Unraveling the Role of Microcystin-LR in Ferroptosis and Sepsis Pathogenesis: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
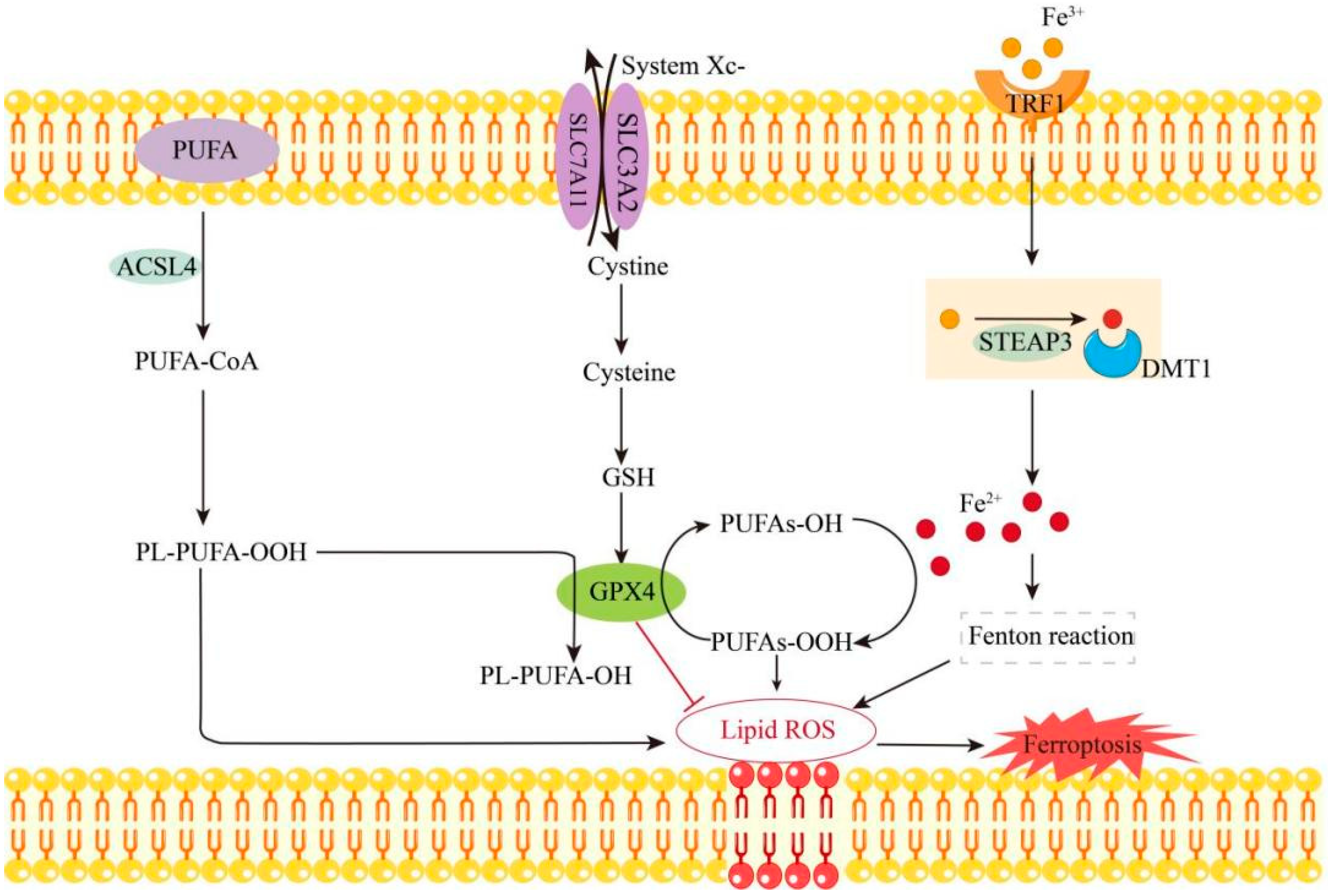
2. MC-LR Promotes the Occurrence of Ferroptosis
2.1. Mechanism of Ferroptosis
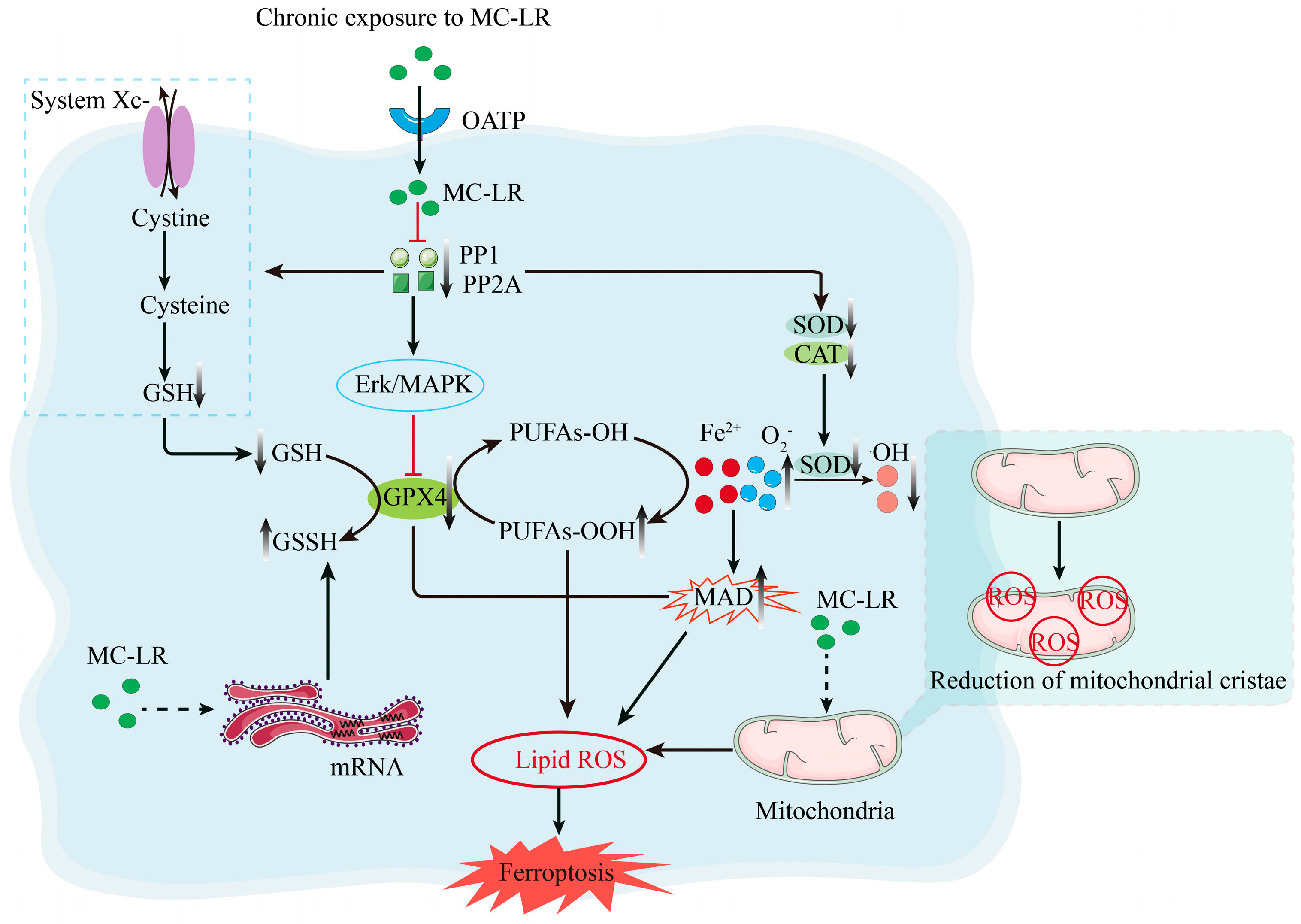
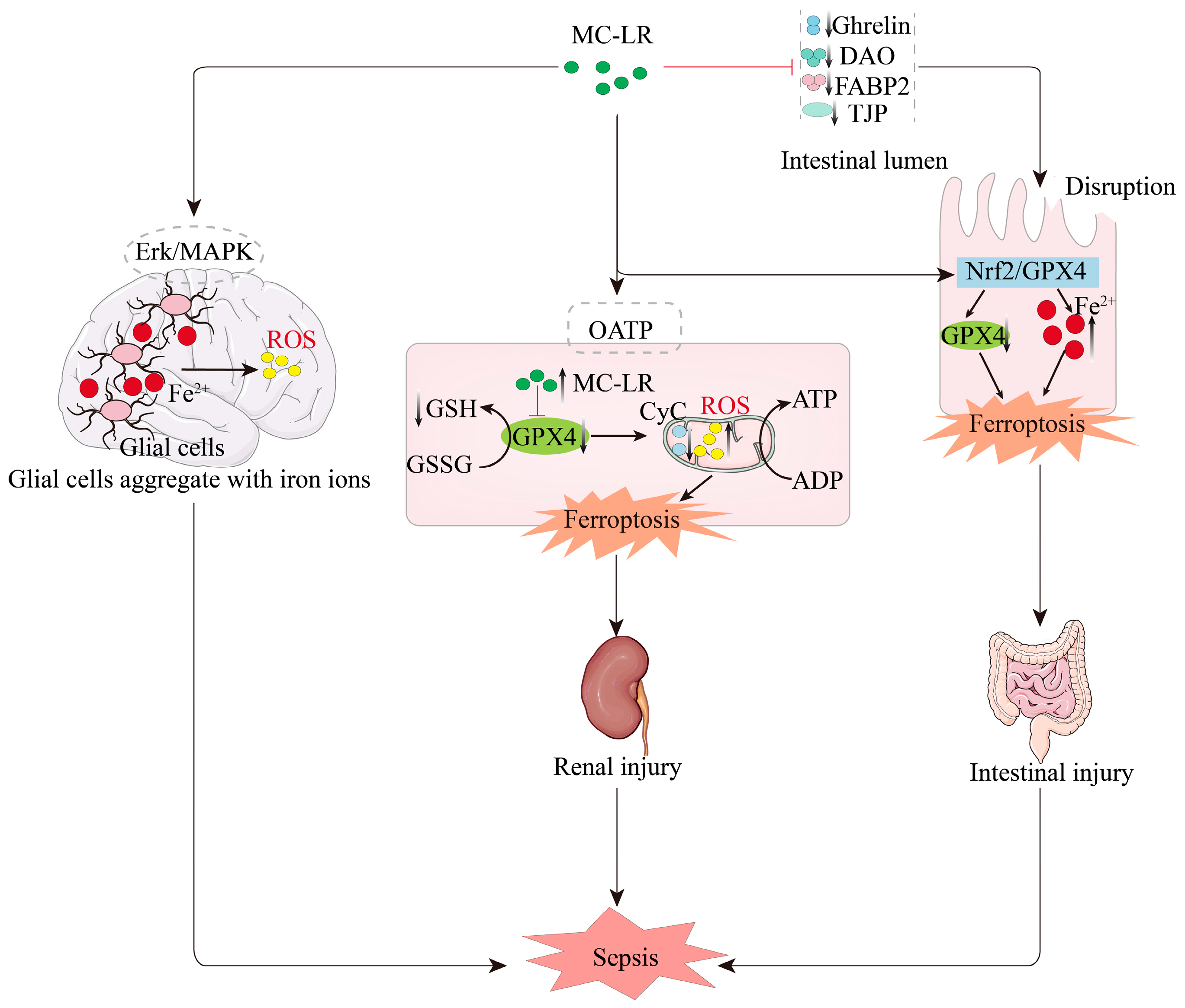
2.2. Mechanisms Associated with the Promotion of Ferroptosis by MC-LR
2.3. MC-LR Promotes Ferroptosis
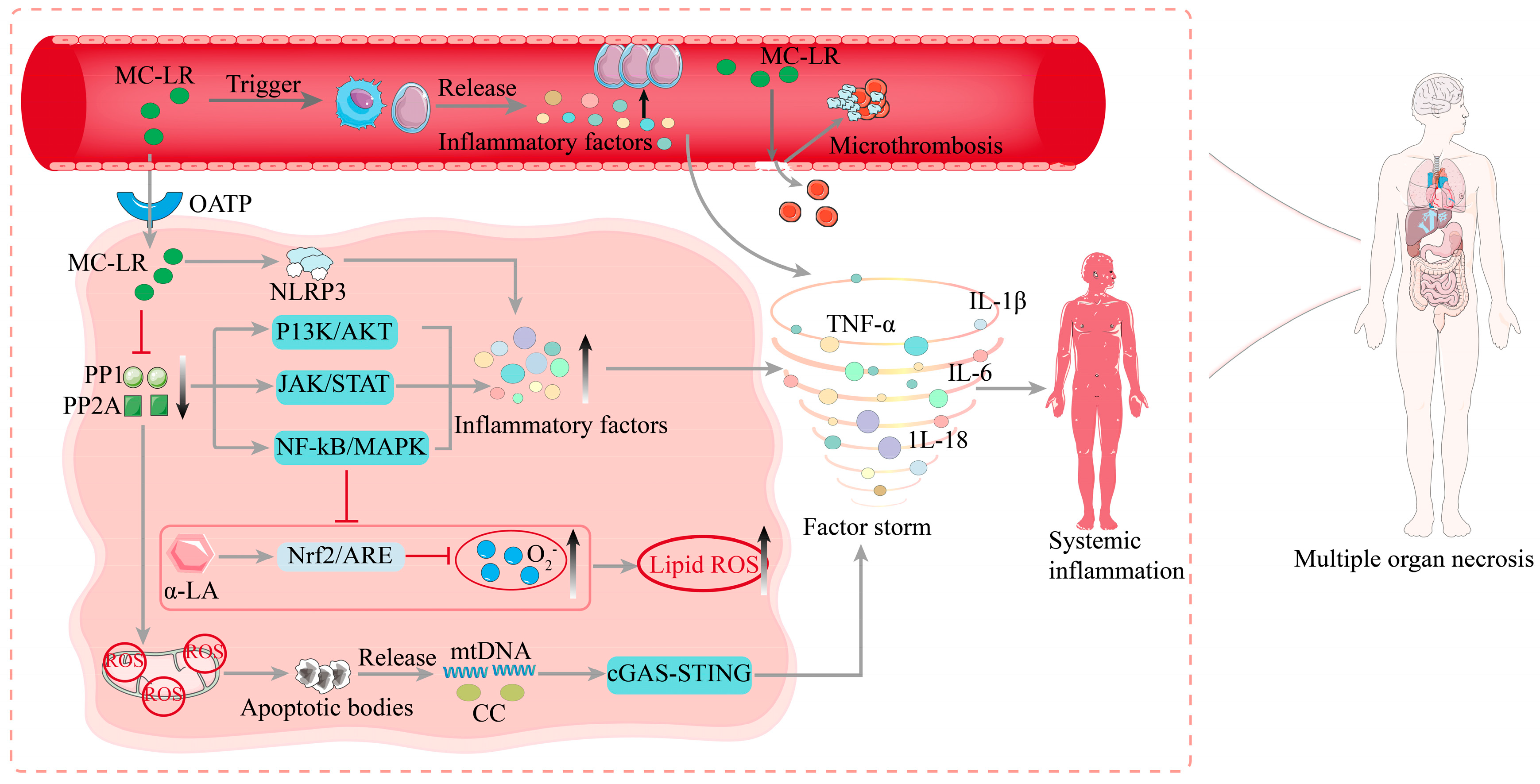
3. MC-LR-Associated Pathogenic Pathways in Sepsis Progression
3.1. Pathogenesis of Sepsis
3.2. Molecular Mechanisms of MC-LR-Induced Sepsis
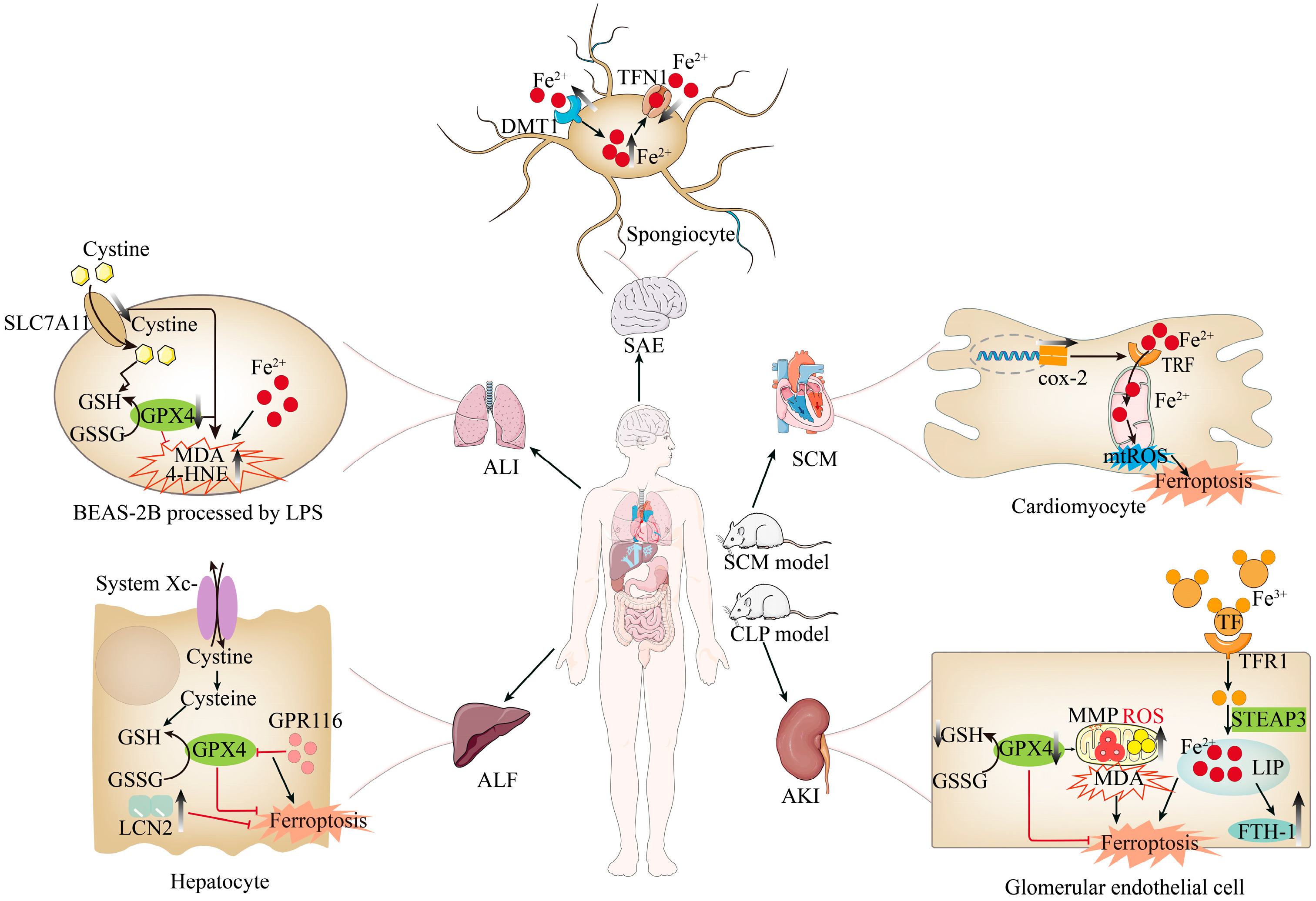
4. Ferroptosis Contributes to Organ Damage in Sepsis
4.1. Sepsis-Induced Liver Injury and Ferroptosis
4.2. Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury and Ferroptosis
4.3. Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury and Ferroptosis
4.4. Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy and Ferroptosis
4.5. Gastrointestinal Injury in Sepsis and Ferroptosis
4.6. Septic Cardiomyopathy and Ferroptosis
5. MC-LR Induces the Onset of Sepsis Through the Ferroptosis Pathway
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALF | Acute Liver Failure |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| ALI | Acute Lung Injury |
| COX-2 | Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2 (Cyclooxygenase-2) |
| DAO | Diamine Oxidase |
| DMT1 | Divalent Metal Transporter 1 |
| FABP2 | Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 2 |
| FTH1 | Ferritin Heavy Polypeptide 1 |
| GCLC | Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase Catalytic Subunit |
| GCLM | Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase Modifier Subunit |
| GCS | Gamma-Glutamylcysteine Synthetase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GPX4 | Glutathione Peroxidase 4 |
| HAMP1 | Hepcidin Antimicrobial Peptide 1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| LCN2 | Lipocalin-2 |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MC-LR | Microcystin-LR |
| MDT1 | Multidrug Transporter 1 |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 |
| OATP | Organic Anion-Transporting Polypeptides |
| PP1 | Protein Phosphatase 1 |
| PP2A | Protein Phosphatase 2A |
| PTGS2 | Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2 |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SAE | Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy |
| SCM | Septic Cardiomyopathy |
| SLC7A11 | Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11 |
| STEAP3 | Solute Carrier Family 17 Member 3 |
| TFR1 | Transferrin Receptor 1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| TJP | Tight Junction Protein |
