Proteomic Study Between Interstitial Channels Along Meridians and Adjacent Areas in Mini-Pigs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
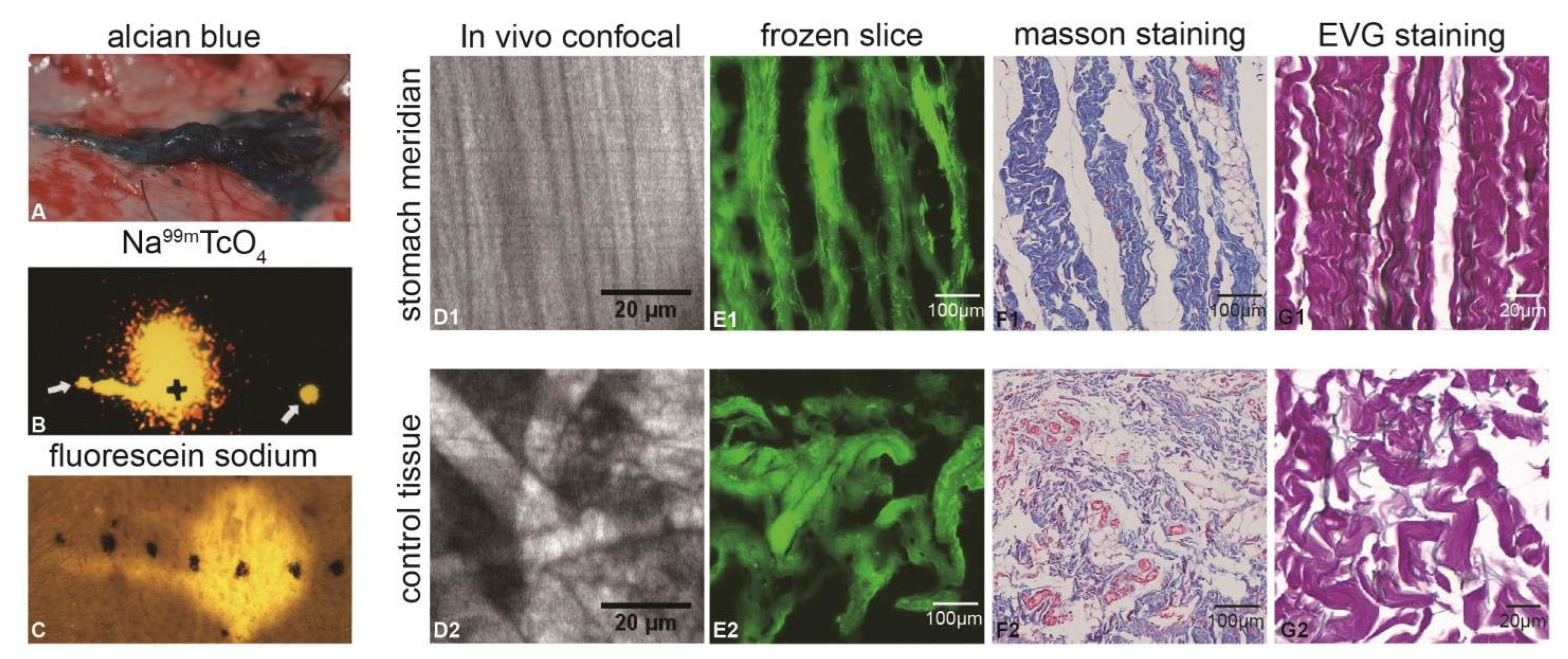
2.2. Tracer Injection and Observation
2.3. In Vivo Confocal Observation of Micro-Migration Trajectory Structure
2.4. Fresh Frozen Sections of Migration Trajectories and MASSON, EVG Staining Observation
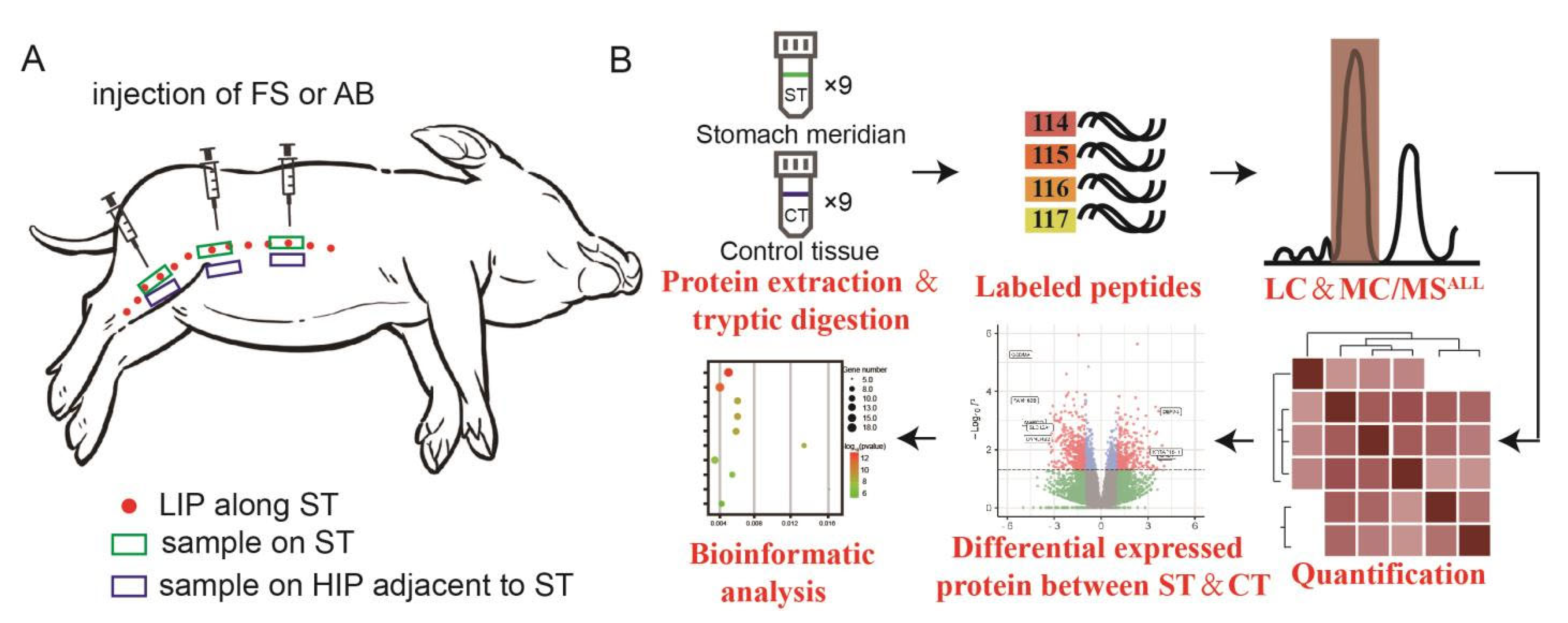
2.5. Extraction of Connective Tissue from the Interstitial Channels of the ST and Adjacent Non-Meridian Areas
2.6. Preparation, Extraction, and Quantification of Total Protein from Samples
2.7. Protein Precipitation
2.8. Protein Sample Preprocessing and Peptide Solution Preparation
2.9. Establishment of DDA Mass Spectrometry Data Acquisition Method for Mini-Pigs
2.10. Protein Qualitative Identification
2.11. Sample Protein Quantitative Data Collection
2.12. Data Processing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Migration Characteristics and Morphological Observation After Dye Injection into Lips Along the ST in Mini-Pigs
3.2. Identification of Protein Composition in the ST and CT
3.3. Analysis of Differential Proteins Between the ST and CT
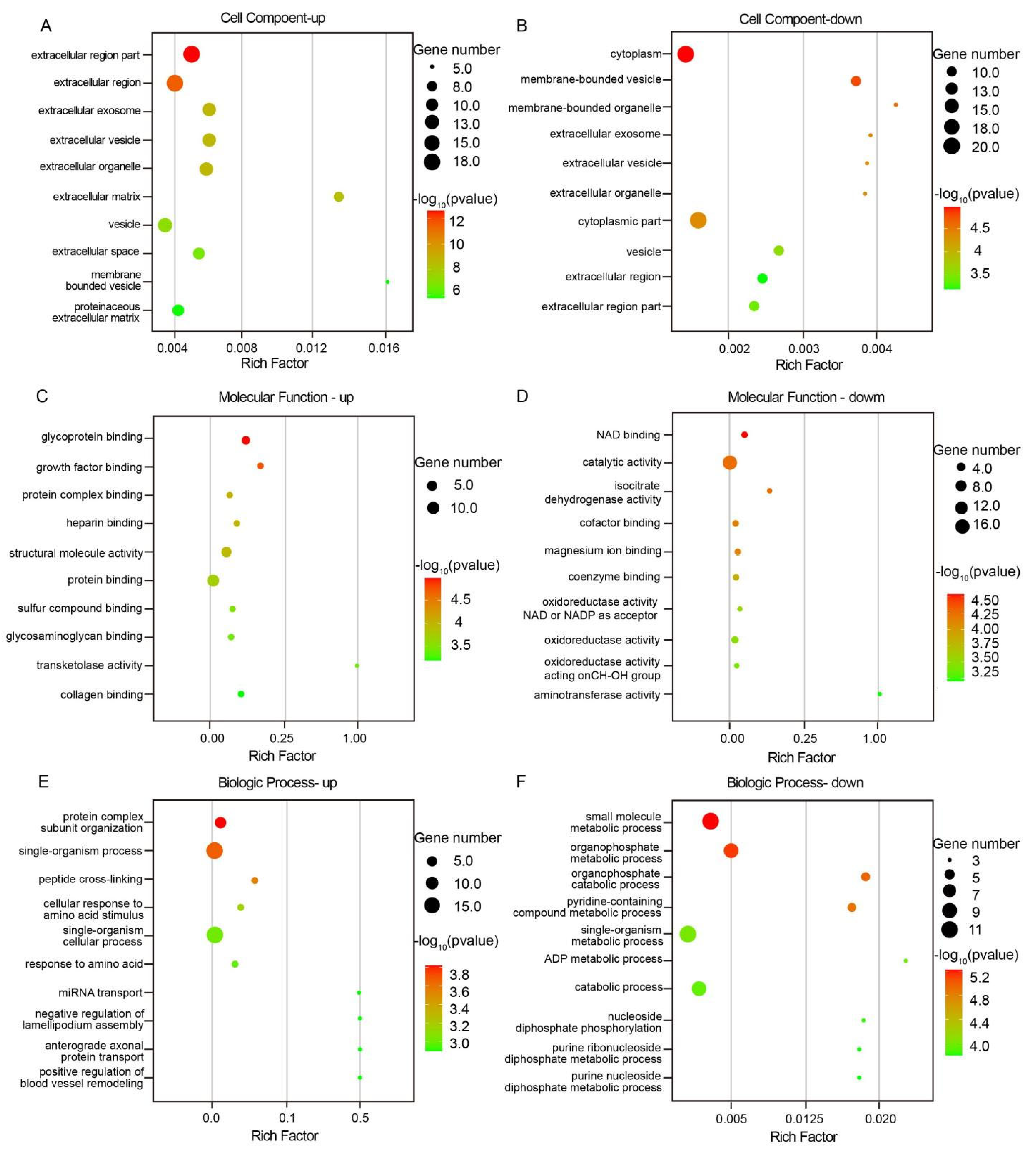
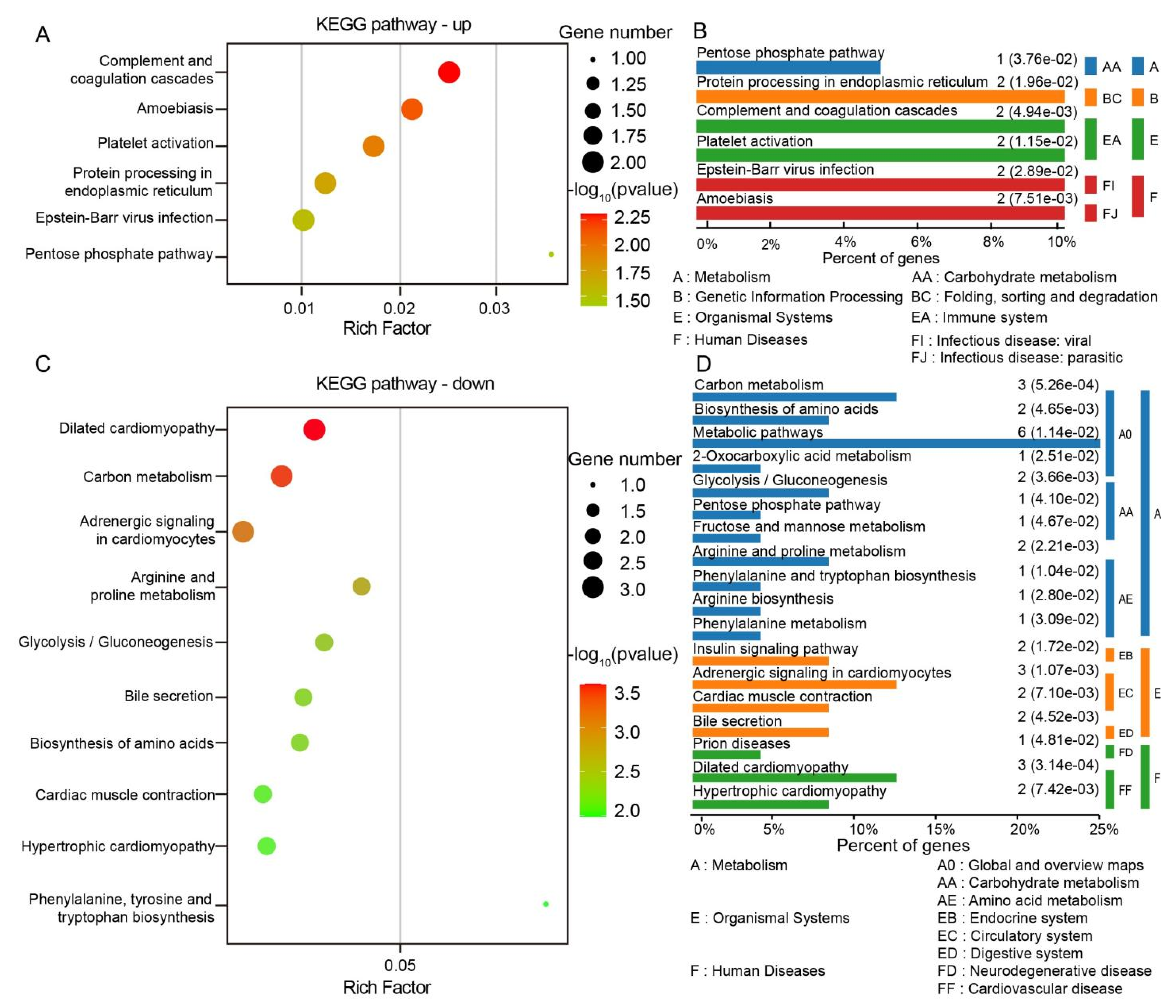
3.4. Differential Protein GO Function Enrichment Analysis and KEGG Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Structural-Functional Dichotomy of Meridian Tissues: ECM Signaling and Intracellular Metabolic Reprogramming
4.2. Metabolic Adaptation and Redox Signaling in Meridian Tissues: A Nexus of Energy Homeostasis, Oxidative Stress, and Calcium Dynamics Underlying Acupuncture Efficacy
4.3. Structural Blueprint of Meridian Channels: Collagen–Proteoglycan Networks as Molecular Scaffolds Linking ECM Architecture to Gastrointestinal Pathobiology
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.B.; Song, X.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.J.; Jia, S.Y.; Tian, Y.Y.; Li, H.Y. Longitudinal directional movement of Alcian blue in Gephyrocharax melanocheir fish: Revealing interstitial flow and related structure. World J. Acup.-Moxib. 2019, 29, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.B.; Jia, S.Y.; Tian, Y.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Li, H.Y. Finding blue tracks in Gephyrocharax melanocheir fish similar to the locations of acupuncture meridians after injecting Alcian blue. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2015, 8, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, G.J.; Song, X.J.; Jia, S.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Ye, F.Y.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, W.B. In vivo display of low hydraulic resistance channels along conception vessel in rats by photofluorography. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2020, 45, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, F.; Song, X.J.; Jia, S.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Li, H.Y.; Gu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.B. Preliminary observation of the migration of sodium fluorescein along meridians in the limbs of mini-pigs. Zhong Guo Ke Xue·Sheng Ming Ke Xue 2020, 50, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tang, B.Q.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhao, M.Y.; Hu, Q.C.; Ahn, A. In Vivo Visualization of the Pericardium Meridian with Fluorescent Dyes. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5581227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Xu, R.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, Q.; Song, X.; Wang, G.; Su, H.; Jia, S.; Wang, S.; et al. Application of Biophysical Properties of Meridians in the Visualization of Pericardium Meridian. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2023, 16, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Jia, S.Y.; Song, X.J.; Wang, G.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, W.B. The effect of exercise on the migration of sodium fluorescein along meridians on the limbs of mini-pig. Zhong Guo Yun Dong Yi Xue Za Zhi 2022, 41, 465–471. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Xiong, F.; Wang, G.J.; Jia, S.Y.; Song, X.