Heparin, Heparin-like Molecules, and Heparin Mimetics in Breast Cancer: A Concise Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Breast Cancer
3. Role of Heparin/Heparan Sulfate in Breast Cancer
4. Heparin and Mimetics as Anti-Breast Cancer Agents
5. Combinations and Delivery Systems Involving Heparin and Mimetics in Breast Cancer
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esko, J.D.; Kimata, K.; Lindahl, U. Proteoglycans and Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Freeze, H.H., Stanley, P., Bertozzi, C.R., Hart, G.W., Etzler, M.E., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-87969-770-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) Biosynthesis and GAG-Binding Proteins. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2010, 93, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Esko, J.D. Demystifying Heparan Sulfate-Protein Interactions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, J.T.; Walker, A. Molecular distinctions between heparan sulphate and heparin. Analysis of sulphation patterns indicates that heparan sulphate and heparin are separate families of N-sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem. J. 1985, 230, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneghetti, M.C.; Hughes, A.J.; Rudd, T.R.; Nader, H.B.; Powell, A.K.; Yates, E.A.; Lima, M.A. Heparan sulfate and heparin interactions with proteins. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20150589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afosah, D.K.; Al-Horani, R.A. Sulfated Non-Saccharide Glycosaminoglycan Mimetics as Novel Drug Discovery Platform for Various Pathologies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 3412–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, G.; Alkabban, F.M.; Ferguson, T. Breast Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Chan, P.S.; Lok, V.; Chen, X.; Ding, H.; Jin, Y.; Yuan, J.; Lao, X.-Q.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Wong, M.C. Global Incidence and Mortality of Breast Cancer: A Trend Analysis. Aging 2021, 13, 5748–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzaman, K.; Karami, J.; Zarei, Z.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Kazemi, M.H.; Moradi-Kalbolandi, S.; Safari, E.; Farahmand, L. Breast Cancer: Biology, Biomarkers, and Treatments. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brufsky, A.M.; Dickler, M.N. Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer: Exploiting Signaling Pathways Implicated in Endocrine Resistance. Oncol. 2018, 23, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurti, U.; Silverman, J.F. HER2 in breast cancer: A review and update. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2014, 21, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, A.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Modi, S. Management of patients with advanced-stage HER2-positive breast cancer: Current evidence and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Aggarwal, R. An overview of triple-negative breast cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016, 293, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aysola, K.; Desai, A.; Welch, C.; Xu, J.; Qin, Y.; Reddy, V.; Matthews, R.; Owens, C.; Okoli, J.; Beech, D.J.; et al. Triple Negative Breast Cancer—An Overview. Hered. Genet. 2013, 2013 (Suppl. S2), 001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapati, A.; Lukong, K.E. Triple negative breast cancer: Approved treatment options and their mechanisms of action. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 3701–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Z. Immunotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Combination Strategies to Improve Outcome. Cancers 2023, 15, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Xu, P.; Wang, J.; Ji, H.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Z. Advancements in clinical research and emerging therapies for triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 988, 177202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comşa, Ş.; Cîmpean, A.M.; Raica, M. The Story of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line: 40 Years of Experience in Research. Anticancer. Res. 2015, 35, 3147–3154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chavez, K.J.; Garimella, S.V.; Lipkowitz, S. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines: One Tool in the Search for Better Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Dis. 2010, 32, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrörs, B.; Boegel, S.; Albrecht, C.; Bukur, T.; Bukur, V.; Holtsträter, C.; Ritzel, C.; Manninen, K.; Tadmor, A.D.; Vormehr, M.; et al. Multi-Omics Characterization of the 4T1 Murine Mammary Gland Tumor Model. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-T.; Sun, H.-F.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, W.-Y.; Yang, L.-P.; Gao, S.-P.; Li, L.-D.; Jiang, H.-L.; Jin, W. Comparison of Patterns and Prognosis among Distant Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients by Age Groups: A SEER Population-Based Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.-N.; Mao, Z.-X.; Wu, Y.; Liang, M.-X.; Wang, D.-D.; Chen, X.; Chang, P.-A.; Zhang, W.; Tang, J.-H. The Anti-Cancer Properties of Heparin and Its Derivatives: A Review and Prospect. Cell. Adh. Migr. 2020, 14, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theocharis, A.D.; Skandalis, S.S.; Tzanakakis, G.N.; Karamanos, N.K. Proteoglycans in Health and Disease: Novel Roles for Proteoglycans in Malignancy and Their Pharmacological Targeting. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3904–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasisekharan, R.; Shriver, Z.; Venkataraman, G.; Narayanasami, U. Roles of Heparan-Sulphate Glycosaminoglycans in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, R.D. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Invasion and Metastasis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 12, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitovic, D.; Assouti, M.; Sifaki, M.; Katonis, P.; Krasagakis, K.; Karamanos, N.K.; Tzanakakis, G.N. Chondroitin Sulfate and Heparan Sulfate-Containing Proteoglycans Are Both Partners and Targets of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor-Mediated Proliferation in Human Metastatic Melanoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundhenke, C.; Meyer, K.; Drew, S.; Friedl, A. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans as Regulators of Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Receptor Binding in Breast Carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afratis, N.A.; Karamanou, K.; Piperigkou, Z.; Vynios, D.H.; Theocharis, A.D. The Role of Heparins and Nano-Heparins as Therapeutic Tool in Breast Cancer. Glycoconj. J. 2017, 34, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Ma, S. Corrigendum to: Recent Advances in the Discovery of Heparanase Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Agents [Eur. J. Mech. 121 (2016) 209-220]. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Roy, S.; Cochran, E.; Zouaoui, R.; Chu, C.L.; Duffner, J.; Zhao, G.; Smith, S.; Galcheva-Gargova, Z.; Karlgren, J.; et al. M402, a Novel Heparan Sulfate Mimetic, Targets Multiple Pathways Implicated in Tumor Progression and Metastasis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignon, F.; Prebois, C.; Rochefort, H. Inhibition of Breast Cancer Growth by Suramin. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1992, 84, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woll, P.J.; Ranson, M.; Margison, J.; Thomson, Y.; van der Water, L.; George, N.; Howell, A. Suramin for Breast and Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study of Intermittent Short Infusions without Adaptive Control. Ann. Oncol. 1994, 5, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Gao, F.; Maissy, E.; Xu, P. Repurposing Suramin for the Treatment of Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis with Glycol Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foekens, J.A.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Stuurman-Smeets, E.M.; Peters, H.A.; Klijn, J.G. Effects of Suramin on Cell-Cycle Kinetics of MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 67, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Soff, G.; Liu, J.; Cisneros, A.; French, S.; Rademaker, A.; Benson, A.B.; Bouck, N. A Pilot Trial of Suramin in Metastatic Breast Cancer to Assess Antiangiogenic Activity in Individual Patients. Oncology 2000, 58, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Yu, B.; Wei, Y.; Wientjes, M.G.; Au, J.L.-S. Low-Dose Suramin Enhanced Paclitaxel Activity in Chemotherapy-Naive and Paclitaxel-Pretreated Human Breast Xenograft Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6058–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foekens, J.A.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Stuurman-Smeets, E.M.; Dorssers, L.C.; Berns, E.M.; Klijn, J.G. Pleiotropic Actions of Suramin on the Proliferation of Human Breast-Cancer Cells In Vitro. Int. J. Cancer 1992, 51, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marchetti, D.; Reiland, J.; Erwin, B.; Roy, M. Inhibition of Heparanase Activity and Heparanase-Induced Angiogenesis by Suramin Analogues. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, A.; Liu, P.; Mellone, P.; Lorenzon, L.; Vincenzi, B.; Datta, K.; Yang, B.; Linhardt, R.J.; Lingle, W.; Chien, J.; et al. HSulf-1 Modulates FGF2- and Hypoxia-Mediated Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2152–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, S.M.; Iskenderian, A.; Cook, L.; Romashko, A.; Tobin, K.; Jones, M.; Norton, A.; Gómez-Yafal, A.; Heartlein, M.W.; Concino, M.F.; et al. Human Sulfatase 2 Inhibits in Vivo Tumor Growth of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Xenografts. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemjabbar-Alaoui, H.; van Zante, A.; Singer, M.S.; Xue, Q.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Tsay, D.; He, B.; Jablons, D.M.; Rosen, S.D. Sulf-2, a Heparan Sulfate Endosulfatase, Promotes Human Lung Carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2010, 29, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, V.; Schuh, H.J.M.; Mirza, S.; Vaaßen, V.J.; Schmidt, M.S.; Sylvester, K.; Idris, R.M.; Renn, C.; Schäkel, L.; Pelletier, J.; et al. Heparins Are Potent Inhibitors of Ectonucleotide Pyrophosphatase/Phospho-Diesterase-1 (NPP1)—A Promising Target for the Immunotherapy of Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1173634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrio, I.d.M.d.; Meeson, A.; Cooke, K.; Malki, M.I.; Barron-Millar, B.; Kirby, J.A.; Ali, S. Contribution of Heparan Sulphate Binding in CCL21-Mediated Migration of Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabenstein, D.L. Heparin and Heparan Sulfate: Structure and Function. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 312–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Afosah, D.K. Recent Advances in the Discovery and Development of Factor XI/XIa Inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1974–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah, J.; Khachfe, H.H.; Berro, J.; Assi, H.I. The Use of Heparin and Heparin-like Molecules in Cancer Treatment: A Review. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2020, 24, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Scully, M.; Dawson, G.; Goodwin, C.; Xia, M.; Lu, X.; Kakkar, A. Perturbation of the Heparin/Heparin-Sulfate Interactome of Human Breast Cancer Cells Modulates pro-Tumourigenic Effects Associated with PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK Signalling. Thromb Haemost 2013, 109, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettelaie, C.; Fountain, D.; Collier, M.E.W.; Beeby, E.; Xiao, Y.P.; Maraveyas, A. Low Molecular Weight Heparin Suppresses Tissue Factor-Mediated Cancer Cell Invasion and Migration In Vitro. Exp. Ther. Med. 2011, 2, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluhr, H.; Seitz, T.; Zygmunt, M. Heparins Modulate the IFN-γ-Induced Production of Chemokines in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 137, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Kim, Y.-S.; Bae, S.M.; Kim, S.K.; Jin, S.; Chung, S.W.; Lee, M.; Moon, H.T.; Jeon, O.-C.; Park, R.W.; et al. Polyproline-Type Helical-Structured Low-Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH)-Taurocholate Conjugate as a New Angiogenesis Inhibitor. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2755–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.W.; Bae, S.M.; Lee, M.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, I.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, Y. LHT7, a Chemically Modified Heparin, Inhibits Multiple Stages of Angiogenesis by Blocking VEGF, FGF2 and PDGF-B Signaling Pathways. Biomaterials 2015, 37, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Park, J.; Choi, J.U.; Mahmud, F.; Jeong, J.-H.; Kim, I.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; Hwang, S.R.; Byun, Y. Multi-Stage Inhibition in Breast Cancer Metastasis by Orally Active Triple Conjugate, LHTD4 (Low Molecular Weight Heparin-Taurocholate-Tetrameric Deoxycholate). Biomaterials 2016, 86, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, J.M.; Hassan, H.; Ibrahim, S.A. Revisiting the Syndecans: Master Signaling Regulators with Prognostic and Targetable Therapeutic Values in Breast Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dredge, K.; Hammond, E.; Handley, P.; Gonda, T.J.; Smith, M.T.; Vincent, C.; Brandt, R.; Ferro, V.; Bytheway, I. PG545, a Dual Heparanase and Angiogenesis Inhibitor, Induces Potent Anti-Tumour and Anti-Metastatic Efficacy in Preclinical Models. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, E.; Brandt, R.; Dredge, K. PG545, a Heparan Sulfate Mimetic, Reduces Heparanase Expression in Vivo, Blocks Spontaneous Metastases and Enhances Overall Survival in the 4T1 Breast Carcinoma Model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todosenko, N.; Yurova, K.; Khaziakhmatova, O.; Malashchenko, V.; Khlusov, I.; Litvinova, L. Heparin and Heparin-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Pleiotropic Molecular Effects at Multiple Drug Resistance of Osteosarcoma and Immune Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollari, S.; Käkönen, R.S.; Mohammad, K.S.; Rissanen, J.P.; Halleen, J.M.; Wärri, A.; Nissinen, L.; Pihlavisto, M.; Marjamäki, A.; Perälä, M.; et al. Heparin-like Polysaccharides Reduce Osteolytic Bone Destruction and Tumor Growth in a Mouse Model of Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.U.; Chung, S.W.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Alam, F.; Park, J.; Mahmud, F.; Jeong, J.-H.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, Y. A Heparin Conjugate, LHbisD4, Inhibits Lymphangiogenesis and Attenuates Lymph Node Metastasis by Blocking VEGF-C Signaling Pathway. Biomaterials 2017, 139, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.J.; Sharon, C.; Baranwal, S.; Boothello, R.S.; Desai, U.R.; Patel, B.B. Heparan Sulfate Hexasaccharide Selectively Inhibits Cancer Stem Cells Self-Renewal by Activating P38 MAP Kinase. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 84608–84622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boothello, R.S.; Patel, N.J.; Sharon, C.; Abdelfadiel, E.I.; Morla, S.; Brophy, D.F.; Lippman, H.R.; Desai, U.R.; Patel, B.B. A Unique Nonsaccharide Mimetic of Heparin Hexasaccharide Inhibits Colon Cancer Stem Cells via P38 MAP Kinase Activation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, P.; Harvey, J.R.; Murphy, K.J.; Pye, D.; O’Boyle, G.; Lennard, T.W.J.; Kirby, J.A.; Ali, S. Modulatory Effects of Heparin and Short-Length Oligosaccharides of Heparin on the Metastasis and Growth of LMD MDA-MB 231 Breast Cancer Cells in Vivo. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhami, S.P.S.; Patmore, S.; Comerford, C.; Byrne, C.M.; Cavanagh, B.; Castle, J.; Kirwan, C.C.; Kenny, M.; Schoen, I.; O’Donnell, J.S.; et al. Breast Cancer Cells Mediate Endothelial Cell Activation, Promoting von Willebrand Factor Release, Tumor Adhesion, and Transendothelial Migration. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 2350–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignoli, A.; Marchetti, M.; Russo, L.; Cantalino, E.; Diani, E.; Bonacina, G.; Falanga, A. LMWH Bemiparin and ULMWH RO-14 Reduce the Endothelial Angiogenic Features Elicited by Leukemia, Lung Cancer, or Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Investig. 2011, 29, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Moon, C.; Shin, M.C.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Yang, V.C.; Huang, Y. Heparin-Regulated Prodrug-Type Macromolecular Theranostic Systems for Cancer Therapy. Nanotheranostics 2017, 1, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarzadeh Zare, E.; Khorsandi, D.; Zarepour, A.; Yilmaz, H.; Agarwal, T.; Hooshmand, S.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Ozdemir, F.; Sahin, O.; Adiguzel, S.; et al. Biomedical Applications of Engineered Heparin-Based Materials. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 31, 87–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Novel Tumor-Targeting Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment-A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Cao, D.