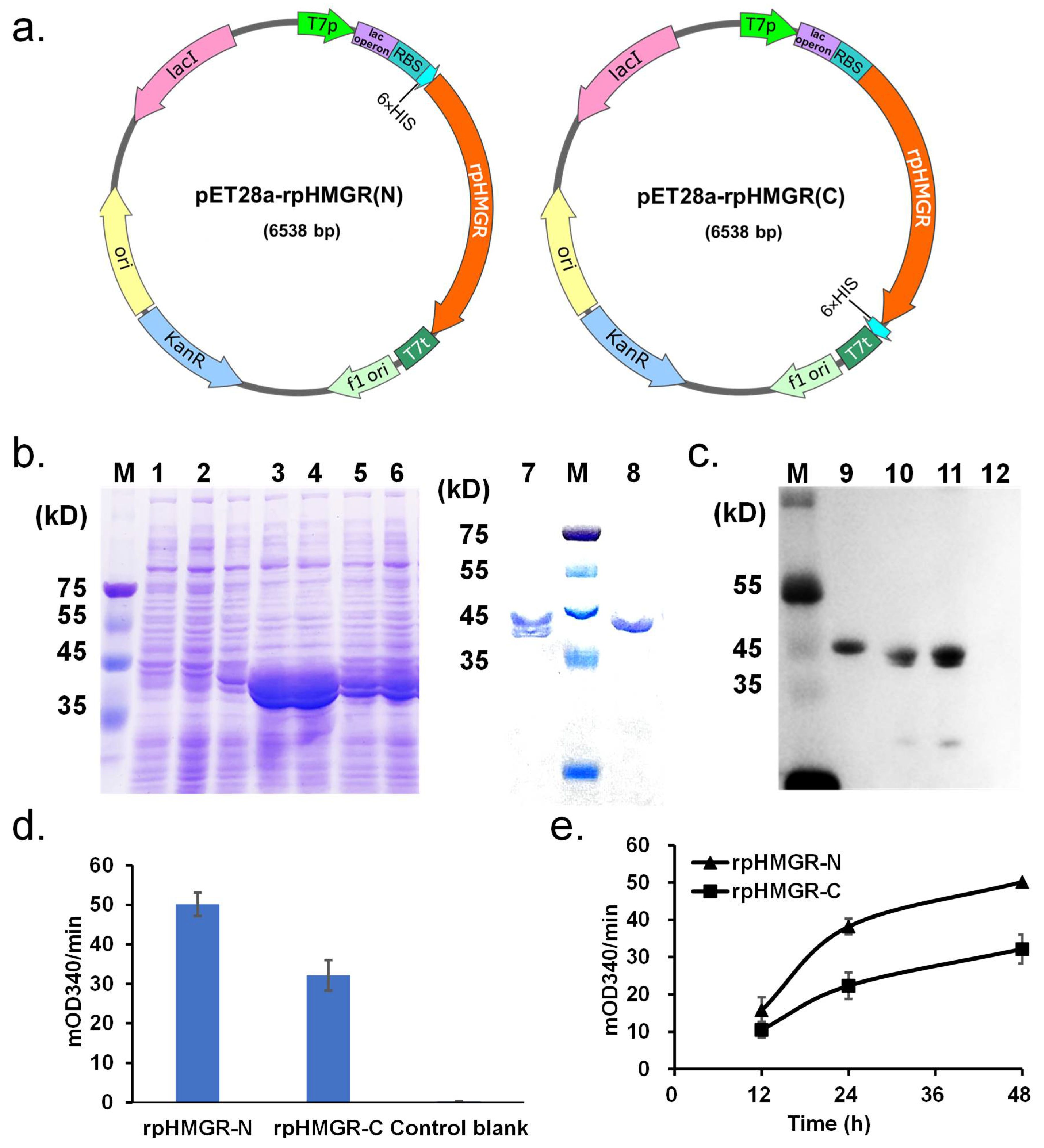
3.1. Expression of rpHMGR
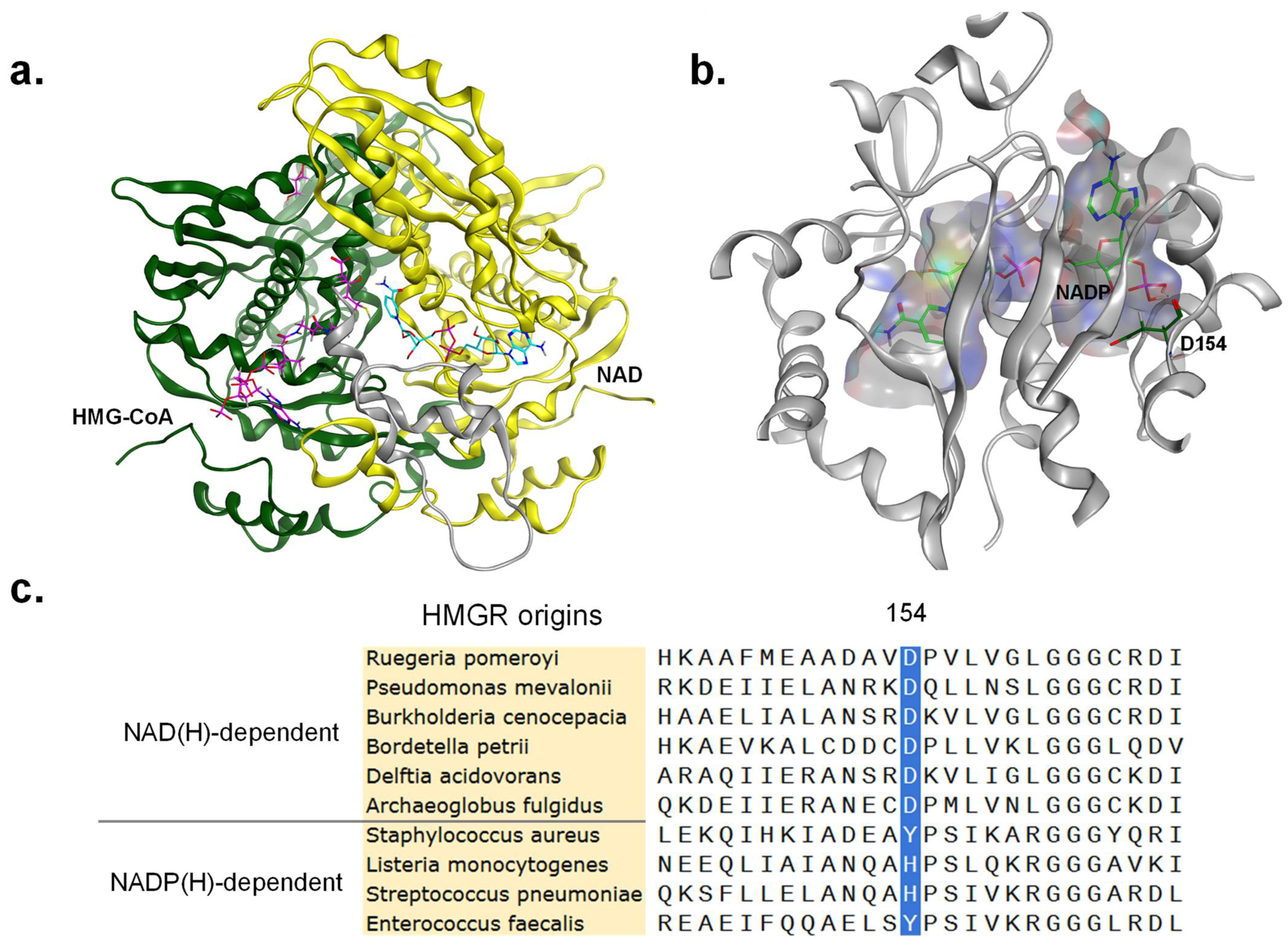
3.2. Rational Design of Site-Directed Mutagenesis
3.3. Activity Analysis of rpHMGR
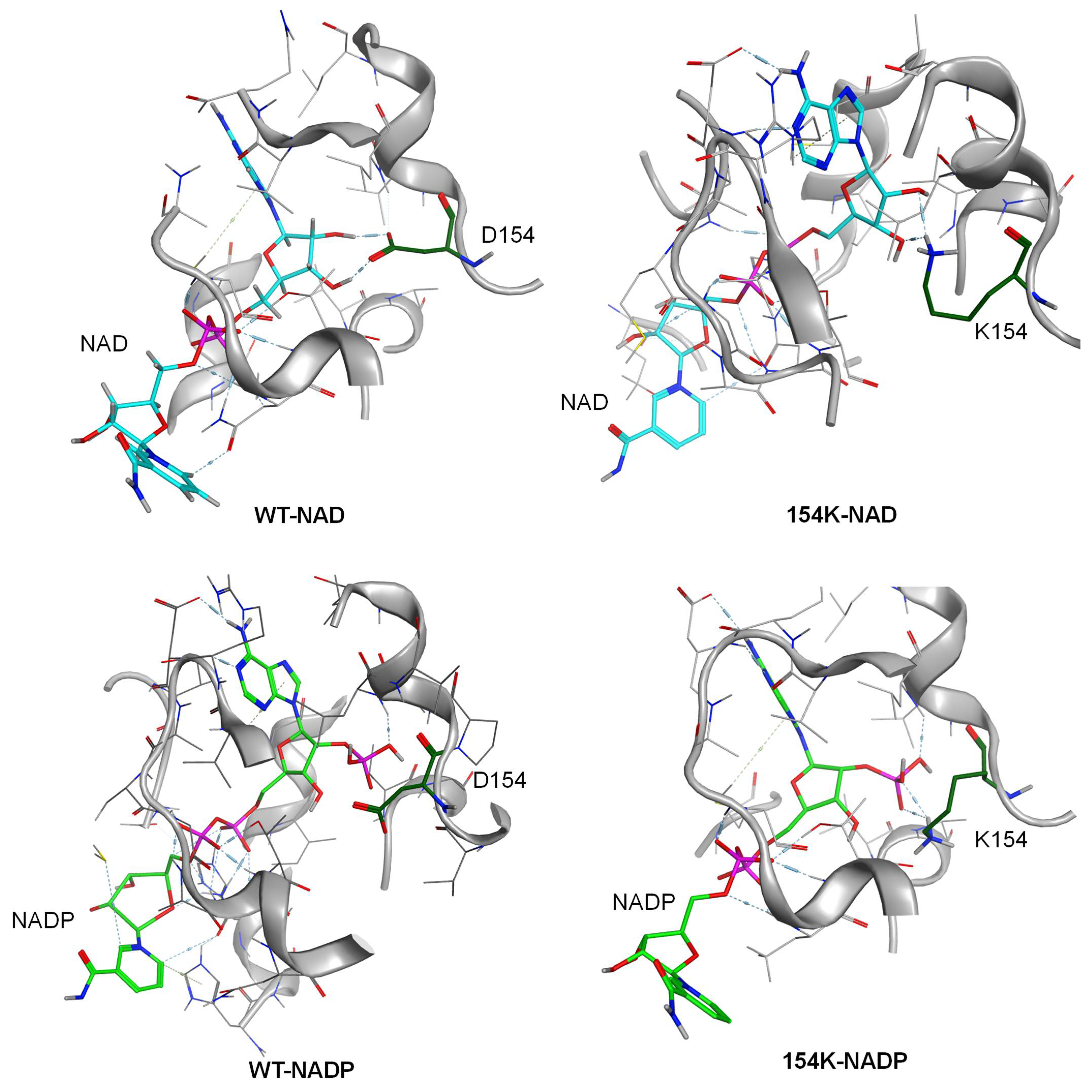
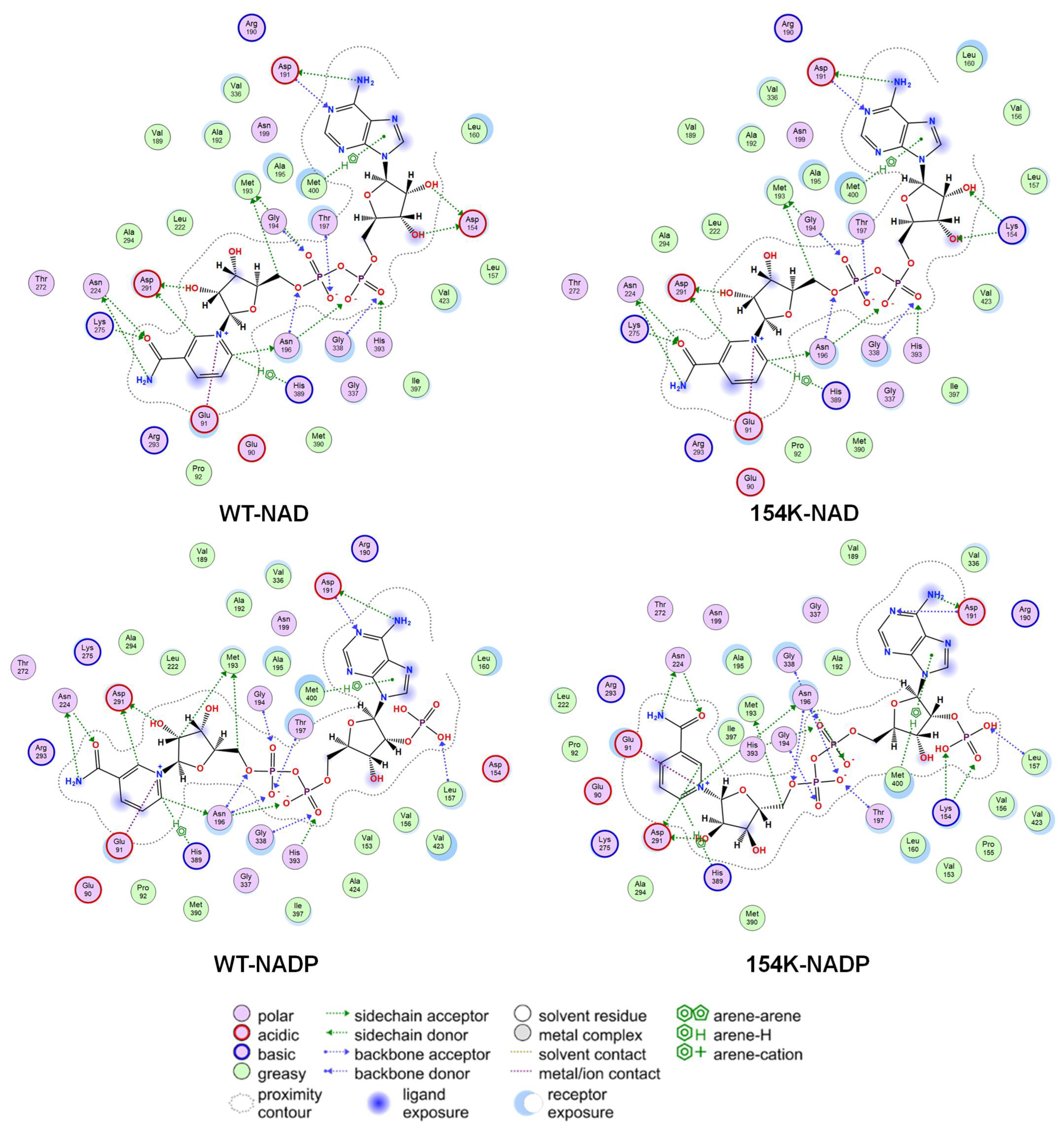
3.4. Analysis of Structure–Activity Relationship in Mutants
3.5. Analysis of Thermal Stability of Mutants
3.6. Effect of pH on rpHMGR Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMGR | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase |
| NAD | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide |
| NADP | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate |
References
- Sacchettini, J.C.; Poulter, C.D. Creating isoprenoid diversity. Science 1997, 277, 1788–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, J.N.; Leferink, N.G.H.; Johannissen, L.O.; Hay, S.; Scrutton, N.S. Decoding catalysis by terpene synthases. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 12774–12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, D.W. Structural and chemical biology of terpenoid cyclases. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 11570–11648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, A.L.; Hawkins, K.M.; Tsegaye, Y.; Antipov, E.; Kim, Y.; Raetz, L.; Dahl, R.H.; Tai, A.; Mahatdejkul-Meadows, T.; Xu, L.; et al. Rewiring yeast central carbon metabolism for industrial isoprenoid production. Nature 2016, 537, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Biosynthesis of monoterpenoid and sesquiterpenoid as natural flavors and fragrances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 65, 