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Gu, S.Y.; Zhang, W.B. Observation on the effect of electroacupuncture on the migration of sodium fluorescein in mini-pigs along the low impedance line of meridians. Shan Xi Zhong Yi 2022, 43, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Rao, P. Is acupuncture meridians a novel system for superoxide disposition? In Acupuncture—Concepts and Physiology; InTech: London, UK, 2011; pp. 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Song, X.J.; Huang, J.W.; Jia, S.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, Q.; Shen, Y.H.; Tu, N.; Jiang, Y.Q.; et al. Three-dimensional visualization of interstitial channels in the limbs of mini-pigs and a comparison with humanmeridians. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2024, 54, 1466–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.N.; Liu, J.C.; Zhang, W.C. Literature study on the correlation between the characteristics of terahertz wave and the balance of meridians and collaterals of the yuan-primary points of twelve meridians. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2022, 37, 5277–5280. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.C. Study on the correlation between five zang organs and meridians based on Terahertz wave spectroscopy. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2022, 37, 348–352. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.J.; Wu, Z.H.; Qiu, L.Z.; Zhang, W.C. Study on correlation between terahertz spectral characteristics of acupoints and the airway theory of fascia meridians. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2019, 34, 3728–3731. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.Y.; Pan, L.J.; Liu, J.; She, Y.F. Reflections on the calculation methods of the imbalance degree in the biophysical properties of meridian points. J. Acupunct. Tuina Sci. 2021, 19, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.S.; Wang, H.; Zou, L.; Su, Y.X.; Shen, Y.; Guo, Y.T.; Cui, J.J.; Bai, W.Z. Neural interconnection between acupoint “Chengshan” (BL57) and sciatic nerve in the rat. World J. Acupunct.-Moxibustion 2021, 31, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Study on the characteristic substances of meridian and kidney Qi in Traditional Chinese Medicine based on minor splicesome snRNA. Mo Yu Kang Fu Yi Xue 2023, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, H.M.; Yandow, J.A. Relationship of acupuncture points and meridians to connective tissue planes. Anat. Rec. 2002, 269, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.W.; Zhao, G.; Cui, H.F.; He, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.Q. Clinical observation of the effect of sodium channel blocker on meridians and acupoints. Zhong Guo Yao Wu Yu Lin Chuang 2020, 20, 3081–3082. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Liu, F.; Fang, Y.H.; Liu, K.; Ma, C.; Xie, Y.K. Dendritic projections of motor neurons in the rat spinal cord anterior horn associated to the large intestine channel of hand-yangming and the pericardium channel of hand-jueyin. Ji Chu Yi Xue Yu Lin Chuang 2016, 36, 627–632. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.H. “Hypothesis of meridian protein coupling band”and meridian essence. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Gu Shang Ke Za Zhi 2003, 15, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.C. Views on the essence of meridians—Summary of the theory of intramolecular and intermolecular energy transfer system of fibrin. Mo Yu Kang Fu Yi Xue 2003, 19, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.X.; Shao, Z.Y.; Xu, J.L. Approach to meridian essence and mechanisms from molecular biological specificity of sensory nerve specific protein 29KD. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2001, 21, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Meng, F.X.; Dang, R.S.; Liu, F.; Chen, E.Y.; Zhou, J.F.; Wang, Y.B. Analysis of electrophoretic patterns of structural proteins in rat adipose tissue after acupuncture. Jiang Su Zhong Yi Yao 2006, 27, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.H.; Huang, G.Y.; Zhang, M.M.; Xiao, Y.L. Experimental study on expression of connexin 43 in meridians of rats. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2005, 025, 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Q.; Zhong, R.; Liu, Y.N.; Zhao, C.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, H.D.; Wu, L.Y. Mechanism of electroacupuncture and herb-partitioned moxibustion on ulcerative colitis animal model: A study based on proteomics. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 7, 3644–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.H.; Chen, S.P.; Wang, J.Y.; Qiao, L.N.; Meng, F.Y.; Xu, Q.L.; Liu, J.L. Differential proteomics analysis of the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture intervention in the hippocampus following neuropathic pain in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Tang, T.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Lv, S.; Qi, Q.; Liu, H.; Shi, Z.; et al. Acupuncture Regulates Serum Differentially Expressed Proteins in Patients with Chronic Atrophic Gastritis: A Quantitative iTRAQ Proteomics Study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 7, 9962224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Wang, J.; Nabar, N.R.; Pan, S.; Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Hao, M.; Yang, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Proteomic response to acupuncture treatment in spontaneously hypertensive rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, S.; Wan, J.; Lei, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, N.; Yin, R.; Zhu, J.; Ding, M.; Ding, Y. The involvement of the primo vascular system in local enteritis and its modification by electroacupuncture. Front. Immunol. 2023, 1, 1072996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Ma, F.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Qin, W. Effect of electroacupuncture on global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: A urine proteome analysis. Brain Behav. 2024, 14, e3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, W.; Jia, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Xiong, F.; Li, H. Differential Proteomics Analysis of the Subcutaneous Connective Tissues in Alcian Blue Tracks along Conception Vessel and Adjacent Nonmeridian in Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 5, 5550694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.G.; Xu, R.M.; Zhu, Z.X.; Yu, S.Z.; Huang, S.F. An experimental study of locating the line of latent propagated sensation along stomach meridian and its low impedance characteristic. Zi Ran Za Zhi 1989, 11, 840–844. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.; Gao, L.Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, W.H. Studies on the low impedance line along meridian of mini-pigs. Bei Jing Nong Xue Yuan Xue Bao 1993, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.B.; Tian, J.H. An Exploration of Imaging the Fourteen Meridians; Press of Science and Technology: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B. What Is the Meridian; China Press of Science and Technology: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 55–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Zhuang, F.Y.; Li, H.; Tian, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhu, B.J.; Xu, Q.Y.; Dai, Y.T. An improve Guyton’s method to measure hydraulic conductance and its use in meridian tissue of animals. Bei Jing Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng 1997, 16, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Jing, X.H.; Li, C.H.; Li, Z.C.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhang, L.J. Study on the interstitial fluid permeability of meridian in rats. Ji Chu Yi Xue Yu Lin Chuang 1994, 1, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Tian, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Tian, J.H.; Luo, M.F.; Xu, F.L.; Wang, G.J.; Huang, T.; Xu, Y.H.; Wang, R.H. A Discovery of Low hydraulic Resistance Channel along Meridians. J. Acupunct. Merid. Res. 2008, 1, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.B.; Wang, G.J.; Fuxe, K. Classic and modern meridian studies: A review of low hydraulic resistance channels along meridians and their relevance for therapeutic effects in traditional Chinese medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 5, 410979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.B.; Zhuang, F.Y.; Tian, Y.Y.; Li, H. A simulating study of biophysical features along meridians on gel model. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Za Zhi 2001, 18, 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.J.; Zhang, W.B.; Jia, S.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Li, H.Y.; Ye, F.Y.; Gu, X.; Xiong, F. Preliminary observation of the interstitial fluid distribution along the meridian path of abdominal wall in rats by vivo laser confocal imaging. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020, 26, 474–478. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.J.; Xiong, F.; Jia, S.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, W.B. Observation of microstructure of midline interstitial channels of the inner abdominal wall in rat for in vivo confocal laser imaging. Ji Guang Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2021, 30, 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Theocharis, A.D.; Skandalis, S.S.; Gialeli, C.; Karamanos, N.K. Extracellular matrix structure. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 2, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanos, N.K.; Theocharis, A.D.; Piperigkou, Z.; Manou, D.; Passi, A.; Skandalis, S.S.; Vynios, D.H.; Orian-Rousseau, V.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Schmelzer, C.E.H.; et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 6850–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Anker, A.; Klein, S.; Dean, J.; Knoedler, L.; Remy, K.; Pagani, A.; Kempa, S.; Terhaag, A.; Prantl, L. Autologous Fat Grafting-A Panacea for Scar Tissue Therapy? Cells 2024, 13, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, B.P.; Patel, H.H.; Insel, P.A. Interaction of membrane/lipid rafts with the cytoskeleton: Impact on signaling and function: Membrane/lipid rafts, mediators of cytoskeletal arrangement and cell signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.L.; Xu, J.S.; Wang, P.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Gao, L.Y.; Wu, B.H. Preliminary exploration on the mechanism underlying the formation infrared radiant track along meridian cross over human body surface. Hong Wai Yu Hao Mi Bo Xue Bao 2003, 22, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Huang, B.; Chen, J. Oxygen metabolism and meridian qi. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2012, 32, 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Li, H.; Xu, R.M. Observation on the effect of acupuncture on skin carbon dioxide exhalation of meridians. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 1996, 16, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.W.; Ji, B.; Dai, J.; Zhao, G.Z.; Wang, D.; Yan, M.N.; Bai, H.X.; Sun, X.M.; Guo, M.W.; Mao, Q.Q.; et al. Influence of electro-acupuncture of different frequency and stimulation times on skin blood perfusion around Neiguan (PC6) and sham acupoint in rats with myocardial ischemia. Bei Jing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2016, 39, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.F.; Dong, X.T.; Song, X.J.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J.L.; Han, Y. Study on the dynamic compound structure composed of mast cells, blood vessels, and nerves in rat acupoint. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 6, 160651. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Pagadala, V.; Mueller, D.M. Understanding structure, function, and mutations in the mitochondrial ATP synthase. Microb. Cell 2015, 2, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.M.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Novak, I. ATP release, generation and hydrolysis in exocrine pancreatic duct cells. Purinergic Signal. 2015, 11, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, W. Ins-ATP: Deep estimation of ATP for organoid based on high throughput microscope images. Methods 2025, 235, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.P.; Chang, H.Y.; Zhou, Y. Expression, purification and preliminary crystallographic studies of human glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 1 (GOT1). Protein Expr. Purif. 