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Ke, X.; Ci, T. Development of Low Molecular Weight Heparin Based Nanoparticles for Metastatic Breast Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Li, H.; Luo, Y.; Feng, N.; Ci, T. Heparin Modified Photosensitizer-Loaded Liposomes for Tumor Treatment and Alleviating Metastasis in Phototherapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, J.; Kazemi, M.; Hasanzadeh, F.; Minaiyan, M.; Mirian, M.; Lavasanifar, A. Novel pH-Triggered Biocompatible Polymeric Micelles Based on Heparin-α-Tocopherol Conjugate for Intracellular Delivery of Docetaxel in Breast Cancer. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 492–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Juan, S. Combination Therapy with Low Molecular Weight Heparin and Adriamycin Results in Decreased Breast Cancer Cell Metastasis in C3H Mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhu, X.; Sun, R.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Zeng, H. Oleanolic Acid Derivative Self-Assembled Aggregates Based on Heparin and Chitosan for Breast Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Scully, M. The Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells Is Reduced upon Treatment with Small Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Heparin-Treated Cell Cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, K.T.; Kar, S.; Goyal, N.; Mottamal, M.; Afosah, D.K.; Al-Horani, R.A. Discovery of Heparin Mimetic, Potent, and Selective Inhibitors of Human Clotting Factor XIIIa. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 31105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiles, R.; Afosah, D.K.; Al-Horani, R.A. Investigation of the anticoagulant activity of cyclic sulfated glycosaminoglycan mimetics. Carbohydr. Res. 2023, 529, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koirala, N.; Poudel, M.; Shrivastava, A.K.; Subba, R.K.; Panthi, M.; Paudel, S.; Almarhoon, Z.M.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Calina, D. Multifaceted role of heparin in oncology: From anticoagulation to anticancer mechanisms and clinical implications. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
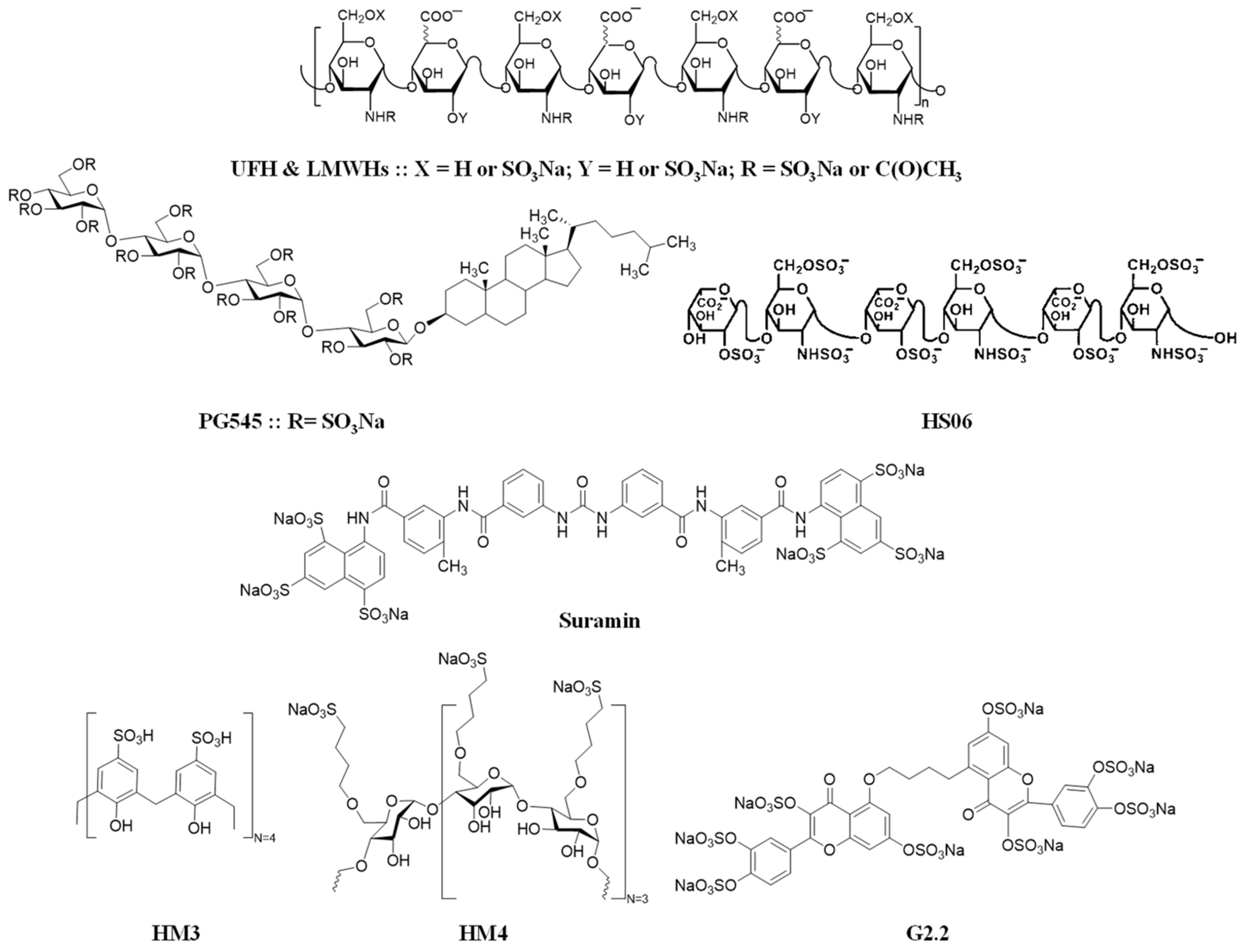
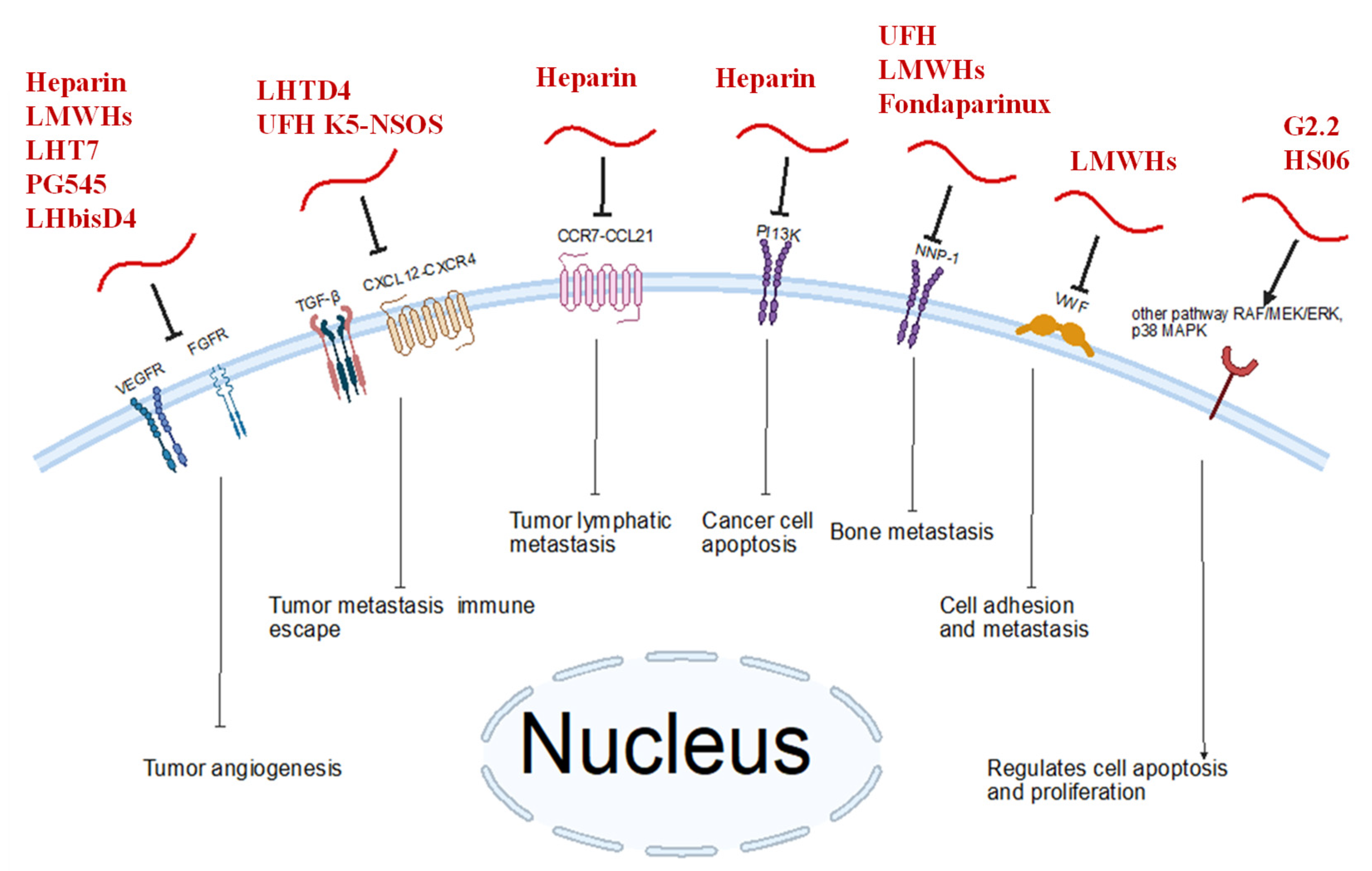
| Molecule | Primary Anti-Cancer Effect |
|---|---|
| LHT7 |
|
| LHTD4 |
|
| Nano-heparin (Styela plicata) |
|
| PG545 |
|
| UFH K5-NSOS |
|
| LHbisD4 |
|
| HS06 |
|
| G2.2 |
|
| Heparin |
|
| Bemiparin (LMWH) and RO-14(ULMWH) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gatica Portillo, D.R.; Li, Y.; Goyal, N.; Rowan, B.G.; Al-Horani, R.A.; Anbalagan, M. Heparin, Heparin-like Molecules, and Heparin Mimetics in Breast Cancer: A Concise Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071034
Gatica Portillo DR, Li Y, Goyal N, Rowan BG, Al-Horani RA, Anbalagan M. Heparin, Heparin-like Molecules, and Heparin Mimetics in Breast Cancer: A Concise Review. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGatica Portillo, Diego R., Yishu Li, Navneet Goyal, Brian G. Rowan, Rami A. Al-Horani, and Muralidharan Anbalagan. 2025. "Heparin, Heparin-like Molecules, and Heparin Mimetics in Breast Cancer: A Concise Review" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071034
APA StyleGatica Portillo, D. R., Li, Y., Goyal, N., Rowan, B. G., Al-Horani, R. A., & Anbalagan, M. (2025). Heparin, Heparin-like Molecules, and Heparin Mimetics in Breast Cancer: A Concise Review. Biomolecules, 15(7), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071034








