Bilirubin Metabolism and Thyroid Cancer: Insights from ALBI and PALBI Indices
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Bilirubin Measurement
2.2. Cancer Case Ascertainment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
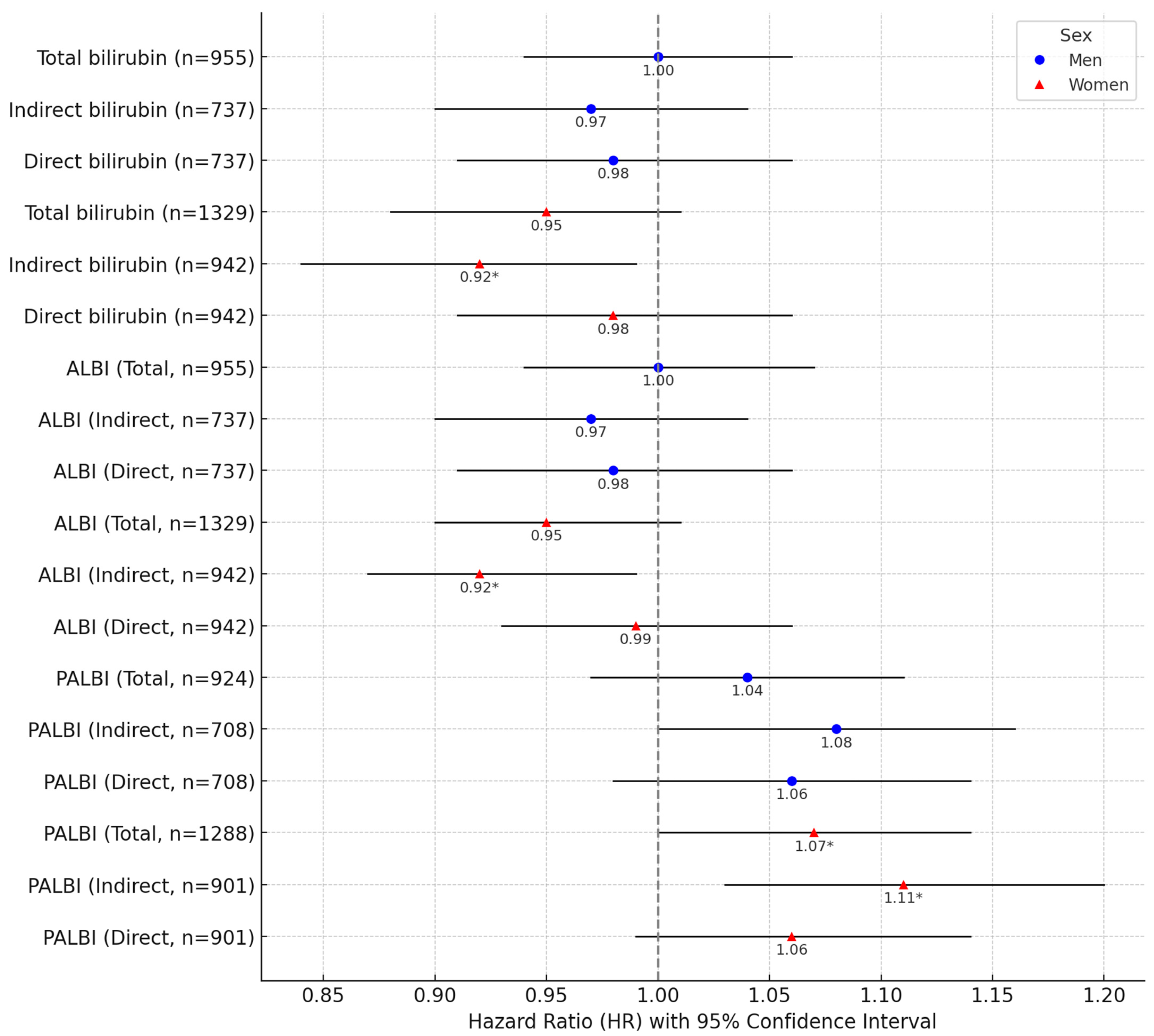
3. Results
4. Discussion
Redox Metabolism and Thyroid Cancer
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, H.; Devesa, S.S.; Sosa, J.A.; Check, D.; Kitahara, C.M. Trends in thyroid cancer incidence and mortality in the United States, 1974–2013. JAMA 2017, 317, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, L.; Morris, L.; Hankey, B. Increases in thyroid cancer incidence and mortality. JAMA 2017, 318, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.K.; Bae, J.S.; Park, Y.J. Re-increasing trends in thyroid cancer incidence after a short period of decrease in Korea: Reigniting the debate on ultrasound screening. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 37, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Welch, H.G. Korea’s thyroid-cancer “epidemic”—Screening and overdiagnosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1765–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Ko, M.J.; Brito, J.P. Thyroid cancer screening in South Korea increases detection of papillary cancers with no impact on other subtypes or thyroid cancer mortality. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hassani, R.A.; Buffet, C.; Leboulleux, S.; Dupuy, C. Oxidative stress in thyroid carcinomas: Biological and clinical significance. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, R131–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karger, S.; Krause, K.; Gutknecht, M.; Jeßnitzer, B.; Tannapfel, A.; Schmid, K.W.; Gimm, O.; Dralle, H.; Führer, D. Oxidative stress in the thyroid—DNA damage and repair: Important mechanisms in the pathogenesis of thyroid tumours? Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2007, 115 (Suppl. 1), P01_026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M. Oxidative stress: A new risk factor for thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, C7–C11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karger, S.; Krause, K.; Engelhardt, C.; Weidinger, C.; Gimm, O.; Dralle, H.; Sheu-Grabellus, S.-Y.; Schmid, K.W.; Fuhrer, D. Distinct pattern of oxidative DNA damage and DNA repair in follicular thyroid tumours. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 48, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; McDonagh, A.F.; Glazer, A.N.; Ames, B.N. Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 1987, 235, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, H.-U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Guha, M.; Choubey, V.; Maity, P.; Srivastava, K.; Puri, S.K.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Bilirubin inhibits Plasmodium falciparum growth through the generation of reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barañano, D.E.; Rao, M.; Ferris, C.D.; Snyder, S.H. Biliverdin reductase: A major physiologic cytoprotectant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16093–16098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.