| TF | Transferrin |
| Xc- | System Xc- (Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter) |
References
- Faix, J.D. Biomarkers of sepsis. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2013, 50, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Cai, S.; Su, J. The Pathogenesis of Sepsis and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensiv. Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartelli, M.; Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Catena, F.; Griffiths, E.A.; Di Saverio, S.; Coimbra, R.; Ordoñez, C.A.; Leppaniemi, A.; Fraga, G.P.; Coccolini, F.; et al. Global validation of the WSES Sepsis Severity Score for patients with complicated intra-abdominal infections: A prospective multicentre study (WISS Study). World J. Emerg. Surg. 2015, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srzić, I.; Adam, V.N.; Pejak, D.T. Sepsis definition: What’s new in the Treatment Guidelines. Acta Clin. Croat. 2022, 61, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Xu, Y.; Yin, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Peng, J.-M.; Dong, R.; Hu, X.-Y.; et al. National incidence and mortality of hospitalized sepsis in China. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Berghe, T.; Linkermann, A.; Jouan-Lanhouet, S.; Walczak, H.; Vandenabeele, P. Regulated necrosis: The expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolma, S.; Lessnick, S.L.; Hahn, W.C.; Stockwell, B.R. Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagoda, N.; Von Rechenberg, M.; Zaganjor, E.; Bauer, A.J.; Yang, W.S.; Fridman, D.J.; Wolpaw, A.J.; Smukste, I.; Peltier, J.M.; Boniface, J.J.; et al. RAS–RAF–MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 2007, 447, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Schneider, M.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Hammond, V.J.; Herbach, N.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Eggenhofer, E.; et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; He, D.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Li, B. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: Opportunities and challenges in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell-Badge, R.; Anthony, E.; Barker, R.A.; Bubela, T.; Brivanlou, A.H.; Carpenter, M.; Charo, R.A.; Clark, A.; Clayton, E.; Cong, Y.; et al. ISSCR Guidelines for Stem Cell Research and Clinical Translation: The 2021 update. Stem Cell Rep. 2021, 16, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Shi, P.; Ba, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, P. The neuroprotective effects of carvacrol on ischemia/reperfusion-induced hippocampal neuronal impairment by ferroptosis mitigation. Life Sci. 2019, 235, 116795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Bautista, C.; Vento, M.; Baquero, M.; Cháfer-Pericás, C. Lipid peroxidation in neurodegeneration. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 497, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, B.A.; Ameenuddin, S.; Uchida, K.; Suo, W.Z.; SantaCruz, K.; Festoff, B.W. Membrane lipid peroxidation in neurodegeneration: Role of thrombin and proteinase-activated receptor-1. Brain Res. 2016, 1643, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Rao, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Fu, S.; Xiao, J. Attenuation of Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Exogenous H2S via Inhibition of Ferroptosis. Molecules 2023, 28, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Wang, P.; Jia, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, X.; Wang, Y. A review on factors affecting microcystins production by algae in aquatic environments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sinha, R.P.; Incharoensakdi, A. The cyanotoxin-microcystins: Current overview. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2014, 13, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cao, P.; Yang, S.; Lin, F.; Wang, J. Prolonged exposure to environmental levels of microcystin-LR triggers ferroptosis in brain via the activation of Erk/MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Fan, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Microcystin-LR induces ferroptosis in intestine of common carp. (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G. Ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Sun, S.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Mitochondrial Regulation of Ferroptosis in Cancer Cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2025, 21, 2179–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Iron Metabolism in Ferroptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 590226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Ru, Y.; Luo, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, X.; Linghu, M.; Xu, W.; Gao, F.; et al. Identification of a targeted ACSL4 inhibitor to treat ferroptosis-related diseases. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Jin, X. Amentoflavone attenuates homocysteine-induced neuronal ferroptosis-mediated inflammatory response: Involvement of the SLC7A11/GPX4 axis activation. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 215, 111005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Maiorino, M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim. Biophys. Act. 2013, 1830, 3289–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, W. p53 in ferroptosis regulation: The new weapon for the old guardian. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yu, M.; Wang, W.-K.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.-C.; Feng, L.-F. The regulation and function of Nrf2 signaling in ferroptosis-activated cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, T.; Yang, H.; Lei, L.; Guo, M.; Ding, H.-F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; et al. ATF3 promotes erastin-induced ferroptosis by suppressing system Xc–. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilka, O.; Shah, R.; Li, B.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Griesser, M.; Conrad, M.; Pratt, D.A. On the Mechanism of Cytoprotection by Ferrostatin-1 and Liproxstatin-1 and the Role of Lipid Peroxidation in Ferroptotic Cell Death. ACS Central Sci. 2017, 3, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Apeldoorn, M.E.; van Egmond, H.P.; Speijers, G.J.A.; Bakker, G.J.I. Toxins of cyanobacteria. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 7–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.D.; Iverson, D.T.; Bachhav, N.K.; Call, M.R.; Yue, G.E.; Prasad, B.; Clarke, J.D. Involvement of the p38/MK2 Pathway in MCLR Hepatotoxicity Revealed through MAPK Pharmacological Inhibition and Phosphoproteomics in HepaRG Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, M.; Gutiérrez-Praena, D.; Prieto, A.; Guzmán-Guillén, R.; Jos, A.; Cameán, A. Neurotoxicity induced by microcystins and cylindrospermopsin: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 668, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaram, R.; Newton, A.R.; Chafin, J. Microcystin Contamination and Toxicity: Implications for Agriculture and Public Health. Toxins 2022, 14, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.M.; Cagido, V.R.; Ferraro, R.B.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; Rocco, P.R.; Zin, W.A.; Azevedo, S.M. Effects of microcystin-LR on mouse lungs. Toxicon 2007, 50, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, A.I.; Jos, A.; Pichardo, S.; Moreno, I.; de Sotomayor, M.Á.; Moyano, R.; Blanco, A.; Cameán, A.M. Time-dependent protective efficacy of Trolox (vitamin E analog) against microcystin-induced toxicity in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 24, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; et al. MC-LR induces dysregulation of iron homeostasis by inhibiting hepcidin expression: A preliminary study. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-C.; Gu, L.-H.; Wang, Y.-F.; Wang, L.-M.; Chen, L.; Giesy, J.P.; Tuo, X.; Xu, W.-L.; Wu, Q.-H.; Liu, Y.