2015, 9, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-García, L.C.; García-Castillo, V.; Pérez-Toledo, E.; Trujano-Camacho, S.; Millán-Catalán, O.; Pérez-Yepez, E.A.; Coronel-Hernández, J.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.; Pérez-Plasencia, C. HOTAIR Participation in Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis Through Lactate and Glutamate Production in Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2025, 14, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aniello, A.; Fisher, G.; Migliaccio, N.; Cammisa, G.; D’Aniello, E.; Spinelli, P. Amino acids and transaminases activity in ventricular CSF and in brain of normal and Alzheimer patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 388, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tönjes, M.; Barbus, S.; Park, Y.J.; Wang, W.; Schlotter, M.; Lindroth, A.M. BCAT1 promotes cell proliferation through amino acid catabolism in gliomas carrying wild-type IDH1. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, S.M.; Babarinde, T.O.; Holt, K.T.; Sontheimer, H. Role of glutamate transporters in redox homeostasis of the brain. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 7, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, E.; Giammarioli, A.M.; Chiandotto, S.; Spoletini, S.; Rosano, G. Exercise-Induced Skeletal Muscle Remodeling and Metabolic Adaptation: Redox Signaling and Role of Autophagy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Rahlfs, S.; Jortzik, E.; Schirmer, R.H.; Przyborski, J.M.; Becker, K. Subcellular localization of adenylate kinases in Plasmodium falciparum. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3037–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.C.; Xu, J.S.; Zheng, S.X.; Zhu, X.X.; Lin, L.J. Review on the characteristic of energy metabolism in the running routes of meridians. Huan Qiu Zhong Yi Yao 2015, 8, 636–640. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Zhou, L.H. Formation mechanism of high-energy metabolism along meridians. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2014, 34, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; D’Alessandro, A.; Nemkov, T.; Song, A.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Adebiyi, M.; Huang, A.; Wen, Y.E.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes erythrocyte glycolysis and oxygen release for adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccoli, G.S.; Guest, P.C.; Martins-De-Souza, D. Effects on Glial Cell Glycolysis in Schizophrenia: An Advanced Aging Phenotype? Rev. Biomark. Stud. Aging Anti-Aging Res. 2019, 1178, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pietras, Ł.; Stefanik, E.; Rakus, D.; Gizak, A. FBP2-A New Player in Regulation of Motility of Mitochondria and Stability of Microtubules in Cardiomyocytes. Cells 2022, 11, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Wen, J. Metabolic reprogramming and astrocytes polarization following ischemic stroke. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 228, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, G.; Monsorno, K.; Paolicelli, R.C. Metabolic control of microglia in health and disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2025, 209, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evanthia, D.K.; Andrea, D. Insulin Resistance and the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Revisited: An Update on Mechanisms and Implications. Endoc. Rev. 2012, 33, 981–1030. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hajka, D.; Budziak, B.; Rakus, D.; Gizak, A. Neuronal extracellular vesicles influence the expression, degradation and oligomeric state of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 2 in astrocytes affecting their glycolytic capacity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Hu, S.; Wen, B.; Wu, D.; Song, F.; Yin, J.; Wu, J. Expression Regulation of Gluconeogenesis Related Genes in Ovine Skeletal Muscle Cells. Front. Biosci. 2024, 29, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahabeer, S.; Jialal, I.; Norman, R.J.; Naidoo, C.; Reddi, K.; Joubert, S.M. Insulin and C-peptide secretion in non-obese patients with polycystic ovarian disease. Horm. Metab. Res. 1989, 21, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Liu, D.; Xu, Y.; Mao, W.; Li, W. Role of PFKFB3-driven glycolysis in sepsis. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, S.J.; Kikuchi, D.S.; Hernandes, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganini, D.; Petrovich, R.M.; Edwards, L.L.; Mason, R.P. Iron incorporation into MnSOD A (bacterial Mn-dependent superoxide dismutase) leads to the formation of a peroxidase/catalase implicated in oxidative damage to bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Lv, G.Y.; Cheng, J.W.; Cai, W.M.; Fan, L.F.; Miao, L.X. Characterization and biological activities of polysaccharides from artificially cultivated Phellinus baumii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 5, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.K.; Liu, S.T.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, J.W.; Ke, L.J.; Chen, X.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Rao, P.F. Revealing acupuncture meridian-like system by reactive oxygen species visualization. Biosci. Hypotheses 2009, 2, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Yu, J.C.; Zhang, X.Z.; Fu, W.W.; Wang, T.; Han, J.X. Acupuncture prevents cognitive deficits and oxidative stress in cerebral multi-infarction rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 393, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.T.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Yin, C.S.; Choi, S.M.; Chae, Y.; Lee, H.; Park, H.J. Acupuncture enhances superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in the serum of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.P.; Ju, W.P.; Li, Z.G.; Wang, D.Z.; Wang, Y.C.; Xie, A.M. Acupuncture inhibits oxidative stress and rotational behavior in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rat. Brain Res. 2010, 1336, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureshino, R.P.; Erustes, A.G.; Bassani, T.B.; Wachilewski, P.; Guarache, G.C.; Nascimento, A.C.; Costa, A.J.; Smaili, S.S.; da Silva Pereira, G.J. The Interplay between Ca2+ Signaling Pathways and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, J.S. Ca2+ Signaling and Regeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a035485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, E.Y.; Dang, R.S. Effect of extracellular Ca2+ on vessels at points of leg. Jie Pou Xue Za Zhi 2000, 23, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, M.; Assali, E.A.; Ben-Kasus Nissim, T.; Stutzmann, G.E.; Shirihai, O.S.; Hershfinkel, M.; Sekler, I. NCLX controls hepatic mitochondrial Ca2+ extrusion and couples hormone-mediated mitochondrial Ca2+ oscillations with gluconeogenesis. Mol. Metab. 2024, 87, 101982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Han, X.; Wu, K.; Mei, G.; Wu, B.; Cheng, Y. The regulation role of calcium channels in mammalian sperm function: A narrative review with a focus on humans and mice. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Chen, J.Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Guo, Y. Advances of studies on correlation of acupoints with calcium. World J. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2013, 23, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, T.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Miao, W.F.; Hu, L.M.; Zhang, C.X.; Chen, J.S.; Jiang, P. The Correlative Study between Activity of Meridians and Collaterals and Ca2+ in Peripheric Meridians. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 1998, 4, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Z.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.M. Nonlinear dynamics-based study on the role of calcium ions in electroneurographic signal transduction of acupuncture. Shang Hai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2018, 37, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, G.