-W.; Nguyen, T.-M.; Jee, S.-H. Association Between Creatinine and Lung Cancer Risk in Men Smokers: A Comparative Analysis with Antioxidant Biomarkers from the KCPS-II Cohort. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.E.; Kimm, H.; Jee, S.H. Combined effects of smoking and bilirubin levels on the risk of lung cancer in Korea: The severance cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsfall, L.J.; Burgess, S.; Hall, I.; Nazareth, I. Genetically raised serum bilirubin levels and lung cancer: A cohort study and Mendelian randomisation using UK Biobank. Thorax 2020, 75, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepien, M.; Fedirko, V.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Ferrari, P.; Freisling, H.; Trepo, E.; Trichopoulou, A.; Bamia, C.; Weiderpass, E.; Olsen, A.; et al. Prospective association of liver function biomarkers with development of hepatobiliary cancers. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyed Khoei, N.; Anton, G.; Peters, A.; Freisling, H.; Wagner, K.-H. The Association between Serum Bilirubin Levels and Colorectal Cancer Risk: Results from the Prospective Cooperative Health Research in the Region of Augsburg (KORA) Study in Germany. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, S.D.; Horn, P.S.; Sherman, K.E. Serum bilirubin levels in the U.S. population: Gender effect and inverse correlation with colorectal cancer. Hepatology 2004, 40, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoei, N.S.; Wagner, K.H.; Carreras-Torres, R.; Gunter, M.J.; Murphy, N.; Freisling, H. Associations between Prediagnostic Circulating Bilirubin Levels and Risk of Gastrointestinal Cancers in the UK Biobank. Cancers 2021, 13, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoei, N.S.; Jenab, M.; Murphy, N.; Banbury, B.L.; Carreras-Torres, R.; Viallon, V.; Kühn, T.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, B.; Aleksandrova, K.; Cross, A.J.; et al. Circulating bilirubin levels and risk of colorectal cancer: Serological and Mendelian randomization analyses. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, R.; Glazer, A.N.; Ames, B.N. Antioxidant activity of albumin-bound bilirubin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 5918–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.W.; Jung, K.J.; Ryu, M.; Kim, J.; Kimm, H.; Jee, S.H. Causal association between serum bilirubin and ischemic stroke: Multivariable Mendelian randomization. Epidemiol. Health 2024, 46, e2024070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.W.; Kim, N.; Minh, N.T.; Chapagain, D.D.; Jee, S.H. Serum bilirubin subgroups and cancer risk: Insights with a focus on lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2025, 94, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.W.; Minh, N.T.; Jee, S.H. Sex-Specific Associations of Total Bilirubin, ALBI, and PALBI with Lung Cancer Risk: Interactions with Smoking and Alcohol. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro-Wills, M.F.; Imitola-Madero, A.; Alvarez-Londoño, A.; Hernández-Blanquisett, A.; Martínez-Ávila, M.C. Thyroid cancer in women of reproductive age: Key issues for the clinical team. Women’s Health 2022, 18, 17455057221136392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, Y.H.; Emberson, J.; Jung, K.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.; Back, J.H.; Hong, S.; Kimm, H.; Sherliker, P.; Jee, S.H.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Korean Cancer Prevention Study-II (KCPS-II) Biobank. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 385–386f. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coolidge, T.B. Chemistry of the van den Bergh reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1940, 132, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach—The ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hsia, C.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Lee, F.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Huo, M.C.; Huo, T.I. ALBI and PALBI grade predict survival for HCC across treatment modalities and BCLC stages in the MELD Era. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 32, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Tan, C.; Li, Q.; Ma, Z.; Wu, M.; Tan, X.; Wu, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Assessment of the albumin-bilirubin score in breast cancer patients with liver metastasis after surgery. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kut, E.; Menekse, S. Prognostic significance of pretreatment albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) grade and platelet–albumin–bilirubin (PALBI) grade in patients with small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, E.-S.; Shin, S.-J.; Lee, H.S.; Koh, H.-H.; Lee, K.Y.; Kang, J. Clinical significance of combining preoperative and postoperative albumin-bilirubin score in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, S.; Bao, B.; Cong, H.; Lu, X.; Shi, A. Albumin-bilirubin score: A promising predictor of postoperative distant metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer. Biomark. Med. 2025, 19, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metere, A.; Frezzotti, F.; Graves, C.E.; Vergine, M.; De Luca, A.; Pietraforte, D.; Giacomelli, L. A possible role for selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase (GPx1) and thioredoxin reductases (TrxR1) in thyroid cancer: Our experience in thyroid surgery. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azouzi, N.; Cailloux, J.; Cazarin, J.M.; Knauf, J.A.; Cracchiolo, J.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Hartl, D.; Polak, M.; Carré, A.; El Mzibri, M.; et al. NADPH oxidase NOX4 is a critical mediator of BRAFV600E-induced downregulation of the sodium/iodide symporter in papillary thyroid carcinomas. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taverna, M.; Marie, A.-L.; Mira, J.-P.; Guidet, B. Specific antioxidant properties of human serum albumin. Ann. Intensive Care 2013, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares De Oliveira, L.; Ritter, M.J. Thyroid hormone and the Liver. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 9, e0596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.; Hodgson, H. The relationship between the thyroid gland and the liver. QJM Int. J. Med. 2002, 95, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asad, S.F.; Singh, S.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, N.U.; Hadi, S.M. Prooxidant and antioxidant activities of bilirubin and its metabolic precursor biliverdin: A structure-activity study. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2001, 137, 59-74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kościuszko, M.; Buczyńska, A.; Krętowski, A.J.; Popławska-Kita, A. Could oxidative stress play a role in the development and clinical management of differentiated thyroid cancer? Cancers 2023, 15, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, P.J.; Mousa, S.A.; Schechter, G.P.; Lin, H.Y.; Platelet, A.T.P. Thyroid hormone receptor on integrin αvβ3 and cancer metastasis. Horm Cancer. 2020, 11, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naciu, A.M.; Nusca, A.; Palermo, A.; Piccirillo, F.; Tabacco, G.; D’Amico, A.; Di Tommaso, A.M.; Sterpetti, G.; Viscusi, M.M.; Bernardini, F.; et al. Platelet Function and Markers of Atherothrombotic Risk in Individuals With Parathyroid Disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, dgaf138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chu, H.-Y.; Zhong, Z.-M.; Qi, X.; Cheng, R.; Qin, R.-J.; Liang, J.; Zhu, X.-F.; Zeng, M.-S.; Sun, C.-Z. Platelet-secreted CCL3 and its receptor CCR5 promote invasive and migratory abilities of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells via MMP-1. Cell. Signal. 2019, 63, 109363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergh, J.J.; Lin, H.-Y.; Lansing, L.; Mohamed, S.N.; Davis, F.B.; Mousa, S.; Davis, P.J. Integrin αVβ3 contains a cell surface receptor site for thyroid hormone that is linked to activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and induction of angiogenesis. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Men (n = 83,371) | Men (n = 66,875, Age < 50) | Women (n = 50,225) | Women (n = 40,976, Age < 50) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 41.6 (9.5) | 37.93 (6.00) | 39.7 (10.7) | 35.81 (7.07) |
| Body mass index † | 24.4 (2.9) | 24.42 (2.97) | 22.0 (3.0) | 21.53 (2.86) |
| Serum bilirubin, mg/dL | ||||
| Total | 0.95 (0.38) | 0.95 (0.38) | 0.75 (0.30) | 0.76 (0.31) |
| Indirect | 0.59 (0.26) | 0.59 (0.26) | 0.47 (0.21) | 0.47 (0.21) |
| Direct | 0.36 (0.14) | 0.36 (0.14) | 0.29 (0.12) | 0.29 (0.12) |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.58 (0.25) | 4.59 (0.24) | 4.45 (0.25) | 4.45 (0.25) |
| platelet, 103/µL | 244.69 (48.91) | 246.82 (48.30) | 254.36 (51.28) | 254.53 (51.22) |
| Alcohol drinking, g/d | 22.67 (29.45) | 22.40 (27.91) | 5.98 (13.77) | 6.65 (14.98) |
| Smoking status, % | ||||
| Never | 22.7 | 22.8 | 89.4 | 88.7 |
| Previous | 32.7 | 29.5 | 6.4 | 6.7 |
| Current | 44.6 | 47.7 | 4.2 | 4.6 |