-Q.; et al. A proteomic study on gastric impairment in rats caused by microcystin-LR. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 917, 169306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagoya, Y.; Yoshimi, A.; Kataoka, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Kumano, K.; Arai, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Saito, T.; Iwakura, Y.; Kurokawa, M. Positive feedback between NF-κB and TNF-α promotes leukemia-initiating cell capacity. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor Nf-kappa B pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: From cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Inflammation and coagulation. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, S26–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeger, V.; Djafarzadeh, S.; Jakob, S.M.; Takala, J. Mitochondrial function in sepsis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 43, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arman, T.; Clarke, J.D. Microcystin Toxicokinetics, Molecular Toxicology, and Pathophysiology in Preclinical Rodent Models and Humans. Toxins 2021, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Williams, C.D.; Ni, H.; Kumer, S.C.; Schmitt, T.; Kane, B.; Jaeschke, H. Microcystin-LR induced liver injury in mice and in primary human hepatocytes is caused by oncotic necrosis. Toxicon 2017, 125, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Y. The role of PP2A-associated proteins and signal pathways in microcystin-LR toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 236, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegoke, E.; Wang, C.; Machebe, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Adeniran, S.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, G. Microcystin-leucine arginine (MC-LR) induced inflammatory response in bovine sertoli cell via TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 63, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Dai, M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F. Microcystin-LR induces lung injury in mice through the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2025, 88, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Chen, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; He, R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Huang, Y.; Tan, A.; Yuan, L.; et al. α-LA attenuates microcystin-LR-induced hepatocellular oxidative stress in mice through Nrf2-mediated antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes. Toxicon 2023, 235, 107313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Z. Metabolic Reprogramming and Its Regulatory Mechanism in Sepsis-Mediated