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhai, W.; Xue, W. The m6A-suppressed P2RX6 activation promotes renal cancer cells migration and invasion through ATP-induced Ca2+ influx modulating ERK1/2 phosphorylation and MMP9 signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorigo, M.; Quintaneiro, C.; Lemos, M.C.; Martinez-de-Oliveira, J.; Breitenfeld, L.; Cairrao, E. UV-B Filter Octylmethoxycinnamate Induces Vasorelaxation by Ca2+ Channel Inhibition and Guanylyl Cyclase Activation in Human Umbilical Arteries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.M.; Foell, J.D.; Balijepalli, R.C.; Shah, V.; Hell, J.W.; Kamp, J.T. Unique modulation of L-type Ca2+ channels by short auxiliary beta1d subunit present in cardiac muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H2363–H2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, S.L.; Powers, P.A.; Shin, H.S.; Morgans, C.W.; Peachey, N.S.; Gregg, R.G. Role of the β2 Subunit of Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channels in the Retinal Outer Plexiform Layer. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeh, M.H.; Tzeng, Y.J.; Fu, T.Y.; You, J.J.; Chang, H.T.; Ger, L.P.; Tsai, K.W. Extracellular Matrix-receptor Interaction Signaling Genes Associated with Inferior Breast Cancer Survival. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 4593–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllyharju, J.; Kivirikko, K.I. Collagens, modifying enzymes and their mutations in humans, flies and worms. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, J.R. Recent advances in the study of zebrafish extracellular matrix proteins. Dev. Biol. 2015, 401, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.K.; Hahn, R.A. Collagens. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricardblum, S. The Collagen Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspecti Biol. 2010, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boudko, S.P.; Engel, J. Structure formation in the C terminus of type III collagen guides disulfide cross-linking. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 335, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borst, R.; Meyaard, L.; Pascoal Ramos, M.I. Understanding the matrix: Collagen modifications in tumors and their implications for immunotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Ma, K.; Wang, S. Advances in Molecular Function and Recombinant Expression of Human Collagen. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zell, J.A.; Rhee, J.M.; Ziogas, A.; Lipkin, S.M.; Anton-Culver, H. Race, socioeconomic status, treatment, and survival time among pancreatic cancer cases in California. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. Mechanism of Action of Collagen and Epidermal Growth Factor: A Review on Theory and Research Methods. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2024, 24, 453–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaresma, M.; Coleman, M.P.; Rachet, B. 40-year trends in an index of survival for all cancers combined and survival adjusted for age and sex for each cancer in England and Wales, 1971–2011: A population-based study. Lancet 2015, 385, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, A.; Cescon, M.; D’Agostino, C.; Schilardi, F.; Sabatelli, P.; Merlini, L.; Faldini, C. Collagen VI in the Musculoskeletal System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.H.; Qiu, K.Y.; Tang, W.T.; He, Z.W. Identification of a novel chimeric mutation in the COL6A1 gene of a child with Bethlem myopathy: A case report and literature review. Xin Yi Xue 2021, 52, 941–946. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Lin, M.X.; Qiu, M.Q.; Wu, C.J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.H. Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy caused by COL6A1 intron variation: A case report and literature review. Lin. Chuang Er Ke Za Zhi 2021, 39, 822–824+828. [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet, M.; Birk, D.E.; Bönnemann, G.G.; Koch, M. Collagen XII: Protecting bone and muscle integrity by organizing collagen fibrils. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 53, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zwolanek, D.; Izu, Y.; Gandhy, S.; Schreiber, G.; Brockmann, K.; Devoto, M.; Tian, Z.; Hu, Y.; Veit, G.; et al. Recessive and dominant mutations in COL12A1 cause a novel EDS/myopathy overlap syndrome in humans and mice. Hum. Mol. Gene 2014, 23, 2339–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigi, M.; Son, H.S.; Moon, L.; Matthaei, M.; Srikumaran, D.; Jun, A.S.; Eberhart, C.G.; Soiberman, U.S. Collagen type XII is undetectable in keratoconus Bowman’s layer. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 108, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, C.A.; Ma, J.; Lomeli, S. The coordinated activities of collagen VI and XII in maintenance of tissue structure, function and repair: Evidence for a physical interaction. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1376091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punetha, J.; Kesari, A.; Hoffman, E.P.; Gos, M.; Kamińska, A.; Kostera-Pruszczyk, A.; Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz, I.; Hu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Bönnemann, C.G.; et al. Novel Col12A1 variant expands the clinical picture of congenital myopathies with extracellular matrix defects. Muscle Nerve 2017, 55, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, D.; Antunes, H. A novel mutation in the COL12A1 gene. Gene 2020, 768, 145266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Fang, M.; Wu, C.Y.; Ling, E.A. Scutellarin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Cerebral Ischemia. Neuromolecular Med. 2016, 18, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocking, A.M.; Shinomura, T.; Mcquillan, D.J. Leucine-rich repeat glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 1998, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiberg, C.; Heinegård, D.; Wenglén, C.; Timpl, R.; Mörgelin, M. Biglycan organizes collagen VI into hexagonal-like networks resembling tissue structures. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49120–49126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiberg, C.; Klatt, A.R.; Wagener, R.; Paulsson, M.; Bateman, J.F.; Heinegård, D.; Mörgelin, M. Complexes of Matrilin-1 and Biglycan or Decorin Connect Collagen VI Microfibrils to Both Collagen II and Aggrecan. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 37698–37704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiberg, C.; Hedbom, E.; Khairullina, A.; Lamandé, S.R.; Oldberg, A.; Timpl, R.; Mörgelin, M.; Heinegård, D. Biglycan and decorin bind close to the n-terminal region of the collagen vi triple helix. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 276, 18947–18952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidler, D.G.; Faiyaz-Ul-Haque, M.; Hansen, U.; Yip, G.W.; Zaidi, S.H.; Teebi, A.S.; Kiesel, L.; Götte, M. Defective glycosylation of decorin and biglycan, altered collagen structure, and abnormal phenotype of the skin fibroblasts of an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patient carrying the novel Arg270Cys substitution in galactosyltransferase I (β4GalT-7). J. Mol. Med. 2006, 84, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, L.; Aszódi, A.; Reinholt, F.P.; Fässler, R.; Heinegård, D.; Oldberg, A. Fibromodulin-null mice have abnormal collagen fibrils, tissue organization, and altered lumican deposition in tendon. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 9636–9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, F.; Jia, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Tu, N.; Zhu, S.; Song, X.; et al. Proteomic Study Between Interstitial Channels Along Meridians and Adjacent Areas in Mini-Pigs. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060804
Xiong F, Jia S, Wang G, Wang S, Zhou L, Liu Q, Shen Y, Tu N, Zhu S, Song X, et al. Proteomic Study Between Interstitial Channels Along Meridians and Adjacent Areas in Mini-Pigs. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060804
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Feng, Shuyong Jia, Guangjun Wang, Shuyou Wang, Li Zhou, Qi Liu, Yaohua Shen, Na Tu, Shuxiu Zhu, Xiaojing Song, and et al. 2025. "Proteomic Study Between Interstitial Channels Along Meridians and Adjacent Areas in Mini-Pigs" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060804
APA StyleXiong, F., Jia, S., Wang, G., Wang, S., Zhou, L., Liu, Q., Shen, Y., Tu, N., Zhu, S., Song, X., & Zhang, W. (2025). Proteomic Study Between Interstitial Channels Along Meridians and Adjacent Areas in Mini-Pigs. Biomolecules, 15(6), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060804