| Any alcohol use, % | ||||
| Never | 5.8 | 4.80 | 30.8 | 24.4 |
| Previous | 7.9 | 7.6 | 16.5 | 17.8 |
| Current | 86.3 | 87.5 | 52.7 | 57.9 |
| Bilirubin Subtypes | Case | Q1 HR (95% CI) § | Q2 HR (95% CI) § | Q3 HR (95% CI) § | Q4 HR (95% CI) § | p Value for Trend | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Total Bilirubin | 955 | 1 | 1.03 (0.86–1.25) | 0.94 (0.77–1.14) | 1.00 (0.83–1.20) | 0.7811 |
| Indirect Bilirubin | 737 | 1 | 1.00 (0.79–1.26) | 0.87 (0.69–1.08) | 0.91 (0.73–1.13) | 0.2385 | |
| Direct Bilirubin | 737 | 1 | 1.03 (0.84–1.25) | 0.96 (0.77–1.20) | 0.92 (0.74–1.13) | 0.3103 | |
| Women | Total Bilirubin | 1329 | 1 | 0.93 (0.82–1.06) | 0.93 (0.79–1.09) | 0.89 (0.75–1.06) | 0.1560 |
| Indirect Bilirubin | 942 | 1 | 0.84 (0.71–0.99) | 0.88 (0.74–1.04) | 0.79 (0.65–0.97) | 0.0221 | |
| Direct Bilirubin | 942 | 1 | 0.97 (0.83–1.13) | 1.02 (0.83–1.24) | 1.02 (0.82–1.26) | 0.8734 | |
| ALBI Index | |||||||
| Men | Total Bilirubin | 955 | 1 | 1.10 (0.90–1.33) | 0.94 (0.77–1.14) | 1.03 (0.85–1.24) | 0.7803 |
| Indirect Bilirubin | 737 | 1 | 0.80 (0.64–0.99) | 0.89 (0.72–1.10) | 0.84 (0.69–1.04) | 0.3042 | |
| Direct Bilirubin | 737 | 1 | 1.03 (0.83–1.28) | 0.98 (0.79–1.21) | 0.90 (0.73–1.11) | 0.2237 | |
| Women | Total Bilirubin | 1329 | 1 | 0.92 (0.80–1.05) | 0.87 (0.75–1.01) | 0.89 (0.75–1.05) | 0.0639 |
| Indirect Bilirubin | 942 | 1 | 0.84 (0.71–0.98) | 0.87 (0.73–1.04) | 0.79 (0.65–0.97) | 0.0209 | |
| Direct Bilirubin | 942 | 1 | 1.02 (0.87–1.21) | 0.95 (0.80–1.13) | 1.01 (0.83–1.22) | 0.8047 | |
| PALBI Index | |||||||
| Men | Total Bilirubin | 924 | 1 | 0.93 (0.79–1.11) | 0.99 (0.83–1.18) | 1.04 (0.86–1.26) | 0.6764 |
| Indirect Bilirubin | 708 | 1 | 0.94 (0.77–1.15) | 1.10 (0.90–1.34) | 1.09 (0.88–1.35) | 0.2563 | |
| Direct Bilirubin | 708 | 1 | 1.10 (0.90–1.34) | 1.15 (0.93–1.41) | 1.16 (0.93–1.45) | 0.1451 | |
| Women | Total Bilirubin | 1288 | 1 | 0.98 (0.81–1.20) | 1.07 (0.89–1.29) | 1.12 (0.93–1.33) | 0.0967 |
| Indirect Bilirubin | 901 | 1 | 0.92 (0.73–1.17) | 1.15 (0.92–1.42) | 1.18 (0.96–1.45) | 0.0185 | |
| Direct Bilirubin | 901 | 1 | 0.97 (0.78–1.21) | 1.04 (0.85–1.28) | 1.10 (0.90–1.34) | 0.2172 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.W.; Sull, J.W.; Minh, N.T.; Jee, S.H. Bilirubin Metabolism and Thyroid Cancer: Insights from ALBI and PALBI Indices. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071042
Shin JW, Sull JW, Minh NT, Jee SH. Bilirubin Metabolism and Thyroid Cancer: Insights from ALBI and PALBI Indices. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071042
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jong Won, Jae Woong Sull, Nguyen Thien Minh, and Sun Ha Jee. 2025. "Bilirubin Metabolism and Thyroid Cancer: Insights from ALBI and PALBI Indices" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071042
APA StyleShin, J. W., Sull, J. W., Minh, N. T., & Jee, S. H. (2025). Bilirubin Metabolism and Thyroid Cancer: Insights from ALBI and PALBI Indices. Biomolecules, 15(7), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071042