Inflammation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H. Mitochondrial DNA-activated cGAS-STING pathway in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2025, 1880, 189249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Yang, M.; Zhuang, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, H.; Fu, X. Microcystin-LR induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deng, M.; Loughran, P.A.; Yang, M.; Lin, M.; Yang, C.; Gao, W.; Jin, S.; Li, S.; Cai, J.; et al. LPS Induces Active HMGB1 Release From Hepatocytes Into Exosomes Through the Coordinated Activities of TLR4 and Caspase-11/GSDMD Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Yin, T.; Gregersen, H.; Hu, T.; Wang, G. Microcystin-LR induces angiodysplasia and vascular dysfunction through promoting cell apoptosis by the mitochondrial signaling pathway. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raia, L.; Zafrani, L. Endothelial Activation and Microcirculatory Disorders in Sepsis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 907992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-W.; Yin, Y.-M.; Yao, Y.-M. Advances in the management of acute liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7069–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmer, P.; Sowa, J.; Bulut, Y.; Strnad, P.; Canbay, A. Mechanisms and aetiology-dependent treatment of acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2023, 4, e15739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Hui, Y.; Mao, L.; Fan, X.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Sun, C. Regulating Nrf2-GPx4 axis by bicyclol can prevent ferroptosis in carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Chen, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, J.; Yao, Q.; Feng, B.; Feng, X.; Shi, X.; Pan, Q.; Yu, J.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells protect against ferroptosis via exosome-mediated stabilization of SLC7A11 in acute liver injury. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Xiang, Q.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; Bian, J. GPR116 promotes ferroptosis in sepsis-induced liver injury by suppressing system Xc–/GSH/GPX4. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2023, 39, 3015–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Cai, J.W.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, G.; Nie, H.M.; Ling, Q.H. LCN2 attenuates sepsis-induced liver injury by alleviating PTGS2-mediated Ferroptosis. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Evans, R.G.; Iguchi, N.; Tare, M.; Parkington, H.C.; Bellomo, R.; May, C.N.; Lankadeva, Y.R. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: A disease of the microcirculation. Microcirculation 2019, 26, e12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2019, 394, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddali, M.V.; Churpek, M.; Pham, T.; Rezoagli, E.; Zhuo, H.; Zhao, W.; He, J.; Delucchi, K.L.; Wang, C.; Wickersham, N.; et al. Validation and utility of ARDS subphenotypes identified by machine-learning models using clinical data: An observational, multicohort, retrospective analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.-F.; Ward, P.A. Role of oxidants in lung injury during sepsis. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, M.; Choe, K.; Song, E.; Seo, H.; Hwang, Y.; Ahn, J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, Y.H.; et al. Neutrophils disturb pulmonary microcirculation in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1800786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scindia, Y.; Leeds, J.; Swaminathan, S. Iron Homeostasis in Healthy Kidney and its Role in Acute Kidney Injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xie, W. The role of ferroptosis in acute lung injury. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Liu, B.; Xiong, R.; Geng, B.; Meng, H.; Lin, W.; Hao, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Jiang, W.; et al. Itaconate inhibits ferroptosis of macrophage via Nrf2 pathways against sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L. Ferrostatin-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarina, A.V.; Branchini, G.; Bettoni, L.; De Oliveira, J.R.; Nunes, F.B. Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy: From Pathophysiology to Progress in Experimental Studies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 2770–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shi, X.; Diao, M.; Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, W.; Xi, S. A retrospective study of sepsis-associated encephalopathy: Epidemiology, clinical features and adverse outcomes. BMC Emerg. Med. 2020, 20, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaja, M. Septic Encephalopathy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbuya, J.S.; Li, S.; Liang, L.; Zeng, Q. Paediatric sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE): A comprehensive review. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; Shi, B.; Yu, B.; Luo, W.; Peng, S.; Du, X. The Role of Iron Metabolism in Sepsis-associated Encephalopathy: A Potential Target. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 4677–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Song, Z.; Jin, H.; Cui, Y.; Hou, M.; Gao, Y. Protective effect of rhBNP on intestinal injury in the canine models of sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Vogl, T.; Segal, E.; Weersma, R.K. Antibody signatures in inflammatory bowel disease: Current developments and future applications. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Yu, X. Role of Nrf2/GPX4 mediated ferroptosis in intestinal injury in sepsis. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2023, 35, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Dou, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, B. Shielding the Gut: Ghrelin and Ferrostatin-1’s Protective Role Against Sepsis-Induced Intestinal Ferroptosis. Biomedicines 2024, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bu, G. Identification of two novel ferroptosis-associated targets in sepsis-induced cardiac injury: Hmox1 and Slc7a11. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1185924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Fang, X.; Zhou, K.; Bao, H.; Li, L. Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and pathogenetic mechanisms (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 28, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Yuan, L.; Luo, Z.; Tang, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Liang, P.; Huang, L.; Jiang, B. COX-2 optimizes cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis and exerts a cardioprotective effect during sepsis. Cytokine 2024, 182, 156733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R.; Yeung, D.S.K. Cytoskeletal changes in hepatocytes induced by Microcystis toxins and their relation to hyperphosphorylation of cell proteins. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1992, 81, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Feng, H.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Z.; Wu, N. Unraveling the Role of Microcystin-LR in Ferroptosis and Sepsis Pathogenesis: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070947
Ying H, Zhao H, Zhang X, Feng H, Zhou M, Wu Z, Wu N. Unraveling the Role of Microcystin-LR in Ferroptosis and Sepsis Pathogenesis: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070947
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Honglian, Hongli Zhao, Xiaqiu Zhang, Haoyuan Feng, Manjuan Zhou, Zunqiu Wu, and Ning Wu. 2025. "Unraveling the Role of Microcystin-LR in Ferroptosis and Sepsis Pathogenesis: A Comprehensive Review" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070947
APA StyleYing, H., Zhao, H., Zhang, X., Feng, H., Zhou, M., Wu, Z., & Wu, N. (2025). Unraveling the Role of Microcystin-LR in Ferroptosis and Sepsis Pathogenesis: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules, 15(7), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070947