108151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, J.S.; Perestrelo, R.; Ferreira, R.; Berenguer, C.V.; Pereira, J.A.M.; Castilho, P.C. Plant-derived terpenoids: A plethora of bioactive compounds with several health functions and industrial applications—A comprehensive overview. Molecules 2024, 29, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakumu, Y.; Chaudhri, A.A.; Helfrich, E.J.N. The role and mechanisms of canonical and non-canonical tailoring enzymes in bacterial terpenoid biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2025, 42, 501–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Shang, Y.; Stephanopoulos, G. Engineering peroxisomal biosynthetic pathways for maximization of triterpene production in Yarrowia lipolytica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2314798121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ji, X.; Yi, R.; Li, D.; Shen, X.; Liu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Shi, S. Heterologous biosynthesis of terpenoids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. J. 2025, 20, e202400712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhao, Q.-W.; Li, Y.-Q. De novo biosynthesis of a bioactive meroterpene bakuchiol in yeast. ACS Synth. Biol. 2024, 13, 3600–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedl, M.; Tabernero, L.; Stauffacher, C.V.; Rodwell, V.W. Class II 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductases. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombard, J.; Moreira, D. Origins and early evolution of the mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in the three domains of life. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, J.S.; Espenshade, P.J. Regulation of HMG-CoA reductase in mammals and yeast. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Tamariz, J.; Chamorro, G.; Medina-Franco, J.L. Inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase: Current and future prospects. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobert, J.A. Lovastatin and beyond: The history of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, B.E.; Wiest, O.; Stauffacher, C.V. The increasingly complex mechanism of HMG-CoA reductase. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2416–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochar, D.A.; Stauffacher, C.V.; Rodwell, V.W. Sequence comparisons reveal two classes of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Mol. Genet. Metab. 1999, 66, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, J.A.; Rodwell, V.W. The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A (HMG-CoA) reductases. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvan, E.S. Bacterial and mammalian HMG-CoA reductases: Related enzymes with distinct architectures. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, J.A.; Rodwell, V.W.; Stauffacher, C.V. Structural determinants of nucleotide cofactor specificity in the distinctive dinucleotide binding fold of HMG-CoA reductase from Pseudomonas mevalonii. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 11945–11950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, B.H.; Driver, J.; Peacock, R.B.; Dembinski, H.E.; Corson, M.H.; Gordon, S.S.; Watson, J.M. Kinetic characterization of an oxidative, cooperative HMG-CoA reductase from Burkholderia cenocepacia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2014, 1844, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, R.B.; Hicks, C.W.; Walker, A.M.; Dewing, S.M.; Lewis, K.M.; Abboud, J.-C.; Stewart, S.W.A.; Kang, C.; Watson, J.M. Structural and functional characterization of dynamic oligomerization in Burkholderia cenocepacia HMG-CoA reductase. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 3960–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragwan, E.R.; Arai, E.; Kung, Y. New crystallographic snapshots of large domain movements in bacterial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5715–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.R.; Kung, Y. Structural features and domain movements controlling substrate binding and cofactor specificity in class II HMG-CoA reductase. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, E.I.; Kim, D.Y.; Bryant, A.P.; Gwynn, M.N.; Lunsford, R.D.; McDevitt, D.; Myers, J.E.; Rosenberg, M.; Sylvester, D.; Stauffacher, C.V.; et al. Essentiality, expression, and characterization of the class II 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5147–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theivagt, A.E.; Amanti, E.N.; Beresford, N.J.; Tabernero, L.; Friesen, J.A. Characterization of an HMG-CoA reductase from Listeria monocytogenes that exhibits dual cofactor specificity. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 14397–14406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Stauffacher, C.V.; Rodwell, V.W. Dual cofactor specificity of Archaeoglobus fulgidus HMG-CoA reductase. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Steussy, C.N.; López-Pérez, D.; Schmidt, T.; Kulathunga, S.C.; Seleem, M.N.; Lipton, M.; Mesecar, A.D.; Rodwell, V.W.; Stauffacher, C.V. Targeting Enterococcus faecalis HMG-CoA reductase with a non-statin inhibitor. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan-Starck, T.C.; Rodwell, V.W. Pseudomonas mevalonii 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase: Characterization and chemical modification. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 17913–17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C.M.; Chi, Y.I.; Rodwell, V.W.; Stauffacher, C.V. Crystallization of HMG-CoA reductase from Pseudomonas mevalonii. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1995, 51, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C.M.; Rodwell, V.W.; Stauffacher, C.V. Crystal structure of Pseudomonas mevalonii HMG-CoA reductase at 3.0 angstrom resolution. Science 1995, 268, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istvan, E.S.; Deisenhofer, J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science 2001, 292, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wei, W.; Chao, Z.; Qi, R.; He, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Rao, Y.; Zhou, J. Electron transfer engineering of artificially designed cell factory for complete biosynthesis of steroids. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ent, F.; Löwe, J. RF cloning: A restriction-free method for inserting target genes into plasmids. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2006, 67, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, T.; Jacobovitch, Y.; Dantes, A.; Bernheim, R.; Peleg, Y. Applications of the restriction free (RF) cloning procedure for molecular manipulations and protein expression. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 172, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.K. Engineering d-Lactate Dehydrogenase to Favor an Non-natural Cofactor Nicotinamide Cytosine Dinucleotide. Chembiochem 2020, 21, 1972–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steussy, C.N.; Critchelow, C.J.; Schmidt, T.; Min, J.-K.; Wrensford, L.V.; Burgner, J.W.; Rodwell, V.W.; Stauffacher, C.V. A novel role for coenzyme A during hydride transfer in 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 5195–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chánique, A.M.; Parra, L.P. Protein Engineering for Nicotinamide Coenzyme Specificity in Oxidoreductases: Attempts and Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, H.; Huang, Y.; Shah, A.M.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.K. Improving Cofactor Promiscuity of HMG-CoA Reductase from Ruegeria pomeroyi Through Rational Design. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070976
Xue H, Huang Y, Shah AM, Wang X, Hu Y, Zhang L, Zhao ZK. Improving Cofactor Promiscuity of HMG-CoA Reductase from Ruegeria pomeroyi Through Rational Design. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070976
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Haizhao, Yanzhe Huang, Aabid Manzoor Shah, Xueying Wang, Yinghan Hu, Lingyun Zhang, and Zongbao K. Zhao. 2025. "Improving Cofactor Promiscuity of HMG-CoA Reductase from Ruegeria pomeroyi Through Rational Design" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070976
APA StyleXue, H., Huang, Y., Shah, A. M., Wang, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, L., & Zhao, Z. K. (2025). Improving Cofactor Promiscuity of HMG-CoA Reductase from Ruegeria pomeroyi Through Rational Design. Biomolecules, 15(7), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070976





